Natty D

Explore Earth's Dynamics Quiz
Test your knowledge of geology and volcanology with our comprehensive quiz on Earth's processes and structures. This quiz covers a variety of topics, from plate tectonics to volcanic activity, and is designed to challenge your understanding of the dynamic planet we call home.
Whether you're a student looking to enhance your learning or a geology enthusiast eager to test your expertise, this quiz is perfect for you! Key features include:
- 58 thought-provoking questions
- Multiple choice and checkbox answers
- Instant feedback on your performance
Portion of the mantle that behaves plastically, upon which the outer layer of the Earth moves
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Outer core
Atmosphere
Rigid layer of the earth that is composed of the upper mantle and the crust
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Mantle
Crust
As you move away from the mid-Atlantic Ridge toward North America, what would you expect to find? (choose all that apply)
Thickness of sediments increases
Increasing magnetism
More earthquakes
Decrease in heat flow
Where two lithospheric plates are moving toward each other, the boundary is called_
Transform
Rifting
Divergent
Convergent
Earthquakes occur along which type of plate boundaries?
Divergent
Convergent
Transform
All of the Above
The lithospheric and asthenospheric mantle have similar compositions. The distinction between them is:
The asthenosphere is brittle and the lithosphere is plastic
The lithosphere is denser
The asthenosphere is part of the core
The lithosphere is brittle and the asthenosphere is plastic
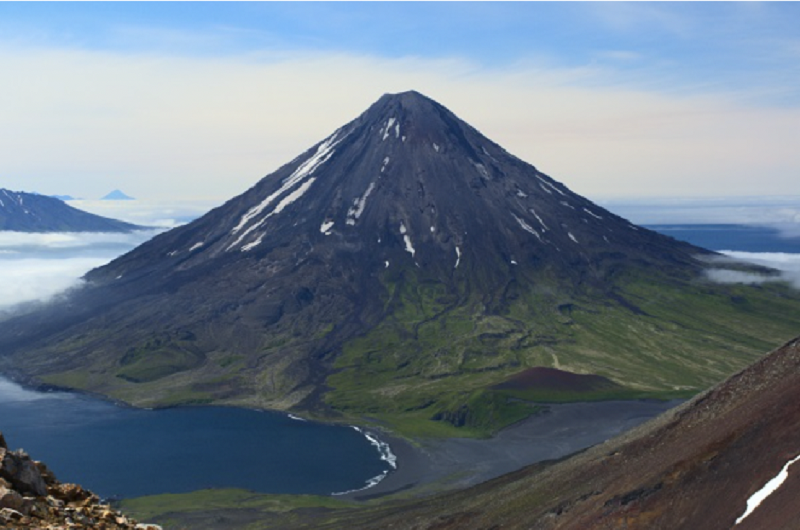

What type of volcano is this?
Stratovolcano
Shield Volcano
Cinder Cone
Lava Dome
Explosive volcanoes tend to have (choose all that apply)
High volatile content
High silica content
Low silica content
High temperature magmas

What type of volcano is this?
Composite
Shield
Lava Dome
Cinder Cone
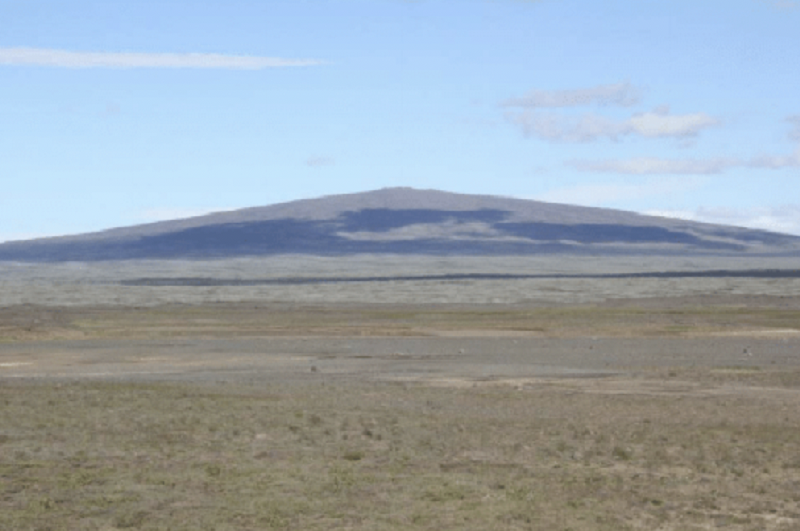

What type of volcano is this?
