Placement test AS Level Physics V01
1) The magnitude of gravitational acceleration at the surface of Earth is approximately 9.81 m/s2. What is the approximate magnitude of the gravitational acceleration in kilometres per hour squared, km/h2?
0.756×10-3
0.589
2.72
35.3
1.27×105
2) An elevator with a total mass of 1,200 kg is hung by a cable which can withstand only 9 kN of tension. Given g = 9.8 m/s2, in order not to break the cable, the elevator must:
travel upwards with an acceleration of at least 2.3 m/s2.
travel upwards with an acceleration at most 2.3 m/s2.
travel downwards with an acceleration of at least 2.3 m/s2.
travel downwards with an acceleration at most 2.3 m/s2.
travel either upwards or downwards with a constant speed.
3) A car starts moving from rest. The acceleration vs time is shown in the graph.
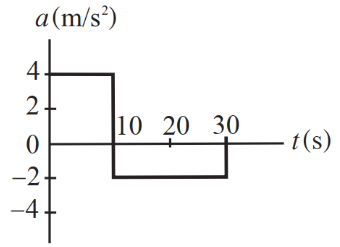
what is the magnitude of the total displacement of the car during this 30-second interval?
0 m
100 m
200 m
400 m
600 m
4) A car of mass 1,000 kg is travelling along a straight line. The driver applies the brake at 5 seconds.
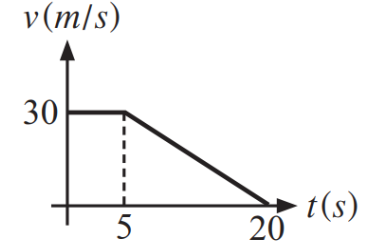
The magnitude of braking force is almost nearly:
2 kN
10 kN
15 kN
20 kN
50 kN
5) A horizontal weightless spring scale is attached to two identical masses of 10 kg at both ends. What is the spring scale reading in kg?
0 kg
5 kg
10 kg
20 kg
6) A rocket moves upwards during its launch. Which of the following statements is true?
Exhaust gas pushes Earth downwards, creating an equal but upward force.
Exhaust gas pushes air molecules downwards, creating an equal but opposite upward force.
The weight of the rocket is the action force, and the opposite force that pushes the rocket back is the reaction force.
The force from the exhaust gas must be small so that it does not add much downward force to gravity. If it does, the rocket will not be acted by enough upward force.
All of these are incorrect.
7) A box of mass 4.0 kg is dragged on a rough surface for a straight distance of 5.0 m. Then, it is dragged straight back to the starting point. Given the kinetic friction coefficient is 0.5, what is the net work from the friction? (g = 10 m/s2)
–200 J
–100 J
0 J
100 J
200 J
8) A mass of 4.0 kg moves to the North with a speed of 3 m/s and strikes a 0.5 kg mass which initially stays at rest. The magnitude of the average force during the contact is 20 N. The 4.0 kg mass moves with the speed of 1 m/s to the North after the collision. What is the contact time between the two masses?
0.1 s
0.2 s
0.4 s
0.8 s
1.6 s
9) Which of the following best describes the absolute pressures between A and B?
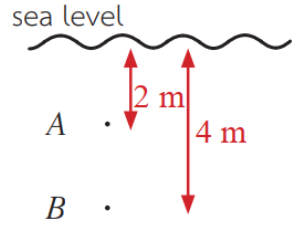
2PA < PB
2PB < PA
PA < PB = 2PA
PA < PB < 2PA
PB < PA < 2PB
1) When object A is brought near object B, they attract each other. When object A is brought to touch object B, the objects still attract each other. Then, object A is grounded and becomes neutral. What would happen if we bring object A near object B again?
The objects will repel.
The objects will attract.
The objects will not repel or attract.
The objects will either repel or attract depending on the charge on object B.
Not enough information.
2) A current of 5.0 A flows through a conductor. Calculate the number of electrons flowing through the conductor in 20 seconds. Given the charge of an electron is –1.6x10-19 C.
4
100
1.56x1018
2.5x1019
6.25x1020
3) A wire has a length of 2.0 cm, a diameter of 3.0 mm, and a resistivity of 1.75×10-8 Ω⋅m. What is the approximate resistance of the wire?
7.43×10-8 Ω
1.24×10-5 Ω
3.89×10-5 Ω
4.95×10-5 Ω
1.56×10-4 Ω
4) A circuit consists of an 8.0 Ω resistor and a variable resistor R connected in series with a battery. The variable resistor has a minimum resistance of 4.0 Ω and a maximum resistance of 16 Ω. The battery and the connecting wires have negligible resistance. What is the ratio of maximum to minimum current obtained from this circuit?
0.25
0.50
1.0
2.0
4.0
5) The critical angle of light between the air-plastic boundary is 30°. What is the speed of light in this plastic?
1.5×108 m/s
2.6×108 m/s
3.0×108 m/s
3.5×108 m/s
6.0×108 m/s
6) An orange light ray with a wavelength of 620 nm passes from air into liquid. What are the wavelength and the colour of the light in the liquid? Given the index of refraction of the liquid is 1.33.
155 nm and the light is invisible
465 nm and the light is blue
465 nm and the light is orange
827 nm and the light is orange
827 nm and the light is invisible
7) A wave is described as 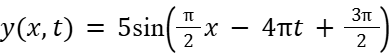 where y, x, and t are in SI units (metres and seconds). What is the speed of this wave?
where y, x, and t are in SI units (metres and seconds). What is the speed of this wave?
0.5 m/s
1.0 m/s
1.5 m/s
2.0 m/s
2.5 m/s
8) Which of the following correctly orders the energy of a photon in each electromagnetic wave from the least to the greatest?
Radio waves, Violet light, Red light, Gamma-ray
Radio waves, Red light, Violet light, Gamma-ray
Gamma-ray, Violet light, Red light, Radio waves
Gamma-ray, Red light, Violet light, Radio waves
None of them is correct.
9) If a metal bar is shone by a beam of light with a wavelength of 400 nm, the maximum kinetic energy of an emitted electron is 0.30 eV. However, if it is shone by a different beam with a wavelength of 620 nm, what would be the maximum kinetic energy of an emitted electron?
2.80 eV
2.00 eV
0.80 eV
0.30 eV
No electron will be emitted.
{"name":"Placement test AS Level Physics V01", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/Q4O9SLAHP","txt":"Name:, Surname:, Email:","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}