Oral Pathology Midterm Review 1

Oral Pathology Midterm Review
Welcome to the Oral Pathology Midterm Review Quiz! Test your knowledge on key concepts and significant lesions in oral pathology. Designed for students and educators alike, this quiz will help you reinforce your understanding and prepare for exams.
Topics covered include:
- Inflammatory responses
- Oral lesions and their characteristics
- Immune system fun
- Clinical conditions and diagnoses
Which descriptive term is described as a segment that is part of the whole?
Bulla
Vesicle
Lobule
Pustule
Which condition is not diagnosed through clinical appearance?
Mandibular tori
Fordyce granules
Black hairy tongue
Compound odontoma
Retrocuspid papillae are located on the
Palate.
Floor of the mouth.
Gingival margin of the lingual aspect of mandibular cuspids.
Canine eminence.
A Stafne bone cyst contains
Salivary gland tissue
An empty void.
Inflammatory cells
An epithelium-lined cyst containing serous fluid.
Another term for an amalgam tattoo is a
Melanoma.
Focal argyrosis.
Nevus.
Multiple myeloma.
A pathologic lesion found frequently in 30-year-old black women that requires a radiographic image and historical data for diagnosis is termed
Verrucous vulgaris
Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia.
Amalgam tattoo.
Each condition is considered a variant of normal except one. Which is the exception?
Melanin pigmentation
Linea alba
Geographic tongue
Retrocuspid papilla
Urticaria is an example of a(n)
Genetic disorder.
Developmental disturbance.
Immediate response to an allergen.
Immunodeficiency response
What is the radiographic appearance of periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia in its earliest stage?
Radiolucent
Radiopaque
Radiolucent and radiopaque
Cotton-wool radiolucencies
A “white” hairy tongue indicates an increase in the amount of
Keratin.
Medications.
Fluoride use.
HPV circulating in the blood.
A decrease in the size and function of a cell, a tissue, an organ, or the body is referred to as
Emigration.
Atrophy.
Hyperplasia.
Phagocytosis.
Which type of inflammation occurs when the injury is minimal and brief and its source is removed from the tissue?
Acute
Chronic
Local
Systemic
Which cell is the first to arrive at the site of injury and is the primary cell type involved in acute inflammation?
Macrophage
Neutrophil
Plasma cell
Mast cell
The first microscopic event in the inflammatory response is
Decreased blood flow
Constriction of the microvasculature.
Phagocytosis.
Dilation of microvasculature.
Which habit is not a cause of abrasion?
Pipe placement by smokers
Playing wind instruments
Holding needles or pins with the teeth
Frequent sucking of lemons
The major cause of a mucocele is
A sialolith.
Salivary duct obstruction
Trauma to a minor duct.
Allergic reaction.
Which inflammatory periapical lesion is most painful?
Periapical abscess
Periapical granuloma
Radicular cyst
Residual cyst
During the acute inflammatory process, the second type of white blood cell to emigrate from the blood vessel into the injured tissue is termed
Macrophage.
Neutrophil.
Plasma cell.
Lymphocyte.
Aspirin burn to the oral mucosa appears as
White.
Pigmented.
Bulbous.
Papillary.
Your patient presents with tooth structure that has been lost around occlusal restorations. The amalgam restorations appear raised from the surrounding demineralized tooth structure. Identify the traumatic injury to the teeth that has occurred:
Attrition
Abrasion
Abfraction
Erosion
The breakdown of cellular adhesion between epithelial cells is termed
Cell-mediated immunity.
Acantholysis
Nikolsky sign.
Anaphylaxis.
Which is an example of type I hypersensitivity?
Immune complexes formed between microorganisms and antibody in the circulating blood
Asthma
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Serum sickness
Wickham striae is a term used to describe the oral mucosal lesions of
Linea alba.
Frictional keratosis.
Lichen planus
Erythema multiforme.
Which one is not a characteristic feature of pemphigus vulgaris?
Epithelial acantholysis
Bullae
Tzanck cells
Occurrence most commonly in females
In which condition is the Langerhans cell not the proliferating cell?
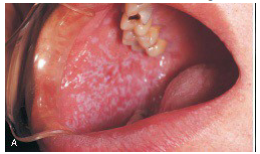
Lichen planus
Letterer–Siwe disease
Hand–Schüller–Christian disease
Eosinophilic granuloma
The major divisions of the immune response are the cell-mediated and humoral responses. Both of these responses originate from what type of cell?
Plasma cell
Stem cell
T-lymphocyte
B-lymphocyte
Anaphylaxis occurs as a result of what type of hypersensitivity?
I
II
III
IV
In the mildest form of this autoimmune disease, oral lesions appear as erythematous plaques or erosions. White striae radiating from the center of the lesion are also commonly present. These oral lesions are indicative of what autoimmune disease?
Mucous membrane pemphigoid
Pemphigus vulgaris
Lupus erythematosus
Behçet syndrome
Acantholysis, or the dissolution of the intercellular bridges of the prickle cell layer of the epithelium, is an oral manifestation of which disease?
