DES part2 episode 6
167) A 22-year-old male student presents with an acute onset of fever, double vision, and painful swelling around his eyes. He also has significant muscle pain in his neck and jaw muscles. A week earlier, he experienced a period of abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, all of which resolved spontaneously. He has a history of intravenous drug abuse but has recently completed of a drug rehabilitation program. He is febrile. Physical examination shows "splinter" hemorrhages, periorbital edema, and chemosis. Chest is clear to auscultation. Cardiac exam reveals no murmur. Abdomen is soft and nontender with no organomegaly. His complete blood count is shown below: Hemoglobin 13.0 g/L, MCV 85 fl, Platelets 228,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 10,500/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 21%, Lymphocytes 23%. Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Trichinellosis
Guillain-Barre syndrome
. Botulism
Angioedema
Infective endocarditis
168) A 19-year-old woman comes to the physician because of fever, joint pain, and rash. The rash started on her face and is spreading down her body. She has pain in her fingers, wrists, and knees. She denies any neck stiffness, nausea, or vomiting. She has been sexually active with multiple partners. Her vaccination status is unknown. Her pulse is 86/min, blood pressure is 125/75 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F). Physical examination reveals a maculopapular rash on her face and chest. Posterior auricular, cervical, and suboccipital lymphadenopathy is present. She has mild conjunctivitis. Oropharynx is clear. Chest is clearto auscultation. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Rubella
Infectious mononucleosis
Chicken pox
. Secondary syphilis
Disseminated gonococcal infection
169) An elderly bedridden patient in the hospital develops cough, fever, and shortness of breath. On examination, the JVP is 4 cm, heart sounds are normal, and there are crackles on inspiration in the right lower lobe. A CXR reveals a new right lower lobe infiltrate and his WBC is 15,000/mL. He was admitted to the hospital 7 days ago for the treatment of congestive heart failure. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hospital-acquired pneumonia
Community-acquired pneumonia
Atelectasis
Asymmetric congestive heart failure
Pulmonary embolism
170) A 35-year-old male complains of inability to close his right eye. Examination shows facial nerve weakness of the upper and lower halves of the face. There are no other cranial nerve abnormalities, and the rest of the neurological examination is normal. Examination of the heart, chest, abdomen, and skin show no additional abnormalities. There is no lymphadenopathy. About one month ago the patient was seen by a dermatologist for a bull’s-eye skin rash. The patient lives in upstate New York and returned from a camping trip a few weeks before noting the rash. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Sarcoidosis
. Syphilis
Idiopathic Bell palsy
. Lacunar infarct
. Lyme disease
171) An 18-year-old woman presents with headache, anorexia, chilly sensations, and discomfort on both sides of her jaw. She has also noticed discomfort in both lower abdominal quadrants. Physical examination reveals bilateral enlarged parotid glands that are doughy, elastic, and slightly tender; with a reddened orifice of Stensen’s duct. Her abdomen is soft with bilateral lower quadrant abdominal tenderness; a temperature of 38.5°C; and a pulse rate of 92/min. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 13 g/dL; hematocrit 40%; white blood cells (WBC) 9000/mL, with 35% segmented neutrophils, 7% monocytes, and 58% lymphocytes. Which of the following is the most likely cause for her abdominal pain and tenderness?
Mesenteric lymphadenitis
Peritoneal metastases
Oophoritis
Intestinal hyperperistalsis
Gonorrhea
172) A 20-year-old woman presents with headache, fever, and neck stiffness. On examination, her blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse 100/min, temperature 38.6°C, and the neck is stiff and painful to flex and extend. The ears, throat, and sinuses are normal, there are no focal neurologic signs, and the remaining examination is normal. There are no reported similar cases in the community. Which of the following is the most likely source of her infection?
An infected heart valve
Oral ingestion
Nasopharynx
Bowel
Skin
173) A 32-year-old woman acutely develops high fever, hypotension, and rash. This is followed by vomiting, diarrhea, confusion, and abdominal pain. In the hospital, evidence of multiorgan failure develops. Desquamation of the skin occurs 1 week after the acute illness. On further history, the illness started 3 days after the onset of menstruation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
S. Aureus toxic shock syndrome (TSS
RMSF
Streptococcal infection (scarlet fever)
Staphylococcal scaled skin syndrome
Clostridial infection
174) The dental condition illustrated in Fig is usually associated with a congenital infectious disease. The teeth are characterized by centrally notched, widely spaced, peg-shaped upper central incisors and molars that have poorly developed cusps. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
For Student DES 2016-2017 last (1).bmp 2

Congenital rubella
Congenital HIV
Congenital syphilis
Congenital measles
Congenital toxoplasmosis
175) A 22-year-old man is an avid spelunker (cave explorer) and has recently been exploring several caves. A routine CXR taken for a new job reveals hilar adenopathy and two patches of pneumonitis. His physical examination is completely normal. Careful questioning reveals he has just gotten over a cold with mild fever, cough, and malaise. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Tuberculosis (TB)
Histoplasmosis
Sarcoidosis
Coccidioidomycosis
Candidiasis
176) A 53-year-old man with alcoholic cirrhosis presents with increasing jaundice and abdominal discomfort. He reports no fevers or chills. On examination, his blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse 100/min, temperature 38.1°C. He has a distended abdomen, peripheral edema, and shifting dullness. The abdomen is tender and bowel sounds are present. A diagnostic paracentesis is performed; the total cell count is 940/mL with polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) equal to 550/mL, Gram stain is negative, and cultures are pending. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Pancreatic ascites
Secondary peritonitis
Malignant ascites
Tuberculous ascites
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP)
177) A 20-year-old woman presents with headache, anorexia, chilly sensations, pain, and drawing sensations in both sides of her jaw. She has also noticed discomfort in both lower abdominal quadrants. Physical examination reveals bilateral enlarged parotid glands that are doughy, elastic, and slightly tender; with a reddened orifice of Stensen’s duct. Her abdomen is soft with bilateral lower quadrant abdominal tenderness, a temperature of 38.5°C, and a pulse rate of 92/min. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 13 g/dL; hematocrit 40%; WBC 9000/mL, with 35% segmented neutrophils, 7% monocytes, and 58% lymphocytes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cervical lymphadenitis
Uveoparotid fever
Mikulicz’s syndrome
Mumps
Parotid gland tumor
178) An 18-year-old woman visits her physician because of 3 weeks of malaise, 2 weeks of fever, and a sore throat. Physical examination shows pharyngeal infection with enlarged tonsils and a patchy, white exudate; enlarged, palpable anterior and posterior cervical, axillary, and inguinal lymph nodes; tenderness in the right upper quadrant; and minimal splenomegaly. Laboratory data show hemoglobin 14 g/dL; hematocrit 42%; platelets 380,000/mL; WBC 8500/mL, with 35% segmented neutrophils, 1% eosinophils, and 64% lymphocytes, of which 36% were atypical. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Infectious hepatitis
Hodgkin’s disease
Lymphocytic leukemia
Cat-scratch fever
Infectious mononucleosis
179) A 43-year-old man developed a cough shortly after returning from a 1-month hiking trip in California. While there, he was hiking in the central California valleys. During his trip, he had developed a flu-like‖ illness consisting of fever, cough, and muscle pains, which resolved spontaneously. A CXR shows a thin-walled cavity in the right upper lobe, and the sputum reveals fungal elements. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Ringworm
Mycobacteria
Cryptococcus neoformans
Coccidioidomycosis
Candida albicans
180) A 34-year-old man presents with diarrhea 3 weeks after returning from a trip to rural South America. Over the past few days, he has gradually developed lower abdominal pain and diarrhea. Now the symptoms are much worse with eight stools a day consisting mostly of mucus and blood. He is afebrile, the abdomen is tender in left lower quadrant, and the remaining examination is normal. His stool is mostly comprised of blood and mucus, and stools tests show trophozoites of Entamoeba hitolytica. Which of the following is the most likely site of extra intestinal involvement?
