Histology Quiz (Final)

Histology Quiz: Test Your Knowledge
Welcome to the Histology Quiz! This quiz is designed to challenge your understanding of histological concepts related to cartilage and bone tissues. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or someone simply passionate about histology, this quiz provides an excellent opportunity for you to enhance your knowledge.
Key features:
- Multiple choice questions
- Covers various aspects of histology
- Ideal for all levels of expertise
In cartialge, the extra cellular matrix is:
Surround chondrogenic cells
Rich in glycosaminoglycan
In hyaline cartilages it is rich in elastic fiber
All of the listed.
Only found in hyaline cartilage
Stem cells of cartilage tissue is present at:.
Extracellular matrix.
Perichondrium.
Perioesteum.
Lacunae.
None of the listed
The type of collagen fiber in fibrocatrilage and bone matrices is:
Collagen type 1.
Collagen type 2.
Collagen type 4.
Collagen type 7.
Collagen type 9
What do glenoid labrum and intervertebral discs have in common:
Both made of fibrocartilge
Both are made of hyaline cartilage.
Both made of elastic cartilage.
Both have perichondrium.
All of the listed
All of the following cartilages have perichondrium EXCEPT:
Costochondral cartilage
Minisci of Knee joints.(Fibrocartilage)
Laryngeal cartilage
Trachial cartilage.
Nasal cartilage
What do cartilage and epithelial tissues have in common:
Both are avascular
Both covers internal cavities.
Both have similar cell types.
Both have same power of regeneration
Both have same architecture
In Hyaline cartilage, fibers not well seen under LM because :
Because it is not stained
GS and fibers do not share the same refractive index
GS is basophilic
GS and fibers share the same refractive index
None of the above
In Hyaline cartlige , group of chondrocytes in lacunae is:
Territorial
Interterritorial
Isogenous
Center of chondrification
A+C
In Hyaline cartlige, appositional growth take palce in :
Immature cartilage
Mature cartilage
Chondroblasts
Chondrocytes
B+d
Regarding fibrocartilage, Mark the Wrong statement:
Made of chonrocytes within lacunae.
Chonrdocytes are arranged in pairs within the matrix.
It is present in articular discs of bone joints.
It is present in intervertebral discs.
All of the listed
In which week Bone development begins in the embryo development ?
The 7th week
The 8th week
The 5th week
None of the followin
Which of the following is mismatched?
Intramembranous ossification- flat bones
Intramembranous ossification- fibrous membrane
Endochondral ossification- long bones
Endochondral ossification- flat bones
One of the following is wrong about Osteomalacia?
Children’s form.
Includes many disorders in which osteoid is produced but inadequately mineralized.
Causes can include insufficient dietary calcium.
Includes insufficient vitamin D.
What cartilage and bones have in common:
Both undergo continous remodelling.
Both have similar architecture.
Both are avascular
Both tissues contain osteoclasts.
What is The function of canaliculi in the compact bone ?
Transmit blood capillaries.
Connection of Haverian canals
Diffusion of nutrition from blood capillaries
Support.
What is the difference between cartilages and bones?
Bones undergo remodeling.
Cartilage have different architecture.
Cartilage derivative of c.t but bones don’t.
Bone’s cells are placed within lacunae.
What is the The premature bone cell that laydown bone tissue?
Osteoblast.
Osteoclast
Osteocyte.
Mesenchymal cells.
Regarding bone tissue, one of the following is wrong?
Collagen type I is the dominant form in bone.
There are 3 main types of cells in bone tissue.
Osteocytes are immature bone cells that secrete matrix compounds.
Osteocytes are present in lacunae.
Regarding periosteum, one of the following is true?
The Outer fibrous layer is dense regular connective tissue.
The outer osteogenic layer is composed of osteoblasts and osteoclasts
Avascular membrane.
The inner layer is composed of osteoclasts only.
The structure that binds periosteum to the underlying bone is:
Endosteum.
Volksman canal.
Sharpey's fibers.
None of the above.
