Piston 2 - Week 2B
What does the radial engine nose section do?
Contains the compressor
It is a mount for the cylinders
Drives the accessories
Houses the prop shaft, bearings and gear reduction
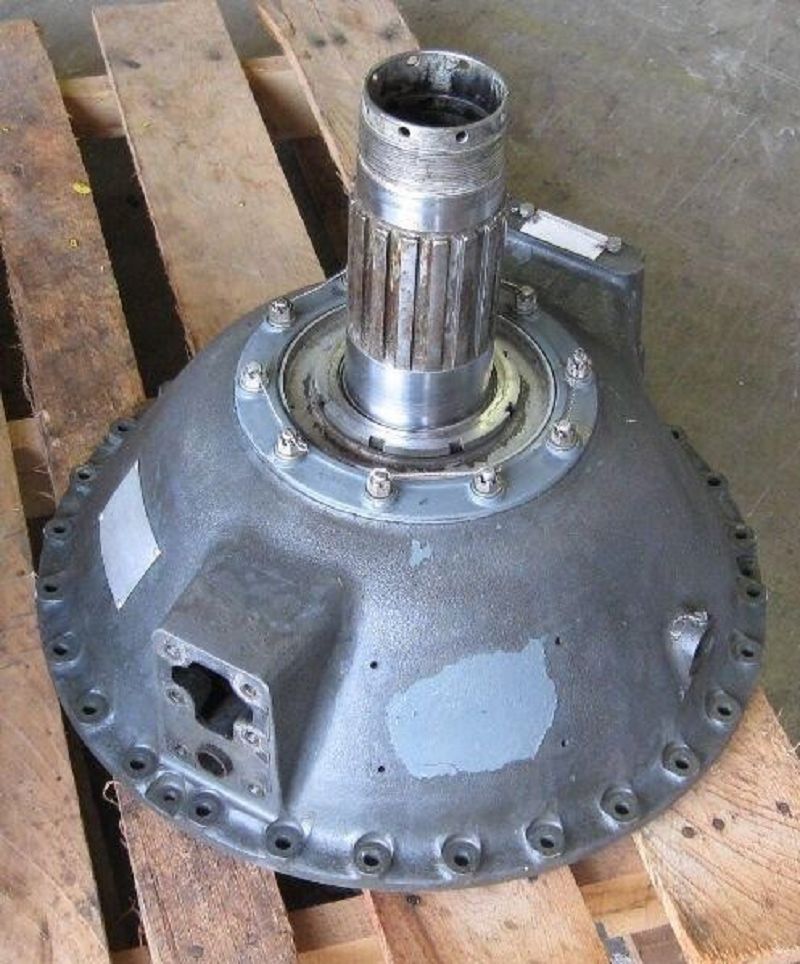

Which part of a radial engine is shown here? #4
Nose section
Accessory section
Power section
Supercharger section
What does the radial supercharger section do?
It is a mount for the cylinders
Houses the prop shaft, bearings and gear reduction
Contains the compressor
Drives the accessories
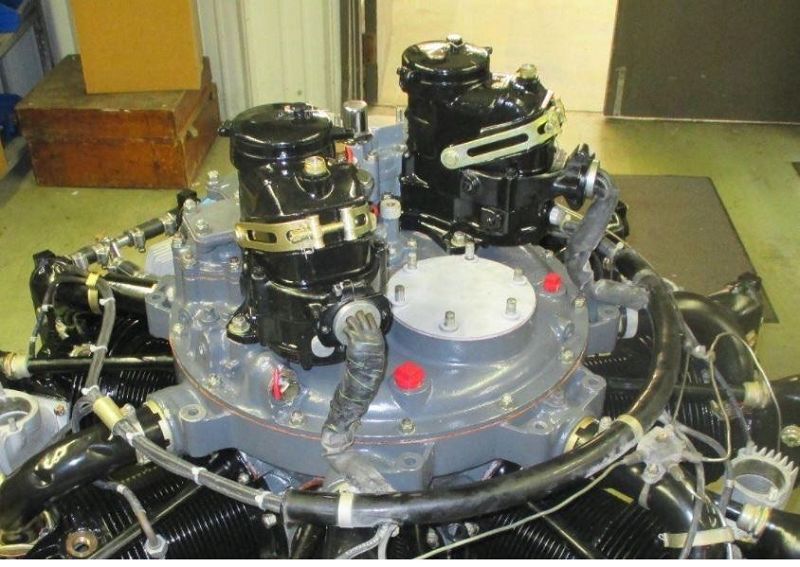

Which part of a radial engine is shown here? #3
Accessory section
Supercharger section
Nose section
Power section
What is the radial engine accessoryr section made from?
Magnesium
Titanium
Aluminum
Steel
What is the radial engine nose section made from?
Steel
Magnesium
Titanium
Aluminum
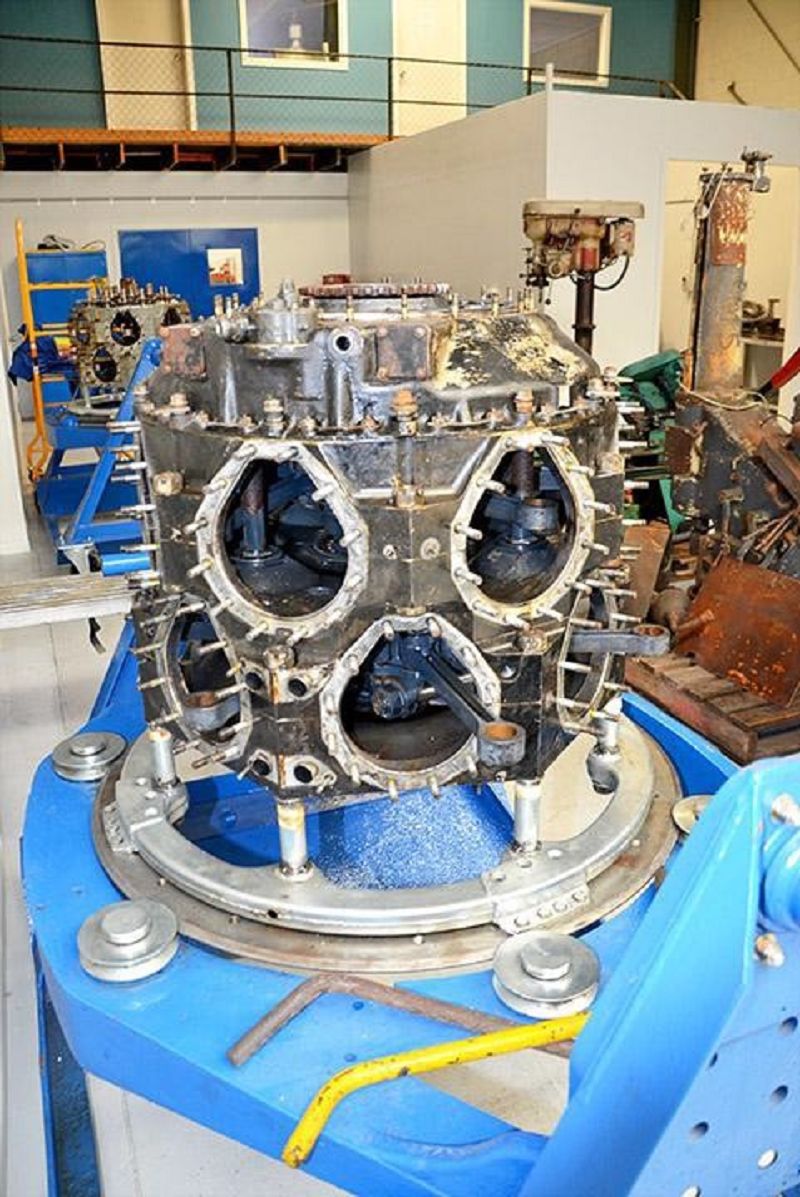

Which part of a radial engine is shown here? #1
Supercharger section
Power section
Nose section
Accessorry section
What does the radial accessory section do?
Contains the compressor
It is a mount for the cylinders
Drives the magnetos, generators, vacuum pumps, hydraulic pumps
Houses the prop shaft, bearings and gear reduction
What does the radial engine power section do?