Genitals
Liver
Pleura
Cerebral cortex
Pericardium
181) A 40-year-old man develops erythema nodosum, conjunctivitis, and a pleural effusion. Over several weeks, pulmonary lesions lead to cavitation and a large, thin-walled cavity. He was traveling in Arizona before becoming ill. Sputum samples reveal mature spherules. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Streptococcus
Staphylococcus
Coccidioidomycosis
Pneumocystis carinii
Candidiasis
182) A 25-year-old man is admitted with fever and rust-colored sputum. He looks unwell, temperature 38.4°C, pulse 100/min, and blood pressure 115/80 mm Hg. On auscultation, there are bronchial breath sounds in the right axilla and inspiratory crackles. The CXR is shown in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
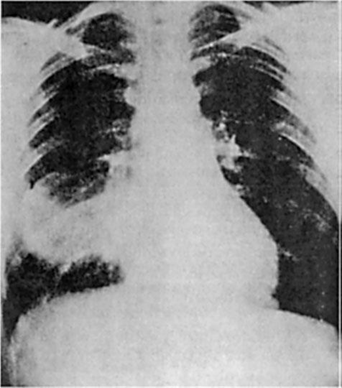
For Student DES

Right middle lobe pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia
Loculated pleural effusion
Right lower lobe pneumonia
Aspergilloma
183) A 7-year-old child, unvaccinated because of his parents’ religious beliefs, develops malaise, cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis with a high fever. Examination of his mouth reveals blue white spots on a red base beside his second molars. The next day he develops an erythematous, nonpruritic, maculopapular rash at his hairline and behind his ears, which spreads over his body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hand-foot-and-mouth disease (coxsackievirus
Mumps
Measles (rubeola)
Pertussis
Rubella (German measles
184) A 51-year-old man is admitted to the hospital because of renal failure. His past medical history is significant for recurrent episodes of bilateral flank pain over the past several years as well as nocturia 2 to 3 times per night for the past 10 years. He has no weight loss. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 160/100 mm Hg. His mucous membranes are pale. There is a palpable mass located at the right flank. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Horseshoe kidney
. Polycystic kidney disease
Nephrolithiasis
Renal cell carcinoma
Papillary necrosis
185) A 30-year-old African American man comes to the physician because of a two-week history of fatigue and ankle edema. He is HIV-positive. He takes no medications. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 140/86 mm Hg and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows mild ankle edema. Laboratory studies show: Hb 12.5 g/dl, WBC 6,000/cmm, Platelets 140,000/cmm, Serum Na 135 mEq/L, Serum K 5.0 mEq/L, BUN 28 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 2.4 mg/dl. Urinalysis revealed 2+ proteinuria but otherwise shows no abnormalities. CD4 count taken three weeks ago was 550. Which of the following is the most probable form of kidney disease in this patient?
. Membranous glomerulonephritis
Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
Mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis
Acute interstitial nephritis
Collapsing focal and segmental glomerulosclerosis
186) A 43-year-old man complains of occasional red urine. He denies fever, edema, flank pain or weight loss. Specifically, he says that each urine stream starts out transparent, but turns red by the end of the stream. At times he has noticed small clots in his urine. Physical examination is within normal limits. What is the most likely cause of his complaints?
Glomerular disease
Nephrolithiasis
. Urinary tract infection
Bladder disease
. Urethral injury
187) A 74-year-old man comes to the physician because of a one-year history of increased urinary frequency and urgency. He feels that his bladder is "not emptying properly", and has a constant sensation of incomplete voiding. His only other medical problem is hypertension, for which he takes hydrochlorothiazide. He never had any surgeries. Urine culture shows no abnormality. Which of the following is true regarding this patient's disorder?
. It is best treated with oral antibiotics
. It responds well to beta blockers
. It usually starts in the central part of the prostate
It usually starts in the peripheral part of the prostate
. It can be treated with continuous suprapubic catheter irrigation
188) A 26-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a sudden onset of severe, colicky, leftsided flank pain that radiates to the scrotum. He also has nausea, vomiting and dark-colored urine. He has never had these symptoms before. Examination shows no abnormalities. Non-contrast helical CT shows a 5 mm radiopaque stone in the left upper ureter. His laboratory studies are as follows: Serum calcium 9.8 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.9 mg/dl, BUN 15 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows hematuria but no casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Calcium oxalate stones
. Cysteine stones
. Calcium phosphate stones
Struvite stones
Uric acid stones
189) A 36-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and generalized edema. He was recently diagnosed with Hodgkin's lymphoma. Laboratory studies show: Serum sodium 145 mEq/L, Serum potassium 3.8 mEq/L, Serum albumin 2.0 g/dl, Serum globulin 7.0 g/dl, Total serum bilirubin 0.9 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.2 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows proteinuria 4+. Which of the following glomerulopathies is more likely to be present in this patient?
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
Minimal change disease
Membranous glomerulonephritis
. Crescentic glomerulonephritis
Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
190) A 30-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of periorbital edema and abdominal distention. She has no other complaints. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 125/75 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows ascites. Urinalysis shows proteinuria; 24-hour urinary protein excretion is 4 g/day, total serum protein is 5 g/dl and serum albumin is 2.5g/dl. A diagnosis of nephrotic syndrome is made. Renal biopsy is performed. She is started on diuretics and her salt and protein intake is restricted. Her edema begins to improve. However, the patient suddenly develops severe abdominal pain, fever, and gross hematuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis that will be revealed by renal biopsy?
Minimal change disease
. Membranous glomerulonephritis
Systemic amyloidosis
Diabetic nephropathy
Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
191) A 30-year-old African American man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of periorbital edema and abdominal distention. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.7°F), blood pressure is 125/75mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. His height is 170cm (5'7") and weight is 104kg (2301bs). He has been in a drug rehabilitation program for the past 2-months, for a long history of IV drug abuse. Examination shows significant ascites. Urinalysis shows proteinuria; 24-hr urinary protein excretion is 4g/day. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Minimal change disease
Membranous glomerulonephritis
. Systemic amyloidosis
. IgA nephropathy
. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
192) A 50-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine check-up. He has no present complaints. He has diabetes mellitus, type 2, stable angina, and gout. He takes glyburide and atenolol. He smokes two packs a day and, occasionally, consumes alcohol. His father had an early myocardial infarction; his brother has diabetes mellitus. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg and heart rate is 65/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. There is concern about end organ damage in this patient due to diabetes mellitus. Which of the following is the earliest renal abnormality that could be seen in this patient?
Nodular sclerosis
Immune deposits
. Glomerular basement membrane (GBM) thickening
Glomerular hyperfiltration
Mesangial expansion
193) A 70-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a 12-hour history of inability to void. He also complains of nocturia and problems with initiating micturition for the past few weeks. He denies fever, weakness, numbness, dysuria or hematuria. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities, except absent Achilles tendon reflexes bilaterally. Straight catheterization of the bladder produces 600 ml of urine. Further evaluation will most likely show which of the following?
