Astronomy Test 3
Which of the following correctly shows tidal bulges on Earth when the Moon is in the position shown?
0%
0
0%
0
0%
0
0%
0
The highest tides of a month occur......
At New Moon and Full Moon
At Waxing Crescent and Waning Crescent
At 1st Quarter and 3rd Quarter
At Waxing Gibbous and Waning Gibbous
Lines of a particular element appear at the same wavelength in both emission and absorption line spectra.
True
False
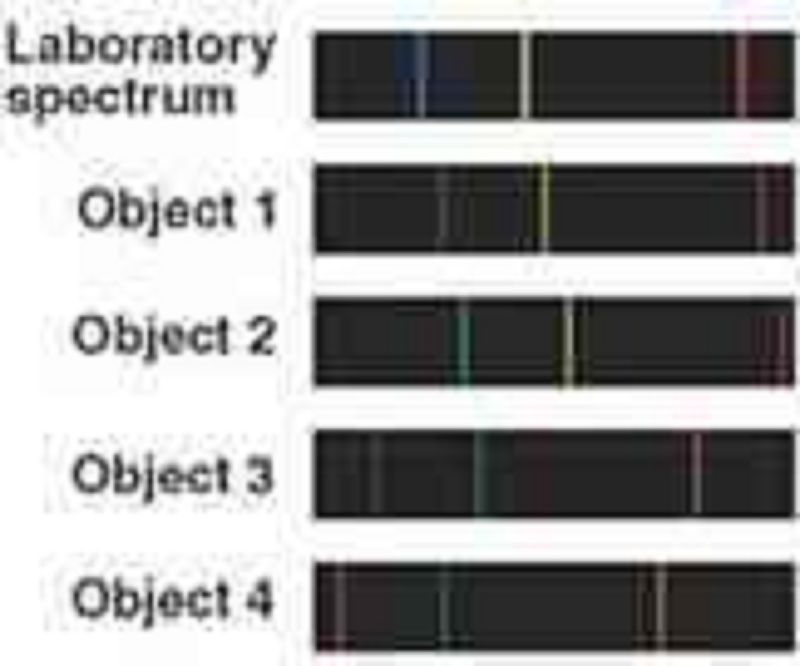

Consider the spectra of the four objects shown beneath the laboratory spectrum. Based on these spectra, what can you conclude about Object 3?
It is a star with a thin upper atmosphere.
It is moving away from us.
It is moving toward us.
It is composed mostly of hydrogen, helium, and iron.
It is a very hot object, with a temperature above 1 million K.
Suppose that Star X and Star Y both have redshifts, but Star X has a larger redshift than Star Y. What can you conclude?
Star X is hotter than Star Y.
Star X is moving away from us and Star Y is moving toward us.
Star X is coming toward us faster than Star Y.
Star X is moving away from us faster than Star Y.
Star Y is moving away from us faster than Star X.
Consider an atom of carbon in which the nucleus contains 6 protons and 7 neutrons. What is its atomic number and atomic mass?
Atomic number = 13; atomic mass number = 6
Atomic number = 7; atomic mass number = 13
Atomic number = 6; atomic mass number = 13
Atomic number = 6; atomic mass number = 7
If you heat a gas so that collisions are continually bumping electrons to higher energy levels, when the electrons fall back to lower energy levels the gas produces
An absorption line spectrum.
Thermal radiation.
Radio waves.
X-rays.
An emission line spectrum.
From laboratory measurements, we know that a particular spectral line formed by hydrogen appears at a wavelength of 121.6 nanometers (nm). The spectrum of a particular star shows the same hydrogen line appearing at a wavelength of 121.8 nm. What can we conclude?
The star is getting colder.
The "star" actually is a planet.
The star is moving toward us.
The star is getting hotter.
The star is moving away from us.
What is the purpose of adaptive optics?
It allows ground-based telescopes to observe ultraviolet light that normally does not penetrate the atmosphere.
It reduces blurring caused by atmospheric turbulence for telescopes on the ground.
It allows several small telescopes to work together like a single larger telescope.
It is a special technology that allows the Hubble Space Telescope to adapt to study many different types of astronomical objects.
The stars in our sky twinkle in brightness and color because of _______.
Turbulence in Earth's atmosphere
Rapid changes in the brightnesses and colors of stars caused by changes in their spectra
The bubbling and boiling of gases on the surfaces of stars
Light pollution
The spectra of most galaxies show redshift. This means that their spectral lines _________.
