DES C_Diagnosis (12) Prepared : CHILLY
A 78-year-old diabetic man has undergone surgical repair of a large abdominal aortic aneurysm. Postoperatively, he develops left lower quadrant abdominal pain followed by bloody diarrhea. He has a history of prostate cancer and received radiation therapy several years ago. He eats a low fiber diet. He quit smoking recently. Vital signs show a low grade fever. Examination shows tenderness in the left lower quadrant and rectal examination reveals blood in the stool. CT scan of the abdomen demonstrates thickening of the colon at the recto-sigmoid junction. On colonoscopy, ulcerations are seen in the same area while the colon above and below the lesions is completely normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
Acute diverticulitis
Clostridium difficile colitis
Radiation proctitis
Ischemic colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease
A 78-year-old man comes to the physician because of a bloody urethral discharge for 3 days. He has had increasing frequency of urination and hesitancy for the past 2 years, but these symptoms have never been severe enough to require medical attention. Digital rectal examination reveals a slightly enlarged and firm prostate. Expressed prostatic secretions are negative for bacteria and leukocytes. Collection of clean-catch urine in separate aliquots reveals initial hematuria, with blood present in the first 5 mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Gonococcal infection
Nonbacterial prostatitis
Prostatic carcinoma
Testicular cancer
Urethral carcinoma
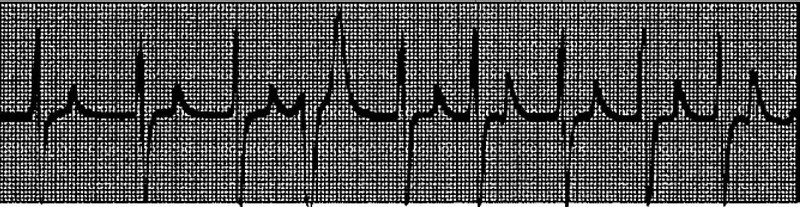
A 78-year-old man with advanced renal disease has the ECG shown in Fig. (lead II). What is the diagnosis?
Hyperkalemia
Hypercalcemia
Hypernatremia
Pericarditis
Ventricular aneurysm
A 78-year-old woman is brought to the ED by EMS complaining of vomiting and abdominal pain that began during the night. EMS reports that her BP is 90/50 mm Hg, HR is 110 beats per minute, temperature is 101.2°F, and RR is 18 breaths per minute. After giving her a 500 mL bolus of NS, her BP is 115/70 mm Hg. During the examination, you notice that her face and chest appear jaundiced. Her lungs are clear to auscultation and you do not appreciate a murmur on cardiac examination. She winces when you palpate her RUQ. An ultrasound reveals dilation of the common bile duct and stones in the gallbladder. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cholecystitis
Acute hepatitis
Cholangitis
Pancreatic cancer
Bowel obstruction
A 78-year-old woman is seen in the emergency department for difficulty breathing and cough over the past 4 hours. She has a history of congestive heart failure for which she takes hydrochlorothiazide, metoprolol, and enalapril. Her oxygen saturation is 92% on room air. On examination there is a high-pitched systolic crescendodecrescendo murmur best heard at the right upper sternal border with radiation to the carotids, and rales are present in both lung fields on inspiration. There is 2+ symmetrical pitting edema bilaterally in the lower extremities. X-ray of the chest shows an enlarged heart and prominent pulmonary vasculature. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s pulmonary edema?
Decreased interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
Increased capillary fluid hydrostatic pressure
Decreased capillary fluid oncotic pressure
Increased capillary permeability
Increased interstitial fluid oncotic pressure
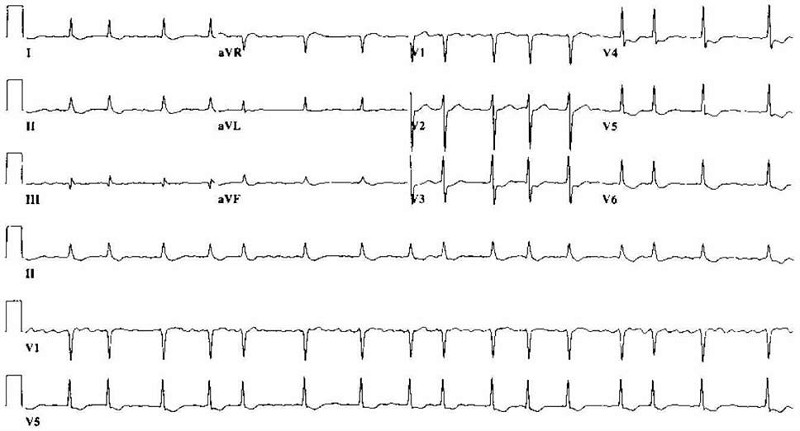
A 78-year-old woman presents to a nursing home physician complaining of palpitations over the past several months. Her episodes are not associated with any chest pain, dizziness, or loss of consciousness. The patient reports that she spent several weeks in the hospital as a child with rheumatic fever. ECG is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Atrial fibrillation
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia
Atrial flutter
Multifocal atrial tachycardia
A 79-year-old man with atrial fibrillation develops an acute abdomen. When seen 2 days after the onset of the abdominal pain, he has a silent abdomen, with diffuse tenderness and mild rebound. There is a trace of blood on the rectal examination. He also has acidosis and looks quite sick. X-ray films show distended small bowel and distended right colon, up to the middle of the transverse colon. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute pancreatitis
Mesenteric ischemia
Midgut volvulus
Perforated viscus
Primary peritonitis
A 9-month-old boy is taken to the emergency room because of high fever. Breath sounds are diminished in the lungs, and a chest x-ray film shows lobar pneumonia. Probable streptococcal pneumonia is demonstrated in Gram's stain of sputum and then later confirmed by culture. The child responds to antibiotic therapy. A detailed history is taken during the admission, which reveals that this is the third episode of pneumonia in this young child; the two previous episodes occurred at 6 and 7.5 months of age. One of the mother's brothers had died of infection at age 9. Immunoglobulin studies demonstrate the following: IgG 80 mg/dL [normal 723-1685 mg/dL], IgA 60 mg/dL [normal 81-463 mg/dL], IgM 20 mg/dL [normal 48-271 mg/dL]. Studies of the lymphocyte population demonstrate normal numbers of T cells and markedly decreased B cells. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Common variable immunodeficiency
Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy
Bruton agammaglobulinemia
DiGeorge syndrome
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
A 9-year-old boy is brought to the office by his parents due to headaches, vomiting and visual disturbances. One week ago, he began to experience headaches that were most prominent in the morning. He also became lethargic, and had a decreased appetite and decline in school performance. The pertinent physical findings include an unbalanced gait, trunk dystaxia, horizontal nystagmus, and papilledema. If this child had a medulloblastoma, which structure would most likely be affected?
Cerebellar hemispheres
Cerebellar vermis
Spinocerebellar tracts
Cerebellar peduncles
Frontal lobe
A 9-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician's office for bed-wetting. His mother states that he has never been dry at night. Occasionally, he has problems controlling his bladder during the day. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 98/56 mm Hg. Both his weight and height are below the 5th percentile for his age. His bladder is enlarged and palpable above the symphysis pubis. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his problem?
Obstructive uropathy
Primary polydipsia
Reflux nephropathy
Sickle cell trait
Unstable bladder
A 9-year-old boy presents with a 3-month history of multiple episodes of sudden awakening at night. His mother states that when he wakes up suddenly, he screams, "Go! Get away! Go!" and does not respond to the parents. His eyes are wide open, and he sweats heavily and looks scared. The parents have had to struggle to awaken him. After the episodes, he has no memory of what happened. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Confusional arousals
Night terrors
Nightmares
Obstructive sleep apnea
Panic disorder
A 9-year-old boy presents with a several-day history of progressive arm and leg weakness. He has been well except for an upper respiratory infection 2 weeks ago. The patient is alert and oriented. On repeated examination, the heart rate varies between 60 and 140 beats/min, and the blood pressure (BP) varies between 90/60 and 140/90 mmHg. Respirations are shallow, with a rate of 50/min. There is symmetric weakness of the face and all four extremities. Deep tendon reflexes are absent. Sensation is intact. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Polymyositis
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Viral encephalitis
Myasthenia gravis
Transverse myelitis
A 9-year-old Caucasian male complains of fever, sore throat and difficulty swallowing. Small tender lymph nodes are palpated in the cervical region. The symptoms subside quickly on penicillin therapy. Ten days later, the patient presents again with fever, skin rash and fleeting joint pain in the lower extremities. Physical examination reveals scattered urticaria and palpable lymph nodes in the cervical, axillary and inguinal regions. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
Rheumatic fever
Lymphoproliferative disorder
Drug-induced reaction
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
Infective endocarditis
A 9-year-old girl is brought by her sister to her pediatrician with the complaint of severe, intermittent headaches for the past several months, one of which resulted in her going to the ER. The physical examination today, including a careful neurologic examination, is normal. The headache is diffuse, throbbing, lasts several hours, and is not associated with vomiting or other symptoms. The child cannot feel the headaches coming on; they appear on all days of the week; and usually the headaches are gone when she awakens from a nap. The child reports that she is doing well in school, plays clarinet in the school band, and has “lots of friends.” The sister is not sure, but she thinks their father, who lives in another state, may have headaches. The most likely explanation for this girl’s headache is which of the following?
