DES C_Diagnosis (4) Prepared : CHILLY
A 25-year-old previously healthy man is scheduled for elective inguinal hernia repair under general anesthesia. After induction of anesthesia and initial inguinal incision, the patient develops tachycardia, muscle rigidity, fever of 38.5°C, and elevated end-tidal carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Pneumonia
Atelectasis
Urinary tract infection
Myocardial infarction
Malignant hyperthermia
A 25-year-old white female presents to the clinic with persisting pain in her wrists and ankles for the last 3 months. The pain is 3/10 in intensity, and partially relieved by ibuprofen. She also has a rash on her face. She denies smoking, and drinks alcohol occasionally. Her temperature is 37.3°C (99.2°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 79/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination reveals swollen joints of the hands and ankle, as well as erythema over the bridge of the nose and the upper cheeks. There is no muscle weakness. Labs show: Hemoglobin 11.0 g/dL, Hematocrit 33%, Platelets 240,000/mm3, WBC 13,600/mm3. Leukocyte distribution:Segmented neutrophils 76%, Lymphocytes 20%, Bands 2%, Monocytes 2%. RF, ANA, and antibodies to double stranded-DNA are positive in high titers. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Scleroderma
Dermatomyositis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Polymyositis
Mixed connective tissue disease
A 25-year-old white female presents with a 5-day history of sore throat, extreme fatigue, and headaches. She has just returned from a spring break in Jamaica where she had "the time of her life." She smokes 2-3 cigarettes daily and occasionally drinks alcohol. Her vital signs are stable. She is afebrile. Physical examination reveals posterior cervical lymphadenopathy, mild splenomegaly, and exudative pharyngitis. Palatal petechiae are present. CBC shows: WBC 16,000/cmm with 55% lymphocytes, Hemoglobin 13.5gm/dl, Hematocrit 41%, Platelets 216,000/cmm. Many variant forms of lymphocytes are seen, including cells with convoluted nuclei and highly vacuolated cytoplasm. Rapid streptococcal throat test, urinalysis, and heterophilic antibody test are all negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute myeloid leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic myeloid leukemia
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Infectious mononucleosis
A 25-year-old woman brings her 5-day-old infant to the emergency room after noticing that he bruises very easily. Her pregnancy was normal, and the baby was born at term via vaginal delivery at home. This is the child's first visit to the doctor. He is exclusively breast-fed, and there is no family history of bleeding disorders. On physical examination, his vital signs are within normal limits. You note several ecchymotic skin lesions, but his exam is otherwise normal. Laboratory studies show the following: Prothrombin time 20 sec, Partial thromboplastin time 37 sec, Platelets 200,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
Impaired synthesis of von Willebrand factor
Consumption of coagulation factors
Factor VIII deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency
Excessive destruction of platelets
A 25-year-old woman comes to the office and complains of intermittent dizziness and an unsteady gait for the last few days. Her symptoms worsen with exercise. Her past medical history is significant for tingling and numbness of her right foot that lasted 3-4 days (1 year ago), and visual loss in her right eye which spontaneously resolved (3 years ago). She is currently nursing her 2-month-old baby. Her obstetrical history was uncomplicated. Her neurological examination shows right hyperactive deep tendon reflexes. On attempted left gaze, her left eye abducts and exhibits horizontal jerk nystagmus, but her right eye remains stationary. When she attempts to look to the right, her right eye abducts and exhibits horizontal jerk nystagmus, but her left eye remains stationary. The patient is able to converge both eyes together, without any associated nystagmus. The facial muscles show no signs of weakness. Where is the most likely site of this patient's lesion?
Optic nerve
Optic tract
Optic chiasma
Optic radiations
Medial longitudinal fasciculus
A 25-year-old woman comes to the physician because of pain and burning with urination. She states that the symptoms started two days ago and have worsened since. She has no fever or chills and has never had these symptoms before. She has hypothyroidism for which she takes thyroid hormone replacement. Otherwise she has no medical problems. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F). Examination is unremarkable including a normal pelvic examination. A KOH and normal saline "wet prep" is performed on her vaginal discharge and is negative. Urinalysis reveals numerous white blood cells. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Escherichia coli
Pseudomonas species
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Trichomonas vaginalis
A 25-year-old woman in her 15th week of pregnancy presents with uterine bleeding and passage of a small amount of watery fluid and tissue. She is found to have a uterus that is much larger than estimated by her gestational dates. Her uterus is found to be filled with cystic, avascular, grapelike structures that do not penetrate the uterine wall. No fetal parts are found. Immunostaining for p57 was negative in the cytotrophoblasts and villi mesenchyme. Which of the following is the best diagnosis?
Partial hydatidiform mole
Invasive mole
Complete hydatidiform mole
Placental site trophoblastic tumor
Choriocarcinoma
A 25-year-old woman is diagnosed with schizophrenia when, after the sudden death of her mother, she begins complaining about hearing the voice of the devil and is suddenly afraid that other people are out to hurt her. Her history indicates that she has also experienced a 3-year period of slowly worsening social withdrawal, apathy, and bizarre behavior. Her family history includes major depression in her father. Which of the following details of her history leads the physician to suspect that her outcome may be poor?
She had an insidious onset of her illness
There is a history of affective disorder in her family
She had an acute precipitating factor before she began hearing voices
She is female
She was age 25 at diagnosis
A 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency room complaining of redness and pain in her right foot up to the level of the midcalf. She reports that her right lower extremity has been swollen for at least 15 years, but her left leg has been normal. On physical examination, she has a temperature of 39°C (102.2°F) and the right lower extremity is nontender with nonpitting edema from the groin down to the foot. There is cellulitis of the right foot without ulcers or skin discoloration. The left leg is normal. Which of the following is the most likely underlying problem?
Congenital lymphedema
Venous insufficiency
Lymphedema praecox
Deep venous thrombosis
Acute arterial insufficiency
A 25-year-old woman presents with lower abdominal pain, fever, and a vaginal discharge. Pelvic examination reveals bilateral adnexal (ovarian) tenderness and pain when the cervix is manipulated. Cultures taken from the vaginal discharge grow Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s adnexal pain?
Adenomatoid tumor
Endometriosis
Ectopic pregnancy
Luteoma of pregnancy
Pelvic inflammatory disease
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 32 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of acute onset severe uterine contractions and moderate vaginal bleeding. Her first pregnancy was uncomplicated. She has a history of cocaine addiction but she is now participating in a drug rehabilitation program. Ultrasonogram performed at the 16th week showed no abnormalities and an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7F), blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 15/min. Physical examination shows uterine tenderness, hyperactivity, and increased uterine tone. Fetal heart tracing shows 140/min with good long-term and beat-to-beat variability. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Abruptio placenta
Placenta previa
Vasa previa
Uterine rupture
Normal labor
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2 is 4days status post cesarean section and develops a temperature to 100.7 F (38.2 C). She had her cesarean section when she went into unstoppable preterm labor with a breech fetus. She had an uncomplicated postoperative course until this temperature elevation. Her pulse is 100/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, and respirations are 16/min. There is discoloration and cyanosis around the incision. The area around the incision is completely numb. There is no uterine tenderness on bimanual exam. Which of the following is of the most concern in this patient?
Endometritis
Mastitis
Necrotizing fasciitis
Preeclampsia
Wound infection
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, comes to the physician to discuss birth control options. She and her partner have tried to use condoms; however, they find it difficult to use them consistently and she would like to try another form of contraception. She has no medical problems, takes no medications, and has no family history of cancer. Her examination is within normal limits. After a discussion with the physician, she chooses to take the oral contraceptive pill (OCP). She stays on the pill for the next three years. She now has most significantly decreased her risk of developing which of the following malignancies?
Bone cancer
Breast cancer
Cervical cancer
Endometrial cancer
Liver cancer
A 25-year-old, HIV-positive male presents to the office with an altered mental status. He is disoriented, lethargic, and has loss of recent memory. These symptoms have been present for the last month. His current medications include zidovudine, didanosine, indinavir, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and azithromycin. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/80mm Hg, and respirations are 16/min. The neurological examination is non-focal. His CD4 count is 40/microl and viral load is 25,000 copies/ml by PCR. MRI scan reveals a solitary, irregular, weakly ring-enhancing mass in the periventricular area. The serology for Toxoplasma is positive. PCR of CSF shows EBV DNA. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Primary CNS lymphoma
AIDS dementia complex
Cerebral toxoplasmosis
Bacterial abscess
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
A 26-year-old black gravida 2, para 1, at 32 weeks' gestation presents to the physician for a prenatal visit. Her prenatal course has been remarkable for hyperemesis gravidarum in the first trimester. She also had a urine culture in the first trimester that grew out Group B Streptococcus. She has had type 1 diabetes for the past 2 years and has had good control of her blood glucose levels during this pregnancy. Her first pregnancy resulted in a low transverse cesarean section for dystocia. Other than insulin, she takes no medicines and has no known drug allergies. After a routine prenatal visit, the physician sends her to the antepartum fetal testing unit to undergo a non-stress test (NST). Which of the following characteristics makes this patient a good candidate for antepartum fetal testing with an NST?
Black race
History of cesarean section
Group B Streptococcus urine culture
Diabetes mellitus
Hyperemesis gravidarum
A 26-year-old Caucasian female calls your office with a question about levothyroxine dosage during pregnancy. She is contemplating her first pregnancy very soon. You have been following her for primary hypothyroidism for several years. Her thyroid functions have been stable on a daily levothyroxine dose of 100µg. Her TSH level three months ago was 2.0 µU/ml (0.35 - 5.0 µU/ml is normal). What would be the most appropriate answer to this patient's question?
