Practice Exam
A patient has retropatellar pain and an MRI finding of softened and fibrillated cartilage. These are characteristics of:
Chondromalacia patellae
Rheumatoid arthritis
Osteomalacia
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Two weeks ago, a patient fell on an open hand with the wrist extended. Pain is present on palpation of the space between the abductor pollicis longus and the extensor pollicis brevis. The physical therapist should suspect a fracture of which of the following bones?
Scaphoid
Hamate
Trapezium
Radius
A patient is unable to perform a standing heel raise with the knee extended. During this attempted movement, the physical therapist observes toe flexion, inversion, and limited movement of the calcaneus. The MOST likely cause of this deviation is:
Substituition by the extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus muscles
Weakness in the peroneus longus muscle
Weakness in the tibalis anterior muscle
Substitution by the flexor digitorum and flexor hallucis longus muscles
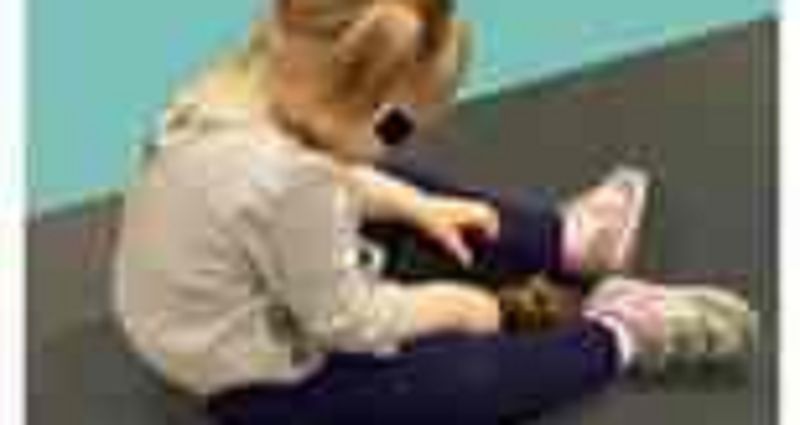

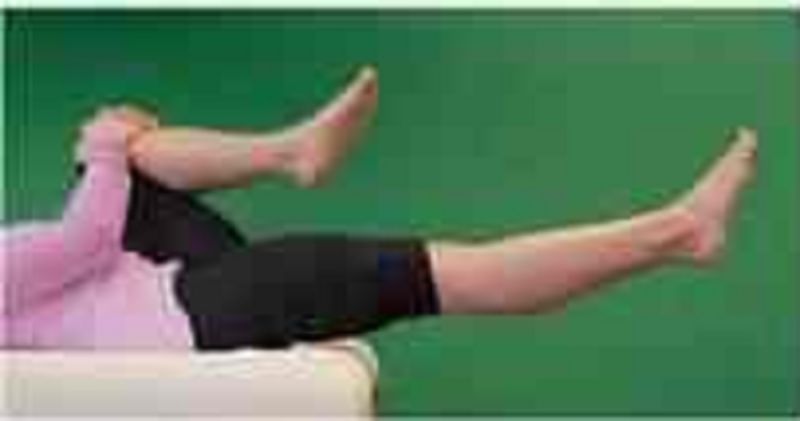
Which of the following interventions would be MOST appropriate fo the patient who prefers to sit as illusrated?
Stretching of the gastrocnemius
Strengthening of the upper trapezius
Stretching of the hamstrings
Strengthening of the quadriceps
To test a patient's response to compression of the right lumbar facet joints, the combination of lumbar spine movements that should be used is:
Extension and right side flexion
Extension and left side flexion
Flexion and right side flextion
Flexion and left side flexion
A physical therapist is performing a work-site evaluation of a person who is using a computer at a workstation. Which of the following elements of posture or positioning are MOST desirable for preventing overuse injuries or postural dysfunction?
Top of screen even with the top of the forehead, monitor 12 in (30 cm) away
Elbows bent 90 degrees, top of the screen even with the top of forehead
Elbows bent greater than 100 degrees, shoulders relaxed with arms at the side
Hips fixed to 90 degrees, front edge of the chair 6 in (15 cm) from the popliteal crease
During postural evaluation of a patient, a physical therapist observes a leg length discrepancy. Which of the following gait deviations is MOST likely seen by the therapist?
Increased dorsiflexion with early heel rise of the long limb at the heel off (terminal stance) and increased plantar flexion of the short limb during stance
Increased dorsiflexion of the short limb during swing and increased plantar flexion of the long limb during stance
Decreased knee flexion and increased dorsiflexion of the long limb during stance and increased dorsiflexion of the short limb during swing
Increased plantar flexion of the long limb at heel strike (initial contact) and decreased knee flexion of the short limb during heel off (terminal stance)
A patient who has acromioclavicular joint arthritis will most likely have the GREATEST discomfort when performing which of the following tasks?
Pulling a wallet out of the back pocket on the same side as the involved extremity
Bending forward to pick up a pen that is lying on the floor
Pushing a heavy shopping cart using the involved extremity
Reaching across the body to scratch the back of the opposite shoulder
A patient sustained an ankle sprain in a bicycle accident. The patient's paint is provoked with subtalar eversion. These symptoms are MOST likely the result of a tear of which ligament?
Calcaneofibular
Deltoid
Anterior talofibular
Spring
A patient with ankylosing spondylitis reports having had a diagnostic test that showed "increated uptake" in the spine and pelvis. Which of the following tests was MOST likely performed?
Computed tomography
Plain film radiography
Magnetic resonance imaging
Bone Scan
Which of the following patellar mobilizations will BEST facilitate active terminal knee extension for a patient who has had the knee immobilized for 6 weeks?
Inferior glide
Medial glide
Superior glide
Lateral glide
A patient has decreased passive terminal knee extension. Which mobilization will be MOST beneficial?
Lateral patellar mobilization
Inferior patellar mobilization
Anterior glide of the tibia on the femur
Posterior glide of the tibia on the femur
A patient is unable to control descent when moving from standing to sitting. Which of the following therapeutic interventions would be MOST appropriate to address this problem?
Hamstring strengthening with concentric contractions
Quadriceps strengthening with concentric contractions
Hamstring strengthening with eccentric contractions
Quadriceps strengthening with eccentric contractions
A patient displays a positive sign for the test shown in the photograph. After physical therapy intervention, a successful outcome should be assessed by observing what phrase of the patient's gait cycle?
Foot flat (loading response)
Heel strike (initial contact)
Midstance
Heel off (terminal stance)
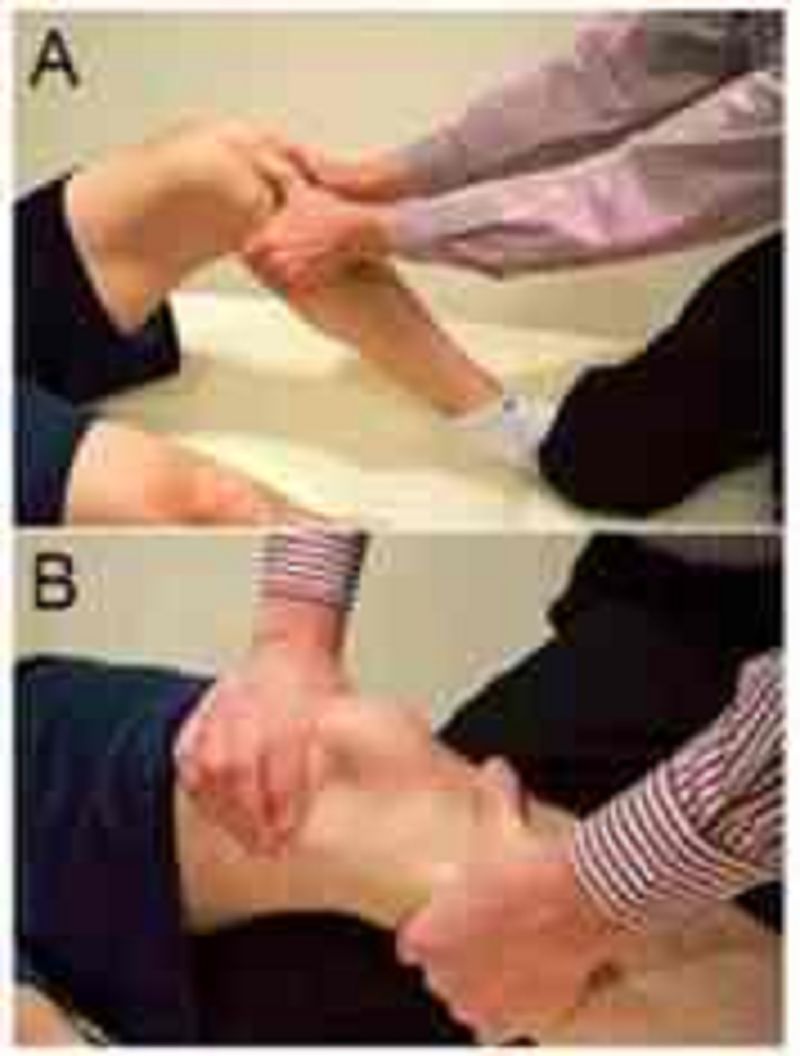
A physical therapist is evaluating the knee of a patient who sustained a severe twisting injury 2 days ago. While performing test A, the therapist notes minimal anterior movement of the tibia on the femur. However, when performing test B, the therapist notes at least 1 cm of anterior movement. What MOST likely explains the difference in findings?
The posterior cruciate ligament can prevent anterior glide of the tibia during test A.
The therapist has a better mechanical advantage in test B
The quadriceps are move relaxed in test B
The hamstrings are more capable of stabilizing the knee during test A
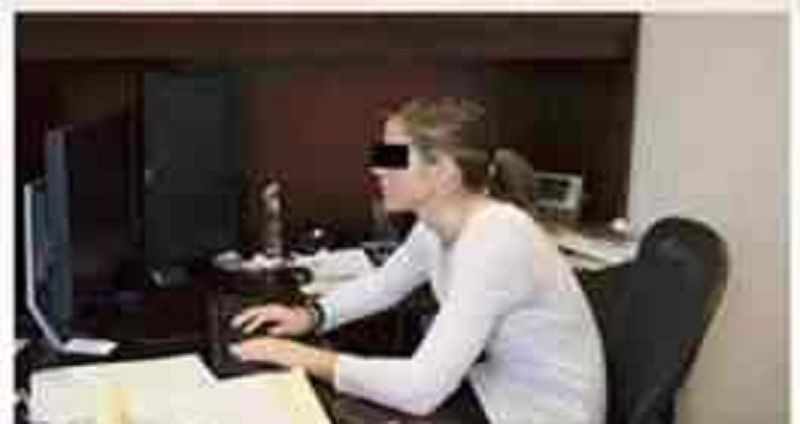

The patient in the photograph reports headaches associated with prolonged sitting. Her posture suggests the headache are MOST likely caused by which of the following conditions?
Thoracic outlet compression
Myofascial tightness in posterior cervical musculature
Myofascial tightness in the pectoralis muscles
Myofascial tightness in the anterior cervical spine muscles
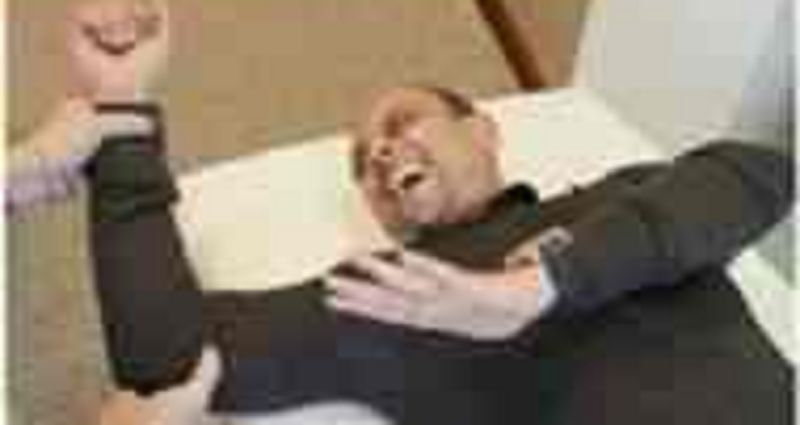
Which of the following findings or history would prompt a physical therapist to perform the test shown in the photograph?