Have wavelengths that are longer than normal
Always are in the red part of the visible spectrum
Have wavelengths that are shorter than normal
Have a higher intensity in the red part of the spectrum
Suppose you want to know the chemical composition of a distant star. Which piece of information is most useful to you?
The wavelengths of spectral lines in the star's spectrum.
The peak energy of the star's thermal radiation
Whether the star's spectrum has more emission lines or more absorption lines
The Doppler shift of the star's spectrum
According to the laws of thermal radiation, hotter objects emit photons with _________.
A lower average frequency
A lower average energy
A shorter average wavelength
A higher average speed
The Chandra X-ray Observatory must operate in space because
X-ray telescopes require the use of grazing incidence mirrors
It was built by NASA.
X-rays are too dangerous to be allowed on the ground.
X-rays do not penetrate Earth's atmosphere.
Suppose you see two stars: a blue star and a red star. Which of the following can you conclude about the two stars? Assume that no Doppler shifts are involved. (Hint: Think about the laws of thermal radiation)
The red star is more massive than the blue star.
The blue star is farther away than the red star.
The blue star has a hotter surface temperature than the red star.
The blue star is more massive than the red star.
The red star has a hotter surface temperature than the blue star.

Which of the six numbered features represents emission lines>
1
2
3
4
5
6

Which of the six features represents absorption lines?
1
2
3
4
5
6

Which portion(s) of the spectrum represent(s) reflected sunlight?
1 only
2,3, and 4
3 and 6
The entire spectrum

What does the wavelength of the peak labeled 6 tell us about Mars?
Its orbital speed
Its surface temperature
Its chemical composition
Its color

What feature(s) of this spectrum indicate(s) that Mars appears red in color?
The wavelength of the peak labeled 3
The wavelength of the peak labeled 6
The fact that the intensity of region 4 is higher than that of region 2
The fact that the peak labeled 3 is higher than the peak labeled 6
The atomic nuclei of the same element always have the same number of protons.
True
Falso
The study of energy levels in atoms is called
Particle physics.
Classical mechanics.
Quantum mechanics.
Special relativity.
General relativity.
When an electron in an atom goes from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, the atom
Absorbs a photon of a specific frequency.
Can absorb a photon of any frequency.
Absorbs several photons of a specific frequency.
Can emit a photon of any frequency.
Emits a photon of a specific frequency.
The energy levels for electrons vary from one element to another.
True
False
Which of the following wavelength regions cannot be studied with telescopes on the ground?
Radio waves
Ultraviolet
X rays
Both ultraviolet and X rays
Both radio waves and X rays
Which of the following statements best describes the difference between a refracting telescope and a reflecting telescope?
It is much easier to make a large refracting telescope than a large reflecting telescope.
Reflecting telescopes make much clearer images than can refracting telescopes of the same size.
A refracting telescope uses a transparent glass lens to focus light while a reflecting telescope uses a mirror to focus light and allows telescopes to be shorter.
The Hubble Space Telescope obtains higher-resolution images than most ground-based telescopes because it is:
Larger.
Closer to the stars.
Above Earth's atmosphere.
What do astronomers mean by light pollution?
Light pollution refers to the lights that must be used inside major observatories and that make it difficult for astronomers' eyes to adapt to darkness.
Light pollution refers to light used for human activities that brightens the sky and hinders astronomical observations.
Light pollution is another name for sunlight, which makes it impossible to see stars in the daytime.
Light pollution refers to harmful gases emitted by common street lights.
Light pollution refers to pollution caused by light industry as opposed to heavy industry.
Which of the following is not an advantage of the Hubble Space Telescope over ground-based telescopes?
Stars do not twinkle when observed from space.
It never has to close because of bad weather.
Observers on the ground can use it at any time of day (i.e., not only during their night).
It can observe infrared and ultraviolet light, as well as visible light.
It is closer to the stars.
Which of the following wavelength regions can be studied with telescopes on the ground?
All light with wavelengths longer than ultraviolet wavelengths
Xray and gamma ray
All light with wavelengths shorter than infrared wavelengths
Radio and visible
Shown following are five different colors of visible light that travel to Earth from the Sun. Rank these colors of visible light from left to right based on the altitude in the atmosphere where they are completely absorbed, from highest to lowest (Earth’s surface). If two (or more) of the choices reach the surface, rank them as equal by dragging one on top of the other(s).