She is most likely to decrease her levothyroxine dose during pregnancy
Levothyroxine is contraindicated in pregnancy and she has to switch to liothyronine (T3)
Her levothyroxine dose will not change after she becomes pregnant
She is most likely to increase her levothyroxine dose during pregnancy
Ask her to increase her levothyroxine dose before becoming pregnant
A 26-year-old G0P0 comes to your office with a chief complaint of being too hairy. She reports that her menses started at age 13 and have always been very irregular. She has menses every 2 to 6 months. She also complains of acne and is currently seeing a dermatologist for the skin condition. She denies any medical problems. Her only surgery was an appendectomy at age 8. Her height is 5ft 5 in., her weight is 180 lb, and her blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. On physical examination, there is sparse hair around the nipples, chin, and upper lip. No galactorrhea, thyromegaly, or temporal balding is noted. Pelvic examination is normal and there is no evidence of clitoromegaly. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient’s problem?
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor of the ovary
Idiopathic hirsutism
Late-onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Adrenal tumor
A 26-year-old male complains of itching and excessive watering of both eyes since this morning. He denies blurring of vision. He uses albuterol inhaler regularly for his bronchial asthma. His vital signs are normal. On examination, both eyes are noted to have conjunctival edema, hyperemia, swollen eyelids, and profuse watery discharge. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis
Toxic conjunctivitis
Blepharitis
Dacryocystitis
A 26-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of a sudden onset of severe, colicky, leftsided flank pain that radiates to the scrotum. He also has nausea, vomiting and dark-colored urine. He has never had these symptoms before. Examination shows no abnormalities. Non-contrast helical CT shows a 5 mm radiopaque stone in the left upper ureter. His laboratory studies are as follows: Serum calcium 9.8 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.9 mg/dl, BUN 15 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows hematuria but no casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Calcium oxalate stones
Calcium phosphate stones
Uric acid stones
Cysteine stones
Struvite stones
A 26-year-old man comes to the physician with the chief complaint of a depressed mood for the past 5 weeks. He has been feeling down, with decreased concentration, energy, and interest in his usual hobbies. Six weeks prior to this office visit, he had been to the emergency room for an acute asthma attack and was started on prednisone. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Mood disorder secondary to a general medical condition
Substance-induced mood disorder
Major depression
Adjustment disorder
Dysthymia
A 26-year-old man comes to your office with a one-week history of right-sided ear pain. The pain often wakes him up at night, and increases in severity when he chews food. He cannot recall any recent episodes of pharyngitis. He denies having any ear discharge, sinus tenderness, or skin rash. He exercises by swimming frequently at a local club. He is sexually active and uses condoms "quite regularly." He lives with his brother, who often comments on his habit of grinding his teeth at night. On examination, his ears are normal with a mild amount of wax. Pain is not elicited by pulling on the pinna. There are no hearing deficits appreciated. Mobility of the tympanic membrane is normal, and the Weber and Rinne test results are within normal limits. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Ramsay Hunt syndrome
Otitis media
Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
Otitis externa
A 26-year-old man is resuscitated with packed red blood cells following a motor vehicle collision complicated by a fractured pelvis and resultant hemorrhage. A few hours later the patient becomes hypotensive with a normal central venous pressure (CVP), oliguric, and febrile. Upon examination, the patient is noted to have profuse oozing of blood from his intravenous (IV) sites. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hypovolemic shock
Gram-negative bacteremia
Acute adrenal insufficiency
Transfusion reaction
Ureteral obstruction
A 26-year-old man presents with increased thirst, urinary frequency, and nocturia over the past several months. Physical examination is unremarkable. Twenty-four-hour urine osmolarity is < 300 mOsm/L. A fluid deprivation test does not result in an increased urine osmolarity. Administration of 0.03 μg/kg of desmopressin results in a urine osmolarity of 450 mOsm/L after 2 hours. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Central diabetes insipidus
Psychogenic polydipsia
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of ADH
Diabetes mellitus
A 26-year-old man with a history of kidney stones presents with 1 week of severe burning epigastric pain. He also notes several days of diarrhea and nausea but denies emesis or fever. His family history is remarkable for a paternal uncle with pancreatic cancer. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), heart rate is 88/min, respiratory rate is 16/min, and blood pressure is 125/85 mm Hg. Abdominal examination is significant for tenderness in the mid-epigastrium. Upper endoscopy reveals a 1-cm ulceration in the first part of the duodenum. This is the third episode of confirmed peptic ulcers in this patient. Laboratory studies show: Na+: 140 mEq/L, K+: 4.9 mEq/L , Cl−: 105 mEq/L, HCO −: 25 mEq/L, Ca2+: 12.0 mg/dL, PO4: 1.4 mg/dL, Mg2+: 2.0 mg/dL, Blood urea nitrogen: 10 mg/dL Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL , Glucose: 87 mg/dL. Which of the following is most likely to be found in this patient?
Medullary thyroid carcinoma
Pheochromocytoma
Papillary thyroid carcinoma
Prolactinoma
Squamous cell lung cancer
A 26-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the emergency department because of severe right lower quadrant pain. She states that the pain started last night. This morning she was awakened from sleep with severe pain in the same area. During the episode of pain, she also had nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. On admission to the emergency department she required 5 mg of morphine to control her pain. Examination is significant for right lower quadrant tenderness and a tender right adnexal mass on pelvic examination. Urine hCG is negative. Urinalysis is negative. Transvaginal ultrasound reveals an 8 cm right ovarian mass. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Appendicitis
Ectopic pregnancy
Nephrolithiasis
Ovarian torsion
Pelvic inflammatory disease
A 26-year-old previously healthy white female is brought to the emergency department after having an episode of seizures one hour ago. She has a two-day history of fever and headaches, for which she has been taking acetaminophen and ibuprofen without much relief. She has no family history of seizures. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 18/min. Complete blood count and CT scan of the head are unremarkable. Her cerebral spinal fluid study shows: Opening pressure 220 mm H2O, Protein 200 mg/dl, Glucose 55 mg/dl, WBC 150/mm3, Lymphocytes 90%, Polymorphs 10%, RBC 200/cmm. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
Pneumococcal meningitis
Hemophilus influenza meningitis
Meningococcal meningitis
Herpes simplex encephalitis
Cryptococcal meningitis
A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 32 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of swelling of her hands and feet. Her previous prenatal check-up was normal. Blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg, and five minutes later following lateral rest her blood pressure is 140/95 mmHg. Physical examination shows 2+ pitting edema of the legs and a macular eruption on the cheekbones. Optic fundi show no abnormalities. Laboratory studies are as follows: Urinalysis: 4+ protein, RBC casts, Urine protein: 8 g/24hr, Uric acid: 5 mg/dl, BUN: 28 mg/dl, Serum creatinine: 2.1 mg/dl, Serum electrolytes, liver function tests and coagulation studies are within normal limits. A serum antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is positive in high titers Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chronic hypertension with superimposed pre-eclampsia
Glomerulonephritis
Pregnancy induced hypertension
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
HELLP syndrome
A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 32 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of swelling of her hands and feet. Her previous prenatal check-up was normal. Blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg, and five minutes later following lateral rest her blood pressure is 140/95 mmHg. Physical examination shows 2+ pitting edema of the legs and a macular eruption on the cheekbones. Optic fundi show no abnormalities. Laboratory studies are as follows: Urinalysis: 4+ protein, RBC casts, Urine protein: 8 g/24hr, Uric acid: 5 mg/dl, BUN: 28 mg/dl, Serum creatinine: 2.1 mg/dl, Serum electrolytes, liver function tests and coagulation studies are within normal limits. A serum antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is positive in high titers. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Pregnancy induced hypertension
Glomerulonephritis
Chronic hypertension with superimposed pre-eclampsia
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
HELLP syndrome
A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 42 weeks' gestation comes to the labor and delivery ward for induction of labor. The prenatal course was significant for a positive group B Streptococcus culture performed at 35 weeks. Antenatal testing over the past 2 weeks has been unremarkable. The patient is started on lactated Ringer's IV solution. Sterile vaginal examination shows that the patient's cervix is long, thick, and closed. Prostaglandin (PGE2) gel is placed into the vagina, and electronic fetal heart rate monitoring is continued. In approximately 60 minutes, the fetal heart rate falls to the 90s, as the tocodynamometer shows the uterus to be contracting every 1 minute with essentially no rest in between contractions. Which of the following was most likely the cause of the uterine hyperstimulation?
Infection
Postdates pregnancy
IV fluids
Prostaglandin (PGE2) gel
Vaginal examination
A 26-year-old white female comes to the Emergency Room with severe shortness of breath. She has a long history of asthma with periodic exacerbations. She is taking an inhaled albuterol, inhaled steroid, salmeterol and cromolyn. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 24/min. On examination, she has moderate respiratory distress, prolonged expiratory phase, and significant wheezing all over the lung fields. Patient is admitted and is given nebulized albuterol, intravenous methyl prednisone, and oxygen. The next day her respiratory status improved. Her vital signs did not change much, except normalization of respiratory rate. Still scattered bilateral wheezes are heard on lung auscultation. The next day her laboratory values are: Hemoglobin 14 g/dL, MCV 95 fL, Leukocyte count 19,000/cmm, Segmented Neutrophils 80%, Bands 5%, Lymphocytes 13%, Eosinophils 0%, Basophils 0%, Monocytes 2%. Chest x-ray obtained at the time of admission is normal, except for hyperinflated lung fields. What is the most probable cause of the abnormal lab findings in this patient?