. Urinary tract infection
Multiple sclerosis
. Enlarged prostate
. Urinary fistula
. Carcinoma of the bladder
194) A 36-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of excruciating flank pain. The pain radiates to the groin. His temperature is 36.9°C (98.5°F), blood pressure is 115/75 mm Hg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 14/min. Urinalysis shows six RBCs/HPF. Laboratory studies show BUN of 12mg/dl and serum creatinine of 0.9mg/dl. X-ray film of the abdomen shows nephrocalcinosis and IVP shows multiple contrast filled cysts. Ultrasonogram of the kidneys is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Medullary cystic kidney
. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
. Hydronephrosis
Acquired cystic kidney disease
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
195) A 22-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of dark urine. He has had an upper respiratory tract infection for 3 days. His temperature is 37.1° C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 145/90mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show: Urinalysis: Glucose Negative, Protein 1+, Ketones Negative, Leukocyte esterase Negative, Nitrites Negative, WBC 3-6/hpf, RBC 30-50/hpf, Casts RBC. Serum chemistry: Serum Na 138 mEq/L, Serum K 4.5 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 22 mEq/L, BUN 30 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 1.8 mg/dL. Serum complement level is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. IgA nephropathy
Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease
Acute interstitial nephritis
. Benign recurrent hematuria
. Acute post-infectious glomerulonephritis
196) A 27-year-old man comes to the physician because of red urine. He has had no pain or burning on urination. He has infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis (diagnosed recently). He takes isoniazid, rifampin, and pyrazinamide. He smokes two packs a day and consumes alcohol occasionally. Vital signs are stable Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute cystitis
Nephrolithias
Renal tuberculosis
. Glomerulopathy
. Drug reaction
197) An 18-year-old girl comes to the emergency department with a rash and arthralgias. She is sexually active and has had the same sexual partner for the past 4-months. Recent medical history is significant for an episode of dysuria and increased urinary frequency, both of which started 5-days ago. Her primary care physician prescribed TMP+SMX (Bactrim) for this. She developed her present symptoms 3-days after starting the medication. Her aunt has Lupus. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows a disseminated maculopapular rash; there is no costovertebral tenderness or flank pain; serum creatinine is 2 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows 2-5 RBC/hpf, numerous white blood cell casts made mostly of eosinophils, and mild proteinuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Disseminated gonococcemia
. Lupus nephritis
. Post-infectious acute glomerulonephritis
. Pyelonephritis
Drug induced interstitial nephritis
198) A 26-year-old woman presents with a one-week history of dysuria and increased urinary frequency. She admits to having multiple sexual partners in the past. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows suprapubic tenderness. Mucopurulent discharge is observed at the urethral os. Urinalysis shows: Blood Negative, Glucose Negative, Ketones Negative, Leukocyte esterase Positive, Nitrites Negative, WBC 40-50/hpf, RBC 1-2/hpf, Bacteria None. Urine culture after 24hours < 100colonies/ml. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute pyelonephritis
Gonococcal urethritis
. Acute bacterial cystitis
Trichomonal vaginitis
Chlamydial urethritis
199) A 60-year-old man comes to the physician's office because of fatigue and hematuria. His past medical history is significant for fatty liver, gout, and anemia. He has smoked two packs of cigarettes daily for 40 years. He is a heavy alcohol drinker. His last visit to his physician was 1 month agoforthe 'flu'. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 145/90mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. Dipstick testing is positive for hematuria. Laboratory studies show: Urinalysis: Glucose Negative, Ketones Negative, Leukocyte esterase Negative, Nitrites Negative, WBC 1-2/hpf, RBC 1-2/hpf, Casts Epithelial cell. Serum chemistry: Serum Na 140 mEq/L, Serum K 5.0 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 20 mEq/L, BUN 36 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 34 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Post infectious glomerulonephritis
Bladder cancer
Hepatorenal syndrome
. Renal cell cancer
Rhabdomyolysis
200) A 50-year-old man comes to the physician because of a skin rash, joint pains, malaise and fatigue. He has a history of intravenous drug abuse. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows palpable purpura and hepatosplenomegaly. Urinalysis shows hematuria, red blood cell casts and proteinuria. The results of the laboratory studies are as follows: BUN 30 mg/dl, Creatinine 2.0 mg/dl, Serum complement Low, Anti-HCV Positive. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Alpert's syndrome
Mixed essential cryoglobulinemia
Acute interstitial nephritis
. Benign recurrent hematuria
Acute post infectious glomerulonephritis
201) A 27-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of periorbital swelling. He was treated with oral dicloxacillin for a skin infection 3-weeks ago. His urine has turned darker. His temperature is 37.4°C (99.4°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows periorbital swelling. Urinalysis shows 8 RBCs/HPF with RBC casts and a mild proteinuria. Laboratory studies show low serum C3 levels; BUN is 40 mg/dl and serum creatinine is 2 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis
. IgA nephropathy
Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
202) A 27-year-old man comes into the emergency department because of a 2-week history of hemoptysis, breathing difficulty, ankle edema, and dark urine. His past medical history is insignificant. He is not taking any medication. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Laboratory studies show: Hb 10.5 g/dl, Serum Na 135 mEq/L, Serum K 4.8 mEq/L, BUN 36 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 2.8 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows numerous dysmorphic red blood cells/HPF, moderate proteinuria, and red cell casts. Chest x-ray reveals bilateral alveolar infiltrates. Diagnosis of which of the following pulmonary-renal syndromes require emergency plasmapheresis?
. Good pasture's syndrome
. Polyarteritis nodosa
Wegener's granulomatosis
Idiopathic rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN
SLE-associated nephritis
203) A 64-year-old man is scheduled for hemodialysis due to end stage renal disease. He has a several year history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, hypercholesterolemia, peripheral vascular disease, gout, and diverticulosis. Six months ago, he was admitted for urosepsis. Recently, his haemoglobin has ranged between 8.5 to 9.5 g/dl. He has already been on iron therapy, and now you are considering erythropoietin injections twice weekly. Which of the following is most likely to be seen following erythropoietin therapy?
Worsening of his hypertension
Increased susceptibility to infections
. Increase in insulin requirement
Flare-up of gout
Deterioration in renal function
204) A 70-year-old man is brought to the hospital by his son because of worsening fatigue. His son states that his father does not like seeing doctors and has not seen a physician in the past 20 years. He has no medical problems. Physical examination of the prostate shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show: Hb 10.5 g/dl, WBC 7,400/cmm, Platelets 160,000/cmm, Serum Na 135 mEq/L, Serum K 5.0 mEq/L, BUN 50 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 3.0 mg/dl. Ultrasonogram of the abdomen shows bilateral small kidneys and no evidence of hydronephrosis. Kidney biopsy shows intimal thickening and luminal narrowing of renal arterioles with evidence of sclerosis. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's findings?
. Hypertension
. Analgesic abuse
. Diabetes mellitus
. Renal lithiasis
. Multiple myeloma
205) A 35-year-old woman who recently emigrated from Russia comes to the physician because of hematuria. She has a history of frequent headaches. Extensive evaluation did not reveal the cause of her headaches. They occur almost every day, and she tried various analgesics to relieve them. Her family history is significant for hypertension and diabetes mellitus. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg and heart rate is 80/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows numerous unchanged red blood cells/hpf. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Malignancy
. Infection
Glomerular injury
Nephrolithiasis
Papillary necrosis
206) A 55-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual physical examination. She has no new complaints, except fatigue. She has an 8-year history of chronic low back pain; severe degenerative joint disease has been documented on MRI. She had an anterior wall myocardial infarction four years ago. Her current medications include naproxen, acetaminophen, oxycodone, aspirin, atenolol, and simvastatin. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 72/min. Laboratory studies show: Hb 10 g/dl, WBC 6,000/cmm, Blood sugar 82 mg/dl, BUN 36 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 2.0 mg/dl. Urinalysis : Protein 2+, Glucose Absent, RBC AbsentWBC 10-15/HPF, Nitrite Negative, Esterase Negative, Sediment WBC casts. Serum protein electrophoresis is negative for monoclonal gammopathy. Two years ago, her BUN level was 22 mg/dl, and creatinine level was 1.6 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely pathology involved in this patient's renal failure?
Acute tubular necrosis
. Recurrent pyelonephritis
. Chronic glomerulonephritis
Renal tuberculosis
. Tubulointerstitial nephritis
207) A 50-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine follow-up visit. He has hypertension, diabetes mellitus, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and end-stage renal disease. He has been on hemodialysis for the past three years. He was admitted three months ago for line sepsis, which was treated with antibiotics. He had a right below-the-knee amputation two years ago following a non-healing foot ulcer. Physical examination shows a right carotid bruit. If this patient dies within the next five years, what would be the most likely cause of his death?
