
What is Spasticity?
The stretchiness of a rubber band
Velocity-dependent increase in stretch reflexes with exaggerated tendon jerks
Velocity-dependent decrease in stretch reflexes with exaggerated tendon jerks
Loss of muscle control

What is the definition of Clonus?
The singular noun for a clone trooper from Star Wars
When the foot does that weird bouncing thing
Involuntary muscular contraction in rapid succession
The process of cloning a clone
Voluntary muscular contraction in rapid succession

When should Stroke pt commence out of bed activity?
ASAP - Time is brain
Within 24hr
Within 48hr
Within 72hr

What is heavier? 1 kg of steel or 1000g of feathers?
Steel because steel is heavier than feathers
1000g of feathers cause 1000 is a bigger number than 1

Define Neural plasticity
Ability of the CNS to adapt to functional demands and the systems capacity to reorganise
Ability of the CNS to adapt to sensory demands and the systems capacity to reorganise
The amount of brain capacity and will power it takes a toddler to not eat play-doh
How the brain re-learns stuff in a functional manner

Select the mechanisms of neural plasticity. (hint: there are 3)
Habituation
Learning and memory
Cellular recovery pre-injury
IQ >100
Cellular recovery post injury
Motor cortex excitation

With TBI, processes of neural plasticity remain the same, however how does the presence of damaged neural environments complicates things?
Oedema & inflammation significantly impair neural function
Oedema, inflammation & altered neuronalexcitability impair neural function
Oedema, inflammation & altered thalamic processes impair neural function
Their brain is now broken and no longer functions how it should
What do you mean?
What are the 3 patterns of cortical re-organisation
Greater degree of bilateral motor cortex activity
Increased recruitment of secondary cortical areas in the non-affected hemisphere
Increased recruitment of secondary cortical areas in the affected hemisphere
Increased Ipsilateral cortical involvement
Greater degree of ipsilateral cortex activity

In TBI, what happens when entire neural circuits are gone?
When they're gone they're gone
Other structures not designed for that purpose must compensate
The brain will repair those circuits over time
If you ask nicely they might come back
Select the common symptoms of Stroke
Dysarthria
Severe pain in the 3rd toe
Acute sensory loss
Halucinations
Sudden or severe headache
Weakness/numbness in face
Weakness/numbness in arm or leg

What are the special questions you should ask a stroke patient?
Double vision
Any thing good on TV today?
Pain levels
Their perception of their current level of function

Select the correct definition of Salience
The neurological condition where patients are involuntarily silent
To induce plasticity the task must be important to the pateint
Training that drives a specific brain function leading to enhancement of that function
The sequel song to the 2011 Hit Sail by Awolnation

When would you know to stop therapy with your patient?
When the patient has completed the session you set out for them
Fatigue and quality of movement begins to decline
You get bored
Repetition is important

Stance phase: Initial contact components include:
Forward pelvis rotation
Centre of mass moving vertically
Centre of mass moving forwards & laterally
Knee flexion via eccentric quads
Knee extension via eccentric Hamstring
Ankle at neutral
Foot everted

Stance phase: Loading response includes:
Weight bear stability + progression of COM
Hip flexion --> extension
Concentric glutes + Hamstring cause Hip extension
Knee flexion via concentric Hamstring
Knee extension via eccentric hamstring
Ankle DF via concentric Tib Ant
Ankle PF via eccentric Tib Ant
Hip flexion via concentric quads
Stance Phase: Mid-stance includes
Progress over stance foot
Knee flexion begins
Stance foot leaves ground
Maintain Limb + trunk stability
Hip Extension
Knee flexion peaks
Knee hyperextends
Ankle moves into active PF

What is the correct order of stance phase
1. Loading response, 2. Initial Contact, 3. Mid Stance, 4. Terminal Stance, 5. Pre-Swing
1. Pre-Swing, 2. Initial Contact, 3. Mid Stance, 4. Terminal Stance, 5. Loading response
1. Initial Contact, 2. Loading response, 3. Mid Stance, 4. Terminal Stance, 5. Pre-Swing
Wait there are phases

