DES C_ParaClinic (2) Prepared : CHILLY
A 24-year-old Caucasian male undergoes pulmonary function testing. The following values are obtained: FEV 80% of predicted, FEV1/FVC 85%, FRC 110% of predicted. He has no current complaints except for occasional low back pain treated with naproxen. He smokes one pack per day and drinks a six-pack of beer each weekend. His ESR is 47 mm/hr. Which of the following best explains the pulmonary function test findings in this patient?
Emphysema
Pulmonary fibrosis
Small airway obstruction
Chest wall motion restriction
Pulmonary vascular disease
A 24-year-old Caucasian man is brought to the emergency room with acute asthma exacerbation. His current medications include inhaled fluticasone and salmeterol. The attack started 10 hours ago and did not respond to numerous albuterol inhalations and systemic steroids. His blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and heart rate is 110/min. The patient is tachypneic and speaks with difficulty. Lung auscultation reveals decreased breath sounds, prolonged expiration, and bilateral wheezing. Pulse oximetry showed 86% at room air. ABG at room air are: pH 7.43, Po2 68 mmHg, PCO2 40mmHg. The chest x-ray demonstrates hyperinflated lungs. Which of the following findings indicates that the patient is getting worse?
Lung hyperinflation
Tachypnea
Tachycardia
Hypoxia
Normal PCO2
A 24-year-old man woke up from sleep 1 hour ago with severe pain in his right testicle. He states that he is sexually active with multiple partners. On examination, the right scrotum is swollen, tender, and firm. You cannot elicit a cremasteric reflex. His BP is 145/75 mm Hg, HR is 103 beats per minute, RR is 14 breaths per minute, temperature is 98.9°F, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Administer one dose of ceftriaxone and doxycycline for 10 days and have him follow-up with a urologist
Swab his urethra, send a culture for gonorrhea and Chlamydia, and treat if positive
Order a statim (STAT) color Doppler ultrasound and urologic consultation
Treat the patient for epididymitis and have him return if symptoms persist
Send a urinalysis and treat for a urinary tract infection (UTI) if positive
A 24-year-old patient recently emigrated from the tropics. Four weeks ago she noted a small vulvar ulceration that spontaneously healed. Now there is painful inguinal adenopathy associated with malaise and fever. You are considering the diagnosis of lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV). The diagnosis can be established by which of the following?
The presence of serum antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis
Culturing Haemophilus ducreyi
Staining for Donovan bodies
Culturing Calymmatobacterium granulomatis
Positive Frei skin test
A 24-year-old primigravid woman comes for her initial prenatal visit at 24 weeks' gestation. Her only complaint is low back pain. She has no significant past medical history, and she has had no complications of pregnancy thus far. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Complete physical examination shows no abnormalities. During the interview she requests screening for diabetes because her friend was diagnosed with gestational diabetes at 26-weeks of gestation. Which of the following is the most appropriate screening procedure for this patient?
75gram oral glucose tolerance test
Three hour 100gram oral glucose tolerance test
Fasting and random urine sugar
One time fasting blood sugar
One hour 50gram oral glucose tolerance test
A 24-year-old white female is brought to the emergency department (ED) by her mother due to altered mental status. According to her mother, she suffered from viral gastroenteritis 4 days ago. Since then, she has been on oral fluids. Over the past 2 days, her condition had been deteriorating, but she kept refusing admission to the hospital. Her past history is not significant, except for excessive thirst, water intake and weight loss over the past two months. Her blood pressure is 100/56 mmHg, pulse is 120/min (regular and weak), temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), and respirations are 28/min (rapid and deep). Pulse oximetry is 94% on room air. She is arousable and moves all her extremities. Her mucous membranes are very dry. Her neck is supple. The chest is clear on auscultation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Obtain electrocardiogram
Fingerstick glucose
Obtain arterial blood gases
Intubate the patient
Obtain CT scan of head
A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 24-hour history of right flank pain, burning micturition and high-grade fever with chills. Her temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 130/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination shows costovertebral angle tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely urine dipstick finding in this patient?
Positive for nitrites and esterase
Negative for both esterase and nitrites
Positive for nitrites only
Positive for esterase only
Negative for esterase and positive nitrites
A 24-year-old woman comes to your office complaining of an 8-week history of amenorrhea. She is sexually active and uses OCPs for contraception. Her medical history is unremarkable. She does not have any particular complaints except moderate fatigue and a decline in mood. She denies headaches, visual disturbances, or any gastrointestinal symptoms. She denies cigarette smoking or any drug use, and drinks alcohol socially. Breast examination reveals a white, milky secretion upon expression of both nipples. A pelvic examination reveals a uterus of normal size. BMI is 28 kg/m2. Initial investigations reveal a negative serum beta-hCG level. According to these findings, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Determine serum TSH level
Perform visual field study
Determine serum TRH level
Order sellar MRI
Order sellar CT scan
A 24-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of right lower quadrant pain and vaginal spotting. Her last menstrual period was 5 weeks ago. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 112/70 mm Hg, pulse is 74/min, and respirations are 14/min. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Pelvic examination reveals scant blood in the vagina, a closed cervical os, no pelvic masses, and right pelvic tenderness. Her leukocyte count is 8000/mm3, hematocrit is 38%, and a platelet count is 250,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most appropriate step next in diagnosis?
Serum hCG
Serum TSH
Abdominal x-ray
Abdominal/pelvic
CT Laparoscopy
A 24-year-old woman presents with nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and gross hematuria. She had a sore throat 2 weeks ago that resolved on its own. On examination, her blood pressure is 160/90 mm Hg, pulse 90/min, JVP is 7 cm, heart sounds are normal, there is 1+ pedal edema, and the lungs are clear. She has a renal biopsy. Which of the following electron microscopy findings on the renal biopsy is most likely in keeping with poststreptococcal GN?
Diffuse mesangial deposits
No deposits
Electron-dense endothelial deposits
Closed capillary lumen
Subepithelial humps
A 24-year-old woman presents with new-onset right lower quadrant pain, and you palpate an enlarged, tender right adnexa. Which of the following sonographic characteristics of the cyst in this patient suggests the need for surgical exploration now instead of observation for one menstrual cycle?
Lack of ascites
Diameter of 5 cm
Unilocularity
Papillary vegetation
Demonstration of arterial and venous flow by Doppler imaging
A 24-year-old woman sustains multiple injuries in a car accident, including a pelvic fracture. She is hemodynamically stable. Initial assessment shows no vaginal or rectal injuries; however, when a Foley catheter is inserted, bloody urine is recovered. Which of the following would be the best way to evaluate her urologic injury?
Cystoscopy
Retrograde cystogram including views of the ureters
Sonogram of the bladder
Retrograde cystogram including post-void films
Intravenous pyelogram
A 24-year-old woman, G1 P1, comes to your office because she has been amenorrheic for two months. She has been taking low dose combined oral contraceptive pills (OCPs) for the past three months. She had withdrawal bleeding after the first month, but has had no bleeding over the past two months. Over the past few days, she has had nausea, vomiting and abdominal bloating. She does not use alcohol, tobacco, or drugs. Menarche occurred at the age of 14; menses have always been irregular. She is requesting a change in her contraception regimen because of these problems. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Measure serum FSH and LH
Discontinue OCP and recommend intrauterine contraceptive device
Measure serum beta-HCG
Advise her to stop taking oral contraceptives temporarily and advise condom use until symptoms resolve
Tell her this is normal with patients who have recently begun taking oral contraceptives, and that her symptoms will resolve eventually
A 25-year-old female presents to her physician with a painful ulcerative lesion on her labia for the past 2 days. She also complains of dysuria. She admits to having sexual intercourse with multiple partners for the last 6 years. Tzanck preparations of one of her lesions reveal multi-nucleated giant cells. She is encouraged to undergo testing for HIV and other STDs. Which of the following is the most appropriate screening test for HIV infection?
HIV serology by ELISA
HIV serology by western blot
HIV viral load
Absolute CD4 count
P 24 antigen assay
A 25-year-old female presents to the emergency department with sudden-onset severe shortness of breath and wheezing. She has a history of asthma. On examination, she is unable to speak in full sentences and is using accessory muscles of respiration. She is intubated, mechanically ventilated and treated with continuous albuterol nebulization and intravenous methylprednisolone. Within six hours, her condition is improved. She is extubated and treated with hourly nebulizer treatments. The next morning, she complains of muscle weakness. On physical examination, she has difficulty lifting her arms over her head and mild hand tremors. Her vital signs are stable. What should be the immediate next step in her management?
Check peak expiratory flow rate
Check serum TSH level
Check chest x-ray, PA view
Check serum electrolyte panel
Obtain electromyography (EMG)
A 25-year-old female presents to the physician's office complaining of fatigue, joint pains, and frequent mouth ulcers over the past three months. She has no medical problems and does not take any medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg and pulse is 78/min. Examination shows erythema over the cheeks and nose. Labs reveal a serum creatinine of 2.8 mg/dl and her urinalysis shows 2+ protein and 20 RBC/HPF. Anti-double stranded antibodies (anti-dsDNA) are positive. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Kidney biopsy
Methylprednisolone
Methotrexate
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide and methylprednisolone
A 25-year-old female presents to your office complaining of exertional dyspnea and fatigue. Her past medical history is insignificant. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and heart rate is 90/min. Physical examination reveals pale conjunctiva. The laboratory values are: ESR 15 mm/hr, Hemoglobin 7.5 g/dL, MCV 70 fl, MCHC 29%, Leukocyte count 7,000/cmm, Segmented Neutrophils 55%, Bands 3%, Eosinophils 3%, Basophils 0%, Lymphocytes 32%, Monocytes 7%. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Bone marrow sampling
Iron studies
Serum folate level
Schilling test
HbA2 measurement
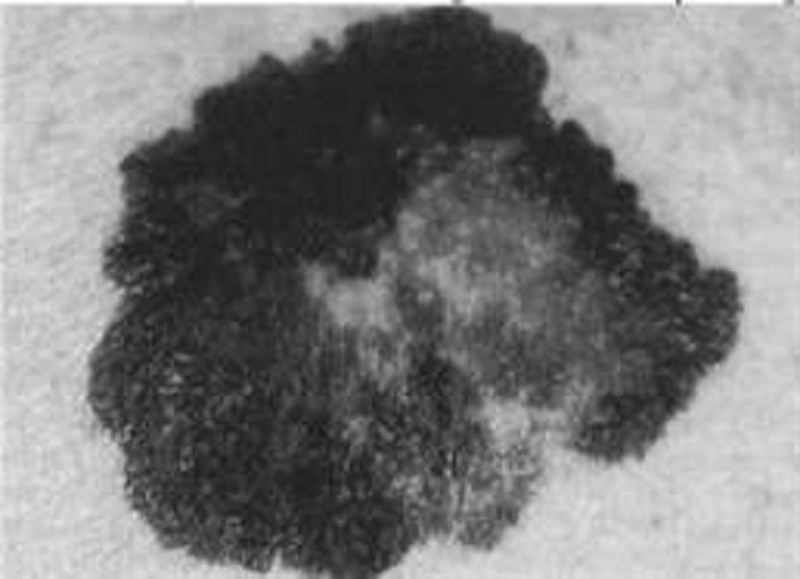
A 25-year-old female with blonde hair and fair complexion complains of a mole on her upper back. The lesion is 8 mm in diameter, darkly pigmented, and asymmetric, with an irregular border (see illustration below). Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Tell the patient to avoid sunlight
Obtain full-thickness excisional biopsy
Obtain shave biopsy
Follow the lesion for any evidence of growth
Obtain metastatic workup
A 25-year-old G2, PI at 28 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department by her boyfriend, who found her lying on her bed in a pool of blood. She is very drowsy, but denies any pain or uterine contraction. Her temperature is 38°C (100.4°F) and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination is suggestive of a transverse lie. Inspection of the perineum reveals gross blood and active bleeding per vagina. Which of the following set of parameters would most likely be seen in this patient?