Composite
Shield
Lava Dome
Cinder Cone
The addition of volatiles leads to melting because it helps break the bonds between the silica-oxygen molecules
True
False
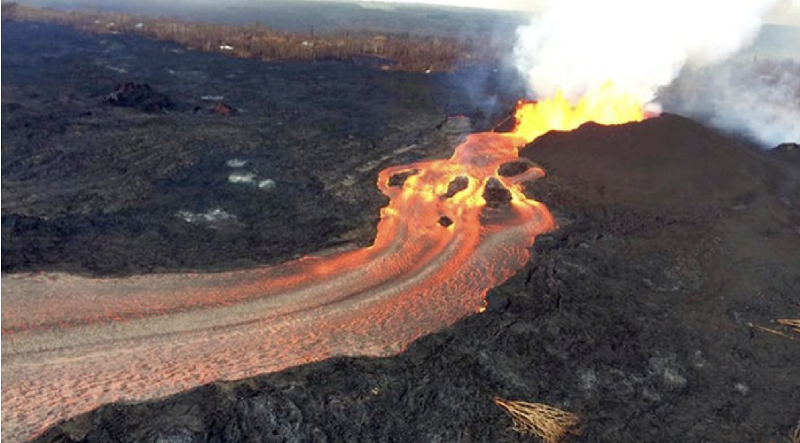

The type of lava here is
Basalt
Rhyolite
Cheese
Andesite
The P-wave (choose all that apply)
Are shear waves
Only travels through solids
Are compressional waves
Arrives first
We measure the waves of an earthquake using this tool.
Anemometer
Seismometer
Barometer
Gas detector
Earthquakes at convergent boundaries can be (choose all that apply)
Large magnitude
Tensional
Shallow focus
Deep focus
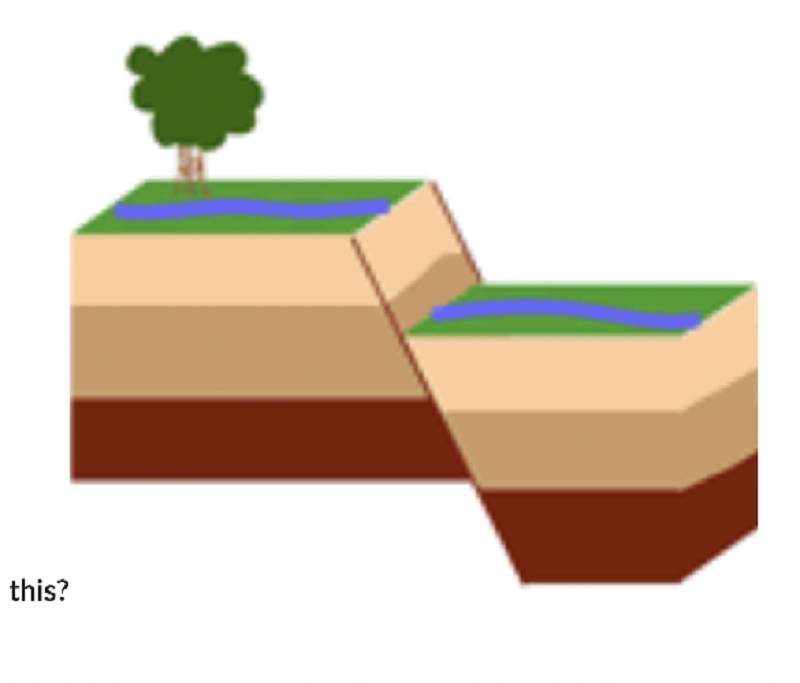
What type of fault is this?
Normal
Reverse
Strike slip
Thrust
The geographic location of an earthquake, above the hypocentre is called
P-wave
Hypercentre
Scarp
Epicentre
Canada is on what lithospheric plate?
