DES C_Diagnosis (10) Prepared : CHILLY
A 60-year-old female comes to your office for progressive exertional dyspnea and new-onset ankle swelling. She has been recently worked up for proteinuria and easy bruisability. Otherwise her past medical history is insignificant. She has a ten pack-year history of smoking and she drinks two to three glasses of wine every day. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), blood pressure is 130/70 mmHg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 14/min. There is mild jugular venous distention on physical examination. Chest auscultation shows scattered bibasilar crackles. Echocardiography reveals symmetrical thickening of the ventricular walls, normal ventricular dimensions and a slightly reduced systolic function. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Alcohol-related heart disease
Hemochromatosis
Constrictive pericarditis
Sarcoidosis
Amyloidosis
A 60-year-old Hispanic female is brought to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of worsening, left-sided hemiplegia, which was followed by a headache and altered mental status. She was taking her regular morning walk when she developed these symptoms. Her past medical history is remarkable for uncontrolled essential hypertension. She has been a chronic smoker for the last 30 years. The neurological examination shows flaccid paralysis on the left side, and deviation of eyes towards the right side. The CT scan is consistent with a hemorrhagic stroke. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Putamen haemorrhage
Pontine hemorrhage
Cerebellar hemorrhage
Subarachnoid haemorrhage
Ventricular haemorrhage
A 60-year-old male complains of recent onset gait imbalance and visual illusion of to-and-fro environmental motion. The symptoms are constant. He has no associated nausea or vomiting. His past medical history includes diabetes, hypertension, and chronic renal failure, and recent enterococcal endocarditis for which he is taking ampicillin and gentamicin. On physical examination, his temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Neurologic examination shows 5/5 power and 2+ reflexes in all four extremities. Cranial nerve examination is normal. There is no nystagmus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
Drug toxicity
Hypoglycemia
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Meniere's disease
Cerebellar infarction
A 60-year-old male is admitted to the hospital because of right lower lobe pneumonia. His medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, severe degenerative disease of the spine, and longstanding lower back pain. He is a chronic smoker with a 40-pack year smoking history. During his hospitalization, the laboratory report shows decreased serum calcium levels and increased phosphate levels. Further evaluation reveals increased serum intact parathyroid hormone levels. Which of the following medical conditions is most likely responsible for this patient's abnormal lab findings?
Lung cancer
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Renal failure
Thyroidectomy
Plasma cells in marrow
A 60-year-old male presents to the office and complains of muscle weakness in his extremities. Other accompanying symptoms include progressive difficulty in performing weight-carrying tasks, and a 7 kg (15 lb) weight loss during the last three months. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes daily, and consumes alcohol occasionally. His muscle strength is 3/5 in the proximal muscle groups symmetrically. His reflexes are normal. No sensory abnormality is present. Chest x-ray reveals a right lower lobe ill-defined mass. Which of the following is the most likely localization of the pathologic process in this patient?
Peripheral nerves
Presynaptic membrane
Postsynaptic membrane
Muscle membrane
Spinal cord
A 60-year-old male with a history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, asthma, and cigarette smoking undergoes emergent laparotomy for a perforated peptic ulcer. He receives 4 liters of intravenous normal saline intraoperatively. Following the procedure, he is extubated without complication, but subsequently develops respiratory distress. Immediate arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows: PaO2 60mmHg, pH 7.46, PaCO2 37mmHg, HCO3 22mmHg. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F) and blood pressure is 126/76 mm Hg. Lung auscultation reveals bilateral rales. His arterial blood gas fails to improve with administration of 100% oxygen. What is the most likely cause of his respiratory distress?
Excessive anesthesia
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary edema
Exacerbation of bronchial asthma
Aspiration pneumonia
A 60-year-old man comes to the physician's office because of fatigue and hematuria. His past medical history is significant for fatty liver, gout, and anemia. He has smoked two packs of cigarettes daily for 40 years. He is a heavy alcohol drinker. His last visit to his physician was 1 month agoforthe 'flu'. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 145/90mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows no abnormalities. Dipstick testing is positive for hematuria. Laboratory studies show: Urinalysis: Glucose Negative, Ketones Negative, Leukocyte esterase Negative, Nitrites Negative, WBC 1-2/hpf, RBC 1-2/hpf, Casts Epithelial cell. Serum chemistry: Serum Na 140 mEq/L, Serum K 5.0 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 20 mEq/L, BUN 36 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 34 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Post infectious glomerulonephritis
Hepatorenal syndrome
Rhabdomyolysis
Renal cell cancer
Bladder cancer
A 60-year-old man complains of anal itching and discomfort, particularly toward the end of the day. He works as a salesman in a department store, where he has to be on his feet all day. When he goes home in the evening, he finds himself sitting sideways to avoid the discomfort. He has no fever, rectal bleeding, or soiling of his underwear, and he has never had surgery in that area. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anal fissure
External hemorrhoids
Fistula in ano
Perirectal abscess
Internal hemorrhoids
A 60-year-old man presents to the emergency department after being awoken from sleep by severe pain in his right great toe. He reports that his toe is suddenly swollen and very tender to touch. On review of systems, the patient also describes occasional headaches and pruritus that can be "unbearable" after a hot bath. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. On physical examination, his lungs are normal. The liver span is 10 cm and the spleen is palpable 2 cm below the costal margin. Aspiration of the affected toe joint reveals negatively birefringent crystals. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
Chronic kidney disease
Hemochromatosis
Inherited enzyme deficiency
Hyperparathyroidism
Myeloproliferative disorder
A 60-year-old otherwise healthy woman presents to her physician with a 3-week history of severe headaches. A contrast CT scan reveals a small, circular, hypodense lesion with ringlike contrast enhancement. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Brain abscess
Parenchymal hemorrhage
High-grade astrocytoma
Metastatic lesion
Toxoplasmosis
A 60-year-old Vietnam war veteran comes for his annual examination. He does not have any complaints, other than getting tired very quickly. Physical examination reveals pallor and an enlarged spleen. CBC reveals: WBC 14,000/cmm, Hemoglobin 9.9 g/dL, Hematocrit 30%, Platelets 100,000/cmm. The lymphocytes have fine, irregular cytoplasmic projections. Cytochemical testing reveals a strong acid phosphatase reaction, which is not inhibited by tartaric acid. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Lymphoblastic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia
Chronic myeloid leukemia
Hodgkin's disease
A 60-year-old white male is brought to the physician's office for the evaluation of worsening confusion and memory loss for the past three weeks. His other complaints are muscle twitching and gait problems. He denies any fever, headache or urinary problems. He does not drink nor smoke. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.1°C (98.7°F). He displays poor grooming and is disoriented. The pertinent physical findings are nystagmus and positive extensor plantar response bilaterally. The laboratory studies are as follows: Hematocrit 40%, WBC 6,000/microl, Platelets 160,000/microl. A non-contrast head CT scan is normal. The EEG shows periodic sharp waves. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
Alzheimer disease
Pseudodementia
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Multi-infarct dementia
A 60-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of severe pain in her left eye with blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. The symptoms began a few minutes ago, while she was watching a movie in a nearby theatre. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 98.4°F. Examination reveals decreased visual acuity. Her left eye appears red, with a hazy cornea, shallow anterior chamber, and dilated, fixed pupil. Her left eye is stony hard to touch. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Primary open angle glaucoma
Conjunctivitis
Acute angle closure glaucoma
Anterior uveitis
Corneal abrasion
A 60-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual examination. She has no complaints. She had her last menstrual period at age 55 and has had no vaginal bleeding since. She has no medical problems and has never had surgery. She takes no medications and has no allergies to medications. The physical examination is unremarkable. She is concerned about cancer and wants to know which type is the major cause of cancer death in women. Which of the following is the correct response?
Breast cancer
Cervical cancer
Endometrial cancer
Lung cancer
Ovarian cancer
A 60-year-old woman complains of decreasing vision and a dull ache over her left eye for the past 12 hours. She had a successful surgical cataract extraction in her left eye five days ago. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.1°C (101.7°F). Examination of the left eye reveals a swollen eyelid, edematous conjunctiva, and exudates in the anterior chamber. Testing with Snellen's chart demonstrates decreased visual acuity in her left eye. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Conjunctivitis
Uveitis
Corneal ulceration
Postoperative endophthalmitis
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
A 60-year-old woman is transferred to a physician from an outside hospital following a motor vehicle collision. Her medical history is notable for Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome. She is otherwise healthy. Which of the following triads is most likely to characterize her medical history prior to the collision?
Venous stasis, hypercoagulability, and endothelial damage
Telangiectasia, recurrent epistaxis, and positive family history
Symptoms of hypoglycemia, low blood sugar, and relief with increase in blood sugar
Jaundice, fever, and right upper quadrant pain
Hypertension, bradycardia, and irregular respirations
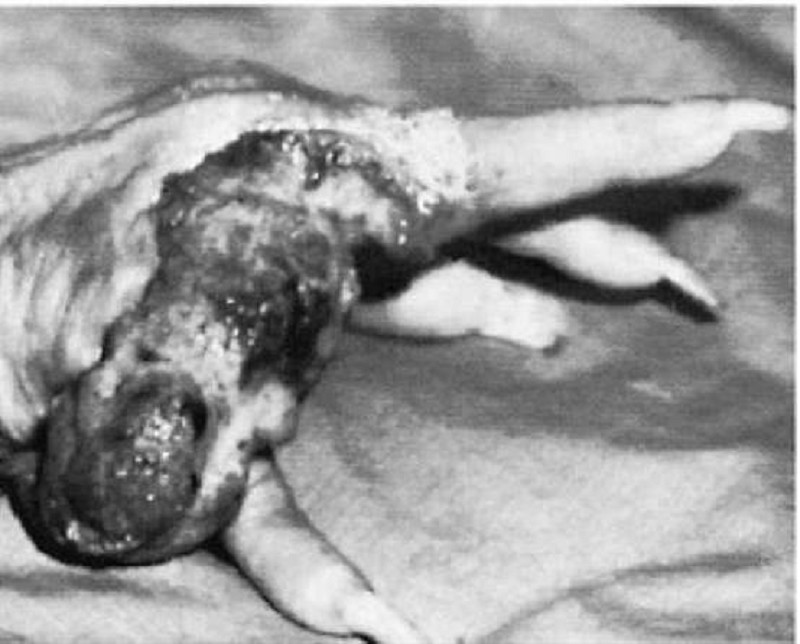
A 60-year-old woman presents with the skin lesion shown here. She reports a history of a burn injury to the hand while cooking a few years ago. She reports the wound has never healed completely. You are concerned about the skin lesion and perform a punch biopsy. Which of the following is the most accurate diagnosis given the patient’s history?
