DERMATOLOGY
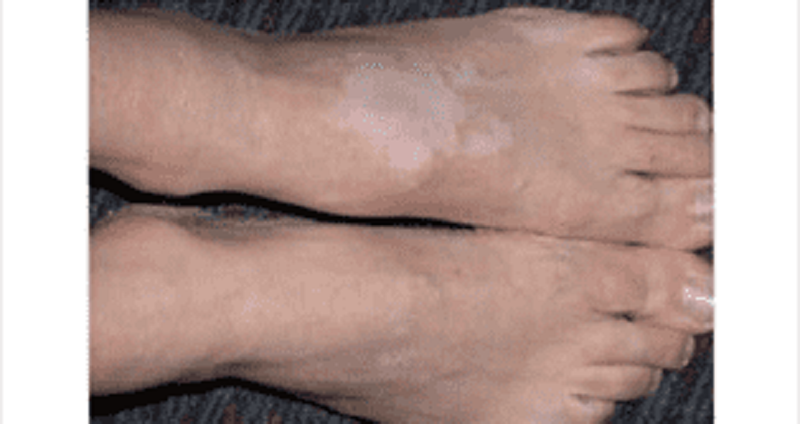
A 22-year-old female is referred to the dermatology clinic. Over the past few years, she has noticed small areas of depigmentation on her arms and legs. Some of these areas are well-circumscribed, as shown in the picture below. She is otherwise well. Her only medication is the oral contraceptive pill. She is currently sexually active with more than one partner. Which of the following diseases is most likely to be associated with her skin condition?
Type-2 diabetes mellitus
Hypoparathyroidism
Pernicious anemia
Zollinger-EIIison syndrome
HIV infection
A 65-year-old man comes to the office and complains of pain and a rash with blisters over the left side of his chest. He has experienced pain over the area for the past 2 days. This morning, he noticed blisters while changing his shirt. He also complains of malaise and headache. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, respirations are 14/min and temperature is 36.8C (98.4F). Physical examination reveals grouped, tense vesicles arranged in a band along the left side of his chest. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of his condition?
Herpes simplex virus
Varicella zoster virus
Poison ivy
Human papilloma virus
Poxvirus
A 65-year-old man comes to the office with a six-month history of a non-healing ulcer on his right forearm. Physical examination demonstrates a scaling plaque with central ulceration and 1.5 cm diameter. The biopsy shows polygonal cells with atypical nuclei at all levels of the epidermis with zones of keratinization. What is the single most important risk factor for this condition?
Sunlight
Arsenic
Aromatic hydroc
Chronic osteomyelitis
Chronic scars
A 62-year-old woman comes to the office for evaluation of a pigmented lesion on her left forearm. The lesion occasionally itches but is otherwise asymptomatic. She admits that she only came because her daughter had persuaded her to do so. On examination, there is a slightly elevated, brown-colored lesion measuring 7 mm in diameter with irregular borders. What is the best next step in management?
Shave biopsy
Excisional biopsy
Dermoscopy
Excision with 1 em margins
Ncisional biopsy
A 17-year-old white male presents to your office because the "spots" on his face "got so much worse recently!" He has several months history of acne. He has not visited a doctor before. Inspection reveals multiple papules with several pustules and nodules. Atrophic scars are seen. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Topical retinoids
Topical antibiotic
Oral antibiotic
Benzyl peroxide
Oral isotretinoin
A 35-year-old Caucasian male with aplastic anemia undergoes bone marrow transplantation. The donor is an HLA-matched sibling. Two weeks after the procedure, he develops a maculopapular pruritic rash that is predominantly found on his face, hands, and feet. He also complains of diarrhea. The stool is positive for occult blood. Liver function tests are abnormal. Which of the following is the most likely pathophysiologic mechanism of this patient's condition?
Activation of the donor T lymphocytes
Activation of the donor 8-lymphocytes
Activation of the host T lymphocytes
Virus-induced lymphocyte proliferation
Depression of the donor myelopoiesis
A 36-year-old male AIDS patient comes in due to a painful red eye. He complains of pain, discharge and redness in his left eye for the past 10 days. On physical examination, you notice redness in his left eye as well as multiple skin lesions on his face, left eyelid, inner thighs, penis and pubis. The lesions are painless, pale, shiny, dome-shaped papules with a central umbilication measuring 2-5mm in diameter. These lesions were not present on his previous visit. His CD4 count thirty days ago was 100/uL. What is the most likely etiology of this patient's skin lesions?
Human herpes virus 8
Staphylococcus
Poxvirus
Herpes simplex 1
Human papilloma virus
A 50-year-old man comes in for his annual check-up. There is a swelling on his left eyelid, which he casually acknowledges by saying that it has appeared "on-and-off for the past 2 years." It initially starts as a painful lesion which regresses with hot compresses, but then eventually reappears. On examination of his left eye, you note a nodular, painless, rubbery lesion on the eyelid without any discharge, redness or other abnormalities. What is the best next step in the management of his eye lesion?
Anti-staphylococcal antibiotics
Direct steroid injection
Incision and curettage
Frequent hot compresses
Histopathological examination
A 47-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of two days of pain and itching over her left chest. Her medical history is significant for breast cancer for which she underwent a left-sided mastectomy six months ago. She has also been receiving chemotherapy and radiation. Physical examination reveals erythema around the mastectomy scar, with excoriations and occasional vesicles. Which of the following is the best treatment for her condition?
Topical 5- fluorouracil
Topical corticosteroids
Acyclovir
Mupirocin
Fluconazole
A 25-year-old woman comes to the office for the evaluation of pale patches of skin around her mouth. She noticed these lesions a few months ago, but they have become more prominent now. There is no itching, burning, or numbness over the patches. Her vital signs are stable. On examination, you notice pale white patches symmetrically distributed around her mouth. The borders of these macules are well-circumscribed and hyperpigmented. Similar lesions are also found over the areola of her breasts. She denies any history of trauma or infection. Which of the following best explains the pathology of her condition?
Post inflammatory
Destruction of melanocytes
Inherited absence of melanocytes
Infection with mycobacterium leprae
Superficial fungal infection
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother for a routine check-up. He has fair skin, blond hair and blue eyes. His past medical history is insignificant. His mother wants to know what the best possible photo-protection is for her son, because "his skin has always been sensitive to the sun, and he is almost unable to tan." He had two episodes of sunburn recently. Physical examination reveals several junctional nevi. Which of the following is the best response to this patient's mother?
