DES C_Management (3) Prepared : CHILLY
A 24-year-old female presents to you for the evaluation of acne. Further questioning, reveals that she also has had irregular periods for a long time. She is single and not sexually active. On examination, her BMI is 31 Kg/m2 and she has evidence of hirsutism. Further evaluation reveals increase in serum free testosterone and LH/FSH ratio of 2.4. Glucose tolerance testing reveals two-hour blood glucose of 155 mg/dl. Apart from prescribing oral contraceptive pills, which of the following is indicated in this patient?
Clomiphene citrate
No other medication needed
Metformin
Insulin
Glipizide
A 24-year-old female veterinary assistant is referred to a psychiatrist for the presumptive diagnosis of dysthymia. She reports having a three-year history of low energy levels and gradual worsening in her ability to focus on her work. She feels "sad, hopeless," and experiences little pleasure. She denies any suicidal thoughts. She has never been on any psychotropic medications before, and denies any family history of psychiatric illness. She has gastroesophageal reflux disease, for which she takes omeprazole. She has no known allergies, and does not drink alcohol or smoke cigarettes. The psychiatrist decides to treat her dysthymia with bupropion. Which of the following is a contraindication to the use of bupropion?
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Bipolar disorder
Narcolepsy
Anorexia nervosa
Smoking cessation
A 24-year-old G1P0 woman at 31 weeks’ gestation presents to the emergency department with a 4-hour history of abdominal cramping and contractions. The contractions have been regularly spaced at 10 minutes, but seem to be increasing in intensity. She has had a small amount of vaginal discharge, but is unable to definitively say whether her water has broken. She has not had any vaginal bleeding. Her temperature is 36.8C (98.3F), blood pressure is 137/84 mm Hg, pulse is 87/min, and respiratory rate is 12/min. Physical examination reveals a non-tender abdomen with palpable contractions every 8 minutes. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Ultrasound examination of the fetus
Speculum examination to rule out rupture of membranes and visually assess cervical dilation and effacement
Quantification of strength and timing of contractions with an external tocometer
Digital cervical examination and assessment of dilation and effacement
Cervical culture for Group B streptococci
A 24-year-old G1P1 presents for her routine postpartum visit 6 weeks after an uncomplicated vaginal delivery. She states that she is having problems sleeping and is feeling depressed over the past 2 to 3 weeks. She reveals that she cries on most days and feels anxious about taking care of her newborn son. She denies any weight loss or gain, but states she doesn’t feel like eating or doing any of her normal activities. She denies suicidal or homicidal ideation. Which of the following is true regarding this patient’s condition?
Prenatal preventive intervention for patients at high risk for postpartum depression is best managed alone by a mental health professional
A history of depression is not a risk factor for developing postpartum depression
About 8% to 15% of women develop postpartum depression
Postpartum depression is a self-limiting process that lasts for a maximum of 3 months
Young, multiparous patients are at highest risk
A 24-year-old Jehovah’s Witness who was in a high-speed motorcycle collision undergoes emergent splenectomy. His estimated blood loss was 1500 mL. Which of the following strategy should be employed for his resuscitation?
Vasopressors should be primarily utilized for maintenance of his blood pressure
Synthetic colloids should be administered as the primary resuscitation fluid in a 3:1 ratio to replace the volume of blood lost
Lactated Ringer solution should be administered in a ratio of 3:1 to replace the blood lost
0.45% normal saline should be administered in a 3:1 ratio to replace the volume of blood lost
0.9% normal saline should be administered in a 1:1 ratio to replace the volume of blood lost
A 24-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He complains of severe back pain and abdominal discomfort. He was placed on a board in the field for spinal immobilization.His blood pressure is 111/78 mm Hg, pulse is 55/min and regular, and respirations are 16/min. Pulse oximetry shows 96% on room air. He is alert and fully oriented. There are several lacerations on the face and anterior chest. Air entry is bilaterally symmetric. There is weakness and decreased pain sensation in both legs. Proprioceptive sensation is preserved. Chest x-ray and CT scans of the abdomen and spine are performed. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in managing this patient?
Intravenous atropine
Nasogastric tube placement
Intravenous lorazepam
Bladder catheterization
Femoral line placement
A 24-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He has severe low back pain. Examination shows weakness and decreased pain and temperature sensation in both legs. Fine touch, vibration, pressure and proprioceptive sensations are intact. He is immobilized and his airway, breathing and circulation are restored. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of his spinal injury?
CT scan of the spine
Watchful observation
Immediate surgery
Intravenous steroids
MRI of the spine
A 24-year-old man is found to be HIV positive. He is asymptomatic. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory tests show: CD4 count 400/micro-L, HIV viral load 9,000 copies/mL, VDRL negative, Toxoplasma serology negative, PPD test 6mm induration. His chest x-ray is unremarkable. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Rifampin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide for 6 months
Rifampin, isoniazid, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for 2 months, then isoniazid and rifampin for 4 months
Isoniazid and pyridoxine for 9 months
Rifampin for 9 months
Reassurance and repeat testing in 2 months
A 24-year-old man with chronic schizophrenia is brought to the emergency room after his parents found him in his bed and were unable to communicate with him. On examination, the man is confused and disoriented. He has severe muscle rigidity and a temperature of 39.4°C (103°F). His blood pressure is elevated, and he has a leucocytosis. Which of the following is the best first step in the pharmacologic treatment of this man?
Lithium
Haloperidol
Lorazepam
Bromocriptine
Benztropine
A 24-year-old patient comes to the doctor because she has concerns regarding her sexuality. She states that for as long as she can remember she has been sexually attracted to other women. She was raised in a family where homosexuality is considered "unacceptable," so she has never discussed these feelings before. Now, however, she feels that she can no longer hide her feelings, but she is concerned that she will cause deep and irreparable harm to her relationship with her parents if she tells them. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Reassure her that time will change her feelings
Refer her for psychological counselling
Prescribe a benzodiazepine
Prescribe haloperidol
Prescribe estrogen
A 24-year-old primigravid woman at 10 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding. She has colicky pain in the suprapubic region radiating to her back. Her temperature is 37.0C (98.7F), blood pressure is 110/76 mm Hg, pulse is 84/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows a dilated cervix and the products of conception are seen through it. Blood is sent to the laboratory for type and antibody screen. The patient is treated with dilation and curettage and all products of conception are evacuated. She is stabilized and transferred to the ward. Her laboratory results are as follows: Hematocrit: 32%; Leukocyte count: 8,000 cells/µL; Blood type: AB; Rh-negative; Anti-Rh antibody titer: 1:4. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Obtain karyotyping of the mother
Order anti-nuclear antibodies
Screening for TORCH infections
Monitor coagulation profile
Administer anti-D immune globulin
A 24-year-old primigravid woman at 10 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding. She has colicky pain in the suprapubic region radiating to the back. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7F), blood pressure is 110/76 mmHg, pulse is 84/min and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows a dilated cervix and products of conception are seen through it. Blood for grouping and typing is sent. The patient is treated appropriately, and all products of conception are evacuated. She is stabilized and transferred to the ward. Laboratory studies there show: Hematocrit: 33%; WBC: 6,000/mm3; Blood type: AB; Rh negative; Antibody titer: 1:4. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Obtain karyotyping of the mother
Order anti-nuclear antibodies
Screening for TORCH infections
Monitor coagulation profile
Administer RhoGAM
A 24-year-old primigravid woman at 28 weeks gestation comes to the physician because she has not felt her baby's movements for the past two weeks. Fetal heart tones are not heard by Doppler. Ultrasound shows absence of fetal cardiac activity. Fetal demise is diagnosed. Laboratory studies show: Serum fibrinogen level: 160 mg/dl (normal is 150 - 450 mg/dL), Platelets: 150, 000/mm3, Prothrombin time: 14 sec, Partial thromboplastin time: 28 sec, First trimester platelets were: 250,000/mm3. There are no signs of active bleeding. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Weekly fibrinogen monitoring and expect spontaneous delivery
Platelet transfusion and fibrinogen replacement
Emergency cesarean section
Induction of labor
Transfusion of fresh frozen plasma
A 24-year-old primigravid woman at 35 weeks gestation comes to the emergency department with uterine contractions. She started these contractions six hours earlier, and they have not increased in intensity since then. The contractions started in the lower abdomen and are irregular. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests and fetal growth have been normal. She has no history of trauma. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Vital signs are normal. Examination shows a firm, posterior and closed cervix. Ultrasonogram in the emergency department shows a gestational age of 35-weeks and the fetus in the vertex presentation. Fetal heart tones are heard. She feels better after mild sedation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Begin tocolysis
Reassure and discharge the patient home
Intravenous penicillin
Corticosteroids
Admit to the hospital for delivery
A 24-year-old primigravid woman comes for her initial prenatal visit at 24 weeks' gestation. Her only complaint is low back pain. She has no significant past medical history, and she has had no complications of pregnancy thus far. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Complete physical examination shows no abnormalities. During the interview she requests screening for diabetes because her friend was diagnosed with gestational diabetes at 26-weeks of gestation. Which of the following is the most appropriate screening procedure for this patient?