Set A
Set B
Set C
Set D
Set E
A 25-year-old G3P1011 presents to the ED with a 6-hour history of worsening lower abdominal pain, mostly in the RLQ. She also noticed some vaginal spotting this morning. She is nauseated, but did not vomit. Her last menstrual period was 2 months ago, but her cycles are irregular. She is sexually active and has a history of pelvic inflammatory disease. Her BP is 120/75 mm Hg, HR is 95 beats per minute, temperature is 99.2°F, and RR is 16 breaths per minute. Her abdomen is tender in the RLQ. Pelvic examination reveals right adnexal tenderness. Her WBC count is slightly elevated and her β-hCG is positive. After establishing IV access, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Order an emergent CT scan of the abdomen
Order a urinalysis
Call the OR to prepare for laparoscopy
Swab her cervix and treat for gonorrhea and Chlamydia
Perform a transvaginal ultrasound
A 25-year-old male is brought to the trauma center by the paramedics after being involved in a road traffic accident that occurred 90 minutes ago. He was a front seat passenger in a 3-car accident. His initial blood pressure at the scene of the accident was 90/60 mm Hg and pulse was 126/min. The paramedics administered 2 liters of normal saline in the ambulance. In the ED, his blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg and pulse is 90/min. His abdomen is tender in the left upper quadrant. Ultrasound shows fluid in the spleno-renal angle. The most appropriate next step is?
Perform exploratory laparotomy
Perform a CT scan
Admit to the surgical ICU
Admit to the ward
Laparoscopy
A 25-year-old male presents with progressive shortness of breath over the past 6 months. His past medical history is significant only for neonatal hepatitis that resolved spontaneously when he was 6 months of age. The man has never smoked. On lung auscultation today, there are decreased breath sounds over both lower lobes. Chest x-ray demonstrates emphysematous changes in the bilateral lower lobes. Routine blood work is normal. Which of the following analyses would be most helpful in establishing this patient's diagnosis?
Open lung biopsy
High resolution CT scan of chest
Video-assisted lung biopsy
Pulmonary function testing
Serum alpha-1 antitrypsin level
A 25-year-old male student presents with the chief complaint of rash. He denies headache, fever, or myalgia. A slightly pruritic maculopapular rash is noted over the abdomen, trunk, palms of the hands, and soles of the feet. Inguinal, occipital, and cervical lymphadenopathy is also noted. Hypertrophic, flat, wartlike lesions are noted around the anal area. Laboratory studies show the following: Hct: 40%, Hgb: 14 g/dL, WBC: 13,000/μL, Diff: 50% segmented neutrophils, 50% lymphocytes. Which of the following is the most useful laboratory test in this patient?
Weil-Felix titer
Chlamydia titer
Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) test
Blood cultures
Biopsy of perianal lesions
A 25-year-old man is shot with a .22 caliber revolver. The entrance wound is in the anteromedial aspect of his upper thigh, 5 cm below the groin crease. The exit wound is in the posterolateral aspect of the thigh, half way between the greater trochanter and the knee. He has palpable pulses in the dorsum of his foot and in the posterior tibial artery behind the malleolus. The popliteal pulse is reported normal by one examiner, but cannot be felt by another. There is no hematoma under the entrance wound, and blood is oozing from both wounds but not at an alarming rate. He is hemodynamically stable. Neurologic examination of the leg is normal. X-ray films show the femur to be intact. In addition to local wound care and the appropriate tetanus prophylaxis, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Discharge home
Digital exploration of the wounds in the emergency department
Formal surgical exploration of the area in the operating room
Hospitalization to observe for development of complications
Arteriogram
A 25-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the physician because of chronic pelvic and low sacral back pain for several months. The pain is usually worse premenstrually. She tried over the counter anti-inflammatory medications but had little relief. She has been in a monogamous relationship with her boyfriend for the past 4 years. She has no fever or abnormal vaginal discharge. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), and blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg. Physical examination shows tender posterior vaginal fornix and pain upon uterine motion. Complete blood count is normal. Pelvic ultrasonogram is normal. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is most appropriate diagnostic test in her management?
Endometrial biopsy
Laparoscopy
CA-125 levels
Hysterosalpingogram
CT scan of the pelvis
A 25-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the physician because of constant pelvic and low sacral back pain for several months. The pain is usually worse premenstrually. She tried over the counter anti-inflammatory medications but had little relief. She has been in a monogamous relationship with her boyfriend for the past 4 years. She has no fever or abnormal vaginal discharge. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), and blood pressure is 120/78 mm Hg. Physical examination shows tender posterior vaginal fornix and pain upon uterine motion. Complete blood count is normal. Pelvic ultrasonogram is normal. Which of the following is most appropriate diagnostic test in her management?
Endometrial biopsy
Laparoscopy
CA- 125 levels
Hysterosalpingogram
Serial beta-hCG
A 25-year-old postal worker presents with a pruritic, nonpainful skin lesion on the dorsum of his hand. It began like an insect bite but expanded over several days. On examination, the lesion has a black, necrotic center associated with severe local swelling. The patient does not appear to be systemically ill, and vital signs are normal. Which of the following is correct?
The lesion is ecthyma gangrenosum, and blood cultures will be positive for Pseudomonas aeruginosa
A skin biopsy should be performed and Gram stain examined for gram-positive rods
The patient has necrotizing fasciitis and needs immediate surgical debridement
The patient has the bubo of plague
The patient has been bitten by Loxosceles reclusa, the brown recluse spider
A 25-year-old who has been living in Washington, DC, presents with a diffuse vesicular rash over his face and trunk. He also has fever. He has no history of chickenpox and has not received the varicella vaccine. Which of the following information obtained from history and physical examination suggests that the patient has chickenpox and not smallpox?
The rash is most prominent over the face
All lesions are at the same stage of development
There are vesicular lesions on the palms and soles
Vesicular lesions are concentrated on the trunk
The patient experienced high fever several days prior to the rash
A 25-year-old woman presents to your office for evaluation of primary infertility. She has regular periods every 28 days. She has done testing at home with an ovulation kit, which suggests she is ovulating. A hysterosalpingogram demonstrates patency of both fallopian tubes. A progesterone level drawn in the mid–luteal phase is lower than expected. A luteal phase defect is suspected to be the cause of this patient’s infertility. Which of the following studies performed in the second half of the menstrual cycle is helpful in making this diagnosis?
Serum estradiol levels
Serum follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels
Endometrial biopsy
Urinary pregnanetriol levels
Serum luteinizing hormone (LH) levels
A 25-year-old woman who is “about 5 months” pregnant with her first child presents for the first time to an obstetrician. She has had no prenatal care. When asked about her medical history, she states she sometimes takes medicine for “depression,” and she produces a prescription bottle with lithium tablets in it. She is otherwise healthy and her pregnancy has been uncomplicated to date. The fundus of her uterus is 22 cm from the pubic symphysis, fetal movement is felt, and fetal heart tones are present at 130/min. Which of the following tests should be advised given the patient’s lithium ingestion?
Chorionic villus sampling
Fetal echocardiography
Fetal renal ultrasound
Maternal oral glucose tolerance test
Measurement of α-fetoprotein, β-human chorionic gonadotropin, and estriol levels
A 25-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease is exploring the benefits of renal transplantation. Which of the following is an advantage of dialysis over renal transplantation?
Better patient survival
Improved quality of life
More cost-effective longterm
No need for lifelong immunosuppression
More cost-effective if the renal transplant functions for more than 2 years
A 25-year-old woman, 8 weeks pregnant, is found to have a 1-cm mass in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast. Core biopsy diagnoses infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Technically, the tumor is amenable to a lumpectomy. Palpation of the axilla is negative. When confronted with her therapeutic options, the patient indicates that her first consideration is the welfare of her unborn child, the second consideration is her own chance of cure, and the last consideration is the cosmetic outcome of the treatment. To help her achieve those ends, which of the following is the most appropriate first step of her treatment?
Lumpectomy and axillary dissection
Radiation treatment to the affected breast
Lumpectomy and sentinel node biopsy
Systemic chemotherapy
Modified radical mastectomy
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, presents to your office at 20 weeks' gestation for a routine prenatal check-up. She is known to be 0 (-) while her husband is 0 (+). Her obstetric history is significant for intrapartum placental abruption, which did not require caesarian delivery. She received a standard dose of anti-0 immune globulin at 28 weeks of her first pregnancy and immediately postpartum. You decide to determine her anti-0 antibody titers, and they turn out to be 1:34. Which of the following is the most likely explanation of the positive antibody screen in this patient?
No prophylaxis early in this pregnancy
Too early administration of anti-0 immune globulin postpartum
Low dose of anti-D immune globulin at 28 weeks of her first pregnancy
No prophylaxis between the pregnancies
Low dose of anti-D immune globulin postpartum
A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2 para 1, presents to your office at 20 weeks' gestation for a routine prenatal check-up. This pregnancy has been uncomplicated thus far. She is known to be D (-) while her husband is D (+). Her obstetric history is significant for intrapartum placental abruption, which did not require caesarian delivery. She received a standard dose of anti-D immune globulin at 28 weeks of her first pregnancy and immediately postpartum. You decide to determine her anti-D antibody titers, and they turn out to be 1:34. Which of the following is the most likely explanation of the positive antibody screen in this patient?
No prophylaxis early in this pregnancy
Too early administration of anti-D immune globulin postpartum
Low dose of anti-D immune globulin at 28 weeks of her first pregnancy
No prophylaxis between the pregnancies
Low dose of anti-D immune globulin postpartum
A 26-year-old Caucasian male comes to the physician because of severe productive cough for the past two months. He also complains of occasional blood in sputum, and dyspnea for the last three weeks. His past medical history is significant for otitis media, two episodes of pneumonia, and sinusitis. He and his wife were recently worked up for infertility. Physical examination shows crackles in the left upper lobe. Chest x-ray shows dilated and thickened airways and irregular peripheral opacities in the left upper lobe. Which of the following is the most appropriate test to make the diagnosis of his condition?
