Biomech

Biomechanics Quiz
Test your knowledge on the fascinating field of biomechanics with our comprehensive quiz! This quiz consists of 72 multiple-choice questions that cover various topics, including structural properties, mechanical behavior of bones, and joint fun
- Explore topics related to bone, tendons, and cartilage.
- Assess your understanding of crucial biomechanical concepts.
- Perfect for both learning and reinforcing knowledge in biomechanics.
Which of the following are structural properties
Ultimate force
Ultimate stress
Strain
Elastic modulus
None of the above
In the equation F= k∇x, k is...
Stiffness
Elastic modulus
A structural property
None of the above
A and c
Which of the following is not a contact force
Weight
Bone force
Ligament force
Tendon force
If we are solving a force system analysis questions and we assume the system is 2D and static, we can solve for how many unknowns?
2
3
4
5
This stress is parallel to the analysis surface of the material
Axial
Tensile
Shear
Bending
Compressive
When asked to solve for the force in the tibia-femoral joint, which of the following is not a possible system of interest?
Tibia
Femur
Thigh
Patella
The units of strain and Young's modulus are respectively
M, N/m^2
No unit, Nm^2
M, Nm^2
M, Pa
No unit, N/m^2
The mechanicals properties of a homogeneous material do not depend on:
Speed of loading
Time
Direction
Location
A rigid body has how many equations of motion
9
3
4
5
6
Bone cells associated with the absorption of bone are:
Osteogenic cells
Osteoblasts
Osteocytes
Osteoclasts
None of the above
As the rate of loading decreases:
Bone becomes less brittle
Bone becomes more brittle
Bone becomes stiffer
Bone becomes less compliant
Constant compression in bone results in
Endochondral ossification
Intramembranous ossification
The production of cartilage
Fibrous tissue
None of the above
The following is not a primary function of bone
To protect internal organs
To generate force
To support the body
To form blood cells
The epiphyseal plate (growth plate) is found in the __ of long bones
Epiphysis
Metaphysis
Cortex
Cartilage
Diaphysis
During adolescence, in comparison to males, females
Have higher total bone mass
Have a higher peak in bone mass gain
Have a later peak in bone mass gain
Have an earlier peak in bone mass gain
During running, impact forces
Are a major source of injuries
Can be reduced by using softer shoes
Are higher than active forces
Increase with increasing running speed
None of the above
The benefit of a hollow bone to a solid bone is:
Greater intertia
Less inertia
Greater strength
Less bone mineral density
As we age, the largest decrease in bone occurs in
Ultimate compressive strain
Ultimate tensile strain
Ultimate tonsil strength
Ultimate compressive stress
Energy absorption/failure energy
Cortical bone is approximately __ times stiffer than trabecular bone
5
10
20
50
In cartilage, collagen is oriented perpendicular to the surface in __ zone and parallel to the surface in __ zone
Deep, superficial
Superficial, deep
Deep, middle
Middle, deep
Middle, superficial
The meniscus in your knee joint
Distributes joint contact forces
Prevents osteoarthritis
Is highly vascularized
Can be easily replaced
None of the above
Cartilage cells are called
Proteoglycan
Collagen
Fibroblasts
Aggrecan
Chondrocytes
The weight of a tendon is primarily made up of
Elastin
Proteoglycans
Glycoproteins
Water
Collagen
Failure stress of tendon is approximately
100 Pa
100 MPa
200 MPa
100 GPa
200 Pa
The molecular component of a collagen fibre in tendons consist of __ polypeptide chains coiled around one another
2
3
4
5
None of the above
Proteoglycan content in cartilage peaks in the:
Superficial zone
Middle zone
Deep zone
Calcified zone
None of the above
Cartilage is:
Anisotropic
Viscoelastic
Heterogeneous
Biphasic
All of the above
To solve force system analysis problems, we use the following equations of motion
Hamilton's
Newton's
D'Alembert's
Euler's
Kane's
Which of the following are possible effects of forces
Deformation fo the calcaneus
Acceleration of the calcaneus
Fracture of the calcaneus
All of the above
None of the above
When standing on your toes on one foot, the force in your achilles tendon is approximately
1BW
4000N
0
1000N
2BW
The moment of inertia has the following units
Kg
Kgm^2
M^2
Kg/m^2
None of the above
When using the resultant forces and moments approach in force system analysis