Basal cell carcinoma
Erythroplasia of Queyrat
Bowen disease
Marjolin ulcer
Malignant melanoma
A 61-year-old alcoholic man presents with severe epigastric pain radiating to his back. His amylase and lipase are elevated, and he is diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. Over the first 48 hours, he is determined to have 6 Ranson’s criteria, including a PaO2 less than 60 mm Hg. His chest x-ray reveals bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, and his wedge pressure is low. Which of the following criteria must be met to make a diagnosis of adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
Lack of improvement in oxygenation with administration of a test dose of furosemide
Presence of a focal infiltrate on chest x-ray
A pulmonary capillary wedge pressure greater than 18 mm Hg
Hypoxemia defined as a PaO2 of less than 60 mm Hg
Hypoxemia defined as a PaO2/FiO2 ratio of less than 200
A 61-year-old man with severe three-vessel coronary disease and diabetes mellitus is scheduled for abdominal surgery. The patient has a long history of coronary disease and had a q-wave myocardial infarction 2 years ago. He has had type 1 diabetes mellitus for 12 years. His medications include atenolol, insulin, and captopril. His last hemoglobin Alc, 3 months ago, was 9.2%. Which of the following is the most predictive of a perioperative complication in this patient?
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) on ECG
Recent shortness of breath
Poor exercise tolerance
Recent myocardial infarction (MI)
Use of a beta blocker in the preoperative period
A 61-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department drowsy and disoriented, able only to follow simple commands. On examination her abdomen is distended and nontender, her skin has a yellow hue, and there are multiple spider nevi on her chest. In her purse, the physician finds prescriptions for peginterferon and ribavirin. When asked to raise her hands, the physician notices a coarse tremor. Laboratory tests show: Blood urea nitrogen: 17 mg/dL Creatinine kinase: 1.1 mg/dL Aspartate aminotransferase: 89 U/L Alanine aminotransferase: 93 U/L Total bilirubin: 3.1 mg/dL Ammonia: 124 μg/dL Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bleeding esophageal varices
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatorenal syndrome
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
A 62-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office because of a non-productive cough that is 'quite disturbing.' The cough has been present for several weeks. He visited your office two times before for poorly controlled hypertension, and was started on lisinopril. He usually takes aspirin, amlodipine, and metoprolol. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 130/90 mmHg and heart rate is 60/min. Physical examination reveals a bruit over the right carotid artery, but is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaint?
Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis
Low level of circulating catecholamines
Inhibition of beta-adrenoreceptors
Increased serum renin level
High kinin level
A 62-year-old Caucasian man presents to your office with occasional ear pain and a lump in his neck. His past medical history is significant for hypertension treated with hydrochlorothiazide and diabetes mellitus treated with metformin. He smokes two packs of cigarettes per day and consumes alcohol occasionally. He is not sexually active. Physical examination reveals a hard, non-tender submandibular mass that is 3 cm in diameter. Chest examination is unremarkable. Abdomen is soft and non-tender. The liver span is 8 cm and the spleen is not palpable. His extremities have no cyanosis, clubbing, or edema. Complete blood count is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaint?
Bacterial infection
Herpes simplex infection
Squamous cell carcinoma
Connective tissue disease
Hodgkin's lymphoma
A 62-year-old Caucasian woman complains of difficulty remembering important dates and appointments. She also describes poor concentration, daytime sleepiness and easy fatigability. She is concerned about her forgetfulness because her mother suffered from recurrent strokes and had severe memory loss. Her father died of chronic leukemia. Her daughter's recent job loss has caused her a lot of stress. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her appetite is decreased but she has gained 4 pounds over the last three months. She visited an otolaryngologist for hoarseness of recent onset. She takes over- the-counter laxatives for constipation and occasional aspirin for knee pain. She denies any other medication use. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Alzheimer's dementia
Multiinfarct dementia
Hypothyroidism
Normal pressure hydrocephalus
Dementia with Lewy bodies
A 62-year-old male is brought to the ER after passing out at work. He reports having had difficulty walking over the past couple of days due to an infected wound on his right foot. His past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 80/40 mm Hg and his heart rate is 120/min, regular. His skin is cold and clammy. Right heart catheterization is performed, and the following readings are obtained: Right atrial pressure 18 mmHg, Pulmonary artery pressure 40/20 mmHg, Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure 9 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Aortic dissection
Myocardial infarction
Pulmonary embolism
Hypovolemic shock
Septic shock
A 62-year-old male treated for hypertension and hyperlipidemia complains of nagging right knee pain that is worse in the evening. The pain has been present for several months and it seems to limit his physical activities. His blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 70/min. His BMI is 32 kg/m2, and palpation of the knee reveals a cool joint with bony tenderness. His blood cholesterol level is 200 mg/dl and his serum uric acid level is 9.0 mg/dl. Which of the following additional findings is likely on further examination of the right knee?
Soft tissue swelling
Palpable popliteal mass
Painful tibial tuberosity
Bony crepitus
Subcutaneous nodules
A 62-year-old man complains of perineal discomfort and reports that there are streaks of fecal soiling in his underwear. Four months ago, he had a perirectal abscess drained surgically. Physical examination shows a perineal opening in the skin lateral to the anus, and a cord-like tract can be palpated going from the opening toward the inside of the anal canal. Brownish purulent discharge can be expressed from the tract. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anal fissure
Anorectal carcinoma
Fistula-in-ano
Pilonidal cyst
Thrombosed hemorrhoids
A 62-year-old man has been diagnosed by endoscopic biopsy as having a sigmoid colon cancer. He is otherwise healthy and presents to your office for preoperative consultation. He asks a number of questions regarding removal of a portion of his colon. Which of the following is most likely to occur after a colon resection?
The majority (> 50%) of normally formed feces will comprise solid material
Patients who undergo major colon resections suffer little long-term change in their bowel habits following operation
Sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate will be absorbed by the colonic epithelium by an active transport process
The remaining colon will absorb less water
The remaining colon will absorb long-chain fatty acids that result from bacterial breakdown of lipids.
A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision where he suffered serious burns. On physical examination there are second degree burns covering both upper extremities and third degree burns over the anterior aspects of both lower extremities. On day three of his hospitalization, the patient develops tachycardia and decreased urine output. His blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, temperature is 95°F (35°C), and respirations are 26/min. Laboratory analysis reveals: Blood glucose 230 mg/dL, WBC 16,000/mm3, Platelets 80,000/mm3. Which of the following is the best explanation for this patient's current condition?
Extensive protein breakdown
Bacterial infection
Myocardial injury
Immune reaction to heterologous proteins
Renal glomerular injury
A 62-year-old man presents to his primary care physician's office with progressive exertional dyspnea. His past medical history is significant for hypertension treated with hydrochlorothiazide and diabetes mellitus treated with metformin. He was an industrial worker for 30 years and retired one year ago. He smokes one pack of cigarettes per day and consumes alcohol occasionally. His blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. His BMI is 31 kg/m2. Chest x-ray reveals pleural calcifications. Pulmonary fun
Impaired lung expansion due to pleural calcifications
Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
Impaired lung expansion due to obesity
Interstitial lung disease from occupational exposure
Emphysema from smoking
A 62-year-old man presents with a 3-month history of an enlarged lymph node in the left neck. He is a long-time smoker of cigarettes and denies fevers, night sweats, fatigue, or cough. On physical examination there is a 1.5 cm hard, fixed mass below the angle of the mandible in the left neck. Which of the following is the most likely cause of an enlarged lymph node in the neck?
Thyroglossal duct cyst
Carotid body tumor
Dermoid tumor
Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
Branchial cleft cyst
A 62-year-old man with a history of hypertension presents to the ED with severe constant mid-epigastric pain for the past hour. Over the last several months, he has had intermittent pain shortly after eating, but never this severe. He states he now has generalized abdominal pain that began suddenly about 15 minutes ago. He has no history of trauma, has never had surgery, and takes no medications. His vitals include HR of 115 beats per minute lying supine, increasing to 135 when sitting up, BP of 170/105 mm Hg supine, falling to 145/85 mm Hg when sitting up. He appears pale. His abdomen is rigid and diffusely tender with guarding and rebound. Bowel sounds are absent and stool hemoccult is positive. The white blood cell (WBC) count is 8500/μL, hemoglobin 8.5 mg/dL, hematocrit 27%, and platelets 255/μL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Boerhaave syndrome
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)
Perforated gastric ulcer
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Diverticulosis
A 62-year-old man with chronic schizophrenia is brought to the emergency room after he is found wandering around his halfway house, confused and disoriented. His serum sodium concentration is 123 meq/L and urine sodium concentration is 5 meq/L. The patient has been treated with risperidone 4 mg/day for the past 3 years with good symptom control. His roommate reports that the patient often complains of feeling thirsty. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
Renal failure
Addison disease
Psychogenic polydipsia
Nephrotic syndrome
Inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (ADH) secretion
A 62-year-old woman had an abdominal hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy 3 days ago. She had an indwelling bladder catheter during the procedure, which was removed in the recovery room. She has been voiding at will since then. She also had compression pneumatic stockings on both lower extremities during the operation. She began ambulation on the 1st postoperative day, and has been as active as possible under the circumstances, including faithful adherence to a prescribed program of incentive spirometry. On the evening of the 3rd postoperative day, she spikes a fever, with a temperature to 39.4C (103F). Which of the following is the most likely source of the fever?