Reassure and provide routine care
Recommend applying sunscreens before sun exposure
Minimize sun exposure in the middle of the day
Rest under trees or umbrellas during the day
Emphasize that clothing is typically useless for sun protection
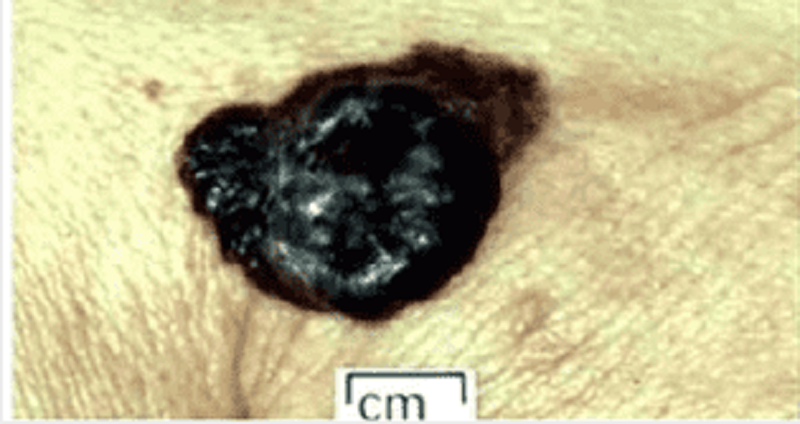
A 28-year-old Caucasian woman comes to the office for a routine skin exam. On exam, you encounter a dark-colored lesion. The patient states that she has had a spot there her whole life. She does state that it has recently "been a little itchy and hurts sometimes." She gives a history of sunburns during childhood, and says that she is very "sun-sensitive." A picture of the mole is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Keratoacanthoma
Blue nevus
Melanoma
Melanocytic nevus
Lentigo simplex
A 60-year-old male farmer presents to the office for the evaluation of a slightly painful ulcer on the top of his lower lip. The ulcer has not healed since he first noticed it three months ago. He has always been healthy and denies any sexual activity during the past year. He is afebrile. Physical examination shows a 3x7 mm, partially encrusted ulcer in the vermilion zone near the moist line (mucocutaneous junction) of the lower lip, surrounded by a 6 x 12 mm area of induration. There are no palpable submental or submandibular lymph nodes. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Complete blood count and differential are normal. Biopsy of the ulcer will most likely to show:
Invasive clusters of spindle cells surrounded by palisaded basal cells
Granulomatous inflammation
Invasive cords of squamous cells with keratin pearls
Shallow fibrin-coated ulceration with an underlying mononuclear infiltrate
Giant cells in a Tzanck preparation
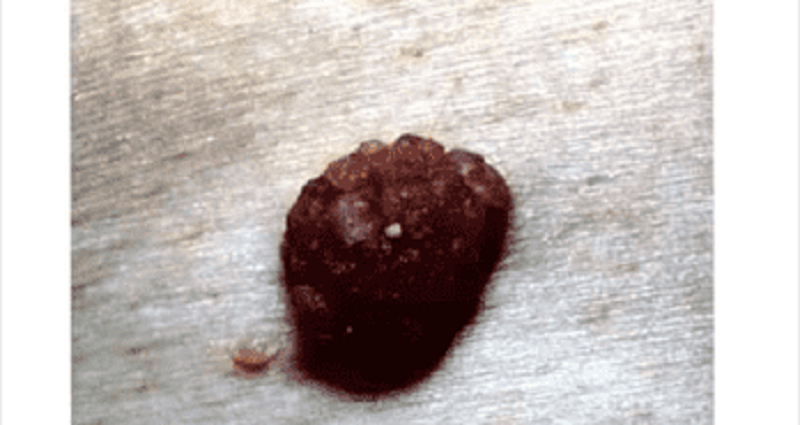

An 80-year-old woman comes to the office and appears very upset. She requests removal of a lesion on her neck because "it is greasy and unsightly." She is tired of people constantly staring at her neck. The lesion has been present "for quite a while," and has been gradually darkening. Aside from occasional itching, there are no other symptoms. A picture of the lesion is shown below.What is the most likely diagnosis?
Basal cell carcinoma
Melanoma C. Seborrheic keratosis
Seborrheic keratosis
Actinic keratosis
Crochordon
An 18-year-old girl comes to the emergency department for sudden-onset redness and swelling of her skin over exposed areas. She had just spent 1 hour at the beach when she began to experience a burning sensation, followed by redness and swelling of those areas. Her face has a few inflammatory nodules as well as open and closed comedones, and she was recently prescribed "some medication for the past month or so" for her facial lesions. Her pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, respirations are 14/min and temperature is 37.2C (99F). On examination, you notice erythema, edema and vesicles on her face, neck, dorsal hands and upper chest. She has no mucosal lesions. Which of the following best explains her condition?
Allergic contact dermatitis
Erythromycin-induced phototoxicity
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Doxycycline-induced phototoxicity
Benzoyl peroxide induced phototoxicity
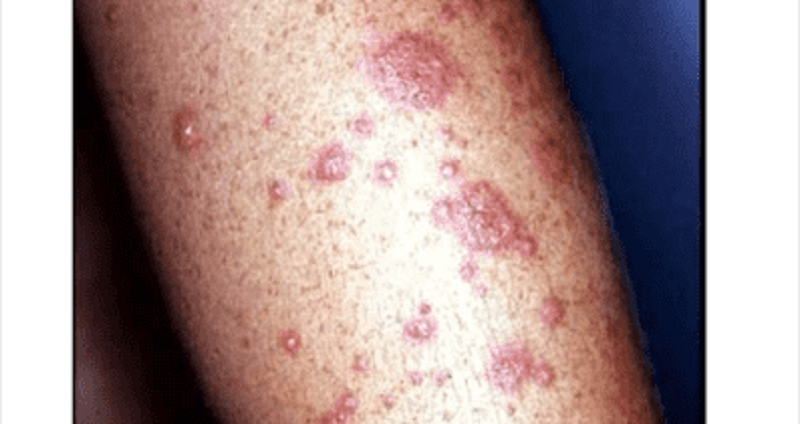
A 45-year-old man is brought to the office due a sudden onset of skin lesions and fever. He is unable to eat or drink due to the pain in his mouth and throat. His wife says that he was complaining of a headache, malaise, and joint pain prior to developing the skin lesions. Generally, he has been in good health, other than an episode of sinusitis, for which he was prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 5 days ago. His pulse is 92/min, blood pressure is 110/80 mmHg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8C (98.4F). On examination, both conjunctivae are inflamed. There is erythema, blistering and ulceration over the oral mucosa. There is an erythematous rash over the trunk and cutaneous lesions over the hands, arms and feet. Some of the lesions are shown in the picture below.What is the most likely diagnosis?
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Erythema multiforme minor
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome
Impetigo
A 55-year-old man comes to the office due to a sudden onset of blisters all over his body. He complains of pain in the involved areas. He first noticed the lesions in his mouth a few days ago. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8C (98.4F). On examination, there are crops of flaccid bullae over normal-appearing skin, and large erosions at sites where the bullae had ruptured. The oral mucosa shows erosions and ulcerations. Slight rubbing of the uninvolved skin causes easy separation of the epidermis. Immunofluorescence microscopy shows deposits of IgG intercellularly in the epidermis. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Bullous pemphigoid
Bullous impetigo
Pemphigus vulgaris
Erythema multiforme
Dermatitis herpetiformis
A 45-year-old woman comes to the office for the evaluation of reddened areas over her face (flushed skin). These areas worsen every time she drinks something hot or goes out in hot, sunny weather. Her vital signs are stable. On examination, there is evident erythema over her nose, cheeks, forehead and chin with telangiectasias, pustules and papules. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Acne vulgaris
Seborrheic dermatitis
Carcinoid syndrome
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Rosacea.
A 30-year-old female presents with a circumferential pruritic rash over her right wrist. The rash has been present for the last two days, and she denies ever having a similar rash before. She bought a new bracelet two weeks ago, and has been wearing it on her right forearm since. Which of the following metals in jewelry is most likely to cause such symptoms?