One time fasting blood sugar
Fasting and random urine sugar
Three hour 100gram oral glucose tolerance test
One hour 50gram oral glucose tolerance test
75gram oral glucose tolerance test
A 24-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician because of recent onset amenorrhea. Her last menstrual period was 7 weeks ago, and she has had nausea for the past 2 weeks. A urine pregnancy test is positive. She is being evaluated for dysphagia, and one-week ago she had a barium swallow examination. She is concerned for the baby because of her recent exposure to radiation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Advise amniocentesis and karyotyping
Pelvic ultrasonogram
Explain the risks and benefits of abortion
Reassurance and regular antenatal check-ups
Advise therapeutic abortion
A 24-year-old woman asks her physician about the possibility of genetic screening for BRCA1 mutations. Her mother died of breast carcinoma at age 44, and a sister had a diagnosis of in situ ductal carcinoma at age 38. Which of the following is the most appropriate advice to give this woman?
Not recommend counselling before genetic screening is undertaken
Suggest prophylactic bilateral mastectomy instead of screening
Recommend counselling before genetic screening is undertaken
Recommend screening only if she is of Ashkenazi Jewish descent
Explain that BRCA1 mutations are not associated with an increased risk of breast cancer
A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician's office because of breast pain. She has a 2-month-old baby who she breastfeeds. Her temperature is 38.5C (101.9F). Examination shows a hard, red, tender and swollen area on her right breast. There is no fluctuance noted. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Antibiotics, analgesics and nursing only from unaffected breast
Antibiotics, analgesics and continue breast feeding
Antibiotics and lactation suppression with bromocriptine
Incision and drainage
Recommend mammogram
A 24-year-old woman comes to your office with vaginal spotting 2 weeks after a missed menstrual period. Her past medical history is significant for pelvic inflammatory disease. She has never had surgery. She takes no medications and is allergic to penicillin. Examination demonstrates scant blood in the vaginal vault and minimal right adnexal tenderness. Laboratory evaluation reveals a beta-hCG value of 1600 mIU/mL. Blood type is O positive. Hematocrit is 39%. Pelvic ultrasound demonstrates nothing in the uterus and a right adnexal mass consistent with ectopic pregnancy. The decision is made to proceed with intramuscular methotrexate for medical treatment of the ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following is the most likely side effect from this treatment?
Alopecia
Infertility
Neutropenia
Stomatitis
Cardiotoxicity
A 24-year-old woman has fever, right upper quadrant pain, and lower abdominal pain. She reports having multiple sexual partners and does not use condoms. She has no medical history, does not take any medications, and has no drug allergies. Her temperature is 38.9 C (102.0 F). Her lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdomen examination is notable for right upper quadrant tenderness. Pelvic examination reveals mucopurulent drainage and tenderness with cervical motion. She also has adnexal tenderness. Her leukocyte count is 14,000/mm3. Liver fun
Check hepatitis B status
Start therapy with penicillin
Start therapy with ceftriaxone and doxycycline
Check HIV status
Consult surgery for a cholecystectomy
A 24-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital for a broken femur. The patient was in a motor vehicle accident 20 hours ago and was brought to the hospital by EMS. On the scene, she was found belted in her car in the driver’s seat, and her only documented injury was the leg fracture. She had no loss of consciousness or altered mental status. On arrival to the hospital, radiographs confirmed a fracture of her femur. She was stabilized overnight and scheduled for surgery the next day. Which of the following is the major surgical risk for this patient?
Air embolism
Osteomyelitis
Permanent disability
Fat embolism
Cerebrovascular accident
A 24-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after being stabbed by her boyfriend. The examining physician notes a 1.5 cm puncture wound lateral to her sternum. She has a blood pressure of 70/min palpable, distended neck veins, and muffled heart sounds. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Cardiac surgery consult
Pericardiocentesis
Chest tube placement
Echocardiogram
Chest x-ray film
A 24-year-old woman lost her previous two pregnancies at approximately 20 weeks’ gestation, without having noted any contractions. She is currently at 15 weeks’ gestation and denies having uterine contractions. Her cervix is undilated and uneffaced. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
Bed rest
Terbutaline
Hydroxyprogesterone
DES
A cervical cerclage
A 24-year-old woman presents for her first prenatal visit at 12 weeks gestation. She was diagnosed with HIV two years ago, and her most recent CD4 count three months ago was 600cells/mm3. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Physical examination is within normal limits. Which of the following is the single most important intervention for reducing maternal-fetal transmission of HIV infection?
Zidovudine treatment of the mother during pregnancy and of the neonate after birth
Reassurance
Administering HIV immunoglobulin and vaccine to the neonate
Use of forceps to expedite delivery
Elective cesarean section at 38 weeks gestation
A 24-year-old woman presents to the ED after being sexually assaulted. She is a college student with no past medical history. Her BP is 130/75 mm Hg, HR is 91 beats per minute, temperature is 98.6°F, and RR is 16 breaths per minute. On physical examination you observe vaginal trauma and scattered bruising and abrasions. Which of the following medications should be offered to the patient in this scenario?
Ceftriaxone, azithromycin, tetanus, metronidazole, antiretrovirals, emergency contraception
Ceftriaxone, azithromycin, tetanus, antiretrovirals, emergency contraception
Ceftriaxone, azithromycin, tetanus, metronidazole, emergency contraception
Ceftriaxone, tetanus, metronidazole, antiretrovirals, emergency contraception
Ceftriaxone, azithromycin, metronidazole, antiretrovirals, emergency contraception
A 24-year-old woman presents to your office with a self-palpated breast lump. She discovered the mass 2 days ago while taking a shower and noted that it is mildly tender. Her menstrual periods are regular, occurring every 26 days. Her last menstrual period (LMP) was 3 weeks ago. Her past medical history is insignificant. She has no family history of breast cancer. Physical examination reveals a lump in the superior outer quadrant of the right breast without palpable lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is the most reasonable next step in the management of this patient?
Reassure that the mass is benign and no follow-up is necessary
Proceed with fine needle aspiration biopsy
Suggest excisional biopsy
Ask her to return shortly after the menstrual period
Order mammography
A 24-year-old woman presents with lethargy, anorexia, tachypnea, and weakness. Laboratory studies reveal a BUN of 150 mg/dL, serum creatinine of 16 mg/dL, and potassium of 6.2 mEq/L. Chest x-ray shows increased pulmonary vascularity and a dilated heart. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
A 100-g protein/day diet
Renal biopsy
Placement of a catheter in the internal jugular vein and initiation of hemodialysis
Creation and immediate use of a forearm arteriovenous fistula
Emergency kidney transplantation
A 24-year-old woman with chronic hypothyroidism presents to her gynecologist for her annual examination. She recently got married, and she and her husband would like to conceive. Her hypothyroidism is well controlled and stable on thyroxine, and she has no other medical conditions. She is healthy and does not smoke or drink alcohol. She would like to know if she should keep taking her thyroxine. Which of the following is the best advice to give this patient?