Pneumonia
Hypersensitivity reaction
Myeloproliferative state
Metabolic disorder
Drug reaction
A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician's office for evaluation of a vulvar ulcer that she noticed two days ago. Initially she had a small painless papule that later became ulcerated. Upon further questioning she reluctantly admits to using sex to obtain drugs. She also reports using oral contraceptives to prevent pregnancy. On vulvar examination there is a 2-cm ulcer with a non-exudative base and a raised, indurated margin. Painless bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy is present. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Syphilis
Chancroid
Herpes genitalis
Granuloma inguinale
Basal cell carcinoma
A 26-year-old woman complains of a vaginal discharge causing burning and itching of the perineum. The pH of the discharge is 4.5. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her discharge?
Monilial vaginitis
Chlamydial cervicitis
Trichomonas vaginitis
Gonococcal cervicitis
Bacterial vaginosis
A 26-year-old woman develops acute lower abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. While in the bathroom she passes a cast of tissue composed of clot material and then collapses. She is brought to the hospital, where a physical examination reveals a soft, tender mass in right adnexa and pouch of Douglas. Histologic examination of the tissue passed in the bathroom reveals blood clots and decidualized tissue. No chorionic villi or trophoblastic tissue are present. Which of the following conditions is most likely present in this individual?
Aborted intrauterine pregnancy
Complete hydatidiform mole
Ectopic pregnancy
Endometrial hyperplasia
Partial hydatidiform mole
A 26-year-old woman in the third trimester of her first pregnancy develops persistent headaches and swelling of her legs and face. Early during her pregnancy, a physical examination was unremarkable; however, now her blood pressure is 170/105 mmHg and urinalysis reveals slight proteinuria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Eclampsia
Nephritic syndrome
Gestational trophoblastic disease
Nephrotic syndrome
Preeclampsia
A 26-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her husband after she begins screaming that her children are calling to her and becomes hysterical. The husband states that 2 weeks previously, the couple’s two children were killed in a car accident, and since that time the patient has been agitated, disorganized, and incoherent. He states that she will not eat because she believes he has been poisoning her food, and she has not slept for the past 2 days. The patient believes that the nurses in the emergency room are going to cause her harm as well. The patient is sedated and later sent home. One week later, all her symptoms remit spontaneously. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
Delirium
Brief psychotic disorder
Schizophreniform disorder
Major depression with psychotic features
Posttraumatic stress disorder
A 26-year-old woman presents to her physician because of pain in her breast. She gave birth 3 months ago and is breast-feeding. Soon after she began lactating she developed cracks in the nipples, and for the past 5 days her left breast has become progressively more tender. On physical examination, her affected breast is red, hot, swollen, and painful to palpation. Her temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), and her white cell count is 13,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Breast abscess
Breast cancer
Intraductal papilloma
Mastalgia
Traumatic hematoma
A 26-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of fatigue. Her past medical history is insignificant. She was adopted in Greece and came to the United States when she was three years old. Her menstrual periods are regular and bleeding lasts three days. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. She takes no medication. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 10.1 g/L, MCHC 28%, MCV 70 fL, Platelets 200,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 7,500/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 33%, Monocytes 10%. Fecal occult blood test is negative. Iron therapy is initiated. When the patient returns four weeks later, her lab findings are essentially the same. This patient most likely suffers from:
Iron deficiency
Cobalamin deficiency
Folic acid deficiency
Erythropoietin deficiency
Hemoglobinopathy
A 26-year-old woman presents with a one-week history of dysuria and increased urinary frequency. She admits to having multiple sexual partners in the past. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows suprapubic tenderness. Mucopurulent discharge is observed at the urethral os. Urinalysis shows: Blood Negative, Glucose Negative, Ketones Negative, Leukocyte esterase Positive, Nitrites Negative, WBC 40-50/hpf, RBC 1-2/hpf, Bacteria None. Urine culture after 24hours < 100colonies/ml. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute pyelonephritis
Chlamydial urethritis
Acute bacterial cystitis
Gonococcal urethritis
Trichomonal vaginitis
A 26-year-old woman with panic disorder notes that during the middle of one of her attacks she feels as if she is disconnected from the world, as though it were unreal or distant. Which of the following terms best describes this symptom?
Mental status change
Illusion
Retardation of thought
Depersonalization
Derealization
A 27-year-old African-American woman presents with several complaints. She has had pain and swelling of her hands and wrists for the past few days. She also complains of easy fatigability and frequent mouth ulcers. She has no significant past medical history and does not take any medications. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 140/90mmHg, and pulse is 76/min. Examination reveals swollen, tender metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints. There are superficial ulcers on her buccal mucosa. X-ray of hands and wrists shows no bony erosions. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 11.0 g/L, Platelets 90,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3. Urinalysis shows 2+ protein and red blood cell casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her joint pains?
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Dermatomyositis
Sarcoidosis
Neuropathic joint disease
Systemic iron overload
A 27-year-old Caucasian woman presents with abdominal pain, diarrhea and a 4.5 (2kg) weight loss for the past two months. She describes the abdominal pain as intermittent, moderate-to-severe, and located in the right lower quadrant. Over the past 48 hours, the pain has intensified. Her temperature is 37.6°C (99.6°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 14/min. Several shallow ulcers are present in her mouth. Abdominal examination shows tenderness in the right lower quadrant without rebound. Rectal examination shows mucus. Rectosigmoidoscopy is unremarkable. An x-ray film of the abdomen shows gas in the small and large bowels. Laboratory studies show: Hb 10.2 g/dL, WBC 16,500/cmm, Platelet count 530,000/cmm, ESR 48/hr. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Diverticulitis
Celiac disease
Irritable bowel syndrome
Crohn's disease
Ulcerative colitis
A 27-year-old female at 30 weeks gestation complains of difficulty hearing, especially on the right side. She denies any ear pain or discharge. Her pregnancy was complicated by acute pyelonephritis at 22 weeks gestation, which was treated with antibiotics. She does not smoke or consume alcohol, and she eats a balanced diet. She has no preexisting medical problems and takes no medications aside from a multivitamin. Her blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and heart rate is 75/min. Cardiac and pulmonary examinations are unremarkable. No focal abnormalities are found on neurologic examination. When a tuning fork is placed on the right mastoid process, she appreciates the tone louder than when it is held near the external auditory meatus. Audiometry shows right low-frequency hearing loss. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
Antibiotic treatment
Hypertension of pregnancy
Meniere's disease
Otosclerosis
Chronic otitis media
A 27-year-old female is brought to the emergency department by her husband after she fainted at home. The patient admits that she has been fasting and exercising vigorously for the past two days to compensate for the excessive amount of food she ate three days ago. She admits to a similar pattern of eating large amounts of food followed by a period of fasting since she lost her job a few months ago. She is very distressed by these "uncontrollable eating episodes" because she feels awful afterward. Periodically, she breaks down in tears while telling her story. Review of systems is otherwise unremarkable. Her menstrual periods are regular. Vital signs are temperature 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 98/62 mmHg, pulse 96/min, and respiratory rate 14/min. Her height is 5'4" (163 cm) and weight is 120 lbs (54 kg). Physical examination is unremarkable. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Anorexia nervosa
Bulimia nervosa
Borderline personality disorder
Histrionic personality disorder
Major depression
A 27-year-old G4P3 at 37 weeks presents to the hospital with heavy vaginal bleeding and painful uterine contractions. Quick bedside ultrasound reveals a fundal placenta. The patient’s vital signs are blood pressure 140/92 mmHg, pulse 118 beats per minute, respiratory rate 20 breaths per minute, and temperature 37C (98.6F). The fetal heart rate tracing reveals tachycardia with decreased variability and a few late decelerations. An emergency cesarean section delivers a male infant with Apgar scores of 4 and 9. With delivery of the placenta, a large retroplacental clot is noted. The patient becomes hypotensive, and bleeding is noted from the wound edges and her IV catheter sites. She requires 12 units of packed red blood cells and fresh frozen plasma for resuscitation. After a short stay in the intensive care unit the patient recovers. When can long-term complications related to sequela of postpartum hemorrhage first be noted?
6 hours postpartum
1 week postpartum
1 month postpartum
6 month postpartum
1 year postpartum
A 27-year-old has just had an ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following events would be most likely to predispose to ectopic pregnancy?
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Induction of ovulation
Previous cervical conization
Exposure in utero to diethylstilbestrol (DES)
Use of a contraceptive uterine device (IUD)
A 27-year-old immigrant from El Salvador has a 14 × 12 × 9 cm mass in her left breast. It has been present for 7 years and has slowly grown to its present size. The mass is firm, nontender, rubbery, and completely movable, and it is not attached to the overlying skin or the chest wall. There are no palpable axillary nodes or skin ulceration. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Breast cancer
Cystosarcoma phyllodes
Chronic cystic mastitis
Intraductal papilloma
Mammary dysplasia
A 27-year-old male presents to clinic complaining of "marital problems." He says that for the past year that he has been married, he and his wife have not successfully had sexual intercourse on even one occasion. He strongly feels that she either finds him physically unattractive or is having an affair with another man. He adds that he is extremely frustrated with his wife "contracting herself," which prevents any kind of vaginal penetration. After several failed attempts, his wife now avoids any sexual intimacy with him. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hypoactive sexual desire
Female sexual arousal disorder
Sexual aversion disorder
Female orgasmic disorder
Vaginismus
A 27-year-old male presents to the physician's office because of pain on the medial side of the tibia just below the knee. The pain does not radiate and is continuous. He relates the onset of his pain to falling on the ground while playing football two weeks ago. He denies fever, malaise and weight loss. His past medical history is not significant. On examination, a well-defined area of tenderness is present on the upper tibia below the medial knee joint. There is no redness, warmth or swelling. His gait is normal. A valgus stress test has no effect on his pain. X-ray of the knee and tibia shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current symptoms?