Copper
Silver
Gold
Platinum
Nickel
A 42-year-old woman presents with painful skin lesions. She is unable to eat or drink because the lesions have involved her mouth and throat. Her other complaints include malaise, headache, sore throat, cough, nausea and vomiting prior to the onset of the skin lesions. She was in perfect health in the past, other than an episode of urinary tract infection 3 days ago. She was prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combination for this infection. Her pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, and temperature is 38.3C (101 F). On examination, the skin is hot and tender with erythematous macules. The oral mucosa shows blistering and erosions. A picture of her back is shown below.What is the most likely diagnosis?
Exfoliative dermatitis
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Erythema multiforme minor
Stevens Johnson's syndrome
A 28-year-old Caucasian woman presents to the primary care physician with complaints of painless blistering on the backs of her hands, accompanied by an increased fragility of the surrounding skin. She first noted the blisters one week ago, after spending some time gardening outdoors. She denies ever having similar symptoms, but suspects that her mother may occasionally have had a similar presentation that eventually resolved without treatment. Her past medical history is significant for chronic infection with Hepatitis C virus. Current medications include oral contraceptives, which were begun last month. Physical examination reveals mild hyperpigmentation of the face. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Allergic contact dermatitis
Porphyria cutanea tarda
Herpes zoster
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Lmpetigo
A 34-year-old Caucasian female presents to the ER with a rash and pruritis. She says that she has had a sore throat for several days, and her friend gave her amoxicillin that turned out to be out dated. The rash developed about 30 minutes after she took the drug. Her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and heart rate is 80/min. Physical examination reveals wide spread urticaria and excoriations. Pharyngeal mucosa and tonsils are hyperemic, and tender lymph nodes are palpated in the submandibular area. Lungs are clear on auscultation. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Continue amoxicillin therapy with non-outdated drug
Administer adrenalin immediately
Prescribe steroids
Prescribe antihistamines
Schedule for dialysis
A 36-year-old male presents to clinic complaining of a pruritic eruption on his forearms. He denies fever, chills and malaise. Physical examination reveals an erythematous rash with occasional vesicles affecting both forearms. No lymphadenopathy is appreciated. Vesicular fluid grows coagulase-negative staphylococci. His only relevant history is recent work in the woods behind his home chopping and transporting firewood. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Herpes simplex infection
S. Aureus cellulitis
S. Epidermidis cellulitis
Suppurative hidradenitis
Contact dermatitis
A 64-year-old female presents with complaints of lesions over her breasts and thighs. She had been experiencing severe pain in those areas prior to developing redness and blisters. Her past medical history is significant for valvular heart disease with atrial fibrillation, ulcerative colitis diagnosed 20 years ago, and a resection of part of her colon. She is a known patient of yours, and four days ago, you started her on treatment for atrial fibrillation with antiarrhythmics and oral anticoagulants. Her pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8C (98.4F). On examination, you notice well-demarcated lesions with bullae and necrotic changes over her thighs and breasts. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Necrotizing fasciitis
Venous gangrene
Warfarin-induced necrosis
Pyoderrma gangrenosum
Cholesterol embolisation syndrome
A mother brings her 6-month-old infant to your office for evaluation of scaly, erythematous lesions around his eyebrows and sides of his nose. She also notes a scaly scalp that improves with baby shampoo. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Atopic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
Tinea capitis
Psoriasis
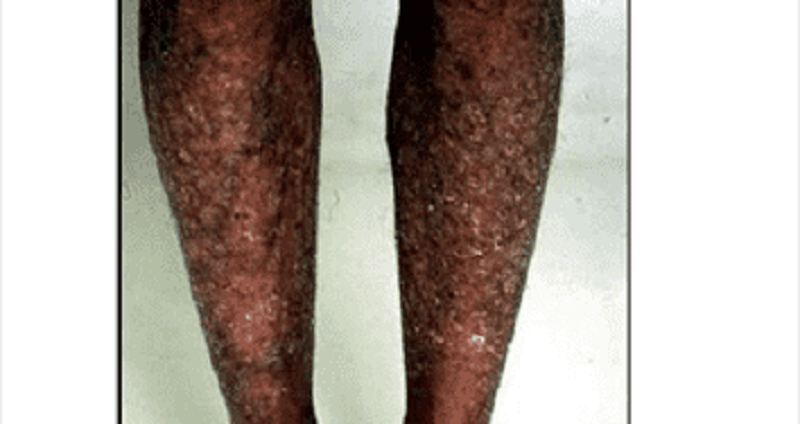
A 20-year-old female comes to the office and complains of rough, dry and scaly skin. Her skin was normal at birth, but gradually became dry. The dryness increases during the winter months, despite regular application of body-moisturizing lotion. An image of the patient's skin lesions is shown below.What is the most likely diagnosis?
Atopic dermatitis
Irritant contact dermatitis
Ichthyosis vulgaris
Lmpetigo
Psoriasis
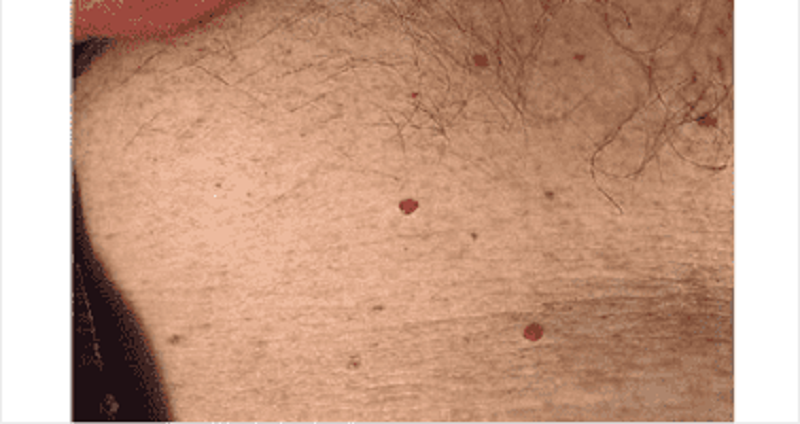
A 35-year-old male presents to your office with red skin lesions on his back that were first noticed by his wife. His past medical history is not significant. Physical examination reveals the following findings (see the slide below).Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Strawberry (capillary) hemangioma
Cherry hemangioma
Spider angioma
Cavernous hemangioma
Cystic hygroma
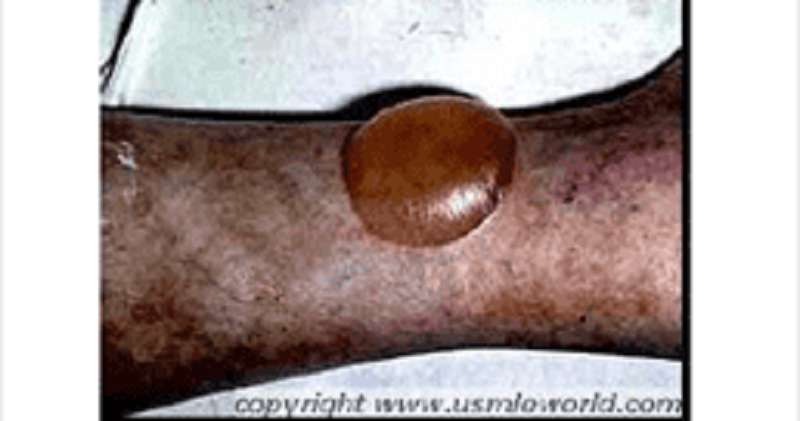
A 65-year-old male comes to the office on a hot summer afternoon. He complains of blisters and intense itching all over his body for the past 2 days. He has been having "itchy red swelling all over" for the past 2 months, which he thinks is due to the summer heat. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8C (98.4F). On examination, lesions are seen on both normal and erythematous skin over flexural areas of the groin, axilla and legs. An image of one of these lesions is shown below. Which of the following is most likely seen with this patient's condition?
