Ortho Exam 3 Practice Questions

Ortho Exam 3 Practice Quiz
Test your knowledge and skills in orthopedic evaluation with this comprehensive quiz designed specifically for healthcare professionals. Covering key concepts related to hip, knee, and ankle conditions, this quiz provides an excellent opportunity to assess your understanding and identify areas for improvement.
Features:
- 32 thoughtful and challenging multiple-choice questions
- Covers various orthopedic topics, including anatomy, pathology, and rehabilitation
- Ideal for clinicians, students, and anyone looking to deepen their orthopedic knowledge
You are doing an evaluation in an outpatient orthopedic clinic and you are completing a general observation for a patient who is reporting hip and low back pain. You note that they have an increased lumbar lordosis upon standing. What could contribute to this?
Short abdominals
Weak glute med bilaterally
Short hip flexors
Weak hip flexors
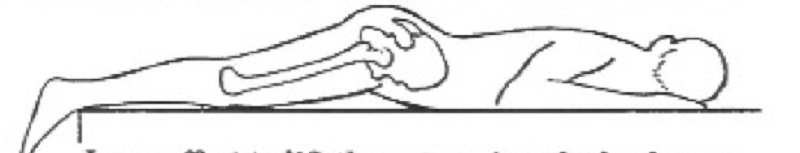
When you ask your patient to lift their lower extremity off the mat, this is the motion you see. What is weak?
Trunk extensors
Hip extensors
Trunk and hip extensors
Hamstrings
Which position would a patient with a hip injury (for example, a labral tear) likely be most comfortable in?
30 degrees flexion, 30 degrees abduction, slight lateral rotation
60 degrees flexion, 60 degrees abuction, slight lateral rotation
Extension, medial rotation, abduction
Extension, lateral rotation, abduction
You are performing a musculoskeletal exam on a patient who has reported general hip pain, with no MOI. You get a positive FABER special test - based on the sensitivity of the test, what pathology can you conclude is likely present?
Extra-articular hip pathology
Intra-articular hip pathology
Labral tear
OA
You are treating an elderly patient with hip pain. Upon examination, you discover they have pain when they sit down on low chairs, when they climb stairs they have pain in the side of their hip, and upon ROM assessment, passive IR is 35 degrees. Can you, using the likelihood ratio, confidently diagnose that the patient has hip OA?
Yes
No
You are evaluating a 2 year old patient in an outpatient pediatric clinic whose parent brought them in because they noticed they prefer sitting and have begun limping when walking. The child does not report pain. Upon examination, you determine there is a mild hip flexion contracture which explains why the child prefers sitting instead of standing. What is your initial hypothesis for this patient?
Legg calve perthes
Hip dysplasia
Coxa vara
AVN
Which of the following structures is not involved in medial extraarticular snapping hip syndrome?
Iliopsoas
ASIS
Lesser trochanter
Greater trochanter
You are evaluating an older patient with hip OA and you need to assess their ROM. Which would you expect to be the most limited?
Hip flexion
Hip extension
Internal rotation
External rotation
You are evaluating a patient in an outpatient clinic who presents with what they describe as a snapping in their hip. They report that when walking, it sometimes feels like their hip is catching, locking, or giving way. They cannot point to a specific MOI, but they play soccer and report that the pain started a few hours after their last game this season. What is the most likely pathology?
Labral tear
Snapping hip syndrome
OA
Coxa valga
Which of the following is not true of hip fractures?
Most commonly at the femoral neck
Common in >50 age group
Complications can include AN, DJD, nonunion
The complications which follow the fracture are more problematic than the fracture itself
Which of the following would likely not be injured when a valgus test at 20-30 degrees is positive?
ACL
MCL
PCM
Posteromedial capsule
Which of the following warrants radiographs of the knee?
Tenderness over tibial tuberosity
Isolated patellar tenderness
Cannot flex to 100 degrees
Age 65 or older
Which of the following is the best special test to rule out an ACL tear?
Lachman
Pivot Shift
Anterior Drawer
McMurray's
Which of the following is not part of the meniscus CPR?
History of catching or locking
Pain with forced hyperextension
Joint laxity with varus/valgus stress
Joint line tenderness
You are seeing an athlete in the on-campus ortho clinic who has anterior knee pain, especially when squatting, jumping, or going up stairs. You note faulty patellar tracking upon exam. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Patellar subluxation/dislocation
Patellofemoral pain syndrome
Patellar tendonitis
Osgood Schlatter Disease
Which activity places the most stress on the knee joint?
Stair climbing
Running
Deep squat
Level ground walking
A female high school lacrosse player presents to PT with swelling and pain in the front of her knee. Upon examination, you notice decreased quadriceps muscle bulk on the affected side, as well as tenderness inferior to the patella. MMT reveals 4/5 score and pain with knee extension, 5/5 flexion (non-painful) and ROM screen reveals pain with passive knee flexion and no pain with passive knee extension. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Patellar tendinitis
PFPS
Osgood-schlatter's
Quadriceps strain
You are doing on-field coverage for a men's soccer game at the college. One of the players fell during the game while playing defense and cutting to the left with his right foot planted. His foot went lateral, and the rest of his body went medially. Which ligament do you most likely need to assess?