Anserine bursitis
Medial compartment osteoarthritis
Medial collateral ligament strain
Patellofemoral syndrome
Prepatellar bursitis
A 27-year-old male presents to you with complaints of cough, chest discomfort and dyspnea on exertion. He says that he has lost 10 pounds over the past 2 months. He has been smoking 1 pack per day for the past 10 years. He drinks 2 beers every weekend. He denies illegal drug use and has not had multiple sexual partners. Physical examination is unremarkable. Chest x-ray reveals a large anterior mediastinal mass. Blood work reveals that he has elevated levels of HCG and alpha-fetoprotein (AFP). What is the most likely diagnosis?
Benign teratoma
Seminoma
Nonseminomatous germ cell tumors
Pericardial cysts
Thymoma
A 27-year-old male presents with a history of intermittent abdominal distention, flatulence and greasy stools. He also complains of fatigue. He has no other medical problems. His family history is unremarkable. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or smoking. His vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows a pruritic, papulovesicular rash over the extensor surfaces of the extremities and over the trunk, scalp and neck. His abdomen is soft, nontender and non-distended. Stool for occult blood testing is negative. Lab studies show: Hemoglobin 10.0 g/L, MCV 75 fl, Platelets 340,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 4,500/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 33%, Monocytes 10%. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis of his skin condition?
Guttate psoriasis
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Pityriasis rosea
Seborrheic dermatitis
Bullous pemphigoid
A 27-year-old male presents with dyspnea and fatigue. He has no family history of asthma, heart disease or any blood disorder. His vital signs are stable, and he is afebrile. The only significant findings on examination are pallor and splenomegaly. Lab studies show: Hematocrit 20%, WBC count 4,000/micro-L, Platelet count 85,000/miro-L, Bilirubin 7 mg/dl, Direct bilirubin 1.2 mg/dl, Serum LDH 500 U/L (normal value is 80-280 U/L), Serum haptoglobin 20mg/dl (normal value is 30-220 mg/dl). Peripheral blood smear shows microcytic hypochromic cells. Serum ferritin is low while total iron binding capacity (TIBC) is elevated. Reticulocyte count is 5 %. Urine dipstick testing is positive for hematuria and microscopy of urine shows 1 RBC/HPF. Repeated G6PD assays are normal. Coomb's and micro-Coomb's tests are negative. Bone marrow examination shows hypocellular marrow. Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?
Aplastic anemia
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
G6PD deficiency
Hereditary spherocytosis
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
A 27-year-old male returning home after a three-month visit to Puerto Rico presents with diarrhea for the past 6 weeks. Other accompanying symptoms include cramps, gas, fatigue and progressive weight loss. Abdominal auscultation shows hyperactive bowel sounds, and borborygmi. The family history is unremarkable for intestinal disease. Laboratory studies show anemia with a hematocrit of 25% and MCV of 105fl; stool examination for ova and parasites is negative. Small intestinal mucosal biopsy shows blunting of villi with infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells, including lymphocytes, plasma cells, and eosinophils. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Celiac disease
Amoebiasis
Tropical sprue
Bacterial overgrowth
Giardiasis
A 27-year-old man comes into the emergency department because of a 2-week history of hemoptysis, breathing difficulty, ankle edema, and dark urine. His past medical history is insignificant. He is not taking any medication. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Laboratory studies show: Hb 10.5 g/dl, Serum Na 135 mEq/L, Serum K 4.8 mEq/L, BUN 36 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 2.8 mg/dl. Urinalysis shows numerous dysmorphic red blood cells/HPF, moderate proteinuria, and red cell casts. Chest x-ray reveals bilateral alveolar infiltrates. Diagnosis of which of the following pulmonary-renal syndromes require emergency plasmapheresis?
Good pasture's syndrome
Polyarteritis nodosa
Wegener's granulomatosis
SLE-associated nephritis
Idiopathic rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
A 27-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of periorbital swelling. He was treated with oral dicloxacillin for a skin infection 3-weeks ago. His urine has turned darker. His temperature is 37.4°C (99.4°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows periorbital swelling. Urinalysis shows 8 RBCs/HPF with RBC casts and a mild proteinuria. Laboratory studies show low serum C3 levels; BUN is 40 mg/dl and serum creatinine is 2 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute pyelonephritis
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis
IgA nephropathy
Post streptococcal glomerulonephritis
A 27-year-old man comes to the physician because of red urine. He has had no pain or burning on urination. He has infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis (diagnosed recently). He takes isoniazid, rifampin, and pyrazinamide. He smokes two packs a day and consumes alcohol occasionally. Vital signs are stable Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute cystitis
Renal tuberculosis
Drug reaction
Nephrolithiasis
Glomerulopathy
A 27-year-old man is shot point blank with a .22-caliber revolver. The entrance wound is in the anterior chest wall, just to the left of the sternal border, at the level of the 4th intercostal space. There is no exit wound. He is diaphoretic, cold, shivering, and anxious, and is asking for a blanket and a drink of water. His blood pressure is 65/40 mm Hg, and his pulse is 145/min and barely perceptible. He has large, distended veins in his neck and forehead. He is breathing adequately and has bilateral breath sounds. He is neurologically intact. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Extrinsic cardiogenic shock due to pericardial tamponade
Extrinsic cardiogenic shock due to tension pneumothorax
Hemorrhagic shock
Intrinsic cardiogenic shock due to myocardial damage
Vasomotor shock
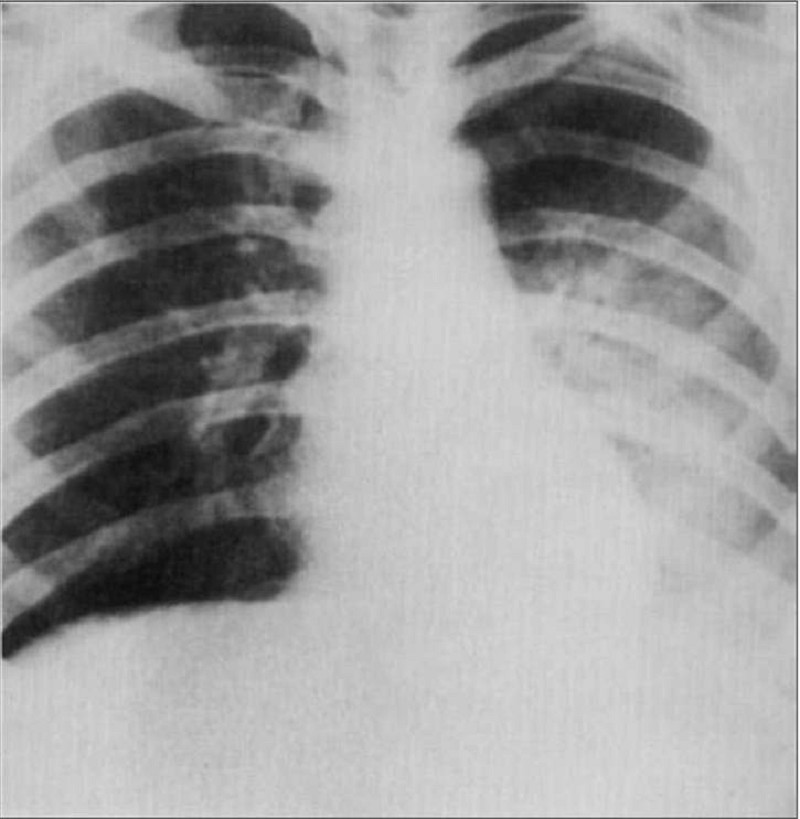
A 27-year-old man presents with chest pain and feeling unwell. He describes cough with blood-tinged sputum, chills, and fever of 2 days’ duration. Physical findings reveal dullness and moist rales in the left lower chest. His CXR is shown in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Pneumonia
Left lower lobe atelectasis
Left lower lobe PE
Tuberculosis
Sarcoidosis
A 27-year-old man sustained penetrating injuries of the chest and abdomen when he was repeatedly stabbed with a long ice-pick. At the time of admission, he had a right pneumothorax, for which a chest tube was placed prior to undergoing a general anesthetic for exploratory laparotomy. The operation revealed no intraabdominal injuries and was terminated sooner than had been anticipated. The patient remained intubated, waiting for the anesthetic to wear off. Because he was not moving enough air, he was placed on a respirator. Then, he suddenly went into cardiac arrest and died. All through this time he had been hemodynamically stable, and never had any signs of hypotension or arrhythmias. Which of the following was the most likely cause of the cardiac arrest?
Air embolism
Fat embolism
Myocardial infarction
Pulmonary embolus
Tension pneumothorax
A 27-year-old primigravid woman at 10 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding and cramping lower abdominal pain. She continues to have cramping in the ER. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 100/76 mmHg, pulse is 84/min and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows an effaced and dilated cervix. Gestational tissue is visualized through the internal cervical os. Bimanual examination shows the uterus is soft and enlarged, and vaginal bleeding is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Inevitable abortion
Threatened abortion
Molar pregnancy
Complete abortion
Missed abortion
A 27-year-old primigravid woman at 30 weeks’ gestation comes to the emergency department complaining of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Earlier in the day she began to experience severe epigastric and later right upper quadrant pain. Until now her pregnancy has been uneventful and she has had regular prenatal care. Her past medical history and review of symptoms are unremarkable. On examination she is a pregnant woman in moderate distress, lying still on the hospital bed. Vital signs are: temperature 38.9 C (102.0 F), blood pressure 105/68 mm Hg, and pulse 108/min. Her abdomen is extremely tender to palpation in the right upper quadrant with guarding. There is no vaginal bleeding or discharge. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit: 36%, Leukocytes: 15,000/mm3 (88% neutrophils), Platelets: 158,000/mm3. Liver function tests, including transaminases, are normal. Prothrombin time is within normal limits. Urinalysis is unremarkable except for a few red blood cells on microscopy. X-ray is deferred out of concern for the fetus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
Pregnancy outside the uterine endometrium
Premature separation of a normally implanted placenta
Luminal obstruction of the appendix from lymphoid hyperplasia or fecalith
Acute fatty infiltration of the liver
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
A 27-year-old woman has been feeling blue for the past 2 weeks. She has little energy and has trouble concentrating. She states that 6 weeks ago she had been feeling very good, with lots of energy and no need for sleep. She says that this pattern has been occurring for at least the past 3 years, though the episodes have never been so severe that she couldn’t work. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Borderline personality disorder
Cyclothymic disorder
Seasonal affective disorder
Major depression, recurrent
Bipolar disorder, depressed
A 27-year-old woman presents to the ER with severe vomiting and abdominal pain that started several hours ago. She describes her emesis as "yellowish." She has a history of alcohol and cocaine use. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 98/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 140/86 mmHg. Physical examination reveals dryness of the oral mucosa. Her abdomen is soft, non-distended, and without hepatosplenomegaly. Mild epigastric tenderness is present on deep palpation. Bowel sounds are increased. No rebound or rigidity is noted. She is treated with intravenous normal saline and metoclopramide. Several hours later she complains of neck pain and her neck muscles are noted to be stiff and tender. Which of the following best explains this patient's current complaints?