Anterior shoulder pain after falling down the stairs, with an attempt to break the fall by grasping the hand rail
Insidious onset of interrupted sleep patterns due to aching discomfort in the shoulder
Gradual onset of pain in the shoulder and difficulty with dressing, especially donning and doffing a coat
Difficulty washing the opposite axilla due to superior shoulder pain after painting the house
A physical therapist is treating a teenaged athlete who sustained a hematoma from a blow to the anterior thigh 2 weeks ago. The patient exhibits moderate knee pain with knee flexion greater than 90 degrees. The patient has a palpable mass in the quadriceps muscle. The MOST likely diagnosis for this patient is:
Patellofemoral syndrome
Femoral hairline fracture
Quadriceps tendon rupture
Myositis ossificans
A nurse caring for a patient who is 2 days post cerebrovascular accident asks the physical therapist for positioning recommendations when the patient lies on the hemiplegic side. The therapist's recommendations should include positioning the:
Wrist in a flexed position
Elbow in a flexed position
Scapula in a protracted position
Forearm in a pronated position
During a physical therapy examination, a patient complains of numbness, burning, and paresthesias in both feet. A neurological examination reveals bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation in a stocking-and-glove distribution, diminished ankle reflexes, normal knee-jerk reflexes, and decreased strength in the feet and ankles bilaterally. The patient MOST likely has:
L4-L5 nerve root compression
Intermittent claudication
Peripheral vascular disease
Peripheral neuropathy
The parent of a child with myelomeningocele at L2 asks a physical therapist to provide information regarding the child's prognosis for walking. The therapist should respond by telling the parent that the child will MOST likely be able to:
Walk with ankle-foot orthoses throughout the home and school
Walk with knee-ankle-foot orthoses throughout the home and school
Walk with knee-ankle-foot orthoses within the home
Stand using a parapodium; walking will not be possible
A patient has a diagnosis of right C5 radiculopathy. Which of the following arm movements is MOST likely to be weak?
Elbow extension
Shoulder adbuction
Wrist extension
Cervical spine lateral flexion
A physical therapist is teaching a patient wheelchair transfers. Which of the following techniques is MOST appropriate for the physical therapist to employ to facilitate the patient's ability to generalize the learning?
Provide verbal feedback immediately after each transfer is completed
Practice transfers back and forth between the bed and wheelchair repeatedly
Encourage the patient to perform transfers at a consistent rate with the wheelchair situated at a set angle
Vary the speed of the transfers and practice transfers in the bathroom, at the raised mat, and in the patient's room.
The BEST position to stretch the right iliopsoas is hip extension combined with:
Posterior pelvic tilt and right lateral flexion of the trunk
Posterior pelvic tilt and left lateral flexion of the trunk
Anterior pelvic tilt and left lateral flexion of the trunk
Anterior pelvic tilt and right lateral flexion of the trunk
A physical therapist plans to perform a home assessment for a patient who had a T10 complete spinal cord transection 6 months ago. Which of the following information would be MOST critical to obtain prior to the home visit?
Patient's present level of function as judged by the patient and all involved disciplines
Patient's previous level of function as judged by the patient and all involved disciplines
Results of general health outcome measures
Result of disease-specific outcome measures
Which of the following observations indicates an improvement in a patient with dysdiadochokinesia?
Decreased resting tremor
Increased one-foot standing balance
Increased typing speed
Decreased horizontal nystagmus
A physical therapist is preparing to give instructions in the use of a new standing device to the family of a 3-year-old-child who has myelomeningocele. Which of the following actions should the therapist perform FIRST?
Ask the family what problems they would have with using a standing device.
Give the family product literature and a video about the standing device.
Ask the family what method would be best for them to learn to use the standing device.
Show the family how to place the child into the standing device.
A physical therapist is working with a patient who has complete loss of vestibular function. As a compensatory strategy, the therapist should work with the patient on exercises that will:
Facilitate agility.
Improve gaze stability.
Improve coordination.
Increase muscle strength.
A patient with multiple sclerosis wants to transfer independently. The patient progressed from moderate to minimal assistance for transfers within 3 days; however, no progress has been made in the past 2 weeks. The physical therapist should:
Discharge the patient without further intervention.
Provide the patient with a home program and re-evaluate in 1 month.
Increase the patient's treatments to 5 times/week for 2 weeks.
Decrease the patient's treatments to 1 time/week until the goal is achieved.
To determine whether a patient who is recovering from obturator nerve palsy has regained a muscle grade of Fair (3/5) or better, which of the following testing positions is most appropriate?
Prone
Supine
Sidelying
Long-sitting
A patient reports difficulty in raising the right arm. During examination, manual muscle testing of shoulder abduction reveals strength of Good (4/5) without pain. Which of the following is the MOST likely cause of these findings?
Deltoid tendinitis
Suprascapular nerve damage
Subacromial bursitis
Supraspinatus tendinitis
A physical therapist working with a patient who is borderline hypotensive can minimize orthostatic hypotension by:
Loosening tight legwear and footwear before gait training.
Elevating the head during a hypotensive episode.
Instructing the patient to perform ankle pumps before standing.
Encouraging the patient to consume meals prior to therapy.
Which of the following words would MOST likely describe neurogenic pain?
Throbbing
Aching
Agonizing
Burning
A child with myelomeningocele and a history of hydrocephalus begins to exhibit irritability, lethargy, and vomiting. Which of the following is the MOST likely cause of these symptoms?
Tethered cord
Urinary tract infection
Arnold-Chiari malformation
Shunt malfunction
A patient with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis will MOST likely experience which of the following over time?
Continuous and steady decline, followed by a plateau
Acute worsening, following by full recovery without additional episodes
Acute worsening, followed by improvement and disease stability
Continuous and steady decline without improvement
A physical therapist is setting up an exercise program for a patient who is interested in improving cardiovascular fitness. When performing a submaximal cycle ergometer test the therapist should expect a relatively constant value for:
Oxygen consumption.
Heart rate.
Systolic blood pressure.
Diastolic blood pressure.
A patient, who has many risk factors for coronary artery disease and is presently not taking any cardiac medications, is interested in beginning an exercise program at a gym to improve cardiac health. The BEST self-assessment of exercise intensity during the exercise sessions of this patient is:
Change in systolic blood pressure.
MET (metabolic equivalent) level.
Rating of perceived exertion.
Respiratory rate.
Which of the following conditions must be ruled out when a physical therapist evaluates a patient with nonspecific neck pain?
Kidney stones
Pancreatic cancer
Colon cancer
Myocardial infarction
An inpatient is referred to physical therapy after undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery 5 days ago. The patient's medical history includes hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and type 2 diabetes. Which of the following sets of factors should a physical therapist consider when developing a plan of care?
History of smoking, electrocardographic changes, and parental/family history
Premorbid physical activity level, current physical condition, and motivation to exercise
Lower extremity muscle strength, waist to chest ratio measurement, and endurance on treadmill test
Exercise history, daily caloric intake and dietary habits, and job responsibilities
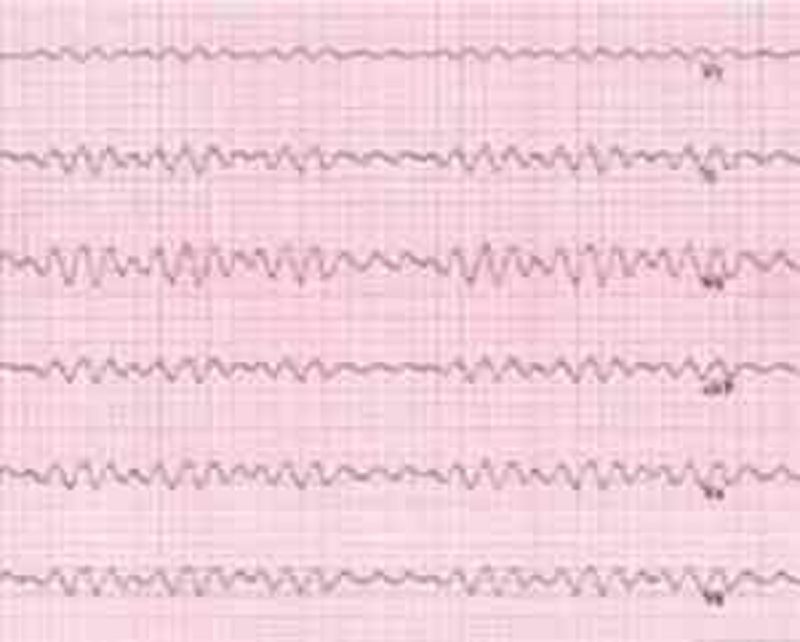
A physical therapist is performing passive range of motion of all extremities with a patient in the intensive care unit who is in a coma. The therapist notes the electrocardiogram in the photograph. The physical therapist's INITIAL response should be to:
Continue with present treatment
Continue passive ranger of motion of lower extremities only.
Stop the treatment and monitor electrocardiogram for 5 minutes.
Activate the emergency system.
Which of the following photographs shows the MOST appropriate placement of the stethoscope to determine if a patient has aortic stenosis?
0%
0
0%
0
0%
0
0%
0
During initial examination of a patient, a physical therapist notices severe clubbing of the patient's fingernails. The therapist should further investigate for the presence of signs and symptoms associated with which of the following conditions?
Skin cancer
Renal failure
Lung cancer
Liver dysfunction
A newborn's Apgar test evaluates heart rate, color, and which additional clinical characteristics?
Respiration, temperature, and weight
Reflex irritability, temperature, and weight
Respiration, muscle tone, and weight
Respiration, muscle tone, and reflex irritability
A patient's electrocardiogram shows a new ST-segment displacement from baseline and a sinus rhythm of 70 bpm. What is the MOST likely diagnosis?
Bradycardia
Anxiety reaction
Acute myocardial infarction
Congestive heart failure
A patient reports a 2 week history of left upper abdominal quadrant pain, left flank pain, and mid-back pain as a result of a motor vehicle accident. The patient also reports being fatigued and generally not feeling well. Which of the following differential diagnoses would MOST likely account for the patient's symptoms?
Chronic fatigue syndrome
Referred pain from the spleen
Conversion disorder from emotional distress
Acute onset of bladder infection
A physical therapist is preparing to perform a bed to chair transfer with a patient who underwent an extensive surgery 24 hours ago and is taking an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. During this transfer, the physical therapist should monitor the patient for the possibility of a:
Rise in systolic and a drop in diastolic blood pressure.
Rise in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Drop in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Drop in systolic and a rise in diastolic blood pressure.
When evaluating the lower extremity muscle strength of a patient, the physical therapist positions the patient prone with the knee flexed. The therapist asks the patient to point the toes upward toward the ceiling. The patient completes the motion, but inverts the foot slightly. This observation indicates:
Tightness of the peroneals.
Substitution by the soleus.
Substitution by the tibialis posterior.
Tightness of the tibialis anterior.
During warm-up on a stationary bike, a patient reports feelings of fatigue. Following the activity, the physical therapist observes the patient sitting in a chair with elbows resting on the knees. The physical therapist should examine the patient for which of the following?
Trunk muscle weakness
Poor sitting posture
Lower extremity weakness
Use of accessory muscles for breathing
Prolonged bed rest would MOST likely cause an increase in which of the following cardiovascular parameters?
Cardiac output
Resting systolic blood pressure
Blood volume and viscosity
Resting and submaximal heart rates
A patient has completed a 12 week strength and conditioning program. Which of the following measures would be MOST appropriate to assess change in fitness and conditioning from week 1 to week 12?
Resting respiration rate before starting exercise
Amount of time until the heart rate returns to baseline exercise
Amount of time until the onset of perspiration during exercise
Amount of increase in diastolic blood pressure during exercise
A patient has a dry, yellow wound located on the anterolateral aspect of the left lower extremity. The patient experiences pain when walking continuously for 5 minutes and therefore avoids walking. Which of the following home exercise programs is MOST appropriate for the patient?
Swimming in a heated therapeutic pool
Upper extremity progressive resistive exercise program
Lower extremity progressive resistive exercise program
Intermittent walking program to tolerance
A patient who is performing a vigorous treadmill test is MOST likely to have an immediate increase in which of the following physiologic repsonses?