Migraine
Fungal meningitis
Tensionheadache
Brain tumor
Sinusitis
A 9-year-old girl presents for evaluation of regular vaginal bleeding. History reveals thelarche at age 7 and adrenarche at age 8. Which of the following is the most common cause of this condition in girls?
Idiopathic
McCune-Albright syndrome
Gonadal tumors
Hypothyroidism
Tumors of the central nervous system
A 90-year-old G5P5 with multiple medical problems is brought into your gynecology clinic accompanied by her granddaughter. The patient has hypertension, chronic anemia, coronary artery disease, and osteoporosis. She is mentally alert and oriented and lives in an assisted living facility. She takes numerous medications, but is very fun
Normal examination
Third-degree uterine prolapse
Complete procidentia
First-degree uterine prolapse
Second-degree uterine prolapse
A 90-year-old male complains of hip and back pain. He has also developed headaches, hearing loss, and tinnitus. On physical examination the skull appears enlarged, with prominent superficial veins. There is marked kyphosis, and the bones of the leg appear deformed. Serum alkaline phosphatase is elevated. Calcium and phosphorus levels are normal. Skull x-ray shows sharply demarcated lucencies in the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones. X-rays of the hip show thickening of the pelvic brim. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Multiple myeloma
Vitamin D intoxication
Paget disease
Metastatic bone disease
Osteitis fibrosa cystica
A baby is born at 34 weeks gestation. The amniotic fluid is brown and murky. The baby has low APGAR scores and appears to be septic, with lethargy, apnea, bradycardia, and temperature instability. The mother lives on a farm and gives a history of a flu-like illness one month before delivery. Gram's stain of a smear from the mother's cervix demonstrates abundant, pleomorphic, gram-variable coccobacillary forms. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital cytomegalovirus infection
Congenital syphilis
Congenital rubella
Neonatal herpes simplex infection
Neonatal listeriosis
A beekeeper’s previously healthy 6-month-old son develops gradual onset of lethargy, poor feeding, constipation, and generalized weakness. On taking a history, you determine that the child has recently been placed on a homemade formula consisting of evaporated milk, water, and honey. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this symptom complex?
Sodium intoxication
Hirschsprung disease
Hypothyroidism
Spinal cord tumor
Botulism
A blond, blue-eyed, 69-year-old sailor has a non-healing, indolent, 1.5-cm ulcer on the lower lip, arising from the vermilion border. The ulcer has been present and growing for the past 8 months. He is a pipe smoker, but has no history of alcohol or drug abuse. Physical examination shows "weather-beaten" facial skin, but no other ulcers. There are no enlarged lymph nodes in his neck. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Adenocarcinoma
Benign ulceration due to chronic trauma
Basal cell carcinoma
Invasive malignant melanoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
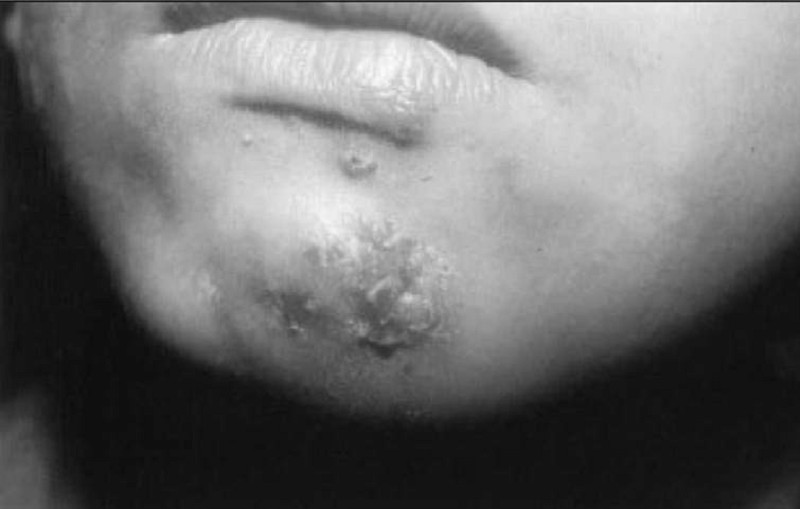
A boy has returned home from visiting his grandmother in a rural area. He spent most of his time swimming, playing in the yard, helping in the gardens, and chasing his Chihuahua; his grandma says “he was generally dirty!” He was noted 2 weeks ago to have “infected mosquito bites” on his neck and chin for which the local doctor had him just scrub with soap; a few remain and are shown in the photograph below. His mother brings him into the office with the complaint of dark urine, swelling around his eyes, and shortness of breath. You also find him to have hypertension and hepatomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his problem?
IgA nephropathy
Idiopathic hypercalciuria
Pyelonephritis
Sexually transmitted disease
Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
A boy is delivered at 37 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery. He is the product of a normal pregnancy and was delivered without complications. Prenatally the mother was blood type B and was rubella immune and negative for Rh antibody, group B streptococci, rapid plasma reagin, hepatitis B surface antigen, gonorrhea, and chlamydia. The patient appears cyanotic. He is breathing at a rate of 60/min and his heart rate is 130/min. He has a normal S1 and S2. There is a harsh holosystolic murmur that is loudest at the left lower sternal border. His examination reveals palpable nonbounding peripheral pulses bilaterally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Coarctation of the aorta
Patent ductus arteriosus
Dextraposed transposition of the great arteries
Tetralogy of Fallot
Truncus arteriosus
A brain-dead potential donor has become available. You must plan for the dispersal of the thoracic organs. Which of the following will necessitate a heart-lung transplant?
Idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy with long-standing secondary pulmonary hypertension
End-stage pulmonary fibrosis secondary to sarcoidosis
Primary pulmonary hypertension
Cystic fibrosis
End-stage emphysema
A cardiologist is called to consult on the care of a 2-day-old girl delivered at 33 weeks’ gestation. The infant is lying supine in her isolette. She is acyanotic, but has a heart rate of 192/min and a respiratory rate of 60/min. She has a nonradiating continuous machinery murmur at the left upper sternal border that remains the same with compression of the ipsilateral, then contralateral jugular veins. S1 and S2 are normal. Her peripheral pulses are bounding. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Aortic stenosis with aortic regurgitation
Systemic arteriovenous fistula
Patent ductus arteriosus
Venous hum
Ventricular septal defect
A child has a 2-week history of spiking fevers, which have been as high as 40°C (104°F). She has spindle-shaped swelling of finger joints and complains of upper sternal pain. When she has fever, the parents note a faint salmon-colored rash that resolves with the resolution of the fever. She has had no conjunctivitis or mucositis, but her heart sounds are muffled and she has increased pulsus paradoxus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Rheumatic fever
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Toxic synovitis
Septic arthritis
Osteoarthritis
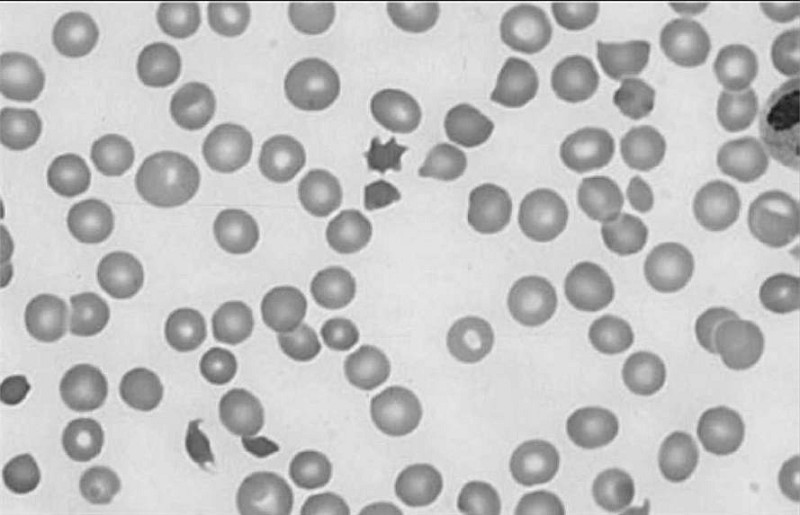
A college sophomore is found by his roommate emergency department. After resuscitation, the man complains of a severe headache and photophobia that is accompanied by dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and neck pain. Physical examination is noteworthy for positive Kernig’s and Brudzinski’s signs as well as petechiae on the trunk and mucocutaneous bleeding. Laboratory studies show: WBC count: 17,000/mm3, Hemoglobin: 11 g/dL, Platelet count: 70,000/mm3, Bleeding time: 10 min, Prothrombin time: 17 sec, Activated partial thromboplastin time: 47 sec, Thrombin time: 18 sec. A peripheral blood smear is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Protein C deficiency
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Factor V Leiden
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
A cyanotic newborn is suspected of having congenital heart disease. He has an increased left ventricular impulse and a holosystolic murmur along the left sternal border. The ECG shows left-axis deviation and left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Transposition of the great arteries
Truncus arteriosus
Tricuspid atresia
Tetralogy of Fallot
Persistent fetal circulation
A female neonate is undergoing an examination after birth. She was born to a 33-year-old primigravid mother at term via a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery. The pregnancy was uncomplicated, except for a positive maternal group B Streptococcus culture at 36 weeks' gestation, for which the mother received penicillin during labor. The infant's APGAR scores are 8 at 1 minute and 9 at 5 minutes. The mother notices that the infant has prominent labia and a dull pink vaginal epithelium. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the appearance of the infant's genitalia?