Drives the accessories
It is a mount for the cylinders
Contains the compressor
Houses the prop shaft, bearings and gear reduction
What is the radial engine power section made from?
Steel
Aluminum
Magnesium
Titanium
What is the radial engine supercharger section made from?
Steel
Titanium
Magnesium
Aluminum
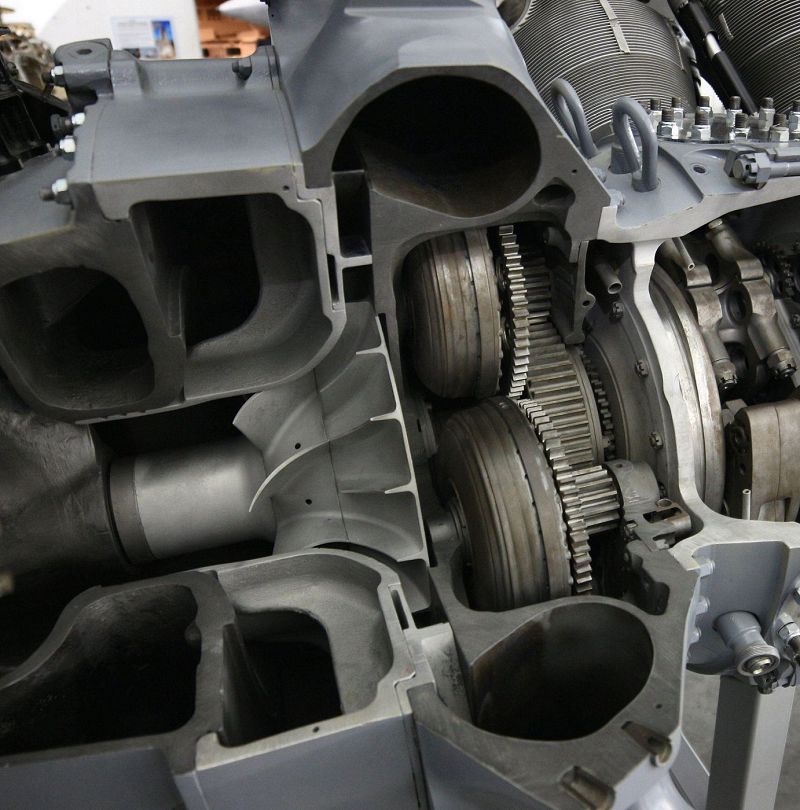

Which part of a radial engine is shown here? #2
Power section
Accessory section
Supercharger section
Nose section
What is a cylinder barrel made from?
Chrome-aluminum or nickel-molybdenum steel
Nickel-steel and aluminum
Chrome-molybdenum or nickel-molybdenum steel
Nickel-titanium and chromed steel
Which of the following describes a nitrided cylinder?
The walls are tapered inwards towards the top
The walls are hardened to reduce wear
The walls are plated to reduce wear and prevent corrosion
The walls are not treated to prevent wear or corrosion
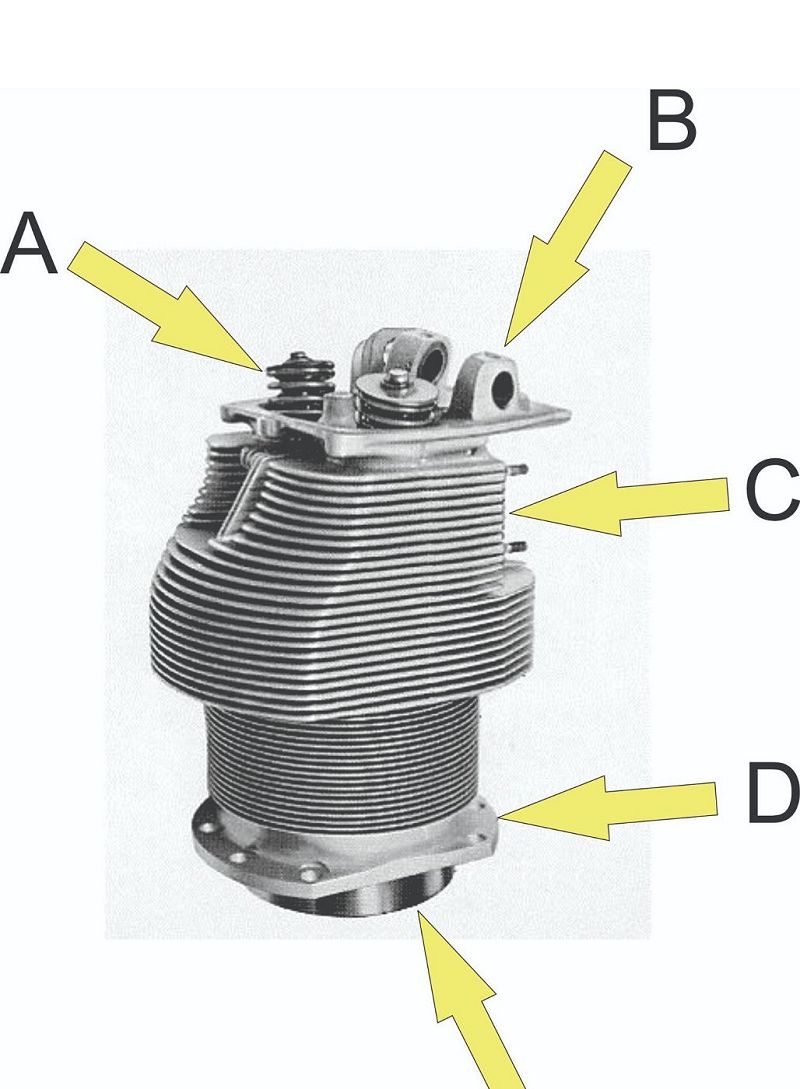
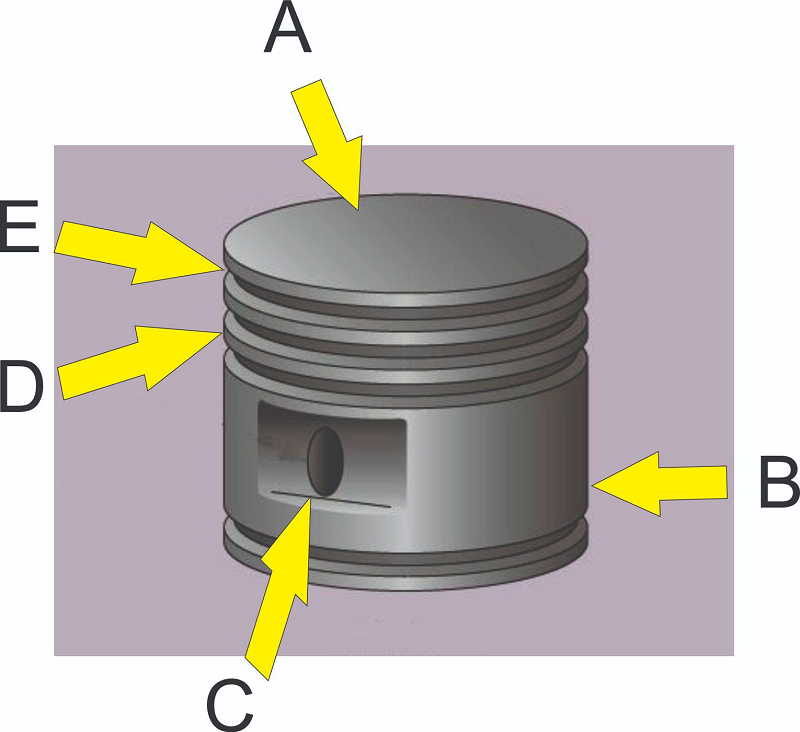
What is located at C?
Rocker shaft boss
Valve spring assembly
Port
Flange
Skirt
What is the problem with chromed cylinders?
The piston fit is too loose at TDC
The piston fit is too tight at TDC
The surface is too smooth
Too smooth to hold oil unless etching or channeling
What are cylinder heads used for?