Cardiovascular disease
. Cancer
. Stroke
Withdrawal from dialysis
. Infection
208) A 15-year-old boy comes to the physician because of hematuria and lower abdominal pain. This is his third episode of hematuria in the past 2 years. He has a family history of renal disease. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows mild sensorineural deafness bilaterally. Urinalysis shows hematuria and proteinuria. Laboratory studies show BUN of 50 mg/dl and serum creatinine of 3.1 mg/dL; serum complement levels are normal. Renal biopsy shows foam cells, and immunofluorescence shows no immunoglobulins or complement. Electron microscopy shows alternating areas of thinned and thickened capillary loops with splitting of GBM. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Alport's syndrome
. Anti-glomerular basement membrane disease
Acute interstitial nephritis
. Benign recurrent hematuria
Acute post infectious glomerulonephritis
209) A 17-year-old African American man comes to the physician after an episode of gross hematuria that resolved spontaneously. He has no other complaints. His past medical history is insignificant. He takes no medications. He smokes occasionally. He does not use drugs or alcohol. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 70/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows many unchanged red blood cells/HPF, but is otherwise normal. Laboratory studies show a creatinine level of 0.9 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute glomerulonephritis
Sickle cell trait
. Acute interstitial nephritis
Coagulopathy
Acute cystitis
210) A 30-year-old woman comes to the physician due to several weeks history of generalized edema, fatigue, and decreased appetite. She has no other medical problems. She takes no medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination shows generalized edema. Laboratory studies show a low serum albumin level. HBsAg is positive, and liver function tests are abnormal. Urinalysis shows +4 proteinuria and microhematuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
. Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
Minimal change disease
Membranous glomerulonephritis
. Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
211) A 64-year-old man is admitted for hematuria after slipping on an icy pavement. His physical examination is normal. A selective angiogram of the left kidney is shown in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
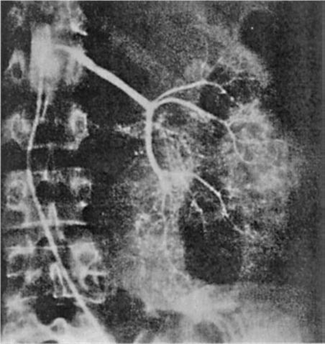
For Student DES 2016-2017 last (1)

Renal cell carcinoma
Renal hamartoma
Kidney contusion and laceration
Renal hemangioma
Transitional cell carcinoma
212) A 64-year-old man presents with weight gain, shortness of breath, easy bruising, and leg swelling. On examination, his blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg, pulse 100/min, JVP 4 cm, heart sounds normal, and lungs are clear. There is a 3+ pedal and some periorbital edema. Investigations include a normal chest x-ray (CXR), electrocardiogram (ECG) with low voltages, anemia, high urea and creatinine, and 4 g/day of protein in the urine. A renal biopsy, which shows nodular deposits that have an apple-green birefringence under polarized light when stained with Congo red. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Amyloidosis
Minimal change disease
Multiple myeloma
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy
213) A 25-year-old man is referred to you because of hematuria. He noticed brief reddening of the urine with a recent respiratory infection. The gross hematuria resolved, but his physician found microscopic hematuria on two subsequent first-voided morning urine specimens. The patient is otherwise healthy; he does not smoke. His blood pressure is 114/72 mm Hg and the physical examination is normal. The urinalysis shows 2+ protein and 10 to 15 RBC/hpf, with some dysmorphic erythrocytes. No WBC or casts are seen. What is the most likely cause of his hematuria?
. Kidney stone
. Chronic prostatitis
Renal cell carcinoma
. IgA nephropathy (Berger disease
. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
214) A 17-year-old man is brought to the emergency room with confusion and incoordination. He is uncooperative and refuses to provide further history. Physical examination reveals an RR of 30; the vital signs are otherwise normal as is the general physical examination. Laboratory values are as follows: Na: 135 mEq/L, K: 2.7 mEq/L, HCO3: 15 mEq/L, Cl: 110 mEq/L. Arterial blood gases: PO2 92, PCO2 30, pH 7.28 Urine: pH 7.5, glucose—negative, Ca: 9.7 mg/dL, PO4: 4.0 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the acid base disorder?
. GI loss owing to diarrhea
. Distal renal tubular acidosis
Proximal renal tubular acidosis
. Respiratory acidosis
Disorder of the renin-angiotensin system
215) A 28-year-old woman presents with a recent episode of coughing up some blood, frequent nosebleeds, and now decreased urine output. A nasal mucosa ulcer was seen on inspection. Her urinalysis is positive for protein and red cells consistent with a GN. The CXR shows two cavitary lesions and her serology is positive for antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Wegener’s granulomatosis
Goodpasture’s syndrome
Bacterial endocarditis
Poststreptococcal disease
Lupus erythematosus
216) A 74-year-old woman develops acute sepsis from pneumonia and is admitted to the intensive care unit because of hypotension. She is started on antibiotics, and her blood pressure is supported with intravenous normal saline. Despite this she remains oliguric and develops ARF. Her urinalysis has heme-granular casts and the urine sodium is 56 mEq/L. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her ARF?
Nephrotoxic antibiotics
Contrast nephropathy
Acute infectious GN
Cholesterol emboli
Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)
217) A 76-year-old man presents to the emergency room. He had influenza and now presents with diffuse muscle pain and weakness. His past medical history is remarkable for osteoarthritis for which he takes ibuprofen, and hypercholesterolemia for which he takes lovastatin. Physical examination reveals blood pressure of 130/90 mm Hg with no orthostatic change. The only other finding is diffuse muscle tenderness. Laboratory data include: BUN: 30 mg/dL, Creatinine: 6 mg/dL, K: 6.0 mEq/L, Uric acid: 18 mg/dL Ca: 6.5 mg/dL, PO4: 7.5 mg/dL, UA: large blood, 2+ protein. Microscopic study shows muddy brown casts and 0 to 2 rbc/hpf (red blood cells/high power field).Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced acute kidney injury (AKI)
. Urinary tract obstruction
Volume depletion
Hypertensive nephrosclerosis
Rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury
218) A 73-year-old man undergoes abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. The patient develops hypotension to 80/50 mm Hg for approximately 20 minutes during the procedure according to the anesthesia record. He received 4 units of packed red blood cells. Postoperatively, his blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, heart rate is 110, surgical wound is clean, and a Foley catheter is in place. Over the next 2 days his urine output slowly decreases. His creatinine on post-op day 3 is 3.5 mg/dL (baseline 1.2). His sodium is 140 mEq/L, K 4.6 mEq/L, and BUN 50 mg/dL. Hemoglobin and hematocrit are stable. Urinalysis shows occasional granular casts but otherwise is normal. Urine sodium is 50 mEq/L, urine osmolality is 290 mosmol/L, and urine creatinine is 35 mg/dL. The FENa (fractional excretion of sodium) based on these data is 3.5. What is the most likely cause of this patient’s acute renal failure?
Acute interstitial nephritis
Prerenal azotemia
Acute glomerulonephritis
Contrast induced nephropathy
Acute tubular necrosis
219) A 73-year-old woman with arthritis presents with confusion. Neurologic examination is nonfocal, and CT of the head is normal. Laboratory data include: Na: 140 mEq/L, K: 3.0 mEq/L, Cl: 107 mEq/L, HCO3: 12 mEq/L. Arterial blood gases: PO2 62, PCO2 24, pH 7.40. What is the acid-base disturbance?
Respiratory alkalosis with appropriate metabolic compensation
. No acid-base disorder
High anion-gap metabolic acidosis with appropriate respiratory compensation
Hyperchloremic (normal anion gap) metabolic acidosis with appropriate respiratory compensation
Combined metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
220) A 63-year-old man alcoholic with a 50-pack-year history of smoking presents to the emergency room with fatigue and confusion. Physical examination reveals a blood pressure of 110/70 mm Hg with no orthostatic change. Heart, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal and there is no pedal edema. Laboratory data are as follows: Na: 110 mEq/L, K: 3.7 mEq/L, Cl: 82 mEq/L, HCO3: 20 mEq/L, Glucose : 100 mg/dL, BUN : 5 mg/dL, Creatinine: 0.7 mg/dL Urinalysis: normal Specific gravity: 1.016. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Volume depletion
. Cirrhosis
Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone
. Congestive heart failure
Psychogenic polydipsia
221) A 65-year-old white female comes to the ER because of persistent vomiting and epigastric pain. She has been suffering from left knee osteoarthritis for the past 6 years, and has been taking ibuprofen for the past year. She also has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease but is well controlled on her current medications. She quit smoking a few years ago. Her laboratory results are given below: ABG: pH 7.55, PCO2 46 mm Hg. Chemistry panel: Serum sodium 132 mEq/L, Serum potassium 3.0 mEq/L, Chloride 88 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 38 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl. Which of the following would describe her primary acid-base status?
