DES C_Management (6) Prepared : CHILLY
A 34-year-old man presents with substernal discomfort. The symptoms are worse after meals, particularly a heavy evening meal, and are sometimes associated with hot/sour fluid in the back of the throat and nocturnal awakening. The patient denies difficulty swallowing, pain on swallowing, or weight loss. The symptoms have been present for 6 weeks; the patient has gained 20 lb in the past 2 years. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial approach?
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Coronary angiography
CT scan of the chest
Exercise test with thallium imaging
Therapeutic trial of ranitidine
A 34-year-old obese female returns to the physician's office for a follow-up appointment at 16 weeks gestation. She was diagnosed with gestational diabetes at 12 weeks gestation and since then has been following dietary recommendations. She eats a balanced diabetic diet three times a day and avoids snacks. Her fasting blood sugars for the past two weeks have been in between 120 to 150 mg/dl. Her temperature is 37.0C (98.7F), blood pressure is 130/88 mmHg, pulse is 76/min and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most appropriate therapy for this patient?
Chlorpropamide
Continue dietary therapy
Tolbutamide
Insulin
Exenatide
A 34-year-old primigravid woman at 30 weeks' gestation comes to the physician with regular contractions every 6 minutes. Her prenatal course was significant for type 1 diabetes, which she has had for 10 years. Over the course of 1 hour, she continues to contract, and her cervix advances from closed and long to a fingertip of dilation with some effacement. The patient is started on magnesium sulfate, penicillin, and betamethasone. Which of the following is the most likely side effect from the administration of corticosteroids to this patient?
Maternal infection
Neonatal infection
Neonatal adrenal suppression
Increased maternal insulin requirement
Decreased childhood intelligence
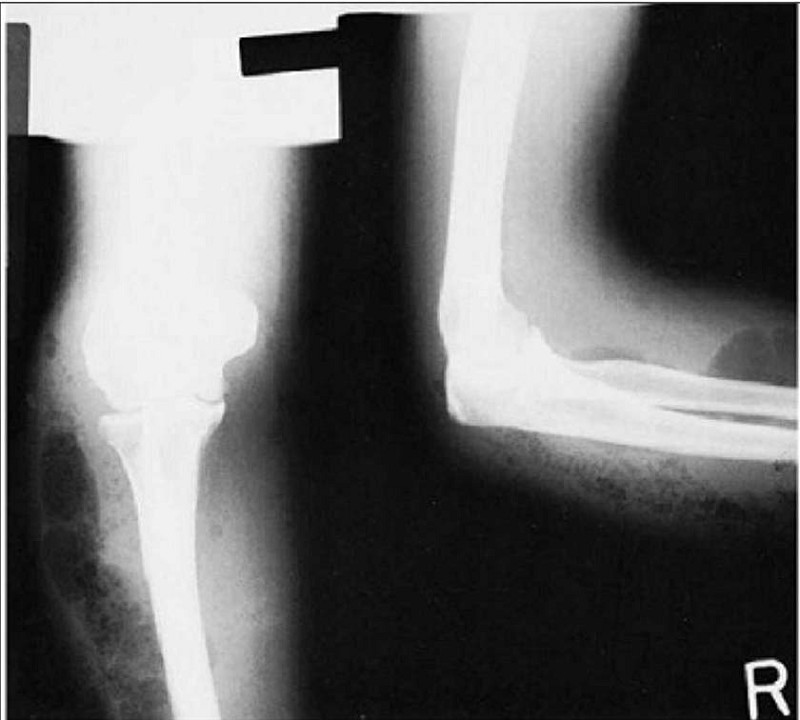
A 34-year-old prostitute with a history of long-term intravenous drug use is admitted with a 48-hour history of pain in her left arm. She is tachycardic to 130 and her systolic blood pressure is 80 mm Hg. Physical examination is remarkable for crepitus surrounding needle track marks in the antecubital space with a serous exudate. The plain x-ray of the arm is shown here. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in her management?
Treatment with penicillin G and close observation
Surgical exploration and debridement
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy
MRI of the arm
CT scan of the arm
A 34-year-old unrestrained male driver is brought to the ER after a motor vehicle accident. His cervical spine is immobilized. He is stuporous. At the scene of the accident, his blood pressure is 70/30 mm Hg and heart rate is 130/min. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdominal wall ecchymosis is present. Abdomen is mildly distended. Bowel sounds are decreased. Neck veins are collapsed. After two liters of intravenous fluids, his blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg. A focused assessment with sonography for trauma shows blood in the peritoneal cavity but no obvious solid organ injury. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
X-ray films of the abdomen and pelvis
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
CT scan of the abdomen
Laparoscopy
Laparotomy
A 34-year-old woman comes the physician because of lower abdominal cramping. The cramping started 2 days ago. Examination is unremarkable except for a pelvic examination that reveals a 10-week sized uterus. Urine hCG is positive, and pelvic ultrasound reveals a 10-week intrauterine pregnancy with a fetal heart rate of 160. The patient states that she is not sure whether to keep the pregnancy. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Tell the patient that she is likely to have a miscarriage
Schedule a termination of pregnancy
Notify the patient's partner
Counsel the patient or refer to an appropriate counselor
Notify the patient's parents
A 34-year-old woman comes to the ER because of right lower leg swelling, redness, and pain. She has no significant past medical history and does not use any medications. Her mother has a history of pulmonary embolism. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 80/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg. Examination shows tenderness to palpation in the right calf. Compressive ultrasonogram shows a deep vein thrombosis of the right leg. Further evaluation reveals an elevated plasma homocysteine level. She is started on heparin and warfarin therapy. What other additional therapy is indicated in this patient?
Clopidogrel
Pyridoxine
Simvastatin
Streptokinase
Vitamin E
A 34-year-old woman comes to the physician for infertility evaluation. Her cycles have been irregular for the past 12 months and she has had no periods for the past 3 months. Before that time, her cycles were quite regular. She also has hot flashes, dyspareunia, and mood disturbances. She has been married for 6 years and has a 3-year-old daughter. The patient has a history of Hashimoto's thyroiditis and is on thyroid replacement therapy. She smokes a pack of cigarettes a day. Both her father and mother have type 2 diabetes mellitus. Vital signs are normal. Pelvic examination reveals atrophic vaginal mucosa. Serum FSH is markedly elevated, serum prolactin is normal, and pregnancy test is negative. Serum TSH is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for her infertility?