Stance Phase: Terminal Stance Components include:
Heel begins to leave the ground
Body progresses beyond supporting foot
COM is at its lowest
COM is at its highest
Hip passively extends maximally
Hip actively extends maximally
Passive Ankle PF
Ankle PF concentrically
Knee hyperextends
Knee reaches near full Extension
Stance Phase: Pre-swing
Ends at Toe-off
Hip flexion
Knee Extension
Knee flexion
Ankle PF
Ankle DF
Positions limb for swing and accelerate progression

What is the correct sequence for Swing phase
1. Mid Swing, 2. Terminal Swing, 3. Initial Swing
1. Initial Swing, 2. Mid Swing, 3. Terminal Swing
1. Initial Swing, 2. Mid Swing, 3. End Swing
1. Initial Swing, 2. End Swing
Swing Phase: Initial Swing components include:
Aims: foot clearance + progression of following limb
Aims: Not trip over
Active hip flexion
Momentum causes hip flexion
Peak Knee flexion
Knee extension
Concentric Tib Ant for DF
Eccentric Gastroc for DF
Swing Phase: Mid Swing components include:
Momentum generated Hip, Knee & Ankle flexion
Momentum generated Hip flexion, knee extension, & ankle DF
Momentum generated Hip flexion & knee extension
Concentric DF via Tib Ant
Eccentric DF via Gastroc
Swing Phase: Terminal Swing components include:
Aims to complete limb advancement
Prepares for for stance
Eccentric Hip flexion via Hamstring/Glute max
Eccentric knee Extension --> Concentric Knee Extension via Quads
Concentric knee Extension --> Eccentric Knee Extension via Quads
Eccentric Ankle PF
Ankle DF for heel strike

What is the definition of a stroke? (May have multiple answers)
Sudden death of brain cartilage
Sudden death of brain cells in localised area
Caused by lack of O2 due to blockage or rupture
Gradual death of brain cells in localised area
Caused by lack of CO2 due to blockage or rupture
The phase of the combustion cycle is designated by the sequential strokes of the piston (intake, compression, expansion, exhaust)

True or False: penumbra is salvageable brain area
False
True

What is the cell death process during stroke?
Still unknown
ATP depletion --> Ca mediated cytokinetic reactions causing excitatory neurotransmitters to fail
ATP depletion --> membrane pump fails --> Ca mediated cytotoxic reactions & release of excitatory neurotransmitters
Increase in CO2 in the penumbra post stroke causes ATP depletion and cell death as a consequence
Select the options which categorise a Total Anterior Circulation Syndrome (TACS)
Large middle cerebral artery infarct
Posterior middle cerebral artery infarct
Contains all of the following: higher cerebral dysfunction, Homonymous Hemianopia & motor sensory deficit
Has only one of the following: higher cerebral dysfunction, Homonymous Hemianopia & motor sensory deficit
Neglect is never present, but will express ataxia
Will present with neglect & Apraxia
Presents with Aphasia
Not that big of a deal compared to other strokes
Select the options which categorise a Partial Anterior Circulation Syndrome (PACS)
Middle cerebral Artery branch occlusion
Posterior cerebral Artery branch occlusion
Poor Prognosis
Good prognosis
2 out of the 3 following: higher cerebral dysfunction, Homonymous Hemianopia & motor sensory deficit
Contains all of the following: higher cerebral dysfunction, Homonymous Hemianopia & motor sensory deficit
High motor/sensory deficit
Limited motor/sensory deficit
Select the options which categorise a Posterior Circulation Syndrome (POCS)
Infarct in Middle cerebral Artery and/or cerebellum
Infarct in posterior cerebral artery, brain stem, or cerebellum
Occlusion in the posterior cerebral artery
Cranial nerve palsy
Contralateral motor/sensory deficit
Conjugate eye movement issues
Cerebellar dysfunction
Isolated Homonymous Hemianopia
Select the options which categorise a Lacunar Syndrome (LACS)
Sub-cortical stroke
Infarct in the Lacunar artery
Pure motor or sensory stroke
Ataxic Hemiparesis
Dysphasia
Hemianopia
Bilateral Ataxia