The origin of muscular tissue come from :
Mesodermal germ layers
Ectodermal germ layers
Endodermal germ layers
None of the above
The layer that surrounded the fascicles called :
Epimysium
Perimysium
Endomysium
None of the above
The name of protein that keeps the filaments ( actin&myosin ) within sarcomere called :
Alfa-actinin
Cap-z
Nebulin
Titin
Which of the following about type1 fiber is true ?
Its white fiber
Fast type of muscle contraction
Used to sustain production of force
High ATPase activity
Zone of myosin filaments only :
H-band
A-band
I-band
None of the above
In order for muscles to contract, they need calcium ions. Muscle cells have an organelle that stores the needed calcium ions. This organelle is called __________.
Fascia
Sarcolemma
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Myosin cross”bridges are extensions of __________.
Actin
Myosin
Troponin
The plasma membrane around a muscle cell is called a __________.
Sarcoplasm
Sarcolemma
Sarcomere
The actin filaments are attached to the __________.
Z discs
Myosin
Sarcolemma
The troponin/tropomyosin complex is associated directly with which of the following filaments?
Actin
Myosin
The thick filament
What is the role of tropomyosin in muscle contraction?
To release troponin from tropomyosin, allowing myosin to bind to the actin filament.
To release calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum .
To prevent myosin from continuing to slide up the actin filament
To aid in myosin 'cocking' on the actin filament
Which of the following correctly identifies muscle components in order from largest to smallest?
Muscle fiber, fasciculus, myofibril .
Sarcolemma, sarcoplasm, fasciculus.
Fasciculus, muscle bundle, myofibril
Fasciculus, muscle fiber, myofibril
The space between two Z lines constitutes the:
Sarcomere
Sarcoplasm
Sarcolemma
Sarcophagus
Ganglia :
The aggregation of nervous cell bodies outside the CNS
Personality traits
The functional unit of N.S
A+B
The longest cell in our human body:
Neuroglial Cells
Neuron
Enteric plexus
None of the above
Which of the followings found in the inner ear & olfactory
Pseudounipolar
Multipolar
Bipolar
C+B
Vital structure is:
Perikaryon