. Normal profile
. Respiratory acidosis
Metabolic acidosis
Respiratory alkalosis
. Metabolic alkalosis
222) A 36-year-old male is brought to the emergency department due to confusion, nausea and decreased arousal. He is unable to answer questions and no other history is available. His temperature is 36.7ׄ°C (98.2°F), respirations are 22/min and pulse is 86/min. His ABG and serum electrolyte levels are shown below: pH 7.21, PaO2 96 mmHg, PaCO2 28 mmHg, Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Serum potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Chloride 90 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 12 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 30 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.2 mg/dl. What is the most likely primary acid-base disorder in this patient?
. Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
Respiratory alkalosis
Anion gap metabolic acidosis
Respiratory acidosis
. Metabolic alkalosis
223) A 56-year-old male comes to the emergency room because of a 2-day history of fever, chills, shortness of breath and productive cough. He also threw up once in the emergency room. He has been smoking for several years and occasionally drinks alcohol. On admission, his BP was 90/60, but with one liter of normal saline it improved to 120/80 mm Hg. His temperature is 38.8°C (102°F). His arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is as follows: Blood pH 7.53, PaO2 70 mmHg, PaCO2 30 mmHg, HCO3- 22 mEq/L. Which of the following best describes his primary acid-base status?
Respiratory acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Respiratory alkalosis
Normal acid base status
. Metabolic acidosis
224) A 67-year-old male is brought to the ER because of increasing abdominal pain and nausea for the past few hours. He has multiple medical problems including type-2 diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, peripheral vascular disease, ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation. He has not been on anticoagulation because of recurrent bleeding peptic ulcer disease. He has had a cholecystectomy. He takes multiple medications at prescribed doses and lives at home with his family. He quit smoking 10 years ago and does not use alcohol or drugs. His temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination shows an elderly male in acute distress. Lungs have few crackles at the bases. Heart rate is irregular. Bowel sounds are decreased and diffuse tenderness is present. There is no peripheral edema. Initial laboratory studies show the following: Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Chloride 103 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 14 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 20 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Blood glucose 198 mg/dl, Amylase 255 U/L. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Diabetic ketoacidosis
. Acute pancreatitis
Bowel ischemia
Peptic ulcer perforation
. Acute appendicitis
225) A 56-year-old male with a history of type-2 diabetes presents for a routine office visit. His blood work from two months ago showed hyperkalemia, and at that time his physician discontinued lisinopril. His repeat blood work done today is shown below: Chemistry panel: Serum sodium 136 mEq/L, Serum potassium 5.6 mEq/L, Chloride 110 mEq/L,Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 26 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.9 mg/dl. He currently takes glipizide, furosemide, nifedipine and aspirin. His blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg. Examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his low bicarbonate and elevated potassium?
Chronic renal failure
. Glipizide
. Renal tubular acidosis
. Nifedipine
Furosemide
226) A 33-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room because of altered mental status. En route to the ER, she suffers a generalized tonic clonic seizure, and once at the hospital she is confused and no further history can be obtained. You know only that she has a history of schizophrenia. On physical examination, her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows normal pupils. Her chest is clear to auscultation and her heart sounds are normal. Her abdomen is soft and nontender. Extremities have no edema. Laboratory studies show: Serum sodium 118 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dL, Serum calcium 8.4 mg/dL, Serum glucose 98 mg/dL, Urine osmolality 100 mosm/kg, Urine specific gravity 1.002. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Primary polydipsia
. Drug-induced water retention
Drug-induced ADH resistance
Deficient ADH secretion
Increased ADH production
227) A 56-year-old male comes to the emergency room because of increasing shortness of breath for the last 3 days. He had a cold recently, and since then his symptoms have been worse. He has a mild productive cough but denies fever or chills. He has a several year history of smoking and has been diagnosed with emphysema. He also has a history of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and hypothyroidism. He takes glipizide, metformin, lisinopril, furosemide, aspirin, atorvastatin and levothyroxine. Physical examination shows trace bilateral lower extremity edema and a diffuse decrease in breath sounds along with wheezing. Heart sounds are distant. His arterial blood gas shows the following: Blood pH 7.23, PaO2 88mm Hg, PaCO2 40 mm Hg, HCO3- 16mEq/L. Which of the following best describes the acid-base status of this patient?
Metabolic acidosis
Mixed metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
Respiratory acidosis
. Normal acid-base balance
Mixed metabolic and respiratory acidosis
228) A 45-year-old male is brought to the emergency department in a stuporous state. He appears agitated and disoriented. His temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), respirations are 22/min, pulse is 90/min and blood pressure is 110/70 mm of Hg. His lab findings are as follows: Blood pH 7.21, PaO2 100 mmHg, PaCO2 30 mmHg, HCO3- 13 mEq/L, Serum osmolarity 350 mOsm/L, Blood glucose 90 mg/dl, Na+ 141 mEq/L, K+ 4.6 mEq/L, Cl- 100 mEq/L, BUN 28mg/dl, Creatinine 2.5 mg/dl. His urine shows the presence of rectangular, envelope-shaped crystals. His creatinine three months ago was 1.2 mg/dl. What is the most likely cause of this lab abnormality in this patient?
. Aspirin ingestion
. Uremic acidosis
Ethylene glycol poisoning
. Lactic acidosis
. Methyl alcohol poisoning
229) A 21-year-old female comes to the office for the evaluation of fatigue and weakness. She first noticed these symptoms nine months ago. She says, "I can't exercise a lot anymore because I get fatigued very easily, but after resting for a while, I feel better, and my fatigue disappears." She then describes a recent episode of weakness while swimming in a pool, where she experienced double vision (especially when she did not look straight ahead), difficulty raising her eyelids, and swallowing problems. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
. Multiple sclerosis
. Myasthenia gravis
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Brain tumor
230) A 27-year-old woman presents to the ER with severe vomiting and abdominal pain that started several hours ago. She describes her emesis as "yellowish." She has a history of alcohol and cocaine use. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 98/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 140/86 mmHg. Physical examination reveals dryness of the oral mucosa. Her abdomen is soft, non-distended, and without hepatosplenomegaly. Mild epigastric tenderness is present on deep palpation. Bowel sounds are increased. No rebound or rigidity is noted. She is treated with intravenous normal saline and metoclopramide. Several hours later she complains of neck pain and her neck muscles are noted to be stiff and tender. Which of the following best explains this patient's current complaints?
Meningeal irritation
. Eosinophilic myositis
. Fat necrosis
Nerve root compression
Medication side effect
231) A 55-year-old Caucasian male comes to the office because of numerous falls for the past few weeks. Yesterday, he felt so dizzy that he fell on the ground and hurt his knees. He has also noticed dry mouth, dry skin, and erectile dysfunction over this period. His past medical history is significant for the recent onset of resting tremors. He was diagnosed with diabetes six months ago, which is controlled with diet. His blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg supine, and 90/60 mmHg standing. Physical examination reveals rigidity and bradykinesia. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
. Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension
Diabetic neuropathy
Horner's syndrome
Shy-Dragger syndrome
Familial dysautonomia (Riley-Day syndrome
232) A 65-year-old, obese, white female comes to the office for the evaluation of her progressively worsening memory. She considers herself "very independent," and lives alone; however, the development of her new symptoms is causing her some distress, as she often forgets to pay her bills. A detailed review of systems reveals no other symptoms, except for mild urinary incontinence. She has hypertension controlled with a beta-blocker and type 2 diabetes mellitus controlled with diet. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her blood pressure is 130/90 mmHg, pulse is 72/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 14/min. Lungs are clear to auscultation and percussion. A grade 2/6, systolic ejection murmur is heard. Abdominal examination shows no tenderness or masses. Neurological examination shows broad-based, shuffling gait and a right-sided carotid bruit. Complete blood count and serum chemistry panel are within normal limits MRI shows enlarged ventricles. What is the most likely diagnosis
Parkinsonism
Pick's disease
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Alzheimer's disease
Multi-infarct dementia
233) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the clinic for a routine health maintenance exam. He has no complaints, but mentions some spots on his back, which he noticed during his physical education class. He does not know how long they have been there. He denies any allergies. He remembers having a few seizures some years ago, which have not recurred since. He does not take any medication. The physical examination reveals several white spots and nodules measuring 2x3 cm on his back. There are freckles on his face and axilla. Closer examination reveals some nodules on his iris. What is the concerning complication that this boy is prone to?