They provide the combustion chamber and mounting areas for spark plugs and valve parts
They provide a places for the cylinders, camshaft and valve lifters to mount
The provide a place for the connecting rods and push rods to mount
They provide a mounting place for the accessories and the gears to drive them
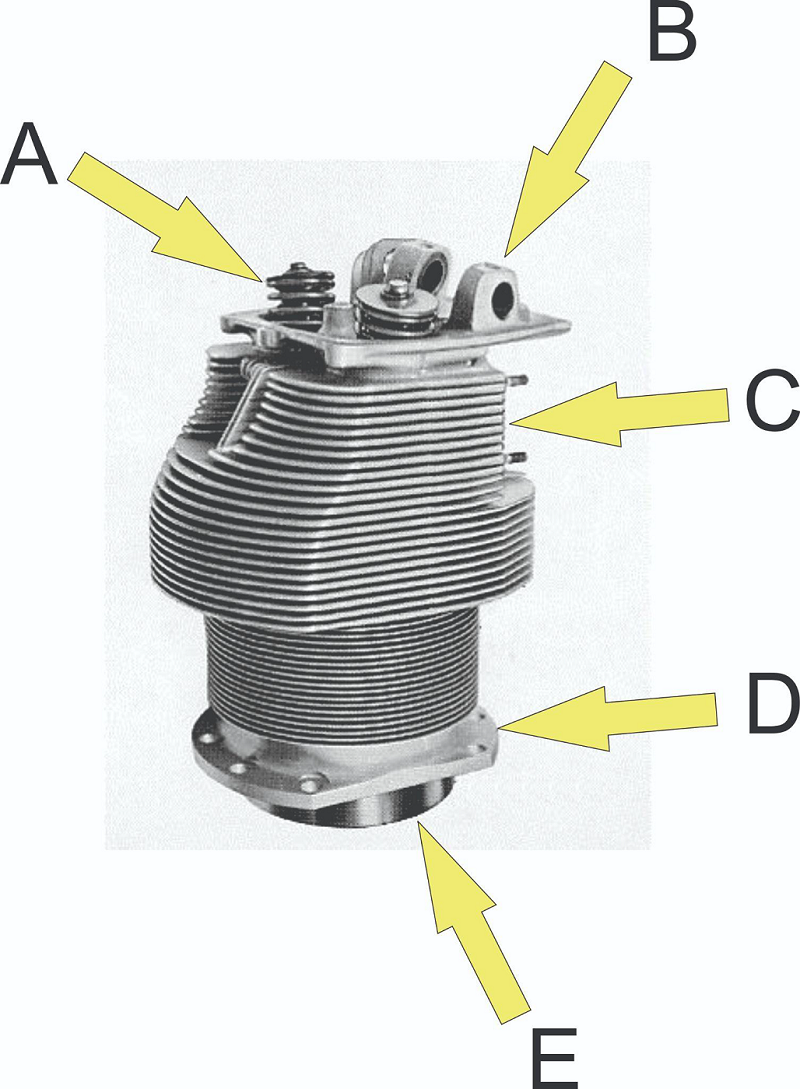
What is located at E?
Flange
Rocker shaft boss
Port
Skirt
Valve spring assembly
What is the purpose of honing?
To create a surface that is rough enough to hold oil and smooth enough to reduce friction
To create a surface that is more resistant to corrosion
To create a surface that I s smooth enough to hold oil and rough enough to reduce friction
To create a surface that is more resistant to wear
What is done to the cylinder walls to hold oil?
Honing
Shot peening
Sand blasting
Nitriding
Which of the following describes a plain steel cylinder?
The walls are plated to reduce wear and prevent corrosion
The walls are tapered inwards towards the top
The walls are not treated to prevent wear or corrosion
The walls are hardened to reduce wear
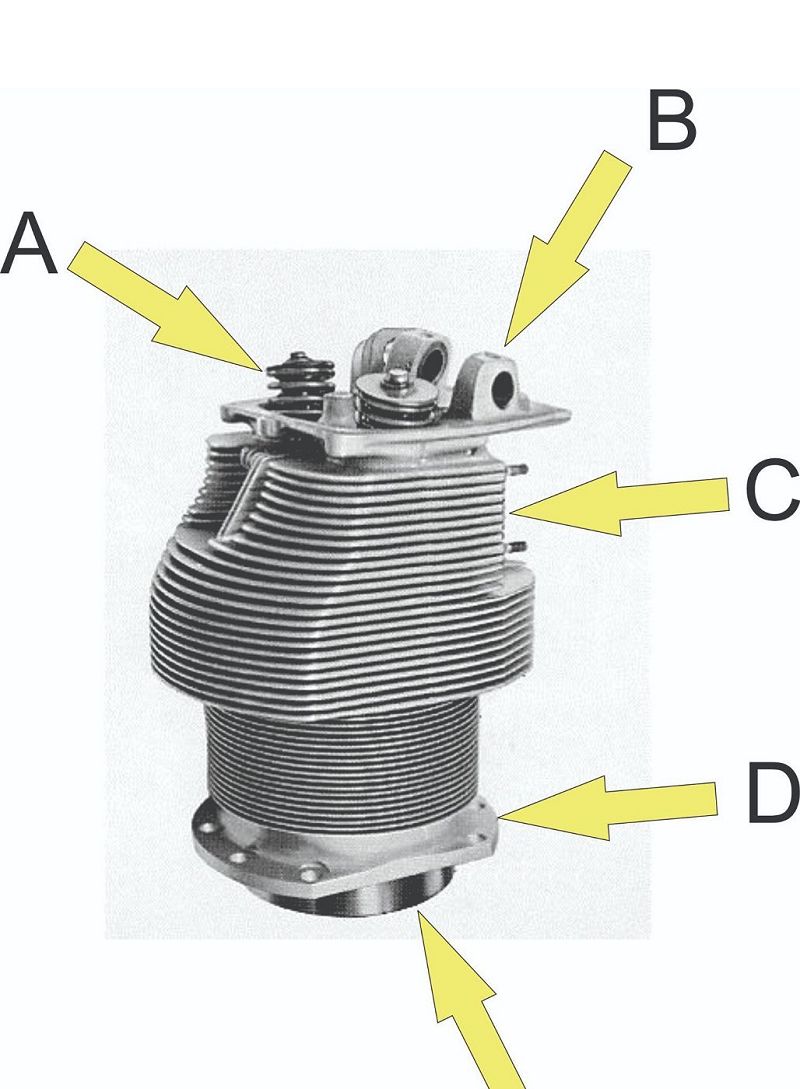
What is located at D?
Skirt
Port
Rocker shaft boss
Flange
Valve spring assembly
Which of the following describes a chromed cylinder?
The walls are hardened to reduce wear
The walls are not treated to prevent wear or corrosion
The walls are plated to reduce wear and prevent corrosion
The walls are tapered inwards towards the top
Which of the following describes a choked cylinder?