Exposure to maternal estrogen
Infection with group B Streptococcus
Infection with Chlamydia
Sexual abuse
Exposure to penicillin
A fetus is delivered at 40 weeks' gestation. During labor, the fetal heart monitor shows late decelerations and loss of short- and long-term variability. The membranes are ruptured to expedite the delivery. The fluid is noted to contain meconium. The infant is delivered 45 minutes later. At delivery, the infant appears to be cyanotic and limp. He has poor tone and deep reflexes. Moro's reflex is absent. Ten hours later, he experiences a seizure. Which of the following best explains this infant's perinatal course?
Encephalopathy from asphyxia
Respiratory distress
Inborn error of metabolism
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Werdnig-Hoffman disease
A four-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of discomfort in the left hip and left knee that is causing him to limp. Examination shows normal knee joints bilaterally, but there is marked limitation of internal rotation and abduction of the left hip. His temperature is 37.1 C (98.6F), blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. Laboratory studies including complete blood count and basic metabolic profile show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
Hematogenous osteomyelitis
Septic arthritis of the hip joint
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
A front-seat passenger in a car involved in a head-on collision relates that he hit the dashboard with his knees, however, he is specifically complaining of severe pain in his right hip, rather than knee pain. He lies in the stretcher in the emergency department with the right lower extremity shortened, adducted, and internally rotated. Which of the following is the most likely injury?
Femoral neck fracture
Posterior dislocation of the hip
Fracture of the shaft of the femur
Intertrochanteric fracture
Posterior dislocation of the knee
A full term neonate is being evaluated following an uncomplicated pregnancy and delivery on day 1 of life. He weighs 3.6kg (8ib), is 20in (50.8cm) tall, and has a head circumference of 13.5in (34cm). His physical examination is unremarkable. Initial laboratory data is shown below. Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 20g/L, Hematocrit 73%, Platelets 200,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 5,500/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 33%, Monocytes 10%. Which of the following findings is most likely to be detected in this neonate?
Respiratory distress
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Hyperglycemia
Renal failure
A full-term 2200-g (4.9-lb) boy was born to a 30-year-old G4P3 woman whose pregnancy was complicated by a seizure disorder for which she inconsistently took carbamazepine. The pregnancy was also notable for an abnormal triple screen for which an amniocentesis was declined. His Apgar scores are 7 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. His temperature is 37.0C (98.6F), blood pressure is 65/45 mm Hg, heart rate is 110/min, and respiratory rate is 30/min. His head circumference is < 5th percentile. There is a small fleshy sac protruding from the sacral spine. His reflexes are 2+ throughout, and his strength is 5/5 in all extremities. His fingernails are very small. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anoxia due to maternal seizing
Fetal alcohol syndrome
Perinatal exposure to carbamazepine
Trisomy 18
Trisomy 21
A full-term 5-day-old African-American girl is taken to the pediatrician because her “eyes look yellow.” She is being exclusively formula- fed with an iron-rich formula. She has six wet diapers a day and stools twice a day. The pregnancy was uncomplicated and she was delivered by spontaneous vaginal delivery. Her Apgar scores were 9 and 10 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), her head circumference is in the 50th percentile, and her weight is 3420 g (3 g below her birth weight). Her sclerae are icteric. There is no hepatomegaly or splenomegaly. Her total bilirubin is 9 mg/dL and her conjugated bilirubin is 0.2 mg/dL. Hemoglobin is 15 g/dL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
α1-Antitrypsin deficiency
Biliary atresia
Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Physiologic jaundice
Rotor syndrome
A full-term neonate presents with hypotonia, lethargy and poor feeding over the past three hours. The pregnancy was uneventful, but during delivery, the neonate presented with shoulder dystocia and subsequently obtained a fracture of the clavicle. His Apgar scores are 7 and 8 at one and five minutes, respectively. His birth weight is 4000g. His vital signs are normal. Physical examination reveals an enlarged tongue, mild microcephaly, prominent occiput, prominent eyes and omphalocele. Abdominal palpation reveals an enlarged liver and kidneys. The initial work-up reveals hypoglycemia and hyperinsulinemia. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital hypothyroidism
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
Maternal diabetes
WAGR syndrome
Denys-Drash syndrome
A full-term newborn develops cyanosis a few hours after birth. Oxygen administration does not improve color or oxygen saturations. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Atrial septal defect
Aortic stenosis
Ventricular septal defect
Patent ductus arteriosus
Pulmonary stenosis
A healthy 1-year-old child comes to your office for a routine checkup and for immunizations. His parents have no complaints or concerns. The next day, the CBC you performed as customary screening for anemia returns with the percentage of eosinophils on the differential to be 30%. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
Bacterial infections
Chronic allergic rhinitis
Fungal infections
Helminth infestation
Tuberculosis
A healthy 33-year-old man comes for a pre-employment examination. He has no complaints and has no medical problems. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs and takes no medications. He has no occupational exposures and has lived his entire life in suburban Mississippi. His temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 16/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. His chest x-ray shows a 1 .5 cm nodule in his right mid-lung field. Other labs are unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Coccidioidomycosis
Histoplasmosis
Tuberculosis
HIV infection
Pneumocystis jiroveci infection
A healthy 36-year-old Caucasian woman comes to the physician because of dyspnea on exertion. She has no other medical problems. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her father has prostate cancer and her mother had a stroke. She takes no medication and has no known drug allergies. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, pulse is 84/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows clear lung fields. Her chest x-ray shows prominent pulmonary arteries and an enlarged right heart border. EKG shows right axis deviation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Mitral stenosis
Mitral valve prolapse
Left ventricular failure
Emphysema
Pulmonary hypertension
A healthy 42-year-old G2P1001 presents to labor and delivery at 30 weeks gestation complaining of a small amount of bright red blood per vagina which occurred shortly after intercourse. It started off as spotting and then progressed to a light bleeding. By the time the patient arrived at labor and delivery, the bleeding had completely resolved. The patient denies any regular uterine contractions, but admits to occasional abdominal cramping. She reports no pregnancy complications and a normal ultrasound done at 14 weeks of gestation. Her obstetrical history is significant for a previous low transverse cesarean section at term. Which of the following can be ruled out as a cause for her vaginal bleeding?
Cervicitis
Placental abruption
Preterm labor
Placenta previa
Subserous pedunculated uterine fibroid
A healthy 59-year-old woman with no history of urinary incontinence undergoes vaginal hysterectomy and anteroposterior repair for uterine prolapse, large cystocele, and rectocele. Two weeks postoperatively, she presents to your office with a new complaint of intermittent leakage of urine. What is the most likely cause of this complaint following her surgery?
Detrusor instability
Rectovaginal fistula
Overflow incontinence
Stress urinary incontinence
Vesicovaginal fistula
A healthy 7 -year-old Caucasian boy is brought to the office by his mother because of fever and pain in the ear. He has had these symptoms for the past three days. He has no other medical problems. Family history is not significant. He takes no medication. His temperature is 38.3 C (101 F). Otoscopic examination reveals an ear discharge, and the tympanic membrane is immobile with insufflation. He has a boil just behind the pinna of the involved ear. His WBC count is 12,000/mm3. He is diagnosed with otitis media. Which of the following is most specific for the diagnosis of otitis media?
Presence of a septic focus (boil)
Presence of light reflex
Presence of ear discharge
Immobile tympanic membrane
Elevated WBC count
A Hispanic married couple brings in their 17-year-old son because his behavior has been abnormal for the past two weeks. Normally, the boy is polite and soft spoken but he has recently become irritable and rude. His parents dismissed his behavior as a "phase" with the expectation that he would grow out of it, but they became very concerned upon discovering that he had been spending large sums of money from his college fund without their consent. When questioned by his father about his strange behavior, the boy responded, "I'm on a secret mission. The king of Norway has sent me here to spy on the U.S. government." His vital signs include temperature of 36.6°C (98.0°F), blood pressure of 132/94 mm Hg, pulse of 105/min, and respirations of 18/min. On physical examination, the boy appears to be in no distress. His pupils are dilated. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Brief psychotic episode
Manic episode
Heroin intoxication
Schizophrenia
Amphetamine intoxication
A male child born to a 25-year-old Caucasian mother by normal vaginal delivery at 36 weeks of gestation is found to have a small face, a small jaw, and a prominence on the back of his head. There are no skin creases on the palmar aspect of his digits. There is overlapping of his fingers bilaterally, along with rocker bottom feet and limited hip abduction. Heart murmur is present. Which of the following cardiovascular abnormality is most likely seen in this patient?