In vitro fertilization with donor oocyte
Clomiphene citrate
Progesterone supplement
Metformin
GnRH agonist
A 34-year-old woman complains bitterly of heartburn. Physical examination reveals healing lesions of the fingertips that she says were small ulcers, and there are small areas of telangiectasias on her face. Esophageal manometry reveals a decrease in the expected amplitude of smooth muscle contraction. Lower esophageal sphincter tone is subnormal, but relaxes normally with swallowing. Which of the following statements regarding this condition is most likely correct?
Characterized by death secondary to a renal crisis
Characterized by a poor prognosis
Usually more frequent in men
Predominantly treated symptomatically
Characterized by systemic signs of inflammation
A 34-year-old woman is admitted for septic shock secondary to a urinary tract infection. In the intensive care unit, she receives dopamine, intravenous fluids and antibiotics and requires central line placement for venous access. Which of the following is the most important safeguard to prevent respiratory and cardiac complications following central line placement?
Chest x-ray confirmation of catheter tip location after placement
Cardiac ultrasound after placement
Free aspiration of blood after final catheter placement
Insertion via right jugular vein
ECG monitoring
A 34-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after being hit by a motorbike. Examination shows a 3 cm x 2 cm laceration on the left calf. The wound is dirty and the underlying fascia can be seen. She has had four doses of tetanus toxoid in her life; the last dose was 7-years ago. In addition to wound debridement and surgical management, which of the following is the most appropriate course of action to protect her from developing tetanus?
Observe the patient and give her tetanus immunoglobulin and tetanus toxoid if she develops any signs of tetanus
Give her both tetanus immunoglobulin and tetanus toxoid
Give her tetanus immunoglobulin
Give her tetanus toxoid
Nothing more is required as the patient is already vaccinated
A 34-year-old woman is referred by an OB-GYN colleague for the onset of fatigue and dyspnea on exertion 1 month after her second vaginal delivery. Physical examination reveals a laterally displaced PMI, elevated jugular venous pressure and 2+ pitting lower extremity edema. Echocardiogram shows systolic dysfun
This condition will require endomyocardial biopsy for diagnosis
This condition will require a different therapeutic approach than the typical dilated cardiomyopathy
The condition is idiosyncratic; the risk of recurrence with a future pregnancy is no greater than average
About half of similar patients will recover completely
This disease may occur unexpectedly years after pregnancy and delivery
A 34-year-old woman presents to the physician's office for infertility evaluation. Her cycles have been irregular for the past 12 months and she hasn't had any periods for the past 3 months. Previously, her cycles were quite regular. She also has hot flashes, dyspareunia and mood disturbances. She has been married for 6 years and has a three-year-old daughter. She has a history of Hashimoto thyroiditis and is on thyroid replacement therapy. She smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. Vital signs are normal. Pelvic examination reveals atrophic vaginal mucosa. Serum FSH is markedly elevated, and serum prolactin is normal. Serum TSH is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for her infertility?
Clomiphene citrate
In vitro fertilization
Progesterone supplement
Metformin
GnRH agonist
A 34-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of several months of chest pain. She says that the pain is left-sided, does not change with deep inspiration, and typically lasts several hours. The pain has no relation to physical activity, but worsens with emotional stress. The patient has no significant family history, and does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. She takes no medications and has no drug allergies. On exam, her blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg and her heart rate is 78/min. ECG is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in her management?
Lower extremity venous ultrasonography
Chest X-ray
Reassurance
Transthoracic echocardiography
Stress ECG testing
A 34-year-old woman with no PMH presents to the office for intermittent left lower quadrant pain, nonradiating for the past 24 hours. She had her menstruation 1.5 weeks ago. She has no nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation. She denies dysuria, urinary urgency, and urinary frequency. BP, 122/84 mm Hg; P, 90; R, 13 breaths/min; T, 98.7°F. ROS: Denies fever and chills; AS per RPI. PE: Abd: soft, nondistended, left lower quadrant tenderness is present on superficial and deep palpation. The pain radiates toward the midline. Which of the following is the next step in the management of this patient?
BHCG
Abdominal CT
Morphine administration
CBC
Pelvic US
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 16 weeks' gestation comes to the physician concerned that she may have been exposed to an infectious disease. Yesterday, she and her 5-year-old son spent a day at the beach with one of his classmates. This morning, the classmate was sent home from school with a fever and rash that the teacher thought, were suspicious for chickenpox. The patient is unsure whether she had chickenpox as a child. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 16/min. Her examination is unremarkable. An inquiry made by the physician confirms that the classmate has chickenpox. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Administer IV acyclovir
Administer varicella vaccine
Administer oral acyclovir
Wait to see whether a rash develops
Check an IgG varicella serology
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 38 weeks gestation presents to the labor and delivery ward complaining of headache. She has no contractions. Her prenatal course was unremarkable until she noted the onset of swelling in her face, hands, and feet this week. Her obstetric history is significant for two normal spontaneous vaginal deliveries. She has no significant past medical or surgical history. Her temperature is 37 C (98.6 F), blood pressure is 160/92 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 16/min. Examination reveals 3+ patellar reflexes bilaterally. A cervical examination reveals that her cervix is 3 cm dilated and 50% effaced and soft, and that the fetus is at 0 station and vertex. The fetal heart rate has a baseline of 140/min and is reactive. The results from a 24-hour urine collection show 5200 mg of protein (normal < 300 mg/24 hours). The patient is given magnesium sulfate intravenously for seizure prophylaxis. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Intramuscular glucocorticoids
Subcutaneous terbutaline
Cesarean section
IV oxytocin
Expectant management
A 34-year-old woman, gravida 4, para 3, at 32 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding. Her prenatal course, prenatal tests and fetal growth have been normal. Prenatal ultrasound at the 12th week showed an intrauterine gestation consistent with dates. Her temperature is 37.0C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 90/70 mm of Hg, pulse is 98/min and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination shows continuous bright red vaginal bleeding. Ultrasonogram in the emergency department shows complete placenta previa. Fetal heart tracing shows repetitive late decelerations. The patient's vital signs are stabilized with fluids, but the bleeding continues. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Continue expectant management until the bleeding stops
Administer corticosteroids and perform elective surgery later
Immediate induction of labor
Emergency cesarean section
Forceps delivery
A 35-year old male presents to your office complaining of nocturnal wheezing and chest tightness for the past three months. He has also noticed new hoarseness, particularly in the morning. He has no history of bronchial asthma, hypertension or diabetes. He is a non-smoker but occasionally drinks alcohol. On examination, he is an obese male in no acute distress. His pulse is 84/min, blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, and respirations are 16/min. His chest is clear to auscultation and percussion. Laryngoscopy reveals a red and inflamed posterior pharynx and larynx. Which of the following pharmacotherapies would be most helpful for this patient?