Shown following are six different types of light that travel to Earth from sources in space. Rank these types of light from left to right based on the altitude in the atmosphere where they are completely absorbed, from highest to lowest (Earth's surface). If two (or more) of the choices reach the same altitude or the surface, rank them as equal by dragging one on top of the other(s). (x rays, most ultraviolet light, most infrared light, green visible light, most radio waves)
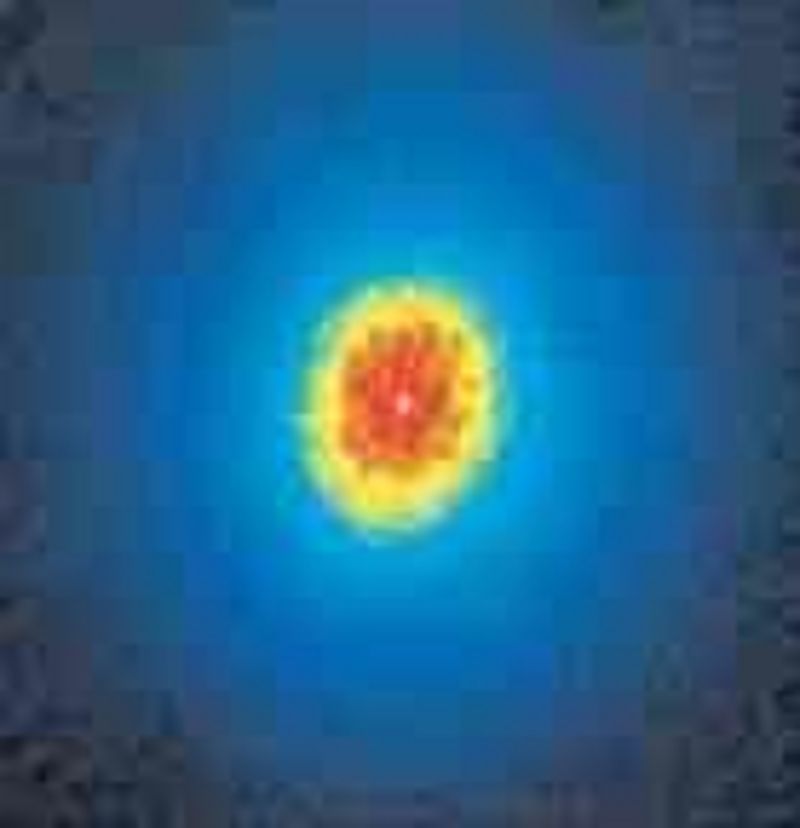

The first telescopic photo shows what appears to be a single star. The second photo shows the same object now revealed to be two distinct stars. What is the difference between the two photos?
The second photo comes from a radio telescope, whereas the first photo comes from a visible-light photo.
The second photo has better (smaller) angular resolution than the first photo.
The second photo was taken with a telescope that has greater light-collecting area.
The second photo was taken by two telescopes rather than one.
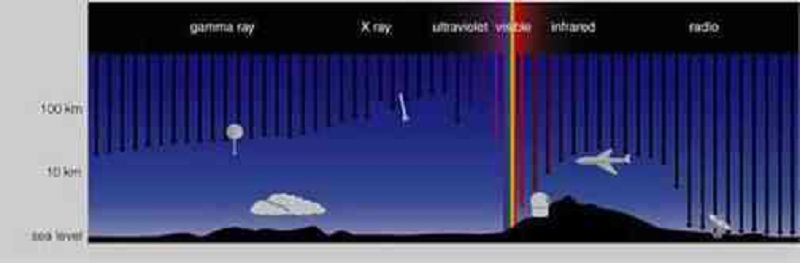
The diagram shows the approximate depths to which different wavelengths of light penetrate Earth's atmosphere. Why does it show an airplane?
Telescopes on airplanes are better than telescopes on the ground for both visible-light and infrared observations.
The airplane is just decorative, indicating that astronomers use airplanes to fly to ground-based observatories.
Airplanes are useful for astronomical observations at all wavelengths of light that do not reach the ground.
Much of the infrared spectrum can be observed from an airplane that flies above the clouds.