LgG and C3 deposits at the dermal-epidermal junction
LgG deposits intercellularly in the epidermis
LgG deposits in a linear band at the dermal-epidermal junction
C3 at the basement membrane zone.
Intradermal edema with leukocyte infiltration
An 83-year-old man is brought to the office by his wife because he has had frequent falls for the past 3 months. The wife says that, "He's not his usual self these days. He needs help with everything, even everyday things." The patient has mask-like facies. He speaks very softly with a poorly modulated voice, and he has a fine tremor in both hands. The resting tremor in his hands disappears with voluntary movements. The other pertinent findings include a shuffling gait with short steps, stooped posture, tendency to fall and rigidity of both upper limbs. What skin condition is associated with this patient's neurologic diagnosis?
Tinea versicolor
Seborrheic dermatitis
Pityriasis rosea
Dermatophytosis
Lichen simplex chronicus
A 43-year-old woman comes to the office because she has "finally decided to see a doctor." For the past four months, she has suffered from itching all over her body. She is tired of using over-the-counter products with no relief. Over the past two months, she has had loose stools, which "take forever to flush." Physical examination reveals jaundice, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. The results of her blood work are as follows: Alkaline phosphatase 200 u/dl Bilirubin 3.3 mg/dl Anti-mitochondrial antibodies positive Which of the following benign lesions of the eye is frequently associated with this patient's condition?
Chalazion
Hordeolum
Molluscum contagiosum
Xanthelasma
Stye
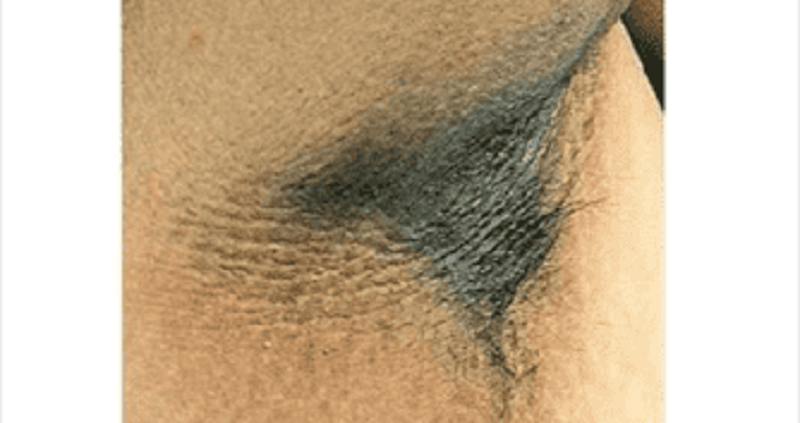
A 31-year-old male presents to your office with a velvety skin rash in his axilla as shown on the slide below.Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Vitamin D resistance
Calcitonin hypersecretion
Testosterone unresponsiveness
Insulin resistance
Serotonin hypersecretion
A 25-year-old male comes to the office due to severe itching and burning of the skin lesions on his knees, elbows and back of his neck. He gives a history of loose stools, flatulence, weight loss of more than 10 lbs, and fatigue for the past 6 months. His vital signs are stable. On examination, there are papules and vesicles over the extensor aspect of his elbows, knees, posterior neck and scalp. The laboratory studies reveal the presence of anti-endomysial antibodies. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Erythema multiforme
Bullous pemphigoid
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Kaposi's sarcoma
Acantholytic dermatosis
A 36-year-old male comes to the office for the evaluation of a skin lesion. For the past two months, he noticed darkening and thickening of the skin over his neck and groin area. These areas occasionally feel itchy. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8C (98.4F). Physical examination reveals symmetrical, hyperpigmented, velvety plaques on the axilla, groin and posterior neck. This patient's condition should alert the physician to check for which of the following?
Gastrointestinal malignancy
Diabetes mellitus
Addison's disease
Pellagra
Hemochromatosis
A 35-year-old white male presents with high-grade fever, chills, rigors, malaise, and pain in his right calf for the last 24 hours. His temperature is 39.5C (103.1F), pulse is 105/min, blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, and respirations are 15/min. Physical examination shows generalized swelling of the calf with linear streaks of erythema. The lesion is warm, tender, and not very well-demarcated. No pain is felt in the calf when the ankle is dorsiflexed. Scaling is found in the toe webs on the right side, and KOH preparation of these lesions show hyphae. Blood cultures are obtained. CBC shows a WBC count of 14,000 with 6% bands. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Oral itraconazole
Oral terbinafine
Intravenous nafcillin
Oral dicloxacillin
Intravenous crystalline penicillin G
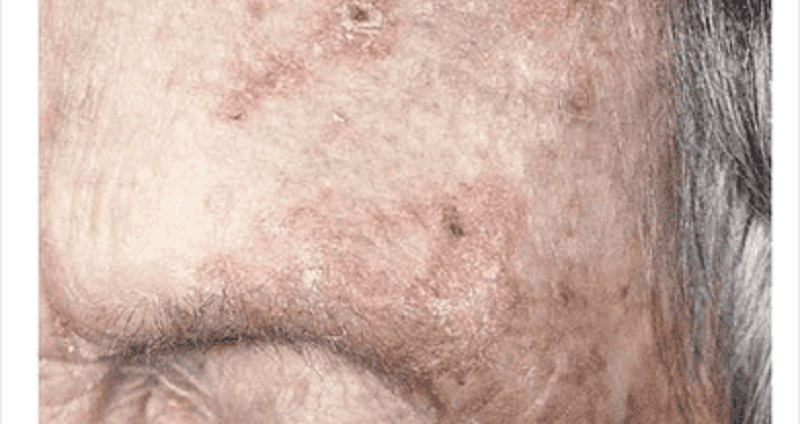

A 70-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office for evaluation of skin lesions on his forehead. On physical exam you find that these papules have a sandpaper texture by palpation. The lesions are illustrated in the slide below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Psoriasis
Seborrheic keratosis
Actinic keratosis
Atopic dermatitis
Pityriasis rose a
A 17 -year-old man presents with a non-pruritic rash in his periumbilical area. The rash consists of firm, dome-shaped, flesh-colored papules with central umbilication. This patient's rash is most commonly associated with which of the following conditions?
Selective lgA deficiency
Cellular immunodeficiency
Complement deficiency
Impaired phagocytosis
Circulating autoantibodies
An 8-year-old boy is brought to the office due to itchy rashes with blisters over his face, trunk and legs for the past 2 days. His vital signs are normal, except for a temperature of 37.7C (100F). On examination, you notice macules, pustules, vesicles, and honey-colored crusts around his mouth, nose, legs, buttocks and trunk area. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Contact dermatitis
Impetigo
Herpes simplex infection
Erythema multiforme
Varicella zoster infection
An 18-year-old white female is brought to the emergency department due to severe vomiting, fever and rashes. She was fine until today, when she developed a fever, flu-like symptoms and dizziness. She has a history of asthma and allergic rhinitis. She denies taking drugs or alcohol, or being exposed to other sick individuals. She had her period yesterday, but did not place a tampon until today, 6 hours prior to becoming ill. Her last menstrual period was 6 weeks ago. She appears alert but listless. Her temperature is 38.8 C, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 23/min, and blood pressures are 100/66 mm Hg, supine and 66/30 mm Hg, standing. On examination, there are erythematous flat and raised rashes on her trunk and extremities. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Toxic shock syndrome
Scarlet fever
Meningococcemia
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
A 9-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because of itching, burning and oozing skin lesions on both of his legs. The boy appears tanned. When asked if he had been spending time outdoors, he replies with great excitement that he just returned yesterday from a camping trip in the woods with his dad. Physical examination of both lower limbs reveals vesicles with erythema arranged in a linear fashion. Weepy and crusted lesions and edema are also present. What type of reaction is responsible for this boy's lesions?