HIV
Urticaria
Pemphigus vulgaris
Behçet syndrome
Which protein molecule is produced by plasma cells and is also termed an immunoglobulin?
An autoimmune disease
A natural killer (NK) cell
Rheumatoid factor
An antibody
Tonsillitis and pharyngitis are caused by group A β-hemolytic streptococci. These conditions are significant because of their relationship to scarlet fever and rheumatic fever. Which condition may be related to heart valve damage?
Rheumatic fever
Strawberry tongue
Scarlet fever
Geographic tongue
Which disease is caused by the spirochete Treponema pallidum?
Tuberculosis
Actinomycosis
Syphilis
Necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (NUG)
The most characteristic form of which disease is the formation of abscesses that tend to drain from the mandible to the skin by the formation of sinus tracts, with sulfur granules in the pus draining from the sinus tracts?
Actinomycosis
Tuberculosis
Syphilis
Impetigo
Pericoronitis is most often associated with
Maxillary canines
Mandibular third molars.
Maxillary second molars.
Mandibular first molars.
Acute osteomyelitis of the jaws may commonly result from which condition?
Extension of a periapical abscess
Surgery
Fracture of the jaw
Paget disease
Candidiasis is the result of an overgrowth of a
Yeastlike fungus.
Spirochete.
Filamentous bacterium
Fusiform bacillus.
The presence of condyloma acuminatum in a child suggests
Hypersensitivity.
Genetic predisposition.
Sexual abuse.
Autoimmune disease.
The patient is HIV seropositive. The most common intraoral locations for this lesion are the gingiva and palate. When diagnosed, this vascular lesion meets the criteria for the diagnosis of acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). What is the name of the vascular lesion?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Kaposi sarcoma
Thrombocytopenia
Hemangioma
In herpes labialis, the amount of virus present is highest in the __________ stage.
Crusted
Prodromal
Vesicle
Healing
Each benign lesion is caused by the HPV except one. Which one is the exception?
Focal epithelial hyperplasia
Condyloma acuminatum
NUG
Verruca vulgaris
Which term describes a disorder present at and existing from the time of birth?
Anomaly
Inherited
Congenital
Developmental
Which term defines the joining of two adjacent teeth by cementum only?
Twinning
Concrescence
Cementogenesis
Fusion
The _____ is characterized by its unique histologic appearance and its frequent recurrence rate.
Radicular cyst
Residual cyst
Dentigerous cyst
Odontogenic keratocyst
The lateral periodontal cyst occurs most often on the lateral aspect of a tooth root, which is usually the
Mandibular third molar.
Maxillary premolars.
Mandibular cuspid/premolars.
Maxillary anteriors
What is the pseudocyst filled with salivary gland tissue that may be an extension of the sublingual gland?
Ranula
Static bone cyst
Lymphoepithelial cyst
Traumatic bone cyst
The most common supernumerary tooth is termed
Distomolar.
Mesiodens
Mulberry molar
Turner tooth.
The developmental anomaly seen in this radiographic image is
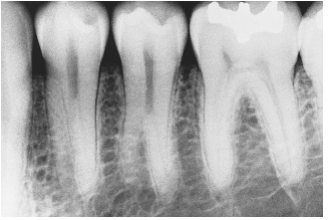
2

Taurodontism
Mulberry molar.
Supernumerary roots on the mandibular premolars.
Dilaceration.
This radiographic image clearly shows which developmental anomaly?
dens
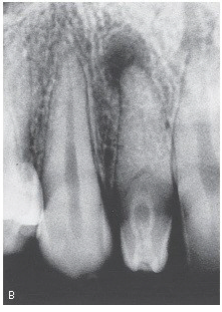
Dens in dente
Periapical pathology (PAP)
Caries
Open contacts
Regional odontodysplasia is also referred to as
Hypodontia
Ghost teeth.
Taurodontism
Supernumerary teeth.
Odontogenic keratocysts are a clinical component of
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome.
Neurofibromatosis of von Recklinghausen.
Cherubism.
Gardner syndrome.
{"name":"Oral Pathology Midterm Review 1", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Welcome to the Oral Pathology Midterm Review Quiz! Test your knowledge on key concepts and significant lesions in oral pathology. Designed for students and educators alike, this quiz will help you reinforce your understanding and prepare for exams.Topics covered include:- Inflammatory responses- Oral lesions and their characteristics- Immune system functions- Clinical conditions and diagnoses","img":"https:/images/course3.png"}
More Quizzes
Oral Path Midterm
50250
Suffix
1780
Momentum Quiz Gabi
630
Safe Sex & Sexual Health Quiz 1
9411
Rocky: How Well Do You Know the Movies?
201020204
Belt and Disc Sander Safety - Free Online
201017029
Cillian Murphy - Which Character Are You?
201018393
10-7 Police Code - How Well Do You Know 10-Codes?
201020204
Literary Device: Free Practice Questions Online
201017674
5.07 Energy Flow in Ecosystems - Free Practice
201015917
Google Government Exam Practice (Free)
201016228
What Fruit Are You - Find Your Fruit Personality
201016908