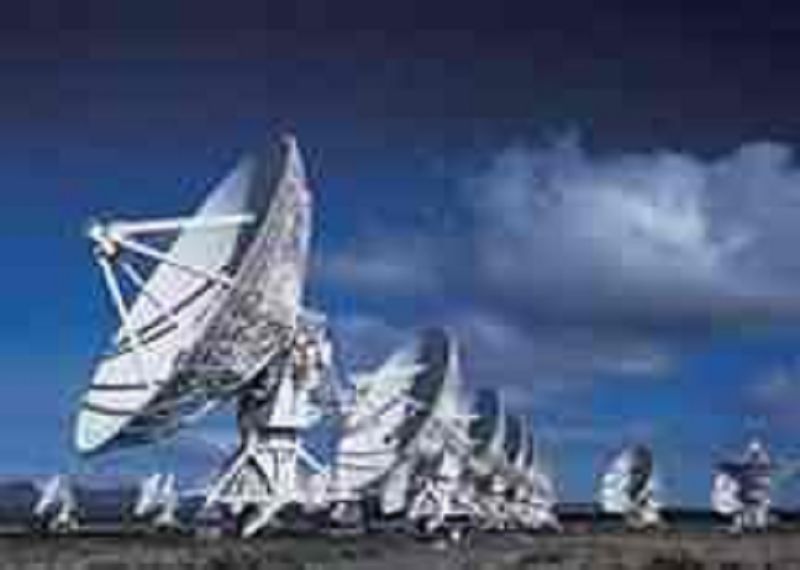

What kinds of light are these telescopes designed to detect?
Radio waves
X rays
Ultraviolet light
Light with extremely short wavelengths
Infrared and visible light
Select the two most important properties of telescopes below:
Adaptive optics and light collecting areas
Adaptive optics and spectral resolution
Adaptive optics and angular resolution
Light collecting area and spectral resolution
Light collecting area and angular resolution
Spectral resolution and angular resolution
What does the technique of interferometry allow?
It allows the same telescope to make images with both radio waves and visible light.It allows the same telescope to make images with both radio waves and visible light.
It allows us to determine the chemical composition of stars.
It allows two or more telescopes to obtain a total light-collecting area much larger than the total light-collecting area of the individual telescopes.
It allows astronomers to make astronomical observations without interference from light pollution.
It allows two or more telescopes to obtain the angular resolution of a single telescope much larger than any of the individual telescopes.
True or False? Gravity waves are a higher frequency form of light than gamma rays.
True
False
True or False? Gravity waves travel at the speed of light
False
True
Gravity waves were predicted more than 100 years ago by who?
Isaac Newton
Niels Bohr
Galileo
Albert Einstein
Rank the forms of light from left to right in order of increasing frequency. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. (visible light, gamma rays, radio waves, ultraviolet, x rays, and infrared)
Rank the forms of light from left to right of increasing energy. To rank items as equivalent, overlap them. (visible light, gamma rays, radio waves, ultraviolet, x rays, and infrared)
What do we mean when we say that energy levels are quantized in atoms?
We mean that the electrons can have only continuous electrical potential energy in atoms.
We mean that the electrons can have only discrete values of electrical potential in atoms.
We mean that the photons can have only discrete values of electrical potential energy in atoms.
We mean that the photons can have only continuous values of electrical potential energy in atoms.
What is demonstrated by the double slit experiment?
That the same pattern results for one slit as for two slits
That light is actually just a particle
That the speed of light is constant
That light is actually just a wave
That light has both wave and particle properties
What role does measurement have in quantum mechanics?
Measurements can trigger a system to take one of it allowed quantum states
Measurement can reveal which quantum state a system was in before the measurement was made.
Measurement has no special role in quantum mechanics.
A quantum of light is called.....
A nucleon
A phonon
A photon
A proton
Which statement is a description of quantum entanglement?
The quantum states of entangled particles exists even before any measurement is made.
The quantum state of one particle instantaneously determines the quantum states of its entangled particle even if it is far away.
The quantum state of one particle determines the quantum state of its entangled particle, but there is a delay while they communicate at the speed of light.