Respiration rate to raise blood pH levels
Respiration rate to lower blood pH levels
Rate of excretion of hydrogen ions by the kidneys to raise blood pH levels
Rate of excretion of hydrogen ions by the kidneys to lower blood pH levels
A patient is performing a therapeutic exercise program while being monitored by telemetry. The physical therapist observes a premature ventricular contraction (PVC) every other heartbeat. This patient is experiencing:
Bigeminy
Couplets
Multifocal PVCs
Ventricular tachycardia
A patient reports a recurrent pattern of chest pain while walking each day. Which of the following measurements will BEST enable the physical therapist to estimate the myocardial oxygen demand at the onset of symptoms?
Heart rate and systolic blood pressure
Rate of perceived exertion and systolic blood pressure
Rate of perceived exertion and oxygen saturation
Oxygen saturation and heart rate
A patient who has a leg wound reports increased pain with walking and decreases pain with rest. Which of the following test results is BEST able to identify the primary etiology?
Spontaneous auditory signal during Doppler ultrasound
Inability to sense the 5.07 monofilament during a monofilament sensory test
Absence of superficial peroneal (fibular) sensory nerve action potential
Positive arteriogram with an ankle-brachial index less than 0.70
When an individual experiences an increase in blood pressure, which of the following reflexive responses should occur?
Increased cardiac contractility and respiratory rate
Bradycardia and vascular constriction
Tachycardia and vascular dilation
Vascular diliation and a decrease in cardiac output
A physical therapist evaluating the posture of an obese patient notes that the patient has an anterior pelvic tilt. The therapist will MOST likely find weakness in the:
Iliopsoas and erector spinae.
Rectus abdominis and gluteus maximus.
Latissimus dorsi and sartorius.
Quadratus lumborum and biceps femoris.
Which of the following wellness programs would BEST promote a healthy lifestyle?
A screening program at a corporate fitness center that addresses strength, range of motion, and posture to design custom workouts for individual participants
A health-screening fair where participants can have heart rate, blood pressure, percentage of body fat, and posture assessed, and then receive suggestions on appropriate exercise programs based on the results
A program that distributes a comprehensive brochure describing healthy lifestyle changes and encourages clients to maintain a log of exercise and nutritional habits that is handed in each week
A multidisciplinary program 2 times/week at the local community center that includes active group exercises and a review of proper lifestyle changes
A patient who had coronary artery bypass surgery is being instructed in the signs and symptoms of myocardial infarction. Which of the following principles of patient education is MOST important to ensure that the patient understands the information the therapist provides?
Invite the patient to ask questions about the information.
Provide a comprehensive medical explanation of each of the signs, symptoms, and implications.
Provide the patient with research articles about myocardial infarction.
Recommend that the patient write down the signs and symptoms as the therapist instructs.
3. Significant
4. Stable
2.
A 20 year-old male soccer player presents with a Grade II right lateral ankle sprain upon evaluation. What are the characteristics of a Grade II ankle sprain?
1. Partial tear of the lateral ligament complex with mild joint instability, moderate intra- capsular swelling and tenderness, and some loss of ROM and jointfunction
2. Complete rupture of the anterior talofibular ligament, calcaneofibular ligament, and capsule with mechanical joint instability; severe intra/extra-capsular swelling, ecchymosis, tenderness and inability toweight-bear.
3. Stretch of the lateral ligament complex with no macroscopic tear or joint instability, little swelling or tenderness
4. Partial tear of the syndesmosis, creating generalized swelling and tenderness throughout the ankle joint complex; inability to bear weight, severe ecchymosis, and mortise widening.
3.
An 11 year-old male presents to the physical therapy clinic with signs of hypertonicity related to cerebral palsy. The boy has significant shortening of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle, creating a severe torticollis to the right. This has led to a pressure ulcer forming on his right ear from contact with the wheelchair headrest. The MOST appropriate course of action is to:
1. Begin a course of active-assisted range of motion exercises, focusing on the upper extremities and creating a home program to improve shoulder active range ofmotion.
2. Inform the patient’s family that the child should not be in a wheelchair to prevent the formation of anymore pressure ulcers and decrease pain associated with torticollis.
Copyright PT Final Exam 4 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. Inform the primary care provider of the child and request him/her to order an oral prescription of Baclofen because the child has developed a tolerance for the current dosage.
4. Begin a course of passive range of motion stretches, focusing on the neck, and instruct the patient’s family on proper positioning and wheelchair adjustments to decrease the likelihood of future ulcers.
4.
A patient with a stroke affecting the right middle cerebral artery has difficulty walking, especially over uneven surfaces. Which of the following describes the MOST appropriate initial treatment to improve the patient’s ability to walk over uneven surfaces?
1. Place a single point cane in the patient’s left hand and train him to use a step-to gait pattern.
2. Place a single point cane in the patient’s right hand and train him to use a step-to gait pattern.
3. Fit the patient with a 4-wheeled walker and instruct him to use a4-point gait pattern.
4. Fit the patient with axillary crutches and instruct him to use a 4-point gaitpattern.
5.
A physical therapist is evaluating a 66 year-old female who has a history of severe head trauma following a motor vehicle accident. The patient has difficulty with rapid alternating movements while performing neurologic testing. The BEST term to describe this specific impairment is:
1. Ataxia
2. Dysmetria
3. Dysarthria
4. Dysdiadocokinesia
6.
A 79 year old female presents to outpatient rehabilitation services 6 weeks following a CVA with right hemiplegia. She complains of right shoulder pain working on functional upper extremity movements and has severe shoulder pain when practicing bed mobility activities such as rolling
Copyright PT Final Exam 5 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
And scooting. On examination, it is observed that the humeral head is inferiorly displaced. Which of the following would be the MOST appropriate for her condition?
1. Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation(TENS)
2. Functional Electrical Stimulation(FES)
3. Short Wave Diathermy (SWD)
4. Interferential Current (IFC) Stimulation
7.
A 30 year old male presents to outpatient rehabilitation with numbness and tingling on the 4th and 5th fingers of the left hand consistent with nerve entrapment symptoms. Upon further examination, it is noted that the patient has normal sensation on the dorsum of the hand on the ulnar side. Where is the MOST likely source of nerve entrapment?
1. Guyon’s Canal
2. Carpal Tunnel
3. Cubital Tunnel
4. 1st Rib
8.
A 45 year old male presents to the burn unit with partial thickness burns over the entire right arm, left arm, front of head, and front of abdomen. Approximately what percentage of his body is burned?
1. 31.5%
2. 36%
3. 40.5%
4. 45%
9.
A patient presents to the inpatient rehabilitation unit who has suffered a vertebro-basilar CVA and has difficulty depressing the eye from an adducted position. Which cranial nerve is the MOST likely cause of this impairment?
1. CN I
2. CN II
3. CN III
4. CN IV
10.
A 59 year old male patient is being evaluated for left shoulder pain. The patient reports that his shoulder pain is closely associated with activity, including stress at work. The patient reports that at worst, the pain radiates into his neck, and he feels shortness of breath which subsides with rest. What would the MOST appropriate intervention be?
1. Begin passive range of motion exercises within the pain free range ofmotion.
2. Postpone treatment and refer the patient to his physician for further evaluation.
3. Apply modalities to the shoulder and instruct the patient on activitymodification.
4. Begin the patient with rotator cuff exercises within the pain reduced range of motion and instruct patient on activitymodification.
11.
A 35 year old patient with a complete T5 spinal cord injury is working on supine to sit transfers on the mat table when he suddenly appears flushed and complains of his heart pounding. Upon examination, his blood pressure is 180/100 and he has a pounding headache. The most appropriate INITIAL course of action is:
1. Lay the patient supine and notify the patient’s physician.
2. Sit the patient up and notify the patient’s physician.
3. Allow the patient to rest longer between sets ofactivity.
6
Copyright PT Final Exam http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Initiate core strengthening exercises to maintain intraabdominalpressure.
12.
A 21 year old female patient presents with neck pain and stiffness that has gradually worsened over the last two weeks. Upon examination, the patient is noted to have pain with left side bending with left rotation and reports pain on the left at the C5-6 junction. Hypomobility is also noted with right side-gliding of C6. Which of the following techniques will be most appropriate to decrease pain?
1. Closing technique for the mid-thoracic spine.
2. Closing manipulation in extension for C5-C6
3. Gapping manipulation in flexion for C5-C6.
4. Flexion/opening manipulation for mid-thoracic spine
13.
A 22 year old female presents to the clinic with a chief complaint of knee pain following a twisting injury while playing soccer 5 days ago. The patient’s knee is swollen significantly and is unable to jump or run. What special test would be the MOST appropriate to diagnose the injury?
1. Lachman’s test
2. Posterior drawer test
3. Active Lachman’s test
4. External Rotation RecurvatumTest
14.
A geriatric patient with “walking” pneumonia and a history of recent falls is receiving physical therapy for general strengthening. What part of this person’s treatment is affected MOST by his lung condition?
1. Decreased stamina/tolerance of activity
2. Inability to participate in endurance type activities
7
Copyright PT Final Exam http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Copyright PT Final Exam 8 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. Diminished tidal volumes
4. Lower oxygen saturation with moderate activity
15.
A patient complains of weakness in the right hip while she is ambulating. Upon examination, you notice that the patient has a significant drop of the left hip while in midstance on the right leg. The MOST appropriate treatment for this impairment wouldbe:
1. Standing hip abduction of the left leg.
2. Standing hip abduction of the right leg.
3. Standing flexion of the left leg.
4. Standing flexion of the right leg.
16.
A patient presents to the clinic with signs of lethargy and mild dizziness. The patient's resting blood pressure is 100/70. Which of the following is MOST likely to cause this decrease in blood pressure?
1. Lisinopril
2. Prednisone
3. Sertraline
4. Metformin
17.
A patient presents to the clinic with right shoulder pain and complains of difficulty reaching overhead, with pain especially from 60-120 degrees of shoulder flexion. Which special test would be MOST informative for this set of symptoms?
1. Neer Test
2. Empty Can Test
3. Crossover Test
4. Push Off Test
Copyright PT Final Exam 9 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
18.
A patient is in the inpatient rehabilitation unit for a total knee replacement. While reviewing the case, you note that the patient has been diagnosed with an infection of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and is in an isolation room. What is the MOST appropriate action to take to prevent contamination?
1. Don gown, mask, gloves, and respirator before entering the room, wash hands after.
2. Limit therapy sessions to less than 15 minutes and limit contact during treatment.
3. Don gloves when in contact with the patient and wash handsafter.
4. Wash hands before and after contact with the patient, but do not touch the patient.
19.
A 32 year old female presents to the clinic complaining of left shoulder pain. The patient’s symptoms include pain with reaching and limited motion in all planes. The patient’s symptoms have been progressively worsening over the last month. What would be the MOST effective initial treatment?
1. Refer the patient to their primary care provider for intracapsular corticosteroid injections.
2. Begin gentle progressive stretching exercises with the focus on increased active range of motion.
3. Initiate rotator cuff strengthening exercises, focusing on external rotation.
4. Instruct the patient on Codman pendulum exercises and apply a moist heatpack.
20.
While treating a patient for cardiac rehab, a physical therapist relies on the Borg RPE scale. The Borg rating of perceived exertion scale (RPE) is MOST representative of which type of data scale?
1. Nominal
2. Ordinal
Copyright PT Final Exam 10 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. Cardinal
4. Marginal
21.
A physical therapist is trying to determine which special test to use for an examination and is researching the statistical values of each. What is the MOST important statistical attribute a special test must have to effectively limit Type I errors?
1. Sensitivity
2. Specificity
3. Positive likelihood ratio
4. Negative likelihood ratio
22.
A physical therapist is evaluating a 50 year old patient with a generally swollen right leg. The patient does not report any trauma to the leg and describes the swelling as increasing gradually over the last 12 months. The swelling is non-pitting, primarily below the knee. The leg is not red or hot, and the patient indicates that his leg just feels “heavy.” What is the MOST likely origin of the swelling?
1. Systemic infection
2. Chronic inflammation
3. Congestive heart failure
4. Lymphedema
23.
A physical therapist is evaluating a patient with pain that radiates throughout his lower extremities. The patient has significant foot drop while ambulating and complains of numbness and tingling extending from the great toe up to the knee along the anterior leg. What is the MOST likely pathology underlying these symptoms?