Bedtime albuterol inhaler
Oral omeprazole
Oral prednisone
Oral theophylline
Bedtime fluticasone inhaler
A 34-year-old woman with breast cancer presents to her physician complaining of increased weakness, lower back pain, and urinary incontinence. She was diagnosed with breast cancer 2 years ago and is undergoing radiation and chemotherapy. Her back pain developed 2 days ago. Physical examination shows lower extremity weakness and hyporeflexia. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in this patient's care?
Administer narcotics for pain relief
Perform a lumbar puncture
Administer high-dose steroids
Obtain an emergency spinal MRI
Obtain a neurologic consultation
A 35-year-old Caucasian female is hospitalized with swelling and tenderness of her right calf. Deep venous thrombosis is diagnosed through imaging studies, and the appropriate therapy is initiated. Three days later, she complains of right arm pain. Physical examination reveals a cold right upper extremity with no palpable peripheral pulse. Her laboratory values are listed below: Hematocrit 42%, WBC count 8,500/mm3, Platelets 76,000/mm3, PT 13 sec, aPTT 63 sec. Which of the following drugs was most likely used to treat this patient's deep venous thrombosis?
Aspirin
Unfractionated heparin
Warfarin
Danaparoid
Enoxaparin
A 35-year-old Caucasian male with a chronic history of paranoid schizophrenia presents to the mental health clinic. He strongly believes that his wife recently stole his pill bottle of risperidone, which he feels caused him to start experiencing more frequent and intense auditory hallucinations. He says that the "voices" tell him to kill his wife because she cannot be trusted. He admits to having homicidal thoughts about his wife but denies any specific plan for harming her. He requests a refill of his risperidone. What is the most appropriate next step?
Increase his dose of risperidone
Call the patient's wife immediately before filling the risperidone prescription
Admit the patient to the psychiatric ward
Refill his prescription of risperidone without calling his wife as he does not have a plan to hurt her
Refill his prescription of risperidone and call his wife after he leaves
A 35-year-old female complains of nipple discharge. The discharge is from both breasts, brown in color and occurs intermittently. She has two children who are 5 and 8 years old. She has not been recently pregnant. Her last menstrual period was one week ago. She describes no other symptoms. Examination shows normal breasts without palpable lumps or nipple abnormalities. Brownish discharge is expressed from the nipples, and it is guaiac negative. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Serum prolactin and TSH levels
Mammogram
Cytologic examination
Ultrasonogram
Surgical evaluation
A 35-year-old female presents to the emergency department with a 30-minute history of severe headache, palpitations, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. She had similar episodes twice during the last month, but those were not so severe and resolved spontaneously in 30-40 minutes. She visited a doctor recently, and hypertension with elevated urinary vanillylmandelic acid level was diagnosed. She is not taking any medications, and denies substance abuse. Her blood pressure is 200/130 mmHg and heart rate is 130/min. She appears frightened. Physical examination reveals hand tremors and excessive sweating. Slow intravenous infusion of propranolol is started while waiting for the routine labs. What is the most probable reaction to the treatment given to the patient?
Blood pressure will rapidly increase
Blood pressure will rapidly decrease
Heart rate will not change
Heart rate will increase
Blood pressure will slowly decrease
A 35-year-old female presents to your office complaining of knee pain. She has a long history of rheumatoid arthritis affecting her hand and knee joints. The stiffness and pain has persisted over the last several months and has responded poorly to NSAIDs. Over the last two days the pain in her right knee has been interfering with her sleep. She had an episode of chills this morning. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, temperature is 38.7°C (102°F) and respiratory rate is 18/min. Physical examination reveals swelling in the joints of her hand and wrist. The right knee is red and swollen; active and passive range of motion at the right knee is limited due to pain. This patient's current condition can be best treated with which of the following?
Colchicine
Antibiotics
Antimetabolites
Corticosteroids
Anti-cytokine agents
A 35-year-old G1 PO woman at 35 weeks gestation by last menstrual period and confirmed by a first trimester ultrasound comes to the hospital because of leakage of fluid one hour ago. She received her prenatal care at an outside hospital and the records are not available. She reports no other complications with this pregnancy thus far. She reports no medical problems, takes no daily medications other than a prenatal vitamin, and has no allergies to medications. She is examined and preterm premature rupture of membranes is confirmed by a positive nitrazine test, positive pooling test, and a positive ferning test. She is 2 cm dilated, 50% effaced, and at -2 station. She is admitted to the hospital. Transabdominal ultrasound confirms that the fetus is in a vertex presentation, and the amniotic fluid index is decreased at 3 cm. Fetal heart rate and contraction monitoring is started, and occasional uterine contractions are noted on the monitor. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Amnio dye test to confirm rupture of membranes
Penicillin prophylaxis
Betamethasone IM
Urgent cesarean section
Tocolysis
A 35-year-old G3P3 presents to your office 3 weeks after an uncomplicated vaginal delivery. She has been successfully breast-feeding. She complains of chills and a fever to 38.3C (101F) at home. She states that she feels like she has flu, but denies any sick contacts. She has no medical problems or prior surgeries. The patient denies any medicine allergies. On examination she has a low-grade temperature of 38C (100.4F) and generally appears in no distress. Head, ear, throat, lung, cardiac, abdominal, and pelvic examinations are within normal limits. A triangular area of erythema is located in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast. The area is tender to palpation. No masses are felt and no axillary lymphadenopathy is noted. Which of the following is the best option for treatment of this patient?
Antipyretic for symptomatic relief
Admission to the hospital for intravenous antibiotics
Oral dicloxacillin for 7 to 10 days
Incision and drainage
Oral erythromycin for 7 to 10 days
A 35-year-old G3P3 with a Pap smear showing high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion of the cervix (CIN III) has an inadequate colposcopy. Cone biopsy of the cervix shows squamous cell cancer that has invaded only 1 mm beyond the basement membrane. There are no confluent tongues of tumor, and there is no evidence of lymphatic or vascular invasion. The margins of the cone biopsy specimen are free of disease. The patient above now asks you for your advice on how to treat her cervical disease. Your best recommendation is for the patient to undergo which of the following?
Simple hysterectomy with pelvic lymphadenectomy
Radical hysterectomy
Implantation of radioactive cesium into the cervical canal
Simple hysterectomy
Treatment with external beam radiation
A 35-year-old G3P3 woman has been experiencing bilateral breast pain for the past year. Breast examination and mammography are normal. Conservative measures have failed. Which of the following medications is most likely to bring relief?