Select the characteristics of a RIGHT CVA
L) Hemiparesis/hemiplegia
R) Hemiparesis/hemiplegia
L) Somato-sensory changes
L) hemianopia
R) hemianopia
L) Unilateral Spatial neglect
Bilateral Spatial neglect
Apraxia
Language problems
Trouble writing
Anosognosia: unaware of condition
Astereognosis

Select the characteristics of a LEFT CVA
L) Hemiparesis/hemiplegia
R) Hemiparesis/hemiplegia
R) Somato-sensory changes
L) Somato-sensory changes
L) hemianopia
R) hemianopia
Language Issues
Dysphasia
Dysgraphia
Apraxia
Anosognosia: unaware of condition
Astereognosis

What is Apraxia?
Disorders of the execution of learned movements which is not due to weakness, co-ordination, sensory loss, or incomprehension of or inattention to command
Crippling fear of Axes
Disorders of the execution of unlearned movements which is not due to weakness, co-ordination, sensory loss, or incomprehension of or inattention to command
Disorders of the execution of learned movements which is due to weakness, co-ordination, sensory loss, or incomprehension of or inattention to command
Select the characteristics of Ideomotor Apraxia:
Unable to perform simple tasks, however complex tasks remain intact
Inability to perform purposeful movement on external command, despite fully understanding the task
Can be able to do the task automatically in a natural setting
Movements lack correct force, direction and timing
Can perform seperate movements but can't co-ordinate all steps into integrated sequence
Disorder of Praxis Production System
Select the characteristics of Ideoational Apraxia:
Unable to perform simple tasks, however complex tasks remain intact
Inability to perform purposeful movement on external command, despite fully understanding the task