Eurasian Plate
African Plate
North American Plate
Pacific Plate
When lithospheric plates move apart, the boundary between them is
Subduction
Convergent
Transform
Divergent
Earth's magnetic reversals produce magnetic stripes on the ocean floor because
The iron in the fossils lines up with the Earth's magnetic field
We don't know
The iron in the magma produced at the ridge lines up with the Earth's magnetic field at the time it formed
The magma produced at the ridge lines up with the Earth's electric field at the time it formed
The Earth's core is made up primarily of what two elements?
Arsenic and mercury
Silicon and potassium
Calcium and potassium
Iron and nickel
Subduction occurs at ______________ boundaries.
Transform
Convergent
Divergent
Well lubricated
At a subduction zone we will find (select all that apply)
A deep trench
Deep earthquakes
Shallow earthquakes
Volcanoes
The type of melting that occurs at divergent margins is
Decompression
Heat transfer
Aliens
Addition of volatiles
Volcanologists monitor volcanic activity using the following: (Choose all that apply)
Changes in water chemistry
Changes in ground elevation
Astrology
Seismometers
The most deadly volcanic hazard is
Volcanic gases
Lava
Pyroclastic flow
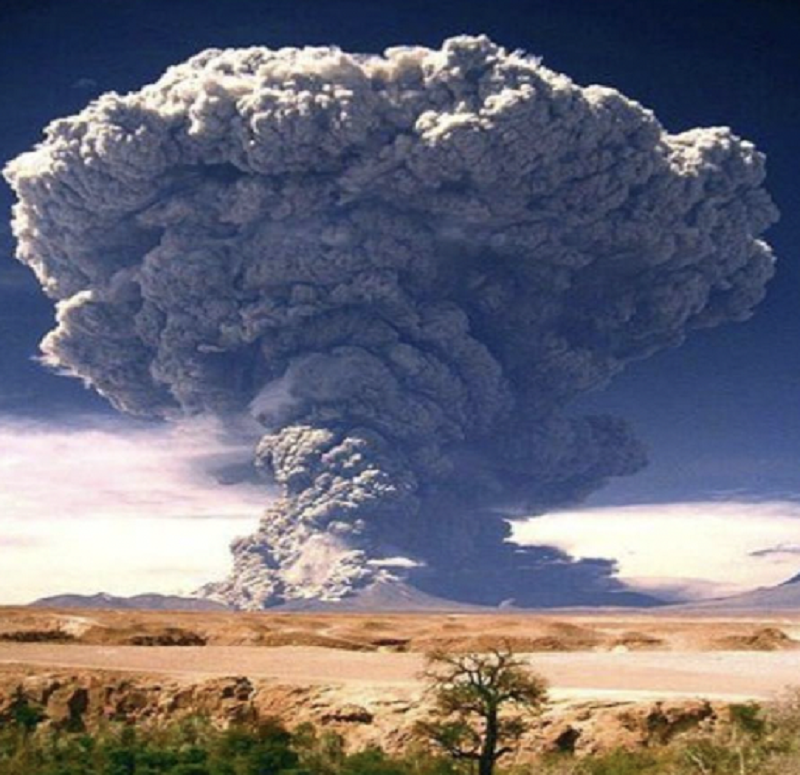

What type of eruption is this?
Strombolian
Plinian
Icelandic
Hawaiian
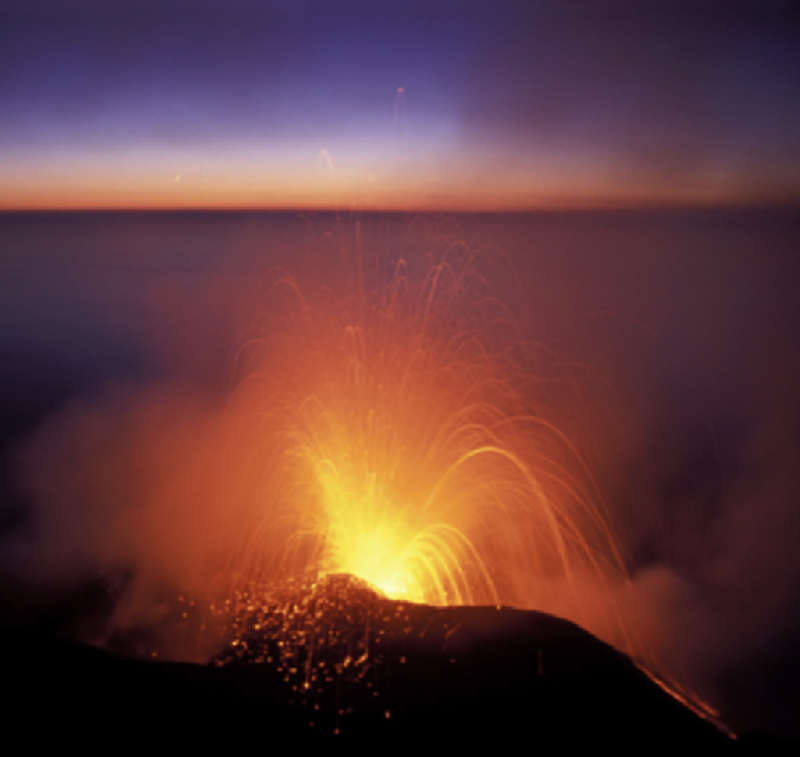

What type of eruption is this?