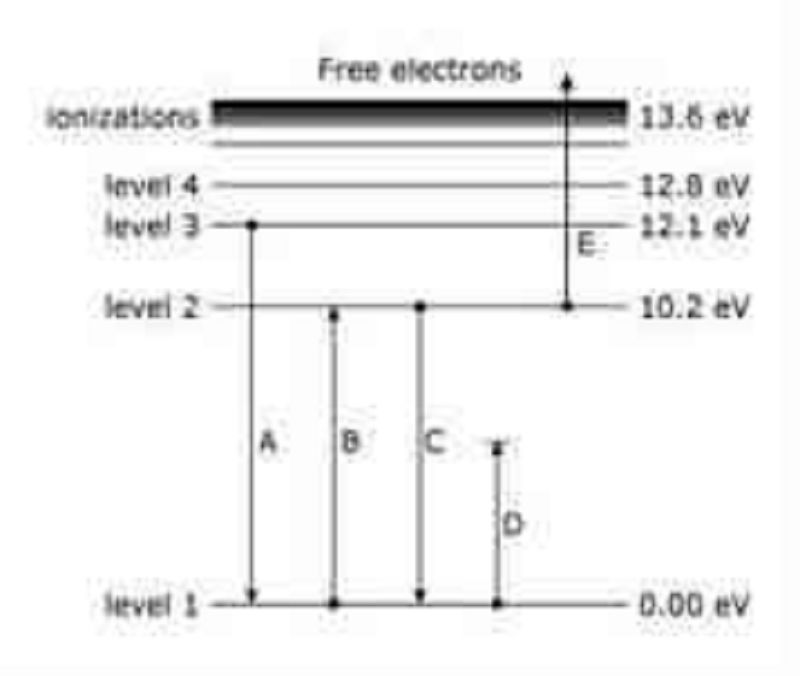
The diagram represents energy levels in a hydrogen atom. The labeled transitions (A through E) represent an electron moving between energy levels. Which labeled transition represents an electron that absorbs a photon with 10.2 eV of energy?
B
A
C
D
E
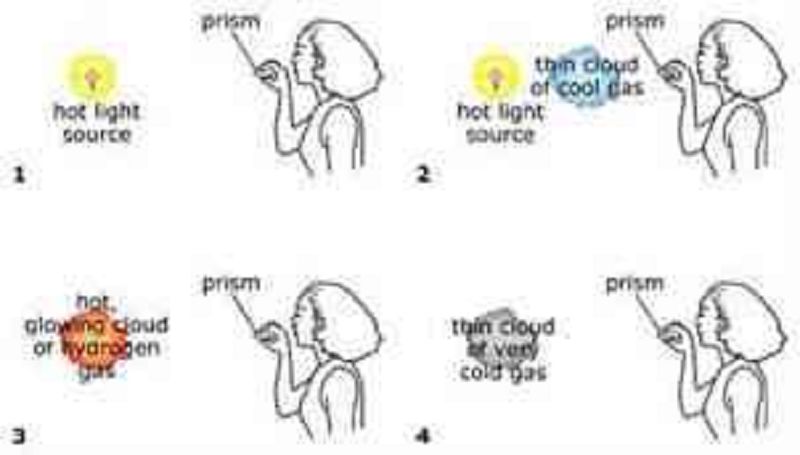
In the figure, assume the woman in each case uses her prism to look at a spectrum of light coming from the object(s) shown. In which case will she see a continuous rainbow of thermal radiation?
1
2
3
4
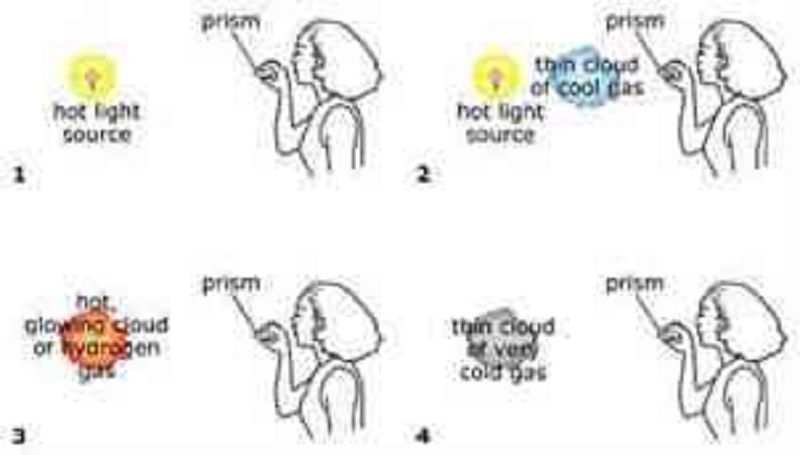
In which case will the woman see a rainbow of color interrupted by a few dark absorption lines?