Actions often overshoot whats necessary or is incomplete
Disorder of the Praxis Conceptual system
Can perform seperate movements but can't co-ordinate all steps into integrated sequence
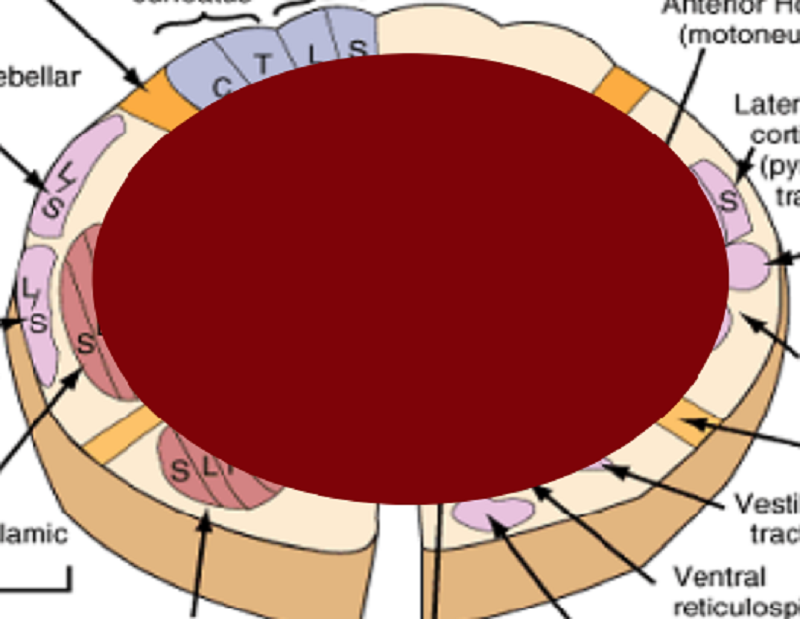
Name the SCI:
Ischaemic Herniation Syndorme
Sacral Sparing
Anterior Cervical Cord Syndrome
Central cord lesion
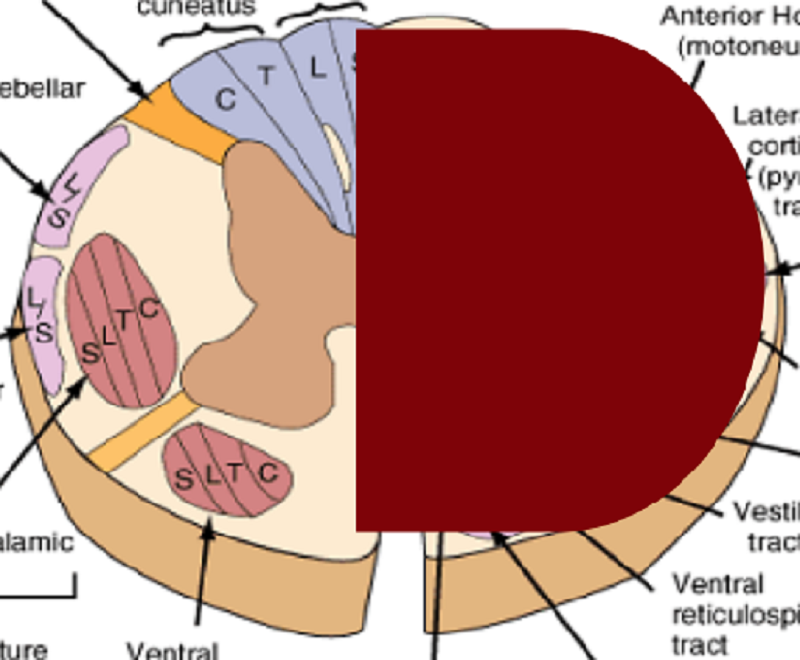
Name the SCI:
Unilateral lesion syndrome
Ipsilateral Haematoma
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Sacral Sparing
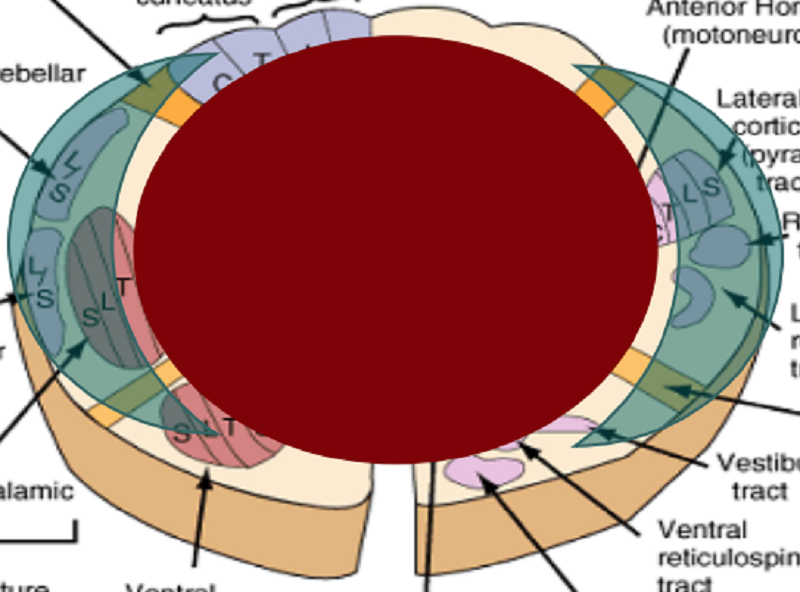
Name the SCI:
Central Cord Lesion
Bilateral Sparing Syndrome
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
UMN Lesion
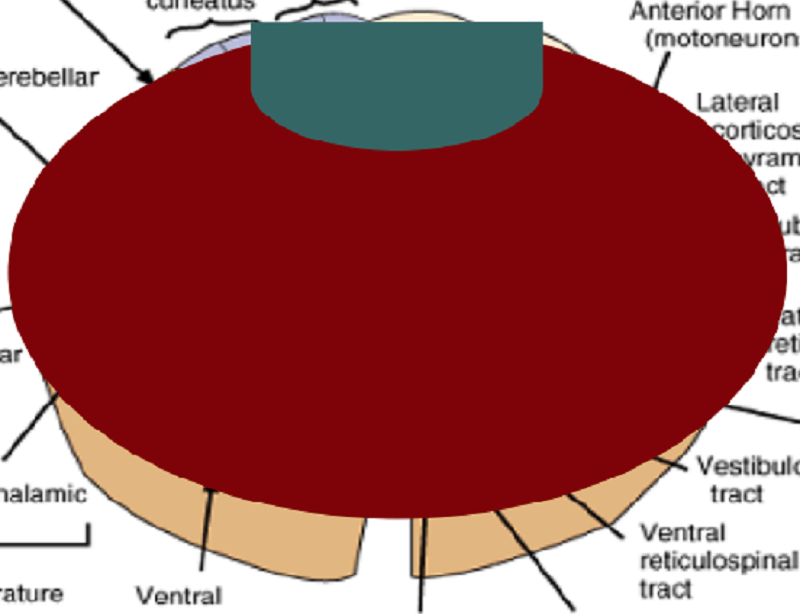
Name the SCI:
Total occlusion Syndrome
Brown-Sequard Syndrome
Anterior Cervical Cord Syndrome
Bilateral UMN Lesion
What is Subjective Visual Vertical
Can we orientate an object to vertical without vision
Can we tell an object is vertical by looking at it
Can we orient our body to vertical without vision
A skatebaord trick on a vertical ramp with eyes closed
What is Subjective Haptic Vertical?
Can we orientate an object to vertical without vision
Can we tell an object is vertical by looking at it
Can we orient our body to vertical without vision
A type of tick that causes paralysis of the nervous system, and has the ability to kill a full grown adult within hours
What is Subjective Postural Vertical
Can we orientate an object to vertical without vision
Can we tell an object is vertical by looking at it
Can we orient our body to vertical without vision
Standing so incredibly still that you cannot be seen by the human eye