Meningeal irritation
Fat necrosis
Medication side effect
Eosinophilic myositis
Nerve root compression
A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, comes to the physician to have her staples removed after an elective repeat cesarean delivery. Her pregnancy course was uncomplicated. She states that she is doing well except that since the delivery she has noticed some episodes of sadness and tearfulness. She is eating and sleeping normally and has no strange thoughts or thoughts of hurting herself or others. Physical examination is within normal limits for a patient who is status post cesarean delivery. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Maternity blues
Postpartum mania
Postpartum depression
Poststerilization depression
Postpartum psychosis
A 28-month-old female has been living with her mother in a shelter for homeless women and children. She is brought to the Emergency Department in status epilepticus, which is stopped with intravenous lorazepam. She is placed on a cardiac monitor and a wide complex tachycardia is noted. The ventricular tachycardia reverts to sinus tachycardia after defibrillation is performed. Her temperature is 38.5 C (101.3 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 195, and respirations are 26. Physical examination reveals a lethargic, pale toddler with dilated and reactive pupils, dry mucous membranes, shallow respirations, diaphoresis and brisk deep tendon reflexes. A urine toxicology screen is most likely to detect which of the following substances?
Barbiturates
Cocaine
Heroin
Marijuana
PCP
A 28-year-old African American female complains of recurrent nasal discharge and increasing nasal congestion. She has a constant sensation of dripping in the back of her throat, and states that food has tasted bland to her recently. She is known to have sickle cell trait. She came to the emergency department for severe wheezing after taking naproxen for menstrual cramping one year ago. She has no history of head trauma. She does not smoke cigarettes, but she admits to smoking marijuana occasionally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Angiofibroma
Inverted papilloma
Nasal polyp
Perforated nasal septum
Pyogenic granuloma
A 28-year-old business executive sees her physician because she is having difficulty in her new position, as it requires her to do frequent public speaking. She states that she is terrified she will do or say something that will cause her extreme embarrassment. The patient says that when she must speak in public, she becomes extremely anxious and her heart beats uncontrollably. Based on this clinical picture, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Panic disorder
Avoidant personality disorder
Specific phobia
Agoraphobia
Social phobia
A 28-year-old Caucasian female comes to the office due to fever for the past 3 days. She also complains of pain and swelling in her right breast for the past 4 days. She exclusively breastfeeds her 3-month-old baby. On examination, she is febrile. Her right breast is engorged, red and tender, without any area of fluctuation. She wants to know if she can continue to breastfeed. Which of the following is a contraindication to breastfeeding?
Mastitis
Maternal rubella infection
Acquired immune deficiency syndrome
Breast milk jaundice
Hemolytic disease of the newborn
A 28-year-old Caucasian male presents to the emergency department complaining of neck pain for the past two days. He states that a chicken bone scratched the back of his throat a week ago. Two weeks ago, he was in Arizona visiting his friends. He is otherwise healthy and has never been hospitalized. His temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), blood pressure is 125/85 mmHg, and heart rate is 120/min. On examination, he refuses to fully open his mouth. Neck movements, especially neck extension, are restricted secondary to pain. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Meningitis
Herpangina
Epiglottitis
Diphtheria
Retropharyngeal abscess
A 28-year-old Caucasian male presents to the office with a rash on his trunk. He complains of constant itching over the area. He has no other medical problems. He denies any family history of diabetes. He currently has two sexual partners, and he does not use condoms. His pulse is 84/min, blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 37°C (98.4°F). On his trunk, there are 4 circular patches with central clearing and scaly borders, measuring approximately 3-8cms in diameter. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Tinea corporis infection
Psoriasis
Erythema multiforme
Pityriasis rosea
Secondary syphilis
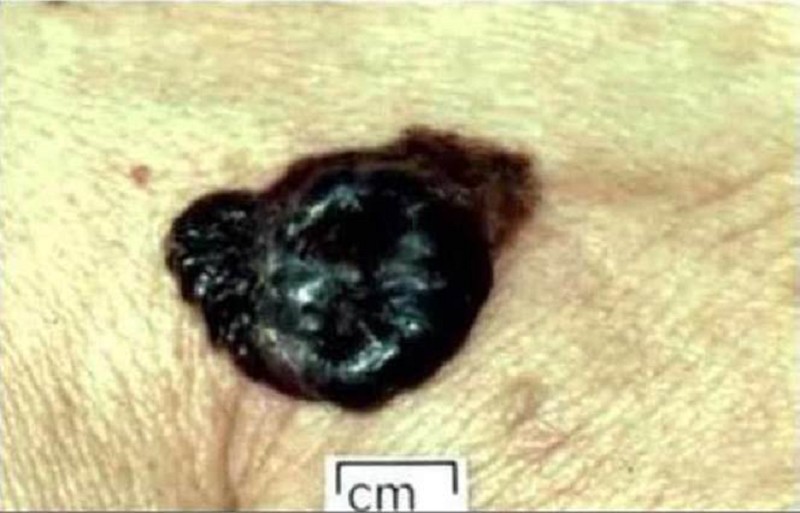
A 28-year-old Caucasian woman comes to the office for a routine skin exam. On exam, you encounter a dark-colored lesion. The patient states that she has had a spot there her whole life. She does state that it has recently "been a little itchy and hurts sometimes." She gives a history of sunburns during childhood, and says that she is very "sun-sensitive." A picture of the mole is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Keratoacanthoma
Blue nevus
Melanoma
Melanocytic nevus
Lentigo simplex
A 28-year-old Caucasian woman presents to the primary care physician with complaints of painless blistering on the backs of her hands, accompanied by an increased fragility of the surrounding skin. She first noted the blisters one week ago, after spending some time gardening outdoors. She denies ever having similar symptoms, but suspects that her mother may occasionally have had a similar presentation that eventually resolved without treatment. Her past medical history is significant for chronic infection with Hepatitis C virus. Current medications include oral contraceptives, which were begun last month. Physical examination reveals mild hyperpigmentation of the face. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Allergic contact dermatitis
Porphyria cutanea tarda
Herpes zoster
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Lmpetigo
A 28-year-old female presents to her family doctor with her mother, who complains that her daughter has been behaving eccentrically and has been socially withdrawn for the past year. The mother says that her daughter used to be very lively and friendly, but that she abruptly quit her job as a data analyst one year ago and now prefers to stay home in her bedroom most of the time. The patient is thoroughly evaluated by a psychiatrist. During that interview, she reveals to the psychiatrist that she constantly hears "so many voices" in her head. The voices tell her various things of a critical and suspicious nature. She also adds that she feels very sad and has had numerous severe crying spells after her pet dog's death four months ago. She prefers to be alone and does not enjoy interacting with others. She has poor sleep and little appetite. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this woman?
Schizophrenia
Major depression with psychotic features
Schizoaffective disorder
Dysthymia
Cyclothymia
A 28-year-old G1 presents to your office at 8 weeks gestation. She has a history of diabetes since the age of 14. She uses insulin and denies any complications related to her diabetes. Which of the following is the most common birth defect associated with diabetes?
Anencephaly
Encephalocele
Meningomyelocele
Sacral agenesis
Ventricular septal defect
A 28-year-old G1A1 woman presents to a gynecology clinic with a chief complaint of reduced menstrual flow for the past 6 months, especially last month. She denies any pain with menstruation or irregularity in her cycle. She says that she had an elective termination by dilation and curettage approximately 9 months ago. She is sexually active with one partner and always uses condoms. Review of her records indicates a past history of abnormal Papanicolaou (Pap) smears, but she has not been followed recently. She denies any history of irregular menses, and says that age of menarche was 13 years. She takes no medications. Physical examination reveals a normally developed 68-kg (150lb) woman who is 183 cm (6') tall. She is in no acute distress. A β-human chorionic gonadotropin test from her original visit 1 week ago is negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Asherman’s syndrome
Endometrial cancer
Cervical stenosis
Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
Kallmann’s syndrome
A 28-year-old G1P0 presents to your office at 18 weeks gestational age for an unscheduled visit secondary to right-sided groin pain. She describes the pain as sharp and occurring with movement and exercise. She denies any change in urinary or bowel habits. She also denies any fever or chills. The application of a heating pad helps alleviate the discomfort. As her obstetrician, what should you tell this patient is the most likely etiology of this pain?