The walls are tapered inwards towards the top
The walls are plated to reduce wear and prevent corrosion
The walls are not treated to prevent wear or corrosion
The walls are hardened to reduce wear
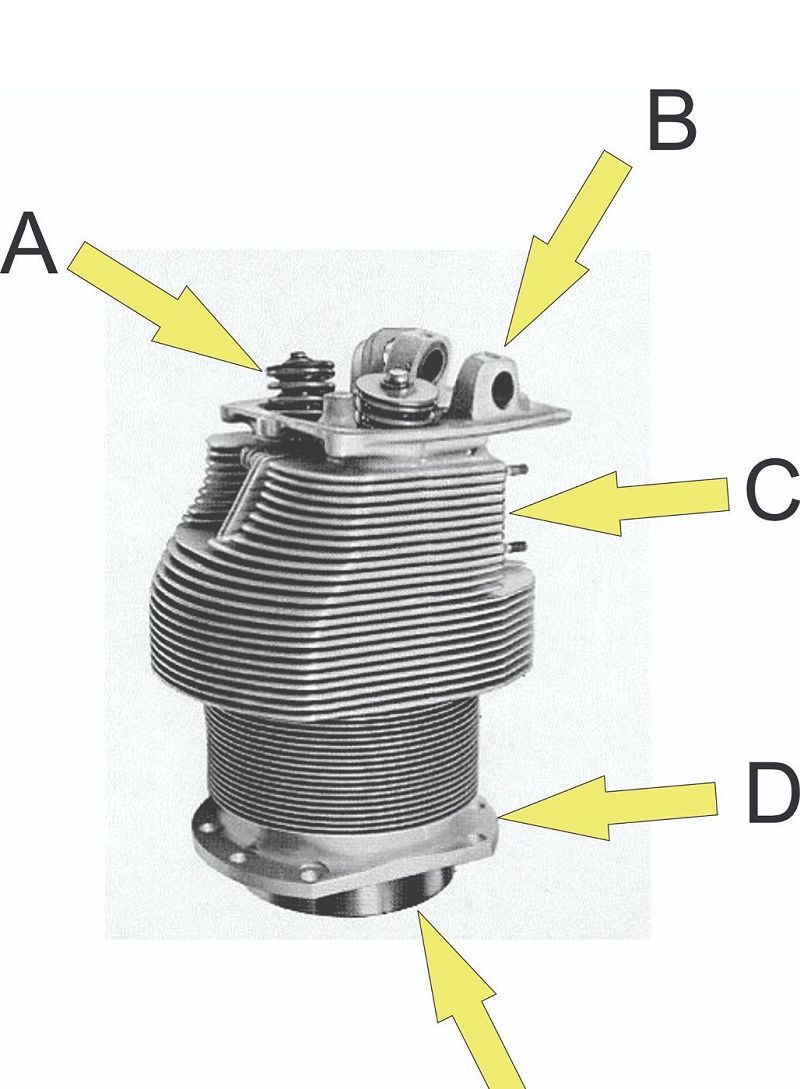
What is located at B?
Valve spring assembly
Port
Skirt
Flange
Rocker shaft boss
How is a cylinder cooled?
By conduction to the fins and by convection to the air
By radiation to the fins and by conduction to the air
By conduction to the fins and by radiation to the air
By convection to the fins and by conduction to the air
What is a cylinder head made from?
Chrome-molybdenum or nickel-molybdenum steel
Nickel-titanium and chromed steel
Aluminum
Chrome-aluminum or nickel-molybdenum steel
Why are some cylinder walls choked?
So that when the cylinder is hot the barrel will be cylindrical
To reduce friction in the cylinder
So that oil will "stick to the cylinder walls"
So that when the cylinder is hot the barrel will be tapered
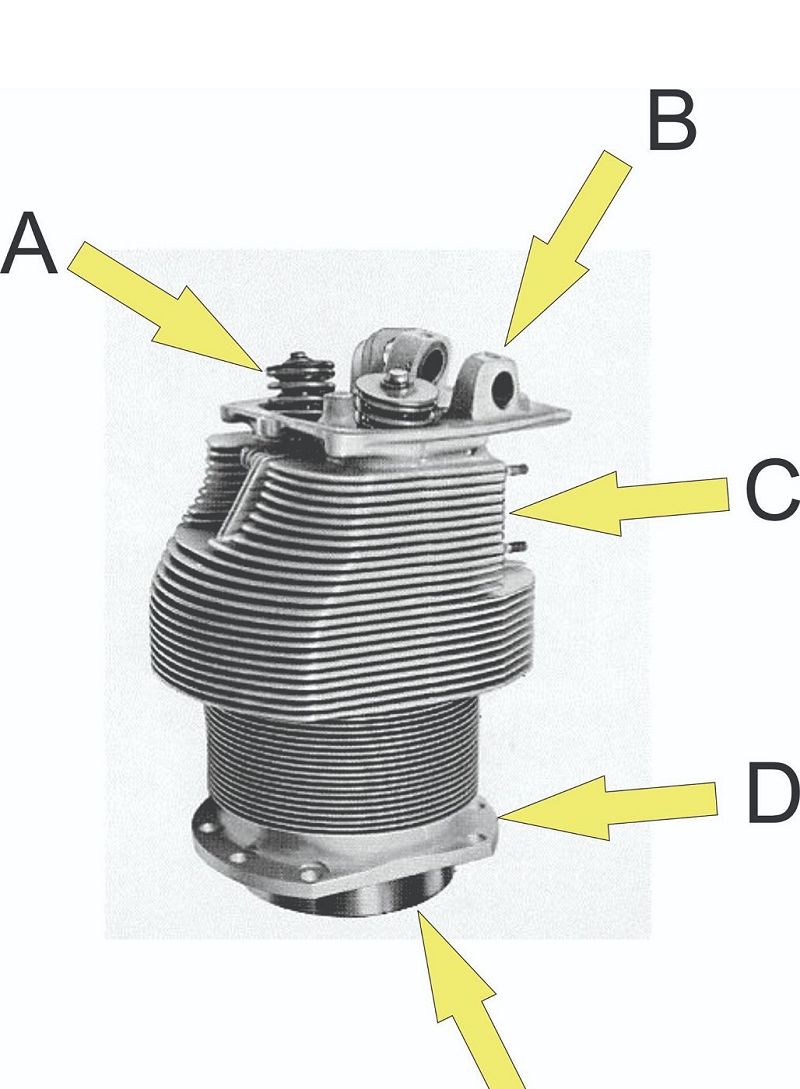
What is located at A?
Valve spring assembly
Port
Flange
Rocker shaft boss
Skirt
What does a tappet do?
It converts the rotating pulling motion of the camshaft into a pulling linear motion
It converts the rotating motion of the camshaft into a pushing linear motion
It converts the rotating motion of the camshaft into a pulling linear motion
It converts the rotating pushing motion of the camshaft into a pulling linear motion
What is used to hold the valve in the cylinder head?
Nut & lock wire
Split key
Nut & lock washer
Bolt & lock wire
What is the purpose of using two valve springs for each valve
To speed valve closing
To prevent valve float
To speed valve opening
To reduce valve operating forces
What part of the valve forms the seal with the cylinder head?
Stem
Tip
Face
Neck
What is used to hold a valve in place?
Stem & valve guide
Retainer & split key
Face & seat
Nuts & bolts
What is used to open an intake or exhaust valve?
Crank, connecting rod, pin, piston
Cam, lifter, push rod & rocker arm
Cam, pusher, push rod and valve spring
The Force
What happens to the valve spring when a valve starts to "Float"
It loses its ability to open the valve
It loses its ability to hold the valve closed
It loses its ability to close the valve
It loses its ability to hold the valve open
Which components are used to tightly seal the valves?
Lifters, push rods, rockers
Valve guides, seats, springs, push rods
Valve guides, seats, springs, spring retainers
Lifters, springs, spring retainers, seats
What is the purpose of the valve guide?
To control fuel flow into the manifold
To keep the face aligned with the seat
To hold the valve springs in the head
To closely fit and seal with the face
What is the purpose of using two valve springs for each valve
To reduce valve operating forces
To reduce the probability of engine failure due to breakage
To reduce the probability of engine failure due to thermal expansion
To speed valve closing
What is a connecting rod made of?
Titanium
Brass
Aluminum
Steel
What kind of bearings are used at the bottom of a connecting rod?
Roller bearings
A plain bushing
A 1 piece plain bearing
A 2 piece plain bearing
What kind of bearings are used at the top of a connecting rod?
Roller bearings
A 1 piece plain bearing
A plain bushing
A 2 piece plain bearing
How many main parts to the connecting rod in a typical horizontally opposed engine?
3 for lowest friction
2 for ease of installation
4 for ease of manufacturing
1 for simplicity
How are the connecting rod bolts secured?