Atelectasis
Intra-abdominal abscess
Deep thrombophlebitis
Urinary tract infection
Wound infection
A 62-year-old woman is seen after a 3-day history of fever, abdominal pain, nausea, and anorexia. She has not urinated for 24 hours. She has a history of previous abdominal surgery for inflammatory bowel disease. Her blood pressure is 85/64 mm Hg, and her pulse is 136. Her response to this physiologic state includes which of the following?
Increase in sodium and water excretion
Decrease in cortisol levels
Increase in renal perfusion
Hyperkalemia
Hypoglycemia
A 62-year-old woman is suffering from advanced colorectal cancer. Despite aggressive surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy, the disease has spread throughout her pelvis and eroded into her left acetabulum. Her pain from the disease has increased dramatically over the last few months. Understandably, her need for pain medications has increased proportionately, and she is now requiring a combination of COX-2 inhibitors, oxycodone and acetaminophen combinations, and gabapentin to take the edge off of her pain. Her pain control plan involves transitioning her to a long-acting sustained-release form of fentanyl. She is extremely worried about her need for increasing doses of narcotics; she has heard that they have awful side effects, and fears becoming “hooked.” Regarding the side effects of narcotic pain medications, she can confidently be told that which of the following is the most common, clinically significant side effect she is likely to experience?
Addiction
Constipation
Nausea and vomiting
Respiratory depression
Sedation
A 62-year-old woman presents for annual examination. Her last spontaneous menstrual period was 9 years ago, and she has been reluctant to use postmenopausal hormone replacement because of a strong family history of breast cancer. She now complains of diminished interest in sexual activity. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her complaint?
Decreased vaginal length
Untreatable sexual dysfunction
Physiologic anorgasmia
Decreased ovarian function
Alienation from her partner
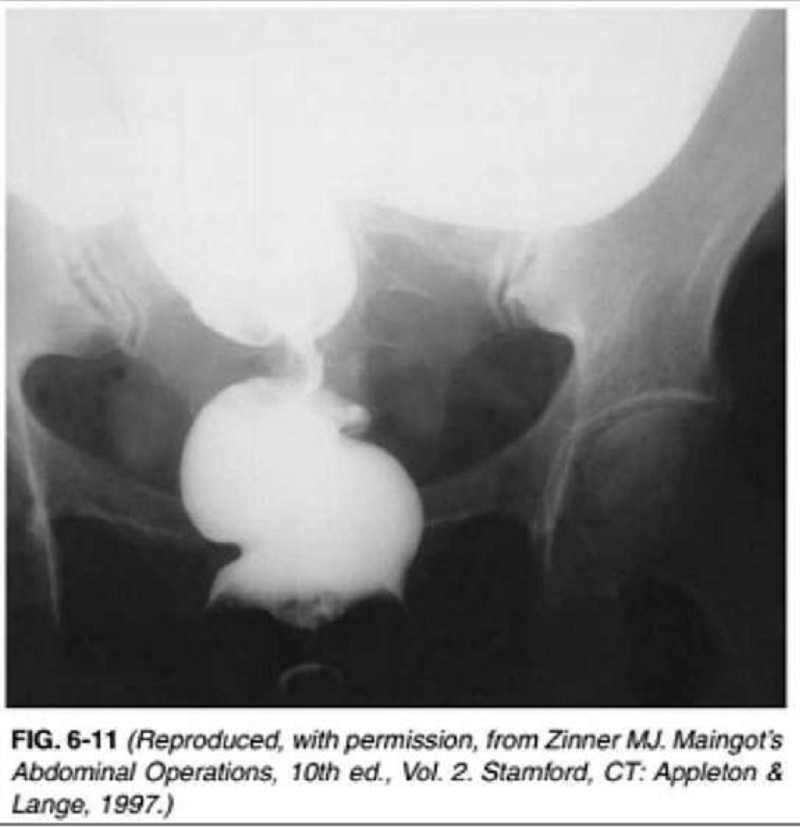
A 62-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office with complaints of constipation. She has had constipation for the last 6 months, which has worsened over the last month, associated with mild bloating. She noted that her stool has become “pencil thin” in the last month, with occasional blood, but she continues to have bowel movements daily. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals normal vital signs and heart and lung examination. Abdominal examination reveals mild fullness, especially in the lower quadrants. Rectal examination shows no rectal masses, but the stool is hematest positive. A barium xray is obtained, and one view is shown in Figure 6-11. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Crohn’s disease
Ischemia with stricture
Rectal carcinoma
Sigmoid volvulus
Diverticulitis with colovesical fistula
A 63-year-old accountant is brought to the emergency department after suddenly collapsing at his desk at work. He is unconscious upon arrival but regains consciousness within several minutes. His medical history is significant for stable angina, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. He has had no surgeries. His medications include atenolol, simvastatin, aspirin, and a multivitamin. Physical examination is remarkable for paralysis of the upper and lower extremities on the right side. Vibration and position sense are absent on the right side. When the flat of the right foot is stroked with a pen, the right great toe is up going and the other toes fan out. The patient's tongue deviates to the left upon protrusion. Given these findings, a lesion in which region of the brain is most likely?
Lateral pons
Medial pons
Lateral medulla
Medial medulla
Central midbrain
A 63-year-old Asian-American woman presents to the ER with a severe right-sided headache that started one hour ago. The pain is located "all around my eye." She has vomited once since the pain began. She also says that bright light aggravates the pain and she complains of seeing "halos" around light. She has never had a headache like this before. Her only medication is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, which she has been taking for the last two days for a urinary tract infection. Her mother has a history of migraine headaches. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. On exam, she is afebrile with a pulse of 90/min. Physical exam reveals a non-reactive, dilated right pupil and erythematous right eye. There is lacrimation present. The remainder of examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies reveal an ESR of 40 mm/hr. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Meningitis
Angle closure glaucoma
Subarachnoid bleeding
Cluster headache
Migraine without aura
A 63-year-old Caucasian female presents to the emergency room with a recent onset of left-sided Weakness. She has been experiencing increased fatigability, low-grade fevers and occasional palpitations over the past two months. She has lost seven pounds during the same period. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 80/min (regular), blood pressure is 120/76mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Her lungs are clear. Cardiac auscultation reveals normal first and second heat sounds and a mid-diastolic rumble at the apex. Echocardiography shows a mass in the left atrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital heart defect
Myxomatous valve degeneration
Intracardiac tumor
Rheumatic fever and atrial thrombus
Infective endocarditis
A 63-year-old Caucasian man reports occasional palpitations when exercising. He denies chest pain. Past medical history includes coronary artery disease status post coronary artery stenting, mitral valve replacement with mechanical valve, and diabetes mellitus. He consumes a well-balanced diet and takes one multivitamin tablet daily. His medications include warfarin, simvastatin, metoprolol, lisinopril, and metformin. Physical examination reveals conjunctival pallor and heart sounds consistent with the presence of a mechanical mitral valve. His hematocrit is 30%. The peripheral blood smear shows occasional schistocytes and his serum LDH level is elevated. His stool is negative for occult blood. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's anemia?
Iron deficiency
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Folate deficiency
Traumatic hemolysis
Autoimmune hemolysis

A 63-year-old female presents to your clinic complaining of palpitations. For the past 3 weeks, she has noticed pounding of her heart that comes and goes. Her symptoms are more frequent at night. Her only medicine is insulin for diabetes mellitus. On physical examination, she is alert and oriented, and in no distress. Her EKG is shown below. Which of the following best accounts for this patient's symptoms?
Sinus arrhythmia
Variable AV node conduction
Atrial ectopy
Ventricular ectopy
Irregularly irregular atrial activation
A 63-year-old male complains of cough and nocturnal wheezing. The cough is mostly non-productive but can sometimes relieve chest tightness if a small amount of yellow sputum is produced. His past medical history is significant for a hospitalization for a 'chest infection' two years ago. His appetite is good but he lost 5 pounds over the last several months. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 40 years. He drinks 2-3 cans of beer per day on the weekends. His mother suffered from diabetes mellitus and his father died of a stroke. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 140/80 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. There is chest hyperinflation and scattered expiratory wheezes on auscultation. The patient expires through pursed lips. His fingers demonstrate prominent clubbing. This patient's clubbing is most likely related to:
Lung hyperinflation
Airflow obstruction
Pulmonary hypertension
Hypoxemia
Occult malignancy
A 63-year-old man alcoholic with a 50-pack-year history of smoking presents to the emergency room with fatigue and confusion. Physical examination reveals a blood pressure of 110/70 mm Hg with no orthostatic change. Heart, lung, and abdominal examinations are normal and there is no pedal edema. Laboratory data are as follows: Na: 110 mEq/L, K: 3.7 mEq/L, Cl: 82 mEq/L, HCO3: 20 mEq/L, Glucose : 100 mg/dL, BUN : 5 mg/dL, Creatinine: 0.7 mg/dL Urinalysis: normal Specific gravity: 1.016. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Volume depletion
Psychogenic polydipsia
Cirrhosis
Congestive heart failure
Inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone
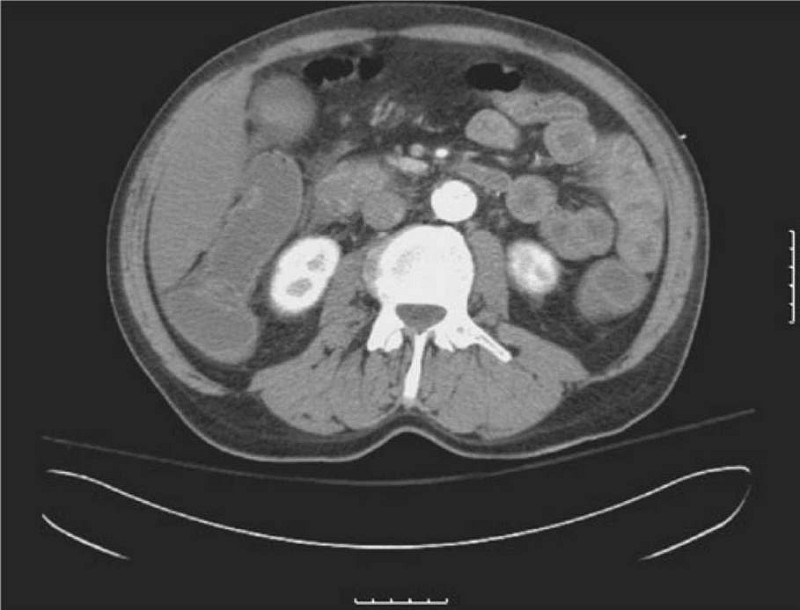
A 63-year-old man is brought to the ED by EMS complaining of severe abdominal pain that began suddenly 6 hours ago. His BP is 145/75 mm Hg and HR is 105 beats per minute and irregular. On examination, you note mild abdominal distention and diffuse abdominal tenderness without guarding. Stool is heme positive. Laboratory results reveal WBC 12,500/μL, haematocrit 48%, and lactate 4.2 U/L. ECG shows atrial fibrillation at a rate of 110. A CT scan is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Mesenteric ischemia
Diverticulitis
SBO
Crohn disease
A 63-year-old man is seen because of facial swelling and cyanosis, especially when he bends over. There are large, dilated subcutaneous veins on his upper chest. His jugular veins are prominent even while he is upright. Which of the following conditions is the most likely cause of these findings?