Atrial septal defect
Supravalvular aortic stenosis
Ventricular septal defect
Conotruncal abnormality
Congenital heart block
A male infant was found to be jaundiced 12 hours after birth. At 36 hours of age, his serum bilirubin was 18 mg/dL, hemoglobin concentration was 12.5 g/dL, and reticulocyte count 9%. Many nucleated RBCs and some spherocytes were seen in the peripheral blood smear. The differential diagnosis should include which of the following?
Pyruvate kinase deficiency
Hereditary spherocytosis
Sickle-cell anemia
Rh incompatibility
Polycythemia
A married 41-year-old G5P3114 presents to your office for a routine examination. She reports being healthy except for a history of migraine headaches. All her Pap smears have been normal. She developed gestational diabetes in her last pregnancy. She drinks alcohol socially, and admits to smoking occasionally. Her grandmother was diagnosed with ovarian cancer when she was in her fifties. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg; height is 5ft 5 in; weight is 150 lb. Which of the following is the most common cause of death in women of this patient’s age?
HIV
Cardiac disease
Accidents
Suicide
Cancer
A married couple brings their 2-week-old infant to the office for the evaluation of lethargy, poor feeding and hypotonia. The infant was "fine" until yesterday, when he started to present with these symptoms. The mother's medical history is unremarkable, and her pregnancy was uneventful. On examination, hypotonia, poor reflexes and bulging fontanel are noted. There are no focal neurological signs. He is hypotensive and tachycardiac. His temperature is 39.4 C (103F). Initial investigation reveals a WBC count of 16,000/mm3 with 18% bands. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital toxoplasmosis
Escherichia coli meningitis
Group B streptococcal meningitis
Herpes simplex encephalitis
Listeria meningitis
A mentally retarded 10-year-old boy presents with arthritis, nephrolithiasis, and progressive renal failure. Since his first years of life, he manifested peculiar neurologic abnormalities consisting of self-mutilative biting of the lips and fingers, choreoathetosis, and spasticity. Two male relatives on his mother's side presented with a similar condition and died in their teens. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chronic lead intoxication
Fragile-X syndrome
Gout
Huntington disease
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
A middle-aged, divorced mother brings her 19-year -old daughter in for an evaluation. She says that her daughter has "a serious problem." The woman is concerned because her daughter always keeps to herself, does not date, has no close friends, and refuses to participate in activities popular with women of her age. The daughter is extremely fascinated by witchcraft, spending countless hours in her room gazing into a crystal ball and muttering under her breath. When confronted about her behavior, she says, "I have some supernatural powers that I am not willing to discuss." She attends college regularly and earns good grades. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Avoidant personality disorder
Schizoid personality disorder
Dependent personality disorder
Schizotypal personality disorder
Schizophrenia
A middle-aged, divorced woman brings her 18-year-old daughter to the physician with the complaint that her daughter "seems abnormal." She is concerned because her daughter has no close friends, does not date, and shows no interest in the activities that are popular with young adults. The girl prefers solitude and keeps to her room for most of the day. When she does go out, she hikes in the woods alone for hours at a time. She attends a local university where she studies engineering and performs well academically. During the office visit, the daughter avoids eye contact. In response to questioning about her reasons for being aloof, she replies, "I just don't enjoy being in the company of others. People do not interest me much and I would rather keep to myself." Her thought process appears devoid of delusions or hallucinations. Which of the following personality disorders is demonstrated by her behavior?
Dependent personality disorder
Avoidant personality disorder
Schizotypal personality disorder
Borderline personality disorder
Schizoid personality disorder
A moderately overweight 34-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with excessive sweating, flushing, tachycardia, and nervousness. Presuming that she might be suffering from thyrotoxicosis, the physician checks her blood levels of thyroid hormones, and finds that her free thyroxine and triiodothyronine levels are elevated, while her thyroid-stimulating hormone is decreased. Her radioactive iodine uptake test shows a complete absence of iodine uptake. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Graves’ disease
Toxic adenoma
Factitious thyrotoxicosis
Toxic multinodular goiter
Thyroid-stimulating hormone-secreting pituitary tumor
A mother brings her 12-year-old daughter in to your office for consultation. She is concerned because most of the other girls in her daughter’s class have already started their period. She thinks her daughter hasn’t shown any evidence of going into puberty yet. Knowing the usual first sign of the onset of puberty, you should ask the mother which of the following questions?
Has her daughter started her growth spurt?
Has her daughter had any vaginal spotting?
Has her daughter had any acne?
Has her daughter started to develop breasts
Does her daughter have any axillary or pubic hair?
A mother brings her 5-year-old daughter to the family physician. The girl is of appropriate height and weight for age. The girl shows changes of early breast development and has had vaginal bleeding. These changes have occurred suddenly. Pelvic examination under sedation reveals a normal vagina, but a sonogram shows a 4 cm unilateral, solid pelvic mass. There is no family history of such events. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Mucinous cystadenoma
Granulosa cell tumor
Benign cystic teratoma
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
Gonadoblastoma
A mother brings her 6-month-old infant to your office for evaluation of scaly, erythematous lesions around his eyebrows and sides of his nose. She also notes a scaly scalp that improves with baby shampoo. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Atopic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
Tinea capitis
Psoriasis
A mother brings her 6-year-old daughter for evaluation because she has never been able to toilet train her. The child states that she perceives the sensation of having to void, and empties her bladder normally at normal intervals, but is nonetheless wet with urine all the time. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Low implantation of one ureter
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Meatal stenosis
Ureterovesical reflux
Urethral valves
A mother brings her 7-year-old son to the clinic because, over the past several days, his urine has become pink and bis eyes have looked puffy. About 2 weeks ago, he missed school because of fever and a sore throat. On examination, the boy's blood pressure is 130/85 mm Hg, his eyelids and scrotum appear puffy, and he has 1+ tibial edema. No rashes are noted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
Nephrotic syndrome
Vesicoureteral reflux
A mother brings her 9-month-old daughter to the pediatrician with complaints of a rash. The mother states that the infant had a high fever [temperature up to 40.0 C (104 F)] for 3 days prior to developing the rash, but is now afebrile. The mother also says that the infant has had a runny nose and a slight cough for the past 3 days. On examination, there is a fine macular rash on the infant's trunk and neck. The examination is otherwise within normal limits, and the infant is playful and smiling. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Erythema infectiosum
Roseola
Rubella
Rubeola
Varicella
A mother brings her daughter in to see you for consultation. The daughter is 17 years old and has not started her period. She is 4ft 10 in tall. She has no breast budding. On pelvic examination, she has no pubic hair. By digital examination, the patient has a cervix and uterus. The ovaries are not palpable. As part of the workup, serum FSH and LH levels are drawn and both are high. Which of the following is the most likely reason for delayed puberty and sexual infantilism in this patient?
Adrenogenital syndrome (testicular feminization)
Kallmann syndrome
McCune-Albright syndrome
Gonadal dysgenesis
Müllerian agenesis
A mother brings in her 3-year-old son to the pediatrician because she is concerned about his "poor development." She says that she thinks her son's behavior is "very different from that of other children his age." She says that ever since he was a toddler, he has seemed indifferent to her presence. She previously attributed this to her son being "unique" compared to his two older sisters. However, she is increasingly worried about her son because he does not play with his siblings or the neighborhood children who come to visit, and she suspects that his speech development is limited. Upon examination, the child is spinning continuously in a circle. When questions are asked of him, he makes no eye contact and responds with "A house for the mouse." His physical appearance is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Tourette's disorder
Avoidant personality disorder
Schizotypal disorder
Schizoid personality disorder
Autism
A mother wishes to breast-feed her newborn infant, but is worried about medical conditions that would prohibit her from doing so. You counsel her that of her listed conditions, which of the following is a contraindication to breast-feeding?
Upper respiratory tract infection
Cracked and bleeding nipples
Mastitis
Inverted nipples
HIV infection
A neonate develops severe cyanosis that begins within minutes of birth. Blood drawn one hour after birth shows metabolic acidosis with respiratory acidosis. A chest x-ray film shows a narrow base to the great vessels and the heart resembles an egg on its side. ECG is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Tetralogy of Fallot
Underdeveloped (hypoplastic) left ventricle syndrome
Aortic valve stenosis
Transposition of the great arteries
Complete atrioventricular canal defect
A neonate has an obviously abnormal foot. The foot is in a markedly plantar flexed position, with the sole facing the adjacent leg in a position of marked adduction. No other anomalies are noted on physical examination. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Epispadias
Hypospadias
Talipes calcaneovalgus
Talipes equinovarus
Torticollis
A neonate has Down syndrome. Maternal hydrammos had been noted prenatally. After the first feeding, the infant has projectile vomiting with bile-stained vomitus. An x-ray film demonstrates a "double-bubble sign" in the abdomen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Duodenal atresia
Hirschsprung disease
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Meconium plug syndrome
Esophageal atresia
A neonate is examined following a protracted breech delivery. One of the infant's arms is partially paralyzed. The affected arm is adducted and internally rotated at the shoulder, and the forearm is pronated. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bell palsy
Erb palsy
Klumpke palsy
Pseudobulbar palsy
Supranuclear palsy
A neonate is very small for gestational age, shows hypotonia, marked skeletal muscle, and subcutaneous fat hypoplasia. During delivery, a large volume of amniotic fluid was released at rupture of membranes. The placenta was small, and only a single umbilical artery was noted. The face has a pinched appearance with hypoplastic orbital ridges, short palpebral fissures, and a small mouth and jaw. The head is small with prominence of the occiput. The ears are low set and malformed. The infant's fists are clenched, with overlapping of the third and fourth fingers. The feet are clubbed, and the great toe is shortened. Which of the following is most likely diagnosis?