Dendrites
Axons
Ganglia
All of the following found in cell body except:
Nissl bodies
Lipofuscin granules
Microtubules
Irregular contour and spines
In CNS maintaining the appropriate environment around the neurons function of:
Neuroglial Cells
Schwann cells
Astrocytes
A+C
All of the following include as glial cell in CNS except :
Astrocyte
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Satellite cells
Input portion of neuron :
Cell body
Dendrites
Axons
Axon hillock
Cone like structure :
Nodes of Ranvier
Schwann cells
Axon hillock
Axon
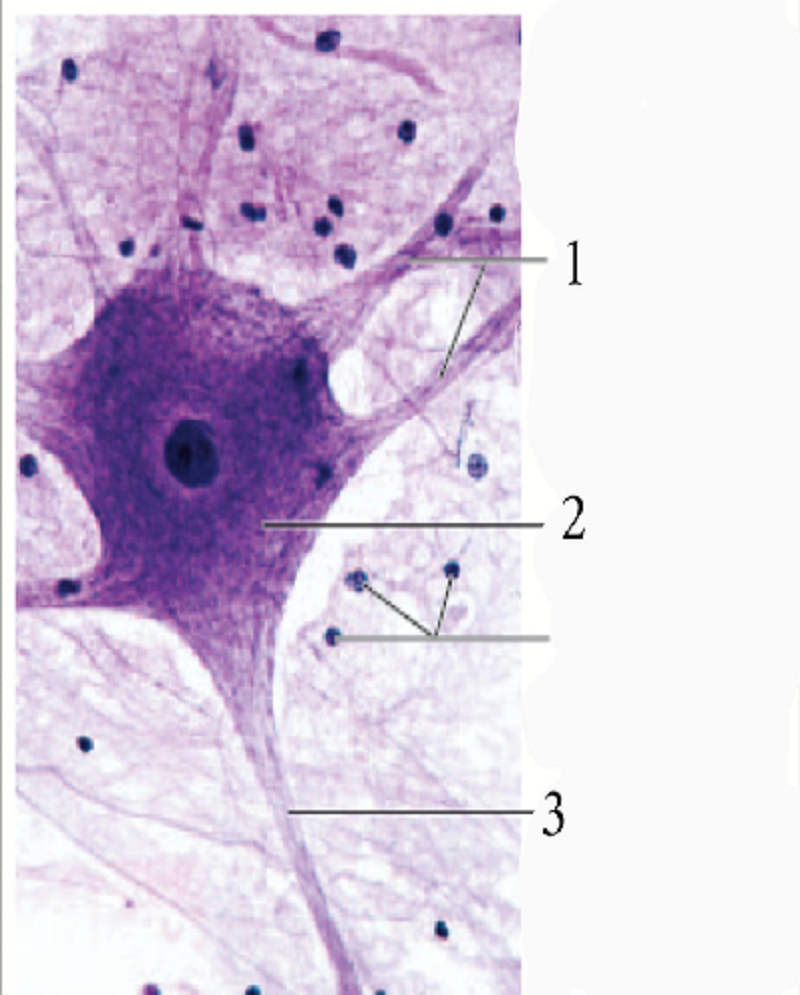
The number 3 is :
Axon hillock
Neurilemma
Dendrites
Axon
The cells found in cartilage tissue are called……… and they’re located in lacuna in which the cells lies
Chondrocytes
Chondroblasts
Chondrogenic cells
Fibroblasts
True or false : Cartilage fibres are composed of fibrils and collagen type II and They’re masked; cannot be seen
True
False
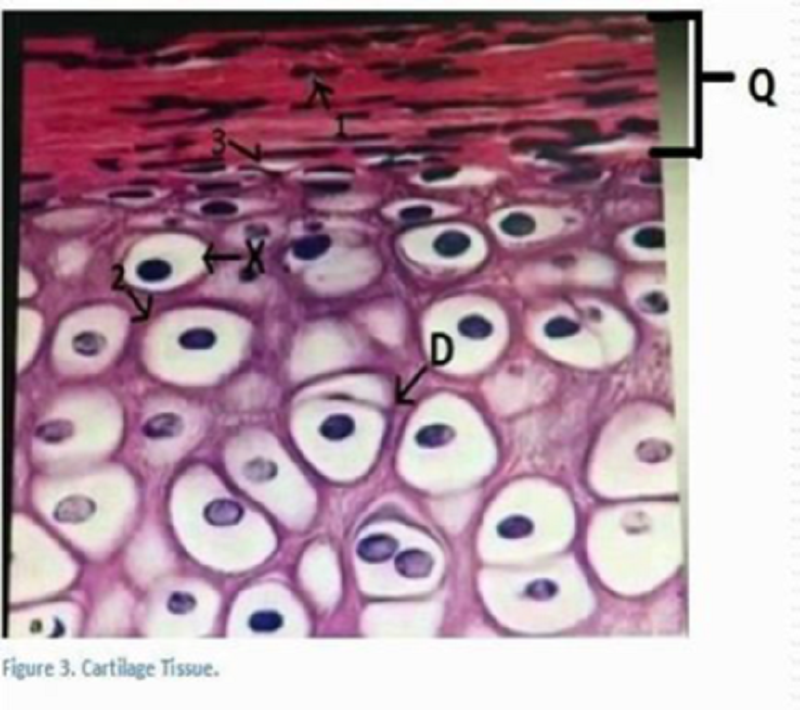
The letter D is :
Chondroblast
Chondrocyte
Isogenous group
Blastocytes
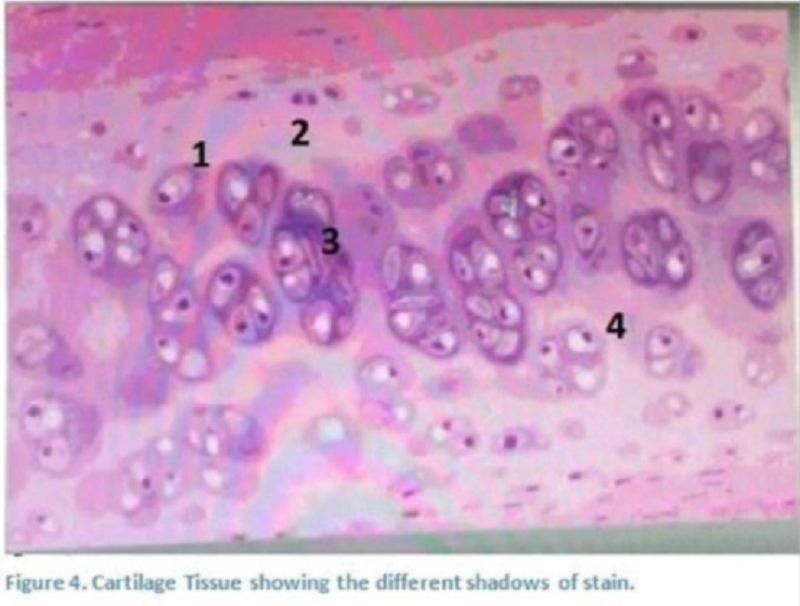