Sweat chloride test
DNA studies
Pulmonary function tests
Semen analysis
Bronchoscopy
A 26-year-old G1P0 patient at 34 weeks gestation is being evaluated with Doppler ultrasound studies of the fetal umbilical arteries. The patient is a healthy smoker. Her fetus has shown evidence of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) on previous ultrasound examinations. The Doppler studies currently show that the systolic to diastolic ratio (S/D) in the umbilical arteries is much higher than it was on her last ultrasound 3 weeks ago and there is now reverse diastolic flow. Which of the following is correct information to share with the patient?
The Doppler studies indicate that the fetus is doing well
With advancing gestational age the S/D ratio is supposed to rise
These Doppler findings are normal in someone who smokes
Reverse diastolic flow is normal as a patient approaches full term
The Doppler studies are worrisome and indicate that the fetal status is deteriorating
A 26-year-old man presents with a 1-week history of intermittent, crampy, lower abdominal pain accompanied by rectal urgency, bloody diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. His symptoms have become more severe over the past 24 hours. His past medical history is unremarkable. He denies any recent travel or antibiotic use. His temperature is 38.5°C (102.0°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, and respirations are 15/min. Abdominal examination reveals distension and tenderness to palpation without rebound or guarding. The bowel sounds are decreased. Rectal examination shows marked rectal tenderness and mucus mixed with blood in the vault. An x-ray film of the abdomen shows distended colon filled with gas. Laboratory studies show: Hb 10.8 g/dl, WBC 19,600/cmm, Platelet count 459,000/cmm, ESR 54/hr. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Barium enema
Serology for Entamoeba histolytica
Stool for ova, parasites and culture
Proctosigmoidoscopy and biopsy
CT scan of the abdomen
A 26-year-old nulligravid patient presents to her physician seeking preconceptional advice. She plans to conceive in about 1 year. Her past medical history is significant for chickenpox as a child. She had an appendectomy 2 years ago. She takes no medications and is allergic to penicillin. Her complete physical examination, including a pelvic examination, is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis to prevent morbidity in this patient's offspring?
Blood cultures
Group B Streptococcus culture
Pelvic ultrasound
Rubella titer
Urine culture
A 26-year-old white female presents with worsening weakness of her right upper extremity, left lower extremity and ataxia. She also complains of unilateral eye pain and visual loss. The eye pain is worsened by ocular movements. On eye examination, there is a central visual field defect in her right eye. Fundoscopy is normal. Neurological examination shows spastic paraparesis in the right upper extremity and the left lower extremity. What is the most appropriate next step in this patient's management?
CT scan with contrast
MRI of the brain
Lumbar puncture
Brain biopsy
PET scan
A 26-year-old woman presents for evaluation of infertility. She describes her menstrual cycles as irregular stating that they occur anywhere between 32 to 35 days. She has no galactorrhea. She eats a balanced diet and exercises regularly. She has no other medical problems. Her BMI is 22 Kg/m2. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial test to evaluate her infertility?
Endometrial biopsy
Mid luteal serum progesterone level
Hysterosalpingogram
Serum testosterone
Karyotyping
A 26-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, comes to the physician for the first time for a prenatal checkup. She changed her physician and in the interim has missed two prenatal checkups. She states that she is at 7months gestation. According to her prenatal records and an ultrasound performed at 16 weeks gestation, she is now at 30 weeks, but her fundal height is only 26 cm (10.2 inches). Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. Blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg. You suspect fetal growth restriction (FGR) and order a repeat ultrasonogram. Which of the following is the single most useful parameter for predicting fetal weight by ultrasonogram in suspected FGR?
Biparietal diameter
Femur length
Abdominal circumference
Head to abdomen circumference ratio
Calculated fetal weight
A 27 year-old African-American woman presents to the emergency room complaining of unilateral leg swelling, pleuritic chest pain and shortness of breath. She reports a rash on her face that worsens in the sun, two previous miscarriages, and complains of recent painful swelling in both knees. A CT angiogram confirms a pulmonary embolus. Which of the following is the most likely laboratory abnormality?
Decreased prothrombin time (PT)
Prolonged partial thromboplastin time (PTT)
Absent Von Willebrand's factor
Increased bleeding time
Thrombocytosis
A 27-year old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of infertility. She and her 31-year-old husband have not been able to conceive after 12 months of unprotected and frequent intercourse. She has regular 28-day menstrual cycles and during the menstrual cycles she develops mild pelvic pain and bilateral breast tenderness. She has no pain during sexual intercourse. Her blood pressure is 128/76 mm Hg and pulse is 82/min. Physical examination is completely unremarkable. Which of the following could most likely be abnormal in this patient?
Serum prolactin level
Mid luteal serum progesterone level
Hysterosalpingogram
Serum testosterone level
Serum inhibin B level
A 27-year-old Caucasian male is diagnosed with medullary thyroid carcinoma that is non-resectable. His past medical history is insignificant. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His family history is significant for thyroid cancer and pheochromocytoma in his father. Which of the following tests could have been most effective in preventing this patient's non-resectable cancer?
Frequent self-examination of the neck
Periodic stimulated serum calcitonin measurement
Annual physical examination
DNA testing
Periodic serum calcium measurement
A 27-year-old G2P1 at 29 weeks gestational age, who is being followed for Rh isoimmunization presents for her OB visit. The fundal height is noted to be 33 cm. An ultrasound reveals fetal ascites and a pericardial effusion. Which of the following can be another finding in fetal hydrops?
Oligohydramnios
Hydrocephalus
Hydronephrosis
Subcutaneous edema
Over-distended fetal bladder
A 27-year-old healthy woman comes to the office for evaluation of infertility. She and her 31 -year-old husband have not been able to conceive after 12 months of unprotected and frequent intercourse. Her husband is healthy and takes no medications. He has a normal semen analysis. She has regular 28-day menstrual cycles. The patient has mid-cycle pelvic pain and an egg white like consistency to her discharge mid-cycle. She has no pain during sexual intercourse. The patient does report having been hospitalized with a pelvic infection in her late teens, during which time she had pain with intercourse, discharge, and fever. Her sister was diagnosed with polycystic ovarian disease. Her blood pressure is 128/76 mm Hg and pulse is 82/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is most likely to be abnormal in this patient?
Serum prolactin level
Mid-luteal phase progesterone
Hysterosalpingogram
Serum testosterone level
Serum inhibin B level
A 27-year-old man complains of difficulty in walking. He noticed leg weakness several days ago, and now he is barely able to walk. He also complains of mild back pain and foot numbness. Two weeks ago, he had an upper respiratory tract infection. Physical examination reveals lower extremity muscle weakness, absent knee and ankle reflexes, and minimal sensory loss. Spinal MRI shows no abnormalities. Which of the following findings would you expect on CSF analysis in this patient? (Protein, WBC, count RBC, count Glucose)
High, increased, increased, low
High, normal, normal, normal
High, increased, normal, normal
Normal, increased, increased, normal
High, increased, normal, low
A 27-year-old man complains of poor appetite, loss of interest in his daily activities, and impaired sleep. He has lost 10 pounds over the last two months. He says that he feels regretful about IV drug abuse in his past, but denies having suicidal or homicidal thoughts. He drinks alcohol occasionally but denies regular alcohol consumption or early morning drinking. He is sexually active with one partner and she uses oral contraceptives. On physical examination, his pulse is 76/min and his blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. His heart and lung exams are unremarkable and his abdomen is soft and non-tender. The liver span is 9 cm and the spleen is not palpable. He is fully oriented to person, place and time but performs poorly on memory tests. Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient?
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
Benzodiazepines
HIV testing
Thyroid function testing
Serum iron studies
A 27-year-old man is seen in the ED for a leak around a surgical G-tube that was placed 2 weeks ago and has been used for enteral feeding for 1 week. Inspection reveals the tube is pulled out from the stoma, but is still in the cutaneous tissue. The abdomen is soft and nondistended and there are no signs of skin infection. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Insert a Foley catheter into the tract and aspirate. If gastric contents are aspirated the tube can be used for feeding
Insert a Foley catheter into the tract, instill water-soluble contrast, and obtain an abdominal radiograph prior to using for feeding
Return to the OR for closure of gastrotomy and placement of a new tube
Remove the tube and immediately obtain a CT scan of the abdomen
Remove the tube and admit the patient for observation
A 27-year-old man presents with diarrhea. He returned 3 weeks ago from a trip to rural South America. Over the past few days, he has gradually developed lower abdominal pain and diarrhea. Now the symptoms are much worse with eight stools a day consisting mostly of mucus and blood. He is afebrile, the abdomen is tender in left lower quadrant, and the remaining examination is normal. His stool is mostly comprised of blood and mucus. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test?
Examination of a dried stool specimen
Examination of a wet stool specimen
Stool culture
Immunofluorescence of stool specimen
Stool toxin assay
A 27-year-old man was assaulted and stabbed on the left side of the chest between the areola and the sternum. He is hemodynamically unstable with jugular venous distention, distant heart sounds, and hypotension. Which of the following findings would be consistent with a diagnosis of hemodynamically significant cardiac tamponade?
More than a 10 mm Hg decrease in systolic blood pressure at the end of the expiratory phase of respiration
Decreased right atrial pressures on Swan-Ganz monitoring
Equalization of pressures across the 4 chambers on Swan-Ganz monitoring
Overfilling of the right atrium
Compression of the left ventricle on echocardiography
A 27-year-old woman comes to the physician for preconception counseling. She takes no medication. Her menses are regular, are moderate in amount, and last 5-6 days. Her diet is well balanced. Her grandparents are from Greece. Her husband's family is also of Mediterranean ancestry. Her mother and sister have been diagnosed with anemia, but she does not know the types. The presence of thalassemia anemia in her family is suspected. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial screening test?
Complete blood count in the patient
Hemoglobin electrophoresis testing in the patient
Hemoglobin electrophoresis testing in the patient and her husband
Solubility testing in the patient
Iron level, total iron-binding capacity, and ferritin level in the patient
A 27-year-old woman complains of fatigue, low-grade fevers, anorexia, headaches and skin rash over the past several weeks. She also notes new exertional dyspnea and an unintentional 5-pound weight gain over the past two weeks. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 190/110 mmHg and her heart rate is 90/min. Which of the following is the most likely finding on this patient's urinary tests?