47,XXY
TripleX
Trisomy 13
Trisomy 18
Trisomy 21
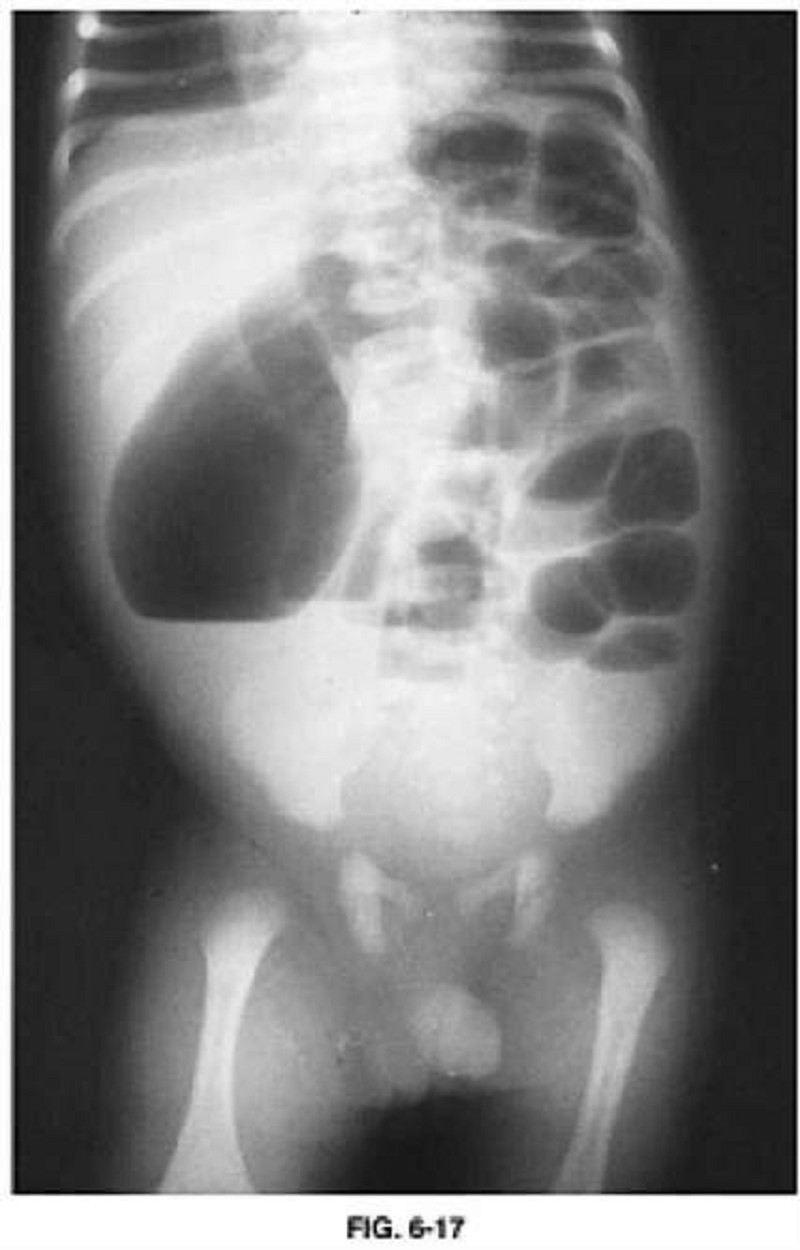
A neonate with bile-stained vomiting, abdominal distention, dilated loops of bowel on plain radiographs, and a small-caliber colon on contrast enema (Figure 6-17). Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Annular pancreas
Duodenal atresia
Midgut volvulus
Jejunal atresia
A newborn baby is noted to have abnormal facies with low-set ears; a small receding jaw; and widely separated eyes. At 30 hours of age, the baby develops multiple muscle spasms. Serum studies are notable for calcium of 4.5 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bruton's agammaglobulinemia
Common variable immunodeficiency
Selective IgA deficiency
Transient hypogammaglobulinemia of infancy
DiGeorge syndrome
A newborn infant born from a mother with polyhydramnios presents with excessive salivation along with coughing and choking with the first oral feeding. An xray of the abdomen shows gas in stomach and a nasogastric tube coiled in the esophagus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Tracheoesophageal fistula
Omphalocele
Esophageal atresia
Gastroschisis
Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF)
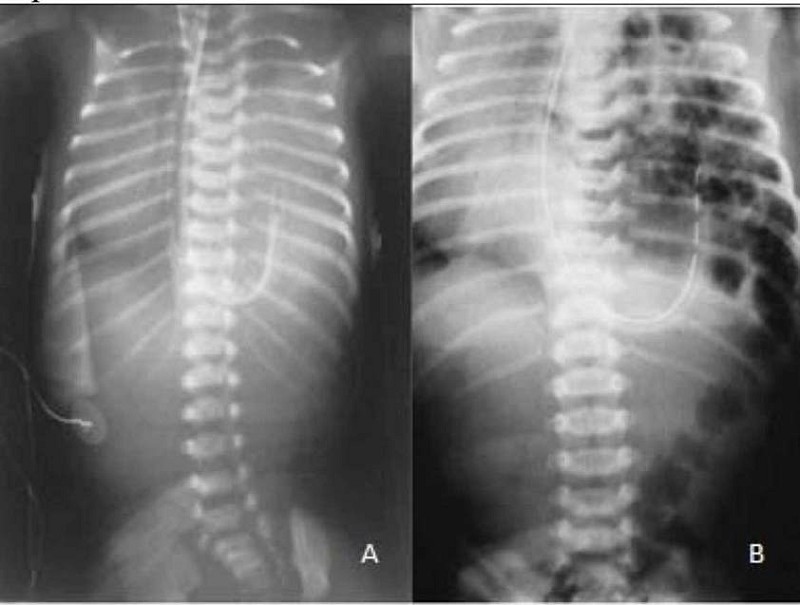
A newborn infant develops respiratory distress immediately after birth. His abdomen is scaphoid. No breath sounds are heard on the left side of his chest, but they are audible on the right. Immediate intubation is successful with little or no improvement in clinical status. Emergency chest x-ray is shown (Image A) along with an x-ray 2 hours later (Image B). Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this infant’s condition?
Pneumonia
Diaphragmatic hernia
Choanal atresia
Pneumothorax
Cystic adenomatoid malformation
A newborn infant has mild cyanosis, diaphoresis, poor peripheral pulses, hepatomegaly, and cardiomegaly. Respiratory rate is 60 breaths per minute, and heart rate is 250 beats per minute. The child most likely has congestive heart failure caused by which of the following?
VSD and transposition of the great vessels
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
Large ASD and valvular pulmonic stenosis
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return
A newborn male has oliguria and a midline mass in the lower abdomen. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Bladder exstrophy
Wilms tumor
Hypospadias
Posterior urethral valves
Cryptorchidism
A one-day-old infant with Down syndrome has developed persistent vomiting. He was delivered vaginally at 34 weeks without any complications. On examination, he appears dehydrated and slightly tachypneic. His abdomen is soft and not distended. Abdominal x-ray reveals two large distinct air bubbles, but there are no dilated bowel loops or air fluid levels. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
Pyloric stenosis
Reflux disorder
Tracheoesophageal fistula
Bowel obstruction
Duodenal atresia
A one-week-old infant is admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit due to vomiting, abdominal distension, and poor feeding. His vomitus is bile-stained. There is frank blood in his stools. He has been formula- fed since birth. Physical examination shows diminished bowel sounds. Abdominal x-rays reveal dilated loops of bowel with intramural air Laboratory studies show elevated WBCs. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Food poisoning
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Hirschsprung's disease
Pyloric stenosis
Duodenal atresia
A one-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department (ED) by her mother due to a one-day history of fever and drowsiness. The child has been irritable since yesterday. On examination, she is hypothermic, lethargic and has nuchal rigidity. She flexes her hips when her neck is flexed. She appears septic, and large petechial and purpuric lesions are developing on her body. In the ED, she suddenly becomes hypotensive. Despite aggressive fluid and antibiotic resuscitation, the child dies. What will most likely be revealed as the cause of death during the autopsy of this child?
