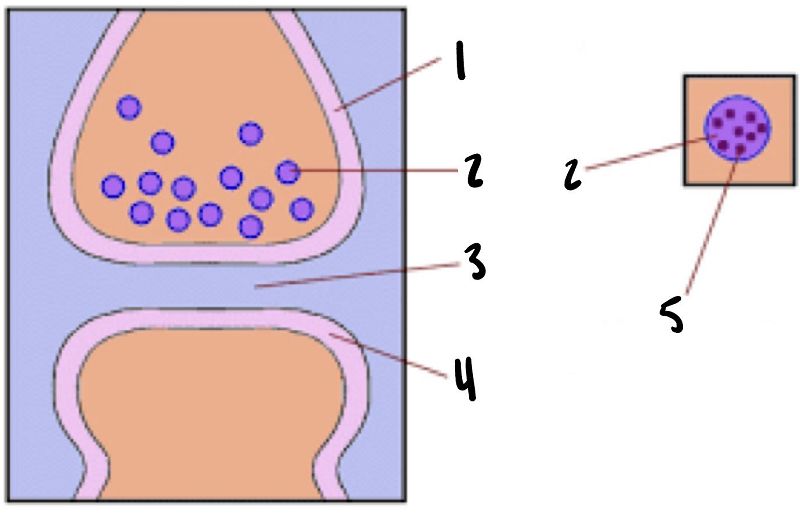
Neuro Practice Quiz 2
{"name":"Neuro Practice Quiz 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Match the four major components of a neuron with the correct anatomical parts or parts of the cell, Match the four major components of a neuron with the correct primary functions, Select everything that is true about Myasthenia Gravis","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/94-4567921/img-1e2148f7803d-1.jpg?sz=1200-00203005050926606425"}
More Quizzes
How well do you know me?
221141
Module 9 ARMU , Dr Sothy , Dr Sunly , Dr Lim Vanna , Dr Hen Vanna
633228
Shakespeare
210
World Affairs Councils of America WorldQuest Weekly Quiz – September 5-11, 2022
1050
AP Style State Abbreviations - Free Online
201025916
Harry Potter Crush - Who's Your Hogwarts Match?
201019026
Free Autism Test - Online Self-Assessment
201018579
What City Should I Live In - Free Personality Match
201021033
Loud Personality - Find Out If You're Loud or Quiet
201021531
What Hairstyle Suits Me? Free to Find Your Best Look
201018493
MBA Trivia - Test Your Business & Management Knowledge
201020340
How Many Calories Should I Eat a Day? Free
201020340