Hemoptysis
. GI bleed
. Pancreatitis
Early dementia
. Tumors
234) A 25-year-old woman comes to the office and complains of intermittent dizziness and an unsteady gait for the last few days. Her symptoms worsen with exercise. Her past medical history is significant for tingling and numbness of her right foot that lasted 3-4 days (1 year ago), and visual loss in her right eye which spontaneously resolved (3 years ago). She is currently nursing her 2-month-old baby. Her obstetrical history was uncomplicated. Her neurological examination shows right hyperactive deep tendon reflexes. On attempted left gaze, her left eye abducts and exhibits horizontal jerk nystagmus, but her right eye remains stationary. When she attempts to look to the right, her right eye abducts and exhibits horizontal jerk nystagmus, but her left eye remains stationary. The patient is able to converge both eyes together, without any associated nystagmus. The facial muscles show no signs of weakness. Where is the most likely site of this patient's lesion?
. Optic nerve
Optic radiations
. Optic tract
Medial longitudinal fasciculus
. Optic chiasma
235) A 60-year-old male complains of recent onset gait imbalance and visual illusion of to-and-fro environmental motion. The symptoms are constant. He has no associated nausea or vomiting. His past medical history includes diabetes, hypertension, and chronic renal failure, and recent enterococcal endocarditis for which he is taking ampicillin and gentamicin. On physical examination, his temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Neurologic examination shows 5/5 power and 2+ reflexes in all four extremities. Cranial nerve examination is normal. There is no nystagmus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
Drug toxicity
. Meniere's disease
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Cerebellar infarction
. Hypoglycemia
236) A 63-year-old accountant is brought to the emergency department after suddenly collapsing at his desk at work. He is unconscious upon arrival but regains consciousness within several minutes. His medical history is significant for stable angina, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. He has had no surgeries. His medications include atenolol, simvastatin, aspirin, and a multivitamin. Physical examination is remarkable for paralysis of the upper and lower extremities on the right side. Vibration and position sense are absent on the right side. When the flat of the right foot is stroked with a pen, the right great toe is up going and the other toes fan out. The patient's tongue deviates to the left upon protrusion. Given these findings, a lesion in which region of the brain is most likely?
. Lateral pons
. Medial medulla
. Medial pons
. Central midbrain
Lateral medulla
237) A 60-year-old white male is brought to the physician's office for the evaluation of worsening confusion and memory loss for the past three weeks. His other complaints are muscle twitching and gait problems. He denies any fever, headache or urinary problems. He does not drink nor smoke. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.1°C (98.7°F). He displays poor grooming and is disoriented. The pertinent physical findings are nystagmus and positive extensor plantar response bilaterally. The laboratory studies are as follows: Hematocrit 40%, WBC 6,000/microl, Platelets 160,000/microl. A non-contrast head CT scan is normal. The EEG shows periodic sharp waves. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
. Pseudodementia
. Multi-infarct dementia
Alzheimer disease
238) A 70-year-old retired engineer is brought to the office by his son for a routine check-up. He believes that his son is too greedy and wants all his property. He is accusing his son of "kicking him out of the house to get all of his property." He has been getting more forgetful over the past few years. His younger sibling has the same problem. He has no significant past medical history, except a history of smoking for 6 years when he was young. His blood pressure is 138/78 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, respirations are 14/min and temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). He cannot remember current events, such as the name of the current American president; however, he can still remember past political history. He is unable to concentrate, but is oriented to time, place and person. The neurological examination is nonfocal. CT scan reveals mild generalized atrophy. His HIV and RPR tests are negative. The serum electrolytes and thyroid function tests are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
Lewy body dementia
. Neurosyphilis
Alzheimer's dementia
. Pick's disease
Multi Infarct dementia
239) A 54-year-old man comes to your office complaining of recurrent headaches. While observing his gait as part of your neurologic examination, you notice that he very prominently flexes his right hip and knee and his right foot slaps to the floor with each step. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this gait abnormality?
. Corticospinal tract lesion
L5 radiculopathy
Basal ganglia lesion
Tarsal tunnel syndrome
Cerebellar dysfunction
240) A 33-year-old female presents to the office for the evaluation of a one-week history of lightning-like pain on the left side of her face. The pain is very sharp and feels like a burn. An episode lasts for 10 seconds, occurs 10-20 times a day, and keeps her from sleeping, eating, or working. She denies any history of trauma; medication use or recent surgery Vital signs are within normal limits. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Maxillary sinusitis
Herpes zoster
Carotidynia
Burning mouth syndrome
Trigeminal neuralgia
241) A 72-year-old woman complains of difficulty "finding the right word" when she is speaking. Her daughter notes that she also frequently complains that her neighbor is stealing her newspapers when this is not the case in actuality. Recently, the patient has been having difficulty balancing her check book as well. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and her heart rate is 90/min. The exam is otherwise unremarkable. Over the course of the next three years, the patient develops a severe memory deficit, and suffers from poor sleep, slowness of movement, shuffling gait and urinary incontinence. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Alzheimer's dementia
Vitamin B12 deficiency
. Dementia with Lewy bodies
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Multi-infarct dementia
242) A 32-year-old man presents to your office with blurred vision in his right eye. He denies any pain, ocular discharge, or gritting sensation. Physical examination findings include anisocoria, right-sided ciliary injection, mild ptosis, and impaired right eye adduction. Fluorescein examination reveals a large geographic corneal staining defect. Dysfunction of which of the following nerves is most likely responsible for this patient's impaired corneal sensation?
. Optic
Trigeminal
. Oculomotor
Vagal
. Facial
243) An 86-year -old known hypertensive woman is brought to the emergency department due to weakness of her left side, confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech for the last 2 hours. Her past medical history is significant for an inferior wall myocardial infarction 12 years ago, chronic atrial fibrillation, and severe backache secondary to osteoarthritis. She is currently on aspirin, warfarin, losartan, indomethacin, atenolol, and simvastatin. She doesn't go to anticoagulation clinic regularly. Her blood pressure is 180/110 mm Hg, temperature is 38°C (100°F), respirations are 16/min, and pulse is 70/min, irregularly irregular. The pertinent physical findings are: carotid bruit on both sides, 2/5-muscle strength in the left arm and leg, and slurred speech. Her deep tendon reflexes are exaggerated on the left side, and the Babinski sign is positive. EKG reveals atrial fibrillation. Her CT scan (performed in the ED) is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
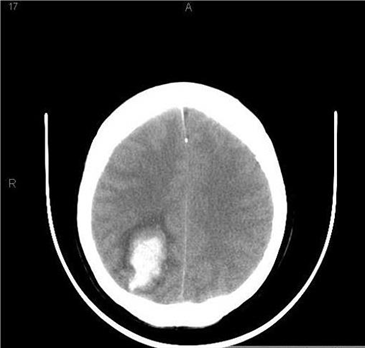
For Student DES 2016-2017

Cerebral haemorrhage
Lacunar infarction
Cerebellar hemorrhage
Subarachnoid haemorrhage
. Cerebral infarction
1) A 40-year-old man is brought to the emergency room because of altered mental status and gait instability. He has had two falls in the last two days. He drinks one pint of vodka daily and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. His temperature is 35.0°C (95.0°F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 14/min. He is disoriented, but not in acute distress. You note prominent horizontal nystagmus and conjugate gaze palsy in both eyes and absent ankle reflexes in both legs. His chest is clear to auscultation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Viral encephalitis
Cerebellar infarction
. Thiamine deficiency
. Opioid intoxication
Hypothyroidism
2) A 16-year-old boy is recommended for admission to the neurology department for rapidly deteriorating clinical symptoms. He is a college student, living in a dormitory. During past week, he was sick. He did not recover fully and during last 3 days, his condition deteriorated. He started to have high fever, terrible headaches. His roommate said he talked about "some foolish happenings" during his high fever, and did not remember what he said later. This morning, he vomited repeatedly and his condition deteriorated rapidly. You examined him and found: febrile man in acute distress with cyanotic pallor, petechiae on his trunk and legs, purpura on his back bilaterally, with cold extremities. He is still alert, but has clammy skin, rapid pulse and labored respiration. His meningeal signs are positive. You diagnose this patient with meningococcal meningitis with systemic progression and you fear that he can develop the Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome. What characterizes this syndrome?