ACL
MCL
LCL
PCL
Check all of the following that are risk factors for non-contact ACL injuries.
Shoe surface interaction (turf)
Increased joint laxity
Increased BMI
Wide femoral notch width
You are treating a patient who plays football and was referred to PT following a blow to the front of his knee. Since the injury, he is unable to extend his knee and has a significant amount of pain in the back of his knee. Which test should you perform with this individual? What will you give you the best information, knowing the mechanism and symptoms?
Modified stroke test/bulge sign
Pivot shift test
Valgus stress test
Posterior drawer
Which of the following is the most significant indication for a total knee replacement?
Severe pain
Failed conservative management
Significant loss of function
Severe radiographic changes
Check all of the following that are part of the Ottawa ankle/foot fracture rules?
Tenderness over lateral malleolus
Tenderness over medial malleolus
Tenderness over calcaneus
Tenderness over the 5th met
At push off, the foot serves as:
A rigid lever to provide a propulsive force
A rigid lever to absorb shock
A shock absorber to adapt to uneven surfaces
A shock absorber to provide a propulsive force
You are treating a patient who presents with calcaneal valgus. Which of these factors would you not expect to contribute?
Laxity of the spring ligament
Decreased strength or endurance of arch muscles
Subtalar joint supination
Rearfoot or forefoot pronation
A hammertoe affects the joints in the toe in the following way:
Extension MP/extension PIP
Extension MP/flexion PIP
Flexion MP/extension PIP
Flexion MP/flexion PIP

What is this special test assessing for?
1st MTP mobility
Ankle instability
Sensation of the plantar surface of the foot
Plantar fasciitis
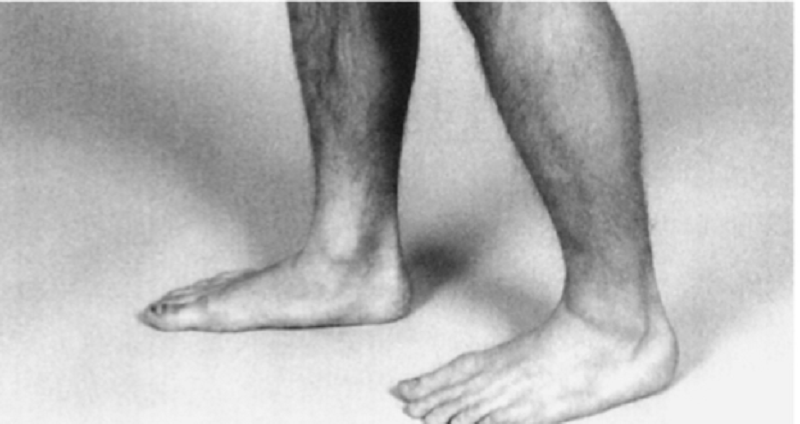
Which of the following does this show?
Pes planus
Pes cavus
Supinated foot
Ankle sprain
You are treating a 45 year old runner who is complaining of pain in the back of his ankle. He reports that it sometimes bothers him when he runs and sometimes does not. He does notice that it sometimes gets better as he continues running too. Upon examination, you note weak PF. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Plantar fasciopathy
Achilles tendinopathy
Sever's disease
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction
Which of the following does the evidence support as providing a short term benefit for treating plantar fasciopathy? Check all that apply.
Taping into antipronation
Foot orthoses
Night splints
Manual therapy
Your patient has sustained an ankle sprain and was able to come in to the clinic to see you the following day. They walk into the clinic with a slight antalgic gait. Upon examination, you note swelling, tenderness at the anterolateral ankle, restricted ROM. There is not much instability, but the patient is unable to raise on their toes. What grade sprain is this?
Grade I
Grade II
Grade III
Grade IV
A patient presents with drop foot and stoppage gait. When performing MMTs, you note weak tib anterior, EHL, and peroneus tertius. Which nerve is most likely involved?
Superficial peroneal nerve
Digital nerve between toes 3&4
Tibial nerve
Deep peroneal nerve
A patient presents to your clinic with weakness in FHL, FDL, and tib posterior. They also note some numbness and tingling into the distal portion of the foot. What is the most likely diagnosis?
PTTD
Lisfranc Injury
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Morton's Neuroma
{"name":"Ortho Exam 3 Practice Questions", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge and skills in orthopedic evaluation with this comprehensive quiz designed specifically for healthcare professionals. Covering key concepts related to hip, knee, and ankle conditions, this quiz provides an excellent opportunity to assess your understanding and identify areas for improvement.Features:32 thoughtful and challenging multiple-choice questionsCovers various orthopedic topics, including anatomy, pathology, and rehabilitationIdeal for clinicians, students, and anyone looking to deepen their orthopedic knowledge","img":"https:/images/course1.png"}