€śNo, but we would want to keep your thyroid levels balanced for the sake of your baby, so you would be switched to methimazole”
€śNo, thyroxine is generally accepted as safe during pregnancy, but if you are not comfortable taking it, there is no evidence that being hypothyroid will affect your baby”
€śNo, thyroxine is not safe when taken during pregnancy; it is better for both you and your baby for you to be hypothyroid”
€śYes, but we would likely decrease your thyroxine during pregnancy because pregnancy is accompanied by mild physiologic hyperthyroidism”
€śYes, in fact we would likely need to increase your thyroxine during pregnancy to avoid hypothyroidism, which may adversely affect your baby”
A 24-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 16 weeks' gestation comes to you for a routine prenatal visit. She has had mild constipation. She has had no nausea, vomiting, fever, burning urination, back pain, or other complaints. She has no history of urinary tract infections. She takes iron and folic acid supplements. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. She is afebrile; her blood pressure is 124/74 mm Hg and pulse is 78/min. Examination shows a uterus consistent in size with a 16-week gestation. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis is within normal limits. A routine clean-catch urine culture grows greater than 100,000 colonies/ml of Escherichia coli. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole for 7 days
Obtain renal ultrasonogram
Nitrofurantoin for 7 days
Reassurance and routine follow-up
Ciprofloxacin for 3 days
A 24-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 26 weeks' gestation comes to the physician complaining of aching and swelling in both legs. The aching of her legs is worst at night. She has no shortness of breath or chest pain. She has no past medical history. Her temperature is 36.9 C (98.2F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 78/min. Physical examination shows symmetrical pitting edema of both calves with no tenderness of either calf. Urinalysis shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Order echocardiogram and serum albumin levels
Start low molecular w eight heparin
Reassurance and routine follow-up
Admit for monitoring of her condition
Doppler ultrasonogram of both lower extremities
A 24-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 34 weeks' gestation comes for a routine prenatal visit. Her dates were confirmed by first trimester ultrasonogram. She has no painful uterine contractions. Her previous pregnancy was uncomplicated and ended with a normal vaginal delivery. Her vitals are stable and fetal heart tones are reassuring. Physical examination shows a closed cervix, vertex is palpable at the fundus, and the presenting part is not engaged. Which of the following is the appropriate next step in management?
Admit the patient and monitor closely
Discuss cesarean section with the patient
Routine follow-up
Attempt internal cephalic version
Attempt external cephalic version
A 24-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, comes to the physician for a yearly physical and birth control counseling. She is currently using the rhythm method of birth control, but has heard that this method has a high failure rate and would like to try a different method. Several of her friends use the intrauterine device (IUD), and she is wondering whether she could also use this method. Past medical history is significant for eczema. Past surgical history is significant for a right ovarian cystectomy 2 years ago. Past gynecologic history is significant for multiple episodes of Chlamydia cervicitis and two episodes of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), the most recent episode occurring 1 year ago. She takes acetaminophen for occasional tension headaches. She is allergic to penicillin. She smokes onehalf pack of cigarettes per day. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following would be the best recommendation for this patient regarding her birth control method?
"The rhythm method is recommended."
"The oral contraceptive pill is absolutely contraindicated."
"The IUD is recommended if cervical cultures are negative."
"The IUD is absolutely contraindicated."
"The IUD is recommended."
A 24-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago, and a home pregnancy test was positive. She states that this pregnancy, like her last two pregnancies, was unintended. She had been using condoms for birth control in all three instances. She had normal vaginal deliveries 2 and 4 years ago. Which of the following is the most likely reason for condom failure?
Allergic reaction
Manufacturing defects
Vaginal infection
Improper and inconsistent use
Breakage
A 24-year-old woman, gravida 4, para 1, abortus 2, is at 28 weeks’ gestation by poor dates. She admits to intravenous (IV) drug use and having sex for drugs. She is unsure who the father of this pregnancy is. She has recently undergone treatment for syphilis identified by a positive venereal disease research laboratory (VDRL) test result and confirmed by a positive fluorescent treponemal antibody (FTA) test. On her last prenatal visit, she underwent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) testing by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which was found to be positive and was confirmed with a positive Western blot assay. She inquires as to the significance of this finding for herself, as well as her baby. Which of the following statements best summarizes what you will say about her medical conditions?
Neonates can be protected from HIV by passive immunization at birth
Breastfeeding does not increase neonatal risk of becoming HIV positive
Mode of delivery has a significant impact on maternal–neonatal transmission of HIV
Pregnancy accelerates maternal progression from HIV positive to acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS)
Rapidity of disease progression is the same in mother and neonate
A 24-year-old, gravida 0, para 0 woman comes to the physician because of an 8-week history of amenorrhea. She is sexually active and uses oral contraceptive pills for contraception. Her only other complaints are moderate fatigue and a decline in mood. She denies headaches, visual disturbances, and gastrointestinal symptoms. She has no other medical problems. She socially drinks alcohol and does not use tobacco or illicit drugs. She denies stress at home or work. She walks 1-2 miles every day. Her BMI is 24 kg/m2. Visual field test is within normal limits. Examination shows no hirsutism. Breast examination reveals a white, milky secretion upon expression of both nipples. Pelvic examination reveals a uterus of normal size. Initial investigations reveal a negative serum β-human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level. According to these findings, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Measure serum TSH level
Order MRI of the brain with pituitary focus
Measure serum testosterone level
Order hysterosalpingogram
Measure serum LH and FSH levels
A 25-year-old Caucasian woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 26 weeks' gestational age presents to her physician's office complaining of spotting from the vagina. She has no contractions and reports normal fetal movement. She denies any history of a bleeding disorder. Her temperature is 37.3 C (99.1 F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 75/min, and respirations are 14/min. Her abdomen is gravid and benign, with a fundal height of 26 cm. A placenta previa is ruled out by ultrasound examination. Pelvic examination reveals some scant blood in the vagina, a closed os, and no uterine tenderness. Leukocyte count is 12,000/mm3, hematocrit is 33%, and platelet count is 140,000/mm3. Her blood type is A, Rh negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
Antibiotics
Platelet transfusion
RhoGAM™
Magnesium sulfate
Blood transfusion
A 25-year-old female comes to the physician because of abdominal bloating, headache, fatigue, weight gain, anxiety, and decreased libido. She experiences these symptoms seven to ten days before the start of each menstrual cycle. She has a past history of postpartum depression, but she denies any recent feelings of hopelessness or guilt. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Complete blood count, serum chemistries and thyroid stimulating hormone levels are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Insight oriented and supportive psychotherapy
Prescribe alprazolam
Prescribe selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Advise menstrual diary
Cognitive behavioral therapy
A 25-year-old G2 P1 woman at 12 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of foul smelling vaginal discharge. She is sexually active and reports no previous problems. Speculum examination reveals a grayish, foul smelling discharge, but no erythema or edema is noted on the vaginal walls or the vulva. There is no cervical or adnexal tenderness. A saline wet mount examination reveals numerous epithelial cells coated with bacteria. No white blood cells are seen. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
Azithromycin
No therapy for now
Metronidazole
Doxycycline
Fluconazole
A 25-year-old G2P0 at 30 weeks gestation presents with the complaint of a new rash and itching on her abdomen over the last few weeks. She denies any constitutional symptoms or any new lotions, soaps, or detergents. On examination she is afebrile with a small, papular rash on her trunk and forearms. Excoriations from scratching are also noted. Which of the following is the recommended first-line treatment for this patient?
Topical steroids and oral antihistamines
Oral steroids
Antibiotic therapy
Delivery
Cholestyramine
A 25-year-old G2P1 woman who is 36 weeks pregnant presents to her obstetrician complaining of restlessness and weakness for the past month. She says her boyfriend recently left her and their 2-year-old son, and she feels overwhelmed with this pregnancy. She denies feeling depressed but does report that she has trouble sleeping. She had an upper respiratory infection last month, “caught from my son,” and states she still has a sore throat. Laboratory tests show: WBC count: 8000/mm3; Hemoglobin: 11.0 g/dL; Hematocrit: 40%, Platelet count: 250,000/mm3; Thyroid-stimulating hormone: 0.5μU/mL; Free thyroxine: 4.0 ng/dL. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Start levothyroxine therapy
Start radioiodine therapy
Start propylthiouracil therapy
Measure postpartum thyroid hormone levels
Perform partial thyroidectomy
A 25-year-old G3P2 at 39 weeks is admitted in labor at 5 cm dilated. The fetal heart rate tracing is reactive. Two hours later, she is reexamined and her cervix is unchanged at 5 cm dilated. An IUPC is placed and the patient is noted to have 280 Montevideo units (MUV) by the IUPC. After an additional 2 hours of labor, the patient is noted to still be 5 cm dilated. The fetal heart rate tracing remains reactive. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this labor?
Perform an operative delivery with forceps
Attempt delivery via vacuum extraction
Continue to wait and observe the patient
Augment labor with Pitocin
Perform a cesarean section
A 25-year-old Gl0 with an intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) at 38 weeks' gestation presents to the labor and delivery unit stating that she thinks she is in labor. She has had routine prenatal care. She states that she has generalized abdominal pain that comes and goes. Thepain has been going on for about 5 hours and is starting to become regular. She thinks it is contractions. Vital sign: BP, 115/75 mm Hg; P, 82 beats/min; R, 12 breaths/min; T, 98.6°F. Contractions: Present, Fetal movement: Present, Vaginal bleeding: Absent, Leakage of fluid: Absent. Physical examination: Gen: Awake, alert, oriented x3, mild pain distress, CVS: S1S2 + RRR no m/ r/ g, Lungs: CTA bilaterally, Abd: Gravid, Ext: 1+ edema bilaterally. What is the next step in the management of this patient?