The number 3 is :
Territorial matrix
. inter- territorial
The matrix
The cells
The number 3 is
. matrix
Perichondrium
. chondroblasts
Chondrocytes
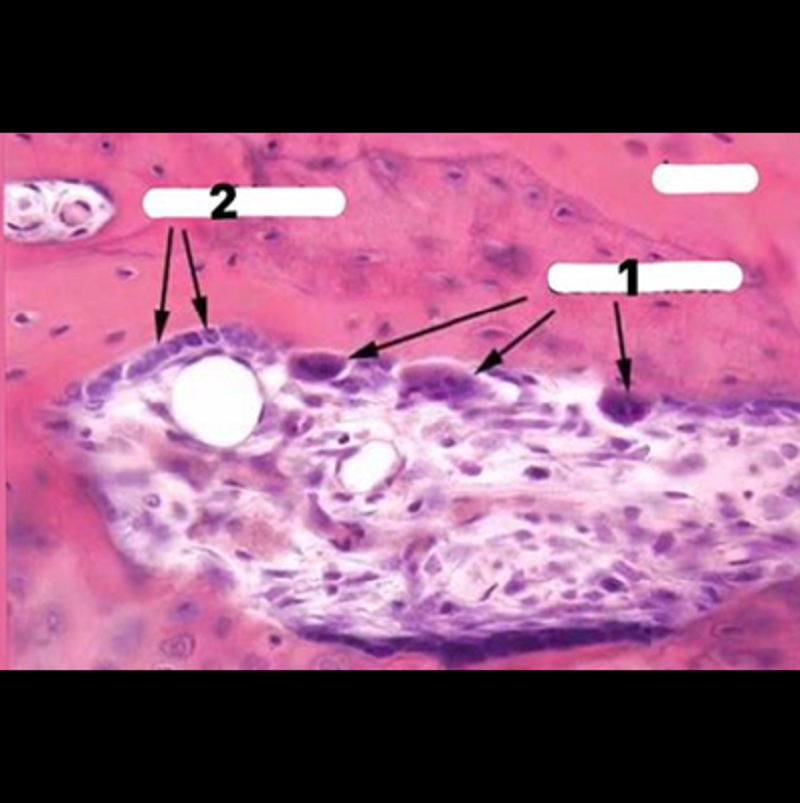
Special type of cells arise in bone tissue that function a on as macrophages for eroding the bone are called (..) and are seen in the number (..):
Osteoblasts >> 1
Osteoclasts >> 1
Osteocyte >> 1
Osteoblasts >> 2
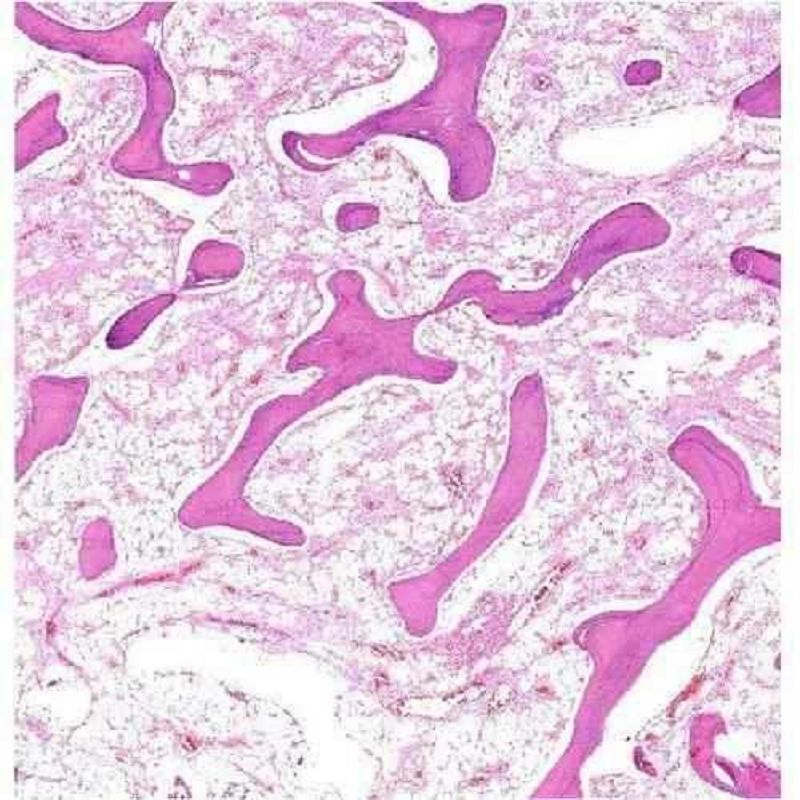
The picture shown represents:
Hyaline cartilage
Cancellous Bone
Compact bone
Elastic cartilage
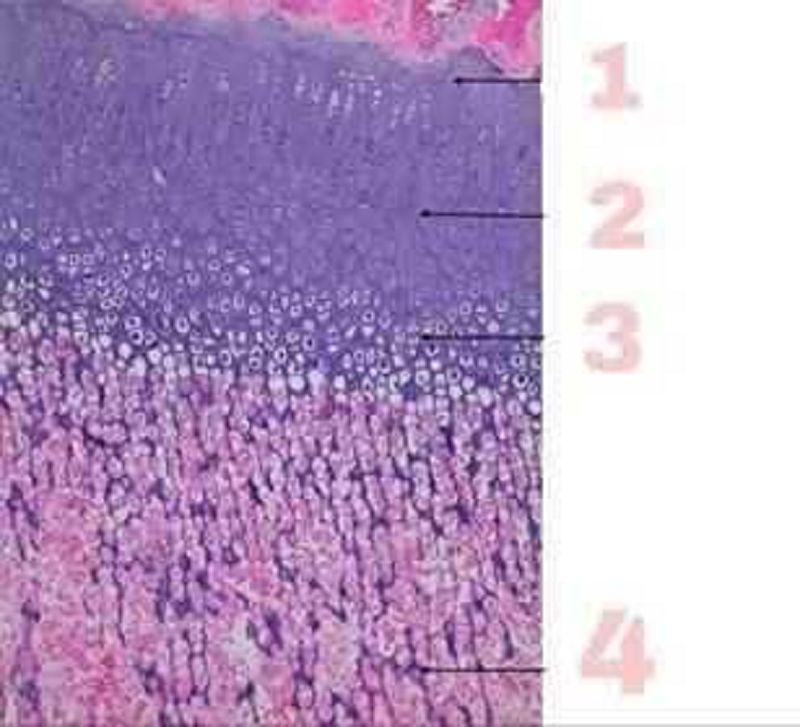
This picture represents the Endochondral ossification, number 4 shows which zone :
Reserve zone
Zone of Hypertrophy
Zone of Calssification
Zone of proliferation

This picture shows (….......) and number 2 represents :
Compact bone, lacunae
Cancellous bone, canaliculi
Compact bone, haversian canal
Compact bone, canaliculi
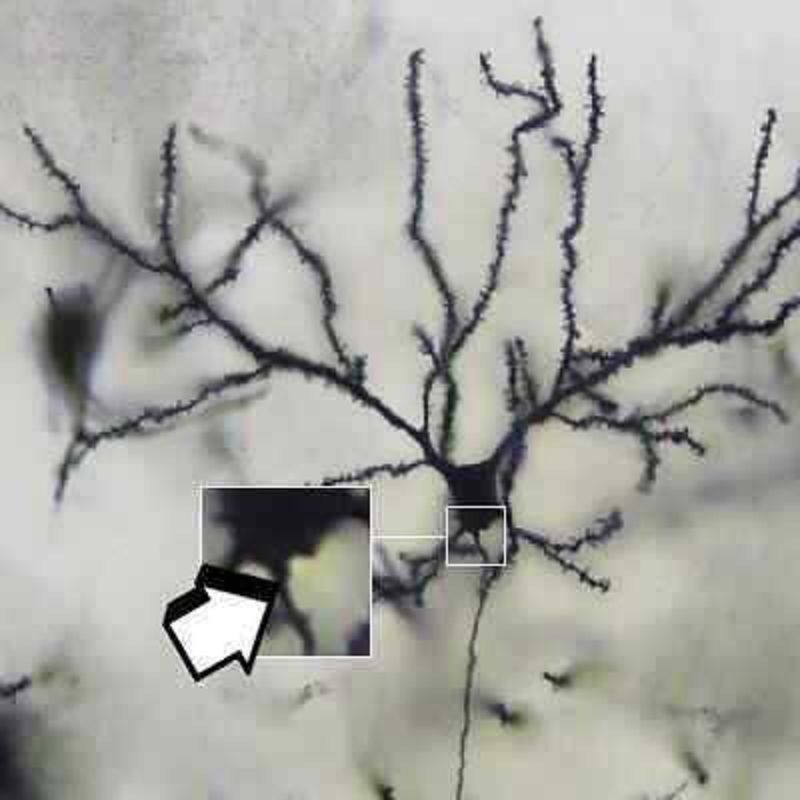
Identify tha histological feature?
Rough endoplasmic reiculum
Axon hillock
Myelin sheath
White matter
Identify the histological feature?
Grey matter