High VMA excretion
High daily cortisol excretion
Red blood cells
Glucosuria
Uric acid crystals
A 27-year-old woman is 7 months pregnant with her first child. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated to date. She presents to the emergency department complaining of sudden-onset, right-sided chest pain that is exacerbated with deep breathing and shortness of breath, which began 1 hour ago. She denies leg pain and notes that her legs began swelling during the sixth month of her pregnancy but the swelling has not worsened. Her temperature is 37.9°C (100.3°F), blood pressure is 130/87 mm Hg, pulse is 107/min and regular, respiratory rate is 24/min, and oxygen saturation is 90% on room air, increasing to 98% with 4 L oxygen via nasal cannula. Physical examination is significant for crackles at the lower right lung field and a negative Homans’ sign bilaterally. X-ray of the chest appears normal. The D-dimer level is elevated. ECG shows sinus tachycardia, right-axis deviation, S wave in lead I, Q wave in lead III, and an inverted T wave in lead III. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
Arterial blood gas analysis
MRI of the lower extremity
Doppler ultrasound of the lower extremity
Pulmonary angiography
Ventilation/perfusion scans
A 27-year-old woman presents to the office due to a significant amount of hair on her cheeks, chin and upper lips. This symptom developed over the past two months. Her last menstrual period was 12 weeks ago, but she did not seek medical help because her home pregnancy test was negative. Her medical history is unremarkable. She denies taking any medications other than oral contraceptive pills. Physical examination reveals acne on the forehead and cheeks; there is terminal hair on the upper lip, cheeks, chin, upper chest and lower abdomen. Examination of the genitals shows clitoromegaly. The abdominal exam is normal; the uterus is normal in size. Ultrasound reveals a normal uterus and ovaries, but there is a left adrenal mass. Which of the following measurements is most specific for this patient's condition?
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Testosterone
Dehydroepiandrosterone-sulfate
Dihydrotestosterone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 12 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of a dark brown vaginal discharge. She had a mild brown vaginal discharge 3 weeks ago, which resolved without any intervention. She noticed similar discharge again two days ago. For the past two weeks, she has not had nausea or breast tenderness, which she used to have before. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her temperature is 37.0C (98.7F), blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg, pulse is 85/min and respirations are 15/min. Physical examination shows a soft uterus and a closed cervix. Fetal heart tones are not present. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Quantitative beta-HCG measurement
Check PT/INR and PTT
Pelvic ultrasonography
Chorionic villous sampling
Reassurance and routine follow-up
A 27-year-old, HIV-positive man comes to his physician with a two-day history of fever, profuse watery diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. He has been taking zidovudine, didanosine, and indinavir for the past eight months. His temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse is 102/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 105/70 mm Hg. He is started on fluid and electrolyte support. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Stop antiretroviral therapy and send stool for Clostridium difficile toxin assay
Loperamide and lactose-free diet until diarrhea subsides
Start empiric treatment for cytomegalovirus
Stool examination for ova and parasites
Colonoscopy with biopsy of the colonic mucosa
A 28-year-old African American woman presents with mild dyspnea on exertion. She reports no coughing, sputum production, or wheezing symptoms, but has noticed a red tender rash on her shins. Physical examination reveals hepatosplenomegaly, generalized lymphadenopathy, and tender erythematous nodules on her legs. CXR shows bilateral symmetric hilar adenopathy. Her pulmonary fun
Tuberculin skin test
Elevated ACE level
Bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy
Serum hypercalcemia
Increased uptake on gallium scan
A 28-year-old Caucasian female presents to the emergency department (ED) appearing very anxious. She is accompanied by her boyfriend. She woke up this morning with severe weakness over the right side of her body. The weakness came on all of a sudden, but gradually resolved during the day. She denies any sensory symptoms. Her boyfriend reports that her speech was "weird, almost as if she was stuttering or struggling to get her words out." This too has resolved. The patient denies any other symptoms. The only other history of note is that she returned from a holiday in Italy 2 days ago. Vitals signs are unremarkable. The neurological examination is normal. Her chest x-ray is within normal limits. EKG shows normal sinus rhythm with a rate of 82/min. An urgent head CT scan is within normal limits. Which of the following investigations is most likely to reveal the underlying cause of this episode?
Carotid Doppler ultrasonography
Psychiatric referral
Transthoracic echocardiogram
Cerebral angiography
MRI head
A 28-year-old G1P0 woman at 12 weeks’ gestation presents for routine follow-up with her obstetrician. She complains of mild nausea and occasional vomiting, but otherwise is doing well and reports no other symptoms or complications. Her physical examination is unremarkable and fetal ultrasound is normal for gestational age. Laboratory tests show: Free triiodothyronine: 180 ng/dL, Free thyroxine: 2.2 ng/dL, Total thyroxine: 12 μg/dL, Thyroid-stimulating hormone: 0.1 μU/mL(normal: 0.4 – 4 μU/mL). Results of a thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor antibody test are negative. Which of the following best explains these findings?
Acute infectious thyroiditis
High serum estrogen concentration
Graves’ disease
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
High serum β-human chorionic gonadotropin level
A 28-year-old G2, P 1woman in her 26th week of gestation comes to the office due to intermittent episodes of abdominal pain. She has been having these episodes for the past 4 days, and thinks that her fetus may be in distress. She points to her right flank when asked about the location of the pain, and says that it occasionally radiates to the groin area. She cannot identify any exacerbating or relieving factors. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated so far. Her past medical history is significant for pelvic inflammatory disease. Her temperature is 37.5 C (99.5 F), blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 88/min. She is in considerable pain at the moment. Deep palpation of the right flank reveals tenderness. There is no CVA tenderness. Urinalysis shows: Specific gravity: 1.020, Blood: ++, Glucose: negative, Ketones: negative, Protein: negative, Leukocyte esterase: negative, Nitrites: negative. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Cervical cultures
Ultrasound of the abdomen
Shockwave lithotripsy
Intravenous pyelogram
CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis
A 28-year-old G3P2 woman at 32 weeks gestation comes to the physician because she has felt only 2 or 3 fetal movements in the past 12 hours. As in her previous pregnancies, she has gestational diabetes, which is under good control with diet and mild exercise. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination is unremarkable. Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient?
Amniotic fluid index
Deliver the fetus immediately
Contraction stress test
Non-stress test
Ultrasound for fetal heart tones
A 28-year-old Glo with an IUP at 26 weeks' gestation presents to the emergency department for shortness of breath. She receives regular prenatal care, and her pregnancy has been uncomplicated thus far. She developed shortness of breath suddenly after a long drive in traffic. She has chest pain when she takes a deep breath. Vital sign: BP, 120/80 mm Hg; P, 120 beats/min; R, 24 breaths/min; T, 98.9°F; pulse ox, 89% on room air. Physical examination: general: awake, alert, oriented x3, mild respiratory distress, cardiovascular: S1S2+RRR no m/r/g, lungs: clear to auscultation bilaterally. Abdomen: gravid; fundal height 25 cm; no tenderness, extrimies: 1+ edema bilaterally; no erythema, chest radiography with an abdominal shield is within normal limits. What is the next best step?
CBC
CMP
N-Dimer
Doppler ultrasonography of the legs
MRI
A 28-year-old man presents to the ED complaining of constant vague, diffuse epigastric pain. He describes having a poor appetite and feeling nauseated ever since eating sushi last night. His BP is 125/75 mm Hg, HR is 96 beats per minute, temperature is 100.5°F, and his RR is 16 breaths per minute. On examination, his abdomen is soft and moderately tender in the right lower quadrant (RLQ). Laboratory results reveal a WBC of 12,000/ μL. Urinalysis shows 1+ leukocyte esterase. The patient is convinced that this is food poisoning from the sushi and asks for some antacid. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Send the patient for an abdominal ultrasound
Order an abdominal CT scan
Administer 40 cc of Maalox and observe for 1 hour
Discharge the patient home with ciprofloxacin
Order a plain radiograph to look for dilated bowel loops
A 28-year-old man presents with coughing up blood and sputum. He gives a history of recurrent pneumonias and a chronic cough productive of foul-smelling purulent sputum. He has no other past medical history and is a lifetime nonsmoker. On physical examination, there are no oral lesions, heart sounds are normal, and wet inspiratory crackles are heard at the lung bases posteriorly. He also has clubbing of his fingers, but there is no hepatosplenomegaly or any palpable lymph nodes. CXR show fibrosis and pulmonary infiltrates in the right lower lung. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test?
Chest CT scan
Bronchoscopy
Bronchography
Open thoracotomy
Bronchoalveolar lavage
A 28-year-old nulligravid patient complains of bleeding between her periods and increasingly heavy menses. Over the past 9 months, she has had two dilation and curettages (D&Cs), which have failed to resolve her symptoms, and oral contraceptives and antiprostaglandins have not decreased the abnormal bleeding. Which of the following options is most appropriate at this time?
Perform a hysterectomy
Treat with a GnRH agonist
Perform hysteroscopy
Perform endometrial ablation
Start the patient on a high-dose progestational agent
A 28-year-old primigravid woman at 8 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit. A home pregnancy test was positive. She has no complaints. She is concerned, however, because she is a carrier of the fragile X mutation. Her husband is also known to be a carrier. This is a highly desired pregnancy. She wants to know whether there is a way to determine whether the fetus is affected. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Offer testing of the parents
Offer 2nd trimester amniocentesis
There is nothing to offer this couple
Offer MRI of the fetus
Offer termination of the pregnancy
A 28-year-old primigravid woman at term comes to the labor and delivery ward with a gush of fluid and regular contractions. Her prenatal course was remarkable for her being Rh negative and antibody negative. Her husband is Rh positive. Over the following 10 hours, she progresses in labor and delivers a 3600-g boy via a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery. The placenta does not deliver spontaneously, and a manual removal is required. To determine the correct amount of RhoGAM (anti-D immune globulin) that should be given, which of the following is the most appropriate laboratory test to send?
Complete blood count
Kleihauer-Betke
Liver function tests
Prothrombin time
Serum potassium
A 28-year-old primigravid woman comes to the physician for a follow-up prenatal visit. According to prenatal records, ultrasound at 16 weeks gestation showed an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates and showed no abnormalities. She is now at 40 weeks gestation. Examination shows a fundal height consistent with dates and the cervix is not favorable. Fetal heart tracing is reassuring. She wishes to continue the pregnancy for two more weeks rather than undergoing induction. She should be closely monitored for which of the following?
Polyhydramnios
Oligohydramnios
Abruptio placenta
Placenta previa
Preeclampsia
A 28-year-old white female presents to the office for the evaluation of goiter. She denies any recent change in appetite or weight, diarrhea, constipation, heat or cold intolerance, dyspnea and hoarseness. Her menses are normal and regular. Examination shows a symmetrically enlarged, non-tender, firm and rubbery thyroid gland. There is no lymphadenopathy. The rest of the physical examination is normal. Laboratory studies reveal an elevated serum TSH level with normal T4 and T3 levels. Serological testing for Hashimoto's thyroiditis is ordered. Which of the following are the most prevalent antibodies in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
Anti-smooth muscle antibodies
Thyroid-stimulating immunoglobulins
Anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies
TSH-receptor blocking antibodies
Anti-mitochondrial antibodies
A 28-year-old woman comes to the physician for routine physical examination and a Pap smear. She has had multiple sexual partners and uses barrier methods for contraception. She was treated for chlamydial cervicitis four months ago. She has no other medical problems. Pelvic examination is unremarkable and a Pap smear was performed. A week later the result came as "satisfactory for evaluation" and shows mild dysplasia (low grade intraepitheliallesion). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Repeat Pap smear in 2 weeks
Repeat Pap smear in 12 months
Reflex HPV testing
Cone biopsy
Colposcopy
A 28-year-old woman is admitted for delivery. She began experiencing regular, painful uterine contractions three hours ago and her water broke en route to the hospital. The cervix is 5 cm dilated and 80% effaced. The fetal presentation is vertex and the baby's head is at -1 station. After placing a fetal heart monitor and external tocometer, repetitive decreases in fetal heart rate are noted which begin at the same time as the contractions and end before the contractions have ceased. Which of the following is most likely responsible for the fetal heart pattern?