Myocarditis and heart failure
Bone marrow failure
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
Adrenal gland failure
Acute renal failure
A patient develops a fever and tachycardia during a blood transfusion after a redo coronary artery bypass procedure. The nurse subsequently discovers that there was a mix-up in the cross-match because of a labeling error. Which of the following is diagnostic in a patient with an immediate hemolytic reaction secondary to a blood transfusion?
Serum haptoglobin above 50 mg/dL
Direct bilirubin greater than 5 mg/dL
Indirect bilirubin greater than 5 mg/dL
Positive Coombs test
Myoglobinuria
A patient involved in a car accident sustains burst fractures of several thoracic vertebral bodies. At the time of admission, he has no neurologic fun
Anterior cord syndrome
Complete cord transection
Cord hemisection
Spinal shock
Central cord syndrome
A patient is able to appreciate subtle nuances in thinking and can use metaphors and understand them. This patient’s thinking can be best defined by which of the following terms?
Intellectualization
Abstract
Rationalization
Concrete
Isolation of affect
A patient presents to the emergency center with a 6-hour history of fever to 38.9C (102F). Her mother reports that the patient appeared to be feeling poorly, that she had been eating less than normal, and that she vomited once. About 2 hours prior to arrival at the ER, the mother states that she noted a few purple spots scattered about the body on the patient, especially on the buttocks and legs. On the 30-minute ride to the ER, the purple areas spread rapidly and became coalesced in areas, and the patient is now obtunded. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
Measles
Toxicshock syndrome caused by S aureus
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Meningococcemia
A patient presents to your office approximately 2 weeks after having a total vaginal hysterectomy with anterior colporrhaphy and Burch procedure for uterine prolapse and stress urinary incontinence. She complains of a constant loss of urine throughout the day. She denies any urgency or dysuria. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this complaint?
Failure of the procedure
Diabetic neuropathy
Urinary tract infection
Vesicovaginal fistula
Detrusor instability
A patient with a chronic psychotic disorder is convinced that she has caused a recent earthquake because she was bored and wishing for something exciting to occur. Which of the following symptoms most closely describes this patient’s thoughts?
Thought broadcasting
Magical thinking
Echolalia
Nihilism
Obsession
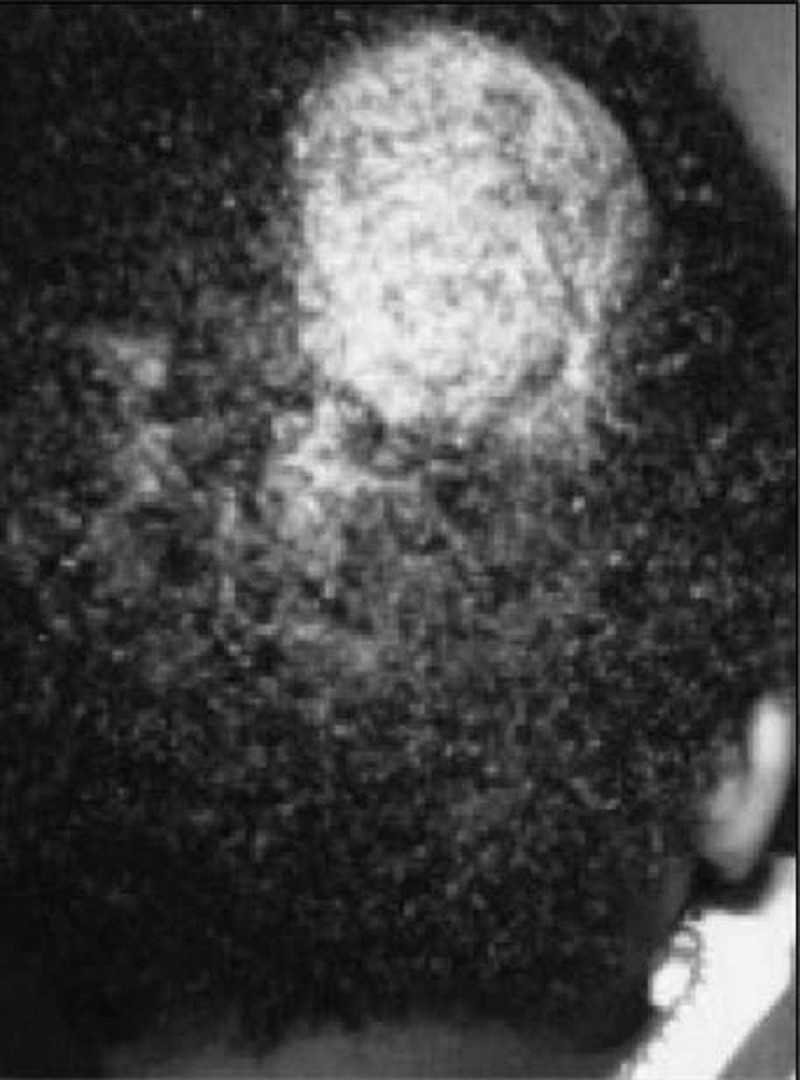
A patient with hair loss is shown below. The lesion does not fluoresce with a Wood lamp and has not responded well to a variety of topical agents. The lesion is boggy, is spreading, and has tiny pinpoint black dots throughout. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Traction alopecia from tight hair braids
Alopecia areata
Biotinidasedeficiency
Hypothyroidism
Infection with Trichophyton tonsurans
A pediatrician examines a 2-month-old infant who had been born at term. The pediatrician hears a continuous murmur at the upper left sternal border. The peripheral pulses in all extremities are full and show widened pulse pressure. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Coarctation of the aorta
Persistent truncus arteriosus
Patent ductus arteriosus
Peripheral pulmonic stenosis
Ventricular septal defect
A pediatrician is called to the delivery room because a full-term infant has developed cyanosis and respiratory distress immediately after birth. A brief examination of the infant reveals cyanosis on room air not completely relieved by oxygen administered by mask, subcostal and intercostal retractions, absent air entry on the left with audible bowel sounds in the left chest, and poor air entry on the right chest. The heart is best heard in the right hemithorax; the abdomen is flat without organomegaly. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Meconium aspiration
Hyaline membrane disease
Pneumonia
Tracheoesophageal fistula
A postmenopausal woman is undergoing evaluation for fecal incontinence. She has no other diagnosed medical problems. She lives by herself and is self-sufficient, oriented, and an excellent historian. Physical examination is completely normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
Rectal prolapse
Diabetes
Obstetric trauma
Senility
Excessive caffeine intake
A postmenopausal woman presents with pruritic white lesions on the vulva. Punch biopsy of a representative area is obtained. Which of the following histologic findings is consistent with the diagnosis of lichen sclerosus?
Blunting or loss of rete pegs
Presence of thickened keratin layer
Presence of mitotic figures
Increase in the number of cellular layers in the epidermis
Acute inflammatory infiltration
A pregnant 16-year-old girl with no prior pre-natal care presents to the emergency department in labor. A male infant is delivered precipitously. Prenatal laboratory test results are unknown. There is no meconium. He has a birth weight of 3 kg (6 lb 10 oz). He is pink and is crying, heart rate is 130/min, and respiratory rate is 36/min, with good respiratory effort. The emergency medicine resident notices the infant has ascites and a membrane-covered anterior abdominal mass at the base of his umbilical cord. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Duodenal atresia
Gastroschisis
Hirschsprung’s disease
Meckel’s diverticulum
Omphalocele
A pregnant 22-year-old Taiwanese woman presents at 15 weeks’ gestation with vaginal bleeding and severe nausea and vomiting. She states she recently experienced vaginal passage of tissue that looked like grapes. Her uterine fundus is at her umbilicus and no fetal heart tones can be heard with a Doppler stethoscope. Ultrasonography of the uterus shows a “snow storm” image with no fetus or placenta. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ectopic pregnancy
Endometrial carcinoma
Vaginal foreign body
Submucous leiomyoma
Molar pregnancy
A premature infant develops respiratory distress several hours after birth. The infant is placed in an incubator with supplemental oxygen. The physician instructs the nurse to cover the infant's eyes to minimize the chance of damage by the high oxygen tension. Which of the following is characteristic of eye damage produced by exposure to high oxygen tensions in premature infants with respiratory distress?
Cotton wool exudates in the retina
Papilledema of the optic nerve head
Blood vessels in the vitreous
Ulcers on the cornea
Microaneurysms of the retinal arterioles
A premature neonate develops respiratory distress syndrome several hours after birth. The infant is placed on a respirator and given other appropriate care. However, when the infant reaches a corrected gestational age of 36 weeks, he does not tolerate weaning from the ventilator. A chest x-ray film demonstrates alternating areas of hyperaeration and pulmonary scarring, resulting in parenchymal streaks and hyperexpanded areas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cystic fibrosis
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
Apnea of prematurity
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia
Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn
A premature newborn is being treated in the neonatal intensive care unit. On the sixth day of life he is noted to be lethargic and in mild respiratory distress. His heart rate is 162/min, blood pressure is 55/38 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 56/min. In addition to a distended abdomen, he has guaiac-positive stools. X-ray of the abdomen shows gas bubbles within the bowel wall. From what potentially life-threatening condition is this patient most likely suffering?