1
2
3
4
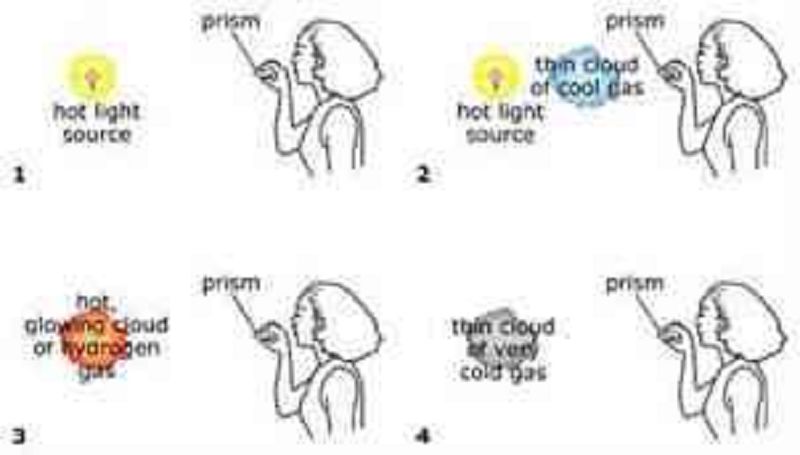
In which case will the woman see a just a spectrum that is almost entirely black except for a few bight emission lines?
1
2
3
4
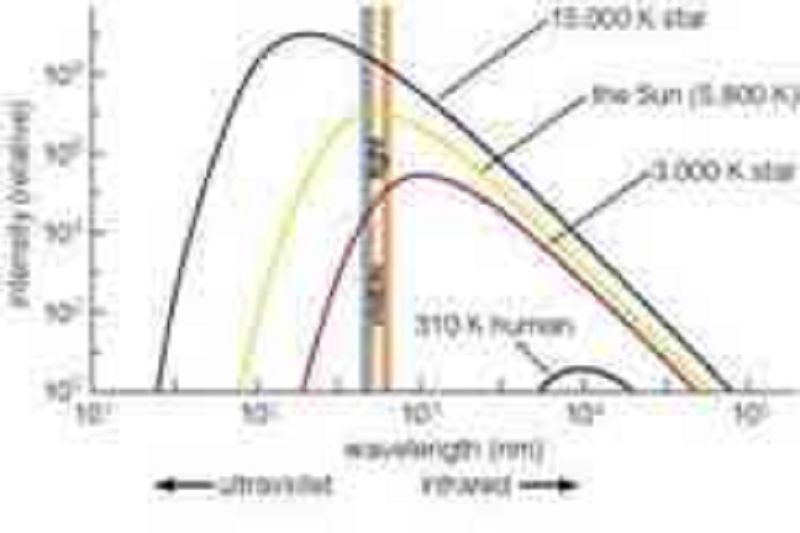

This figure shows idealized thermal radiation spectra from several stars and a human. Based on this graph, at about what wavelength does a 15,000 K star emit its most intense light?
About 100,000 nanometers
About 100 nanometers
About 1,000 nanometers
About 20 nanometers
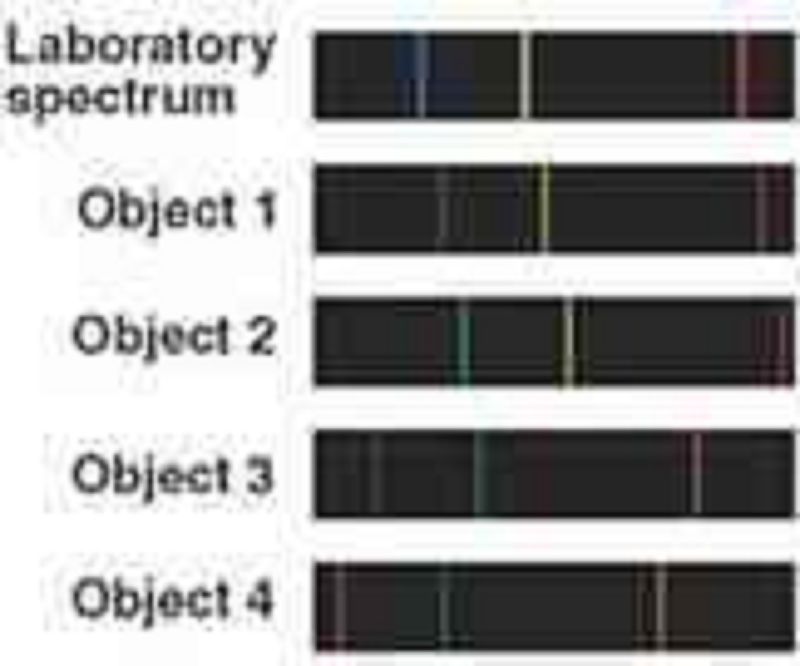

Consider the spectra of the four objects shown beneath the laboratory spectrum. Based on these spectra, what can you conclude about object 1.