Clomiphene
Medroxyprogesterone
Tamoxifen
Danazol
Hydrochlorothiazide
A 35-year-old G4P4 obese woman is referred to her gynecology clinic by her primary care physician for heavy menstruation and irregular cycles. She has noticed these symptoms for several months. She reports being a “late bloomer,” with onset of menses at age 13 years. She is sexually active and monogamous with her partner of 2 years. She is taking oral contraceptive pills and has a 5-year smoking history. An endometrial biopsy is read as “endometrial hyperplasia, cannot rule out intraepithelial carcinoma.” β-Human chorionic gonadotropin testing is negative. Which of the following most likely contributed to this abnormality?
Body habitus
Sexual activity
Smoking history
Late menarche
Multiparity
A 35-year-old Hispanic male comes to the office because of excruciating pain during defecation for the past week. The pain is so severe that he avoids using the toilet. He also adds that he has noticed bright red blood in his stool. The caliber of his stool has not changed. His past medical history is significant for chronic constipation. Rectal examination shows a posterior mucosal tear of the anus. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Lateral sphincterotomy
Gradual dilatation of the sphincter
Antibiotics
Local anesthetic and stool softeners
Colonoscopy
A 35-year-old HIV-positive male comes to the physician's office because of pain on swallowing and substernal burning for the last 3 days. Examination of the oral cavity is unremarkable. Lungs are clear to auscultation and percussion. His current medications include zidovudine, didanosine, indinavir, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and azithromycin. His last CD4 count is 40cells/microl. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Oral Fluconazole
Oral Acyclovir
Oral Ganciclovir
Oral Famotidine
Esophagoscopy with biopsy, cytology and culture
A 35-year-old homeless man presents to the emergency department with chief complaints of a cough and fever. He is intoxicated. He admits to drinking about a fifth of vodka every day and confirms a history of delirium tremens and blackouts. X-ray of the chest is significant for an air-fluid level in the superior segment of the right lower lobe. Which of the following is the most appropriate first-line agent for treating this patient’s condition?
Azithromycin
Piperacillin-tazobactam
Clindamycin
Isoniazid
Moxifloxacin
A 35-year-old male was involved in a motor vehicle injury and suffered serious chest trauma. A chest tube was placed for a hemothorax. 800 cc of blood was evacuated from the chest, and, after ten days, the patient was discharged home. He returns again with a low-grade fever and dyspnea. CT scan reveals a complex loculated effusion with a thick surrounding peel. A chest tube is placed; however, after 24 hours, there is little drainage, and the patient continues to have a low-grade fever. What is the next step in his management?
Pulmonary consult for bronchoscopy
Streptokinase into the chest tube
Place a second chest tube
Increase the dose of IV antibiotics
Surgery
A 35-year-old man falls on an outstretched hand and comes in complaining of wrist pain. He relates that he was not able to break the fall, and that the heel of his hand took the brunt of his full weight as it hit the pavement. On physical examination, he is distinctly tender to palpation over the anatomic snuff box. Anteroposterior and lateral x-rays are negative. Which of the following are the most likely diagnosis and most appropriate next step in management?
Ligamentous injury; Ace bandage and analgesics
No fracture; reassurance
Displaced scaphoid fracture; open reduction and internal fixation
De Quervain tenosynovitis; steroid injections
Carpal navicular fracture; thumb spica cast
A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after suffering a deep laceration from a rusted piece of barbed wire that was hidden in the grass. Examination shows a 6 cm laceration on the lateral leg that is contaminated with dirt and soil. The laceration is bleeding. The patient reports having received a complete set of childhood vaccinations. His last tetanus immunization was at age 23. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Clean the wound, and use antibiotic
Administer tetanus toxoid and immunoglobulin
Administer tetanus toxoid
Administer tetanus immunoglobulin
Clean the wound, no need for vaccination
A 35-year-old man presents to your office with severe back pain. The pain started three days ago when the patient was carrying a heavy pack. The pain radiates to the posterior surface of the right thigh. The straightleg raise test is positive. There is no bladder or bowel incontinence. Pain and temperature perception is preserved in the affected extremity, as well as in the perineal area. Anal reflex is normal. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
Early mobilization and NSAIDs
Surgical decompression
Plain roentgenogram
MRI of the spine
CT scan of the spine
A 35-year-old man presents with right upper quadrant pain, fever, jaundice, and shaking chills. Ultrasound of the abdomen demonstrates gallstones, normal gallbladder wall thickness, and common bile duct of 1.0 cm. The patient is admitted to the hospital and given IV fluids and antibiotics. He continues to be febrile with increasing WBCs. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in this patient’s management?
Emergent operation and decompression of the common bile duct with a T tube
Placement of a cholecystostomy tube
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Open cholecystectomy
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
A 35-year-old man with a history of melanoma status post wide local excision with negative margins and lymph node dissection presents with 2, peripherallylocated pulmonary lesions seen on chest CT scan. Percutaneous biopsy of the lesion is consistent with metastatic melanoma. He has no evidence of recurrence or extrathoracic disease and is in good general health. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
Neoadjuvant radiation therapy followed by pulmonary metastasectomy
Pulmonary metastasectomy followed by radiation therapy
Chemotherapy
Pulmonary metastasectomy
Radiation therapy
A 35-year-old man with new diagnosis of Crohn disease presents with rapidly enlarging painful ulcerations on the lower extremities. Cultures of the lesion are negative, and skin biopsy reveals no evidence of malignancy. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment option?
Saphenous vein stripping and compressive stockings
Systemic steroids and immunosuppressants
Local wound care with silver sulfadiazine
Topical corticosteroids
Surgical debridement of the wound with skin grafting
A 35-year-old previously healthy male develops cough with purulent sputum over several days. On presentation to the emergency room, he is lethargic. Temperature is 39°C, pulse 110, and blood pressure 100/70. He has rales and dullness to percussion at the left base. There is no rash. Flexion of the patient’s neck when supine results in spontaneous flexion of hip and knee. Neurologic examination is otherwise normal. There is no papilledema. A lumbar puncture is performed in the emergency room. The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) shows 8000 leukocytes/μL, 90% of which are polys. Glucose is 30 mg/dL with a peripheral glucose of 80 mg/dL. CSF protein is elevated to 200 mg/dL. A CSF Gram stain shows gram-positive diplococci. Which of the following is the correct treatment option?