Histoplasmosis (sclerosing mediastinitis)
Thoracic aortic aneurysm
Constrictive pericarditis
Bronchogenic carcinoma
Substernal thyroid
A 63-year-old man, who weighs 65 kg, is in his 2nd postoperative day after an abdominoperineal resection for cancer of the rectum. An indwelling Foley catheter was left in place after surgery. The nurses are concerned because, even though his vital signs have been stable, his urinary output in the past 2 hours has been zero. In the preceding 3 hours, they had collected 56 mL, 73 mL, and 61 mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute renal failure
Damage to the ureters during the operation
Dehydration
Plugged or kinked catheter
Damage to the bladder during the operation
A 63-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the outpatient office complaining about intermittent painless vaginal bleeding. Her last menstrual period was 10 years ago. She is not on hormone therapy. She has never used oral contraceptives. She has struggled with obesity all her life. Her last Pap smear was a year ago and was negative for dysplasia or malignancy. Her pelvic examination is unremarkable without vulvar, vaginal, or cervical lesions. Her uterus is small, mobile, and nontender. No adnexal masses are palpable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ectopic pregnancy
Vaginal foreign body
Endometrial carcinoma
Submucous leiomyoma
Molar pregnancy
A 63-year-old obese female undergoes an elective cholecystectomy after two episodes of acute calculous cholecystitis. Three days after surgery, her blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg, her heart rate is 90/min, and her arterial oxygen saturation is 91 % on room air. She is afebrile. Which of the following would most likely increase her fun
Inhaled albuterol
Postoperative benzodiazepines
Decreasing the dose of her postoperative opioids
Elevation of the head of the bed
Sequential compression devices to her lower extremities
A 63-year-old otherwise healthy male presents with a thyroid nodule. He denies any symptoms of anxiety, heat or cold intolerance, and recent changes in appetite or weight. He has hypertension, which is being treated with a beta-blocker. He does not have any other medical problems. He denies any family history of thyroid disease. His pulse is 79/min and blood pressure is 130/76 mmHg. Neck examination shows a hard, fixed, non-tender, 4 cm thyroid nodule in the right thyroid lobe. His serum TSH level is normal. Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) shows follicular cells. Follicular carcinoma is suspected. Which of the following is necessary to make a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer?
Invasion of the tumor capsule and blood vessels
Presence of Hurthle cells on biopsy
Lymph node involvement
Presence of psammoma bodies
Secretion of calcitonin
A 63-year-old painter complains of severe right shoulder pain. The pain is located posteriorly over the scapula. These symptoms began after he fell from a ladder 2 weeks ago. The pain is especially bad at night and makes it difficult for him to sleep. In addition, he has had some pain in the right upper arm. Treatment with acetaminophen and ibuprofen has been unsuccessful in controlling his pain. On examination the patient appears uncomfortable. The right shoulder has full range of motion. Movement of the shoulder is not painful. There is no tenderness to palpation of the scapula. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Subdeltoid bursitis
Rotator cuff tendonitis
Adhesive capsulitis
Osteoarthritis
Cervical radiculopathy
A 63-year-old painter presents with pain in his right shoulder for the past few weeks. He experiences pain when he tries to reach for objects and he is unable to lift his arm above his head. He denies trauma to the shoulder, fevers, chills and weight loss. Vital signs are within normal limits. On exam, the physician raises the patient's arm while asking him to relax the shoulder. At 60 degrees, the patient begins to shrug his shoulder and complain of pain. In spite of the pain, his range of motion is normal. A lidocaine injection into the shoulder leads to a significant decrease in pain upon lifting the arm. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his current condition?
Rotator cuff tear
Adhesive capsulitis
Rotator cuff impingement
Crystal arthritis
Bacterial infection
A 63-year-old white female presents with a thyroid nodule. She denies any weight loss, change in appetite, diarrhea, heat or cold intolerance, menstrual irregularities, hoarseness and dyspnea. Her past medical history is unremarkable. There is no family history of thyroid cancer. She does not take any medications. Physical examination shows a 4-5 cm, fixed, hard, and non-tender thyroid nodule. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. Her serum TSH level is normal. Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the thyroid shows malignant cells. Which of the following is the most likely expected pathology on FNA?
Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid
Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
Lymphoma of the thyroid
Follicular carcinoma of the thyroid
Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid
A 63-year-old woman with cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C is hospitalized because of confusion. She has guaiac-positive stools and a low-grade fever. She has received lorazepam for sleep disturbance. On physical examination, the patient is confused. She has no meningeal signs and no focal neurologic findings. There is hyperreflexia and a nonrhythmic flapping tremor of the wrists. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient’s mental status change?
Tuberculous meningitis
Hepatic encephalopathy
Subdural hematoma
Alcohol withdrawal seizure
Central nervous system vasculitis from cryoglobulinemia
A 64-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office because he has had two falls within the last month. He states that he loses his balance when he tries to turn or stop suddenly while walking. Recently, he says, it has been taking him quite a while to get himself out of bed. He also complains of hand tremors that started last year in his left hand, but that now have been affecting both hands. Which of the following is the best tool to confirm his diagnosis?
Physical examination
CT scan of the head
Lumbar puncture
Electroencephalography
Nerve conduction studies
A 64-year-old female presents with complaints of lesions over her breasts and thighs. She had been experiencing severe pain in those areas prior to developing redness and blisters. Her past medical history is significant for valvular heart disease with atrial fibrillation, ulcerative colitis diagnosed 20 years ago, and a resection of part of her colon. She is a known patient of yours, and four days ago, you started her on treatment for atrial fibrillation with antiarrhythmics and oral anticoagulants. Her pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F). On examination, you notice well-demarcated lesions with bullae and necrotic changes over her thighs and breasts. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Necrotizing fasciitis
Pyoderrma gangrenosum
Venous gangrene
Warfarin-induced necrosis
Cholesterol embolisation syndrome
A 64-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of increasing pain in his right groin for the past several months. The pain increases with activity and is relieved with rest. He also has difficulty moving after a period of rest. He denies any trauma or falls. He has no fever, weight loss or loss of appetite. He has had lumbar disk herniation in the past but denies any current back pain. He has no other active medical problems. His vital signs are within normal limits. He weighs 95 kg (210 lb) and is 168 cm (66 in) tall. Examination shows pain on passive internal rotation of right hip joint. Direct pressure over the groin did not increase the pain. His reflexes are 2+, and there are no sensory deficits. Muscle bulk, tone and power are within normal limits. Pulses are 2+ in both legs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hip pain?
Inflammation of the trochanteric bursa
Disruption of bone vasculature
Cutaneous nerve compression
Degenerative joint disease
Referred pain from the lumbosacral area
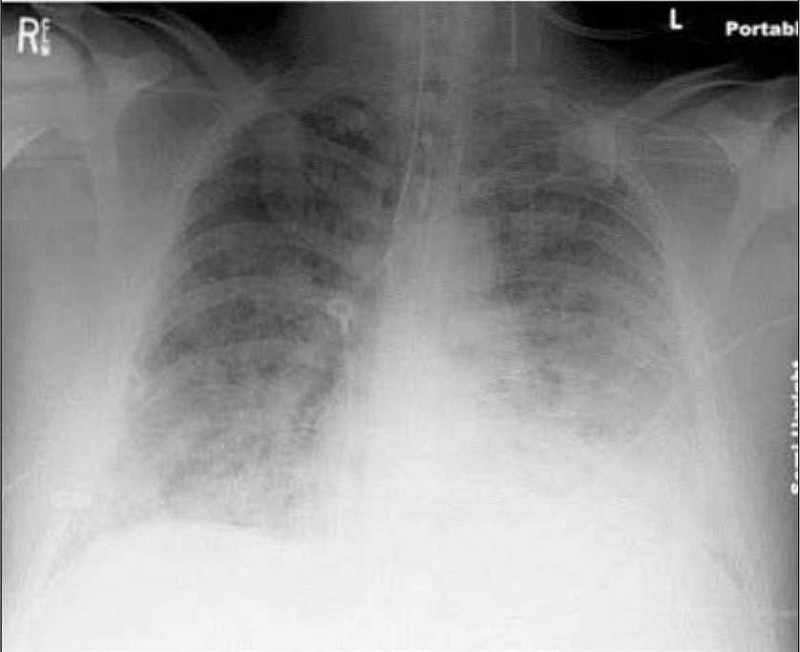
A 64-year-old male is admitted to the hospital with abdominal pain, abdominal distention, and confusion. Upon arrival his blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg and pulse is 120/min. On physical examination, his abdomen is tender, distended, and rigid with positive rebound tenderness. His past medical history is significant for rheumatic fever as a child, hypertension, coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation. He receives a total of 6 liters of normal saline and undergoes emergent laparotomy. Postoperatively he complains of shortness of breath. His respiratory rate is 34/min. He is emergently intubated because of poor oxygenation. His chest x-ray is shown below. This film is compared to a chest x-ray performed one week earlier, which was within normal limits. Currently, the pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is 8 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Left ventricular systolic dysfunction
Iatrogenic fluid overload
Mitral stenosis
Acute respiratory distress syndrome
A 64-year-old male presents to the ER with a one-week history of progressive exertional dyspnea. Each of the past two nights he has awakened with a choking sensation and has had to sit up to catch his breath. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and a myocardial infarction two years ago. He takes a baby aspirin and lisinopril daily. His blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, and his heart rate is 110/min, irregularly irregular. His temperature is 98°F (36.7°C) and his respiratory rate is 24/min. His oxygen saturation is 91% on room air. There is moderate jugular venous distention. Markedly reduced breath sounds are heard over the right lung base. Which of the following most likely underlies this patient's physical findings?