Transvaginal ultrasonography (US)
Emergency surgery
Nonstress test
Digital cervical examination
Transabdominal US
A 25-year-old HIV-positive male comes to a physician with complaints of headache and left-sided weakness of recent onset. His temperature is 38°C (100.8°F), blood pressure is 115/70mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and pulse is 73/min. Neurological examination reveals decreased power, hyperreflexia, and upgoing plantars in the left upper and lower limb. Neuroimaging by CT shows multiple ring-enhancing lesions. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Sulfadiazine and pyrimethamine
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Brain irradiation
Brain biopsy
Anti-tuberculous therapy
A 25-year-old male comes to the clinic because of a painless ulcer on his penis. He denies fever or urethral discharge, but admits to recent sexual activity with a prostitute. He describes severe rash and face swelling with penicillin. Physical examination reveals a shallow, non-tender ulcer. There is no lymphadenopathy. Darkfield microscopy reveals spirochetes. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
Ciprofloxacin
Oral doxycycline
Intramuscular benzathine penicillin
Oral clindamycin
IV aqueous crystalline penicillin
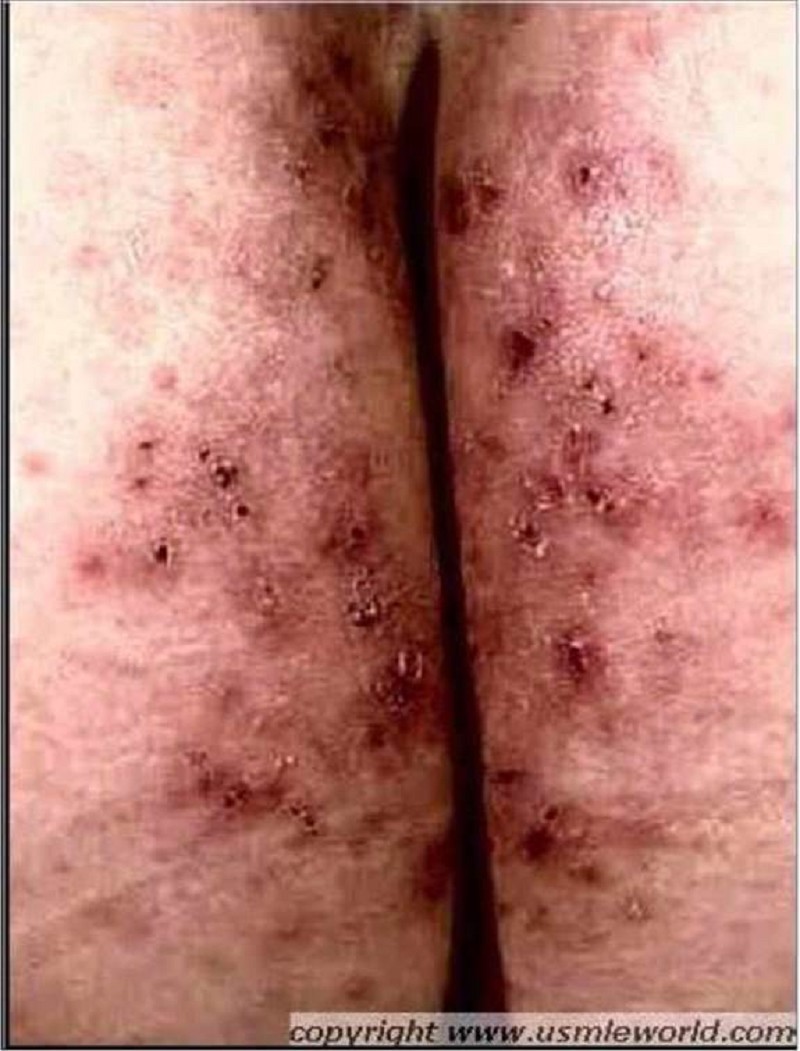
A 25-year-old male presents with skin lesions over his elbows, knees and neck. He complains of intense itching and burning sensation over these lesions for the past 10 days. He was advised to follow a gluten-free diet on his previous visit, but was not compliant. His vital signs are stable. On examination, there are flesh-colored to erythematous vesicles distributed over the extensor aspects of elbows, knees, posterior neck and shoulders. Some of these lesions are shown in the picture below. Which of the following is the drug of choice for his skin condition?
High potency steroids
Azathioprine
Dapsone
1% lindane solution
Low dose acyclovir
A 25-year-old man comes to the physician because of a mass in his mouth. He has just noticed this mass and has had no trauma to his oral cavity. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. He has had no weight loss. Physical examination shows a large mass located on the hard palate of the mouth. On palpation, the mass is immobile, fleshy with bony surroundings and measures 3x 3 cm. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Antifungal treatment
Reassurance
Biopsy
Surgery
Radiation
A 25-year-old man is brought to the emergency room after sustaining burns during a fire in his apartment. He has blistering and erythema of his face, left upper extremity, and chest. He also has circumferential frank charring of his right upper extremity with decreased capillary refill. He is agitated, hypotensive, and tachycardic. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management of his wounds?
Split-thickness skin grafts over the areas of third-degree burns
Excision of all third-degree burns
Escharotomy of the right upper extremity
Excision of facial and hand burns
Topical antibiotics should be applied to the burn wounds
A 25-year-old man is found on a pre-employment chest x-ray film to have a 3-cm peripheral coin lesion. The patient has never smoked, and a chest x-ray film that he had 2 years ago when he enrolled in graduate school had been normal. Prompted by this finding, he undergoes a more thorough physical examination, which discloses the presence of a firm, 2-cm testicular mass of which he was not previously aware. There are also palpable inguinal nodes on the same side. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Radical orchiectomy by the inguinal route
Trans-scrotal orchiectomy and sampling of inguinal nodes
Trans-scrotal incisional biopsy of the testicular mass
Bronchoscopy and biopsy of the lung mass
Supportive symptomatic palliative care
A 25-year-old man is involved in a gang shoot-out and sustains an abdominal gunshot wound from a .22 pistol. At laparotomy, it is discovered that the left transverse colon has incurred a through-and-through injury with minimal fecal soilage of the peritoneum. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
The patient should undergo a 2-stage procedure with resection of the injured portion and reanastomosis 48 hours later when clinically stabilized
Primary repair should be performed and intravenous antibiotics administered for 14 days
Primary repair should be performed with placement of an intra-abdominal drain next to the repair
Primary repair should be performed, but only in the absence of hemodynamic instability
A colostomy should be performed regardless of the patient’s hemodynamic status to decrease the risk of an intraabdominal infection
A 25-year-old man is shot with a .22 caliber revolver. The entrance wound is in the anteromedial aspect of his upper thigh, and the exit wound is about 3 inches lower, in the posterolateral aspect of the thigh. He has a large, expanding hematoma in the upper inner thigh. There are no palpable pulses in the foot. The bone is intact by physical examination and x-ray films. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Doppler studies
Venogram
Arteriogram
Embolectomy
Surgical exploration
A 25-year-old man is shot with a .22-caliber revolver. The entrance wound is in the anterior, lateral aspect of his thigh, and the bullet is seen on x-ray films to be embedded in the muscles posterolateral to the femur. The emergency department physician cleans the wound thoroughly. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Surgical removal of the embedded bullet
Surgical exploration of the femoral vessels
Tetanus prophylaxis
Doppler studies
Arteriogram
A 25-year-old man is stabbed in the right chest. He comes in fully awake and alert, and, in a normal tone of voice, he states that he feels short of breath. His vital signs are normal and stable. On physical examination, he has no breath sounds at the right base, and only faint breath sounds at the apex. He is dull to percussion over the right base. A chest x-ray film confirms that he has a hemothorax on that side. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Intubation and use of a respirator
Oxygen by mask, analgesics, and no specific intervention
Insertion of a chest tube at the right base
Insertion of a chest tube in the right second intercostal space
Exploratory thoracotomy
A 25-year-old man is stabbed once in the right chest. The entrance wound is on the midaxillary line, at the level of the fifth intercostal space. He arrives at the emergency department moderately short of breath, but he is fully awake and alert, is talking with a normal tone of voice, and has no distended veins visible in his neck or forehead. His blood pressure is 130/75 mm Hg, and his pulse is 82/min. Physical examination of the chest shows the wound, which is not visibly "sucking air," and demonstrates no breath sounds at all on the right side, which is tympanitic to percussion. There is no evidence of mediastinal displacement. Which of the following would be the most appropriate next step in management?