Round ligament pain
Appendicitis
Preterm labor
Kidney stone
Urinary tract infection
A 28-year-old G3P0 has a history of severe menstrual cramps, prolonged, heavy periods, chronic pelvic pain, and painful intercourse. All of her pregnancies were spontaneous abortions in the first trimester. A hysterosalpingogram (HSG) she just had as part of the evaluation for recurrent abortion showed a large uterine septum. You have recommended surgical repair of the uterus. Of the patient’s symptoms, which is most likely to be corrected by resection of the uterine septum?
Habitual abortion
Dysmenorrhea
Menometrorrhagia
Dyspareunia
Chronic pelvic pain
A 28-year-old male comes for evaluation of infertility. He has been healthy and otherwise has no complaints. He says the he eats a high protein diet and exercises daily in order to be muscular. He weighs 85 kg (187 1b) and is 175cm (70 in) tall. His temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), and his blood pressure is 130/82 mmHg. Physical examination shows small testes. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable. Initial laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin: 16.0 g/L, Platelets: 200,000/mm3, Leukocyte count: 4,500/mm3, Serum creatinine: 1.4 mg/dl, Serum LH: low, Serum testosterone: low. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his infertility?
Klinefelter syndrome
Mumps orchitis
Varicocele
Exogenous steroid use
Myotonic dystrophy
A 28-year-old man presents with symptoms of frequent bowel movements, crampy abdominal pain, and the passage of mucus. There is no history of any bloody diarrhea, but recently, he developed joint discomfort in his hands, knees, and back. On examination he is thin, and his abdomen is soft with voluntary guarding in the left lower quadrant. His joints are not actively inflamed and there is an asymmetric distribution. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Lymphoma of the bowel
Amyloid infiltration
Chronic pancreatitis
Ulcerative colitis
Tropical sprue
A 28-year-old man with a past history of bilateral orchiopexy for cryptorchidism presents with a painless, unilateral right scrotal enlargement. On examination, there is a palpable right testicular mass and enlarged inguinal nodes. Scrotal ultrasonography demonstrates heterogeneity of the testis, with an associated hydrocele. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated right-sided retroperitoneal adenopathy. CT scan of the chest is normal. Which of the following would help confirm the diagnosis?
Transscrotal exploration and orchiectomy
Laparotomy with pelvic and retroperitoneal node dissection
Radical orchiectomy through an inguinal incision
Transscrotal needle biopsy
Transscrotal aspiration of the hydrocele for cytology
A 28-year-old nulligravid woman is found on routine annual examination to have an asymptomatic, mobile, nontender, 6 cm unilateral pelvic mass. On sonogram, the mass is partially solid and partially cystic, with foci of calcifications. She is sexually active with her husband of 5 years. She has used combination oral contraceptives for the past 3 years. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Mucinous cystadenoma
Benign cystic teratoma
Granulosa cell tumor
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
Gonadoblastoma
A 28-year-old primigravid woman at 34 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident. She had intense abdominal pain and became agitated and restless in the ambulance. She has mild vaginal bleeding and diffuse abdominal pain. She is on continuous fetal heart monitoring. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests and fetal growth have been normal. Prenatal ultrasound at the 16th week showed no abnormalities and an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. Her blood pressure is 110/60mmHg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 32/min. Physical examination shows hyperventilation, cold extremities and a distended abdomen with irregular contours. Fetal heart monitoring shows repetitive late decelerations and a long-term variability of 2 cycles/min. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Abruptio placenta
Vasa previa
Placenta previa
Uterine rupture
Rupture of ectopic pregnancy
A 28-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician for a follow-up prenatal visit. According to prenatal records, ultrasound at 16 weeks gestation showed an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates and showed no abnormalities. She is now at 40 weeks gestation. Examination shows a fundal height consistent with dates and the cervix is not favorable. Fetal heart tracing is reassuring. She wishes to continue the pregnancy for two more weeks rather than undergoing induction. She should be closely monitored for which of the following?
Polyhydramnios
Oligohydramnios
Abruptio placentae
Placenta previa
Preeclampsia
A 28-year-old teacher presents to the clinic complaining of 5 months of polyuria, polydipsia, and weight loss. Additionally, her menses, which have always been irregular, have stopped altogether. She is concerned because both her mother and maternal aunt suffer from noninsulin-dependent diabetes, and they told her they had similar symptoms before they were diagnosed. Upon questioning she reveals that she is in a committed relationship and has no desire to have children, so she uses barrier protection during intercourse. Physical examination reveals an obese woman with hirsutism currently in no acute distress. Testing for β-human chorionic gonadotropin level, random blood sugar level, cholesterol panel, and a luteinizing hormone/follicle-stimulating hormone ratio suggests the patient has polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). Although no one in her family has had cancer, she is concerned that her symptoms are a harbinger of cancer or that she might be likely to suffer from cancer in the future. This diagnosis would most raise her risk for which kind of cancer?
Cervical cancer
Colon cancer
Endometrial cancer
Lung cancer
Ovarian cancer
A 28-year-old woman and her husband present to her obstetrician. They have been married for 7 years and have been trying to become pregnant for the past 2 years. Prior to this the woman used an intrauterine device for contraception, which she had in place for 5 years. Both are healthy without any medical problems, and both deny a history of sexually transmitted diseases. The woman states that her menstrual cycles have always been regular (every 28 days, lasting for 5 days) since she was 14 years old. She also denies menorrhagia and dysmenorrhea. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this couple’s infertility?
Endometriosis
Premature ovarian failure
Low sperm concentration
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Prior placement of an intrauterine device
A 28-year-old woman at 39 weeks gestation is admitted to the hospital. She has regular uterine contractions. Her blood pressure is 120/70mmHg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 18/min. Fetal heart monitoring is placed and shows a baseline rate of 130 beats/min, without any associated abnormalities. Pelvic examination shows the cervix is 50% effaced and 3cm dilated. Amniotomy is performed and a bloody show is noted. Immediately after the rupture of membranes, the baseline fetal heart rate increases to 160 beats/min and then drops to 70 beats/min. As labor progresses, repetitive late decelerations are noted, as well as an increase in vaginal bleeding. Repeat vital signs of the patient shows a blood pressure of 130/70mmHg, pulse of 80/min and respirations of 18/min. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the current condition?
Premature separation of the placenta
Abnormal umbilical vessels
Abnormal placental implantation
Excessive amniotic fluid
Tear in uterine musculature
A 28-year-old woman is admitted for delivery. She began experiencing regular, painful uterine contractions three hours ago and her water broke en route to the hospital. The cervix is 5 cm dilated and 80% effaced. The fetal presentation is vertex and the baby's head is at -1 station. After placing a fetal heart monitor and external tocometer, repetitive decreases in fetal heart rate are noted which begin at the same time as the contractions and end before the contractions have ceased. Which of the following is most likely responsible for the fetal heart pattern?
Periods of fetal sleep
Fetal head compression
Umbilical cord compression
Uteroplacental insufficiency
Intrauterine infection
A 28-year-old woman presents to her physician's office because of pain in her left knee joint. She reports having mild discomfort and pain in right wrist 4 days ago and left ankle pain two days ago. She denies any recent respiratory illness, diarrhea, or urinary symptoms. She has no vaginal discharge. She has no previous medical problems and does not take any medications. She drinks half a pint of vodka daily but denies intravenous drug abuse. She is single and sexually active. Her last menstrual period was one week ago. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination of the knee reveals warmth, tenderness, decreased range of motion, and an effusion. No skin lesions are present and her pelvic examination is unremarkable. Synovial fluid analysis shows a white blood cell count of 75,000/microl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Non-gonococcal septic arthritis
Acute rheumatic fever
Gonococcal septic arthritis
Acute HIV infection
Crystal induced arthritis
A 28-year-old woman presents with a recent episode of coughing up some blood, frequent nosebleeds, and now decreased urine output. A nasal mucosa ulcer was seen on inspection. Her urinalysis is positive for protein and red cells consistent with a GN. The CXR shows two cavitary lesions and her serology is positive for antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Wegener’s granulomatosis
Goodpasture’s syndrome
Bacterial endocarditis
Lupus erythematosus
Poststreptococcal disease
A 28-year-old woman sees her physician with the chief complaint of a depressed mood. She also notes that she is sleeping more than usual––up to 14 hours per night––but does not feel rested and that she feels tired and fatigued all the time. She has gained 14 lb in the last month, something that she is very unhappy about, but she says that she seems to have such a craving for sweets that the weight gain seemed inevitable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Mood disorder secondary to a general medical condition
Cyclothymia
Substance-induced mood disorder
Seasonal affective disorder
Dysthymic disorder
A 28-year-old woman who is 15 weeks pregnant has new onset of nausea, vomiting, and right sided abdominal pain. She has been free of nausea since early in her first trimester. The pain has become worse over the past 6 hours. Which of the following is the most common non-obstetric surgical disease of the abdomen during pregnancy?