Begin high-dose penicillin for meningococcal meningitis
Begin ceftriaxone, vancomycin, and ampicillin to cover both pneumococci and Listeria
Begin ceftriaxone and vancomycin for pneumococcal meningitis
Obtain emergency MRI scan before beginning treatment
Begin acyclovir for herpes simplex encephalitis
A 35-year-old white female presents with pain and stiffness of her wrist and hand joints for the last several months. Her morning stiffness lasts for more than an hour. She also complains of redness and joint swelling. Her past medical history is significant only for a similar episode one year ago. That episode resolved with over the counter ibuprofen. Examination of her joints shows redness, warmth, swelling and tenderness of proximal interphalangeal joints, metacarpophalangeal joints and wrists. X-ray shows periarticular osteopenia and erosions of the proximal interphalangeal and metacarpophalangeal joints. She started taking indomethacin with good relief. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Glucocorticoids
Celecoxib
Azathioprine
Etanercept
Methotrexate
A 35-year-old white male presents with high-grade fever, chills, rigors, malaise, and pain in his right calf for the last 24 hours. His temperature is 39.5°C (103.1°F), pulse is 105/min, blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, and respirations are 15/min. Physical examination shows generalized swelling of the calf with linear streaks of erythema. The lesion is warm, tender, and not very well-demarcated. No pain is felt in the calf when the ankle is dorsiflexed. Scaling is found in the toe webs on the right side, and KOH preparation of these lesions show hyphae. Blood cultures are obtained. CBC shows a WBC count of 14,000 with 6% bands. What is the most appropriate next step in management?
Intravenous crystalline penicillin G
Oral itraconazole
Intravenous nafcillin
Oral dicloxacillin
Oral terbinafine
A 35-year-old woman at 30 weeks’ gestation discovers a lump in her left breast. Examination reveals a 2–3 cm, firm nodule in the upper outer quadrant. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Thermography
Fine-needle aspiration
Breast ultrasound
Application of hot packs
Observation until after delivery
A 35-year-old woman complains of aching all over. She says she sleeps poorly and all her muscles and joints hurt. Her symptoms have progressed over several years. She reports she is desperate because pain and weakness often cause her to drop things. Physical examination shows multiple points of tenderness over the neck, shoulders, elbows, and wrists. There is no joint swelling or deformity. A complete blood count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate are normal. Rheumatoid factor is negative. Which of the following is the best therapeutic option in this patient?
A nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug
Graded aerobic exercise
Weekly methotrexate
Hydroxychloroquine
Prednisone
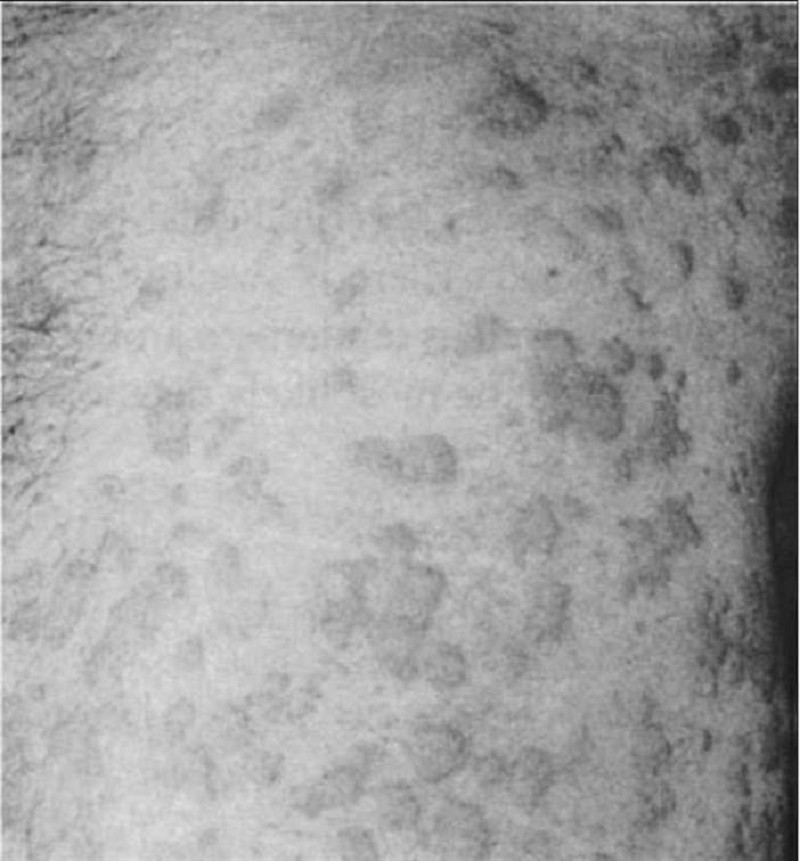
A 35-year-old woman develops an itchy rash over her back, legs, and trunk several hours after swimming in a lake. Erythematous, edematous papules and plaques are noted. The wheals vary in size. There are no mucosal lesions and no swelling of the lips. What is the best first step in management of her symptomatic rash?
Oral antihistamines (H1 blockers)
Aspirin
Oral doxycycline
Subcutaneous epinephrine
Intravenous glucocorticoids
A 35-year-old woman has chronic auditory hallucinations in which she hears her father's voice. His voice said encouraging things to her in the past, but it has recently been scolding her and saying derogatory things about her. The woman is started on risperidone, and she returns two weeks later for a follow-up visit. Although she states that the hallucinations are much better, you notice that she is walking much slower than usual and is not swinging her arms. Also, the patient's facial expressions are rather flat and unchanging, and she admits that her writing has become smaller since starting the medication. Which of the following pharmacologic changes would be most appropriate?
Start propranolol
Start benztropine
Start dantrolene
Start sertraline
Discontinue risperidone and start haloperidol
A 35-year-old woman has dyspnea on exertion, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, cough, and hemoptysis. The symptoms have been slowly progressive for about 5 years. She looks thin and cachectic, and has atrial fibrillation and a low-pitched, rumbling diastolic apical heart murmur. At age 15, she had rheumatic fever. Surgery has been recommended. Which of the following is the most appropriate management?
Prosthetic replacement of the aortic valve
Prosthetic replacement of the mitral valve
Mitral commissurotomy to open a stenotic mitral valve
Closure of the ventricular septal defect
Mitral annuloplasty to tighten an incompetent mitral valve
A 35-year-old woman is being evaluated after having a screening mammography. A 3 x 3 cm speculated mass with coarse calcifications is seen in the upper outer quadrant of her right breast. She has no complaints. She has a history of bilateral reduction mammoplasty for mammary hyperplasia 12 years ago. She has no family history of medical problems. Breast examination shows her right nipple is slightly retracted. A fixed mass is palpated in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast. Ultrasonography of the breast shows a hypo-echoic mass. Multiple core biopsy samples show foamy macrophages and fat globules. Which of the following is the most appropriate course of action?