Lung tissue consolidation
Atelectasis
Bronchoconstriction
Pleural effusion
Emphysema
A 64-year-old male presents to the ER with shortness of breath. The symptoms started one week ago with a dry cough and mild fever. His past medical history includes hypertension and exertional angina. He was hospitalized six months ago for pneumonia. He has a 35 pack-year smoking history. His blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and heart rate is 90 and regular. On examination, the patient is in mild respiratory distress. He uses some accessory respiratory muscles for breathing, but he can speak in full sentences. Chest auscultation reveals bilateral wheezes and crackles at the left lung base. His ABG shows: pH 7.36, pO2 72mmHg, pCO2 51mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
Congestive heart failure ( CHF)
Pulmonary embolism
COPD exacerbation
Pneumothorax
Adult respiratory distress syndrome
A 64-year-old male recovering from an upper respiratory infection develops malaise and productive cough. Two days later he presents to the emergency department with confusion and severe dyspnea. He reports coughing up copious amounts of yellowish sputum streaked with blood today. On physical examination, his temperature is 40°C (104°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 24/min. Chest x-ray reveals infiltrates in the lung midfields bilaterally as well as multiple thinwalled cavities. What is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Legionnaires disease
Tuberculosis
Pulmonary thromboembolism
Bronchiectasis
Staphylococcus infection
A 64-year-old male who has not seen a doctor for the past 20 years presents to the emergency room with excruciating chest pain that stated suddenly about three hours ago. He describes the pain as tearing in quality and says that it radiates to his back. On physical examination, you hear an early diastolic decrescendo murmur at the sternal border. Chest X-ray shows widening of the superior mediastinum. EKG is normal. Which of the following medical conditions most likely accounts for this patients presentation?
Marfan's syndrome
Ehlers-Darlos syndrome
Bicuspid aortic valve
Giant cell arteritis
Systemic hypertension
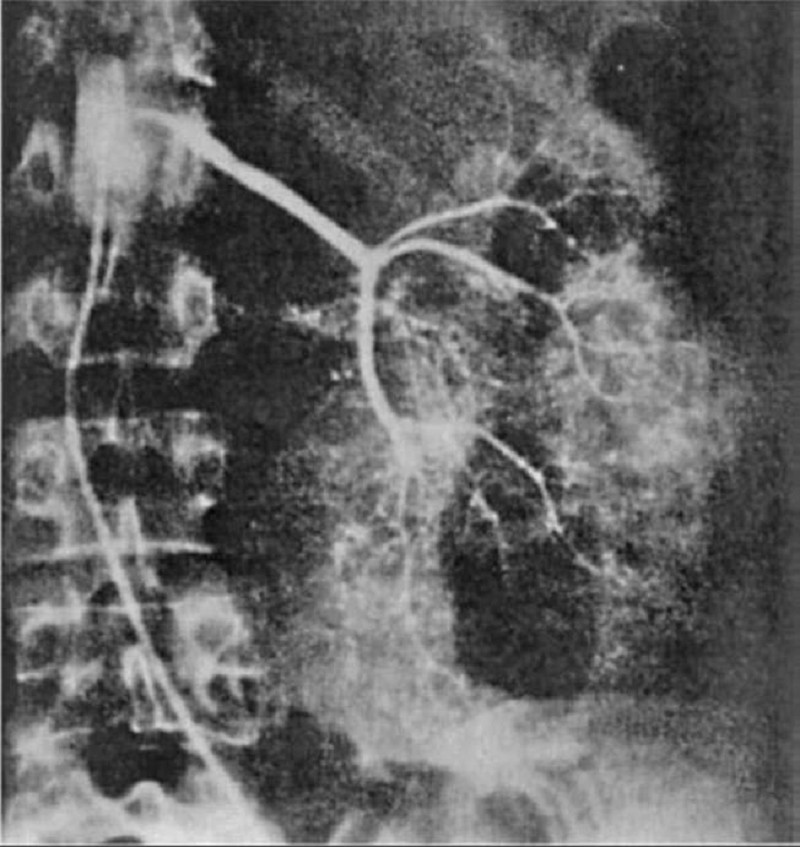
A 64-year-old man is admitted for hematuria after slipping on an icy pavement. His physical examination is normal. A selective angiogram of the left kidney is shown in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Renal cell carcinoma
Transitional cell carcinoma
Renal hamartoma
Renal hemangioma
Kidney contusion and laceration
A 64-year-old man is admitted to the psychiatric unit after an unsuccessful suicide attempt. Following admission, he attempts to cut his wrists three times in the next 24 hours and refuses to eat or drink anything. He is scheduled to have electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) because he is so severely depressed that an antidepressant is deemed too slow acting. Which of the following side effects should the patient be informed is most common after ECT?
Palpitations
Deep venous thromboses
Headache
Interictal confusion
Worsening of the suicidal ideation
A 64-year-old man is scheduled for hemodialysis due to end stage renal disease. He has a several year history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, hypercholesterolemia, peripheral vascular disease, gout, and diverticulosis. Six months ago, he was admitted for urosepsis. Recently, his haemoglobin has ranged between 8.5 to 9.5 g/dl. He has already been on iron therapy, and now you are considering erythropoietin injections twice weekly. Which of the following is most likely to be seen following erythropoietin therapy?
Flare-up of gout
Worsening of his hypertension
Increase in insulin requirement
Increased susceptibility to infections
Deterioration in renal function
A 64-year-old man presents to the ER with back pain and frequent falls. He also describes difficulty initiating urination. The symptoms started one week ago and have progressed gradually. He was diagnosed with prostate cancer one year ago and treated with radiation therapy. Physical examination reveals weakness of knee and hip extension that is more pronounced on the right. Knee and ankle reflexes are absent bilaterally. Babinski sign is negative. Perianal skin is insensitive to touch but sensation in the anterolateral thigh is preserved. Which of the following is the most likely lesion location in this patient?
Peripheral nerves outside the spinal canal
Spinal nerve roots
Lumbar spinal cord
Thoracic spinal cord
Cervical spinal cord
A 64-year-old man presents with weight gain, shortness of breath, easy bruising, and leg swelling. On examination, his blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg, pulse 100/min, JVP 4 cm, heart sounds normal, and lungs are clear. There is a 3+ pedal and some periorbital edema. Investigations include a normal chest x-ray (CXR), electrocardiogram (ECG) with low voltages, anemia, high urea and creatinine, and 4 g/day of protein in the urine. A renal biopsy, which shows nodular deposits that have an apple-green birefringence under polarized light when stained with Congo red. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Amyloidosis
Diabetic nephropathy
Multiple myeloma
Minimal change disease
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy
A 64-year-old white female presents for evaluation of two weeks of decreased appetite and nausea. She also notes occasional palpitations, which have been especially prominent over the past two days. Her medical history is significant for an anterior wall myocardial infarction one year ago and secondary congestive heart failure with left ventricular systolic dysfun
Atrial flutter
Atrial tachycardia with AV block
Multifocal atrial tachycardia
Atrial fibrillation
Mobitz type II second-degree AV block
A 64-year-old white male with a history of severe stable angina and peripheral vascular disease undergoes coronary artery bypass surgery. His post-operative course is complicated by hypotension, which is treated successfully; however, a few hours later, he experiences abdominal pain followed by bloody diarrhea. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 20/min. Abdominal examination is benign. Laboratory studies show a WBC count of 15,000/cmm with 7% bands. The lactic acid level is elevated. A CT scan is ordered. Which of the following areas of the colon will most likely show abnormal findings?
Sigmoid colon
Splenic flexure
Ascending colon
Mid transverse colon
Hepatic flexure
A 64-year-old white woman presents to her primary care physician complaining of difficulty and pain with swallowing, as well as occasional chest pain. She has a history of breast cancer treated with lumpectomy and radiation, hyper- tension, high cholesterol, and ovarian polyps. She indicates that her current problem started with liquids, but has progressed to solids, and that the food “just gets stuck in my throat.” The chest pain was once so bad that she took one of her husband’s nitroglycerin pills and the pain subsided, but it has since occurred many times. The physician orders an x-ray of the chest, but it is not diagnostic. Manometry is conducted, and it shows uncoordinated contractions. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Breast cancer relapse
Esophageal cancer
Diffuse esophageal spasm
Myocardial infarction
Nutcracker esophagus
A 64-year-old woman comes to the physician because she is "leaking" urine. She states that, over the past 3 years, she has had incontinence several times daily. She describes these episodes as small squirts of urine that come out whenever she laughs, coughs, sneezes, or engages in physical activity. Physical examination shows mild uterine prolapse and a moderate cystocele. Urine culture is negative. Postvoid residual is 25 ml (normal < 50 mL) Cystometrogram is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Detrusor instability (DI)
Neurogenic bladder
Genuine stress urinary incontinence (GSUI)
Pyelonephritis
Urinary tract infection
A 64-year-old woman develops sudden-onset abdominal discomfort after eating a large meal. The pain is constant, localizes to the epigastric area with radiation to her right scapula. She also has nausea and vomiting. It eventual subsides 1 hour later. An ultrasound of the abdomen reveals a dilated common bile duct secondary to stones. Which of the following statements regarding common bile duct stones is most likely true?
