GENETICS 2020
Non invasive methods of prenatal diagnosis/screening are
Chorionic villous sampling
Nuchal fold translucency
Cordocentesis
Aminocentesis
FAP level in mothers serum
MLPA method
Is a sequence analysis
Can detect rearrangements in genes
Is used for DMD
Can detect big mutations
Can detect balanced translocations
Which structures in females arise from Mullerian ducts
Uterus
Labia minora
Clitoris
Ovary
Fallopian tubes
The risk of death in breast cancer patients with constitutional PALB2 mutation during 10 years following tumor diagnosis incase of tumor size above 2 cm is around:
10%
70%
20%
100%
40%
Features reducing the risk of breast cancer in BRCA1 carriers include:
Tubal ligation
Adnexectomy
Low cadmium level
Breast feeding
Oral contraceptives
7) HNPCC susp.can be diagnose when 45 years old colorectal cancer patient has
Daughter affected by sarcoma
Brother affected by stomach cancer
father affected by small bowel cancer
Mother affected by brain tumor
Sister affected by endometrial cancer
Chose a cause of deformation
Gene mutation
Olighydramnios
Preterm delivery
Chromosomal aberration
Twin pregnancy
Diseases are inherited with X-chromosome are:
Cystic fibrosis
Huntington disease
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Heamophilia A
Rett syndrome
Two the most common genes among cancers associated with high risk of tumors are:
BRCA2
MLH1
CHECK2
BRCA1
MSH2
Becker muscular dystrophy:
Disease is observed mainly in boys
Is connected with PALB gene mutations
life span may be normal
elevation of serum creatin kinase is characteristic
firs symptoms are observed in late childhood
Surveillance options for BRCA1 carriers include:
USG of breast
MRI of breast
Mammography
USG of ovaries
MRI of ovaries
Infertility is observer in following syndrome:
Swyer sy
Triple X sy
Klinefelter sy
Androgen
Insensitivity sy
Turner sy
In diagnosis of single gene disorders you can use:
PCR - RFLP
FISH with centromeric probe
Real time PCR
Sequencing
Karyotyping
Which of these causes mental retardation in boys:
Becker muscular dystrophy
Down syndrome
Haemophilia B
Fragile X syndrome
Rett syndrome
Huntington disease
Is caused by many CAG repeats in DNA
if mutation is transmitted by father number of CAG repeats might increase
Is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder
All answers above are correct
Area of the brain damaged by Huntington's disease is striatum
What is the safest gestational age to perform amniocentesis:
12 - 14 weeks
6 - 9 weeks
14 - 18 weeks
Any time after 6 weeks
9 - 12 weeks
Genetic risk for polyigenic disorders in relatives of an affected person:
Depends upon number of cases in family
Is accessed by Mendel’s laws
Depends upon mother’s age
is evaluated on the basis of studies of twin concordance
depends upon severity of symptoms
If a patient is suspected to have FAP, what is recommended:
Kidney USG
Gastroscopy
Colonoscopy
Pedigree analysis
Prophylactic colonectomy if confirmed
Which of the following embryonal structures make male organs
Mesonephros
Urogential sinus
Wolffian ducts
Fetal gonads
Mullerian duct
HNPCC should be suspected in family where 41 year old woman is diagnosed with colorectal cancer and additionally:
Son is affected by neuroblastoma
Mother is affected by breast cancer
brother is affected by bladder cancer
sister is affected by ovarian cancer
father is affected by small bowel cancer
25% Risk of disease in siblings of an affected man is characteristic for:
Hemochromatosis
Hypercholesterolemia
Klinefelter syndrome
Lynch sy
Cystic fibrosis
Daughter of a man affected by Hemophilia will be a carrier of this disease with a probability of:
100%
25%
0%
50%
10%
) Sign methods decreasing breast cancer risk in BRCA1/2 carriers:
prophylactic mastectomy
use of tamoxifen
bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy
Breast feeding
Oral contraceptives
Following are the examples of aneuploidy:
46, XY, t(9;22)(q34;q11)
45, X
Frameshift mutation
47, XY, +18
Misense mutation
Familial aggregation of cancers is characteristic for
Polygenic inheritance
Monogenic recessive with low penetrance
Monogenic dominant with high penetrance
Monogenic dominant with low penetrance
Monogenic recessive with high penetrance
Increased risk of following neoplasms in VHL mutation carriers:
Kidney
Ovary
Adrenal gland
Hemangioblastoma cerebelli
Brest
A patient (46,XY) with MIF (AMH) mutation is:
Generally fertile
Male with pseudohermaphroditism
Male appearance with female genitals
Female appearance with undifferenciated genitals
Having Persistent Mullerian Duct syndrome
Pedigree presentation corresponding to autosomal dominant inheritance pattern is characteristic for:
Hereditary breast-ovarian cancer
Becker muscular dystrophy
HNPCC
Huntigton disease
VHL syndrome
In 30 year old patient asymptomatic retinal hemangioblastoma was detected. Proper management includes:
Mutation testing in VHL gene
abdominal ultrasound is indicated
Observation only
Treatment with laser- or kryo-therapy
Colonoscopy is indicated
Prophylactic adnexectomy is indicated in BRCA1 carriers because it:
Decreases the risk of ovarian Ca
Decreases the risk of colorectal cancer
Decreases the risk of Fallopian tube ca
Improves survival in cases of breast cancer
Decreases the risk of breast cancer
Finding of MLH1 constitutional mutation in patient from family with endometrial and small bowel cancers will lead todiagnose:
Breast-ovarian cancer syndrome
Lynch sy
HNPCC
FAP
Li - Fraumeni syndrome
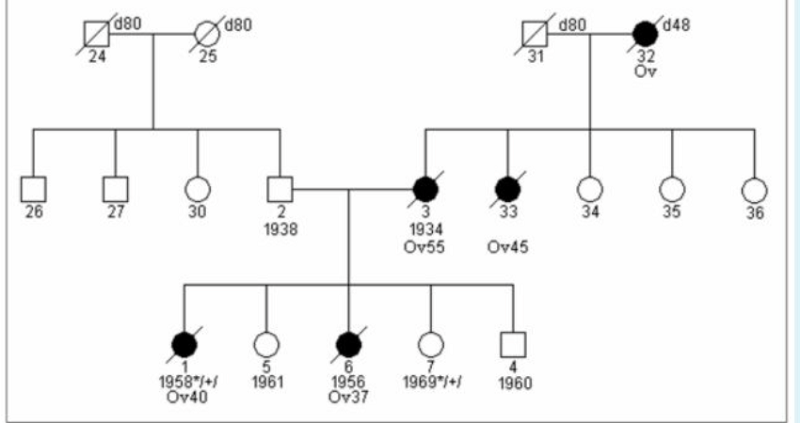
Presented below pedigree is an example of:
Autosomal dominant inheritance
X-linked recessive inheritance
Mitochondrial inheritance
Autosomal recessive inheritance
Definitive diagnosis of HOC
Autosomal dominant traits:
Affected males always have unaffected daughters
appear in every generation
50% chance of inheriting the disease
male and female are equally likely to have the disease and to transmit the disease
Normal members transmit the disease
In differential diagnosis between HNPCC and FAP it is recommended to consider occurrence of:
Polyposis
Endometriosis
Desmoids
Cysts of mandible
Blindness
Optimal treatment of breast cancer patients with BRCA1 constitutional mutation should include:
Tamoxifen
Oral contraceptives
Platins
HRT
Adexectomy
{"name":"GENETICS 2020", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Wilms tumor is frequently observed in:, Non invasive methods of prenatal diagnosis\/screening are, MLPA method","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/95-4644637/skjermbilde-2023-11-08-kl-12-23-05.png?sz=1200-00000000001000005300"}
More Quizzes
TTR EVALUATION - ALL COURSES - DO NOT DELETE OR COPY
840
Which book is right for you? (For kids)
210
Dance Your Way Through Cultures
1058
The Ultimate Personality Quiz
10534
Think You Know Cruella Movie? Take the Ultimate Now!
201025026
Free Solar System Answers & Study Guide
201026699
Server+ Practice Test: 25 Free CompTIA Server+ Questions
201081310
Discover Your Freak Factor with This Free Freak Test
201029975
Ace Our Transcription and Translation Practice Now
201039429
Discover Your Sander Side: Free Personality
201032631
Which Tekken Character Are You? Free Personality
201025949
Bay Area Movies Pop Culture: How Well Do You Know SF?
201051839