Nissl bodies
Perineurium
Myelin sheath

Identify the cell type?
Ganglion cell
Glial cell
Neurone
Satelite cell
Identify the tissue type?
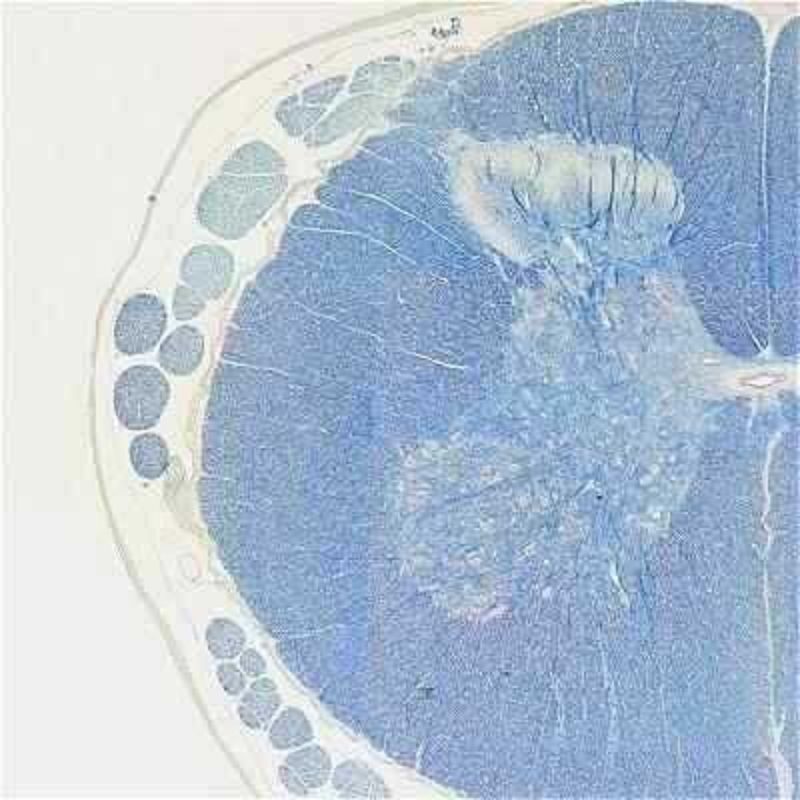
Nervous tissue, forebrain
Nervous tissue, spinal cord
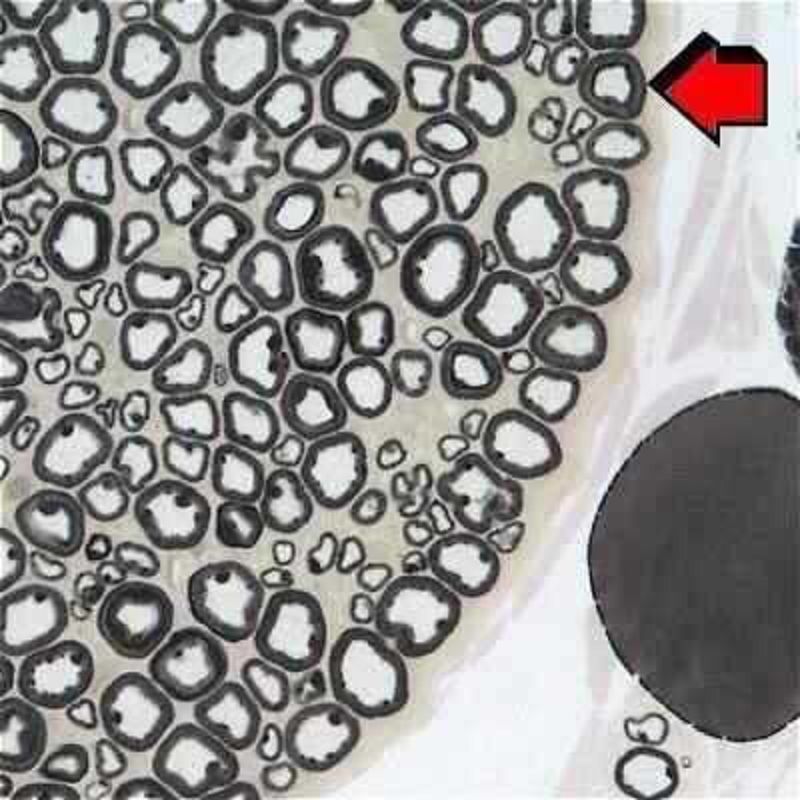
Nervous tissue, peripheral nerve
Nervous tissue, autonomous ganglion
What do you expect to see in a section of bone in a menopusal women:
Osteoblast without ruffle border.
Normal bone structure.
Increase number of osteoblast.
Thick bone outer plate.
All of the listed
In cartialge, the extra cellular matrix is
Surround chondrogenic cells.
Rich in glycosaminoglycan.
In hyaline cartilages it is rich in elastic fibers.
All of the listed
Only found in hyaline cartilage.
Sarcomere arrangement is present in:
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Skeletal muscle
Both cardiac and skeletal muscles.
All types of muscles.
The glial cell that filters cerebrospinal fluid (CSF):
Oilgodendrocyte.
Schwan cell.
Astrocyte.
Ependymal cell.
Microglia.
{"name":"Histology Quiz (Final)", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Welcome to the Histology Quiz! This quiz is designed to challenge your understanding of histological concepts related to cartilage and bone tissues. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or someone simply passionate about histology, this quiz provides an excellent opportunity for you to enhance your knowledge.Key features:Multiple choice questionsCovers various aspects of histologyIdeal for all levels of expertise","img":"https:/images/course5.png"}
More Quizzes
Histo retake on entry cycle 1
221171
A.S Connective tissue quiz
1168
BROW LAMINATION FINAL EXAM
9425
Music of the Medieval Period
191034
What RWBY Character Are You? Ice Queendom
201017556
Human Nature Test - How Human Are You? Free Online
201016625
HCI - Free Practice Exam Questions
15816980
Matrices - Test Your Knowledge Free Online
201017489
What Horse Breed Should I Get? Free to Find Your Match
201019057
Which Chowder Character Are You? Take the Free
201017166
Horse Care - Test Your Horsemanship Basics
201017423
Lip Shape Test - What Type of Lips Do You Have? Free
201017358