IgE mediated hypersensitivity
Antibody mediated hypersensitivity
Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity
Cell mediated hypersensitivity
Woods biopsy
An 18-month-old Caucasian boy is brought to the emergency department due to a 3-day history of fever and facial rash. His past medical history is significant for atopic dermatitis, which was diagnosed 1 week ago and treated with topical steroids. Examination reveals numerous umbilicated vesicles over erythematous skin of both cheeks. Submandibular adenopathy is present. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Varicella
Impetigo contagiosa
Contact dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis exacerbation
Eczema herpeticum
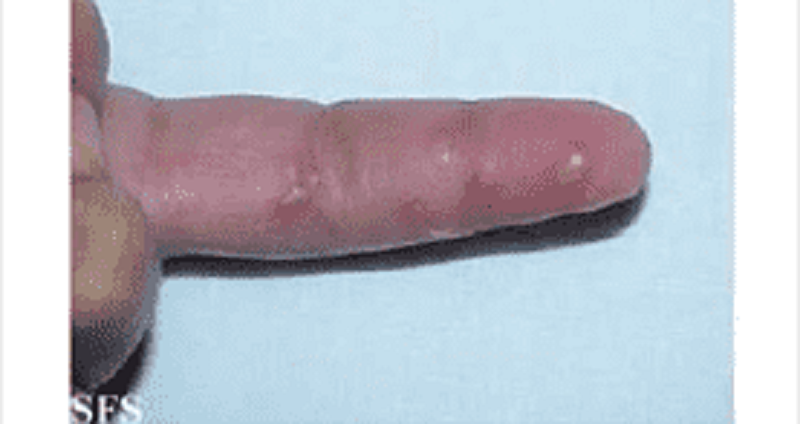
A 45-year-old male comes to you with complaints of throbbing pain over the pulp of his right index finger for the last two days. He has been feeling warm for the last three days. He denies ever having any sexually transmitted disease or cold sores in the past. On examination, he has a swollen, soft, and tender distal pulp space of the right index finger with some non-purulent vesicles. A picture of his hand is shown below. Tzanck smear of the vesicles show multinucleated giant cells. Which of the following is most likely the occupation of this patient?
A dentist
Commercial sex worker
A gardener
A tailor
A Pilot
A 15-year-old male is brought to the emergency department due to sudden-onset difficulty breathing for the past 45 minutes. He also complains of nausea, colicky abdominal pain and a swollen face. He has been suffering from bronchitis for the past 4 days, and his condition had been improving. His mother says that he had a similar episode when he had a tooth extraction 2 year ago. On examination, there is an edematous swelling of his face including the lips, hands, arms, legs, and genitals. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, respirations are 18/min and temperature is 36.8C (984F). Which of the following best explains the pathological process of his condition?
Depressed C1q
Antibody mediated hypersensitivity
C 1 inhibitor deficiency
Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity
Cell mediated hypersensitivity
A 28-year-old Caucasian male presents to the office with a rash on his trunk. He complains of constant itching over the area. He has no other medical problems. He denies any family history of diabetes. He currently has two sexual partners, and he does not use condoms. His pulse is 84/min, blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 37C (98.4F). On his trunk, there are 4 circular patches with central clearing and scaly borders, measuring approximately 3-8cms in diameter. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Tinea corporis infection
Psoriasis
Erythema multiforme
Pityriasis rosea
Secondary syphilis
A 14-year-old white female presents with "spots" on her face that are "so embarrassing!" Physical examination reveals comedones with minimal inflammation. Her past medical history is insignificant. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Dietary modifications
Cream-based cleansers
Topical retinoids
Topical erythromycin
Oral doxycycline
A 30-year-old, Caucasian male comes to the office for the evaluation of some pale patches in a mottled distribution over his trunk area. He just returned from a 2-week summer vacation in the Bahamas, where he first noticed these lesions. His skin is generally well-tanned. Located over his central upper trunk area are multiple, velvety pink, pale macules, measuring approximately 4-5 mm in diameter. These lesions scale on scraping. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Vitiligo
Seborrheic dermatitis
Tinea versicolor
Pityriasis rose a
Tinea corporis
A 48-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office due to a small swelling on her left lower eyelid. She has worked outdoors her whole life. This swelling has been present for the past 6 months. Recently, she noticed a loss of eyelashes on her lower eyelid. On examination, there is a small nodular lesion on the lower eyelid margin. It is firm, painless, pearly and indurated. Loss of lashes on the left lower eyelid is confirmed. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Squamous cell carcinoma
Keratoacanthoma
Basal cell carcinoma
Squamous papilloma
Seborrheic keratosis
A 5-month-old infant is brought to the office by his mother because of a rash on his face, hands and chest. The baby is constantly scratching these areas, and his mother is having a hard time keeping his hands away from the rash. She has tried a variety of over-the-counter products and many home remedies, as advised by her mother, but has noted no improvement. On physical examination, there are erythematous lesions on his cheeks with erosion, scaling, excoriated papules and plaques. Similar lesions are also found on his trunk, scalp and forehead. The lesions are symmetrical, and the diaper area appears spared. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Contact dermatitis
Scabies
Exfoliative dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis
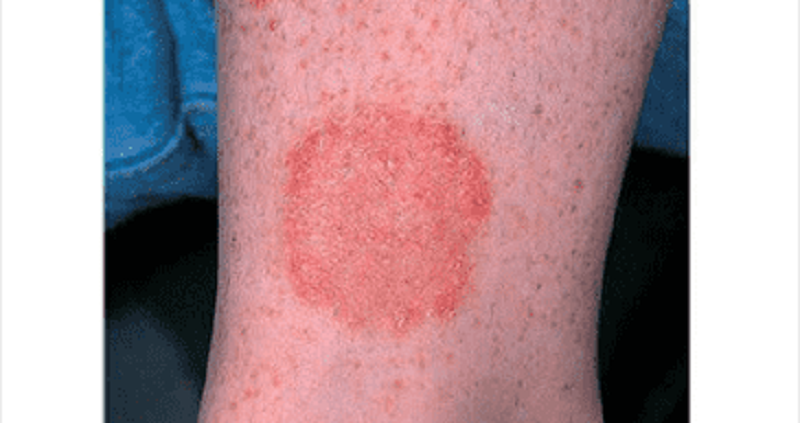
A 12-year-old boy notices a scaly, mildly pruritic rash on his arm (see image below). There is no associated fever, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or back pain. He recently started taking swimming classes. The rash is most likely to clear with which of the following therapies?