Nice
Strombolian
Hawaiian
Plinian
A mudflow caused by the mixing of lava or pyroclastic materials with river water
Nuee Ardente
Lava
Lahar
Pyroclastic surge
S-waves (choose all that apply)
Are compressional waves
Arrive before surface waves
Arrive after P-waves
Are shear waves
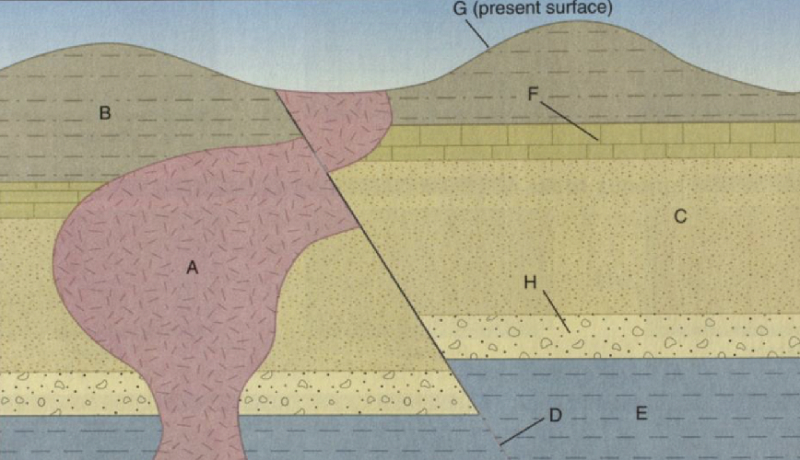
The type of fault represented by the movement along the plane at D is
Normal
Right-lateral
Left-lateral
Reverse
Earthquakes at divergent boundaries are usually (choose all that apply)
Shallow focus
Tensional
Low magnitude
Deep focus
The Mercalli Intensity Scale is a ten stage scale
True
False
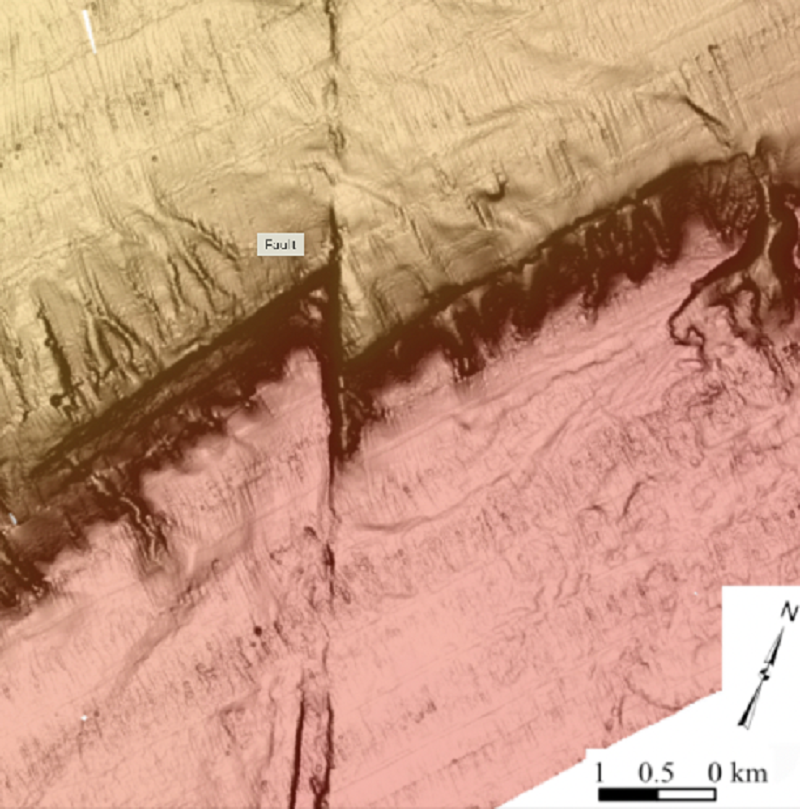
This photo is from above (map view). What type of fault is this?