Appendicitis
Cholecystitis
Pancreatitis
Intestinal obstruction
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
A 28-year-old, G2 P1 woman presented to the hospital at 34weeks gestation because of midepigastric and right upper quadrant pain associated with nausea and vomiting. She has been closely followed for mild hypertension and mild proteinuria (250 mg/24hr) on an outpatient basis since the 28th week of gestation. Her previous pregnancy was without incident. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), blood pressure is 160/94 mmHg and pulse is 80/min. Physical examination shows epigastric and right upper quadrant tenderness; her bowel sounds are slightly reduced. The extremities have 2+ edema. Fetal heart sounds are audible on Doppler. Laboratory studies show: Hb: 8.2g/dl, Platelets: 96,000/mm3, Prothrombin time: 12.4 sec, Partial thromboplastin time: 23.6 sec, Serum creatinine: 1.1 mg/dl, Total bilirubin: 2.6 mg/dl, Direct bilirubin: 0.8 mg/dl, Alkaline phosphatase: 120 U/L, Aspartate aminotransferase: 308 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase: 265 U/L, Lipase: 53 U/L. Peripheral blood smear shows numerous red blood cell fragments. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
HELLP syndrome
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
Viral hepatitis
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
A 29-year-old G0 comes to your office complaining of a vaginal discharge for the past 2 weeks. The patient describes the discharge as thin in consistency and of a grayish white color. She has also noticed a slight fishy vaginal odor that seems to have started with the appearance of the discharge. She denies any vaginal or vulvar pruritus or burning. She admits to being sexually active in the past, but has not had intercourse during the past year. She denies a history of any sexually transmitted diseases. She is currently on no medications with the exception of her birth control pills. Last month she took a course of amoxicillin for treatment of a sinusitis. On physical examination, the vulva appears normal. There is a discharge present at the introitus. A copious, thin, whitish discharge is in the vaginal vault and adherent to the vaginal walls. The vaginal pH is 5.5. The cervix is not inflamed and there is no cervical discharge. Wet smear of the discharge indicates the presence of clue cells. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Candidiasis
Trichomoniasis
Bacterial vaginosis
Physiologic discharge
Chlamydia
A 29-year-old G2P1 at 40 weeks is in active labor. Her cervix is 5 cm dilated, completely effaced, and the vertex is at 0 station. She is on oxytocin to augment her labor and she has just received an epidural for pain management. The nurse calls you to the room because the fetal heart rate has been in the 70s for the past 3 minutes. The contraction pattern is noted to be every 3 minutes, each lasting 60 seconds, with return to normal tone in between contractions. The patient’s vital signs are blood pressure 90/40 mm Hg, pulse 105 beats per minute, respiratory rate 18 breaths per minute, and temperature 36.1C (97.6F). On repeat cervical examination, the vertex is well applied to the cervix and the patient remains 5 cm dilated and at 0 station, and no vaginal bleeding is noted. Which of the following is the most likely cause for the deceleration?
Cord prolapse
Epidural analgesia
Pitocin
Placental abruption
Uterine hyperstimulation
A 29-year-old G3P2 black woman in the thirty-third week of gestation is admitted to the emergency room because of acute abdominal pain that has been increasing during the past 24 hours. The pain is severe and is radiating from the epigastrium to the back. The patient has vomited a few times and has not eaten or had a bowel movement since the pain started. On examination, you observe an acutely ill patient lying on the bed with her knees drawn up. Her blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, her pulse is 110 beats per minute, and her temperature is 38.8C (101.8F). On palpation, the abdomen is somewhat distended and tender, mainly in the epigastric area, and the uterine fundus reaches 31 cm above the symphysis. Hypotonic bowel sounds are noted. Fetal monitoring reveals a normal pattern of fetal heart rate (FHR) without uterine contractions. On ultrasonography, the fetus is in vertex presentation and appropriate in size for gestational age; fetal breathing and trunk movements are noted, and the volume of amniotic fluid is normal. The placenta is located on the anterior uterine wall and no previa is seen. Laboratory values show mild leukocytosis (12,000 cells per mL); a hematocrit of 43; mildly elevated serum glutamicoxaloacetic transaminase (SGOT), serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase (SGPT), and bilirubin; and serum amylase of 180 U/dL. Urinalysis is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute degeneration of uterine leiomyoma
Acute pancreatitis
Acute cholecystitis
Acute appendicitis
Severe preeclamptic toxemia
A 29-year-old G3P2 presents to the emergency center with complaints of abdominal discomfort for 2 weeks. Her vital signs are: blood pressure 120/70 mm Hg, pulse 90 beats per minute, temperature 36.94C, respiratory rate 18 breaths per minute. A pregnancy test is positive and an ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis reveals a viable 16-week gestation located behind a normal-appearing 10×6×5.5 cm uterus. Both ovaries appear normal. No free fluid is noted. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
Primary peritoneal implantation of the fertilized ovum
Tubal abortion
Ectopic ovarian tissue
Uterine rupture of prior cesarean section scar
Fistula between the peritoneum and uterine cavity
A 29-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by his wife after he woke up with paralysis of his right arm. The patient reports that the day before, he had gotten into a verbal altercation with his mother over her intrusiveness in his life. The patient notes that he has always had mixed feelings about his mother, but that people should always respect their mothers above all else. Which of the following diagnoses best fits this patient’s clinical picture?
Adjustment disorder
Major depression
Conversion disorder
Histrionic personality disorder
Fugue state
A 29-year-old man presents to the ED complaining of RLQ pain for 24 hours. He states that the pain first began as a dull feeling around his umbilicus and slowly migrated to his right side. He has no appetite, is nauseated, and vomited twice. His BP is 130/75 mm Hg, HR is 95 beats per minute, temperature is 100.9°F, and his RR is 16 breaths per minute. His WBC is 14,000/μL. As you palpate the LLQ of the patient’s abdomen, he states that his RLQ is painful. What is the name of this sign?
Blumberg sign
Psoas sign
Obturator sign
Raynaud sign
Rovsing sign
A 29-year-old man presents to the ER with persistent vomiting and abdominal pain for the last 24 hours. The pain is crampy, diffuse, and has been getting worse. He had a normal bowel movement two days ago and denies diarrhea. The emesis appears green without blood or coffee grounds. He has not eaten since the onset of the pain due to nausea. On exam, his temperature is 36.8° C (98.2° F}, pulse is 91/min, and blood pressure is 116/75 mmHg while sitting and 94/65 mmHg while standing. His abdomen is distended with hyperactive bowel sounds. Percussion reveals tympany and he is diffusely tender to palpation. There is no rebound tenderness or guarding. Laboratory studies reveal:WBC count 9,600/mm3Hematocrit 45%Sodium 147 mEq/LPotassium 3.1 mEq/LCreatinine 1.0 mg/dLAST 20 U/LALT 12 U/LBilirubin 0.8 mg/dLWhich of the following historical findings would you most expect in this patient?
High alcohol consumption
Appendectomy six months ago
Occasional black or tarry stool
Fatty food intolerance
Recent weight loss
A 29-year-old man presents with a 2-day history of severe left-sided scrotal pain and swelling. He is sexually active and has had "many" sexual partners. His temperature is 38.2 C (100.8 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. Examination shows unilateral intrascrotal tenderness and swelling. Testicular support makes the pain less intense. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Epididymitis
Prostatitis
Testicular torsion
Urethritis
Varicocele
A 29-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of constant, severe lower abdominal pain. She also complains of fever and chills. Three weeks ago she had an intrauterine device (IUD) placed for contraception. Her temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), blood pressure is 110/76 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 16/min. She has bilateral lower quadrant abdominal tenderness. On pelvic examination, she has cervical motion tenderness and bilateral adnexal tenderness. A urinalysis is negative. A pelvic ultrasound is negative, with normal uterus and adnexae and no free fluid. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Appendicitis
Ovarian torsion
Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Pyelonephritis
A 29-year-old woman comes to the office for a periodic health maintenance examination. She has no complaints. Her past medical history is significant for irritable bowel syndrome. She has never had any surgery. She has been taking the oral contraceptive pill for the past 12 years, ever since she became sexually active. She has no known drug allergies. Physical examination, including pelvic examination, is unremarkable. By taking the oral contraceptive pill, this patient is decreasing her risk most significantly for which of the following?
Breast cancer
Cerebrovascular disease
Cervical cancer
Liver cancer
Ovarian cancer
A 29-year-old woman comes to your office because she has been feeling depressed. She states that at times over the past several years she has regular occurrences of depression, anxiety, tearfulness, anger, and difficulty with work and social relationships. These occurrences have been increasing over the past several months. She doesn’t remember when her symptoms start or end. “It’s all a blur,” she says. She has had several urinary tract infections in her life, but otherwise has no medical problems. She takes no medications and has no drug allergies. Physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in caring for this patient?
Have her keep a symptom calendar
Schedule an MRI of the brain
Schedule a pelvic ultrasound
Start the patient on a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
Start the patient on a benzodiazepine
A 29-year-old woman experienced her last menses 9 weeks ago. On her first prenatal visit, she is noted to have a 9–10 cm soft, smooth, symmetrical, midline pelvic mass. The mass is mobile and not tender to palpation. She has experienced morning nausea but no vomiting. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Paraovarian cyst of Morgagni
Tubo-ovarian abscess
Hydrosalpinx
Chronic pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Pregnancy
A 29-year-old woman presents to the delivery room in labor at 35 weeks' gestation with a temperature of 40 C (104 F). She lives on a dairy farm and is in the habit of drinking unpasteurized milk from her cows before sending it to the dairy. For the past 3 days she has been unable to attend to her chores because of fever, headache, mild diarrhea, and a general feeling of illness. When her amniotic membranes rupture, the fluid is dark, cloudy, and brownish-green. At birth, the infant has no malformations or edema, but is in severe respiratory distress. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Congenital syphilis
Congenital toxoplasmosis
Fetal hydrops
Neonatal herpes
Neonatal listeriosis
A 29-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a 3-week history of being awakened by a dull, prolonged chest pain that occurs 3–4 times a week. She is a smoker but has never suffered a myocardial infarction (MI) or had chest pain before and has no family history of early MI. Results of a 12-lead ECG are normal. Her first set of cardiac enzyme measurements (creatine kinase, creatine kinase-MB fraction, troponin I) are negative. If coronary angiography were taken at the time of her chest pain, which of the following findings is most like?