The resultant moments are always equal to zero
The sum of the resultant moments are always equal to zero
The resultant moments are never equal to zero
The sum of the resultant moments are never equal to zero
None of the above
Elastic modulus of biological tissues depends on
The shape of the tissue
The cross sectional area of the tissue
The length of the tissue
All of the above
None of the above
Elastic modulus of biological tissues depends on
The shape of the tissue
The cross sectional area of the tissue
The length of the tissue
All of the above
None of the above
Which of the following are structural properties
Ultimate force
Ultimate stress
Strain
Elastic modulus
None of the above
When a bone is subjected to an excessive bending stress
It fails in the middle of the bone
It fails at the side of compressive stress
It fails at the side of sheer stress
It fails at the side of tensile stress
It fails at the side of torsional stress
Compared to the bones of a 20 year old male, the ultimate compressive stress of bones of an average 60 year old male is
10% less
20% less
30% less
40% less
50% less
Osteoporosis involves
Decreased bone strength
An increased risk of fracture
Decreased bone density
Increased bone porosity
All of the above
Ultimate stress indicates
The slope of the stress-strain curve in the elastic region
The transition point from the elastic region to the plastic region
The maximal stress that the structure can sustain
The failure load
On the ascending limb of the force length relationship
Force increases as length increases
Force decreases as length increases
Force stays constant as length increases
Force is independent of length
Force-velocity relationships could be altered by
Training
Fatigue
Changes in temperatures
All of the above
This statement: "bone structure adapts to the direction of load" corresponds to:
Bone types
Wolff's law
Osteoporosis
Normal stress
Ligament cells are called
Chondrocytes
Fibroblasts
Osteoclasts
Osteoblasts
All of the following are true EXCEPT
Cortical bone is about 20 times stronger than cancellous bone
Trabecular bone makes up about 20% of skeletal mass
Cortical bone has a high rate of remodelling
Trabecular bone can typically be found at the end of long bones
Cortical bone can typically be found at the diaphysis of long bones
A muscle fibre is stretched until failure. It's elastic modulus and failure strain are 10^6 (elastic modulus SI unit) and 5% respectively. The failure stress is:
5 x 10^3 (stress SI unit)
5 x 10^4 (stress SI unit)
5 x 10^5 (stress SI unit)
5 x 10^6 (stress SI unit)
None of the above
The slope of the stress-strain curve is
Linear
Stiffness
Elastic modulus
Hysteresis
None of the above
Ligaments and tendons differ in
Ligaments and tendons don't differ
The amount/type of water
The amount/type of collagen
The amount/type of extracellular matrix
The amount/type of cellular material
When a boy is running, if his femur is rotating at a constant velocity it must:
Have a net resultant force equal to zero
Have a net resultant force not equal to zero
Have a net resultant moment equal to zero
Have a net resultant moment not equal to zero
Ultimate stress indicates
The slope of the stress-strain curve in the elastic region
The transition point from the elastic region to the plastic region
The maximal stress that the structure can sustain
The failure load
The following is viscoelastic material
Bone
Cartilage
Tendon
Muscle
All of the above
Young's modulus
Is the slope of the force-deformation curve
Increases in compliant compared to stiffness
Is higher in skeletal muscles compared to bone
None of the above
___ is primarily responsible for the tensile strength of tendons
Fibroblasts
Elastin
Collagen
Extracellular matrix
According to Wolff's law
Bone is a viscoelastic material
Mechanical properties of bone depend on its porosity
Mechanical properties of bone depend on its porosity
Bone remodels itself according to the mechanical stresses it experiences
Synovial fluid
Is viscoelastic
Provides joint lubrication
Transports waste products
All of the above
Articular cartilage
Has highly viscoelastic behaviour
Is highly inhomogeneous
Has biphasic behaviour
All of the above
In response to a creep test, articular cartilage experiences
A slow initial increase then a rapid increase in force
A rapid increase then a slow increase in deformation
A slow initial increase then a rapid increase in deformation
A rapid initial increase then a slow increase in force