Always produce jaundice
Can be painless
All originate in the gallbladder
Produce constant level of jaundice
Indicate anomalies of the bile duct
A 65-year-old African American man comes to the emergency department due to a sudden loss of vision in his right eye. He has had diabetes, and has been treated with metformin and glyburide for the past 10 years. Visual acuity is reduced to light perception in his right eye, and normal in his left. His vital signs are normal. Ophthalmoscopy reveals loss of fundus details, floating debris and a dark red glow. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Retinal detachment
Central retinal vein occlusion
Vitreous haemorrhage
Age related macular degeneration
Diabetic retinopathy
A 65-year-old Caucasian male presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of weakness in his right arm and right leg. He has had episodes of transitory weakness and numbness in his right extremities over the last month, but those episodes used to resolve quickly. He denies headache, nausea, vomiting and loss of consciousness. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, type 2 and myocardial infarction experienced 2 years ago. His current medications are aspirin, metoprolol, enalapril, simvastatin, and glyburide. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 160/80 mmHg, pulse is 65/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 14/min. The physical examination reveals right-sided hemiplegia and facial paresis. His speech and praxis do not seem to be impaired. He correctly names his left and right arms. Bedside visual field testing is normal. Head CT without contrast shows no intracranial bleeding Where is the most likely location of the lesion responsible for this patient's condition?
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
Internal capsule involvement
Anterior cerebral artery occlusion
Pons lesion
Midbrain lesion
A 65-year-old diabetic male with acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock is admitted in the coronary care unit. His hospital course was complicated by acute renal failure and lower GI bleeding from anticoagulation therapy. His thyroid hormone studies are abnormal. He does not have any previous history of thyroid disease. Physical examination of the thyroid gland is normal. Labs show: Triiodothyronine (T3), serum 1.4 nmol/L (normal 1.8-29 nmol/L), Thyroxine (T 4), serum 6.0 micro-g/dL (normal 5-12 micro-g/dL), Thyroid-stimulating hormone, serum 2.0 micro-U/mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Sick euthyroid syndrome
Subclinical hypothyroidism
Primary overt hypothyroidism
Central hypothyroidism
Reidels thyroiditis
A 65-year-old female is complaining of seeing a sudden burst of flashing lights and blurred vision in her left eye. These symptoms started this morning. She now sees small spots in her field of vision. She felt "like a curtain came down" over her eye. She had a successful cataract extraction in her left eye 4 months ago. Her vital signs are stable. Examination shows a sluggish left pupil. Ophthalmoscopy reveals retinal tears and a grayish-appearing retina. What is the most probable diagnosis?
Choroidal rupture
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
Central retinal artery occlusion
Exudative macular degeneration
Retinal detachment
A 65-year-old Hispanic male comes to the office for a routine medical check-up. He has a history of diabetes for the past twenty years, and hypertension for the past ten years. His daily medications include insulin and ramipril. He was diagnosed with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy at his last ophthalmologic visit. Reports from his previous laboratory studies show microalbuminuria. A detailed neurological examination is performed to check for any neuropathy. Which of the following is the most common type of neuropathy found in diabetics?
Proximal motor neuropathy
Mononeuropathy multiplex
Autonomic neuropathy
Symmetrical distal polyneuropathy
Mononeuropathy
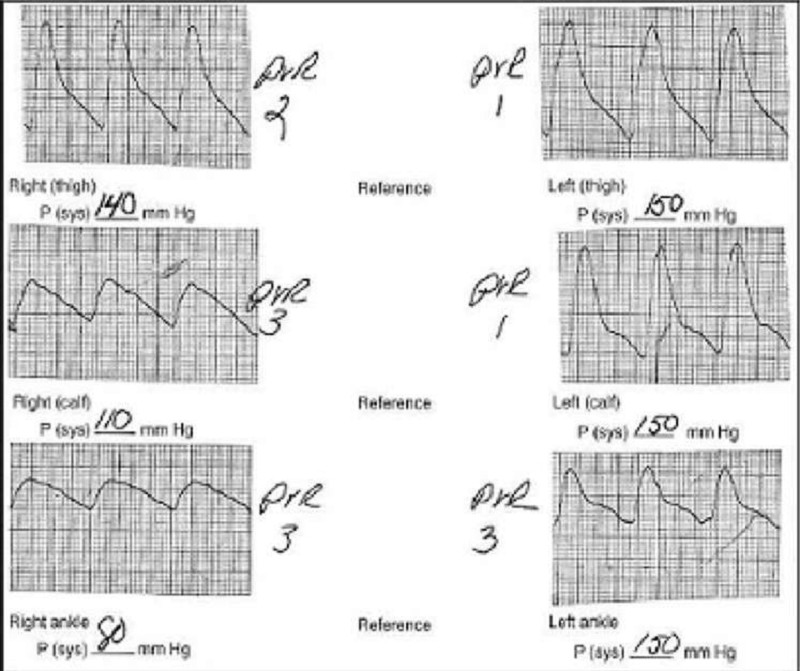
A 65-year-old male cigarette smoker reports onset of claudication of his right lower extremity approximately 3 weeks previously. He can walk 3 blocks before the onset of claudication. Physical examination reveals palpable pulses in the entire left lower extremity, but no pulses are palpable below the right groin level. Non-invasive flow studies are obtained and are pictured here. What is the level of the occlusive process in this patient?
Right anterior tibial artery
Right external iliac artery
Right internal iliac artery
Right superficial femoral artery
Right profunda femoris artery
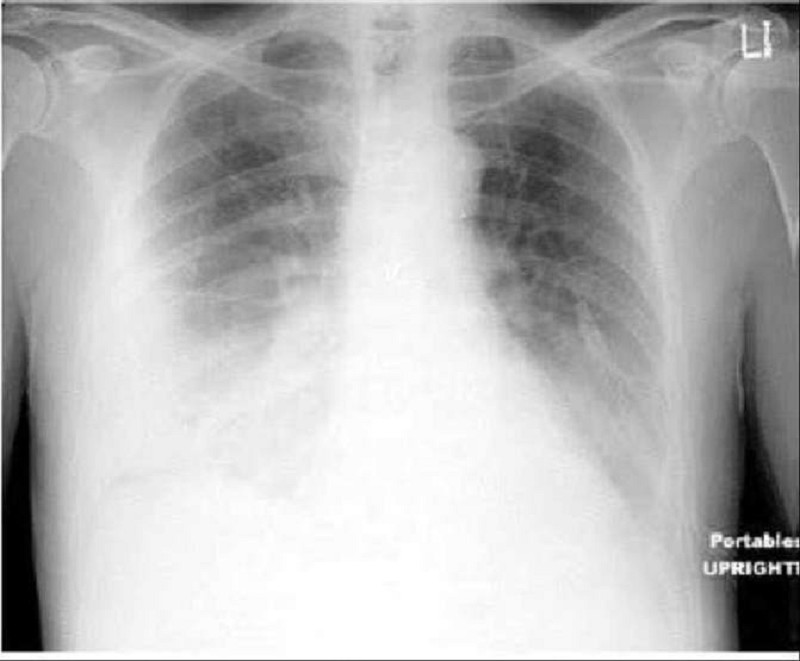
A 65-year-old male comes to the emergency department with severe shortness of breath. The symptoms started one week ago with fever and a non-productive cough. His past medical history is significant for coronary artery disease with bypass surgery two years ago, hypertension and diabetes mellitus. His temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 160/70 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 26/min. Physical examination reveals decreased breath sounds over the right lower lung base. His chest X-ray is shown on the slide below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
Bronchopleural fistula
Lung abscess
Empyema
Pneumothorax
Pulmonary infarction
A 65-year-old male comes to the ER because of sudden onset severe pain in his right leg. He says he has never previously had pain in his leg and denies any recent trauma, fever or chills. He recently suffered an acute anterior wall myocardial infarction that resulted in cardiogenic shock and is currently undergoing cardiac rehabilitation. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min (regular) and respirations are 16/min. His lungs are clear to auscultation. His heart rate is regular with no murmurs. Below the knee the right leg is cool to touch and appears pale. The dorsalis pedis pulse is not palpable while the popliteal pulses are full. Pulses are normal in the contralateral extremity. Neurologic examination shows numbness over the dorsum of the leg and foot. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
Nerve compression
Arterial thrombosis
Arterial embolism
Venous thrombosis
Arterial vasculitis
A 65-year-old male comes to the physician because of fever, chills, and productive cough. The symptoms started four days ago. He also complains of chest pain, which increases with inspiration. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 45 years. He drinks 3-4 ounces of alcohol daily. His chest x-ray showed an infiltrate in the right upper lobe. The sputum examination of the patient reveals capsulated gram-negative bacilli. Sputum culture is growing mucoid colonies. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism in this patient?
Escherichia coli
Klebsiella pneumonia
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Legionella species
Mycoplasma pneumonia
A 65-year-old male is being evaluated for hip pain. The pain has been present for several months and is constant. He denies any weight loss or loss of appetite. His past medical history is significant only for high blood pressure. His temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), blood pressure is 150/88 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 12/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show: Alkaline phosphatase Elevated, Gamma glutamyl, transferase Normal, Serum calcium Normal, 2,5 (OH)2 vitamin D Normal. Bone scan shows increased uptake in several spots. This patient is at high risk of developing?
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Hearing loss
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Renal cell carcinoma
Pulmonary hemorrhage
A 65-year-old male presents to your office with a six-month history of periodic substernal pain. The pain episodes are experienced during strong emotion, last for 10-15 minutes, and resolve spontaneously. He has a long history of hypertension and diabetes mellitus, type 2. His right foot was amputated two years ago due to diabetes-related complications. You suspect angina pectoris and decide to perform myocardial perfusion scanning. It reveals uniform distribution of isotope at rest, but inhomogenesity of the distribution after dipyridamole injection. You conclude that the patient has ischemic heart disease. Which of the following effects of dipyridamole helped you in making the diagnosis?