1. Sciatic nerve entrapment
Copyright PT Final Exam 11 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
2. Deep peroneal nerve inflammation
3. Tibial nerve entrapment
4. L5 nerve root entrapment
24.
A patient has right leg pain and displays redness and swelling throughout the foot and ankle distal to the knee that has developed over the last 3 days. The patient reports no trauma and complains of a deep ache in the calf musculature. What is the MOST appropriate initial treatment?
1. Refer to physician for further examination.
2. Elevate the lower extremity and apply an icemodality.
3. Instruct the patient on range of motion exercises and begin a home exercise program.
4. Perform instrument assisted manual soft tissuemobilization to decrease the swelling.
25.
A patient with cystic fibrosis is receiving postural drainage and percussion for the right lung’s middle lobe. What is the MOST appropriate patient position?
1. Supine on a wedge with the left shoulder elevated on pillows with the head lower than the pelvis.
2. Supine on a wedge with the right shoulder elevated on pillows with the head lower than the pelvis.
3. Prone with the right shoulder elevated on pillows and the head on the same plane as the pelvis.
4. Prone with the left shoulder elevated on pillows and the head on the same plane as the pelvis.
26.
A patient is being evaluated by a physical therapist for a diabetic ulcer that penetrates the subcutaneous tissue, extending into the subcutaneous fat and fascia but without any gangrene or
Copyright PT Final Exam 12 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Osteomyelitis present. The physical therapist wishes to document the severity of the ulcer. What is the MOST appropriate objective measure of the wound?
1. Measure the depth and shape of the ulcer and classify it as a Grade 2 ulcer on the Wagner Ulcer Grade Classification System.
2. Measure the depth and shape of the ulcer and classify it as a Grade 3 ulcer on the Wagner Ulcer Grade Classification System.
3. Measure the depth and shape of the ulcer and classify it as a Grade 4 ulcer on the Wagner Ulcer Grade Classification System.
4. Measure the depth and shape of the ulcer and classify it as a Grade 5 ulcer on theWagner Ulcer Grade Classification System.
27.
A physical therapist is evaluating a patient with ulceration on the lower extremity. The leg is apparently swollen and red upon examination. The wound is irregularly shaped and feels hot to the touch. Which of the following grouping of symptoms is MOST consistent with this type of ulceration?
1. Ulceration is on the lateral leg, pulseless, cool, andpainful.
2. Ulceration is medial leg, shows permanent blanching, and ispainless.
3. Ulceration is upon bony prominences, shows non-blanchable redness at the perimeter of the wound, and has a pink appearance.
4. Ulceration is upon the bony prominence, began as a small scrape or blister several months ago, with a concomitant diagnosis of diabeticneuropathy.
28.
A physical therapist is performing a treadmill exercise stress test using the Bruce protocol. During stage 3 of the test, the P wave increases in height and the S-T segment begins to become significantly upsloping. What is the MOST appropriate course of action?
1. Stop the test and refer patient to aphysician.
Copyright PT Final Exam 13 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
2. Lower the stage back to stage 2 and monitor for improved electrocardiographic indicators.
3. Continue with the test without any modification, monitoring for symptoms of cardiac distress.
4. Discontinue the test, and monitor the patient’s vital signs for 10minutes.
29.
A patient is receiving cardiac rehab and has a heart rate of 110 during moderate intensity exercise. The patient reports a 16 on the Borg RPE scale. Which class of heart medications is MOST likely present?
1. Beta Blockers
2. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
3. Calcium Channel Blockers
4. Angiotensin II ReceptorBlockers
30.
A 12 year old male athlete is being evaluated by a physical therapist. The patient reports pain with running and has a sharp pain over the patellar tendon, particularly on the tibial tubercle. Which of the following disorders is MOST likely present?
1. Legg-Calvé-Perthes’ disease
2. Chondromalacia patellae
3. Osgood-Schlatter disease
4. Pes anserine bursitis
31.
A patient is recovering from a broken tibia and has just been instructed to discontinue use of a walking boot. The patient demonstrates excessive pronation and complains of pain and instability in the ankle while ambulating. Which of the following is the MOST appropriate treatment?
Copyright PT Final Exam 14 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
1. Begin a single leg standing program and advance to eccentric calf strengthening as tolerated.
2. Begin with open-chain exercises and progress to closed-chain strengthening of the ankle as tolerated.
3. Begin with closed-chain exercises and progress to open-chain strengthening of the ankle as tolerated.
4. Begin a strengthening program involving primarily ankle evertors, progressingas tolerated.
32.
A patient reports pain around the anterior aspect of the calcaneus extending toward the 2nd metatarsal head. The patient has the most pain when first standing up after waking which gradually lessens throughout the day. The patient has recently begun a walking program.
Which of the following disorders is MOST likely present?
1. Medial deviation of the 1stmetatarsal
2. Plantar fasciitis
3. Metatarsalgia
4. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
33.
A physical therapist is evaluating a patient with back pain. The patient reports having pain that has increased steadily over the last 2 months and is constant and unremitting. The pain radiates into both lower extremities. The patient also feels marked weakness throughout the right lower extremity. What is the MOST appropriate initial treatment?
1. Discontinue treatment and refer patient to primary care physician for further testing.
2. Begin a program of core strengthening, focusing on transversus abdominis trainingand progressing toward a long term stabilizationprogram.
3. Instruct the patient in appropriate lower extremity exercises to improve legstrength, focusing on the right leg.
4. Initiate piriformis stretching as tolerated and instruct the patient in self mobilization techniques to improve mobility throughout the lumbar spine.
34.
After working for several hours as a mechanic, a patient describes sharp elbow pain over the origin point of the common extensor tendon of the wrist extensors. The pain is alleviated with rest. Which of the following disorders is MOST likely present?
1. Medial epicondylitis
2. Lateral epicondylitis
3. Anconeus tendonitis
4. Olecranon bursitis
35.
A patient presents with rheumatoid arthritis and finger pain. The 2nd digit has a flexed metacarpophalangeal joint, hyperextended proximal interphalangeal joint, and a flexed distal interphalangeal joint. Which of the following is the MOST accurate description of the position?
1. Swan neck deformity
2. Boutonniere deformity
3. Mallet finger deformity
4. De Quervain syndrome
36.
A physical therapist examines a patient and determines that the patient has a positive Active Compression test (O’Brien’s Test). Which of the following pathologies is MOST implicated?
1. Rotator cuff tear
2. Biceps tendonitis
3. Superior labral tear
4. Acromioclavicular joint sprain
15
Copyright PT Final Exam http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Copyright PT Final Exam 16 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
37.
While examining a patient’s lumbar x-ray films, a physical therapist notices that the L5 vertebra is displaced anteriorly on sacrum by approximately 50% of the vertebral body. How will this MOST affect physical therapy if the patient is being treated for low back pain?
1. Emphasize core strengthening, especially in spineneutral
2. Begin progressive gluteal and quad strengthening to assist the lumbopelvic fascia
3. Avoid extension activities, especially instanding
4. Add progressive external oblique training as tolerated to assist proper spinal alignment
38.
A physical therapist is treating a patient with cervical pain. The patient reports that the pain occurs with most movements and feels “stiff” with active range of motion. What is the MOST appropriate course of action?
1. Refer to primary care physician for further testing.
2. Initiate thoracic spine thrustmanipulation.
3. Instruct the patient on cervical spine stabilization exercises and issue a home exercise program.
4. Initiate an upper extremity exercise routine to improve scapular and cervical range of motion and progress as tolerated.
39.
A patient has just undergone a total hip replacement via a posterior surgical approach. Which of the following combinations of movements of the hip are MOST important to avoid?
1. Extension, medial rotation, and abduction.
2. Extension, external rotation, and adduction.
3. Flexion, medial rotation, and adduction.
Copyright PT Final Exam 17 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Flexion, external rotation, and abduction
40.
A patient who has suffered a cutting injury to the entire left half of the spinal cord at the T8 level is being examined by a physical therapist. Which of the following impairments would be MOST apparent on the ipsilateral lower extremity?
1. Loss of pain and temperature sensation
2. Loss of movement and light touch sensation
3. Loss of peripheral smooth muscle control
4. Loss of coordination and accuracy.
41.
A patient with Guillain-Barré syndrome has bilateral lower extremity weakness. Which of the following descriptions BEST represents the underlying cause of this disease?
1. Lower motor neuron demyelination
2. Cerebellar tumor formation
3. Vagal nerve axonotmesis
4. Amyloid plaque formation
42.
A physical therapist is examining a patient with a cervical spinal cord injury and observes that the patient is able to press up from the wheelchair using elbow extensors. Which spinal level MUST be intact to perform this maneuver?
1. C4
2. C5
3. C6
4. C7
Copyright PT Final Exam 18 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
43.
A physical therapist is treating a patient with a diabetic ulcer on the calf, just superior to the medial malleolus. The wound is discharging heavy amounts of purulent drainage. Which type of dressing will be MOST effective for this wound?
1. Calcium Alginate
2. Hydrocolloid
3. Silicon gel sheeting
4. Hydrogel
44.
A physical therapist is performing cranial nerve testing on a patient with a suspected cerebrovascular accident and wishes to examine the Hypoglossal Nerve motor function. Which of the following will MOST effectively test this nerve’s motor function?
1. Instructthe patient to follow an H pattern and observe for impaired tracking.
2. Instruct the patient to shrug the shoulders and turn the head against mild resistance.
3. Instruct the patient to stick out the tongue and move it side to side against resistance.
4. Instruct the patient to shut the eyes tightly and show the teeth and observe for asymmetry.
45.
A patient reports experiencing pain at the right inferior border of the scapula. The physical therapist suspects the origin is referred pain. Which internal organ would MOST likely refer pain to this area?
1. Stomach
2. Kidney
3. Gallbladder
Copyright PT Final Exam 19 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Ureter
46.
A physical therapist chooses to use therapeutic ultrasound for deep heating of the quadriceps muscle. Which set of ultrasound parameters will be MOST effective at increasing the temperature of tissue 3.0 centimeters deep?
1. 1.0 MHz, 1.5 W/cm², 50% duty cycle
2. 3.0 MHz, 1.5 W/cm², 100% duty cycle
3. 1.0 MHz, 1.5 W/cm², 100% duty cycle
4. 3.0 MHz, 1.5 W/cm², 50% duty cycle
47.
A patient reports feeling a frequent need to urinate and often leaks urine before reaching the bathroom. Which type of incontinence is MOST likely present?
1. Stress incontinence
2. Urge incontinence
3. Overflow incontinence
4. Functional incontinence
48.
A patient displays signs of shakiness, slowness of movement, and rigidity. Which of following BEST represents the origin of this condition?
1. Brain stemsclerae
2. Substantia negra cell death
3. Spinal cord demyelination
4. Temporal lobe amyloid plaques
Copyright PT Final Exam 20 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
49.
A patient presents to a physical therapist for rehabilitation in a standard wheelchair following a T12 spinal cord injury. The patient demonstrates excellent functional wheelchair mobility. What is the MOST appropriate technique to transfer the patient from the wheelchair to the mat table?
1. Sliding board
2. 2 person lift
3. Dependent transfer
4. Squat pivot transfer
50.
A physical therapist is treating an individual recovering from a total knee replacement. The therapist desires to make an objective measure regarding the functional ambulation status of this individual. Which of the following devices would be MOST useful?
1. Goniometer
2. Treadmill
3. Stopwatch
4. Stairs
51.
A physical therapist is treating a patient with ulnar nerve entrapment at the cubital tunnel. Which muscle would MOST likely be weak from this type of pathology?
1. Flexor digitorumsuperficialis
2. Flexor carpi radialis
Copyright PT Final Exam 21 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. Flexor pollicis longus
4. Flexor carpi ulnaris
52.
Upon examination, a physical therapist notes weakness in the dorsiflexors of a patient with peripheral neuropathy. Which type of gait abnormality is MOST likely present?
1. Antalgic gait
2. Steppage gait
3. Trendelenburg gait
4. Festinating gait
53.
A patient is recovering from a myocardial infarction and presents to an outpatient physical therapy clinic for cardiac rehabilitation. Which of the following is an absolute indication to cease exercising?
1. Cyanosis
2. Significant fatigue
3. RPE >15 on the Borg scale
4. Rise in systolic BP of 15mmHg
54.