Nafcillin
Corticosteroids
Retinoids
Terbinafine
Acyclovir
A 48-year-old white male comes to the emergency department with complaints of severe pain and swelling in his left leg. He sustained an injury to his left leg while playing tennis five days ago. The pain worsened over the past 2-3 days, and is now unbearable. He also complains of flu-like symptoms. His temperature is 39C (102F), pulse is 104/min, blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination reveals an edematous limb with purplish discoloration of the injured area, along with bullae and a serosanguineous discharge. The leg is extremely tender to touch. A scalpel incision of the skin reveals yellowish green necrotic tissues. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Thrombophlebitis
Cellulitis
Necrotizing fasciitis
Erythema induratum
Toxic shock syndrome
A 10-year-old girl with blue eyes and blonde hair is brought to the office by her mother for a routine check-up. All her immunizations are up to date. Her family history is significant for myocardial infarction in her father and schizophrenia in a maternal uncle. There is no family history of any skin malignancies. Her height is at the 60th percentile, and weight is at the 56th percentile. While you are examining her, the mother says with much concern that she saw a television program that claimed that the incidence of skin cancer is increasing dramatically. She wants to know the best way to prevent skin cancer in her daughter, especially since they live in California. What is the best advice to help prevent malignant melanoma in this child?
Sun screen lotion with SPF (sun protection factor) 15
Sun screen lotion with SPF 30
Protective clothing
Avoid going outdoors
No action needs to be taken, since there is no family history of melanoma
A 50-year-old man comes to the emergency department due to acute onset respiratory difficulty. He also has periorbital, circumoral and facial edema. Two weeks ago, he experienced chest pain, profuse sweating and anxiety, and was subsequently admitted to the cardiac intensive care unit. At that time, his ECG showed ST segment elevation and Q waves in the inferior leads. He was taken to the catheterization lab and had an angioplasty with stent done for 100% occlusion of the right coronary artery. He was discharged with the following medications: aspirin, clopidogrel, metoprolol, enalapril, simvastatin and isosorbide mononitrate. In the ED, his pulse is 102/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, respirations are 24/min and temperature is 36.8C (98.4F). Which of the following is most likely responsible for his present symptoms?
Metoprolol
Lsosorbide
Clopidogrel
Aspirin
Enalapril
A 20-year-old woman presents with complaints of a rash for the past 2 days. She was in good health until 5-6 days ago, when she developed fever, malaise and headache. The rash first appeared on her face, and then rapidly spread to her trunk and extremities. Her pulse is 86/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 37.2C(99F). On examination, there is a pink maculopapular rash involving her face, trunk and extremities. Tender lymph nodes are palpable in the posterior auricular and posterior cervical areas. Her soft palate reveals patchy erythema. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Secondary syphilis.
Rubella
Kawasaki disease.
Rocky mountain spotted fever
Erythema multiforme
A 4-year-old girl is brought to the office by her parents due to a red rash and blisters. Yesterday, she had a fever and was irritable. Today, she developed the rash with blisters. Her pulse is 90/min, blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 39C (102F). On examination, there are superficial flaccid bullae and an erythematous rash diffusely distributed over her body. Nikolsky's sign is positive. Her face is edematous, and there is crusting around the mouth area. Her skin is warm and tender with exfoliation. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Erysipelas
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Scarlet fever
Mpetigo
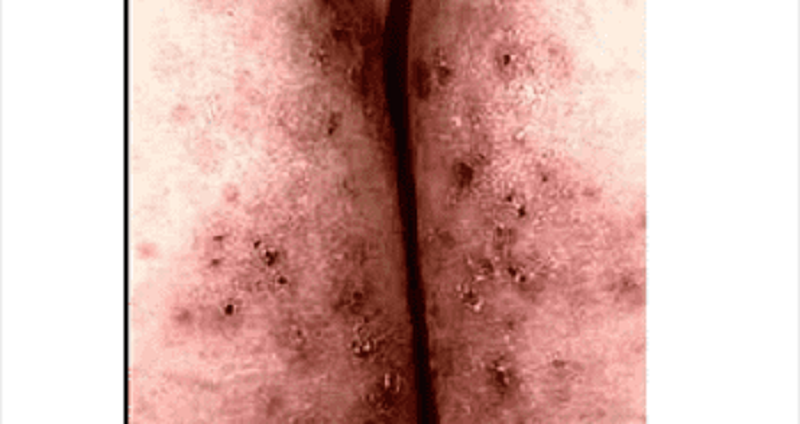
A 25-year-old male presents with skin lesions over his elbows, knees and neck. He complains of intense itching and burning sensation over these lesions for the past 10 days. He was advised to follow a gluten-free diet on his previous visit, but was not compliant. His vital signs are stable. On examination, there are flesh-colored to erythematous vesicles distributed over the extensor aspects of elbows, knees, posterior neck and shoulders. Some of these lesions are shown in the picture below. Which of the following is the drug of choice for his skin condition?
High potency steroids
Low dose acyclovir
1% lindane solution
Azathioprine
Dapsone
A 23-year-old college student comes to the office due to itching all over her body for the past 10 days. She hardly gets to sleep at night because of it. Her roommate has similar complaints. Her vital signs are stable. Physical examination reveals vesicles and pustules arranged in short, gray wavy channels on the finger webs, heels of palms, and in wrist creases. There are papules over the nipples and areola of her breasts. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Insect bites
Urticaria
Scabies
Body lice
Bed bugs
A 32-year-old Asian female presents to the office with a mole on her foot that recently became darker. She has always had skin that is very sensitive to sunlight. She is unable to tan, and has had several sunburns when she did not use sunscreens. Her past medical history is insignificant. Her mother had 'a kind of skin cancer.' Physical examination reveals a dark mole with irregular borders on the left foot. Which of the following is the strongest risk factor for malignancy in this patient?
Asian race
Age
Recently changed mole
Sun sensitivity
Previous sunburns
A 7-year-old girl is brought to the office by her mother due to a rash all over her body. She was apparently in good health until 4 days ago, when she developed fever, cough and eye pain. This morning, she developed a rash on her face, which later spread all over her entire body. Her pulse is 86/min, respirations are 14/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.2C (99F). On examination, there is an erythematous maculopapular rash covering her entire body. There are small red spots with bluish specks on her buccal mucosa. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Roseola infantum.
Rubella.
Varicella zoster infection.
Parvovirus infection.
Paramyxovirus infection.
A 20-year-old woman complains of skin problems and is noted to have erythematous papules on her face with blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones). She has also had cystic lesions. She is prescribed topical tretinoin, but without a totally acceptable result. You are considering oral antibiotics, but the patient requests oral isotretinoin, which several of her college classmates have used with benefit. Which of the following statements is correct?
Intralesional triamcinolone should be avoided due to its systemic effects.
Systemically administered isotretinoin therapy cannot be considered unless concomitant contraceptive therapy is provided.
Antimicrobial therapy is of no value since bacteria are not part of the pathogenesis of the process.
The teratogenic effects of isotretinoin are its only clinically important side effects.
The patient will not benefit from topical antibiotics since she did not respond to topical retinoids.