What are the 3 main features of Pusher syndrome?
Contralesional tilt of spontaneous body posture
Abduction + Extension of extremities
Adduction + Flexion of extremities
Resistance to passive correction
Ipsilateral tilt of spontaneous body posture
Select the correct definition for Pusher Syndrome:
Someone that uses emotional torture to push those close to them away
Someone that uses extreme brute force to push others away
Pushes strongly to hemiplegic side, resisting any passive correction
Pushes towards non-hemiplegic side, resisting any passive correction
What is the definition of Tone?
A word Skinny people use to justify their lack of muscle mass
Sensation that is encounted as a joint is passively moved through a range of motion
Sensation that is encounted as a joint is actively moved through a range of motion
Muscle's resistance to over stretch
Definition of Unilateral Spatial Neglect:
Failure to report, respond or orient to stimuli presented to the same side of brain lesion
Failure to report, respond or orient to stimuli presented to the opposite side of brain lesion
Not studying content on the belief it will not be in the exam
Skipping leg day
Types of Neglect: What is Inattention/Extinction
Failure to respond to stimuli on affected side only when non-affected side is also being stimulated
Failure to respond to stimuli on affected side when non-affected side is not being stimulated
Neglecting that dinosaurs went extinct via meteor
Failure to recognise the severity of their paralysis
Types of Neglect: Anosognosia
Failure to respond to stimuli on affected side when non-affected side is not being stimulated
Disturbed perception of client's own body parts
Failure to recognise the severity of their paralysis
British term for snogging someone's nose