A patient presents to the clinic with coronary artery disease. Which of the following risk factors is MOST important to educate the patient about?
1. Age
2. Gender
3. Obesity
Copyright PT Final Exam 22 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Physical inactivity
55.
A patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease has difficulty breathing while exercising. Which of the following medications is MOST likely to help the patient more easily breathe while exercising?
1. Amlodipine
2. Carvedilol
3. Digoxin
4. Salbutamol
56.
Which of the following arterial blood gas values is MOST indicative of respiratory alkalosis?
1. PaO2 80 mmHg
2. PaO2 100mmHg
3. PaCO2 25 mmHg
4. PaCO2 45 mmHg
57.
A physical therapist is treating a patient who reports having AIDS. What is the MOST appropriate method to prevent transmission of the disease?
1. Wear gloves and mask when treating the patient
2. Treat the patient in a private room to avoid exposure to otherpatients
3. Avoid contact with bodily fluids and clean equipment before and after treatment.
4. Ask the patient to wear gloves and mask duringtreatment.
Copyright PT Final Exam 23 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
58.
A patient is being treated for difficulty with overhead activities and subacromial bursitis. Which of the following strengthening activities will be MOST helpful?
1. Scapular retractionexercises
2. Shoulder flexion exercises
3. Shoulder shrugging exercises
4. Shoulder rotationexercises
59.
A football player reports receiving a blow to the head 4 days ago. He appears to have signs of a concussion. What is the MOST appropriate initial course of action?
1. Stop treatment and refer to aphysician.
2. Assess symptoms and perform cognitive and balancetesting.
3. Begin an exercise routine to prepare the patient to return toplay.
4. Document the symptoms and proceed with sport specificconditioning drills.
60.
A five year old boy presents to a physical therapist for evaluation. The patient has had weakness and difficulty walking for 2 years that has progressively worsened. The boy appears to be developing multiple joint contractures and shows signs of muscular wasting. What is the MOST likely origin of his impairments?
1. Muscular dystrophy
2. Legg-Calvé-Perthe’s disease
3. Charcot-Marie-ToothDisease
4. Cerebellar insufficiency
Copyright PT Final Exam 24 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
61.
A patient with second and third degree burns to the face and neck is receiving treatment by a physical therapist. Which of the following complications will be MOST significant during rehabilitation?
1. Hypertrophic scarring
2. Respiratory distress
3. Joint contractures
4. Nutritional deficiencies
62.
A patient with a decubitus ulcer over the sacrum presents for wound care to a physical therapist. The wound extends through the cutaneous tissue and has subcutaneous fat visible at the bottom of the wound. Which of the following stages is the BEST classification of the wound?
1. Stage I
2. Stage II
3. Stage III
4. Stage IV
63.
A patient has had a full-thickness burn to the right arm. Which of the following is the MOST effective treatment to prevent hypertrophic scarring?
1. Compression bandage
2. Antibiotic ointment
3. Position optimization
4. Appropriate splint use
64.
A patient receiving physical therapy status post 10 weeks after an elbow fracture for a significant flexion joint contracture. The patient’s physician states the fracture is well-healed. Which of the following is the MOST appropriate initial intervention to improve range of motion?
1. Grade II and III jointmobilizations
2. Progressive active-assisted range of motion to elbowjoint.
3. Progressive stretching and passive range of motion to elbowjoint.
4. Progressive resisted active range of motion exercises to elbowjoint.
65.
A patient has just undergone anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction and presents for physical therapy seven days after surgery. Which of the following treatments will be MOST effective at speeding recovery initially?
1. Progressive active range of motionexercises
2. Isometric quadriceps strengthening
3. Resisted hamstring curls
4. Progressive increased weight bearing
66.
A patient with a middle cerebral artery vascular lesion has difficulty raising his arm. Which of the following synergy patterns is MOST likely present in the patient’s involved upper extremity during elevation?
1. Scapular retraction, humeral abduction, elbow flexion, wrist supination
2. Scapular retraction, humeral adduction, elbow extension, wristsupination
3. Scapular protraction, humeral abduction, elbow flexion, wrist supination
4. Scapular protraction, humeral adduction, elbow extension, wrist supination
25
Copyright PT Final Exam http://www.ptfinalexam.com
67.
A patient recovering from a stroke is being evaluated by a physical therapist. The patient is able to voluntarily elevate his arm through the synergy pattern without difficulty, and is beginning to have movements out of the synergy pattern. Spasticity is still present. Which of the following Brunnstrom stages BEST describes this pattern?
1. Stage 1
2. Stage 2
3. Stage 3
4. Stage 4
68.
A physical therapist is treating a patient with shoulder pain and weakness. The patient reports increased pain with overhead activities and displays superior humeral head translation during shoulder elevation. Which of the following interventions is MOST likely to correct the problem?
1. Scapular retraction exercises in closed chainposition
2. Rotator cuff strengthening exercises in open chainposition
3. Tricep extension exercises in closed chainposition
4. Resisted scapular elevation exercises (shrugging) in open chainposition.
69.
A patient reports feeling dizzy and lightheaded upon standing. The patient reports that the condition has been worsening over time and that he commonly sees dark spots when changing positions. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
2. Meniere's disease
3. Orthostatic hypotension
26
Copyright PT Final Exam http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Transient ischemic attack
70.
A physical therapist is treating a patient who had open heart surgery 2 weeks ago to perform a coronary artery bypass. Which of the following BEST describes a precaution following this surgery?
1. Limit left lower extremity to 50% weightbearing
2. Limit shoulder flexion to less than 90 degreesbilaterally
3. Limit cervical rotation less than 45 degreesbilaterally
4. Limit upper extremity lifting to less than 10pounds
71.
During a physical therapy examination, the physical therapist notes pain and tenderness just inferior to the medial malleolus following what the patient reports as a sprained ankle. Which of the following structures is MOST likely sprained?
1. Anterior talofibular ligament
2. Posterior talofibular ligament
3. Calcaneofibular ligament
4. Deltoid ligament
72.
A patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is instructed to perform pursed lip breathing. Which of the following is the MOST appropriate reason for performing this type of breathing?
1. Increase total lung volume to ease the exchange of air
2. Create back-pressure in the airways to ease airflow
3. Decrease the tidal volume to ease air exchange
4. Decrease the amount of breaths required to exchange air
27
Copyright PT Final Exam http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Copyright PT Final Exam 28 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
73.
A patient in the intensive care unit has a Swan-Ganz catheter. What is the PRIMARY purpose of this type of catheter?
1. Introduce pharmaceuticals via a portal in a peripheralvein.
2. Introduce pharmaceuticals directly into the inferior vena cava or rightatrium.
3. Monitor blood pressure and detect heart failure.
4. Collect urine into a receptacle to bediscarded.
74.
A patient in the intensive care unit is in a coma and has a pressure relief turning schedule that requires a change in position every 2 hours. The physical therapist on duty notices that the patient’s position has not changed for 8 hours. Which of the following is the MOST appropriate course of action?
1. Immediately notify the physician and document the event in the patient’s chart.
2. Immediately notify nursing staff and review the importance of pressure offloading.
3. Immediately turn the patient and document the offloading in the patient’s chart.
4. Proceed with routine patient care and document the event in the patient’s chart.
75.
A patient is being treated for neck and shoulder pain by a physical therapist. The physical therapist notes that the patient has a forward head, rounded shoulders posture that cannot be corrected with active movement. Which of the following interventions is MOST likely to correct the problem?
1. Initiate cervical flexor and extensor strengthening and progress astolerated.
2. Performthrust manipulation to themidthoracic spine and applymodalities as needed.
Copyright PT Final Exam 29 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. Initiate pectoralis minor stretching and scapular retractor strengthening and progress as tolerated.
4. Initiate cervical traction to reduce the stress on the cervical spine and begin a program of active range of motion movements for the cervical and thoracicspine.
76.
A patient reports pain in the knee while descending stairs. The pain increases with knee flexion, especially at approximately 30 degrees of flexion. Which of the following disorders is MOST likely present?
1. Meniscal tear
2. Patellofemoral pain syndrome
3. Semitendinosus sprain
4. Gastrocnemius sprain
77.
A patient notes pain in the area highlighted with a star (see photograph) while grasping the thumb in ulnar deviation. Which disorder is MOST likely present?
1. Carpal Tunnel syndrome
2. Ganglion Cyst pain
3. Wartenburg’s syndrome
4. De Quervain syndrome
78.
A patient appears to have a positive Patrick’s Test. Which of the following joints is MOST likely to have pathology present?
Copyright PT Final Exam 30 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
1. Hip
2. Ankle
3. Shoulder
4. Elbow
79.
A patient is being treated for temporomandibular joint dysfunction. The patient describes that his jaw will not open and feels like it is blocked. What is the MOST appropriate treatment?
1. Inferior glide of the temporomandibular joint.
2. Lateral glide of the temporomandibular joint.
3. Superior glide of the temporomandibular joint.
4. Posterior glide of the temporomandibular joint.
80.
A patient experiences a positive Dix-Hallpike Test upon examination, including ageotropic nystagmus and severe dizziness indicating a posterior semicircular canal disturbance. Which of the following interventions is MOST likely to correct the problem?
1. Vestibular desensitizationexercises
2. Grade II mobilization to the cervical spine
3. Instruction to avoid positions that provoke symptoms
4. Epley Maneuver to the involved side
81.
A patient is experiencing numbness and paresthesia on the scalp, forehead, upper eyelids, and nose. Which of the following disorders is the MOST likely origin of the sensory disturbance?
1. C2 spinal nerve root impingement
2. Bell’s Palsy of the facial nerve
3. Trigeminal nerve lesion
4. Vestibulocochlear neuroma
82.
A patient who has received a heart transplant is undergoing cardiac rehabilitation with a physical therapist. Which of the following descriptions BEST represents the cardiovascular effects that occur when this person begins exercising?
1. No initial change in heart rate followed by a gradual increase after severalminutes.
2. Immediate increase in heart rate that gradually stabilizes afterseveral minutes.
3. No initial change in heart rate followed by a gradual decrease after severalminutes.
4. Immediate decrease in heart rate that gradually stabilizes after severalminutes.
83.
A physical therapist is evaluating a patient after a stroke. The physical therapist asks the patient to demonstrate how to brush his teeth, but the patient takes the toothbrush and begins brushing his hair. Which of the following conditions BEST represents the patient’s impairment?
1. Ataxia
2. Aphasia
3. Abulia
4. Apraxia
84.
A physical therapist is evaluating a patient with back pain. The examiner performs the Straight Leg Raising Test and determines that the test is positive. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Lumbar facet osteoarthritis
2. Herniated nucleus pulposus
3. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
31
Copyright PT Final Exam http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Copyright PT Final Exam 32 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Vascular intermittent claudication
85.
A female patient is being examined by a physical therapist. The patient has a decreased heart rate, poor muscle tone, and recent unexplained weight gain and water retention. The patient also reports general feelings of fatigue and depression. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Hyperthyroidism
2. Hypothyroidism
3. Hyperglycemia
4. Hypoglycemia
86.
While examining a pregnant patient, a physical therapist notices a dark line down the center of the rectus abdominis. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Diastasis rectus
2. Inguinal hernia
3. Linea nigra
4. Preeclampsia
87.
A pregnant patient is being treated for low back pain. When placing the patient supine on the plinth, which of the following positions is MOST appropriate?
1. Supine with pillows under the left hip.
2. Supine with pillows under the right hip.
3. Supine with the head slightly elevated.
Copyright PT Final Exam 33 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Supine with the feet slightly elevated.
88.
Which of the following is the MOST common complication following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction?
1. Hip abductionweakness
2. Knee flexionweakness
3. Knee range of motion deficit
4. Decreased patellarmobility
89.
A patient has just undergone an isolated posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Which of the following is the MOST correct description of the primary function of the posterior cruciate ligament?
1. Restrains posterior translation of the tibia
2. Restrains anterior translation of the tibia
3. Restrains valgus forces on the knee joint
4. Restrains varus forces on the knee joint
90.
A physical therapist is reviewing a journal article about rehabilitation following below-knee amputations. Which of the following would be considered the STRONGEST evidence?
1. Expert Opinion
2. Case-control series
3. Randomized controlled trials
Copyright PT Final Exam 34 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Systematic reviews
91.