As we age, bone (compared to young age)
Becomes more ductile because its amount of collagen fibres increases
Becomes more ductile because its mineral density increases
Becomes less ductile because its amount of collagen fibres decreases
Becomes less ductile because its mineral density decreases
Which of the following is not a function of ligaments
To attach articulating bones to one another
To guide movement
To maintain joint congruity
To transfer loads
The following statements are true except:
Cells in articular cartilage are the chondrocytes
Stiffness in articular cartilage decreases with increasing strain
Proteoglycans in articular cartilage resist compressive stresses
Chondrocytes can sense mechanical load
Permeability in articular cartilage
Is independent of the amount of strain
Increases when strain increases
Causes an increase in stiffness when it decreases
None of the above
Beyond the ___ length, the active force decreases
Slack
Maximal
Resting
Optimal
Which of the following does not influence bone deposition and bone mass
Strain rate
Strain frequency
Strain mode
None of the above
Strain is:
Force per initial length
Deformation per initial length
Deformation per cross sectional area
Force per cross sectional area
Viscoelastic material:
Becomes elastic if loaded at high speeds
Relaxes its deformation when submitted to a constant load
Is able to return to its original shape after stretch beyond the yield point
Has time dependent response to loading
Osteoporosis is
Less common as people age
Might be caused by repetitive impact loading and abnormal loading
A degenerative disease of osteon
An increase in bone strength
Which of the following activities would produce the greatest increase in bone mineral density
Cycling
Swimming
Running
All of the above would provide equal contribution to bone health
In the plastic region of the stress-strain curve
Permanent deformation occurs
An elastic modulus can be determines
Force is inversely proportional to deformation
The behaviour of a material is elastic
The statement that better describes the plateau region of the force-length relationship is:
Force increases with length
Force decreases with length
Force is independent of length
Force increases as length stays constant
Power is
Force per unit of time
Work per unit of time
Velocity per unit of time
Length per unit of time
Peak power is observed at about
30% of Vmax
100% of Vmax
50% of Fmax
0% of Vmax
As the elbow flexes, active force produced by the biceps brachii:
Decreases because the length of the biceps brachii decreases
Increases because the length of the biceps brachii decreases
Stays the same
Could increase or decrease depending on its operating length
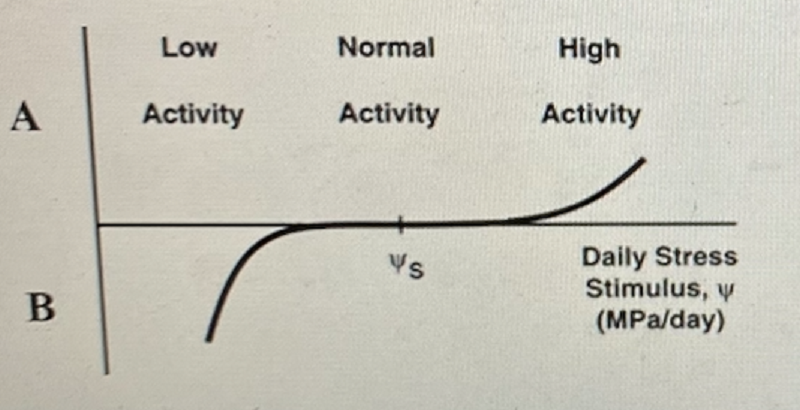
The following figure shows the effect of daily stress on a bone
A is bone deposition by the osteoclasts and B is bone resorption by the osteoblasts
A is bone resorption by the osteoblasts and B is bone deposition by the osteoclasts
A is bone resorption by the osteoclasts and B is bone deposition by the osteoblasts
A is bone deposition by the osteoblasts and B is bone resorption by the osteoclasts
{"name":"Biomech", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on the fascinating field of biomechanics with our comprehensive quiz! This quiz consists of 72 multiple-choice questions that cover various topics, including structural properties, mechanical behavior of bones, and joint functions. Whether you are a student, teacher, or enthusiast, this quiz is designed to challenge and enhance your understanding.Explore topics related to bone, tendons, and cartilage.Assess your understanding of crucial biomechanical concepts.Perfect for both learning and reinforcing knowledge in biomechanics.","img":"https:/images/course4.png"}
More Quizzes
RadioUlnar Assessment LOJUGVICH
10512
Do you have what it takes to be a Doctor of Physical Therapy?
10532
Combined MCQ quiz
2771380
German New Year Quiz
1050
Test Your Ben 10 Trivia Skills with Alien Force
201047135
Ace the Parts of a Book & Their Meanings
201026623
Can You Master the Division of Rome and Empire's Fall?
201036826
Master Surgical Questions: General Surgery Trivia
201095063
Residential Housing Design
15827701
Present Simple & Continuous Test: Free Grammar
201031309
What Celebrity Do I Look Like? Find Your Perfect Match!
201024964
What Is Your Real Name? Discover Your True Name
201023926