Insert an 18-gauge needle into the right pleural space at the second intercostal space
Insert a chest tube at the right pleural base
Cover the wound with Vaseline gauze, taped on three sides
Endotracheal intubation
Cover the wound with a regular dressing and get a chest x-ray
A 25-year-old man presents to the physician's office because of a clenched fist injury ("fight bite") incurred during a gang fight. The injury occurred two days ago and he has now started to develop pain, swelling, and redness around the wound. His immunizations are up to date. His wounds are cleaned in the clinic. Plain films of hand do not show evidence of foreign body or osteomyelitis. Which of the following is the most appropriate antibiotic for his current condition?
Amoxicillin-clavulanate
Erythromycin
Ciprofloxacin
Clindamycin
Ampicillin
A 25-year-old man presents with a painless, hard, 3-cm testicular mass that he discovered serendipitously while taking a shower. Physical examination confirms that the mass arises from the testicle itself, is not part of the epididymis, and is solid rather than a fluid collection. The rest of the physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following would be the most appropriate next step?
Trans-scrotal orchiectomy
Radical inguinal orchiectomy
Trans-scrotal incisional biopsy at the edge of the mass
Trans-scrotal needle biopsy of the mass
Serum levels of alpha-fetoprotein and beta human chorionic gonadotropin
A 25-year-old nulliparous woman at 35 weeks' gestation comes to the labor and delivery ward complaining of contractions, a headache, and flashes of light in front of her eyes. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated except for an episode of first trimester bleeding that completely resolved. She has no medical problems. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 160/110 mm Hg, pulse is 88/minute, and respirations are 12/minute. Examination shows that her cervix is 2 centimeters dilated and 75% effaced, and that she is contracting every 2 minutes. The fetal heart tracing is in the 140s and reactive. Urinalysis shows 3+ proteinuria. Laboratory values are as follows: leukocytes 9,400/mm3, hematocrit 35%, platelets 101,000/mm3. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) is 200 U/L, and ALT 300 U/L. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Discharge the patient
Start terbutaline
Administer oxytocin
Start magnesium sulfate
Encourage ambulation
A 25-year-old primigravid woman at 37 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of severe uterine contractions and moderate vaginal bleeding. She has been followed for pre-eclampsia since her 32nd week of gestation. She is currently having intermittent bleeding. Ultrasonogram in the emergency department shows placental abruption and an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. Placenta previa is ruled out. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg, pulse is 99/min and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination shows uterine tenderness and hyperactivity, increased uterine tone and vaginal bleeding. Her cervix is 1cm dilated and 10% effaced at the time of admission. Fetal heart tracing shows a rate of 110/min, a long-term variability of 4 cycles/min and a beat-to-beat variability of 20/min. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Conservative management in hospital
Tocolysis to prevent the abruption from evolving
Scheduled cesarean section within next 48 hours
Induction of labor
Emergency cesarean section
A 25-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit. Her last menstrual period was 7 weeks ago. She has had some nausea and vomiting but otherwise has no complaints. Past medical and surgical history are unremarkable. Her family history is significant for cystic fibrosis with an affected aunt. Her husband has an affected cousin. Physical examination is unremarkable. Given her family history, she is concerned about the risks of having a child with cystic fibrosis. She inquires about cystic fibrosis screening. Which of the following is the appropriate response?
Screening is unnecessary: she has a 1 in 4 chance of having an affected child
Screening is inappropriate in her case
Screening is not available
Screening is mandatory
Screening is available
A 25-year-old unhelmeted man involved in a motorcycle collision has multiple cerebral contusions on head computed tomographic (CT) scan. He is agitated but hemodynamically stable, with a heart rate of 80 beats per minute and a mean arterial pressure (MAP) of 90 mm Hg. An intracranial pressure monitor is placed, and the initial ICP reading is 30 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most appropriate in the management of his traumatic brain injury (TBI) over the next few days?
Avoidance of all sedating drugs in the first 24 to 48 hours in order to accurately assess his neurologic status
Placement of the patient in Trendelenburg position to increase cerebral perfusion
Administration of mannitol (1 g/kg) to reduce his ICP
Administration of neosynephrine to increase his MAP and, consequently, his cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP)
Hyperventilation to maintain a cerebral PCO2 of 25 to 30 mm Hg
A 25-year-old woman at 28 weeks gestation comes to the ER because of strong, regular and painful uterine contractions that started 4 hours earlier with the passage of clear fluid from her vagina. She denies any vaginal bleeding. She has had no prenatal care. Vital signs are normal. A sterile speculum examination shows pooling of amniotic fluid within the vagina, and a cervix that is 4cm dilated and 80% effaced. Ultrasonogram in the emergency department shows an amniotic fluid index of 4 and bilateral renal agenesis in the fetus. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Administer corticosteroids
Administer prostaglandin
Amnioinfusion and tocolysis
Allow spontaneous vaginal delivery
Consent for cesarean section
A 25-year-old woman comes to the outpatient office complaining of a pruritic, painful vaginal discharge. She is sexually active with two male sexual partners but finds intercourse very uncomfortable because of her vaginal symptoms. For the past 8 months, she has been using the estrogen–progestin contraceptive patch. She exercises regularly by walking 2 to 3 miles a day. She is following a low-carbohydrate diet and takes a multivitamin preparation. Findings of her general examination are unremarkable. Speculum examination of the vagina shows a foul-smelling greenish, frothy discharge. Vaginal pH, using Nitrazine paper, is 6.5. A wet mount of vaginal secretions in a saline suspension reveals a highly motile organism. Which of the following pharmacologic agents would be the most appropriate treatment?
Metronidazole
Azithromycin
Miconazole
Acyclovir
Clotrimazole
A 25-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of burning micturition and increased urinary frequency. She has suprapubic discomfort. She denies having unusual vaginal discharge. She has been sexually active and monogamous for the past 4 years with her husband. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows suprapubic tenderness without flank tenderness. The rest of the examination is normal. Urinalysis shows: Specific gravity 1.020, Blood Trace, Glucose Negative, Ketones Negative, Leukocyte esterase Positive, Nitrites Positive, WBC 40-50/hpf, RBC 6-10/hpf, Bacteria 50+. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Intravenous trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Urine culture
Oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Oral ciprofloxacin
Oral nitrofurantoin
A 25-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual examination. She has been feeling well over the past year. Her past medical and surgical histories are unremarkable. Past obstetrical history is significant for the term vaginal delivery two years ago of a male infant with spina bifida. Examination is within normal limits. The patient states that she would like to try to become pregnant within the next few months and wants to know if she needs to start taking any vitamins or medications. Which of the following supplements should this patient take?
Vitamin A, 10,000 IU/day starting in the first trimester
No supplements are needed
Vitamin A, 10,000 IU/day starting preconceptionally
Folic acid, 4 mg/day starting in the first trimester
Folic acid, 4 mg/day starting preconceptionally
A 25-year-old woman complains of dysuria, frequency, and suprapubic pain. She has not had previous symptoms of dysuria and is not on antibiotics. She is sexually active and on birth control pills. She has no fever, vaginal discharge or history of herpes infection. She denies back pain, nausea, or vomiting. On physical examination she appears well and has no costovertebral angle tenderness. A urinalysis shows 20 white blood cells per high power field. Which of the following statements is correct?
The etiologic agent is more likely to be sensitive to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole than to fluoroquinolones
Low-dose antibiotic therapy should be prescribed while the patient remains sexually active
Obstruction resulting from renal stone should be ruled out by ultrasound
Quantitative urine culture with antimicrobial sensitivity testing is mandatory
A 3-day regimen of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is adequate therapy
A 25-year-old woman delivered a baby boy at 38 weeks gestation. The newborn has a small body size with microcephaly, hypoplasia of the distal phalanges of the fingers and toes, excess hair and a cleft palate. He weighs 2.5kg (5.51b). Further history or evaluation of the mother would most likely reveal which of the following?
Untreated syphilis
Azithromycin use
Alcohol abuse
Cocaine abuse
Phenytoin use
A 25-year-old woman has a positive cervical culture for Neisseria gonorrhoeae. She has had at least two positive cultures for gonorrhea treated in the past. She is afebrile and has no symptoms. The incidence of penicillin-resistant gonorrhea in some areas of the United States is currently as great as 10%. Because of this, the recommended treatment for gonorrhea includes which of the following?