Types of Neglect: Autopagnosia
Neglecting cars who have a automatic gear box
Failure to recognise the severity of their paralysis
Disturbed perception of people's body parts
Disturbed perception of client's own body parts
What does Occulomotor Nerve control:
Up + down + Medial eye movement
Up but not down eye movement
Medial and down
Abduction + up + down
What does the Trochlear nerve do?
Moves eyes Up + Down + medially
Down + Lateral
Medially + down
Adduction
What does Abducens Nerve do?
Abducts eye
Up + down eye movement
This is not a real nerve
Adducts eye
What is the role of Otolith Organs?
Sense Linear Acceleration + orientation of head with respect to gravity
Sense Linear Acceleration
Unblurr vision with movement

What is the purpose of Vestibulo-Occular Reflexes:
Unblurr vision with head movement
Sense Linear acceleration
Detects elevation (i.e. Going up an elevator)
This is not a real thing

What is Vestibular Neuritis?
Degeneration of neurons within Vestibular system
Inflammation of vestibular Apparatus
Degeneration of Semi-circular canals
Inflammation of the vestibular nerve

Select common Symptoms of Vestibular Neuritis:
Acute onset of Rotary Vertigo
Symptoms eased by head movement
Exacerbated by head movement
Postural imbalance
Uncontrollable Sneezing fits
Hearing Loss
Horizontal-rotary Nystagmus beating to affected side
Horizontal-rotary Nystagmus beating away from affected side

What is Meniere's Disease?
Disorder of Vestibular Apparatus due to backed up fluid
Disorder of inner ear function due to backed up fluid
Disorder of Mens ears
Loss of hearing due to immune system attacking ocular nerves

Select common symptoms seen in Meniere's Disease
Spontaneous Vertigo
Constant Vertigo
Lack of aural symptoms
Aural Symptoms
Blocked nose
Hair loss

What is Nystagmus?
Voluntary movement of the eyes
When the eyes flicker
Twitching of the eye in response to staring for too long
Involuntary movement of the eyes
What are Habituation Programs used for?
Designed for patients with motion sensitivity issues
Relocating animals who's homes have been destroyed or lost
Patient's with impaired sensation
Eye-stuff

What is Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
When you drink too much on a night out and get dizzy
A condition where dislodged Otoconia float into semi-circular canals
A type of vertigo
A condition where dislodged Otoconia float into Vestibular aparatus

What is Canalithiasis?
Otoconia is adherent to the cupula
Otoconia is freely mobile in the canal
The process of creating a canal

Select the symptoms of BPPV:
Vertigo <1min
Vertigo >1min
Light Headedness
Imbalance
Nausea
Motion Sensitivity
Attacks come with sustained postures
Attacks come with change of head position

What would you use a Hallpike-Dix Test
Anterior SCC
Posterior SCC
Anterior + Posterior SCC
Horizontal SCC

What Nystagmus would you expect for Right Posterior SCC
Down beating + Right Torsional
Up beating + Right Torsional
Down beating + L) torsional
Up beating + L) torsional

What Nystagmus would you expect for a Left Anterior SCC
Down beating + Right Torsional
Up beating + Right Torsional
Down beating + L) torsional
Up beating + L) torsional
{"name":"What is Spasticity?", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"What is Spasticity?, What is the definition of Clonus?, When should Stroke pt commence out of bed activity?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/50-1700541/01-memes4.jpg?sz=1200-01960005280497511481"}
More Quizzes
10 Random Questions! T/F Version
1050
Ngr.jv
10516
Kitchen Safety
1580
How Well Do You know The Original Mary Poppins?
1050
Periodic Table: Electron Configuration Questions
201026223
Intermediate Current Topics in Psychology
15822206
Finite Element Analysis
15829027
Local Anesthesia Calculation: Test Your Dosage Skills
201058988
Free Employee Leave Entitlements
201022045
Can You Name All the Capital Cities of Central America?
201030368
Slumdog Millionaire Characters: Discover Your Match
201033113
What Would You Look Like as a Gravity Falls Character?
201028408