Bowel obstruction
Intussusception
Meconium ileus
Meningitis
Necrotizing enterocolitis
A previously healthy 11-year old boy presents to the physician with a fever and persistent vomiting for 4-5 days. Initially, the emesis was clear, but now it contains streaks of bright red blood. Findings on a physical examination, complete blood count, and serum electrolytes are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the hematemesis?
Esophageal varices
Esophagitis
Gastritis
Mallory-Weiss tear
Peptic ulcer disease
A previously healthy 13-year-old girl presents to the emergency department with an acute onset of red urine after she played soccer in the morning. Her physical examination is unremarkable. Urinalysis shows a red color; pH, 6.2; specific gravity, 1.024; glucose, negative; blood, +4; protein, trace; nitrite, negative; leukocyte esterase, negative; white blood cell, 0/hpf; red blood cell, 1/hpf. Which of the following is the most likely explanation of the red urine?
Glomerulonephritis
Hematuria
Ingestion of food coloring
Myoglobinuria
Presence of urates
A previously healthy 18-month-old has been in a separate room from his family. The family notices the sudden onset of coughing, which resolves in a few minutes. Subsequently, the patient appears to be normal except for increased amounts of drooling and refusal to take foods orally. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this toddler’s condition?
Severe gastroesophageal reflux
Foreign body in the airway
Croup
Epiglottitis
Foreign body in the esophagus
A previously healthy 18-month-old male comes to the physician for evaluation of fever. His mother reports that he has had a fever ranging from 1 02.2 F (39.0 c) to 104.0 F (40.0 C) for the past five days. He has also become increasingly irritable with decreased appetite. His mother reports that he does continue to take some liquids. There are no known sick contacts. On examination, the infant's temperature is 102.5 F (39.2 C), pulse is 120/min, and respiratory rate is 20/min. He is irritable during the examination. There is conjunctival erythema bilaterally, with serous drainage from both eyes. His oropharynx is erythematous and his lips are fissured. There is a 2 cm anterior cervical lymph node palpable on the right side. His neck is otherwise supple and he is able to flex his chin to his chest without difficulty. There is mild abdominal tenderness to palpation. His hands and feet are slightly erythematous and edematous and there is a maculopapular rash on the trunk. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Scarlet fever
Toxic shock syndrome
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Kawasaki disease
Rocky Mountain spotted fever
A previously healthy 21-year-old woman has a profuse, malodorous vaginal discharge. Examination shows a greenish gray "frothy" discharge with a "fishy" odor and petechial lesions on the cervix. There is no cervical motion tenderness. Her temperature is 37.5 C (99.4 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 16/min. Microscopic evaluation of the discharge is most likely to show which of the following?
"Clue cells"
Gram-positive diplococci
Gram-negative diplococci
Motile, flagellated organisms
Pseudohyphae or hyphae
A previously healthy 28-year-old woman develops significant postpartum hemorrhage, with a rapid drop in hematocrit to 18%. Despite aggressive IV fluid resuscitation, the patient has a persistent tachycardia, labile systolic blood pressure, and poor urine output. Ongoing resuscitation includes emergency transfusion with 2 units of O-negative packed red blood cells. During transfusion of the second unit, the patient develops chills, fever, vomiting, and hypertension. These symptoms are most likely the result of which of the following?
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction
Acute bacterial infection transmitted in the blood product
ABO incompatibility with acute hemolytic transfusion reaction
A febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reaction
An anaphylactic transfusion reaction
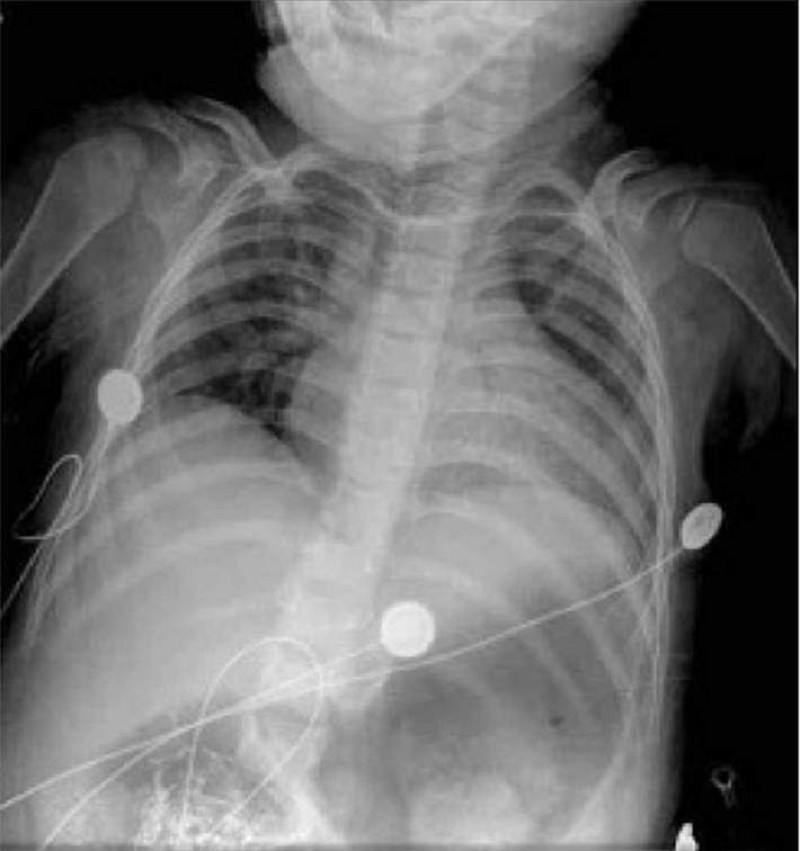
A previously healthy 4-year-old boy is brought to the physician for evaluation of fever and respiratory distress. The patient developed fever three days ago. Since then, he has had increasing fatigue, irritability, and respiratory distress. His temperature is 100 F (38.2C), pulse is 144/min, respiratory rate is 45/min, and blood pressure is 95/60 mm Hg. On examination, the child appears to be in moderate respiratory distress with tachypnea and subcostal retractions. He is tachycardic with an III/IV holosystolic murmur best heard at the cardiac apex. Peripheral pulses are present and capillary refill is three seconds. His liver is palpated three centimeters below the costal margin. A chest radiograph is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Community-acquired pneumonia
Viral hepatitis
Rheumatic fever
Kawasaki disease
Myocarditis
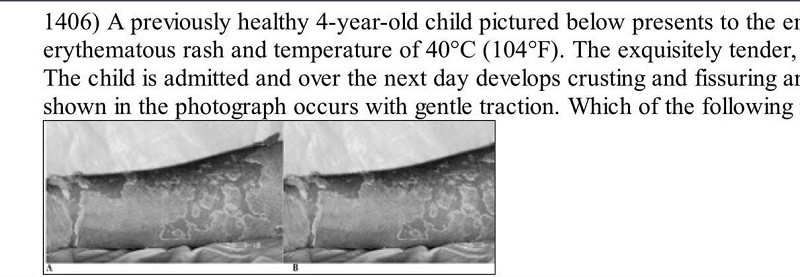
A previously healthy 4-year-old child pictured below presents to the emergency room (ER) with a 2-day history of a brightly erythematous rash and temperature of 40°C (104°F). The exquisitely tender, generalized rash is worse in the flexural and perioral areas. The child is admitted and over the next day develops crusting and fissuring around the eyes, mouth, and nose. The desquamation of skin shown in the photograph occurs with gentle traction. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Epidermolysis bullosa
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Erythema multiforme
Drug eruption
Scarlet fever
A previously healthy 45-year-old man presents with a 9-month history of a slow-growing, painless right neck mass. He is a nonsmoker and has no significant past medical history. On examination, there is a nontender, discrete, 3-cm mass over the angle of the right mandible. Facial muscle fun
Metastatic carcinoma
Hodgkin’s disease
Reactive cervical lymphatic hyperplasia
Infectious parotitis
Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid
A previously healthy 5-year-old girl is brought to the physician for evaluation of night awakenings. She has woken up screaming in each of the past three nights about one hour after going to sleep. When her parents go to her room, she is crying, sweating, and looks frightened. She does not respond to her parents and does not seem fully awake. When her parents hold her, she calms down and goes back to sleep. The next morning, she does not recall the incident. She started kindergarten this week and has just begun going all day without taking a nap. On examination, she is afebrile and her vital signs are within normal limits. A complete physical examination is unremarkable. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Nightmare
Somnambulism
Epilepsy
Night terrors
Benign paroxysmal vertigo
A previously healthy 50-year-old gravida 5, para 4, Caucasian woman comes to the physician complaining of passing small amounts of urine while sneezing or coughing for the past five months. She denies any episodes of weakness, numbness or fecal incontinence. There is no history of dysuria, increased frequency of urination, or hematuria. Her symptoms are progressively getting worse. Her other medical problems include diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosed 3 years ago, treated with glyburide 2.5mg/day. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs, and has no known drug allergies. She mentions that she is an avid jogger, but her problem causes her significant embarrassment. She now has to wear absorbent pads while jogging. Her vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, the abdomen is soft. Neurological examination is within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a cystocele. The patient's labs reveal: Urine: Specific gravity: 1.020, Blood: negative, Glucose: negative, Leukocyte esterase: negative, Nitrites: negative, WBC: 5-10/hpf, Bacteria: none. Random blood sugar is 120 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Interstitial cystitis
Overflow incontinence due to medication
Detrusor instability
Overflow incontinence due to detrusor weakness
Pelvic floor muscle weakness
A previously healthy 55-year-old man undergoes elective right hemicolectomy for a stage I (T2N0M0) cancer of the cecum. His postoperative ileus is somewhat prolonged, and on the fifth postoperative day his nasogastric tube is still in place. Physical examination reveals diminished skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, and orthostatic hypotension. Pertinent laboratory values are as follows:Arterial blood gases: pH 7.56, PCO2 50 mm Hg, PO2 85 mm Hg.Serum electrolytes (mEq/L): Na+ 132, K+ 3.1, Cl- 80; HCO3- 42.Urine electrolytes (mEq/L): Na+ 2, K+ 5, Cl- 6What is the patient’s acid–base abnormality?