Sinistral
Thrust
Reverse
Dextral
The moment magnitude scale is computed from the Seismic Moment which is a measure of (choose all that apply)
The type of waves generated
Amount of slip on the fault
Strength of the rocks faulting
Area of slippage
The Earth's liquid core convects around the solid core, producing Earth's
Lithosphere
Asthenosphere
Magnetic field
Magmas
Earthquakes can be measured using which scales? (choose all that apply)
Mercalli Intensity Scale
Moment Magnitude Scale
Scoville Scale
Richter Scale
You can predict earthquakes by observing slug trails
True
False
Fractures that have motion along them.
Extension
Dip
Fault
Plane
The moment magnitude scale is a twelve stage scale
True
False
The crest is the highest point of a wave
True
False
The trough is the lowest point of the wave
True
False
The wave height is the
Distance from crest to crest
Time between the passage of two wave crests
Vertical distance between crest and trough of wave
The wave length is the
Time between the passage of two wave crests
Distance from crest to crest
Vertical distance between crest and trough of wave
The wave period is the
Vertical distance between crest and trough of wave
Distance from crest to crest
Time between the passage of two wave crests
What is the maximum heigh a tsunami reaches on shore
Peak
Runup
Summit
Trough
Tidal waves can be as high as
20m
15m
22m
17m
Waves in an ocean or late that result from a displacement of water are called
Shifted waves
Displacement waves
Shoaling waves
Resonance
Shoaling: as a wave approaches decreasing water depths, the leading edge ____, the water behind it will “build up” and _____ the wave height
Slows, decreases
Accelerates, increases
Slows, incereases
Accelerates, decreases
Focusing:
As a wave enters a closed bay, waves will reflect and oscillate in the bay. If it is in phase with tsunami wave then a larger amplitude will result
As a wave enters a concave bathymetry the wave front bends due to refraction of the waves
As a wave approaches decreasing water depths, the leading edge slow
Waves resulting from gravitational force between Earth and the Moon or Sun
Resonance:
As a wave enters a closed bay, waves will reflect and oscillate in the bay. If it is in phase with tsunami wave then a larger amplitude will result
As a wave enters a concave bathymetry the wave front bends due to refraction of the waves
As a wave approaches decreasing water depths, the leading edge slow
Waves resulting from gravitational force between Earth and the Moon or Sun
{"name":"Natty D", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of geology and volcanology with our comprehensive quiz on Earth's processes and structures. This quiz covers a variety of topics, from plate tectonics to volcanic activity, and is designed to challenge your understanding of the dynamic planet we call home. Whether you're a student looking to enhance your learning or a geology enthusiast eager to test your expertise, this quiz is perfect for you! Key features include: 58 thought-provoking questions Multiple choice and checkbox answers Instant feedback on your performance","img":"https:/images/course3.png"}
More Quizzes
The Structure of the Earth
9426
Interior of the earth
10526
Pun??? or Nahh???
940
This is a quiz
100
Free The One and Only Ivan Comprehension
201021583
Free Noun Practice Test
201022704
Free Fire Extinguisher Safety Knowledge Test
201022206
Free Gastrointestinal Physiology Knowledge Test
201029930
Am I Gluten Intolerant? Take the Free to Find Out!
201030990
Think You Know The Tempest Play Act 1? Ace This!
201029595
Relative Dating Practice - Test Your Geology Knowledge
201082953
Think You're Brainy? Take the Free Factfulness Online!
201039248