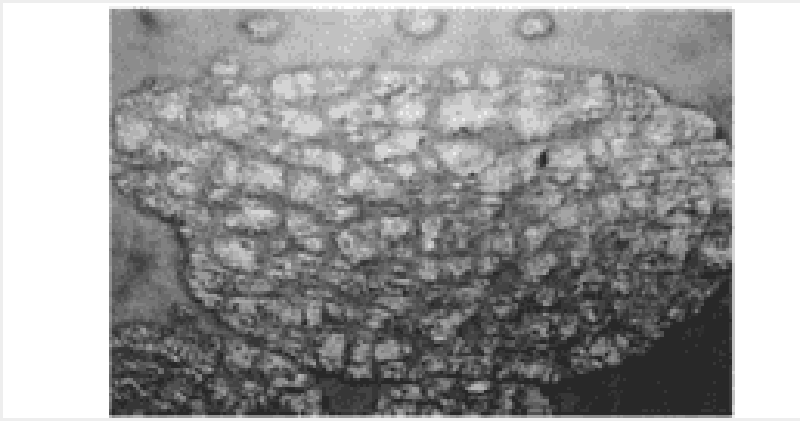
A 22-year-old male presents with a 6-month history of a red, nonpruritic rash over the trunk, scalp, elbows, and knees. These eruptions are more likely to occur during stressful periods and have occurred at sites of skin injury. The patient has tried topical hydrocortisone without benefit. On examination, sharply demarcated plaques are seen with a thick scale. Pitting of the fingernails is present. There is no evidence of synovitis. What is the best first step in the therapy of this patient’s skin disease?
Photochemotherapy (PUVA)
Oral methotrexate
Topical calcipotriene
Oral cyclosporine
Topical fluticasone
A 25-year-old complains of fever and myalgias for 5 days and now has developed a macular rash over his palms and soles with some petechial lesions. The patient recently returned from a summer camping trip in Tennessee. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the rash?
Contact dermatitis
Sexual exposure
Tick exposure
Contaminated water
Undercooked pork
A 17-year-old female presents with a pruritic rash localized to the wrist. Papules and vesicles are noted in a bandlike pattern, with slight oozing from some lesions. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the rash?
Herpes simplex
Shingles
Atopic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
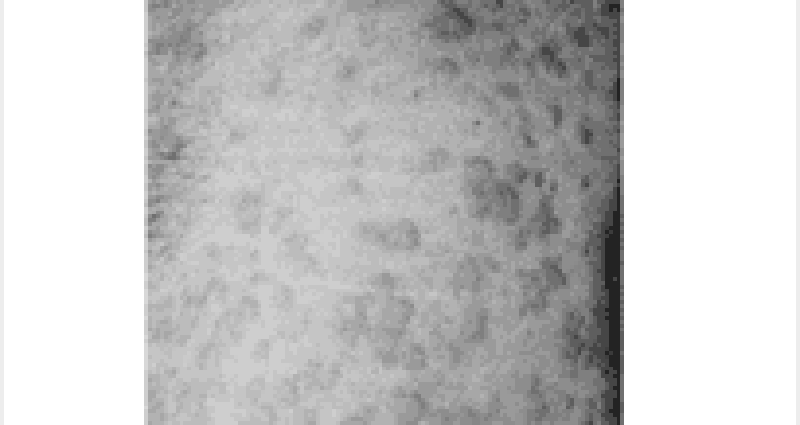
A 35-year-old woman develops an itchy rash over her back, legs, and trunk several hours after swimming in a lake. Erythematous, edematous papules and plaques are noted. The wheals vary in size. There are no mucosal lesions and no swelling of the lips. What is the best first step in management of her symptomatic rash?
Subcutaneous epinephrine
Intravenous glucocorticoids
Oral antihistamines (H1 blocker)
Aspirin
Oral doxycycline
A 64-year-old woman presents with diffuse hair loss. She says that her hair is “coming out by the handfuls” after shampooing. She was treated for severe community-acquired pneumonia 2 months ago but has regained her strength and is exercising regularly. She is taking no medications. Examination reveals diffuse hair loss. Several hairs can be removed by gentle tugging. The scalp is normal without scale or erythema. Her general examination is unremarkable; in particular, her vital signs are normal, she has no pallor or inflammatory synovitis, and her reflexes are normal with a normal relaxation phase. What is the best next step in her management?
Reassurance
Measurement of serum testosterone and DHEA-S levels
Topical minoxidil
Topical corticosteroids
CBC and antinuclear antibodies
A 30-year-old black female has a 2-month history of nonproductive cough and a painful skin eruption in the lower extremities. She denies fever or weight loss. Physical examination shows several nontender raised plaques around the nares and scattered similar plaques around the base of the neck. In the lower extremities she has several erythematous tender nonulcerated nodules, measuring up to 4 cm in diameter. Chest x-ray reveals bilateral hilar adenopathy and a streaky interstitial density in the right upper lobe. What is the best way to establish a histological diagnosis?
Punch biopsy of one of the plaques on the neck
Incisional biopsy of one of the lower extremity nodules
Sputum studies for AFB and fungi
Mediastinoscopy and biopsy of one of the hilar or mediastinal nodes
Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme assay
A 72-year-old woman presents with pruritus for the past 6 weeks. She is careful to moisturize her skin after her daily shower and uses soap sparingly. She has never had this symptom before. The itching is diffuse and keeps her awake at night. Over this time she has lost 15 lb of weight and has noticed diminished appetite. She has previously been healthy and takes no medications. Physical examination shows no evidence of rash; a few excoriations are present. She appears fatigued and shows mild temporal muscle wasting. The general examination is otherwise unremarkable. What is the best next step in her management?
Topical corticosteroids
Oral antihistamines
Psychiatric referral for management of depression
Skin biopsy at the edge of one of the excoriations
Laboratory testing including CBC, comprehensive metabolic panel, and thyroid studies
A 53-year-old female presents to the clinic with an erythematous lesion on the dorsum of her right hand. The lesion has been present for the past 7 months and has not responded to corticosteroid treatment. She is concerned because the lesion occasionally bleeds and has grown in size during the past few months. On physical examination you notice an 11-mm erythematous plaque with a small central ulceration. The skin is also indurated with mild crusting on the surface. Which of the following is true about this process?
It is a malignant neoplasm of the keratinocytes with the potential to metastasize.
It is an allergic reaction resulting from elevation of serum IgE.
It is a chronic inflammatory condition, which can be complicated by arthritis of small and medium-sized joints.
It is a malignant neoplasm of the melanocytes with the potential to metastasize.
It is the most common skin cancer.
A 50-year-old woman develops pink macules and papules on her hands and forearms in association with a sore throat. The lesions are target like, with the centers a dusky violet. What causes of this disorder are most likely in this patient?
Tampons and superficial skin infections
Drugs and herpesvirus infections
Rickettsial and fungal infections
Anxiety and emotional stress
Harsh soaps and drying agents
A 25-year-old female with blonde hair and fair complexion complains of a mole on her upper back. The lesion is 8 mm in diameter, darkly pigmented, and asymmetric, with an irregular border (see illustration below). Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Tell the patient to avoid sunlight
Follow the lesion for any evidence of growth.
Obtain metastatic workup
Obtain full-thickness excisional biopsy
Obtain shave biopsy
A 39-year-old male with a prior history of myocardial infarction complains of yellow bumps on his elbows and buttocks. Yellow-colored cutaneous plaques are noted in those areas. The lesions occur in crops and have a surrounding reddish halo. Which of the following is the best next step in evaluation of this patient?
Biopsy of skin lesions
Lipid profile
Uric acid level
Chest x-ray
Liver enzymes
A 15-year-old girl complains of low-grade fever, malaise, conjunctivitis, runny nose, and cough. After this prodromal phase, a rash of discrete pink macules begins on her face and extends to her hands and feet. She is noted to have small red spots on her palate. What is the most likely cause of her rash?