Periods of fetal sleep
Fetal head compression
Umbilical cord compression
Uteroplacental insufficiency
Intrauterine infection
A 28-year-old woman presents 4 weeks after delivering her first child with a low-grade fever and pain in her right breast. She states that she has been breast feeding her newborn infant. Physical examination finds this breast to be tender, swollen, and erythematous. Microscopic examination of nipple smears from this woman would most likely reveal large numbers of which of the following types of cells?
Adipocytes
Eosinophils
Giant cells
Mast cells
Neutrophils
A 28-year-old woman presents to your office with symptoms of a urinary tract infection. This is her second infection in 2 months. You treated the last infection with Bactrim DS for 3 days. Her symptoms never really improved. Now she has worsening lower abdominal discomfort, dysuria, and frequency. She has had no fever or flank pain. Physical examination shows only mild suprapubic tenderness. Which of the following is the best next step in the evaluation of this patient?
Urine culture
Intravenous pyelogram
Cystoscopy
Wet smear
CT scan of the abdomen with contrast
A 28-year-old woman presents with hematochezia. She is admitted to the hospital and undergoes upper endoscopy that is negative for any lesions. Colonoscopy is performed and no bleeding sources are identified, although the gastroenterologist notes blood in the right colon and old blood coming from above the ileocecal valve. Which of the following is the test of choice in this patient?
Angiography
Technetium 99m (99mTc) pertechnetate scan
Small-bowel enteroclysis
CT scan of the abdomen
Small-bowel endoscopy
A 28-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 28 weeks gestation comes to the physician because she has only felt 2-3 fetal movements in the past 12 hours. As in her previous pregnancies, she has gestational diabetes, which is under good control with diet and mild exercise. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination is unremarkable. Fetal heart tones are heard. Which of the following is the next most appropriate step in management?
Non-stress test
Contraction stress test
Biophysical profile
Ultrasonography
Deliver the baby immediately
A 29-year-old female is brought to the emergency department due to paraplegia, urinary incontinence and urgency. She denies any trauma. She has a history of trigeminal neuralgia. The neurological examination shows spasticity and hyperreflexia in the lower extremities, and impaired vibration and proprioception in her left forearm. Which of the following is the most likely finding in this patient's cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination?
Oligoclonal bands
Increased pressure
Albumino-cytologic dissociation
Increased cell count
Increased total protein concentration
A 29-year-old G2P1001 with an IUP at 35 weeks' gestation presents to the ED for vaginal bleeding. The patient states that she woke up in a puddle of blood. She denies abdominal pain. She also denies other medical history, surgical history, and allergies. The patient is taking prenatal vitamins. Fetal movement: Present, Contractions: Absent, Vaginal bleeding: Present, Leakage of fluid: Absent. Physical examination: CVS: Normal, Lungs: Clear bilaterally, Abd: Gravid, nontender, nondistended, +BS, Ext: No edema bilaterally. What is the next step in the management of this patient?
Transvaginal US
Abdominal US
Digital vaginal examination
Fetal fibronectin level
CT
A 29-year-old G2P1001 with an IUP at 7 weeks' gestation presents to the emergency department (ED) for vaginal bleeding. She started to have abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding overnight. No clots were expressed per the vagina. She denies any other medical history, surgical history, and allergies. The patient is takingprenatal vitamins. The bleeding started after sexual relations. Vital sign: BP, 120/80 mm Hg; P, 76 beats/min; R, 12 breaths/min; T, 98.6°F. Fetal movement: Negative, contractions: Unsure what the abdominal pain is, vaginal bleeding: Positive, leakage of fluid: Negative. Physical examination: CVS: Normal, Lungs: Normal, abdomen: Soft, nontender, nondistended, +BS, Extrimities: No edema, sterile speculum exam: Cervix closed; blood in vaginal vault. What is the next step?
Beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (BHCG)
RhoGAM
Abdominal US
Discharge home with follow-up as an outpatient
Computed tomography (CT) scan
A 29-year-old man is brought to the hospital because he was found running around on the streets with no shoes on in the middle of winter, screaming to everyone that he was going to be elected president. Upon admission to the hospital, he was stabilized on olanzapine and lithium and then discharged home. Assuming the patient is maintained on the olanzapine and the lithium, which of the following tests should be performed at least once per year?
MRI of the brain
Creatinine level
Liver function tests
Rectal exam to look for the presence of blood in the stool
ECG
A 29-year-old woman comes to the physician for follow-up of a right breast lump. The patient first noticed the lump 4 months ago. It was aspirated at that time, and cytology was negative, but the cyst recurred about 1 month later. The cyst was re-aspirated 2 months ago and, again, the cytology was negative. The lump has recurred. Examination reveals a mass at 10 o'clock, approximately 4 cm from the areola. Ultrasound demonstrates a cystic lesion. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Mammography in 1 year
Ultrasound in 1 year
Tamoxifen therapy
Open biopsy
Mastectomy
A 29-year-old woman presents for her first prenatal visit. She is 10 weeks pregnant as determined by her last menstrual period. She does not have any medical problems and does not take any medications. She is devoutly religious and has been in a monogamous relationship with her husband since getting married 5 years ago. They live in a house built in 1983 where she works as a homemaker. Her husband is an accountant. She does not smoke cigarettes or drink alcohol. Her physical exam is within normal limits. Which of the following screening tests is indicated at this time?
Rapid plasma reagin test
Serum lead level
Hepatitis C antibody
Red blood cell folic acid level
Chlamydia PCR
A 29-year-old woman presents with chest pain and exertional dyspnea of 10days duration. Her medical history is significant for a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery three months ago, after which she has had frequent episodes of dark bloody vaginal discharge. The most recent bleeding episode was 6 days ago. The patient denies fever, chills, hemoptysis, orthopnea, or leg pain. She does not smoke cigarettes, drink alcohol, or use illicit drugs. Her temperature is 37.7°C (98.9°F), pulse is 80/min, blood pressure is 110/68 mmHg and respirations are 16/min. Examination shows clear lungs. Pelvic examination shows an enlarged uterus. Complete blood count and serum electrolytes are within normal limits. Chest radiographs reveal multiple bilateral infiltrates of various shapes. Which of the following investigations will be most helpful in establishing the diagnosis?
Ventilation perfusion scan
Quantitative beta HCG
Echocardiogram
Pulmonary function tests
CT scan of the chest
A 29-year-old woman presents with severe pain during menstruation (dysmenorrhea). During workup, an endometrial biopsy is obtained. The pathology report from this specimen makes the diagnosis of chronic endometritis. Based on this pathology report, which of the following was present in the biopsy sample of the endometrium?
Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
Lymphoid follicles
Plasma cells
Decidualized stromal cells
A 3-day-old, full-term baby boy is brought into the emergency department because of feeding intolerance and bilious vomiting. X-rays films show multiple dilated loops of small bowel and a "ground glass" appearance in the lower abdomen. The mother has cystic fibrosis. Which of the following diagnostic tests would also have therapeutic value?
Barium enema
Endoscopic retrograde chokngiopancreatogram (ERCP)
Gastrografin enema
Colonoscopy
Full thickness rectal biopsy
A 3-month old infant is brought to a pediatrician's office because of increased lethargy and irritability. The parents state that the child rolled off the couch and fell on the floor one day prior to presentation. His parents report that the child has been previously healthy and is up to date on his vaccinations. He has been meeting his development milestones. His fontanelles are full. While in office the patient develops a tonic-clonic seizure. Which of the following is the next appropriate step?
Perform a retinoscopic examination
Administer intravenous benzodiazepines
Obtain a head computerized tomography scan
Check serum levels of ammonia
Perform a lumbar puncture
A 3-year-old African American boy is brought to the emergency department with sudden onset of difficulty walking. His mother reports that his right hand also seems "clumsy." The boy's past medical history is significant for a hospitalization one year ago for severe upper extremity pain and hand swelling. On physical examination, he has a blood pressure of 90/60 mmHg, heart rate of 120/min, temperature of 36.7°C (98°F), and respiratory rate of 22/min. Which of the following would be most helpful in diagnosing his condition?
Carotid ultrasonography
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies
CBC and reticulocyte count
Temporal artery biopsy
Lumbar puncture
A 3-year-old boy is admitted for seizure-like activity. He has been a healthy child and has been meeting all development milestones. His immunization schedule is up-to-date. Examination is notable for an erythematous throat and fever. His convulsions require IV administration of a benzodiazepine. Serum analysis reveals a normal white cell count with mild basophilic stippling. The lumbar puncture reveals elevated CSF pressure. Head CT scan is notable for cerebral edema. Which of the following is the next diagnostic step?
Antistreptolysin O titer
Protoporphyrin level
Electroencephalography
Rapid slide (Monospot) test
Spinal fluid culture
A 3-year-old boy is brought to the ER with a two-day history of decreased appetite, neck swelling, and irritability. He keeps his head rotated slightly to the right side. He resists passive flexion of the neck and rotation to the left side. Which of the following is the best next step in managing this patient?
Direct laryngoscopy
Soft neck collar
X-ray of the neck
Lumbar puncture
Botulinum toxin injection
A 3-year-old boy of African descent is brought to your office by his stepfather because of easy bruising. He says that the child bruises easily even without trauma. The child started playing games by himself recently. He has a past history of clavicular fracture, which the stepfather attributes to a fall down a set of stairs. The history of the biological father is unknown. On examination, there is a right knee effusion with decreased range of motion, and multiple soft tissue hematomas on the thigh. What is the most appropriate diagnostic step in management?
Obtain type 1 collagen assay
Obtain factor VIII level
Contact child protective services
Obtain bleeding time
Obtain prothrombin time and liver function tests
A 3-year-old child presents to your office for an evaluation of constipation. The mother notes that since birth, and despite frequent use of stool softeners, the child has only about one stool per week. He does not have fecal soiling or diarrhea. He was born at term and without pregnancy complications. The child stayed an extra day in the hospital at birth because he did not pass stool for 48 hours, but has not been in the hospital since. Initial evaluation of this child should include which of the following?