Acute adrenal insufficiency
Otitis media and sinusitis
Obstructive hydrocephalus
. Brain abscess
. Endocarditis and myocarditis
3) A 67-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office three weeks after having an ischemic stroke. She complains of transient pain in the right upper and lower limbs that can be induced even by light touch. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension and diabetes mellitus, type 2. Her current medications include enalapril, amlodipine, aspirin, and glyburide. She has right hemianesthesia due to the stroke and mild athetosis of the right hand. The strength is preserved in all four extremities. Hypersensitivity to all kinds of stimuli that induce severe pain reaction is present over the right extremities. Which of the following is the most probable location of the stroke experienced by this patient three weeks ago?
Internal capsule
Medulla
Thalamus
Left post-central cortex
Mid-brain
4) A 43-year-old man presents to your office complaining of periodic involuntary head turning and head fixation to the right side. Physical examination reveals a hypertrophied right sternocleidomastoid muscle. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Parkinson's disease
. Akathisia
. Essential tremor
Dystonia
. Chorea
5) A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of right arm weakness. He says that he first noticed the weakness two hours ago when he was unable to grip a pen. He is now unable to shake hands and walks with a mild limp. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and mild headaches over the past several days. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 180/100 mmHg, heart rate is 80/min and regular. There is mild asymmetry of the lower face, decreased muscle strength in the right arm, and an extensor plantar reflex on the right side. Sensory examination is normal. Blood glucose level is 210mg/dL. ECG shows sinus rhythm with occasional ventricular premature beats. His urine is negative for ketones and protein. Non-contrast CT scan of the head does not reveal any abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Migraine-associated vascular spasm
Cardiac embolism
Carotid artery thrombosis
. Brain tumor
Small vessel hyalinosis
6) A 30-year-old, HIV-positive male, presents with left-sided paralysis of recent onset. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/80, and respirations are 16/min. The neurological examination reveals loss of recent memory, expressive aphasia, hyperreflexia, hypertonia, and up going plantars on the left side. His current medications include zidovudine, didanosine, indinavir and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. His CD4 count is 70/dl and viral load is 90,000 copies/ml by PCR. The serology is positive for Toxoplasma. CT scan shows multiple, hypodense, non-enhancing lesions with no mass effect in the cerebral white matter. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Cerebral toxoplasmosis
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
. Primary CNS lymphoma
. AIDS dementia complex
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
7) A 64-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office because he has had two falls within the last month. He states that he loses his balance when he tries to turn or stop suddenly while walking. Recently, he says, it has been taking him quite a while to get himself out of bed. He also complains of hand tremors that started last year in his left hand, but that now have been affecting both hands. Which of the following is the best tool to confirm his diagnosis?
. Physical examination
Electroencephalography
Lumbar puncture
Nerve conduction studies
. CT scan of the head
8) A 60-year-old male presents to the office and complains of muscle weakness in his extremities. Other accompanying symptoms include progressive difficulty in performing weight-carrying tasks, and a 7 kg (15 lb) weight loss during the last three months. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes daily, and consumes alcohol occasionally. His muscle strength is 3/5 in the proximal muscle groups symmetrically. His reflexes are normal. No sensory abnormality is present. Chest x-ray reveals a right lower lobe ill-defined mass. Which of the following is the most likely localization of the pathologic process in this patient?
Peripheral nerves
Muscle membrane
. Presynaptic membrane
. Spinal cord
. Postsynaptic membrane
9) A 47-year-old obese female comes to the office for the evaluation of recent episodes of mood instability. Her mood varies between sad and irritable. She denies any other symptoms, except for some mild forgetfulness. She tearfully shares that she is convinced that she is going to die, as her father also developed similar symptoms around the same age and died subsequently. On physical examination, writhing movements of the extremities are prominent. This patient's clinical presentation is most consistent with
. Alzheimer's disease
Hypothyroidism
Pseudodementia
Pick's disease
Huntington's disease
10) A 70-year-old Caucasian male is brought to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of right-sided weakness and urinary incontinence about ten hours ago. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes for the last 20 years and hypertension for the last 28 years. On examination, there is 3/5 power in the right upper extremity and 1/5 power in the right lower extremity. Babinski's sign is positive on the right side. The sensations are decreased on the right side of the body, more so in the right lower limb than the right upper limb. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lacunar stroke
. Left middle cerebral artery stroke
Anterior cerebral artery stroke
Posterior cerebral artery stroke
. Right middle cerebral artery stroke
11) A 32-year-old woman describes five episodes of intractable vomiting over the last year. The episodes last several hours and are associated with a sensation that the room is spinning or tilting. At these times, it is difficult for her to walk because she loses her balance. She cannot relate the timing of the episodes to any particular inciting event. Physical examination reveals stability in the Romberg position and during tandem walk. Proprioception is intact. Dysfunction of which of the following structures best explains this patient's symptoms?
Posterior columns of the spinal cord
Inner ear
Vagal nerve
Cerebellum
Optic tract
12) A 45-year-old white male presents with a 4-month history of headaches. The headache is generalized, dull, constant, and worsened by bending, coughing and sneezing. It is unresponsive to simple analgesics, and associated with nausea and vomiting. His wife says he has been acting strangely for the last few months, and she has noted a personality change. The neurological examination is non-focal. Fundoscopy reveals papilledema. His CT scan is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis
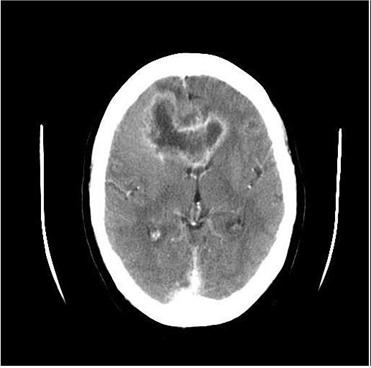
For Student DES 2016-2017 last (1)

. Brain abscess
. Glioblastoma multiforme
. Metastatic brain tumor
Low-grade astrocytoma
Cerebral infarction
13) A 35-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department at 2 am because of severe pain 'behind the left eye' which woke him up in the middle of the night. The pain is intense and has a stabbing quality. He took ibuprofen at home but didn't get any relief. He denies fever, chills, decreased or blurred vision, cough, nausea or vomiting. He has no other medical problems. He drinks 3-4 bottles of beer daily. He has no known drug allergies. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min and respirations are 14/min. The examination is unremarkable, except for left-sided ptosis and miosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Migraine headache without aura
. Sinus headache
. Migraine headache with aura
. Cluster headache
Brain tumor
14) A 63-year-old Asian-American woman presents to the ER with a severe right-sided headache that started one hour ago. The pain is located "all around my eye." She has vomited once since the pain began. She also says that bright light aggravates the pain and she complains of seeing "halos" around light. She has never had a headache like this before. Her only medication is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, which she has been taking for the last two days for a urinary tract infection. Her mother has a history of migraine headaches. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. On exam, she is afebrile with a pulse of 90/min. Physical exam reveals a non-reactive, dilated right pupil and erythematous right eye. There is lacrimation present. The remainder of examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies reveal an ESR of 40 mm/hr. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Meningitis
Cluster headache
. Subarachnoid bleeding
. Migraine without aura
Angle closure glaucoma
15) A previously healthy 8-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because he has multiple staring episodes. During these episodes, he is unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli, and produces lip-smacking movements. Each episode lasts for a few minutes, after which he remains confused for some time. He has no family history of any seizure disorder. His neurological examination is unremarkable. EEG performed before and after hyperventilation is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Complex partial seizure
Atypical absence seizure
Typical absence seizure
. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
16) A 1-year-old female infant is brought to the clinic by his 30-year-old mother due to feeding problems since birth. She still cannot walk nor speak. She began to sit when she was 8 months old. Her weight is in the 15th percentile, height is in the 20th percentile, and head circumference is in the 100th percentile for her age. She has multiple freckles in her armpit and groin area. She has cafe-au-lait spots on her skin, and the diameter of at least 20 of these spots is greater than 1 5mm. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Neurofibromatosis type 2
. Normal development
. Down syndrome
. Neurofibromatosis type 1
. Fetal alcoholic syndrome
17) A 33-year-old Caucasian female comes to the office and complains of occasional diplopia and ptosis. These symptoms become especially prominent when she looks above her head for some time. She also complains of fatigue in her hands and leg muscles after exercising, such as swimming. Her muscle strength and double vision returns to normal after resting for some time. On examination, lid lag is observed after she is asked to look above her head for some time. No pupillary involvement is seen. The rest of the examination is normal. What is the level of the lesion in the disease that is being described?