Coronary artery spasm
No abnormal findings
Greater than 80% stenosis in at least two coronary arteries
Plaque rupture and thrombosis
Coronary artery dissection
A 29-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of easy fatigability over the last several months. She tires easily after walking short distances. She also has difficulties combing her hair due to an inability to hold her hands over her head for a long time. She reports a weight loss of two or three pounds over the last two months. She denies fever or loss of appetite. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. On family history, her father died of a stroke when he was 54 years old and her mother has diabetes mellitus. On examination, she is afebrile with a pulse of 105/min. Cardiac exam reveals regular rhythm with no murmur. Her gait is normal but, when asked to sit down slowly, she drops into the chair. A fine finger tremor is evident when she extends her arms. Her muscles are non-tender to palpation. She appears to have decreased muscle mass in her shoulders. Deep tendon reflexes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Upper motor neuron disease
Inflammatory muscle disease
Polyneuropathy
Thyroid disease
Cerebellar dysfunction
A 29-year-old woman presents with complaints of a vaginal discharge. She has had two sexual partners over the past 4 weeks, and she reports that she uses oral contraceptives and that her partners were not using condoms. Examination shows she is afebrile, with no lymphadenopathy. Pelvic examination shows no ulcers, but a thick white discharge is noted at the cervical os on speculum examination. A Gram stain of the discharge reveals gram negative diplococci. A sample of the discharge is also sent out for culture. The patient is appropriately treated and returns unhappily 3 weeks later with identical symptoms. A Gram stain of the discharge is again done, and this time reveals no organisms. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
A resistant strain of the original organisms
An undetected, underlying immunosuppression
Reinfection due to an occult urethral source
Reinfection from an untreated sexual partner
Noncompliance with antibiotic therapy
A 29-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 35 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding. She has had no uterine contractions. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests and fetal growth have been normal. Prenatal ultrasound at the 12th week showed an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. Four years ago, she had a low transverse cesarean section in her second pregnancy. Physical examination shows bright red vaginal bleeding. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 16/min. Fetal heart monitoring is reassuring. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Abruptio placenta
Placenta previa
Vasa previa
Uterine rupture
Normal labor
A 3 year old male has sudden onset of dry cough with a small amount of bright red blood produced when he coughs. He has had no fevers, runny nose, or vomiting. In the Emergency Department a chest x-ray shows hyperexpansion of the right lung and clear lung fields. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this child's symptoms?
Bacterial pneumonia
Foreign body aspiration
Cystic fibrosis
Pulmonary arteriovenous malformation
Tuberculosis
A 3-day-old female infant is noticed to have copious, purulent discharge from both eyes. Lid edema and chemosis are also noted. She was born by normal vaginal delivery. Her mother is a 20-year-old primigravida who had no prenatal care. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chlamydia trachomatis
Chemical conjunctivitis
Staphylococcus aureus conjunctivitis
Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
Gonococcal conjunctivitis
A 3-day-old infant with a single second heart sound has had progressively deepening cyanosis since birth but no respiratory distress. Chest radiography demonstrates no cardiomegaly and normal pulmonary vasculature. An ECG shows an axis of 120°and right ventricular prominence. Which of the following congenital cardiac malformations is most likely responsible for the cyanosis?
Tricuspid atresia
Total anomalous pulmonary venous return below the diaphragm
Tetralogy of Fallot
Transposition of the great vessels
Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum
A 3-day-old newborn is ready to be discharged from the neonatal nursery, when his mother reports that a rash has appeared on his abdomen and chest. He otherwise appears healthy. He has no fever and no risk factors for infection. Examination reveals a nontoxic neonate with erythematous papules and vesicles surrounded by patches of erythema. Microscopic evaluation of the pustules reveals numerous eosinophils. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Neonatal varicella
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Erythema toxicum
Milia
Sebaceous hyperplasia
A 3-month-old infant has a history of chronic constipation. A fulminant watery diarrhea develops over a period of 2 days, and the infant is taken to the emergency department in an obviously severely dehydrated state. Plain x-ray films of the abdomen demonstrate a massively dilated transverse colon. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Meconium ileus
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Neonatal listeriosis
Newcastle syndrome
Toxic enterocolitis
A 3-week-old female infant born at 38 weeks' gestation through an uncomplicated vaginal delivery, presents to the emergency department with 2-day history of fever. The infant had been healthy since birth. Her temperature in the emergency department is 40.0 C (104.0 F). She appears to be quite lethargic. A culture taken from the infant grows group B Streptococcus (GBS) in 24 hours. Which of the following infections is most consistent with this presentation?
Endocarditis
Gastroenteritis
Meningitis
Pneumonia
Pyelonephritis
A 3-week-old infant is being evaluated for hematochezia. His mother states that the infant passed stools j that contain both blood and mucus. There were no complications during her pregnancy, and the infant has been otherwise healthy. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.1 C (98.9 F), pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 18/min. He appears well, and his fontanelle is flat and level. Abdominal examination reveals normal active bowel sounds; his abdomen is nontender to palpation and there is no mass. His diaper contains stool that has bright red blood on it with mucus. Which of the following is the most likely explanation of his hematochezia?
Food allergy-induced colitis
Meckel diverticulum
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Rectal fissure
Ulcerative colitis
A 3-week-old infant is brought in because of 2 days of protracted bilious vomiting. He looks acutely ill, and plain x-rays show two large air fluid levels in the upper abdomen, the larger one on the left side and a smaller one on the right side. The radiologist describes the finding as a "double bubble sign." He also reports that there is intraluminal gas distal to those two air fluid levels, but that it is sparse and does not outline distended loops. Which of the following is the most likely tentative clinical diagnosis?
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
Malrotation
Intestinal atresia
Meconium ileus
Necrotizing enterocolitis
A 3-year-old boy has had fever for 4 days. On physical examination he has bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy, injected pharynx, and dry cracked lips. A throat swab is done and the rapid strep test is negative. The child is sent home and advised to follow-up if symptoms worsen. The child is brought back 2 days later with all previous findings including a maculopapular rash, swollen hands, and conjunctivitis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Scarlett fever
Kawasaki disease
Toxic shock syndrome
Infectious mononucleosis
Erythema infectiosum
A 3-year-old boy is brought to the clinic due to an abdominal mass that his mother noted while she was bathing him. She seems distressed about the matter, and seeks your "expert opinion." The patient does not have any significant past medical history. On examination, he is calm and quiet. A firm abdominal mass is palpated in the left quadrant, which does not cross the midline. The mass is tender on deep palpation, but is not pulsatile Urinalysis reveals a trace amount of blood. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Pheochromocytoma
Wilms tumor
Neuroblastoma
Lymphoma
Sarcoma
A 3-week-old infant with hypoplastic left heart syndrome comes to the physician for a follow-up visit. The infant was born at term via normal spontaneous vaginal delivery. The patient had the first of 3 palliative heart surgeries shortly after birth. He did well after surgery and was discharged home one week ago. Over the last 24 hours, the infant has difficulty feeding and one episodes of vomiting. On examination, the infant is afebrile, pulse is 160/min, respiratory rate is 55/min, blood pressure is 90/50mmHg, and pulse oximetry is 80% on room air. He is mildly cyanotic, small, but well developed. His cardiovascular exam reveals tachycardia and distant heart sounds with a systolic ejection murmur heard throughout the precordium. His chest radiographs from discharge and today are shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Congestive heart failure
Myocarditis
Pleural effusion
Endocarditis
Pericardial effusion
{"name":"DES C_Diagnosis (4) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 25-year-old previously healthy man is scheduled for elective inguinal hernia repair under general anesthesia. After induction of anesthesia and initial inguinal incision, the patient develops tachycardia, muscle rigidity, fever of 38.5°C, and elevated end-tidal carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?, A 25-year-old white female presents to the clinic with persisting pain in her wrists and ankles for the last 3 months. The pain is 3\/10 in intensity, and partially relieved by ibuprofen. She also has a rash on her face. She denies smoking, and drinks alcohol occasionally. Her temperature is 37.3°C (99.2°F), blood pressure is 120\/80 mm Hg, pulse is 79\/min, and respirations are 18\/min. Physical examination reveals swollen joints of the hands and ankle, as well as erythema over the bridge of the nose and the upper cheeks. There is no muscle weakness. Labs show: Hemoglobin 11.0 g\/dL, Hematocrit 33%, Platelets 240,000\/mm3, WBC 13,600\/mm3. Leukocyte distribution:Segmented neutrophils 76%, Lymphocytes 20%, Bands 2%, Monocytes 2%. RF, ANA, and antibodies to double stranded-DNA are positive in high titers. What is the most likely diagnosis?, A 25-year-old white female presents with a 5-day history of sore throat, extreme fatigue, and headaches. She has just returned from a spring break in Jamaica where she had \"the time of her life.\" She smokes 2-3 cigarettes daily and occasionally drinks alcohol. Her vital signs are stable. She is afebrile. Physical examination reveals posterior cervical lymphadenopathy, mild splenomegaly, and exudative pharyngitis. Palatal petechiae are present. CBC shows: WBC 16,000\/cmm with 55% lymphocytes, Hemoglobin 13.5gm\/dl, Hematocrit 41%, Platelets 216,000\/cmm. Many variant forms of lymphocytes are seen, including cells with convoluted nuclei and highly vacuolated cytoplasm. Rapid streptococcal throat test, urinalysis, and heterophilic antibody test are all negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/18-737621/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Quelle est votre génération
7422
European Capitals
940
Salesmapp Quiz
320
Is Your Lighting Making the Grade? (long)
1360
Test Your Force and Motion Vocabulary - Free
201085188
Which Star Trek Character Are You? Free Personality
201027041
Ace the Net Design Patterns - Test Your C# Skills
201023851
Free 4.05 Unit Test Banking Review
201026778
Could You Ace These Food For Thought Questions?!
201036046
Which Vox Machina Character Are You? Free Personality
201024664
What's an Exabyte? Ace the 16 Exabyte to Gigabyte
201031921
Free Percent Error Practice
201026270