A barium enema and rectal manometry
Dietary log and observation
A child psychiatry evaluation for stool retention and parenting assistance
Plain films of the abdomen
Beginning oral antispasmodic medication
A 3-year-old girl is brought to the pediatrician with complaints of abdominal pain and fever. Her mother states that the fever started 2 days ago, with the highest temperature being 39.0 C (102.2 F). She has had no vomiting or diarrhea. The mother states that her daughter has been complaining of pain on urination. On examination, she is tender in her lower abdomen, and there is some right-sided costovertebral angle tenderness. A urinalysis confirms the suspicion of a urinary tract infection. Which of the following would be the most appropriate diagnostic procedure?
Cystoscopy
Dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scan in 1-2 months
Voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) now
VCUG in 1-2 months
Intravenous pyelogram
A 3-year-old girl with a ventricular septal defect (VSD) presents to the emergency department after a 15-minute focal seizure of her left arm and leg. A brief history reveals that the child has no known seizure disorder and has been having a low-grade fever at home for about 4 days. She also has been less active and has had poor appetite. On physical examination, her temperature is 40.2 C (104.3 F), and her pulse is 82/min. She is not responsive to her name, but she is responsive to painful stimuli with withdrawal of her extremities. Cardiac examination is significant for a grade 3 systolic murmur best heard at the left lower sternal border. Neurologic examination reveals anisocoria with a dilated right pupil. After stabilization, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
CT of the brain
Electroencephalography
MRI of the brain
Complete blood count and blood culture
ECG
A 30-hour-old infant has not passed meconium since birth. He was full term with a birth weight of 3856 g (8 lb 8 oz). The pregnancy was uncomplicated. The baby appears well with no respiratory distress. Slight abdominal distention is noted. Rectal examination reveals a slightly tight rectum and results in a greenish gush of stool. Which of the following tests will probably confirm the likely diagnosis?
A stool culture
A rectal biopsy
A barium enema
An alpha1-antitrypsin level
A serum TSH level
A 30-year old woman has irregular menses. She reports that her last menstrual period (LMP) was 8 weeks ago. She has been experiencing vaginal spotting and left lower quadrant pain. She is afebrile. She has a normal size uterus and mild tenderness in the right lower quadrant with no rebound tenderness. A human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) beta-subunit level of 1400 mIU/ml is reported in her records from an obstetrics visit 2 days ago. Which of the following is the appropriate management?
Perform a culdocentesis
Repeat hCG measurement in 24 hours
Perform a pelvis ultrasound
Refer for diagnostic laparoscopy
Repeat hCG measurement in 1 week
A 30-year-old black female has a 2-month history of non-productive cough and a painful skin eruption in the lower extremities. She denies fever or weight loss. Physical examination shows several non-tenders raised plaques around the nares and scattered similar plaques around the base of the neck. In the lower extremities she has several erythematous tender non-ulcerated nodules, measuring up to 4 cm in diameter. Chest x-ray reveals bilateral hilar adenopathy and a streaky interstitial density in the right upper lobe. What is the best way to establish a histological diagnosis?
Punch biopsy of one of the plaques on the neck
Incisional biopsy of one of the lower extremity nodules
Serum angiotensin-converting enzyme assay
Mediastinoscopy and biopsy of one of the hilar or mediastinal nodes
Sputum studies for AFB and fungi
A 30-year-old G1P0 with a twin gestation at 25 weeks presents to labor and delivery complaining of irregular uterine contractions and back pain. She reports an increase in the amount of her vaginal discharge, but denies any rupture of membranes. She reports that earlier in the day she had some very light vaginal bleeding, which has now resolved. On arrival to labor and delivery, she is placed on an external fetal monitor, which indicates uterine contractions every 2 to 4 minutes. She is afebrile and her vital signs are all normal. Her gravid uterus is non tender. The nurses call you to evaluate the patient. Which of the following is the most appropriate first step in the valuation of vaginal bleeding in this patient?
Vaginal examination to determine cervical dilation
Ultrasound to check placental location
Apt test to determine if blood is from the fetus
Labs to evaluate for disseminated intravascular coagulopathy
Urine culture to check for urinary tract infection
A 30-year-old male comes to the emergency department screaming, "Something blew into my right eye while I was drilling !' He complains of a foreign body sensation in the right eye, photophobia, and excessive lacrimation. Gross examination of the right eye with a penlight after the application of a topical anesthetic is insignificant. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Tonometry
Fluorescein examination
Topical antibiotic
Ultrasonography
MRI of the orbits
A 30-year-old male presents with right upper quadrant pain. He has been well except for an episode of diarrhea that occurred 4 months ago, just after he returned from a missionary trip to Mexico. He has lost 7 pounds. He is not having diarrhea. His blood pressure is 140/70, pulse 80, and temperature 37.5°C (99.5°F). On physical examination there is right upper-quadrant tenderness without rebound. There is some radiation of the pain to the shoulder. The liver is percussed at 14 cm. There is no lower-quadrant tenderness. Bowel sounds are normal and active. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluation of the patient?
Serology and ultrasound
Blood cultures
Stool for ova and parasite
Diagnostic aspirate
Empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy
A 30-year-old male with sickle cell anemia is admitted with cough, rusty sputum, and a single shaking chill. Physical examination reveals increased tactile fremitus and bronchial breath sounds in the left posterior chest. The patient is able to expectorate a purulent sample. Which of the following best describes the role of sputum Gram stain and culture?
Sputum Gram stain and culture lack the sensitivity and specificity to be of value in this setting
If the sample is a good one, sputum culture is useful in determining the antibiotic sensitivity pattern of the organism, particularly Streptococcus pneumoniae . Empirical use of antibiotics for pneumonia has made specific diagnosis unnecessary
Gram-positive cocci in clusters suggest pneumococcal infection
Gram stain in a patient with pneumococcal pneumonia
There is no characteristic
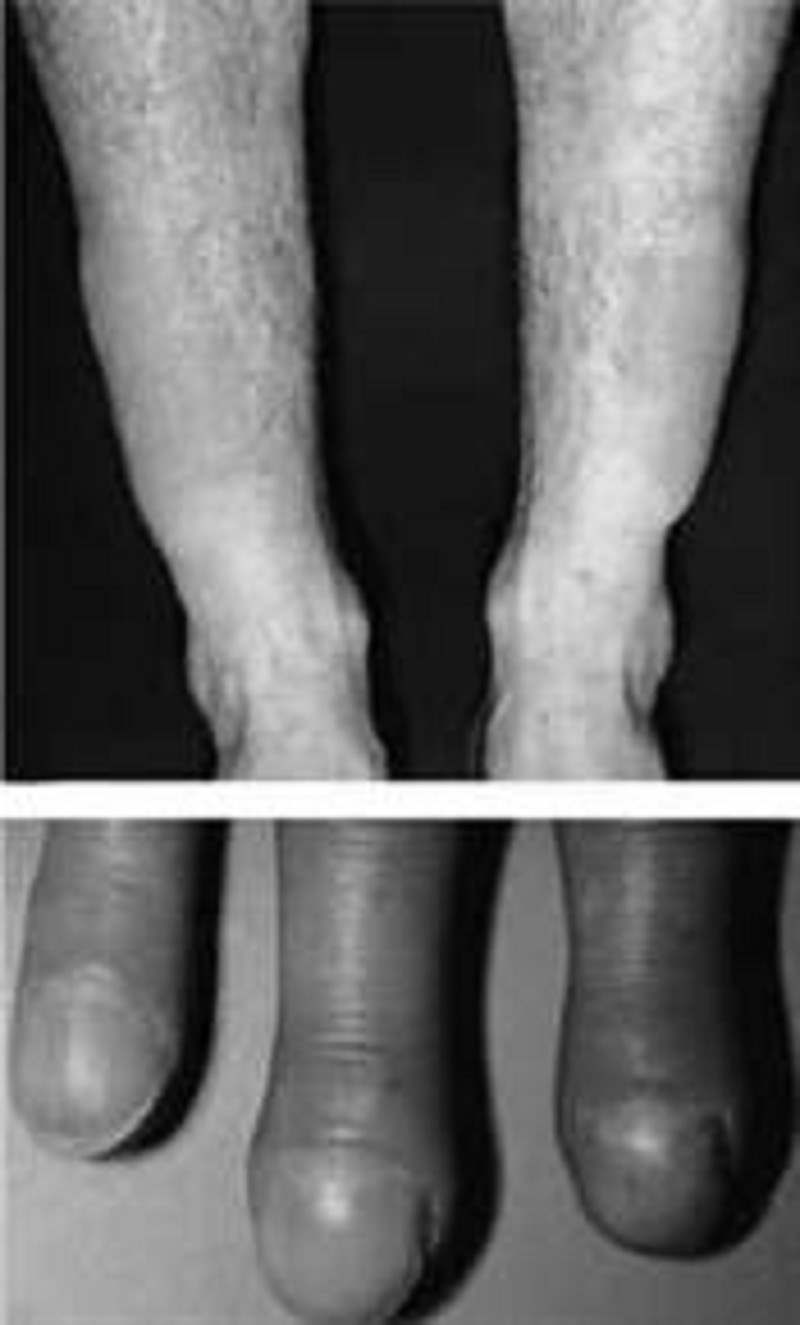
A 30-year-old female complains of palpitations, fatigue, and insomnia. On physical examination, her extremities are warm and she is tachycardic. There is diffuse thyroid gland enlargement and proptosis. There is thickening of the skin in the pretibial area. Mild clubbing of digits is present. Which of the following laboratory values would you expect in this patient?
Increased free thyroxine (free T4), increased TSH
Increased free thyroxine, decreased TSH
Normal free thyroxine, decreased TSH
Normal free thyroxine, elevated triiodothyronine (T3), normal TSH
Increased free thyroxine, normal TSH
A 30-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of severe epigastric pain and vomiting 3 hours ago. He reports a 6-month history of chronic epigastric pain occurring nearly every day and relieved by antacids. On examination, he appears sweaty and avoids movement. Vital signs reveal a temperature of 100°F, BP of 100/60 mmHg, pulse rate of 110/min, and respiratory rate of 12/min. The remainder of his examination reveals diminished bowel sounds and a markedly tender and rigid abdomen. A chest x-ray and abdominal films reveal pneumoperitoneum. Which of the following is the most appropriate next diagnostic test?
CT scan
Lower GI water-soluble contrast study
UGI water-soluble contrast study
Abdominal ultrasound
None of the above
A 30-year-old obese woman comes to the physician with a six-month history of oligomenorrhea. She has never had this problem before. She has no galactorrhea. She has gained significant weight over the past two years despite a regular exercise program. She has also experienced hair loss during this time. She has had regular Pap smears since the age of 21; none of which have shown any abnormalities. She takes no medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Her mother has a history of endometrial carcinoma and her grandmother had a history of ovarian carcinoma. Physical examination shows male pattern baldness. Abdominal and pelvic examination shows no abnormalities. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Serum prolactin level and thyroid function tests are normal. Which of the following is indicated in the initial workup of this patient?