2 g ampicillin orally as a single dose
125 mg intramuscular ceftriaxone as a single dose
1 g spectinomycin
2 g intramuscular cefoxitin
2 g metronidazole as a single dose
A 25-year-old woman is referred to the physician for lactation suppression after the death of her 1-month-old infant from severe sepsis. She is very depressed and complains of breast fullness and tenderness. Examination shows both breasts are warm, firm and tender to palpation. Prenatal records show no abnormalities except mild varicosities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Tight fitting bra and ice packs
Bromocriptine therapy
Frequent emptying of breasts
Conjugated estrogen
Dexamethasone
A 25-year-old woman with no PMH, no PSH, and no allergies presents for unilateral nipple discharge. The patient states that it started about 3 weeks ago, appears whitish, and is unilateral. She does not think she felt any changes in her breast. She denies relation to her menstruation and uses condoms for contraception. She has never been pregnant and her last menstrual period (LMP) was 2 weeks ago. BP, 120/78 mm Hg; P, 85 beats/min; R, 15 breaths/min. Review of systems: Denies fever, chills, and weight loss, Denies chest pain, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. Physical examination: Gen: Awake, alert, oriented x3, no acute distress, CVS: S1S2+RRRno m/r/g, Lungs: Clear to auscultation bilaterally, Abdomen: Soft, nontender, nondistended, + bowel sounds, Ext: No edema bilaterally, Breasts: Symmetric, no masses palpated, clear/whitish fluid expressed on manipulation of left breast. What is the next step in the management of this patient?
Breast US
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level
Refer to breast surgeon
Prolactin level
Mammography
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 22 weeks' gestation comes to the physician with complaints of burning with urination and frequent urination. Her prenatal course has been uncomplicated except for a urinary tract infection (UTI) with E. Coli at 12 weeks' gestation, which was treated at that time. Physical examination is unremarkable. Urine culture demonstrates greater than 100,000 colony-forming units per milliliter of E. coli. After treating this patient for her current infection, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Intravenous antibiotics for the remainder of the pregnancy
Abdominal CT Scan
Intravenous pyelogram
Prophylactic antibiotics for the remainder of the pregnancy
No further treatment or diagnostic study is necessary
A 25-year-old, G3P0 white female in her 8th week of gestation comes to the antenatal clinic. Her obstetric history is significant for two second trimester abortions. She is currently taking folic acid and iron supplementation. She does not smoke, but she drinks alcohol on social occasions. She is in a monogamous relationship with her husband. She has never been diagnosed with or treated for any STDs. Laboratory studies reveal the following: VDRL positive, FTA-ABS negative, Hct 33%, WBC 7,000/mico-L, Platelets 70,000/micro-L, PT 10 sec, APTT 40 sec. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Repeat FTA-ABS
Give heparin and aspirin
Single dose of benzathine penicillin
Repeat VDRL
Three doses of benzathine penicillin
A 26 years old man is about to undergo an orchiectomy for testicular cancer. The anesthesiologist begins isoflurance and succinylcholine, and about 30 minutes later, the patient develops muscle rigidity, herthermia, an elevated heart rate, and abnormal ventilation patterns. There are numerous atrial premature complexes (APCs) and ventricular premature complexes (VPCs) noted on the monitor. The anesthesiologist is unable to open’s mouth because of masseter muscle rigidity. The patient become fever. Vital signs: BP 90/50 mm Hg, HR 140 beats/min, R 18 breaths/min, T0 1050F (40.380C). What is the best next step management?
Check electrolytes
Discontinue isoflurane and succinylcholine
Administer calcium channel blockers
Hyperventilate the patient
Provide intravenous (IV) hydratation
A 26-year-old G0 woman is seen in her gynecologist’s office for a routine examination. She reports that she has been sexually active with four partners and has been treated for gonorrhea once in the past year. She has otherwise been healthy. Physical examination is unremarkable. Results of a Pap smear suggest a low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Test for human papillomavirus types 6 and 11
Refer immediately for colposcopy
Reassure patient of results and instruct her to return to the office in 6 months
Instruct patient to return immediately for repeat Pap smear
Test for human papillomavirus types 16 and 18
A 26-year-old G1 P1 woman requests contraception after delivering a healthy baby three weeks ago. She is breastfeeding the child and plans to continue for at least six months. She does not want to get pregnant for at least one year. She has no medical problems and does not take any medication. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most preferred method of contraception you can advise for this patient?
Coitus interruptus
Tubal ligation
Progestin-only oral contraceptives
Combined estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives
No contraception needed while nursing
A 26-year-old G1P1 woman requests contraception after delivering a healthy baby three weeks ago. She does not want to get pregnant for at least one year. She has no medical problems and does not take any medication. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most preferred method of contraception you can advise for this patient?
No contraception needed while nursing
Tubal ligation
Combined estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives
Progestin-only oral contraceptives
Coitus interruptus
A 26-year-old graduate student presents at her husband's urging, complaining of severe pain during sexual intercourse. She says that she was a virgin when she married her husband two years ago, and that she has been experiencing severe "genital pain" during sex since then. As a result, she avoids sexual intimacy with her husband, which is placing a strain upon their marriage. She also complains of intense pain with her menses and when passing stool. She admits to sporadic pelvic pain that waxes and wanes with no discernible trigger. What would be the most appropriate treatment given this woman's condition?
Psychotherapy and sexual education
Regularly scheduled follow-up visits
Use of vaginal dilators
Oral contraceptive pills
Pain management training
A 26-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a sudden onset of severe right-sided flank pain. The pain is colicky and radiates from the flank to the scrotum. He also has nausea, vomiting and dark-colored urine. He has never had these symptoms before. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 126/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 18/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. He is given adequate analgesia. Non-contrast helical CT shows a 4 mm radiopaque stone in the right upper ureter. Laboratory studies show serum calcium of 9.8 mg/dl, serum creatinine of 0.9 mg/dl, and BUN of 15mg/dl. Urinalysis shows hematuria but no casts. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Fluid intake greater than 2L/day
Restriction of dietary oxalate
Intake of potassium citrate
24 hr urine collection for metabolic evaluation
Reassurance
A 26-year-old man comes with his girlfriend to the emergency department due to a very high fever. He just finished his second cycle of BEP (bleomycin, etoposide, cisplatin) chemotherapy for metastatic seminoma 4 days ago. Other than his fever, he has no complaints. He denies any chest pain, cough, diarrhea or any rash. He stopped smoking ever since he was diagnosed with his "deadly disease," but drinks alcohol occasionally. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 118/70 mm Hg, pulse is 102/min, and respirations are 19/min. Physical examination reveals a pale man without any eyebrows or eyelashes. Chest auscultation is clear. Blood tests reveal: WBC 690/mm3 with 9% neutrophils, Hemoglobin 8.6 g/dl, Hematocrit 25%, Platelets 74,000/mm3. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Order blood cultures and wait for the results
Obtain blood cultures and give cefepime
Give acetaminophen and send him home
Give blood, platelet, and G-CSF transfusion
Obtain blood cultures and give vancomycin
A 26-year-old man is brought to the emergency room after being extricated from the driver’s seat of a car involved in a head-on collision. He has a sternal fracture and is complaining of chest pain. He is hemodynamically stable and his electrocardiogram (ECG) is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate management strategy for this patient?
Discharge to home with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents for the sternal fracture
Immediate operative plating of the sternal fracture
Emergent cardiac catheterization
Admit to the regular ward with serial ECGs for 24 hours
Admit to telemetry for 24-hour monitoring
A 26-year-old man presents to the physician's office with a two-day history of multiple symptoms, including rash on his trunk, headache, fatigue, malaise, myalgias, and high-grade fever. The rash is not associated with pain, itching, or burning. It has expanded over the last two days. He went on a camping trip in Vermont two weeks ago, and recalls a tick bite at that time. There is a single lesion on his trunk, which is erythematous with central clearing. The rest of the examination is unremarkable. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Give him intravenous ceftriaxone
Give him oral doxycycline
Give him oral amoxicillin
Perform western blot for confirmation of Lyme disease
Perform ELISA for confirmation of Lyme disease
A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 10-weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a routine prenatal appointment Her dating is based on a 6-week ultrasound. She has sickle-cell anemia. She has no past surgical history, takes prenatal vitamins, and has no known drug allergies. She tells the physician that she recently learned that the father of the baby has sickle-cell trait. On examination, her uterus is appropriate for a 10-week gestation, and fetal heart tones are heard. Her hematocrit is 37%. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Genetic counseling
IV hydration
Blood transfusion
Obstetric ultrasound
Hydroxyurea
A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 12 weeks' gestation comes to the physician because of pain and swelling in her right thigh. She first noted the onset of the pain 2 days ago, and since then it has grown worse. An ultrasound study performed on her lower-extremity venous system reveals evidence of a proximal thrombus in the right leg. She is started on low-molecular-weight heparin injections. Which of the following is an advantage of low molecular-weight heparin compared with unfractionated heparin?
