ECON Test Review
If aggregate demand shifts right, then eventually price level expectations rise. The increase in price level expectations causes the short run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left.
True
Flase
Which of the following would increase output in the short run?
An increase in stock prices makes people feel wealthier
Firms chose to purchase more investment goods
Government spending increases
All of the above are correct
Suppose the economy is in long run equilibrium. If the government increases its expenditures, eventually the increase in aggregate demand causes price expectations to
Rise. This rise in price expectations shifts the short run aggregate supply curve to the right.
Fall. This fall in price expectations shifts the short run aggregate supply curve to the left.
Rise. This rise in price expectations shifts the short run aggregate supply curve to the left.
Fall. This fall in price expectations shifts the short run aggregate supply curve to the right.
Suppose the economy is in long run equilibrium and the government decreases its expenditures. Which of the following helps explain the logic of why the economy moves back to long run equilibrium?
As people revise their price level expectations upward, firms and workers strike bargains for higher nominal wages.
As people revise their price level expectations downward, firms and workers strike bargains for lower nominal wages
As people revise their price level expectations upward, firms and workers strike bargains for lower nominal wages.
As people revise their price level expectations downward, firms and workers strike bargains for higher nominal wages
Policymakers who control monetary and fiscal policy and want to offset the effects on output of an economic contraction caused by a shift in aggregate supply could use policy to shift
Aggregate supply to the right.
Aggregate demand to the left
Aggregate supply to the left.
aggregate demand to the right.
Suppose a shift in aggregate demand creates an economic contraction. If policymakers can respond with sufficient speed and precision, they can offset the initial shift by shifting
Aggregate supply right.
Aggregate demand left.
Aggregate supply left.
Aggregate demand right.
Which of the following would cause stagflation?
Aggregate demand shifts right
Aggregate supply shifts left
Aggregate demand shifts left
Aggregate supply shifts right
Suppose the economy is in long run equilibrium. If there is an increase in government purchases at the same time there is a large increase in the price of oil, then in the short run
Real GDP will rise and the price level might rise, fall, or stay the same.
the price level will fall, and real GDP might rise, fall, or stay the same.
Real GDP will fall and the price level might rise, fall, or stay the same.
The price level will rise, and real GDP might rise, fall, or stay the same.
In the mid 1970s the price of oil rose dramatically. This
Shifted aggregate supply left, the price level rose, and real GDP fell.
Caused an increase in U.S. Prices and real GDP.
Caused U.S. Prices to fall, and real GDP rose.
Caused a decrease in U.S. Prices and real GDP.
Which of the following would help explain why the aggregate demand curve slopes downward?
An unexpectedly low price level raises the real wage, which causes firms to hire fewer workers and produce a smaller quantity of goods and services.
A lower price level reduces the interest rate, which encourages greater spending on investment goods
A lower price level causes domestic interest rates to rise and the real exchange rate to appreciate, which stimulates spending on net exports.
A higher price level increases real wealth, which stimulates spending on consumption.
When the price level changes, which of the following variables will change and thereby cause a change in the aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded?
the real value of wealth
The value of currency in the market for foreign exchange
The interest rate
All of the above are correct.
During recessions declines in investment account for about
1/6 of the decline in real GDP.
2/3 of the decline in real GDP.
1/7 of the decline in real GDP.
1/3 of the decline in real GDP.