A patient has undergone a below-knee amputation.What is the MOST important clinical consideration in preparing to use a prosthesis?
1. Ambulation endurance
2. Hip range of motion
3. Stumpmaturity
4. Psychological health
92.
A patient is being examined by a physical therapist for shoulder pain. The individual reports that the pain is located in an area around the acromion and has been gradually increasing over the last 3 months. The patient has limited passive motion in external rotation, internal rotation, and flexion, and complains of severe pain with all three motions. Which of the following disorders is MOST likely present?
1. Subacromial bursitis
2. Acromioclavicular joint lesion
3. Scapulothoracic hypomobility
4. Adhesive capsulitis
93.
A patient is recovering from a Grade II hamstring tear. Which of the following BEST describes this type of injury?
1. Mild pain or tightness in the hamstring muscle, especially when stretched or contracted.
2. Burning pain immediately after injury, inability to walk, and significant bruising over the hamstring.
Copyright PT Final Exam 35 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. Immediate pain with injury, painful with stretching, and significant bruising overthe hamstring.
4. Severe pain over the anterior leg, especially with deep knee flexion, with significant bruising over the quadriceps.
94.
A physical therapist is treating a patient who is recovering from a lateral ankle sprain. The physical therapist wishes to improve the patient’s ability to sense joint position while walking and running. Which of the following treatments will be MOST effective at accomplishing these goals?
1. Therapeutic exercise to strengthen the ankle eversion muscles, using elastic tubingand ankle weights.
2. Therapeutic exercise to strengthen the ankle inversion muscles, using elastic tubing and ankle weights.
3. Proprioceptive training drills, using unstable and compliantsurfaces.
4. Gait training drills, focusing on the terminal stance and preswing phases ofgait.
95.
A patient with a forward head/rounded shoulders posture is being examined by a physical therapist. The therapist notes that the patient’s scapulae will not retract, even during passive range of motion testing. Which of the following is the MOST likely cause of the patient’s poor posture?
1. Tight pectoralis minor
2. Weak scapular retractors
3. Tight posterior scalenemuscle
4. Weak rotator cuffmusculature
96.
Copyright PT Final Exam 36 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A 19 year old female patient is being evaluated by a physical therapist. The patient reports weakness and generalized fatigue despite frequent and strenuous exercise. The patient has lost a significant amount of weight in the last month and states that she is hopeful that physical therapy will help her reduce her body mass index. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Hyperthyroidism
2. Lung cancer
3. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
4. Anorexia nervosa
97.
A patient is receiving treatment from a physical therapist for low back pain. The patient has hypermobility with posterior-anterior glides on L3. The patient denies radiculopathy or pain in the lower extremities. Which of the following treatment options will be MOST appropriate?
1. Lumbarmanipulation
2. Lumbar stabilization
3. Intermittent lumbar traction
4. Direction specific lumbar exercises
98.
A patient is being evaluated by a physical therapist. The patient reports that he has difficulty with his balance, especially in low light conditions such as parking garages and movie theaters. Which of the following conditions on the Clinical Test of Sensory Integration on Balance (CTSIB) would the patient have the MOST difficulty with?
1. Condition 1
2. Condition 2
3. Condition 5
4. Condition 6
Copyright PT Final Exam 37 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
99.
A female patient is having difficulty with stress urinary incontinence and is seeking treatment from a physical therapist. Which of the following treatment options will be MOST effective at decreasing the bouts of incontinence?
1. Perineal strengthening exercises
2. Limit fluid intake to 8 oz. every 4 hours
3. Instruct the patient to avoid stressful situations
4. Gluteal strengthening exercises 100.
A physical therapist is treating an individual with residual quadricep weakness following a knee surgery. Which of the following electrical stimulation modalities will be MOST effective at increasing quadricep strength?
1. Interferential current
2. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
3. Neuromuscular electrical nerve stimulation
4. Iontophoresis 101.
A physical therapist is treating an 8 year old patient with a history of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. After several minutes of moderate exercise, the patient begins to perspire and has a heart rate of 120 beats per minute. Which of the following is the MOST appropriate immediate course of action?
1. Continue the activity, closely monitoring symptoms
2. Immediately have the child sit down and monitor vital signs for 5minutes
3. Refer the patient to a physician for shuntevaluation
4. Decrease the activity load until the patient’s heart rate is less than 100 beats per minute and continue the exercise
Copyright PT Final Exam 38 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
102.
A male adolescent patient who has sustained a blow to the head during a high school football game is being evaluated on the sideline by a physical therapist. The patient is exhibiting signs and symptoms of a concussion, but is awake and oriented. What is the MOST appropriate initial course of action?
1. Immediately transport the patient to the emergency room.
2. Remove the player from the game and perform sideline concussiontesting.
3. Monitor the patient on the sideline and return himto play if the symptoms subside.
4. Remove the player from the game and instruct his parents to have him sleep as soon as possible.
103.
A physical therapist is evaluating a patient who has been referred to physical therapy for a Hill- Sach’s lesion. Which of the following is the MOST likely mechanism of injury to produce such a lesion?
1. Posterior hip dislocation
2. Anterior shoulder dislocation
3. Plantar flexion and dislocation of theankle
4. Posterior dislocation of the ulna on the olecranon
104.
A 65 year old patient reports developing shoulder pain over the last 3 months that is exacerbated by overhead activities. The patient displays poor posture and has rotator cuff musculature that is 25% weaker on the involved upper extremity. Which of the following is MOST likely the source of the pain?
1. Primary impingement
2. Secondary impingement
3. Biceps tendinopathy
4. Anterior capsule instability
Copyright PT Final Exam 39 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
105.
While ambulating, a patient reports that she is frequently tripping and is afraid of falling. The patient does not appear to have any gross deficits of strength. Which of the following interventions is MOST likely to correct the problem?
1. Train the patient to circumduct the hip during the terminal swing phase ofgait.
2. Instruct the patient to allow the knees to flex to 40 degrees with the loading response phase of gait.
3. Train the patient to allow the ankle to plantarflexmore fully with the preswing phase of gait.
4. Instruct the patient to increase dorsiflexion of the ankle during the swing phase of gait.
106.
A physical therapist is treating a patient who has undergone an arthroscopic medial meniscus repair two weeks ago. Which of the following is the MOST important consideration during rehabilitation?
1. Avoid full extension of the knee
2. Avoid full flexion of the knee
3. Encourage full weight bearing
4. Encourage gastrocnemius strength
107.
A patient is 6 weeks status post anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Which of the following is the MOST important treatment consideration?
1. The graft reaches its weakest point at thisphase.
2. Use passive range of motion to improve knee flexibility.
3. Inflammation and swelling should be activelymanaged.
Copyright PT Final Exam 40 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Decreased quadricep strength limits ambulation in both time anddistance.
108.
A 30 year old patient is recovering from an ankle fracture has instructions from the physician to ambulate with partial weight bearing on the involved extremity. Which of the following assistive devices would be MOST appropriate for this patient to facilitate ambulation?
1. Single point cane
2. Four wheeled-walker
3. Lofstrand crutches
4. Knee scooter
109.
Which of the following BEST represents a handicap on the International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health?
1. Biomechanical abnormality of the human organism
2. Abnormality of a tissue, organ, or body system
3. Inability to participate in a task or participate in an activity considered normal fora human being.
4. Disadvantage that prevents fulfillment of a role that isnormal.
110.
To be considered eligible to receive Home Health Care Services that are covered by Medicare, which of the following conditions MUST be satisfied?
1. The patient’s home is greater than five miles from a physician’s office or primaryhealth care provider.
2. The patient requires considerable effort to leave thehome.
Copyright PT Final Exam 41 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. The patient has no family or caregiver immediately available to assist with activities of daily living.
4. The patient requires adult day care.
111.
A patient is being treated for flexor hallucis longus tendonitis. Which of the following modalities will be MOST useful in decreasing pain and speeding recovery?
1. Topicalmenthol
2. Iontophoresis
3. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
4. Ultrasound
112.
A patient has had poorly controlled type II diabetes and is being treated for a diabetic foot ulcer on the inferior portion of the heel. The ulcer has a seropurulent discharge and exudes a foul odor. The patient is unable to ambulate without applying direct pressure to the wound site.
Which of the following interventions will be MOST important in speeding the recovery of the wound?
1. Instruct the patient on the importance of glucose monitoring and diabetescontrol.
2. Instruct the patient to offload the pressure point and use bulky dressing to absorb the exudate.
3. Begin whirlpool therapy to assist in nonspecific wounddebridement.
4. Begin sharp debridement of wound bed, carefully removing areas of thickened callus and eschar.
113.
During an initial evaluation by a physical therapist, a patient reports that he has undergone a total knee arthroplasty 2 weeks ago. Which of the following medications will MOST affect the initial physical therapy intervention?
1. Warfarin
2. Simvastatin
Copyright PT Final Exam 42 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. Omeprazole
4. Hydrochlorothiazide
114.
A male patient in the intensive care unit is being treated for multiple trauma injuries after a motor vehicle accident. A physical therapist is reviewing the most recent lab results. Which of the following would be the GREATEST indication to postpone therapy until consulting with the attending physician?
1. Venous O2 saturation 40%
2. Hemoglobin A1C 5.1 %
3. White Blood Cell Count 10,000 cells/mL
4. Hematocrit 29%
115.
Which of the following is the maximum pile allowed for carpet to meet the requirements of the Americans with Disabilities Act?
1. ¼inch
2. ⅜ inch
3. ½inch
4. ⅝ inch 116.
Which of the following activities MUST be performed by a licensed physical therapist?
1. Implement components of patient interventions
2. Modification of the plan of care
3. Make modifications to patient interventions
4. Document progress made by the patient
117.
Which of the following BEST describes an attribute of managed care (such as a health maintenance organization)?
Copyright PT Final Exam 43 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
1. Providers share the financial risk
2. Provides enrollees with freedom of choice
3. Minimal emphasis on health promotion
4. Limited internal cost controls
118.
According to Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, which of the following is the UPPERMOST level of self-actualization?
1. Affiliative needs
2. Physiological needs
3. Esteem needs
4. Psychosocial needs
119.
During which stage of development does a child begin standing briefly without support?
1. 8-9 months
2. 10-11 months
3. 12-15 months
4. 16-24 months
120.
According to the Glasgow Coma Scale, which of the following scores would be MOST indicative of a mild brain injury?
1. Less than 4
2. 5 to 8 3. 9 to 12 4. 13 to 15
121.
A patient presents with an incomplete spinal cord lesion after sustaining a cervical hyperextension injury in a motor vehicle accident. Motor loss that is greater in the upper
Copyright PT Final Exam 44 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Extremities than the lower extremities, with very limited sensory impairments. Which type of spinal cord injury is MOST likely present?
1. Brown-Sequard’s Syndrome
2. Posterior Cord Syndrome
3. Cauda Equina Syndrome
4. Central Cord Syndrome
122.
A patient who has severe swelling of the right lower extremity presents to the clinic with a dehiscence wound on the lateral shin. Which of the following BEST describes a dehiscence type wound?
1. An injury that has a deep hematoma of the underlying tissue, usually caused by trauma.
2. Irregularly bordered wound, typically caused by blunttrauma.
3. A shallow wound with ulceration in a circular pattern, typically caused by prolonged pressure.
4. An injury in which a wound ruptures along a surgical suture, typically from trauma to the wound.
123.
A patient is in the intensive care unit following a motor vehicle accident. While treating the patient, a physical therapist notes that the patient appears unusually lethargic and complains of a headache. Upon reading the most recent lab results, the therapist notes that the patient has hyperalkemia and an increase in creatinine levels. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Acute prostatitis
2. Acute renal failure
3. Urinary tract infection
4. Hematuria
124.
A patient has weakness, low blood pressure, hyperpigmentation of the skin, and decreased amounts of cortisol and aldosterone. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
Copyright PT Final Exam 45 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
1. Conn’s Syndrome
2. Cushing’s Syndrome
3. Addison’s Disease
4. Graves Disease
125.
A patient being treated by a physical therapist has peripheral artery disease. Which of the following values would be MOST indicative of this condition?
1. Ankle-Brachial Index greater than 1.00
2. Ankle-Brachial Index less than 0.90
3. Blood pH lower than 7.35
4. Blood pH greater than 7.45 126.
Which of the following heart sounds is MOST indicative of closure of the mitral valve?