Toxic shock syndrome
Gonococcal bacteremia
Reiter syndrome
Rubeola (measles)
Rubella (German measles)
A 17-year-old girl noted a 2-cm annular pink, scaly lesion on her back. Over the next 2 weeks she develops several smaller oval pink lesions with a fine collarette of scale. They seem to run in the body folds and mainly involve the trunk, although a few occur on the upper arms and thighs. There is no adenopathy and no oral lesions. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Tinea versicolor
Psoriasis
Lichen planus
Pityriasis rosea
Secondary syphilis
A 45-year-old man with Parkinson disease has macular areas of erythema and scaling behind the ears and on the scalp, eyebrows, glabella, nasolabial folds, and central chest. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Tinea versicolor
Psoriasis
Seborrheic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis
Dermatophyte infection
A 20-year-old white man notes an uneven tan on his upper back and chest. On examination, he has many circular, lighter macules with a barely visible scale that coalesce into larger areas. Which test is most likely to establish the diagnosis?
Punch biopsy
Potassium hydroxide (KOH) microscopic examination
Dermatophyte test medium (DTM) culture for fungus
Serological test for syphilis
Tzanck smear
A 33-year-old fair-skinned woman has telangiectasias of the cheeks and nose along with red papules and occasional pustules. She also appears to have conjunctivitis with dilated scleral vessels. She reports frequent flushing and blushing. Drinking red wine produces a severe flushing of the face. There is a family history of this condition. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Carcinoid syndrome
Porphyria cutanea tarda
Lupus vulgaris
Rosacea
Seborrheic dermatitis
A 46-year-old construction worker is brought to the clinic by his wife because she has noticed an unusual growth on his left ear for the past 8 months (see photo below). The patient explains that, except for occasional itching, the lesion does not bother him. On physical examination, you notice an 8-mm pearly papule with central ulceration and a few small dilated blood vessels on the border. What is the natural course of this lesion if left untreated?
This is a benign lesion and will not change.
Local invasion of surrounding tissue.
Regression over time.
Local invasion of surrounding tissue and metastasis via lymphatic spread.
Disseminated infection resulting in septicemia.
A 25-year-old postal worker presents with a pruritic, nonpainful skin lesion on the dorsum of his hand. It began like an insect bite but expanded over several days. On examination, the lesion has a black, necrotic center associated with severe local swelling. The patient does not appear to be systemically ill, and vital signs are normal. Which of the following is correct?
The lesion is ecthyma gangrenosum, and blood cultures will be positive for Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
A skin biopsy should be performed and Gram stain examined for gram-positive rods.
The patient has been bitten by Loxosceles reclusa, the brown recluse spider.
The patient has the bubo of plague.
The patient has necrotizing fasciitis and needs immediate surgical debridement.
25-year-old who has been living in Washington, DC, presents with a diffuse vesicular rash over his face and trunk. He also has fever. He has no history of chickenpox and has not received the varicella vaccine. Which of the following information obtained from history and physical examination suggests that the patient has chickenpox and not smallpox?
There are vesicular lesions on the palms and soles.
Vesicular lesions are concentrated on the trunk.
The rash is most prominent over the face.
All lesions are at the same stage of development.
The patient experienced high fever several days prior to the rash.
A 68-year-old man complains of several blisters arising over the back and trunk for the preceding 2 weeks. He takes no medications and has not noted systemic symptoms such as fever, sore throat, weight loss, or fatigue. The general physical examination is normal. The oral mucosa and the lips are normal. Several 2 to 3 cm bullae are present over the trunk and back. A few excoriations where the blisters have ruptured are present. The remainder of the skin is normal, without erythema or scale. What is the best diagnostic approach at this time?
Culture of vesicular fluid for herpes viruses
Trial of corticosteroids
Biopsy of the edge of a bulla with some surrounding intact skin
CT scan of the chest and abdomen looking for occult malignancy
Combination of oral H1 and H2 antihistamines
A 63-year-old retired farmer presents to the clinic complaining of red scaly spots on his head for the past 9 months. Physical examination is remarkable for numerous erythematous hyperkeratotic papules and plaques. The lesions are confined to the head and forehead and have poorly defined borders. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Punch biopsy of one of the lesions
Application of hydrocortisone cream to affected areas and follow-up in 4 weeks
Reassurance that this is a benign finding and follow-up in 6 months
Application of fluocinide cream to affected areas and follow-up in 4 weeks
Application of 5-fluorouracil cream to affected areas and follow-up in 4 weeks
21-year-old female presents with an annular pruritic rash on her neck. She explains that the rash has been present for the past 3 weeks and that her roommate had a similar rash not long ago. Physical examination is remarkable for a 20-mm scaling, erythematous plaque with a serpiginous border. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial treatment for this condition?
Griseofulvin
Oral cephalexin
Topical mupirocin ointment
Topical ketoconazole
Hydrocortisone cream
A 34-year-old homosexual male with a history of HIV presents to the clinic complaining of a wheezing and multiple violaceous plaques and nodules on his trunk and extremities. Physical examination of the oral mucosa reveals similar findings on his palate, gingiva, and tongue. Chest x-ray is also significant for pulmonary infiltrates. What is the most likely pathogenesis of this process?
Proliferation of neoplastic T cells
Infection with human herpesvirus 6
Infection with Mycobacterium avium due to decreasing CD4 count
Angioproliferative disease caused by infection with human herpesvirus 8
Disseminated HSV infection
{"name":"DERMATOLOGY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 22-year-old female is referred to the dermatology clinic. Over the past few years, she has noticed small areas of depigmentation on her arms and legs. Some of these areas are well-circumscribed, as shown in the picture below. She is otherwise well. Her only medication is the oral contraceptive pill. She is currently sexually active with more than one partner. Which of the following diseases is most likely to be associated with her skin condition?, A 65-year-old man comes to the office and complains of pain and a rash with blisters over the left side of his chest. He has experienced pain over the area for the past 2 days. This morning, he noticed blisters while changing his shirt. He also complains of malaise and headache. His pulse is 82\/min, blood pressure is 140\/90 mmHg, respirations are 14\/min and temperature is 36.8C (98.4F). Physical examination reveals grouped, tense vesicles arranged in a band along the left side of his chest. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of his condition?, A 65-year-old man comes to the office with a six-month history of a non-healing ulcer on his right forearm. Physical examination demonstrates a scaling plaque with central ulceration and 1.5 cm diameter. The biopsy shows polygonal cells with atypical nuclei at all levels of the epidermis with zones of keratinization. What is the single most important risk factor for this condition?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/11-496253/1.png?sz=1200-00000002871000005300"}
More Quizzes
Τι σημαίνουν τα αρχικά των κομμάτων;
1050
Lesson 19
740
Which Greek Goddess are you?
5222
QUIZ (Cast)
1680
Free Foundational Christian Beliefs
201024581
Free Corporate Charity Trivia
201022178
Free Conjuring Character: Which Role Are You?
201026425
The Foot Book AR: Free AR Tests and Answers
201048397
Which Lost Character Are You? Discover Your Island Match
201034382
Strict Parents Test: Is Your Mother Too Strict?
201030297
Free Electrical Fundamentals
201022017
Free Government 12th Grade Practice Test
201023968