Segmental excision and axillary node dissection followed by radiation therapy
Radiation therapy of the right breast
Simple mastectomy
Instruction for regular clinical breast examination and follow-up mammography
MRI of the breast
A 35-year-old woman is being evaluated for a breast mass. She had a bilateral reduction mammoplasty for mammary hyperplasia 12 years ago. She has no family history of cancer. Breast examination shows a slightly retracted right nipple. A fixed mass is palpated in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast. Mammogram shows a 3 x 3 cm spiculated mass with coarse calcifications in the upper outer quadrant of the right breast. Ultrasonogram of the breast shows a hypoechoic mass. Multiple core biopsy samples show foamy macrophages and fat globules. Which of the following is the most appropriate course of action?
Radiation therapy of the right breast
Simple mastectomy
Routine follow-up and no intervention
Lumpectomy and axillary node dissection followed by radiation therapy
MRI of the breast
A 35-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after being rescued from a burning building by firefighters. She had a brief tonic-clonic seizure en route to the hospital. Her past medical history is unknown. She is confused and mildly agitated. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 24/min. Her oxygen saturation is 96% on room air. Physical examination shows no burns and her skin color is normal. There are symmetric breath sounds bilaterally with scattered end-expiratory wheezes. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities except some confusion. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Which of the following is the best initial treatment for the patient?
Intravenous phenytoin
100% oxygen with facemask
50% dextrose with thiamine
Intravenous lorazepam
Intravenous naloxone
A 35-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after being rescued from a burning home by firefighters. She is confused, agitated and tachypneic. Her temperature is 37C (98.6F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 130/min and respirations are 24/min. Physical examination shows no burns and her skin color is normal. Auscultation shows normal bilateral air entry with scattered wheezes. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities except some confusion. Abdominal examination shows a soft abdomen; bowel sounds are present. Which of the following is the best immediate treatment for her acute confusional state?
Administration of 100 % oxygen with facemask
Administration of thiamine
Administration of intravenous morphine
Administration of 50% dextrose
Endotracheal intubation with 100% oxygen
A 35-year-old woman is involved in a motor vehicle crash, sustaining a severe pelvic fracture, with disruption of the pelvic ring. In the trauma resuscitation room, she is confused and tachypneic, with a blood pressure of 90 mmHg systolic and a heart rate of 130/min. Laboratory investigations include serum electrolyte analysis, revealing a sodium of 139, a chloride of 103, and a bicarbonate of 14 meq/L. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this acid-based derangement?
This patient has no acid-based abnormality
IV hydrochloric acid
Intubation and hyperventilation
Restoration of blood volume with aggressive IV fluid resuscitation
Administration of sodium bicarbonate to correct the base deficit
A 35-year-old woman is seeing a psychiatrist for treatment of her major depression. After 4 weeks on fluoxetine at 40 mg/day, her psychiatrist decides to try augmentation. Which of the following is the most appropriate medication?
Lithium
Clonazepam
Haloperidol
Sertraline
An MAO inhibitor
A 35-year-old woman presents to the clinic for a discussion on breast cancer risk. Her family history is pertinent for a grandmother who died of breast cancer at age 53, a mother who died of premenopausal breast cancer, and one of three sisters with breast cancer diagnosed at age 42. The sister with breast cancer underwent genetic testing and was found to have a BRCA1 mutation. Subsequently, the 35-year-old woman underwent genetic testing and was found to be a carrier of the same deleterious BRCA1 mutation. Which of the following ranges represents the lifetime risk for breast cancer that should be quoted for this patient?
0–30%
20–50%
50–80%
70–100%
10–40%
A 35-year-old woman presents to the clinic for a discussion on breast cancer risk. Her family history is pertinent for a grandmother who died of breast cancer at age 53, a mother who died of premenopausal breast cancer, and one of three sisters with breast cancer diagnosed at age 42. The sister with breast cancer underwent genetic testing and was found to have a BRCA1 mutation. Subsequently, the 35-year-old woman underwent genetic testing and was found to be a carrier of the same deleterious BRCA1 mutation.For this patient, which of the following strategies represents an accepted management option for her high-risk status?
Bilateral breast irradiation
Chemoprevention with tamoxifen
Prophylactic unilateral mastectomy
Yearly self-breast examinations
Semiannual mammography
A 35-year-old woman presents with a lump in the left breast. Her family history is negative for breast cancer. On examination the mass is rubbery, mobile, and nontender to palpation. There are no overlying skin changes and the axilla is negative for lymphadenopathy. An ultrasound demonstrates a simple 1-cm cyst in the area of the palpable mass in the left breast. Which of the following represents the most appropriate management of this patient?
Mammography and reevaluation of options with new information
Fluoroscopically guided needle localization biopsy
Aspiration of the cyst with cytologic analysis
Reassurance and re-examination
Immediate excisional biopsy
A 35-year-old woman presents with a right breast mass. You perform a thorough history and physical examination as well as a core biopsy of the right breast mass. In which of the following circumstances would a sentinel lymph node biopsy be indicated?
The core biopsy is consistent with ductal carcinoma in situ without comedo necrosis for which the patient desires partial mastectomy only
The core biopsy is consistent with ductal carcinoma and the patient has a positive pregnancy test
The core biopsy is consistent with ductal carcinoma and the patient desires partial mastectomy
The core biopsy is consistent with ductal carcinoma and the patient has palpable axillary lymph nodes
The core biopsy is consistent with ductal carcinoma and the patient has a bone scan suspicious for metastasis
A 35-year-old woman presents with a serum calcium level of 15.2 mg/dL and an elevated parathyroid hormone level. Following correction of the patient’s hypercalcemia with hydration and furosemide, which of the following is the best therapeutic approach?