Mixed respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
Metabolic alkalosis with respiratory compensation
Respiratory acidosis with metabolic compensation
Combined metabolic and respiratory alkalosis
Uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
A previously healthy 7-year-old child suddenly complains of a headache and falls to the floor. When examined in the emergency room (ER), he is lethargic and has a left central facial weakness and left hemiparesis with conjugate ocular deviation to the right. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hemiplegic migraine
Todd paralysis
Supratentorial tumor
Acute subdural hematoma
Acute infantile hemiplegia
A previously healthy 7-year-old girl comes to the office with complaints of episodic abdominal pain over the past several months. The pain is periumbilical and sharp but does not wake her from sleep or interfere with play. She has no fever, joint complaints, or constipation or diarrhea. Growth and development have been normal. The physical examination is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute appendicitis
Crohn disease
Functional abdominal pain
Irritable bowel syndrome
Acute cholecystitis
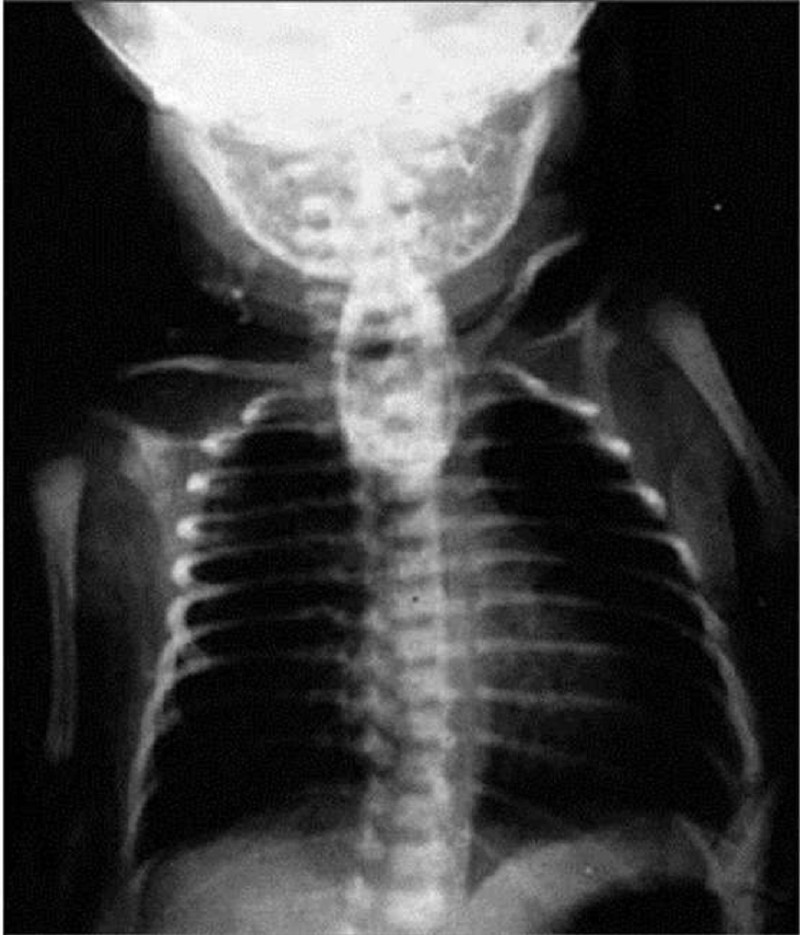
A male infant is delivered at 37 weeks’ gestation via cesarean section for breech presentation. The pregnancy was complicated by polyhydramnios. The 34-year-old mother is rubella immune and has blood type B. She is negative for Rh antibody, Group B streptococci, rapid plasma reagin, hepatitis B surface antigen, gonorrhea, and Chlamydia. At delivery there is no meconium. He has a birth weight of 2.7 kg (6 lb). The baby has a weak cry and is pale and frothing at the nose and mouth. He has nasal flaring and retractions, with a respiratory rate of 56/min. Heart rate is 140/min and he has a regular rhythm and a harsh 2/6 holosystolic murmur that is best heard at the left sternal border. On auscultation he has fine diffuse crackles in his lungs bilaterally. The infant is missing both thumbs and has fusion of the remaining digits of his upper extremities bilaterally. The pediatric resident is able to suction secretions from the patient’s nasopharynx and oropharynx; however, she is unable to pass a nasogastric or orogastric tube more than 10 cm down. X-ray of the chest is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Tracheoesophageal fistula
Pyloric stenosis
Respiratory distress syndrome
Transient tachypnea of the new-born
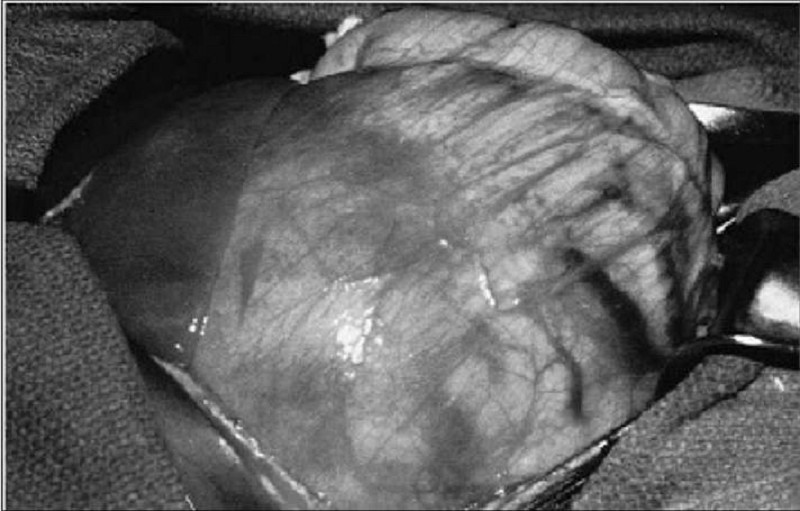
A mother notices an abdominal mass in her 3-year-old son while giving him a bath. There is no history of any symptoms, but the boy’s blood pressure is elevated at 105/85 mm Hg. Metastatic workup is negative and the patient is explored. The mass shown here is found within the left kidney. Genetic testing reveals deletion of 2 genes on chromosome band 11p13. Which of the following anomalies in addition to the identified tumor is associated with these chromosomal deletions?
Cardiac anomalies
Hemihypertrophy
Hypoglycemia
Macroglossia
Aniridia
{"name":"DES C_Diagnosis (12) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 77-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department because of sudden-onset intense diffuse abdominal pain followed by vomiting. Her past medical history is significant for chronic uncontrolled hypertension, cerebrovascular accident, diabetes and hyperlipidemia. She takes multiple medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her temperature is 38.30 C (1010 F), blood pressure is 180\/100 mm Hg, pulse is 110\/min and irregular and her respirations are 22\/min. She is in severe distress. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdominal examination shows severe pain to palpation and nearly absent bowel sounds. There is rigidity and rebound. Rectal examination shows heme-positive stools. EKG shows absent P waves, irregular rhythm and inverted T waves. There are no previous EKGs for comparison. An x-ray film of the chest shows cardiomegaly. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit 49%, Leukocyte count 77,500\/mm3, Troponin I normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/18-747252/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
How well do you know Mr.Lynch
10529
Unfiltered Opinions Quiz
10510
Andrew Quiz
25120
RDesk Skillz Check
11620
Lost TV Show - Season 1 Trivia Challenge
201018512
Colon: Which Sentence Uses It Correctly? (Free)
201019528
Guess Your Accent: Free Voice Accent Test
201019048
Wisconsin Trivia Questions - Free Online
201025974
Contractor Safety Orientation - Free Online
201020148
Sabrina Carpenter - Bestie or Rival?
201018956
Bash Scripting Practice Questions - Free Interview
201019936
What Are My Pronouns - Free & Instant Results
201018599