It is a star with a thin upper atmosphere
It is a hot object, with a temperature above 1 million K.
It is composed mostly of hydrogen, helium, and iron.
It is moving toward us.
It is moving away from us.
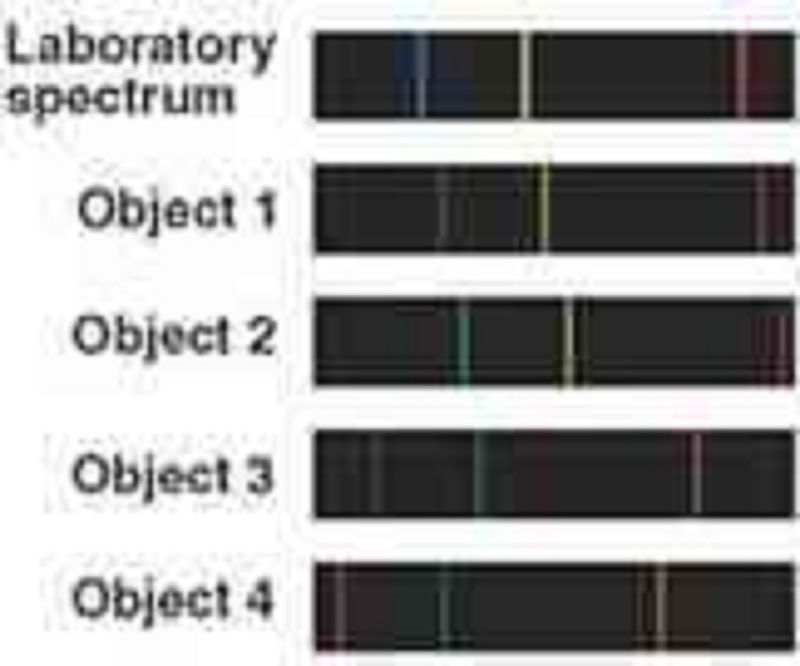

Now consider Object 2. What can you say about Object 2 in comparison to Object 1?
Object 2 is moving toward us while Object 1 is moving away from us.
Object 1 had a higher temperature than Object 2.
Object 2 contains more hydrogen than Object 1.
Object 2 is moving away from us faster than Object 1.
At extremely high temperatures (e.g., millions of degrees), which of the following best describes the phase of matter?
A gas of rapidly moving molecules
A plasma consisting of positively charged ions and free electrons
A gas consisting of individual, neutral atoms, but no molecules
A plasma consisting of rapidly moving, neutral atoms
None of the above (At these extremely high temperatures, matter cannot exist.)
Atomic nuclei consist of protons and electrons.
True
False
Thermal radiation is defined as
Radiation in the form of emission lines from an object.
Radiation produced by a hot object.
Radiation that depends only on the emitting object's temperature.
Radiation in the infrared part of the spectrum.
Radiation that is felt as heat.
{"name":"Astronomy Test 3", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Which of the following correctly shows tidal bulges on Earth when the Moon is in the position shown?, The highest tides of a month occur......, Lines of a particular element appear at the same wavelength in both emission and absorption line spectra.","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/27-1008227/q3.jpg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
How Healthy is my BDSM Relationship?
15846
Which Character is Your Perfect Match from Twelfth Night?
4251
The Tiger Rising Chapter 4 Vocabulary
4251
145720
UK Business & Finance News - Free Online
201016077
Chemistry IQ Test - Solids, Liquids & Gases
201021762
Doctor Who Trivia - How Well Do You Know the Whoniverse?
201017691
SQL Skills Test - Free MS SQL Server Assessment
201018973
Shrek Trivia - Test Your Movie Knowledge for Free
201016859
Quick Math Test - Rapid Arithmetic Challenge (Free)
201018415
Asia Geography - Map of Asia Challenge (Free)
201018043
General Maintenance Test - Free Practice Questions
201020046