1. S1
2. S2
3. S3
4. S4
127.
A physical therapist is treating a patient for hip pain and wishes to position the iliofemoral joint in close packed position. Which of the following BEST describes this position?
1. Full extension and medial rotation
2. 30 degrees of flexion, full medial rotation
3. 30 degrees of flexion,30 degrees of abduction, slight external rotation
4. Full Flexion and external rotation
128.
Copyright PT Final Exam 46 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A physical therapist is treating a patient who has suffered a stroke using primarily postural control activities, movement sequencing, and key therapeutic handling techniques. Which of the following BEST describes the treatment model being used?
1. Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation
2. Neuro-developmental treatment
3. Rood’s sensorimotor learning
4. Hierarchical reflex theory
129.
A patient who is recovering from a traumatic brain injury following a motor vehicle accident is exhibiting signs of bizarre behavior that is nonpurposeful and incoherent. The patient is uncooperative and displays a short and selective attention span. Which level on the Rancho Los Amigos cognitive functioning scale BEST describes the state of this patient?
1. Level III
2. Level IV
3. Level V
4. Level VI
130.
A patient with myasthenia gravis is being treated for weakness and difficulty walking. Which of the following BEST describes the character of the disorder?
1. Lower motor neuron disease
2. Upper motor neuron disease
3. Bulbar palsy
4. Pseudobulbar palsy 131.
When taking goniometric measurements of medial rotation of the shoulder, where should the moveable arm of the goniometer be aligned?
1. Parallel with the humerus toward the coracoidprocess.
2. Parallel with the humerus toward the acromionprocess.
Copyright PT Final Exam 47 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
3. Parallel to the ulna toward the ulnar styloidprocess.
4. Parallel to the radius toward the 2ndmetacarpal.
132.
A physical therapist is examining a patient for signs of carpal tunnel syndrome. Which of the following is the appropriate posture for performing the Phalen Test?
1. Seated, elbows in full extension
2. Seated, elbows in full extension
3. Seated, wrists in full flexion
4. Seated, wrists in full extension
133.
A physical therapist is examining a patient’s shoulder flexion passive range of motion. Which of the following should occur first during the goniometric measurement?
1. Align the goniometer
2. Locate via palpation the appropriate anatomical landmarks
3. Read and record the measurement after moving the distalsegment
4. Make a clinical estimate of the range ofmotion
134.
With neurologic testing, a patient is having difficulty sensing vibratory stimuli. Which of the following joint receptors is MOST likely affected?
1. Pacinian corpuscles
2. Golgi-Mazzoni corpuscles
3. Ruffini endings
4. Free nerve endings
135.
Copyright PT Final Exam 48 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A physical therapist is mobilizing a patient’s glenohumeral joint to improve passive range of motion. The therapist provides a large amplitude oscillation to the limits of available motion. Which of the following grades of mobilization is being provided?
1. Grade II
2. Grade III
3. Grade IV
4. Grade V
136.
Which of the following would align with a plumb line in proper postural alignment?
1. Anterior to the coronal suture
2. Posterior to the lateralmalleolus
3. Center of the iliofemoral joint
4. Vertebral bodies of the lumbar spine
137.
A patient with an above knee prosthetic limb is displaying lateral trunk bending toward the involved lower extremity while ambulating. Which of the following would be the MOST likely cause of this gait abnormality?
1. Socket is too small
2. Prosthetic limb is too long
3. Poor suspension
4. Medial wall too high
138.
A physical therapist is testing reflexes in the upper extremity. Which of the following spinal nerve roots is BEST tested with the brachioradialis reflex?
1. C4
2. C5
3. C6
4. C7
Copyright PT Final Exam 49 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
139.
A patient is experiencing numbness and tingling along the S1 nerve root dermatome. Which of the following BEST describes the innervation area of this dermatome?
1. Lateral aspect of the calcaneus
2. Anterior and medial thigh
3. Dorsum of the foot
4. Medialmalleolus
140.
A patient has suffered a stroke that is affecting the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland. Which of the following regions of the brain was MOST affected?
1. Telencephalon
2. Mesencephalon
3. Metencephalon
4. Diencephalon 141.
Which of the following structures will lead to ipsilateral impairments when damaged?
1. Anterior corticospinal tract
2. Parietal lobe
3. Cerebellar lobe
4. Spinothalamic tract
142.
A physical therapist is evaluating the soundness of Cranial Nerve XI. How would the therapist position the patient to best evaluate this nerve?
Copyright PT Final Exam 50 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
1. Prone
2. Supine
3. Sidelying
4. Sitting
143.
A patient in the intensive care unit is receiving treatment for heart failure. Which of the following characteristics is MOST indicative of left-sided heart failure?
1. Dyspnea
2. Anasarca
3. Ascites
4. Hepatomegaly
144.
A patient has just received the results of a recent blood test. Which of the following blood chemistry values would be the cause for greatest concern?
1. Triglycerides 110mg/dL
2. Total cholesterol 120 mg/dL
3. HDL cholesterol 30mg/dL
4. LDL cholesterol 90mg/dL
145.
During an exercise stress test, a patient begins to display large, irregular ECG signals that are turbulent and asynchronous. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Premature ventricular contraction
2. Ventricular fibrillation
3. Ventricular tachycardia
4. Ventricular asystole
146.
Copyright PT Final Exam 51 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A research article describes the mildly increased risk of heart disease for individuals exposed to a particular pharmacological agent compared to a control group. What would the expected odds ratio be for the study group?
1. 1.1
2. 1.0
3. 0.9
4. 0.05
147.
Which of the following treatment parameters would be MOST appropriate for a patient receiving intermittent lumbar traction for a diagnosis of multifidus muscle spasms?
1. 30 minutes, 10% body weight traction
2. 30 minutes, 25% body weight traction force
3. 30 minutes, 50% body weight traction force
4. 30 minutes, 75% body weight traction force
148.
A patient with a complete C5 spinal cord injury is preparing to perform therapeutic exercises on the floor. Which of the following lifts would be MOST appropriate to use to transfer the patient to the floor?
1. Slide board transfer
2. Dependent squat pivot lift
3. Hoyer lift
4. Two person lift
149.
After sustaining a large superficial partial-thickness burn wound, a patient seeks wound care from a physical therapist. What would be the MOST accurate estimation of wound healing time?
1. 1-3 days
2. 2-5 days
3. 6-20 days 4. 15-30 days
150.
A physical therapist is examining a patient with shoulder pain that has gradually worsened over the past month. The therapist suspects that the patient has adhesive capsulitis. Which of the following end-feels is MOST likely present with this diagnosis?
1. Hard
2. Soft
3. Empty
4. Firm 151.
A patient is being evaluated by a physical therapist for a possible sprain of the anterior talofibular ligament. Which of the following special tests will BEST confirm this diagnosis?
1. Talar tilt test
2. Anterior drawer test
3. Ottowa 2-step test
4. Thompson Test
152.
A patient is asked to flex their shoulder to 90 degrees with the forearm in full supination. The examiner places resistance downward against the flexed arm. Which structure BEST represents what the examiner testing?
1. Acromioclavicular joint pathology
52
Copyright PT Final Exam http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Copyright PT Final Exam 53 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
2. Rotator cuff pathology
3. Anterior deltoid pathology
4. Biceps tendon pathology
153.
A patient has just undergone a procedure to remove an air pocket from the lung that has resulted from several years of COPD. What is the term for this type of procedure?
1. Lobectomy
2. Pneumonectomy
3. Sleeve lobectomy
4. Bullectomy
154.
A patient with cystic fibrosis is receiving segmental breathing treatment. Which of the following BEST describes this treatment?
1. Instruct the patient to breathe in deeply followed by breathing out through puckered lips.
2. Have the patient exhale completely, and then steadily inhale through an incentive spirometer.
3. Have the patient inhale deeply, and then assist exhalation with firm pressure appliedto the chest wall.
4. Instruct the patient to breathe with the diaphragm by using tactile cues to inhibit accessory muscles and facilitate thediaphragm.
155.
Copyright PT Final Exam 54 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A physical therapist is evaluating a patient for general deconditioning when the patient reports that he requires a Ventolin (albuterol) inhaler. Which of the following BEST describes the effects of the inhaler?
1. Decrease mucus secretion viscosity.
2. Block the effects of histamine and decreasecongestion.
3. Stabilize mast-cells and reduce inflammatorybronchoconstriction.
4. Relieve bronchospasm and cause smooth musclerelaxation.
156.
An elderly patient with severe dementia in a skilled nursing facility is being evaluated by a physical therapist. Which of the following activities will be MOST important in creating a treatment plan?
1. Gait training with the focus on transfers.
2. General strengthening and balance activities.
3. Progressive resistance training for the major musclegroups.
4. Focus on the use of an assistive device for all gaitactivities.
157.
A patient who has suffered a stroke is having difficulty walking due to an extensor synergy in the lower extremity. Which of the following will be MOST beneficial initial intervention to improve the patient’s ability to walk?
1. Fit the patient with an ankle-foot orthosis.
2. Begin training with a single Lofstrand crutch to maintainbalance.
3. Practice moving the patient out of the synergy pattern to assist in limbadvancement.
4. Begin weight shifting exercises to encourage weight-bearing through the involved lower extremity.
158.
Copyright PT Final Exam 55 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A patient with schizophrenia is receiving physical therapy treatment for a rotator cuff injury sustained from a recent fall. Which of the following will be the MOST important consideration in treating this individual?
1. Begin a structured routine with little variation in a predictableenvironment.
2. Assure the patient that he is safe in therapy and avoid groupsettings.
3. Begin the patient with several low intensity exercises that increase heart rate.
4. Remain calm and speak softly throughout the treatmentsession.
159.
A patient is having difficulty raising her arm over her head. The physical therapist hypothesizes that the scapulohumeral rhythm is impaired. Which of the following BEST represents the normal combination of movements that will result in full shoulder flexion?
1. Glenohumeral flexion 80°; scapulothoracic upward rotation80°.
2. Glenohumeral flexion 100°; scapulothoracic upward rotation60°.
3. Glenohumeral flexion 100°; scapulothoracic upward rotation80°.
4. Glenohumeral flexion 120°; scapulothoracic upward rotation60°.
160.
A patient is struggling to regain full motion in the thoracic spine following a motor vehicle accident, and appears to have a capsular restriction. Which of the following BEST represents the capsular pattern for the thoracic spine (listed in order of most limited to least limited)?
1. Equal lateral flexion and rotation, extension
2. Equal flexion and extension, side flexion
3. Equal flexion and rotation, extension
4. Equal extension and side flexion, rotation 161.
Copyright PT Final Exam 56 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A patient is receiving physical therapy treatment for weakness and difficulty transferring following an above-knee amputation approximately 4 weeks ago. Which of the following will be the MOST important initial treatment to improve gait mechanics?
1. Have the stump fitted for a customprosthesis
2. Begin performing progressive sidelying hip abductionexercises
3. Perform prone hip extension stretching
4. Initiate progressive well-leg strengthening
162.
A patient in physical therapy wishes to document his decrease in body fat. Which of the following methods would be MOST accurate in tracking the changes in percentage of body fat?
1. Body mass index
2. Anthropometry
3. Hydrostatic weighing
4. Bioelectrical ImpedanceAnalysis
163.
A patient with congestive heart failure is having great difficulty with activities of daily living. Which of the following cardiac factors is MOST likely the cause of such difficulty?
1. Preload
2. Afterload
3. Stroke volume
4. Heart rate
164.
Copyright PT Final Exam 57 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A physical therapist is treating a 12-month old child who has been diagnosed with Down Syndrome. The parents report that the child still has not begun to stand or attempt to walk with help, but is able to sit upright without support.Which of the following will be the BEST initial treatment to help the child begin walking?
1. Begin by working on dynamic sitting balance to encourage corecontrol.
2. Initiate simple weight bearing activities, such as unsupported standing or catching aball while standing.
3. Place the child prone over a small ball and encourage the patient to use her legs to turn toward the therapist.
4. Practice crawling activities up/down small steps to progress crawling stabilityin preparation forwalking.
165.
A 5-year old patient with cerebral palsy appears to tire quickly while playing at school. The fatigue affects the lower extremities more than the upper extremities and limits the child’s ability to play games with his cohorts. According to the ICF model created by the World Health Organization, which of the following categories does this child’s fatigue fit under?