Low-molecular-weight heparin is less likely to cross the placenta
Low-molecular-weight heparin is less likely to cause thrombocytopenia
Low-molecular-weight heparin is less likely to cause birth defects
Low-molecular-weight heparin is cheaper
Low-molecular-weight heparin has a shorter half-life
A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 35 weeks' gestation comes to the labor and delivery ward because of painful uterine contractions and a gush of fluid. Sterile speculum examination reveals a pool of clear fluid in the vagina that is nitrazine positive. When the fluid is examined under the microscope, a "ferning" pattern is seen. Cervical examination shows the patient to be 4 cm dilated, 100% effaced, and at 0 station. Fetal fingers can be felt along side the fetal head. External uterine monitoring shows contractions every 2 minutes. External fetal monitoring shows the fetal heart rate to be in the 130s and reactive. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Expectant management
Oxytocin augmentation
Forceps delivery
Vacuum delivery
Cesarean section
A 26-year-old primigravida at 20th week gestation presents to the emergency room with a sudden onset of tearing chest pain radiating to her back and left arm. The patient is pale and diaphoretic. Her PR: 116/min; BP: 192/ 104 mmHg in left arm, and 123/65 mmHg in right arm; RR: 36/min. Her cardiac examination reveals a diastolic murmur along the left sternal border. Her previous prenatal care is not known. She is a smoker with a 10 pack/year history and drinks alcohol. Her ECG reveals mild left axis deviation and ST segment depression in lead II, III, and AVF. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE)
CT scan of chest
Antihypertensive treatment
Obtain CK-MB and Troponin levels
Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE)
A 26-year-old white nonsmoking woman returns for a follow-up appointment with her primary care provider. At a routine health maintenance visit 8 months earlier, her blood pressure was 179/97 mmHg. Since then she has adhered to a low-fat diet and exercises regularly. On repeat measurement 1 month later, her blood pressure was still elevated, despite her compliance with the prescribed hydrochlorothiazide and lisinopril. She has no complaints and denies headaches, chest pain, or mental status changes. On physical examination she is a slender woman in no apparent distress. An abdominal bruit that lateralizes to the left is heard. Her blood pressure is 178/99 mmHg in her left arm and 181/95 mmHg in her right arm. A basic metabolic panel and complete blood count are within normal range. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in patient care?
Increase the dosage of her antihypertensive regimen
Order duplex imaging of the renal arteries and proceed to percutaneous transluminal angioplasty if renal artery stenosis is found
Order duplex imaging of the renal arteries and proceed to surgical revascularization if renal artery stenosis is found
Add a statin to the patient’s current drug regimen to decrease fatty arterial plaques
Admit patient to the hospital and start intravenous nitroprusside
A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a lump in her vagina. The lump is nontender but is uncomfortable when she walks. She states that for the last 6 years this lump has appeared about once a year. When it occurs she goes to the doctor who puts a catheter into it, which is taken out in a few weeks. She has no other medical problems. She is sexually active with two partners. Examination shows a cystic mass approximately 4 cm in diameter on the right side of the vagina near the hymeneal ring. The mass feels like a discrete cyst. The rest of the pelvic examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Oral antibiotics
Expectant management
Intravenous antibiotics
Incision and drainage
Bartholin's cyst marsupialization
A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician for a routine annual visit. She has no complaints. She has no significant previous medical problems. She has been sexually active since the age of 19 with the same partner. They married 4 years ago. She has never had any sexually transmitted diseases. She had her last Pap smear 4 years ago and was within normal limits. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or illicit drugs. Pelvic examination shows no abnormalities. A repeat Pap smear now shows atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Reflex HPV testing
Repeat Pap smear in 3 years
Repeat Pap smear in 12 months
Immediate colposcopy
Prescribe estrogen cream
A 26-year-old woman G0P0 presents to the office for infertility. The patient states that she and her husband have been trying to conceive for almost 2 years without success. She menstruates regularly. Her cycles occur every 28 days with 5 or 6 days of bleeding. She does have some pain during menstruation but not more than usual. She has no medical, surgical, or sexually transmitted disease. The patient and her husband have sexual relations during ovulation on a daily basis. She has had multiple blood tests by her primary care provider (PCP), all of which are normal. BP, 120/80 mm Hg; P, 82 beats/min; R, 16 breaths/min; T, 97.8°F; body mass index (BMI), 24. Review of systems (ROS): Negative. Physical examination: Gen: Awake, alert, oriented x3, no acute distress, CVS: Normal, Lungs: Normal, Abd: Soft, nontender, nondistended, +bowel sounds, Pelvic exam: Within normal limits. Which of the following is most useful?
Imaging study ofthe pelvis
Prolactin level
Glucose level e. Cortisol level
Growth hormone level
ACTH level
A 26-year-old woman presents to your office for her well-woman examination. She denies any medical problems or prior surgeries. She states that her cycles are monthly. She is sexually active and uses oral contraceptive pills for birth control. Her physical examination is normal. As part of preventive health maintenance, you recommend breast self-examination and instruct the patient how to do it. Which of the following is the best frequency and time to perform breast self-examinations?
Every 6 months, in the week prior to the start of the menses
Every 3 months, in the week prior to the start of the menses
Monthly, in the week after cessation of menses
Monthly, during the menses
Monthly, in the week prior to the start of the menses
A 26-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1 at 28 weeks' gestation, comes to the physician for a follow-up ultrasound after a previous ultrasound demonstrated a marginal placenta previa. The present ultrasound shows complete resolution of the marginal previa, but the fetus is noted to be in breech presentation. The patient has otherwise had an unremarkable prenatal course. She has no medical problems and has never had surgery. She takes prenatal vitamins and is allergic to sulfa drugs. Assuming that the fetus stays in breech presentation, when should an external cephalic version be attempted?
After 30 weeks
After 33 weeks
After 37 weeks
After 40 weeks
After 42 weeks
A 26-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, complains of loss of small amounts of urine immediately after a spontaneous vaginal delivery. She received epidural anesthesia during labor and delivery because of severe pain. She has no fever, dysuria, urgency, or hematuria. She has no other medical problems, takes no medication except prenatal vitamins, and has no known drug allergies. Her vital signs are normal. Examination shows a soft, non-tender abdomen. Pelvic examination is normal. The patient voids 30-40ml of urine each time; her postvoid residual volume is 400 ml. The patient's labs reveal: Urine: Specific gravity: 1.020, Blood: trace, glucose: negative, Leukocytes esterase: negative, Nitrite: negative, WBC: 1-2/hpf, RBC: 3-4hpf. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for her incontinence?
Do intermittent catheterization
Place permanent Foley catheter
Start oxybutynin
Urethropexy
Perform urodynamic testing
A 26-year-old, drug-addicted man develops congestive heart failure over a period of a few days. He is febrile, has a loud, diastolic murmur at the right second intercostal space, and has a blood pressure of 120/20 mmHg. A physical examination performed a few weeks ago, when he attempted to enroll in a detoxification program, was completely normal. His blood pressure at that time was 120/80 mm Hg, and no murmurs were noted. In addition to long-term antibiotic therapy, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Emergency aortic valve replacement
Elective aortic valve repair if he develops a systolic gradient of 50 mm Hg
Closure of the ventricular septal defect with a pericardial patch
Emergency mitral valve repair
Emergency pulmonic valve replacement
A 27-year-old African American woman presents with several months of prolonged menstrual bleeding and increased volume of menstrual flow. She also has a sensation of heaviness in her abdomen. She denies abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and constipation. She fatigues easily. Vital sign: Physical examination: Gen: Awake, alert, oriented x3, no acute distress, CVS: Regular rate and rhythm, no murmurs, rubs, or gallops, Lungs: Clear to auscultation bilaterally, Abd: Soft, nontender, nondistended, + bowel sounds, Pelvis: Cervix appears normal, no cervical motion tenderness, no adnexal masses felt. What is the term for what this patient is experiencing?