Increased heart contractility
Dilation of diseased vessels
Coronary steal
Inhibition of platelet aggregation
Placebo effect
A 65-year-old man comes to the emergency department complaining of left lower abdominal pain that began the prior morning. He became concerned when he developed bloody diarrhea overnight. He has experienced similar pain, although to a lesser degree, over the past 2 months, especially after eating. The pain usually resolved within 1–2 hours, and he never had bloody diarrhea. His past medical history is significant for coronary artery disease and hypertension. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 30 years. On physical examination he is afebrile, heart rate is 90/min, and blood pressure is 135/85 mm Hg. He is visibly uncomfortable but in no apparent distress. His abdominal examination is significant for left lower quadrant tenderness but no guarding or rebound. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute mesenteric ischemia
Colon cancer
Diverticulitis
Infectious colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease
A 65-year-old man comes to the physician's office because of frequent falls. For the past 2 months, he has been having increasing difficulty in maintaining balance when walking or standing. He tends to lose his balance on the left side, and feels that his "left body has become weak." He also complains of occasional headaches and nausea for the past 3 months. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes mellitus-type 2 and a myocardial infarction 10 years ago. He denies the use of tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His medications include glyburide, aspirin and enalapril. His vital signs are within normal limits. When asked to get up from the chair and stand with his feet together, he tends to sway to the left, even with his eyes open. When asked to walk a few steps, he walks cautiously and lurches to the left. There is decreased resistance to passive flexion. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Major depression
Huntington's disease
Parkinsonism
Cerebellar tumor
Hemiparesis
A 65-year-old man comes to the physician's office with a 2-month history of dysphagia. He initially had difficulty swallowing solids, but now this includes liquids. He has occasional heartburn, which usually responds well to antacids. He has lost 20 lbs of weight in the past 2 months. He has a 40 pack-year history of smoking. He has been a chronic alcoholic for 20 years. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 110/80 mmHg, pulse is 66/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Barium studies show a minimally dilated esophagus with beak-shaped narrowing. Manometry shows increased lower esophageal sphincter tone. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Achalasia
Esophageal cancer
Scleroderma
Peptic stricture
Diffuse esophageal spasm
A 65-year-old man comes to your office for a follow-up after his previous visits revealed inadequately controlled hypertension. He has no present complaints except difficulty walking uphill or climbing stairs, because of the pain in the right thigh, which makes him stop and rest. His past medical history includes stable angina, requiring coronary angioplasty and stenting 2 years ago; hypercholesterolemia; a 20-year history of hypertension; and a 10-year history of diabetes mellitus, type 2. His current medications are aspirin, metoprolol, hydrochlorothiazide, enalapril, amlodipine, pravastatin and glyburide. He smokes 1½packs of cigarettes per day and does not consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg in his right arm and 180/110 mmHg in his left arm. Which of the following findings will point to the potential cause of the resistant hypertension in this patient?
Increased urinal excretion of vanillylmandelic acid (VMA)
High aldosterone/renin ratio
Continuous murmur in the paraumbilical area to the right
Increased pulsation of intercostal arteries
Increased 24-hour urinary free cortisol excretion
A 65-year-old man complains of gradual onset blurred vision for the past two months. He also has difficulty driving at night and reading fine print. He has diabetes and hypertension. His medications include ramipril and metoprolol. His vital signs are stable. His best corrected vision is OD (right eye) 20/80, OS (left eye) 20/100, with full fields. Ophthalmoscopic examination with good pupillary dilatation reveals a loss of transparency of lens in both eyes. The red fundal reflex is normal, but retinal details are difficult to visualize. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Open angle glaucoma
Retinal detachment
Macular degeneration
Cataract
Central retinal vein occlusion
A 65-year-old man complains of periodic back pain radiating to his thigh and buttock. The pain is related to walking or climbing the stairs but is promptly relieved by leaning forward. He also has noticed tingling and numbness in both lower extremities. He has a history of hypertension and takes hydrochlorothiazide. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. His pulse is 76/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 140/80 mmHg. Lumbar extension reproduces the pain and tingling, while lumbar flexion relieves the symptoms. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Iliac artery atherosclerosis
Degenerative central canal stenosis
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Lumbar disk herniation
Spina bifida occulta
A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with an abrupt onset of excruciating chest pain 1 hour ago. The pain is localized to the anterior chest, but radiates to the back and neck. On examination, the patient is afebrile, with a BP of 210/110 mmHg, pulse rate of 95/min, and a respiratory rate of 12/min. He appears pale and sweaty. Unequal carotid, radial, and femoral pulses are noted. An electrocardiogram (ECG) shows nonspecific ST-T segment changes. Chest x-ray shows a slightly widened mediastinum and normal lung fields. Which of the following is the preferred modality in establishing the diagnosis?
Transcutaneous echocardiography
Transesophageal echocardiography
CT scan
Coronary angiography
Aortography
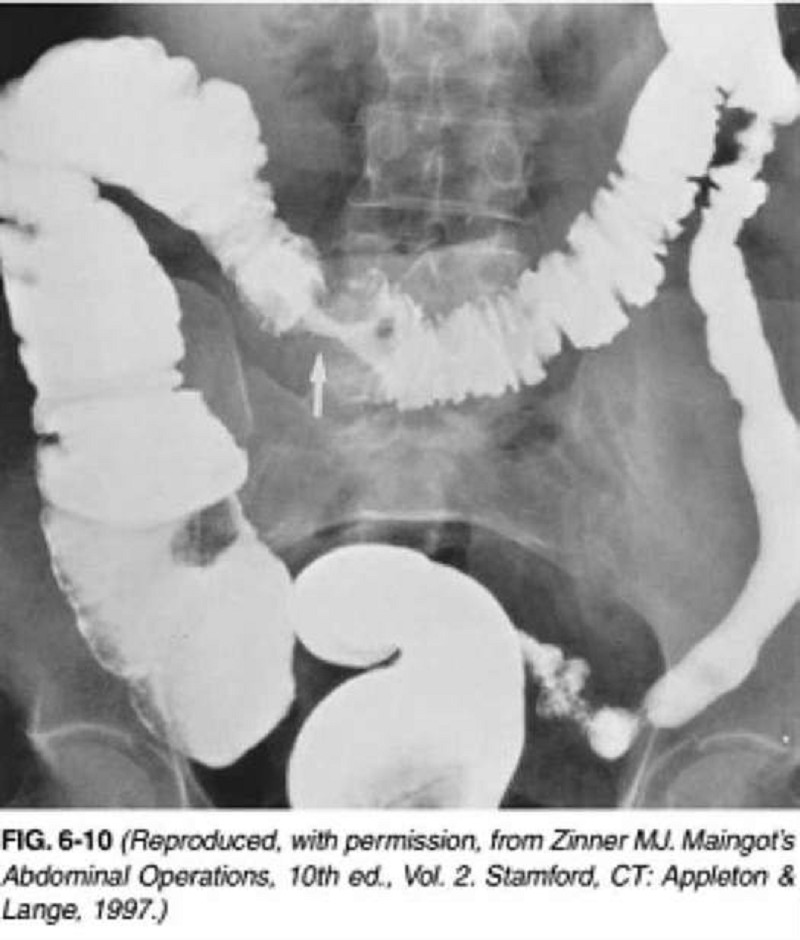
A 65-year-old man presents to the physician’s office for his yearly physical examination. His only complaint relates to early fatigue while playing golf. Past history is pertinent for mild hypertension. Examination is unremarkable except for trace hematest-positive stool. Blood tests are normal except for a hematocrit of 32. A UGI series is performed and is normal. A barium enema is performed, and one view is shown in Figure 6-10. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Diverticular disease
Colon cancer
Lymphoma
Ischemia with stricture
Crohn’s colitis with stricture
A 65-year-old man presents to the physician’s office with complaints of abdominal discomfort and jaundice for the past 3 weeks. Past history is pertinent for 30 pack-year smoking history, occasional alcohol intake, and a 5.5-mm ulcerating melanoma removed from his back 21/ 2 years ago. Examination reveals a mildly jaundiced patient with normal vital signs and a slightly distended abdomen with mild right upper quadrant tenderness and significant hepatomegaly. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
Hepatitis A
Hemolysis
Choledocholithiasis
Liver metastases
Cirrhosis
A 65-year-old man presents with a 1-day history of hematuria and sharp flank pain (rated 10 of 10) radiating toward the groin on the right side. Past medical history is significant for three prior episodes of nephrolithiasis over the past 5 years, all of which presented with a similar clinical picture. He is not taking any medication. There is no family history of renal calculi, renal disease, or endocrine disorders. His temperature is 36.9°C (98.5°F), heart rate is 125/min, and blood pressure is 132/86 mmHg. He is in obvious distress and cannot sit still on the bed. Physical examination is significant for a soft, nontender abdomen and extreme costovertebral angle tenderness on the right. Laboratory values show: Na+: 142 mEq/L, K+: 4.8 mEq/L , Cl−: 104 mEq/L, HCO −: 24 mEq/L , Ca2+: 11.0 mg/dL , PO4: 1.4 mg/dL , Mg2+: 2.0 mg/dL , Blood urea nitrogen: 12 mg/dL, Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL, Glucose: 118 mg/dL, Intact parathyroid hormone: 300 pg/mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Malignancy
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Milk-alkali syndrome
Sarcoidosis
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
A 65-year-old man presents with a 4-day history of worsening lower abdominal pain and constipation. On examination, he is febrile (38.5°C) and has lower abdominal tenderness that is most intense in the midline and left lower quadrant associated with a palpable fullness. Laboratory findings demonstrate a moderate leukocytosis and abdominal roentgenograms show an ileus pattern. Select the most likely diagnosis?
Gastroenteritis
Acute appendicitis
Regional enteritis
Perforated peptic ulcer
Sigmoid diverticulitis
A 65-year-old man presents with complaints of decreased vision in both eyes. His visual impairment has been progressively worsening over the past five months. He was diagnosed with diabetes ten years ago. His current medications are metformin and glyburide. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 98.4°F (36.88°C). Examination shows decreased visual acuity in both eyes. Ophthalmoscopy reveals microaneurysms, dot and blot hemorrhages, hard exudates, and macular edema. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Central retinal vein occlusion
Macular degeneration
Diabetic retinopathy
Retinal detachment
Open angle glaucoma
A 65-year-old man treated for heart failure with enalapril and digoxin presents to the emergency department (ED) with palpitations. His blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg, and heart rate is 110/min. His rhythm is irregular. His lungs are clear on auscultation. His abdomen is soft and non-distended. Mild epigastric tenderness is elicited on deep palpation. ECG shows atrial fibrillation without acute ischemic changes. Cardiac enzyme levels are normal. Treatment with warfarin and verapamil is initiated, and the patient is eventually discharged home. After two weeks, he returns to the ED to complain of profound anorexia. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current complaint?