Screening mammogram
CA-125 levels, annually
Oral glucose tolerance test
Diagnostic laparoscopy
Iron studies
A 30-year-old patient with a history of mild persistent asthma (baseline peak expiratory flow rate of 85%) presents to the emergency department with shortness of breath and wheezing that has not relieved by her albuterol inhaler for the past 12 hours. She was able to tolerate pulmonary fun
Decreased FEV1, normal/increased FVC, decreased FEV1: FVC ratio, with post- bronchodilator FEV1 increased by 13%
Normal FEV1, decreased FVC, increased FEV1: FVC ratio
Increased residual volume, increased total lung capacity, increased FEV1
Increased FEV1, increased FVC, normal FEV1: FVC ratio
Decreased residual volume and total lung capacity
A 30-year-old white female presents with an attack of common migraine. This is her fourth attack of migraine over the last 4 months. Her attacks previously responded well to aspirin and ibuprofen; however, her current headache is very severe and not relieved by NSAIDs. She has been trying to conceive for the past 2 months. Six years ago, she was treated with isoniazid due to a positive PPD test. Her father died at the age of 45 from an acute myocardial infarction. Before starting therapy with serotonin agonists (e.g., sumatriptan), which of the following tests should be performed in this patient?
Liver function tests
Stress echocardiogram
PPD and chest x-ray
Pregnancy test
Visual field testing

A 30-year-old woman comes to the office due to the recent onset of fever, chills, and dysuria. Her temperature is 38.3°C (101.0°F), blood pressure is 110/70mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows tenderness at the right costovertebral angle. Laboratory studies show WBC count of 16,000/microl with left shift. Urinalysis shows bacteriuria and pyuria. Her urine and blood is collected for culture and sensitivity. She is prescribed oral ciprofloxacin and sent home. After three days, she returns for a follow-up visit. She is still febrile, and the physical examination is unchanged. The blood cultures have no growth after 72 hours of incubation. Results of the urine culture show. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Start intravenous ampicillin and gentamicin
Perform renal ultrasound
Renal CT scan
Continue oral ciprofloxacin for another 10 days
Start intravenous ciprofloxacin
A 30-year-old woman presents for a physical examination for work. She denies any medical problems or surgeries in the past. She has had no pregnancies. She is sexually active and has been using oral contraceptive pills for the past 6 years. She denies any allergies to medications. On examination, her weight is 62 kg, blood pressure 120/78 mm Hg, pulse 76 beats per minute, respiratory rate 15 breaths per minute, temperature 36.8C (98.4F). Her physical examination is normal. Laboratory evaluation is also done. Which direct effect of birth control pills could be noted in the laboratory results?
Decreased binding globulins
Decreased triglycerides
Decreased glucose tolerance
Decreased hemoglobin concentration
Decreased high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol
A 30-year-old woman presents with a 5-month history of episodic retrosternal pain that radiates to the interscapular region. The pain episodes typically last 15 minutes, and are precipitated by emotional stress and hot or cold food. Her relative gave her sublingual nitroglycerine tablets, which alleviated the pain. Her past medical history is unremarkable, and she does not take any other medications. There is no family history of coronary artery disease. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. A lipid profile is within normal limits. An EKG shows a normal sinus rhythm. A stress test fails to reproduce the symptoms or to induce ST/T wave changes. Chest x-ray, upper GI endoscopy, and echocardiography show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
Esophageal motility studies (manometric recordings)
Acid perfusion (Bernstein) test
CT scan of the chest with contrast
Pulmonary perfusion/ventilation scintigraphy
Coronary angiogram
A 30-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 26 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of a decrease in fetal movements. She has felt few fetal kicks the past 20 hours. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests and fetal growth have been normal. She has chronic hypertension and is now taking methyldopa and labetalol. Her previous pregnancies were uncomplicated and both delivered vaginally. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. Non-stress test is reactive. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Repeat non-stress test weekly
Biophysical profile
Perform contraction stress test
Give vibroacoustic stimulation
Deliver the baby immediately
A 3010-g (6.6-lb) boy was born to a 37-year-old primagravida by spontaneous vaginal delivery after an uncomplicated pregnancy. On examination he has cyanotic extremities and a significant right precordial heave, a single S2, and a harsh systolic ejection murmur along the sternal border. He also has a prominent squared nose and cleft palate. An echocardiogram is subsequently performed and demonstrates tetralogy of Fallot. Corrective surgery is performed without complications. At 2 months of age the infant is diagnosed with Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, and at 3 months he is diagnosed with fungal septicemia. Additional work-up of this child should include which of the following tests?
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Quantitative immunoglobulin levels
Nitroblue tetrazolium
Renal ultrasound
Serum calcium
A 31-year-old man is brought by helicopter to the trauma center after a motor vehicle accident in which he sustained massive lower extremity crush injury. The patient is alert and awake but in tremendous pain. His blood pressure is 140/80 mm Hg, and his pulse is 110/min. There is copious ongoing blood loss from the sites of injury. Urgent laboratory data will most likely show which of the following electrolyte abnormalities?
Hyperkalemia
Hypernatremia
Hypocalcemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypophosphatemia
A 31-year-old man with severe kyphoscoliosis due to cerebral palsy is experiencing worsening shortness of breath with exertion. On examination, he has a severe scoliosis to the left and decreased air entry to that side. His right lung is clear, JVP is 3 cm, and heart sounds are normal. Pulmonary fun
Increased total lung capacity (TLC)
Decreased TLC
Increased functional residual capacity (FRC)
Increased compliance
Increased vital capacity (VC)
A 31-year-old pregnant woman 6–7 weeks from her last menses comes to the emergency department of your hospital complaining of lower abdominal pain for 3 hours. The pain is diffused in the lower abdomen but worse on the right side. Her serum human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) concentration is 9600 mIU/mL. Which of the following is the strongest evidence that she has a tubal ectopic pregnancy?
Absence of blood on culdocentesis
Absence of an intrauterine sac on ultrasonography
Absence of an extrauterine sac on ultrasonography
Absence of a mass on bimanual examination
Her hCG concentration
A 31-year-old woman comes to the clinic for a preoperative evaluation. She is undergoing an infertility workup and a laparoscopy is planned. She and her husband have been trying to have a child for the last 5 years, but have not had any success. Over that time period, this woman has suffered three miscarriages. Her past medical history is remarkable for anemia, a history of depression, and a deep venous thrombus suffered during her first pregnancy. Her review of systems reveals diffuse arthralgias, but is otherwise unremarkable. She is currently not taking any medications, though she does report having a drug reaction to prenatal vitamins. Early in pregnancy, she had a red facial rash across her face that spared her nasolabial folds. Physical examination today is unremarkable. Laboratory studies, with the exception of a prothrombin time elevated to two times greater than normal, are unremarkable. Which of the following studies will most likely explain this patient’s laboratory abnormality?
Blood smear with manual review
Ristocetin cofactor analysis
Assay for cardiolipin antibody
Serologic test for syphilis
Screening for Factor V Leiden mutation
A 31-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of shortness of breath. She denies associated chest pain or palpitations. She tells you that she recently returned from a trip to Thailand. She smokes one pack of cigarettes per day and drinks alcohol occasionally. She is married and uses oral contraceptives. She has no significant past medical history. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and her heart rate is 120/min. A negative result on which of the following tests would best exclude pulmonary venous thromboembolism in this patient?
Echocardiography
Chest x-ray
Venous ultrasound
Plasma D-dimer
Electrocardiogram
A 32-year-old Caucasian female comes to the physician because of a one-week history of fatigue, progressive worsening of shortness of breath and swelling of feet. She denies any chest pain. She has no other medical problems except a recent cold two weeks ago. She is not taking any medication. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 110/65 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 20/min. Bilateral basal crackles, elevated jugular venous pressure, and 2+ bilateral pitting edema of the ankles are noted. Complete blood count is unremarkable. Transthoracic echocardiogram of her heat will most likely show?
Concentric hypertrophy of the heart
Hypokinesia of the inferior wall
Eccentric hypertrophy of the heart
Mitral stenosis
Dilated ventricles with diffuse hypokinesia
A 32-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office with persistent cough and shortness of breath. She has had three episodes of pneumonia over the last year. She had severe sinusitis one year ago, and an episode of bloody diarrhea that required hospitalization and IV antibiotic therapy six months ago. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. She denies any illicit drug use. She is currently not taking any medications. All her immunizations are up-to-date. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg and heart rate is 90/min. Physical examination reveals fine crackles over the right lower lung lobe. No lower extremity edema is present. Neck palpation does not reveal any lymph node enlargement. The chest x-ray shows right lower lobe infiltrates and left upper lobe fibrosis. The ECG reveals non-specific ST segment and T wave changes. What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Methacholine challenge test
Sweat chloride test
Measurement of serum alpha-1-antitrypsin level
Ventilation/perfusion lung scan
Quantitative measurement of serum lg levels
A 32-year-old Caucasian primigravida presents to your office in her 30'" week of pregnancy. On review of systems, she complains of leg swelling and occasional heartburn. She denies abdominal pain or vaginal discharge. She eats a balanced diet and takes folic acid supplements. Her blood pressure is 165/100 mmHg and her heart rate is 90/min. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient?
Proteinuria
Ketonuria
Thrombocytosis
Splenomegaly
Fasting hyperglycemia
A 32-year-old female from South America presents with a 3-month history of progressive difficulty with swallowing for both liquids and solids. At night she has a bitter taste in her mouth. Over the past two months, she has had a 10 lb (4.54 kg) weight loss. She has not had any previous illnesses, and does not take any medication. Physical examination is unremarkable. A lateral x-ray film of the chest shows extreme dilatation of the esophagus with an air fluid level. Which of the following is the diagnostic test for this patient's condition?
Barium swallow
Endoscopy
PH monitoring
Manometry
CTscan
A 32-year-old female is being evaluated for abnormal uterine bleeding. A urine pregnancy test is negative. Pelvic ultrasound reveals endometrial hyperplasia and a right-sided adnexal mass. In this patient, the adnexal mass is most likely to be a?
Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
Dysgerminoma
Teratoma
Granulosa cell tumor
Fallopian tube cancer
A 32-year-old female is brought to the clinic by her husband because he believes she is a malingerer and is "just being difficult." Sometimes, she appears confused and disoriented. Over the past year, she has complained of visual loss, eye pain and inability to do any household chores. Two months ago, she claimed to have lost control of her bladder. Interestingly, she is "her normal self" when it is time to go for summer trips. The wife insists that she does not understand what is happening to her, and adds that she occasionally loses the ability to move her right hand. The physical examination is basically normal. The patient appears, alert, oriented, and is in no distress. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
MRI of the brain
Lumbar puncture
Tonometry
Serum immunoglobulins
Nerve conduction studies
A 32-year-old male presents to your office with concern about progressive fatigue and lower extremity edema. He has experienced decreased exercise tolerance over the past few months, and occasionally awakens coughing at night. Past medical history is significant for sickle cell anemia and diabetes mellitus. He has had multiple admissions to the hospital secondary to vasoocclusive crises since the age of three. Physical examination reveals a displaced PMI, but is otherwise unremarkable. ECG shows a first degree AV block and low voltage. Chest x-ray shows an enlarged cardiac silhouette with clear lung fields. Which of the following would be the best initial diagnostic approach?