Avoidance of sunlight, vitamin D, and calcium-containing dairy products
Neck exploration and resection of a parathyroid adenoma
Neck exploration and resection of all 4 parathyroid glands
Radiation treatment to the neck
Administration of steroids
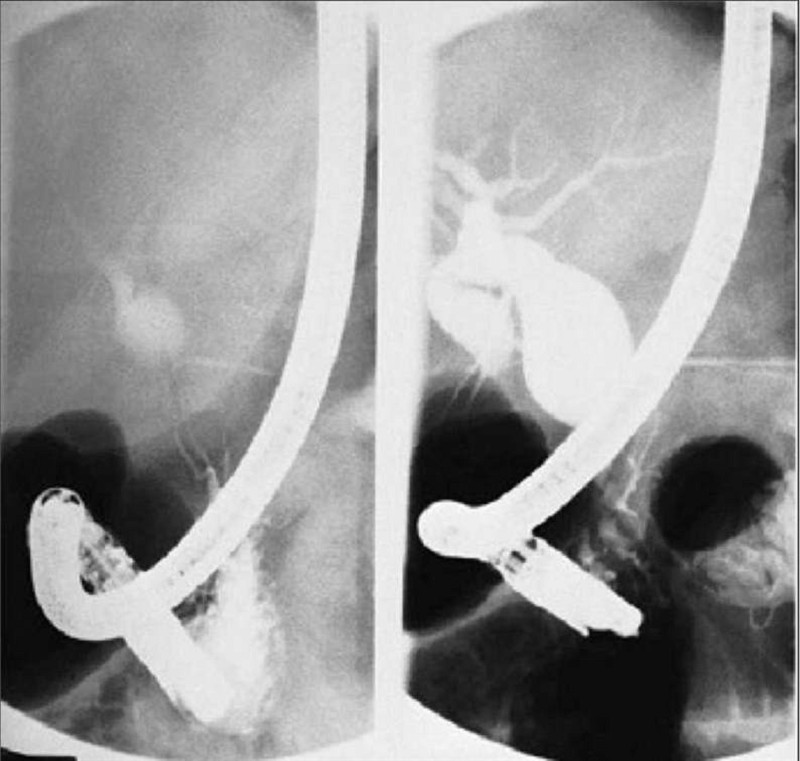
A 35-year-old woman presents with abdominal pain and jaundice. Subsequent ERCP reveals the congenital cystic anomaly of her biliary system illustrated in the film shown here. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage
Liver transplantation
Internal drainage via choledochoduodenostomy
Internal drainage via choledochocystojejunostomy
Cholecystectomy with resection of the extrahepatic biliary tract and Roux-en-Y hepaticojejunostomy
A 35-year-old woman presents with frequent and multiple areas of cutaneous ecchymosis. Workup demonstrates a platelet count of 15,000/μL, evaluation of the bone marrow reveals a normal number of megakaryocytes, and ultrasound examination demonstrates a normal-sized spleen. Based on the exclusion of other causes of thrombocytopenia, she is given a diagnosis of immune (idiopathic) thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP). Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment upon diagnosis?
Referral to surgery for laparoscopic splenectomy
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy
Glucocorticoid therapy
Immediate platelet transfusion to increase platelet counts to greater than 50,000/μL
Expectant management with close follow-up of platelet counts
A 35-year-old woman with a history of previous right thyroidectomy for a benign thyroid nodule now undergoes completion thyroidectomy for a suspicious thyroid mass. Several hours postoperatively, she develops progressive swelling under the incision, stridor, and difficulty breathing. Orotracheal intubation is successful. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
Administration of high-dose steroids and antihistamines
Administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics and debridement of the wound
Wound exploration
Administration of intravenous calcium
Fiberoptic laryngoscopy to rule out bilateral vocal cord paralysis
A 35-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes comes to your office seeking pregnancy advice. Although she is not currently pregnant and has never been pregnant, she and her spouse, are planning to have their first child. She has previously managed her diabetes with diet and exercise. Approximately 4 months ago, however, you started her on metformin, as her fasting blood glucose levels were consistently elevated. Her hemoglobin A1c level at that time was 9%. She has no specific complaints today and her physical examination is unremarkable. A hemoglobin A1c level drawn 1 week before today’s visit is 6.2%. She would like to know which, if any, diabetic medications she can take during her pregnancy. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacologic monotherapy for her?
No medication, continue diet and exercise
Metformin
Acarbose
Glyburide
Insulin
A 35-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 39 weeks' gestation, comes to the labor and delivery ward with contractions. Past obstetric history is significant for two normal spontaneous vaginal deliveries at term. Examination shows the cervix to be 4 centimeters dilated and 50% effaced. The patient is contracting every 4 minutes. Over the next 2 hours the patient progresses to 5-centimeters dilation. An epidural is placed. Artificial rupture of membranes is performed, demonstrating copious clear fluid. 2 hours later the patient is still at 5centimeters dilation and the contractions have spaced out to every 10 minutes. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Forceps-assisted vaginal delivery
Vacuum-assisted vaginal delivery
Expectant management
Intravenous oxytocin
Cesarean delivery
A 35-year-old woman, gravida 4, para 3, at 38 weeks' gestation comes to the labor and delivery ward after a gush of clear fluid from the vagina. After the gush, she has had increasing contractions. Sterile speculum examination shows a pool of clear fluid in the vagina that is nitrazine positive. Cervical examination shows that the patient is 5 cm dilated, with the fetal face presenting in a mentum anterior position. External uterine monitoring shows that the patient is contracting every 2 minutes, and external fetal monitoring shows that the fetal heart rate is in the 140s and reactive. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Oxytocin augmentation
Vacuum delivery
Cesarean section
Forceps delivery
Expectant management
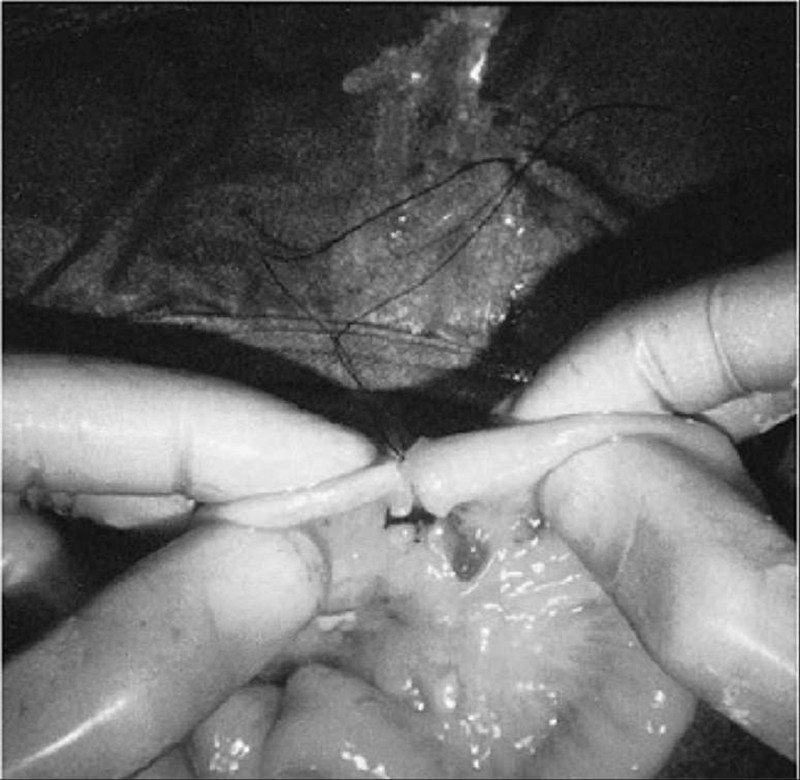
A 36-hour-old infant presents with bilious vomiting and an increasingly distended abdomen. At exploration, the segment pictured here is found as the point of obstruction. What is the best next step in management?