. Neuromuscular junction
Muscle contraction
Nerve conduction
Autonomic nervous system
Corticospinal tract
18) A 25-year-old, HIV-positive male presents to the office with an altered mental status. He is disoriented, lethargic, and has loss of recent memory. These symptoms have been present for the last month. His current medications include zidovudine, didanosine, indinavir, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and azithromycin. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/80mm Hg, and respirations are 16/min. The neurological examination is non-focal. His CD4 count is 40/microl and viral load is 25,000 copies/ml by PCR. MRI scan reveals a solitary, irregular, weakly ring-enhancing mass in the periventricular area. The serology for Toxoplasma is positive. PCR of CSF shows EBV DNA. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Cerebral toxoplasmosis
. AIDS dementia complex
Primary CNS lymphoma
Bacterial abscess
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
19) A 33-year-old Canadian female presents to the office with severe, bilateral, lightning-like pain on her face. The pain is burning and sharp in nature, occurs 20-30 times a day, and each episode lasts a few seconds. She is completely incapacitated by this pain. Prior to this event, she had weakness in her left arm, which gradually improved. She denies any history of trauma or drug use. She has no other medical problems. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 72/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 14/min. Complete neurologic examination shows no focal deficits. This type of disorder is most commonly seen in which of the following?
. Parkinson disease
. Aseptic meningitis
. Huntington chorea
Transient ischemic attack
Multiple sclerosis
20) A 33-year-old white man with a 9-year-history of progressive-relapsing multiple sclerosis is brought to the emergency department (ED) due to a severe flare-up. He has had several attacks before, and has recovered every time with some residual damage. The last physical examination in his medical records revealed cerebellar symptomatology, a visual defect, and central hemiparesis on the right side. MRI showed multiple, bright, signal abnormalities in the white matter supratentorially on the left side, in the cerebellum, and the left optic nerve. CSF examination revealed an increased synthesis of oligoclonal bands. In the ED, the physical examination reveals paraplegia, bladder and fecal incontinency, and absent sensation from the nipples down. What is the most likely location of this patient's new plaque?
. Cerebellum
Lower thoracic spinal cord
Posterior columns
Supratentorially
. Upper thoracic spinal cord
21) A 37-year-old homeless man complains of weakness in his right arm. He says that he was smoking a cigarette when the weakness developed, causing the cigarette to fall from his hand. He also reports having mild headaches, fatigue, and chills over the last week. He admits to regular intravenous heroin use and binge drinking. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. There is asymmetry of the lower face, decreased muscle strength in the right arm, and an extensor plantar reflex on the right side. He has multiple needle tracks on his arms. ECG shows sinus rhythm with occasional ventricular premature beats. Urinalysis shows 2+ proteins. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Migraine-associated vascular spasm
. Brain tumor
. Carotid artery thrombosis
. Cerebral emboli
Small vessel hyalinosis
22) A 45-year-old man comes to the office for the evaluation of excessive wasting of his extremity muscles, which is more apparent on the extensor side. The weakness began distally and asymmetrically. He recently started to have difficulties with swallowing, chewing, and speaking. He feels some movements in his face and tongue. He also has muscle stiffness. His bowel, bladder, cognitive, and sensory functions are intact. The physical examination reveals excessive wasting of his muscles, which is more prominent in the lower extremities. Fasciculation and hyperreflexia of all extremities are noted. His bulbar reflexes are decreased. What neural pathway is most likely damaged?
. Pyramidal tract
Lower and upper motor neuron
Lower motor neuron
Cerebral cortex
Upper motor neuron
23) A 40-year-old Caucasian male comes to the emergency department because he is having "the worst headache" of his life. The headache is of sudden onset, and associated with nausea and vomiting. He denies any fever and trauma to head. He is not taking any medications. He has a history of migraine headaches. The neurological examination is non-focal. CT scan of the head without contrast is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's headache?
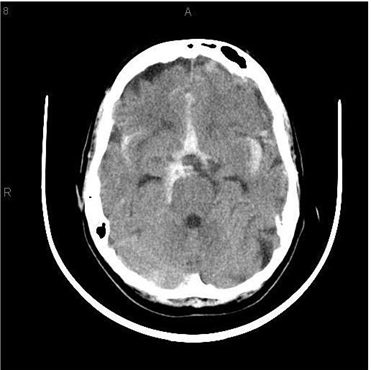
For Student DES 2016-2017 last (1)

. Hypertension
Extension of primary intracerebral hemorrhage
Rupture of saccular aneurysm
Amyloid angiopathy
Rupture of AV malformation
{"name":"DES part2 episode 6", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"167) A 22-year-old male student presents with an acute onset of fever, double vision, and painful swelling around his eyes. He also has significant muscle pain in his neck and jaw muscles. A week earlier, he experienced a period of abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, all of which resolved spontaneously. He has a history of intravenous drug abuse but has recently completed of a drug rehabilitation program. He is febrile. Physical examination shows \"splinter\" hemorrhages, periorbital edema, and chemosis. Chest is clear to auscultation. Cardiac exam reveals no murmur. Abdomen is soft and nontender with no organomegaly. His complete blood count is shown below: Hemoglobin 13.0 g\/L, MCV 85 fl, Platelets 228,000\/mm3, Leukocyte count 10,500\/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 21%, Lymphocytes 23%. Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?, 168) A 19-year-old woman comes to the physician because of fever, joint pain, and rash. The rash started on her face and is spreading down her body. She has pain in her fingers, wrists, and knees. She denies any neck stiffness, nausea, or vomiting. She has been sexually active with multiple partners. Her vaccination status is unknown. Her pulse is 86\/min, blood pressure is 125\/75 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F). Physical examination reveals a maculopapular rash on her face and chest. Posterior auricular, cervical, and suboccipital lymphadenopathy is present. She has mild conjunctivitis. Oropharynx is clear. Chest is clearto auscultation. What is the most likely diagnosis?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}
More Quizzes
Switching Protocols (STP, RSTP, MSTP)
50250
Personality: Are you moody?
630
SCI10_Theory of Plate Tectonics Quiz
10565
Die Resilienz (Quiz)
10514
Test Your Skills with This Cisco Networking Now!
201029824
Think You Know Wine? Take Our Wine Challenge!
201053723
Free APHG Practice Tests: Units 3, 4, 5 & 7
201024099
Is 6/7 a Rational Number? Take Our Free!
201057972
Cell Cycle and Mitosis: Can You Ace It? Free Challenge
201079687
Which BTS Ship Are You? Take the Ultimate Shipping
201028241
I, Robot: Can You Ace Asimov's Robot Trivia?
201026089
Philosophic Inquiry in Mus Ed
15827113