1. Body function and structure
2. Disability
3. Participation
4. Personal factors 166.
A patient with a body mass index of 34.9 is being treated for generalized weakness and difficulty walking. Which of the following will be MOST important when creating a therapeutic exercise routine for this patient?
1. Use recumbent and low impact drills to minimize jarringforces.
2. Monitor heart rate and blood pressure throughouttreatment.
3. Add both strength and endurance activities to promote weightloss.
Copyright PT Final Exam 58 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Instruct the patient tomaintain a Borg RPE less than 13 during endurance activities.
167.
A patient with type II diabetes is coming to the physical therapy clinic for treatment after a total knee replacement. Which of the following will be most important when treating this individual with therapeutic exercise?
1. Include activities for largemuscle groups to improve glucose absorption.
2. Encourage the patient to eat more than½hour before the therapy session.
3. Add appropriate exercises as tolerated, focusing on kneeextension.
4. Instruct the individual to bring small snacks to eat throughout thesession.
168.
A 79 year old patient is receiving physical therapy for weakness and difficulty walking. Which of the following test results would BEST indicate that the patient is at a significant fall risk?
1. Tinetti Performance Oriented Mobility Assessment Score =24
2. Timed Up and Go test = 21 seconds
3. Berg Balance Scale = 45
4. 6 Minute Walk Test = 530meters
169.
A patient with an adrenal medulla adenoma is being examined by a physical therapist. Which of the following metabolic symptoms would be MOST likely present when assessing the patient’s resting vital signs?
1. Decreased respiration rate and decreased heartrate
2. Decreased respiration rate and increased heart rate
3. Increased respiration rate and increased heart rate
4. Increased respiration rate and decreased heart rate
Copyright PT Final Exam 59 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
170.
A patient is having difficulty achieving full knee extension after arthroscopic surgery. The patient appears to have difficulty with the “screw-home” mechanism. Which of the following BEST describes the action of the screw-home mechanism?
1. The tibial plateau rotates medially during the final 10 degrees ofextension.
2. The tibial plateau rotates medially during the final 20 degrees ofextension.
3. The tibial plateau rotates laterally during the final10 degrees of extension.
4. The tibial plateau rotates laterally during the final 20 degrees of extension.
171.
A patient is being examined for elbow/wrist pain which has been worsening for the last few weeks. The patient reports that he is losing strength in his thumb and is unable to perform a “tip to tip pinch grip” with the involved hand. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome
2. Carpal tunnel syndrome
3. De Quervain’s disease
4. Ulnar impaction syndrome
172.
A physical therapist is evaluating a 65 year old patient who complains of progressive weakness that first began 1 year ago. The patient reports increasing fatigue, diminished muscle mass and generalized muscle pain. MRI and lab tests are negative for irregularities. Which of the following conditions is MOST likely present?
1. Multiple Sclerosis
2. Post-polio syndrome
3. Acute inflammatory demyelinatingpolyneuropathy
4. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Copyright PT Final Exam 60 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
173.
A patient is being examined by a physical therapist and is asked to raise both arms up to 90 degrees abduction, 90 degrees external rotation, and 90 degrees elbow flexion. The patient is then asked to open and closed the hands for 3 minutes. Which of the following special tests is being performed?
1. Adson’sManeuver
2. Roos Test
3. Wright Test
4. Cozen’s Test
174.
A 12 year old boy with spina bifida occulta is receiving physical therapy for bilateral leg weakness and difficulty walking. Which of the following will be the MOST important consideration when developing a plan of care for this patient?
1. Train the patient in the use of appropriate adaptiveequipment.
2. Provide training to upper body muscles to promoteindependence.
3. Provide exercises to increase tone in the legs and become as independent aspossible.
4. Train the patient to use crutches to allow for more active participation in socially appropriate activities.
175.
A physical therapist is treating a patient who has had a suffered from a major stroke has increased sympathetic nervous activity. Which of the following signs will be MOST likely present?
1. Constricted pupil size
2. Increased peristalsis
3. Decreased renin production
Copyright PT Final Exam 61 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. Dilated bronchioles
176.
A patient is having difficulty maintaining his balance during static standing, especially in crowded environments. Which of the following balance strategies is the most active during this activity?
1. Ankle strategy
2. Hip strategy
3. Suspensory strategy
4. Stepping strategy
177.
When using the parallel bars for gait training, what is the appropriate adjustment of height that will optimize stability and security for the patient?
1. A height that allows for elbow flexion of approximately 0degrees.
2. A height that allows for elbow flexion of approximately 10degrees.
3. A height that allows for elbow flexion of approximately 15degrees.
4. A height that allows for elbow flexion of approximately 20degrees.
178.
Which of the following is the BEST reason for pregnant women to avoid high intensity exercise?
1. Decreased cardiac output
2. Decreased oxygen availability
3. Morphological changes to the abdominalmuscles
4. Preferential blood flow to workingmuscles
179.
Copyright PT Final Exam 62 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Which of the following is the greatest implication to physical therapy due to the long-term use of Lithobid (lithium) for the treatment of a bipolar disorder?
1. Intense mood swings
2. Vertigo
3. Osteoporosis
4. Myolysis
180.
When treating a patient with Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), which of the following is the MOST important consideration?
1. Thoroughly disinfect all surfaces touched by theindividual.
2. Treat the patient in a private room and avoid contact with otherpatients.
3. Use protective equipment when in contact with bloodproducts.
4. Reduce workloads and use primarily low-impact drills to avoid stress on weight-bearing joints.
181.
A 40 year old female patient receiving treatment in the therapy gym begins to have a great increase in pain in her left arm which she describes as an “intense burning.” The arm also swells, turns slightly blue, and is extremely sensitive. The pain does not subside, despite several days’ rest. Which of the following is the MOST likely source of the pain?
1. Myocardial infarction
2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3. Rheumatoid arthritis
4. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
182.
Copyright PT Final Exam 63 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Which of the following BEST describes a Chopart amputation?
1. A transtibial amputation.
2. Removal of the ankle joint just proximal themalleoli.
3. Amputation of themetatarsals.
4. Disarticulation at the midtarsal joint.
183.
A patient is having difficulty with heel cord tightness while walking. During ambulation, what is the normal range of motion for ankle plantar flexion?
1. 0-5 degrees
2. 0-10 degrees
3. 0-15 degrees
4. 0-20 degrees
184.
According to the Rancho Los Amigos gait terminology, when does terminal swing phase begin?
1. At the point of toe off of the reference foot.
2. When the contralateral tibia is perpendicular to theground.
3. When the reference tibia is perpendicular to theground.
4. At the point of toe off of the contralateral foot.
185.
According to the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, how many days are allowed to Medicare enrollees for post-hospital stays in extended care facilities?
1. 75
2. 100
3. 125
Copyright PT Final Exam 64 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
4. 150
186.
In the daily SOAP note documentation of a physical therapy treatment session, which of the following categories will contain the patient’s complaints?
1. Subjective
2. Objective
3. Assessment
4. Plan
187.
Which of the following cervical spine joints is primarily responsible for the flexion and extension of the cranium that occurs when a person is nodding “yes?”
1. Atlanto-occipital joint
2. Atlanto-axial joint
3. C2-3 zygapophyseal joint
4. C3-4 zygapophyseal joint
188.
A patient reports pain with movement involving the sartorius muscle. Which of the following choices BEST represent the primary actions of the sartorius muscle?
1. Knee extension and hip medial rotation
2. Knee extension and hip lateral rotation
3. Knee flexion and hip medial rotation
4. Knee flexion and hip lateral rotation
189.
Copyright PT Final Exam 65 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
While auscultating a patient’s lungs, the therapist note a harsh, high-pitched wheezing sound emanating from the patient’s upper bronchi during inspiration. Which of the following abnormal breath sounds is MOST likely present?
1. Stridor
2. Wheeze
3. Crackle
4. Rhonchi
190.
According to the American Red Cross, what is the appropriate ratio of chest compressions to rescue breaths for infants during single rescuer cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR)?
1. 15 compressions: 2 breaths
2. 20 compressions: 2 breaths
3. 25 compressions: 2 breaths
4. 30 compressions: 2 breaths
191.
A 15 year old cheerleader reports inability to perform handstands or other aggressive upper extremity activities. Which of the following BEST describes the defining characteristic of glenohumeral multidirectional instability?
1. History of traumatic subluxation
2. Rotator cuff weakness less than 85%of the uninvolved upper extremity
3. Inability to flex shoulder above 100 degrees without symptoms
4. Gross symptomatic instability in more than onedirection
192.
Copyright PT Final Exam 66 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
A patient is being evaluated after a knee injury, and the examiner chooses to use the Reverse Pivot-Shift Test? Which of the following structures is BEST tested with this special test?
1. Anterior Cruciate Ligament
2. Posterior Cruciate Ligament
3. Medial Collateral Ligament
4. Lateral Collateral Ligament
193.
While evaluating a patient with a suspected Morton’s neuroma, which of the following differential diagnoses will be MOST important to rule out before continuing with treatment?
1. Calcaneal bone spur
2. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
3. Anterior talofibular ligament sprain
4. Achilles tendon paratenonitis
194.
While treating a patient who has undergone a medial meniscus strain, the physical therapist wishes to advance the patient to aquatic running. If the water level is even with the patient’s mid-chest, which of the following BEST describes the percentage of body weight loaded through the lower extremities?
1. 10 %
2. 25%
3. 50%
4. 75%
195.
Copyright PT Final Exam 67 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
Which of the following BEST describes the symptoms of anterior compartment syndrome of the lower leg?
1. Exercised-induced shin pain
2. Night pain associated with homoplastic osteoma
3. Acute anterior pain and paresthesia secondary totrauma
4. Exertional pain directly on the tibia secondary to stressfracture
196.
When treating a geriatric patient with osteoporosis, which of the following will be MOST important to include in a treatment plan to improve bone density?
1. Treadmill with high incline
2. Lumbar flexion resistance training
3. Seated rowingmachine
4. Leg press resistance training
197.
After sustaining a traumatic brain injury, a patient presents to physical therapy with symptoms consistent with damage to the amygdala, hippocampus, and thalamic nuclei. Which of the following symptoms will MOST likely be present in this individual?
1. Impaired fine motor skills, including ataxia
2. Disrupted vision, hearing, and sensation to theface/tongue
3. Hemiparesis, with the upper extremity more affected than the lowerextremity
4. Lack of behavior control and memorydifficulties
Copyright PT Final Exam 68 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
198.
A patient receiving physical therapy for a recent shoulder injury demonstrates a 2+/5 manual muscle test for shoulder flexion. Which of the following BEST describes the amount of motion this patient can perform?
1. The patient is able to complete more than ½ of the available range of motion against gravity.
2. The patient is able to complete less than ½ of the available range of motion against gravity.
3. The patient is able to complete the range of motion against gravity against minimal resistance.
4. The patient is able to complete less than ½ of the available range of motion with gravity eliminated.
199.
A physical therapist is examining a patient who is recovering from a motor vehicle accident that injured the left forearm. The patient appears to have damaged the posterior interosseous nerve. Which of the following motions will be MOST impaired?
1. Wrist radial deviation
2. Wrist ulnar deviation
3. Wrist flexion
4. Wrist extension
200.
A patient is recovering from a total knee replacement and reports that he has taken his prescribed OxyContin (oxycodone) 2 hours prior to the session. Which of the following BEST represent the side effects of this type of medication?
Copyright PT Final Exam 69 http://www.ptfinalexam.com
1. Ulcer formation and gastrointestinaldistress
2. Headaches andmigraines
3. Impaired cognitive function
4. Elevated blood pressure
{"name":"Practice Exam", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A patient has retropatellar pain and an MRI finding of softened and fibrillated cartilage. These are characteristics of:, Two weeks ago, a patient fell on an open hand with the wrist extended. Pain is present on palpation of the space between the abductor pollicis longus and the extensor pollicis brevis. The physical therapist should suspect a fracture of which of the following bones?, A patient is unable to perform a standing heel raise with the knee extended. During this attempted movement, the physical therapist observes toe flexion, inversion, and limited movement of the calcaneus. The MOST likely cause of this deviation is:","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/21-831730/2017-09-22-17-56-53.jpg?sz=1200-00000021461000005300"}