Amenorrhea
Metrorrhagia
Dysmenorrhea
Polymenorrhea
Menorrhagia
A 27-year-old Caucasian female with multiple sclerosis (MS) comes to the office for a follow-up visit. Six months ago, she experienced monocular vision impairment and clumsiness of the right hand, and both symptoms resolved completely. Three weeks ago, she experienced incoordination, weakness and spasticity in the right extremities. She was admitted in the hospital for treatment of an acute MS flare, and rapidly improved thereafter. Physical examination currently demonstrates slight weakness of the right leg with a hyperactive knee jerk. Which of the following medications may slow the long-term progression of this patient's disease?
High-dose corticosteroids
Interferon-beta
Cyclosporine
Methotrexate
Mitoxantrone
A 27-year-old female comes to the physician's office for evaluation of infertility. She has not been able to conceive for 12 months despite frequent intercourse. Her menses started at age 12 and have always been irregular. She uses over the counter acne medications. She is also obese and has been unsuccessful with weight loss. Physical examination shows an obese woman with sparse hair over the upper lip. There is no galactorrhea, thyromegaly or clitoromegaly. Which of the following is the most appropriate therapy for this patient's infertility?
Clomiphene citrate
Progesterone supplement
Dexamethasone
Dopamine agonist
In vitro fertilization
A 27-year-old female is found to have a positive hepatitis C antibody at the time of plasma donation. Physical examination is normal. Liver enzymes reveal ALT of 62 U/L (normal < 40), AST 65 U/L (normal < 40), bilirubin 1.2 mg/dL (normal), and alkaline phosphatase normal. Hepatitis C viral RNA is 100,000copies/mL. Hepatitis B surface antigen and HIV antibody are negative. Which of the following statements is true?
Patients with hepatitis C genotype 2 or 3 are more likely to have a favourable response to treatment with interferon and ribavirin
Serum ALT levels are a good predictor of prognosis
This patient should not receive vaccinations against other viral forms of hepatitis
Most patients with hepatitis C eventually resolve their infection without permanent sequelae
Liver biopsy is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of hepatitis C
A 27-year-old female presents to your office for a follow-up. The previous two visits revealed an elevated blood pressure in the range of 150- 155/90-95 mmHg. She has no present complaints. Her past medical history is insignificant. She smokes 1/2 pack of cigarettes per day and does not consume alcohol. Her current medications include a combination oral contraceptive for the last 2 years, and an occasional acetaminophen for tension headache relief. There is no family history of hypertension or heart attacks. This visit, her blood pressure is 155/95 and her heart rate is 80/min. The physical examination is unremarkable. The ECG is normal. Her total cholesterol level, measured 6 months ago, was 170 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Low-dose thiazide diuretic
No intervention at this point
Intravenous pyelography
Lifestyle modification
Discontinuation of the oral contraceptive
A 27-year-old G1P0 woman at 27 weeks’ gestation presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. The patient denies any abdominal pain or cramping, contractions, or vaginal bleeding. Examination reveals a gravid, non-tender abdomen and a closed, non-effaced cervix with no evidence of vaginal bleeding. Fetal heart monitoring shows a fetal heart rate of 145/min, with variable accelerations and no decelerations. The patient is Rh negative with no history of blood transfusion, while the father is of unknown Rh status and unavailable. The results of the Kleihauer-Betke test, in which maternal blood is exposed to acid, shows a combination of pale and stained RBCs. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Treatment with betamethasone
Emergent cesarean section
Amniocentesis to measure the amniotic fluid bilirubin level
Administer an appropriate dose of intramuscular Rh0(D) immune globulin
Induction of vaginal labor with prostaglandins and oxytocin
A 27-year-old G2P1 at 38 weeks gestation was admitted in active labor at 4 cm dilated; spontaneous rupture of membranes occurred prior to admission. She has had one prior uncomplicated vaginal delivery and denies any medical problems or past surgery. She reports an allergy to sulfa drugs. Currently, her vital signs are normal and the fetal heart rate tracing is reactive. Her prenatal record indicates that her Group B streptococcus (GBS) culture at 36 weeks was positive. What is the recommended antibiotic for prophylaxis during labor?
Cefazolin
Erythromycin
Penicillin
Vancomycin
Clindamycin
A 27-year-old G2P1 woman comes to the labor and delivery unit with nausea, vomiting, and right lower-quadrant pain. She is at 19 weeks gestation. The symptoms started 12 hours ago and have become progressively worse. She has no chills, dysuria, or urinary frequency and is uncertain if she has had a fever. Her temperature is 38 C (100.4 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 18/min. Abdominal examination shows a gravid uterus just below the umbilicus. The fetal heart rate is 144/min. There is moderate tenderness to palpation in the right lower quadrant with guarding. Laboratory results are as follows: Hemoglobin: 12.4 g/L, Leukocytes: 16,000/µL. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Flat plate of the abdomen
Ultrasound of the abdomen
Magnetic resonance imaging
Computed tomography of the abdomen
Diagnostic laparoscopy
A 27-year-old G3P2002, who is 34 weeks gestational age, calls the oncall obstetrician on a Saturday night at 10:00 PM complaining of decreased fetal movement. She says that yesterday her baby has moved only once per hour. For the past 6 hours she has felt no movement. She is healthy, has had regular prenatal care, and denies any complications so far during the pregnancy. Which of the following is the best advice for the on-call physician to give the patient?
Instruct the patient to go to labor and delivery for a contraction stress test
Reassure the patient that one fetal movement per hour is within normal limits and she does not need to worry
Recommend the patient be admitted to the hospital for delivery
Counsel the patient that the baby is probably sleeping and that she should continue to monitor fetal kicks. If she continues to experience less than five kicks per hour by morning, she should call you back for further instructions
Instruct the patient to go to labor and delivery for a nonstress test
A 27-year-old G1 woman is 20 weeks pregnant. She is currently in her third year of a family practice residency and would like to travel to Africa and Asia as part of an outreach mission with her program. She has received all of her childhood immunizations. She presents to the obstetric clinic inquiring about the safety of immunizations during pregnancy. Which of the following vaccines is contraindicated in pregnancy?
Varicella
Influenza
Tetanus
Typhoid
Hepatitis B

A 25-year-old female comes to the office for a follow-up visit. She was just diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus a few days ago, when she presented at the emergency department with ketoacidosis. After successful management of her diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), she was sent home on an insulin regimen with the following dosage: Before breakfast 10 units of NPH and 10 units of regular insulin, Before supper 10 units of NPH and 4 units of regular insulin. During this office visit, she shows the record of her fingerstick readings at home. For the last 2 days, her blood glucose levels were (see in pic). What is the most likely explanation for her 7:00 am blood glucose level?
Destruction of glucagon-secreting cells
Decrease Insulin-secretor
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, & glucagon release
Waning of insulin levels
Spikes of growth hormone release
{"name":"DES C_Management (3) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 24-year-old female presents to you for the evaluation of acne. Further questioning, reveals that she also has had irregular periods for a long time. She is single and not sexually active. On examination, her BMI is 31 Kg\/m2 and she has evidence of hirsutism. Further evaluation reveals increase in serum free testosterone and LH\/FSH ratio of 2.4. Glucose tolerance testing reveals two-hour blood glucose of 155 mg\/dl. Apart from prescribing oral contraceptive pills, which of the following is indicated in this patient?, A 24-year-old female veterinary assistant is referred to a psychiatrist for the presumptive diagnosis of dysthymia. She reports having a three-year history of low energy levels and gradual worsening in her ability to focus on her work. She feels \"sad, hopeless,\" and experiences little pleasure. She denies any suicidal thoughts. She has never been on any psychotropic medications before, and denies any family history of psychiatric illness. She has gastroesophageal reflux disease, for which she takes omeprazole. She has no known allergies, and does not drink alcohol or smoke cigarettes. The psychiatrist decides to treat her dysthymia with bupropion. Which of the following is a contraindication to the use of bupropion?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/20-800412/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Estrategia GC
13620
PROYECTO CABEZAS DE ALGODON
940
Kultura v starem veku
1166
Tik12
7493
Dance Documentation
15833226
Can You Guess How Old SpongeBob the Character Is?
201037796
Capstone Seminar
15827074
Take the Ultimate Werewolf - Discover Your Inner Beast
201029441
American States Trivia: Can You Name All 50?
201031973
What Is a Practical Person? Take the to Find Out
201028496
Free e.3 Trace an Argument
201023491
Free APES Unit 6 Progress Check MCQ
201025579