Order serum iron, iron-binding capacity, and ferritin level
Order brain-natriuretic peptide (BNP)
Arrange for cardiac catheterization
Arrange for placement of a 24-hour ambulatory cardiac monitor
Order CT scan of the chest
A 32-year-old man is in a high-speed motorcycle collision and presents with an obvious pelvic fracture. On examination, he has a scrotal hematoma and blood at his urethral meatus. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in his management?
Placement of a Foley catheter
Cystoscopy
CT of the pelvis
Retrograde urethrogram
Nephrostomy tube placement
A 32-year-old man is intubated and mechanically ventilated after an opioid drug overdose. The ventilator triggers 12 breaths per minute, each delivering 500 ml of tidal volume at a flow rate of 60 L/min. You perform an inspiratory hold for 2 seconds following delivery of the tidal volume, and the airway pressure is measured to be 30 cm H2O. The measured pressure reflects which of the following?
Upper airway resistance
Pulmonary compliance
Expiratory muscle strength
End-expiratory pressure
Total airway resistance
A 32-year-old multiparous African-American woman comes for her initial prenatal visit at 14 weeks gestation. She complains of the recent appearance of facial hair and acne. The beta-HCG level is consistent with gestational age. Examination shows hirsutism. Ultrasonogram shows an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates and bilateral solid nodular masses in both ovaries. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Exploratory laparotomy
Diagnostic laparoscopy
Suction evacuation of uterus
Reassurance and follow-up with ultrasonogram
Ultrasound guided aspiration of the mass
A 32-year-old woman comes to the emergency department complaining of sudden onset shortness of breath accompanied by a non-productive cough and left-sided chest discomfort that increases on inspiration. She denies subjective fever, coughing up blood, wheezing, palpitations, leg pain, and swelling of the lower extremities or any recent travel. Past medical history is significant for an appendectomy at age 15. Her medications include birth control pills and over- the-counter vitamins. She is a known carrier of sickle cell trait. Her father, age 65, has had diabetes for 20 years; mother, age 58, has coronary artery disease. She has never been pregnant, drinks alcohol socially and does not smoke. Her temperature is 99°F (38°C), blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, pulse 130/min and respirations are 33/min. Pulse oximetry shows an oxygen saturation of 85% on 6 liters of oxygen. Her BMI is 30 kg/m2. She is alert and cooperative without cyanosis or jaundice. Her lungs are clear to auscultation. Her abdomen is soft, nondistended and non-tender. Which of the following is the best test to confirm this patient's diagnosis?
EKG and cardiac enzymes
Echocardiogram
Spiral CT-Scan of the chest
Chest-x ray and sputum cultures
Doppler ultrasound of lower extremities
A 32-year-old woman consults with you for evaluation of an abnormal Pap smear done by a nurse practitioner at a family planning clinic. The Pap smear shows evidence of a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL). You perform colposcopy in the office. Your colposcopic impression is of acetowhite changes suggestive of human papilloma virus infection (HPV). Your biopsies show chronic cervicitis but no evidence of dysplasia. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Cryotherapy of the cervix
Conization of the cervix
Laser ablation of the cervix
Hysterectomy
Repeat the Pap smear in 3 to 6 months
A 32-year-old woman presents to the ED with a persistent fever of 101°F over the last 3 days. The patient states that she used to work as a convenience store clerk but was fired 2 weeks ago. Since then, she has been using drugs intravenously daily. Cardiac examination reveals a heart murmur. Her abdomen is soft and nontender with an enlarged spleen. Chest radiograph reveals multiple patchy infiltrates in both lung fields. Laboratory results reveal white blood cells (WBC) 14,000/µL with 91% neutrophils, hematocrit 33%, and platelets 250/µL. An ECG reveals sinus rhythm with first-degree heart block. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Obtain four sets of blood cultures, order a TTE, and start antibiotic treatment
Order a monospot test and recommend that the patient refrain from vigorous activities for 1 month
Administer a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) and inform the patient she has pericarditis
Administer isoniazid (INH) and report the patient to the Department of Health
Order a Lyme antibody and begin antibiotic therapy
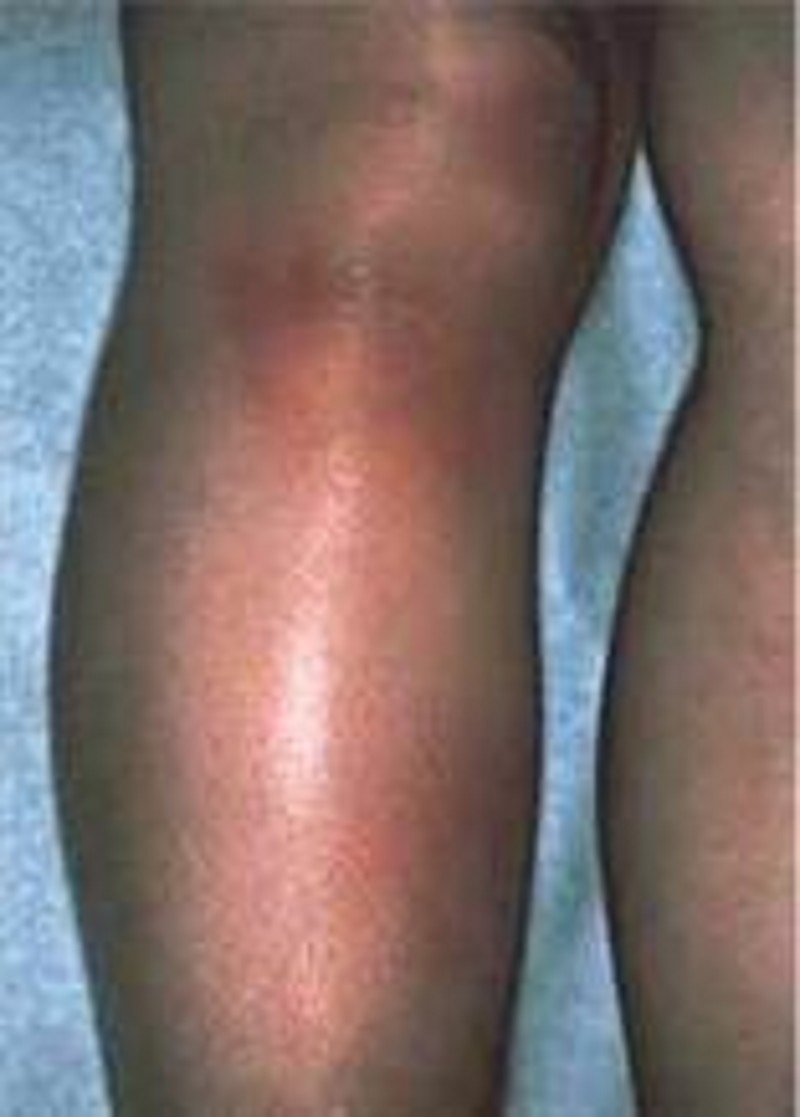
A 33-year-old African-American woman presents with one week of painful skin lesions on her legs. She has no cough, shortness of breath or bowel symptoms, and denies any recent illness or travel. She has no other significant past medical history and does not take any medication. She smokes one pack of cigarettes and drinks one glass of wine daily. She denies a history of sexually transmitted diseases and has been married to a monogamous partner for the past eight years. Her mother was diagnosed with ovarian cancer at age 65. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), and blood pressure is 126/76 mmHg. On examination, she has multiple tender pink to reddish nodules noted below the knee on the extensor surface, as shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in her management?
CT scan of the abdomen
Colonoscopy
HIV testing
Chest x-ray
Rectal swab for culture
A 33-year-old male was involved in a motor vehicle accident with numerous rib fractures. His course in the hospital was complicated by difficulty with deep breathing and later developed pneumonia. The chest x-ray later confirmed that the patient had developed a parapneumonic effusion. Which one of the following laboratory tests on the pleural fluid is currently thought to be most helpful in determining the need for chest tube placement in parapneumonic effusion?
Lactate dehydrogenase
WBC count
Pleural fluid pH
Total protein
Color of the pleural fluid
A 33-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to a 4-day history of left-sided flank pain, nausea, vomiting, fevers and chills. Her temperature is 39°C (102°F) and blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg. Examination shows significant left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urinalysis shows positive nitrites, many WBC and bacteria. Laboratory studies show a WBC count of 17,000/cmm with 8% bands. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Intravenous pyelogram
Blood cultures
Intravenous antibiotics
CT scan of the abdomen
Ultrasound of the abdomen
A 33-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, comes for a routine prenatal visit, for the first time. According to her history, she is at 18-weeks gestation. Her family history is significant for Down syndrome on her maternal side. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Vital signs are normal, and physical examination is unremarkable. Initial laboratory studies show a decreased maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Amniocentesis
Chorionic villus sampling
Ultrasonogram
Cordocentesis
Urinary estradiol levels
A 33-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 3, comes to the physician for an annual examination. She has no complaints. Past medical history is significant for two episodes of Chlamydia and one episode of gonorrhea. Obstetric history is significant for three normal spontaneous vaginal deliveries with gestational diabetes during the last two pregnancies. She takes no medications. Family history is significant for paternal coronary artery disease. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following interventions should this patient most likely have?
Coronary angiography every 3 years
Mammography every 3 years
Chest x-ray every 3 years
Pap testing every 3 years
Fasting glucose testing every 3 years
A 33-year-old woman, otherwise perfectly well, presents with recurrent episodes of hemoptysis. She has no fever, weight loss, cough, or sputum production. Her physical examination is entirely normal. Her CXR, biochemisty, CBC, and coagulation profile are also normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial diagnostic test?
Echocardiogram
Gallium scan
CT scan of chest
Bronchoscopy
Pulmonary function tests
{"name":"DES C_ParaClinic (2) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 24-year-old Caucasian male undergoes pulmonary function testing. The following values are obtained: FEV 80% of predicted, FEV1\/FVC 85%, FRC 110% of predicted. He has no current complaints except for occasional low back pain treated with naproxen. He smokes one pack per day and drinks a six-pack of beer each weekend. His ESR is 47 mm\/hr. Which of the following best explains the pulmonary function test findings in this patient?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/18-725091/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Which MasterChef Junior Semi Finalist/Finalist Are You? (S7)
12615
Chapter 9 Vocabulary quiz
1050
Which Famous Horror Writer Are You?
12675
5A & 5B
740
Take the Ultimate Cynicism Test: How Cynical Are You?
201055605
What Is Your Greatest Fear? Take the Free Now
201026974
Ace These Blender Interview Questions - Take the!
201065703
Research Methods in Learning Sciences
15822048
What Goddess Am I? to Reveal Your Inner Divine
201032627
Free Industrial Revolution Review
201021890
Free AI Workflow Automation Platform Knowledge
201024000
Think You've Mastered Beowulf? Try the Beowulf Test!
201067791