With lock wire
With nylon lock nuts
With cotter pins
With lock washers
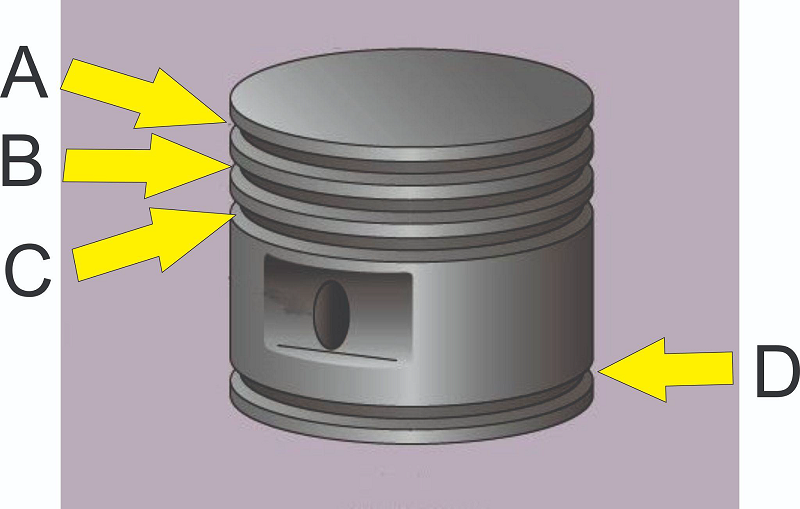
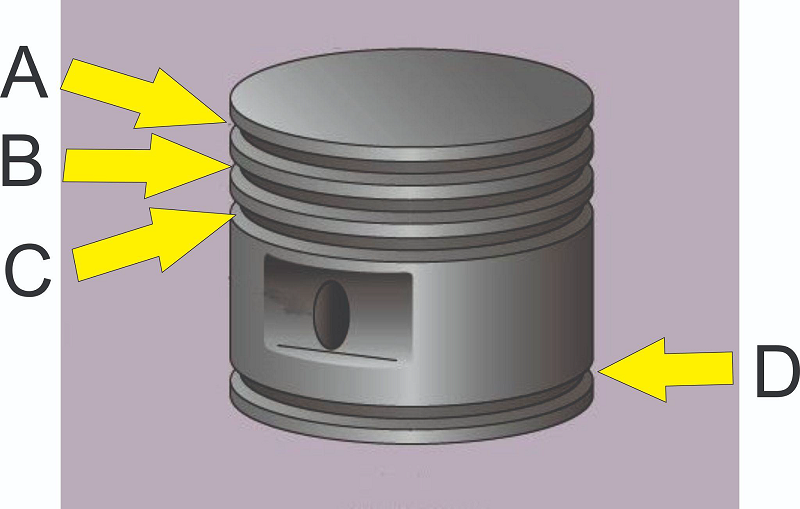
What kind of ring is installed at C?
Locking ring
Oil scraper ring
Compression ring
Oil control ring
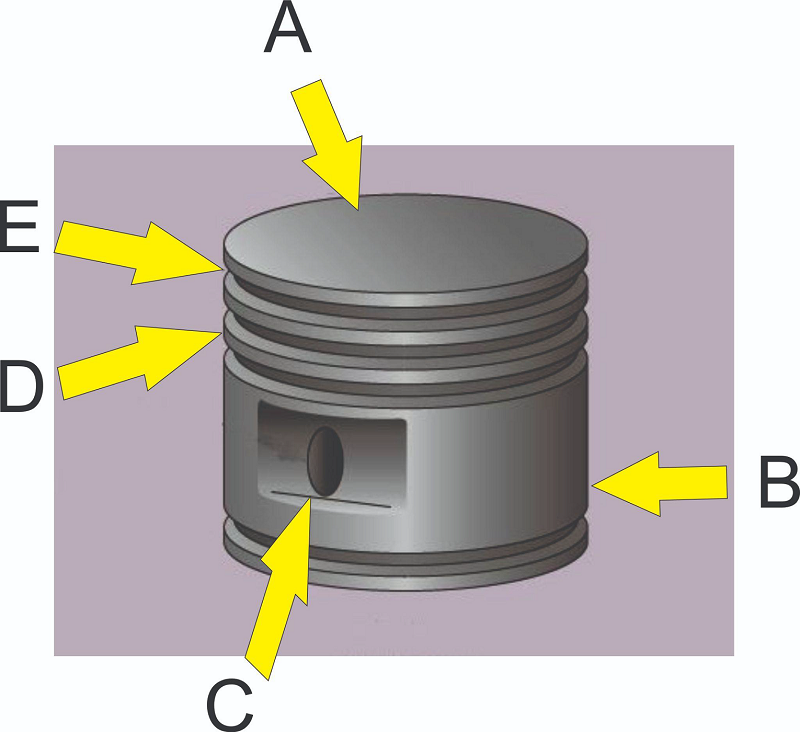
What part of the piston is pointed to by B?
Groove
Lands
Piston pin boss
Head
Skirt
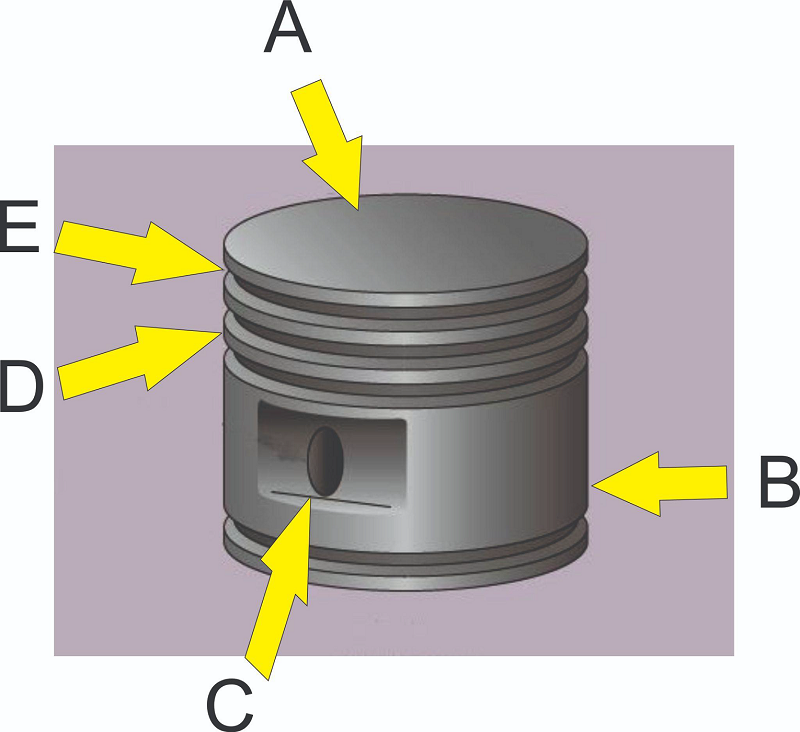
What part of the piston is pointed to by D?
Piston pin boss
Groove
Head
Lands
Skirt
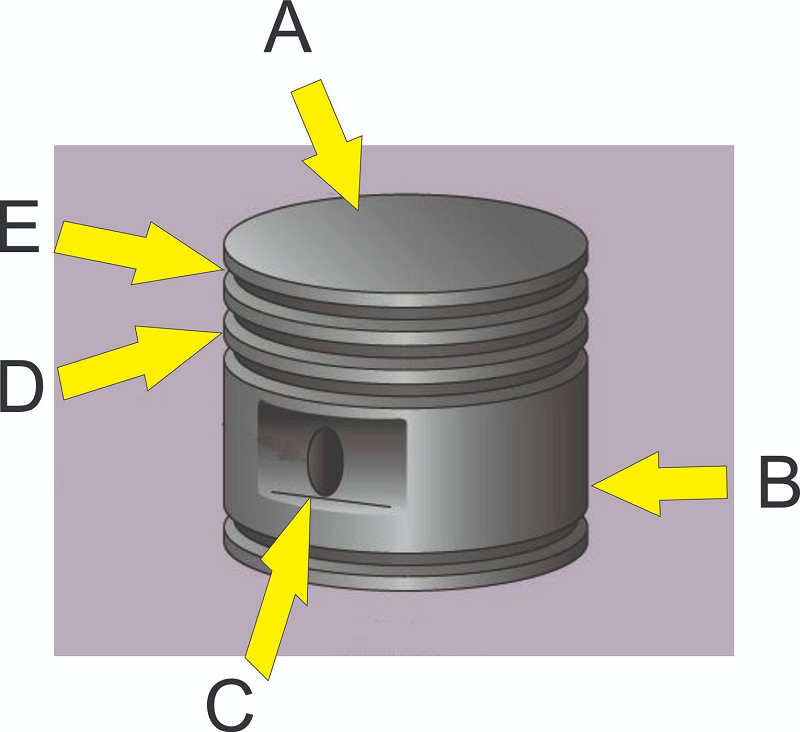
What part of the piston is pointed to by E?