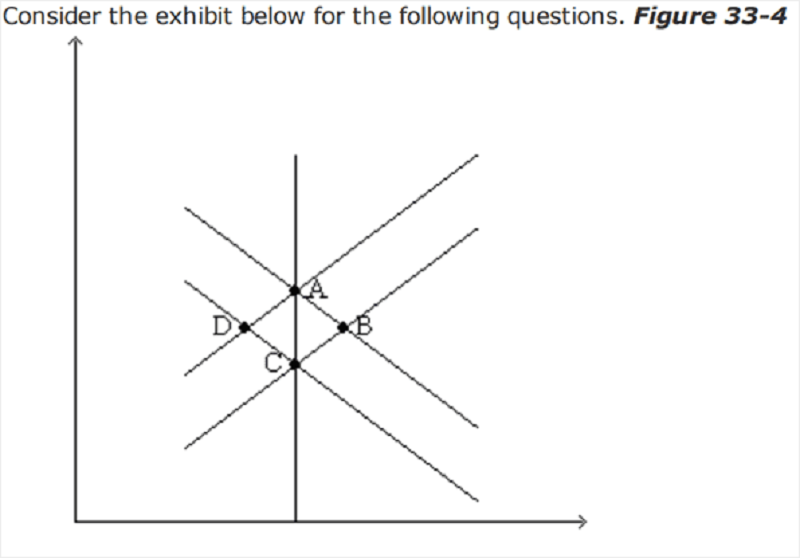
A decrease in taxes would move the economy from C to
B in the short run and the long run.
D in the short run and C in the long run.
D in the short run and the long run
B in the short run and A in the long run.
Which part of real GDP fluctuates most over the course of the business cycle?
Consumption expenditures
Net exports
Government expenditures
Investment expenditures
Other things the same, as the price level falls, the exchange rate rises. A rise in the exchange rate leads to a decrease in net exports
True
False
The aggregate quantity of goods and services demanded changes as the price level rises because
Real wealth falls, interest rates rise, and the dollar appreciates.
real wealth rises, interest rates fall, and the dollar depreciates.
Real wealth falls, interest rates rise, and the dollar depreciates.
Real wealth rises, interest rates fall, and the dollar appreciates.
The exchange rate effect is the idea that a higher U.S. Price level causes the value of the dollar to increase in foreign exchange markets, and this effect contributes to the downward slope of the aggregate demand curve.
True
False
When the price level increases, the real value of people's money holdings
Falls, so they buy more.
Rises, so they buy less.
Falls, so they buy less.
Rises, so they buy more.
If speculators bid up the value of the dollar in the market for foreign currency exchange, U.S. Aggregate demand would shift to the left.
True
False
The effect of a change in the value of the dollar in the foreign exchange market due to a change in the price level helps explain the slope of aggregate demand, but does not shift it. The effects of a change in the value of the dollar in the foreign exchange market due to speculation is shown by shifting the aggregate demand curve.
True
False
The average price level is measured by
The price of oil
The GDP deflator
The rate of inflation
The nominal interest rate
Aggregate demand includes
the quantity of goods and services the government, households, firms, and customers abroad want to buy
The quantity of goods and services households and firms want to buy, but not the quantity of goods and services the government wants to buy.
Neither the quantity of goods and services the government, households, nor firms want to buy nor the quantity of goods and services customers abroad want to buy.
The quantity of goods and service the government wants to buy, but not the quantity of goods and services households, firms, or customers abroad want to buy.
Which of the following would not be included in aggregate demand?
An increase in firms' inventories
Government's tax collections
Purchases of goods by households
Firms' purchases of newly produced machinery
Other things the same, when the price level rises, interest rates
Rise, so firms increase investment
Fall, so firms decrease investment
Rise, so firms decrease investment
Fall, so firms increase investment
If output is above its natural rate, then according to sticky wage theory
Workers and firms will strike bargains for lower wages. In response to the lower wages firms will produce less at any given price level.
Workers and firms will strike bargains for higher wages. In response to the higher wages firms will produce more at any given price level.
Workers and firms will strike bargains for lower wages. In response to the lower wages firms will produce more at any given price level.
Will strike bargains for higher wages. In response to the higher wages firms will produce less at any given price level.
The position of the long run aggregate supply curve
Is determined by resource usage and technology.
is at the point where the economy would cease to grow.
Is at the point where the unemployment rate is zero.
Shifts to the right when the money supply increases.