Gastric irritation
Pancreatitis
Drug interaction
Occult carcinoma
Gastrointestinal bleeding
A 65-year-old man undergoes a low anterior resection for rectal cancer. On the fifth day in hospital, his physical examination shows a temperature of 39°C (102°F), blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg, pulse of 110 beats per minute and regular, and respiratory rate of 28 breaths per minute. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen reveals an abscess in the pelvis. Which of the following most accurately describes his present condition?
Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
Sepsis
Severe sepsis
Septic shock
Severe septic shock
A 65-year-old man with a history of chronic hypertension presents to the ED with sudden-onset tearing chest pain that radiates to his jaw. His BP is 205/110 mmHg, HR is 90 beats per minute, RR is 20 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation is 97% on room air. He appears apprehensive. On cardiac examination you hear a diastolic murmur at the right sternal border. A chest x-ray reveals a widened mediastinum. Which of the following is the preferred study of choice to diagnose this patient’s condition?
Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE)
Computed tomography (CT) scan
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE)
A 65-year-old man with a history of diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and atrial fibrillation presents with loss of vision in his left eye since he awoke 6 hours ago. The patient denies fever, eye pain, or eye discharge. On physical examination of the left eye, vision is limited to counting fingers. His pupil is 3 mm and reactive. Extraocular movements are intact. Slit-lamp examination is also normal. The dilated funduscopic examination is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Retinal detachment
Vitreous hemorrhage
Acute angle-closure glaucoma
Central retinal artery occlusion
Central retinal vein occlusion
A 65-year-old man with cervical spondylosis secondary to degenerative changes in the cervical spine was admitted after being involved in a motor vehicle accident. He regained consciousness after 5 minutes. After regaining consciousness, he had complete weakness in both upper extremities but was able to move his lower extremities. Vital signs are stable. Plain x-ray films of the cervical spine show no abnormalities except those consistent with mild degenerative changes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Brown-Sequard syndrome
Cerebral contusion
Central cord syndrome
Posterior spinal cord syndrome
Anterior spinal cord syndrome
A 65-year-old man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic atrial fibrillation, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus presents with a three-day history of shortness of breath. His condition began with runny nose, itchy eyes, and sore throat, but his symptoms progressed to productive cough, wheeze, and dyspnea. Physical examination reveals a mildly overweight man in moderate respiratory distress. His blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 110/min and irregular. On chest auscultation, expirations are prolonged and there are bilateral wheezes. You administer bronchodilators, facial mask oxygen, and lorazepam for agitation. Thirty minutes later, he is lethargic and confused. While you discuss the case with your attending, the patient experiences a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. Which of the following most likely underlies his neurologic symptoms?
New-onset thromboembolic stroke
Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Cerebral vasoconstriction
Carbon dioxide retention
Metabolic acidosis
A 65-year-old man, who had been hospitalized for an acute pneumonia 3 days previously, begins screaming for his nurse, stating that “there are people in the room out to get me.” He then gets out of bed and begins pulling out his IV line. On examination, he alternates between agitation and somnolence. He is not oriented to time or place. His vital signs are as follows: pulse, 126 beats per minute; respiration, 32 breaths per minute; blood pressure (BP), 80/58; temperature, 39.2°C (102.5°F). Which of the following diagnoses best fits this patient’s clinical picture?
Dementia
Schizophreniform disorder
Fugue state
Delirium
Brief psychotic episode
A 65-year-old white female comes to the ER because of persistent vomiting and epigastric pain. She has been suffering from left knee osteoarthritis for the past 6 years, and has been taking ibuprofen for the past year. She also has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease but is well controlled on her current medications. She quit smoking a few years ago. Her laboratory results are given below: ABG: pH 7.55, PCO2 46 mm Hg. Chemistry panel: Serum sodium 132 mEq/L, Serum potassium 3.0 mEq/L, Chloride 88 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 38 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl. Which of the following would describe her primary acid-base status?
Normal profile
Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Respiratory acidosis
Respiratory alkalosis
A 65-year-old white man is complaining of a sudden loss of vision in his left eye which resolved after 15 minutes. "It seemed like a curtain was falling down in my eye!" said the patient. He recalls having a similar episode 3 months ago. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, for which he takes lisinopril (20mg) and hydrochlorothiazide (25mg) daily. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is normal. Fundoscopy reveals zones of whitened, edematous retina following the distribution of the retinal arterioles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Central retinal artery occlusion
Central retinal vein occlusion
Amaurosis fugax
Vitreous hemorrhage
Hypertensive retinopathy
A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of bleeding from the vagina. She states that her last menstrual period was at age 50 and that she has had no bleeding since. She has no medical problems and takes no medications. She is not sexually active. Examination is unremarkable, including a normal pelvic examination. After informed consent is obtained, an endometrial biopsy is performed. The patient complains of discomfort during and after the procedure but feels well enough to go home. Later that night, with her abdominal pain worsening, the patient comes to the emergency department. An ultrasound is performed that shows a normal uterus and adnexae but a complex fluid collection posterior to the uterus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bowel perforation
Endometritis
Endometrial cancer
Tubo-ovarian abscess
Uterine perforation
A 65-year-old woman complains of leakage of urine. Which of the following is the most common cause of this condition in such patients?
Anatomic stress urinary incontinence
Urethral diverticulum
Overflow incontinence
Unstable bladder
Fistula
A 65-year-old woman has an 8-year history of involuntary loss of urine: she leaks small amounts of urine when she coughs, sneezes, or laughs. In providing a history to her physician, she complains about feeling pelvic pressure, but denies feeling a burning sensation upon urinating or having an abnormally strong urinary urgency or frequency. She has no loss of urine at night; however, the symptoms occur frequently enough that she needs to wear a perineal pad. She underwent menopause 12 years ago. For treatment of hot flashes, she initially used oral estrogen hormone replacement along with 7 days of medroxyprogesterone acetate 1 week of every month. For the last 8 years, she has not used any hormone therapy. Speculum examination reveals an atrophic vagina and cervix without lesions. Bimanual examination reveals a small, symmetrical, midline, mobile, nontender uterus. There are no adnexal masses. With the Valsalva maneuver, there is protrusion of her anterior vaginal wall. Which one of the following is the most likely diagnosis for the physical finding?
Cystocele
Urethral diverticulum
Gartner’s duct cyst
Rectocele
Enterocele
A 65-year-old woman has had pain in her right shoulder and has been treated with analgesics without relief. The CXR reveals a mass in the apex of the right chest. A transthoracic needle biopsy documents carcinoma. Superior pulmonary sulcus carcinomas (Pancoast tumors) are bronchogenic carcinomas that typically produce which of the following clinical features?
Atelectasis of the involved apical segment
Pain in the T4 and T5 dermatomes
Horner syndrome
Nonproductive cough
Hemoptysis
A 65-year-old woman is being evaluated for "generalized depression." She has felt weak and fatigued ever since her husband died 4 months ago. She does not have any suicidal thoughts, but is losing interest in her daily activities. She quit smoking 24 years ago, and drinks 1-2 beers weekly. Physical examination reveals pallor and cervical lymphadenopathy. Blood work reveals: Hemoglobin 12.0 g/L, MCV 85 fl, Platelets 224,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 54,500/mm3, Neutrophils 16%, Lymphocytes 75%, Monocytes 9%. Some variants of lymphocytes and smudge cells are present. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Lymphoblastic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Hodgkin's disease
Chronic myeloid leukemia
Hairy cell leukemia
A 65-year-old woman is involved in a motor vehicle collision and sustains multiple left-sided rib fractures. Upon presentation to the ER her vital signs are stable and she is in no respiratory distress. Chest x-ray reveals fractures of ribs 4 to 7 on the left side without evidence of hemothorax or pneumothorax. She is admitted for observation and a few hours later she develops shortness of breath. A repeat chest x-ray demonstrates a well-defined infiltrate in her left lung. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Pulmonary contusion
Pulmonary embolus
Pneumonia
Myocardial infarction
Cardiac tamponade
A 65-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of an abnormal screening mammogram. She denies any breast masses, nipple discharge, pain, or skin changes. Past history is pertinent for hypertension. Family history is positive for postmenopausal breast cancer in a sister. She has a normal breast examination and no axillary adenopathy. The remainder of her examination is unremarkable. An MLO view of the right breast is shown in Figure 6-6a along with a magnification view of the craniocaudal (CC) film (Figure 6-6b). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Milk of calcium
Involuting fibroadenoma
Phyllodes tumor
DCIS with or without an invasive component
LCIS with or without an invasive component
{"name":"DES C_Diagnosis (10) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 60-year-old female comes to your office for progressive exertional dyspnea and new-onset ankle swelling. She has been recently worked up for proteinuria and easy bruisability. Otherwise her past medical history is insignificant. She has a ten pack-year history of smoking and she drinks two to three glasses of wine every day. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), blood pressure is 130\/70 mmHg, pulse is 80\/min and respirations are 14\/min. There is mild jugular venous distention on physical examination. Chest auscultation shows scattered bibasilar crackles. Echocardiography reveals symmetrical thickening of the ventricular walls, normal ventricular dimensions and a slightly reduced systolic function. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/18-745073/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Test Your Knowledge About Me!
15817
Vocabulary. Evolve 3. Unit 8.
10519
Drown in your own sperm
10515
What Do You Know About Water Safety?
1586
Food and Drink Trivia - 201+ Free Questions & Answers
201015324
What Gem Am I in Steven Universe? Free Personality
201016829
Which Heroes of Olympus Character Are You? Free
201017863
Figures of Speech - Examples with Answers (Free)
201018846
Identify the Highlighted Muscle - Test Your Anatomy
201019803
Which Seinfeld Character Are You? Take the Free
201018928
AP Stats Correlation & Regression - Chapter 3
201017588
What Horse Breed Should I Get? Free to Find Your Match
201019010