Groove
Head
Lands
Skirt
Piston pin boss
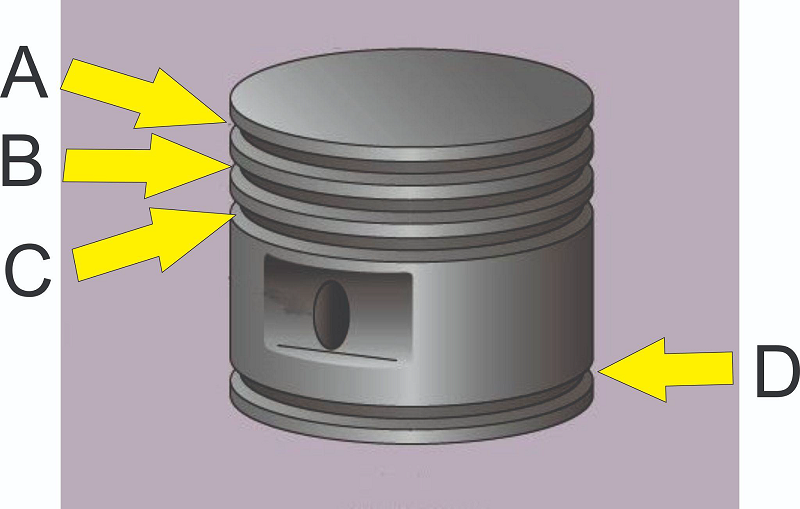
What kind of ring is installed at B?
Locking ring
Compression ring
Oil scraper ring
Oil control ring
What is a piston made of?
Nickel steel
Titanium
Aluminum
Steel
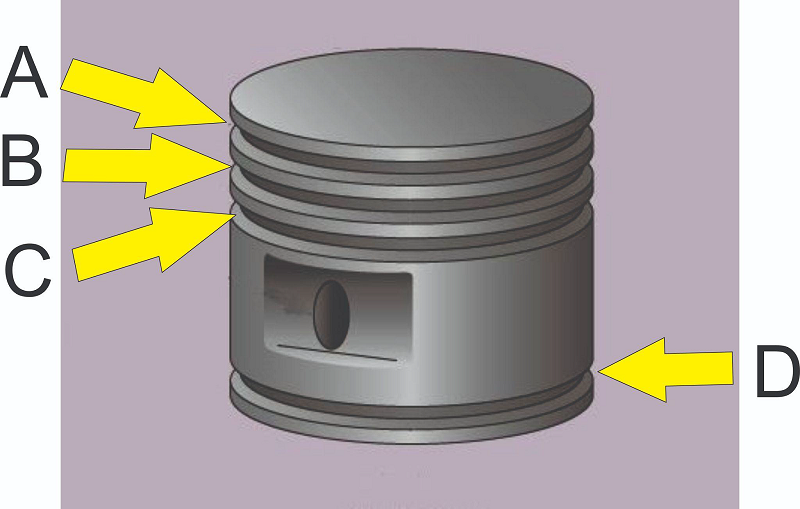
What kind of ring is installed at A?
Compression ring
Locking ring
Oil scraper ring
Oil control ring
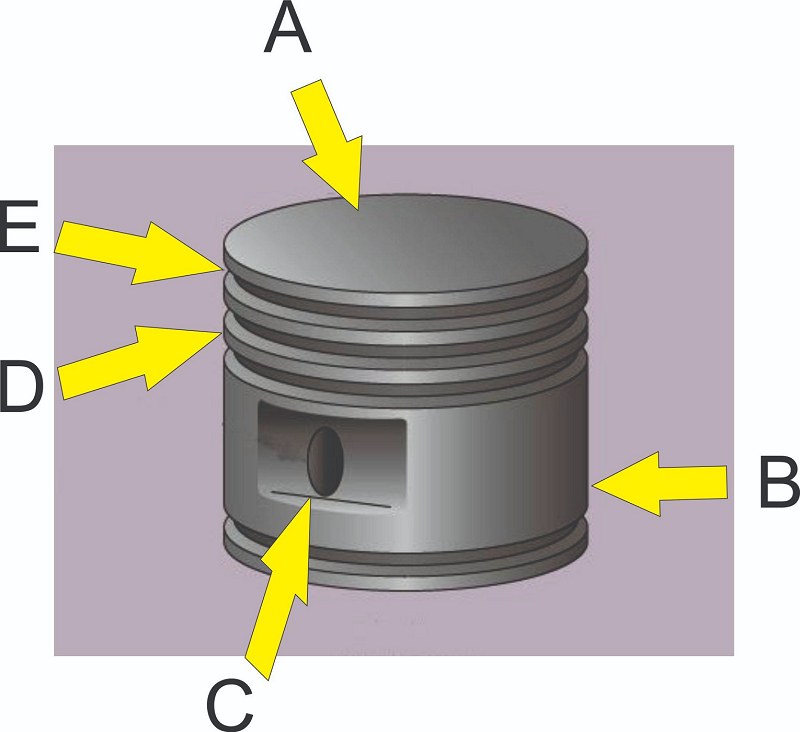
What part of the piston is pointed to by A?
Skirt
Lands
Piston pin boss
Groove
Head
How is the piston cooled?
It is not cooled
By fuel heated by the cooling fins
By oil heated by the cooling fins
By air heated by the cooling fins
What part of the piston is pointed to by C?
Groove
Skirt
Head
Lands
Piston pin boss
What kind of ring is installed at D?
Oil control ring
Locking ring
Compression ring
Oil scraper ring
What are wrist pins made of?
Chromed steel
Hardened steel
Titanium
Annealed aluminum
What are gudgeon pins (piston pins) made of?
Titanium
Hardened steel
Chromed steel
Annealed aluminum
What will typically prevent removal of the piston pin from the piston?
Carbon build up
Self locking nuts
Corrosion
Bolts and lockwire
What are piston pins made of?
Hardened steel
Annealed aluminum
Titanium
Chromed steel
What is used in typical Lycoming or Continental engines to hold the piston pin in place?
Bolts secured with cotter pins
Bolts secured with lock wire
Nothing, they are free floating
Cir-clips in the piston
What is used to prevent piston pins from scoring the cylinder walls?