The long run aggregate supply curve shifts right if
Immigration from abroad increases
Technology advances
The capital stock increases
All of the above are correct
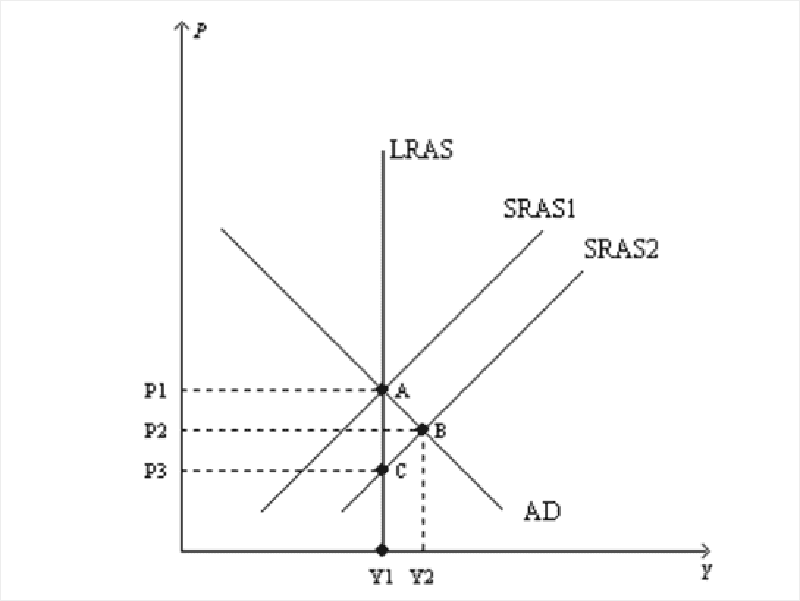
The shift of the short run aggregate supply curve from SRAS1 to SRAS2
Could be caused by an outbreak of war in the Middle East.
Causes the economy to experience stagflation.
Could be caused by a decrease in the expected price level.
Causes the economy to experience an increase in the unemployment rate.
An increase in the actual price level does not shift the short run aggregate supply curve, but an expected increase in the price level shifts the short run aggregate supply curve to the left.
True
False
The sticky wage theory of the short run aggregate supply curve says that when the price level is lower than expected,
Production is more profitable and employment rises.
Production is less profitable and employment falls.
Production is more profitable and employment falls
production is less profitable and employment rises.
If the price level rises above what was expected and nominal wages are fixed, then
Production becomes less profitable so firms will hire fewer workers.
Production becomes more profitable so firms will hire more workers.
production becomes less profitable so firms will hire more workers.
Production becomes more profitable so firms will hire fewer workers.
The sticky price theory implies that
The short run aggregate supply curve is upwardsloping
menu costs influence the speed of adjustment of prices.
an unexpected fall in the price level induces firms to reduce the quantity of goods and services they produce.
All of the above are correct.
Other things the same, when the price level rises more than expected, some firms will have
Higher than desired prices, which increases their sales.
Lower than desired prices, which depresses their sales.
higher than desired prices, which depresses their sales.
Lower than desired prices, which increases their sales.
{"name":"ECON Test Review", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"If aggregate demand shifts right, then eventually price level expectations rise. The increase in price level expectations causes the short run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left., Which of the following would increase output in the short run?, Suppose the economy is in long run equilibrium. If the government increases its expenditures, eventually the increase in aggregate demand causes price expectations to","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/15-654059/screen-shot-2017-03-27-at-9-36-50-pm.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
¿Cómo saber si le gustas a una mujer?
520
Testez vos connaissances sur le Sahel !
1050
Minecraft Friendship Quiz
8471
Discipline Scenarios
5230
Computer Science Trivia - Theory of Computation
201022020
Am I Friendly? Free Personality
201018424
70s TV Trivia - Can You Name the Classics?
201018983
Holes Chapter 13 - Free Novel Knowledge Check
201018501
What Character Am I - Find Your Fictional Match
201018738
Economic Values Test - Which Economic School Are You?
201018501
One Direction Boyfriend - Who's Your Perfect Match?
201018818
Which Black Butler Character Are You? Free Online
201016630