Locking collars
End plugs
Wrist pins
Cotter pins
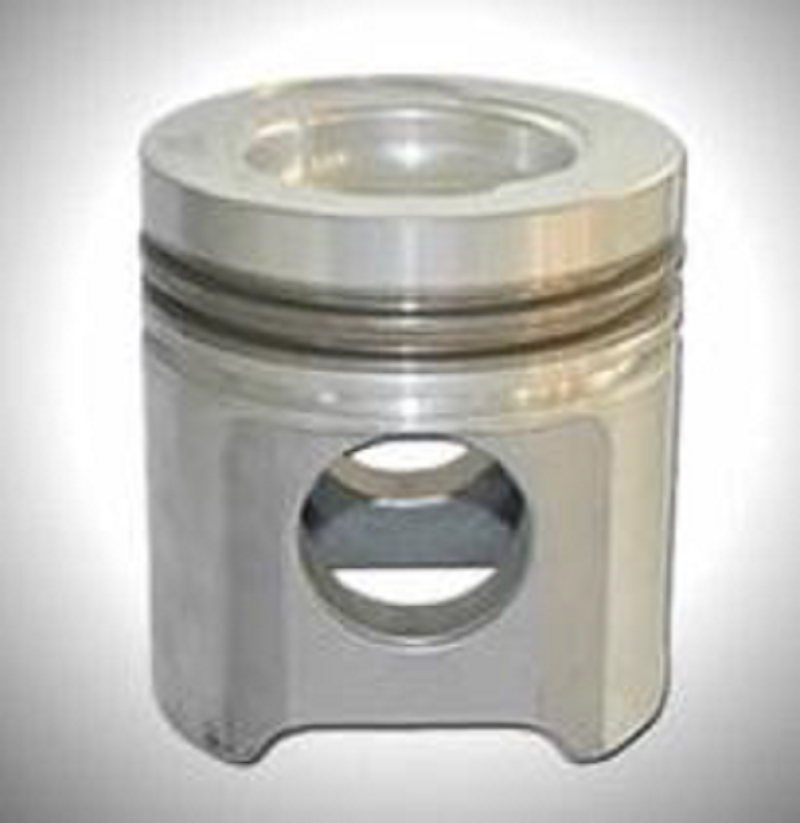

What kind of piston head is this? #1
Flat
Truncated cone
Recessed
Concave
Domed
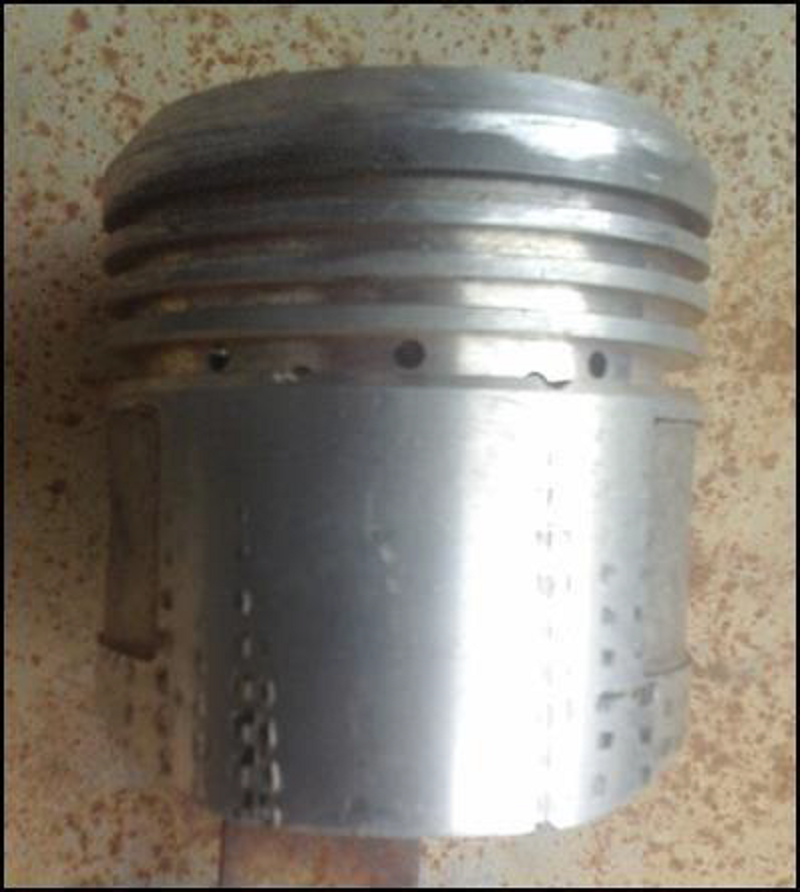

What kind of piston head is this? #5
Flat
Truncated cone
Domed
Recessed
Concave
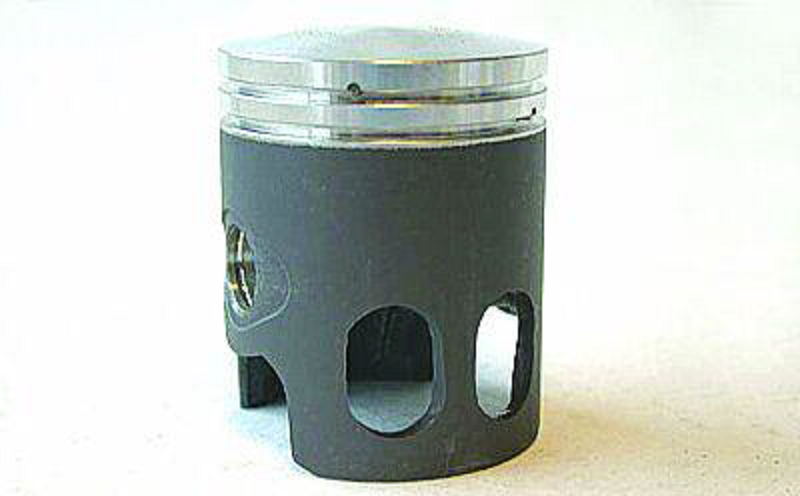

What kind of piston head is this? #2
Truncated cone
Domed
Recessed
Flat
Concave
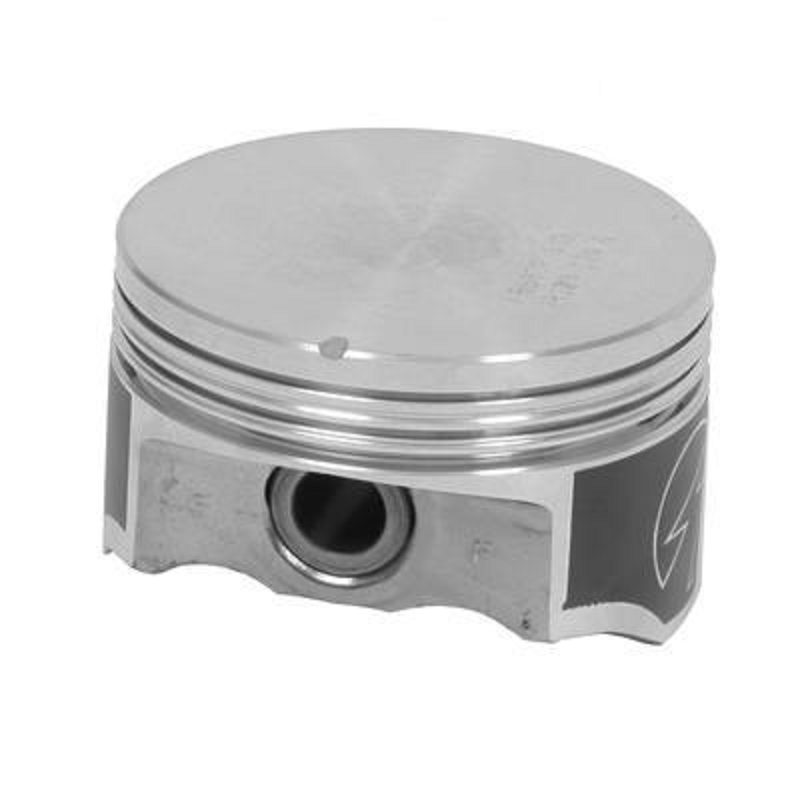

What kind of piston head is this? #3
Recessed
Truncated cone
Concave
Flat
Domed
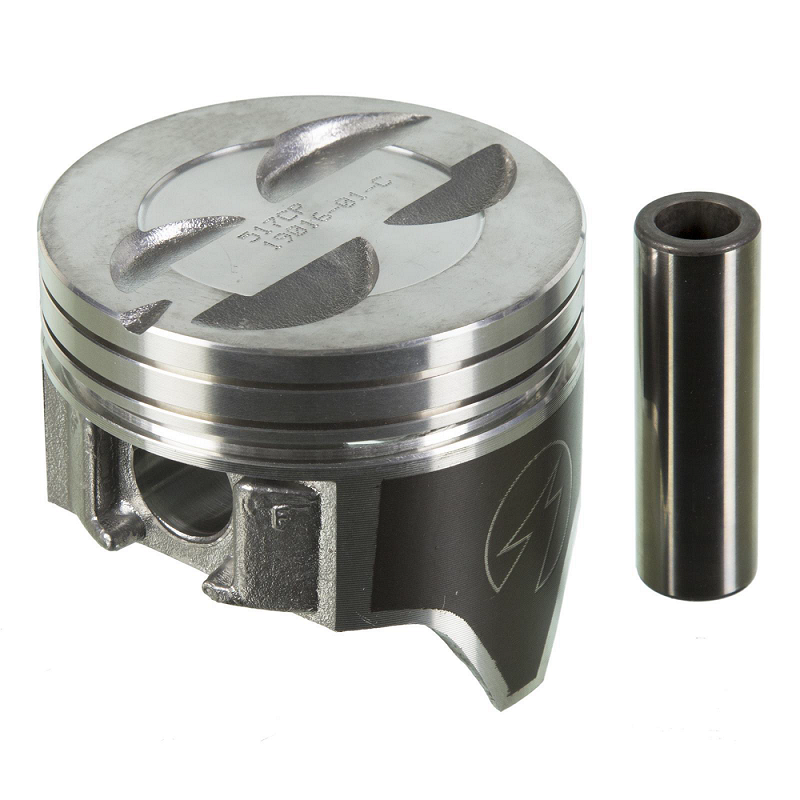

What kind of piston head is this? #4
Flat
Truncated cone
Domed
Concave
Recessed
On a piston with 4 rings, what is the purpose of the second ring from the head of the piston?
To maintain the thickness of oil film on the piston pin boss
To prevent leakage between the piston and the cylinder
To maintain the thickness of oil film on the cylinder wall
To push excess oil back to the crankcase
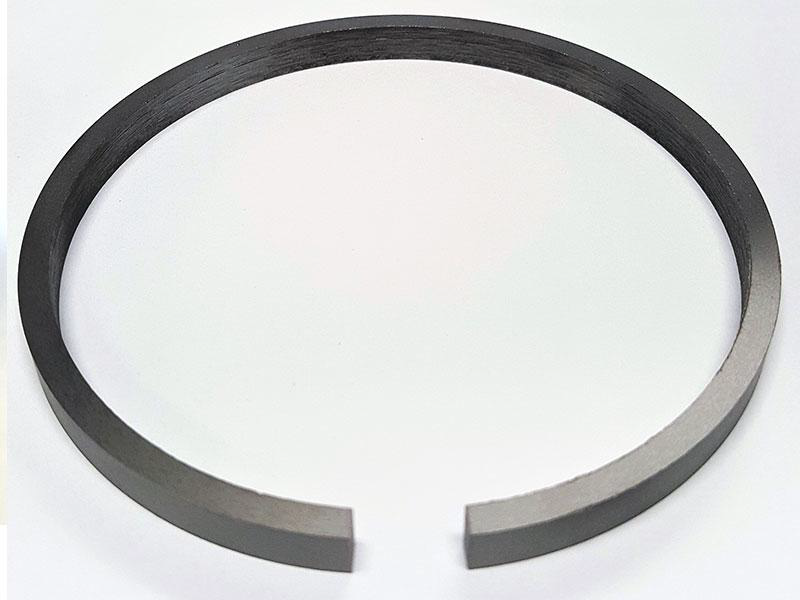

What kind of piston ring gap is this? #2
Hook
Angle
Butt
Step
What is the purpose of the bottom ring on the piston?
To prevent leakage between the piston and the cylinder
To maintain the thickness of oil film on the piston pin boss
To maintain the thickness of oil film on the cylinder wall
To push excess oil back to the crankcase
Why do piston rings have gaps in them?
To allow the correct amount of oil to pass by the ring
To allow the combustion gasses to heat the crank case
To prevent the compression ratio from getting too high
To allow for unevenness in the cylinder wall
Why do piston rings have gaps in them?
To allow the combustion gasses to heat the crank case
To prevent the compression ratio from getting too high
To allow for expansion & contraction due to temperature changes
To allow the correct amount of oil to pass by the ring
On a piston with 4 rings, what is the purpose of the third ring from the top on the piston?
To maintain the thickness of oil film on the piston pin boss
To maintain the thickness of oil film on the cylinder wall
To prevent leakage between the piston and the cylinder
To push excess oil back to the crankcase
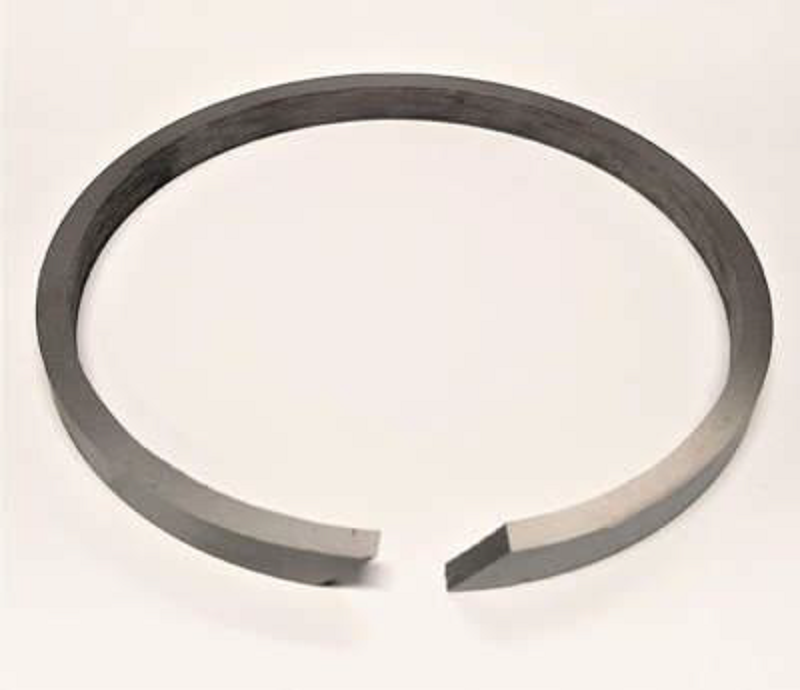

What kind of piston ring gap is this? #3
Hook
Angle
Step
Butt
When installing piston rings what should you always do?
Stagger the end gaps to prevent compression loss
Line up the end gaps to prevent oil loss
Line up the end gaps to prevent compression loss
Stagger the end gaps to prevent oil loss
On a piston with 4 rings, what is the purpose of the top ring on the piston?
To maintain the thickness of oil film on the piston pin boss
To push excess oil back to the crankcase
To maintain the thickness of oil film on the cylinder wall
To prevent leakage between the piston and the cylinder
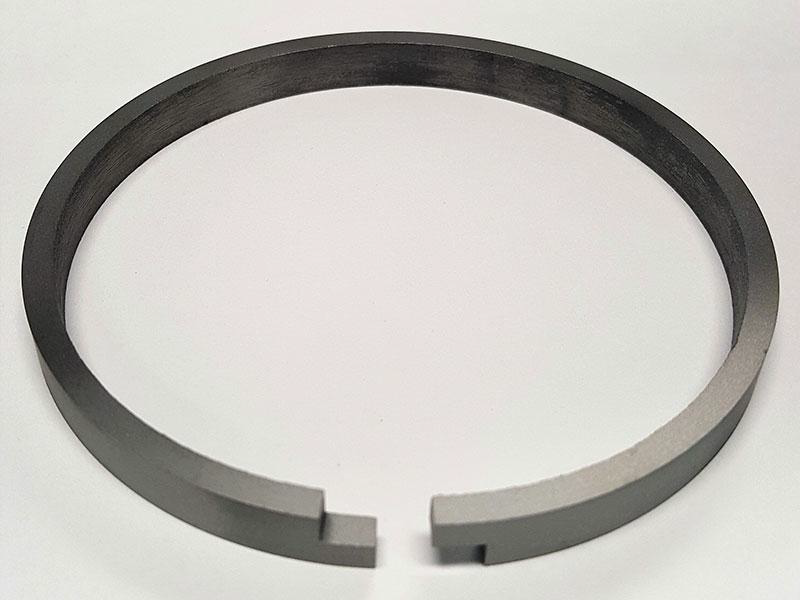

What kind of piston ring gap is this? #1
Step
Angle
Butt
Hook
{"name":"Piston 2 - Week 2B", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"What does the radial engine nose section do?, Which part of a radial engine is shown here? #4, What does the radial supercharger section do?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/95-4636300/radial-nose.jpg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Lab quiz 3
351820
Power Generator
1160
840
#199 UST Trivandrum Toastmasters Club Session
3223
Undergraduate Research
15824416
Free Geometry Angle Relationships
201029689
Ultimate Xbox: Prove Your Xbox Knowledge Now!
201027546
Free Marketing Personalization Knowledge Test
201021735
Free Test & Online Exam Review
201025985
What Do I Want to Do Today: Find Your Ideal Activity
201024010
Goody Two Shoes: Are You the Ultimate Rule-Follower?
201029689
Hide Your Feelings: Can You Keep Emotions Hidden?
201025059