Gentle, persistent traction on the specimen
Small bowel resection with anastomosis
Lysis of Ladd band
Enteroenterostomy
Small bowel resection with exteriorization of the ends
A 36-year-old Caucasian male is brought to the emergency department due to weakness of his upper and lower extremities. Neurological examination reveals weakness, atrophy, fasciculations, spasticity and hyperreflexia of the involved muscles. His sensory, bowel, bladder and cognitive fun
Riluzole
Plasmapheresis
Donepezil
Intravenous immunoglobulins
Corticosteroids
A 36-year-old female presented to the emergency room with fever and a productive cough. The physician on call suspected community acquired pneumonia and prescribed azithromycin for 5 days. After 5 days of treatment, she comes to your office with no improvement of her symptoms and complains of worsening foul smelling sputum. Further inquiry reveals that she had undergone an upper GI endoscopy 8 days ago for a long history of heartburn and suspected peptic ulcer disease. She also reports a history of manic-type bipolar disorder. In your office she has a blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg, her pulse is 108/min, temperature is 38.7°C (101.6°F) and respirations are 26/min. Chest x-ray showed a right upper lobe infiltrate. Which of the following additional therapies would be most helpful for this patient's condition?
Doxycycline
Clindamycin
Gentamicin+ ampicillin
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Ciprofloxacin
A 36-year-old G1P0 woman pregnant with twins presents to her obstetrician for her routine 32-week appointment. She has gained 5.4kg (12-lb) in the past 2 weeks. When questioned about her weight gain, she states she has had headaches and some blurred vision for the past 2 weeks, which she thinks is secondary to dehydration. To circumvent this, she has been drinking a lot of water, which she claims “is making me swell, even my hands.” She also has had some epigastric pain for the past 2 weeks, which she attributes to “all the water I’ve been drinking.” Her blood pressure is 142/90 mm Hg, pulse is 105/min, and respiratory rate is 18/min. Urinalysis reveals 1+ glycosuria and 4+ proteinuria. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
Platelet transfusion
Administer oral antihypertensive therapy
Expectant management
Induce labor
Administer magnesium sulfate only
A 36-year-old G1P1 comes to see you for a routine postpartum examination 6 weeks after an uncomplicated vaginal delivery. She is currently nursing her baby without any major problems and wants to continue to do so for at least 9 months. She is ready to resume sexual activity and wants to know what her options are for birth control. She does not have any medical problems. She is a nonsmoker and is not taking any medications except for her prenatal vitamins. Which of the following methods may decrease her milk supply?
Progestin only pill
Foam and condoms
Combination oral contraceptives
Depo-Provera
Intrauterine device
A 36-year-old male comes to the emergency department because of worsening right lower quadrant (RLQ) abdominal pain. One week ago he was started on cephalexin for furunculosis. He has had type I diabetes mellitus for 10 years and is on insulin. His temperature is 38.3C (101.9F). Examination shows multiple furuncles on the inner side of both thighs; most of them are in regression. Abdominal examination shows tenderness on deep palpation in RLQ without rebound or guarding; no masses are palpated; psoas sign is positive; bowel sounds are present. Rectal examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 13.0 g/L, Leukocyte count 17,500/mm3. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Appendectomy
AP and lateral lumbar films
CT of abdomen
Colonoscopy
Laparoscopy
A 36-year-old male comes to your office complaining of progressive fatigability. His past medical history is significant for infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosed two months ago. His current treatment includes isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. Laboratory values are: Hemoglobin 8 g/dl, MCV 77 fl, MCHC 30%, ESR 17 mm/hr, Serum iron 170 micro-g/dl (N 50- 150 micro-g/dl ), Total iron binding capacity (TIBC) 280 micro-g/dl (N 300-360 micro-g/dl). Microscopy reveals two populations of red blood cells (RBC)-hypochromic and normochromic. What is the next best step in the management of this patient?
Bone marrow biopsy
Folic acid and vitamin B12
Pyridoxine
Iron preparations
Folic acid
A 36-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He is in obvious distress. His blood pressure is 80/30 mm Hg, pulse is 140/min and respirations are 23/min. Examination reveals collapsed neck veins. Breath sounds are present bilaterally, heart sounds are normal and the trachea is midline. He is semiconscious and his pupils are bilaterally reactive. There is no obvious head injury. Abdominal examination shows distention with tenderness in all four quadrants with guarding and rigidity. After initial resuscitation including control of his airway, breathing and circulation, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Chest x-ray
Diagnostic peritoneal lavage
Exploratory laparotomy
CT of the abdomen
Diagnostic laparoscopy
A 36-year-old man presents for a well-patient examination. He gives a history that, over the past 20 years, he has had three episodes of abdominal pain and hematemesis, the most recent of which occurred several years ago. He was told that an ulcer was seen on a barium upper GI radiograph. You obtain a serum assay for H pylori IgG, which is positive. What is the most effective regimen to eradicate this organism?
Ranitidine 300 mg orally once daily at bedtime for 6 weeks
Omeprazole 20 mg orally once daily for 6 weeks
Omeprazole 20 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1000 mg twice daily, and clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily for 14 days
Pepto-Bismol and metronidazole twice daily for 7 days
Benzathine penicillin, 1.2 million units intramuscularly weekly for three doses
A 36-year-old man presents to the emergency room with renal colic. His vital signs are normal and a urinalysis shows microscopic hematuria. A radiograph reveals a 1.5-cm stone. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
Open surgery to remove the stone
α-Adrenergic blocker
Percutaneous nephrostomy tube
Extracorporeal lithotripsy
Hydration and analgesics
A 36-year-old woman comes to your office complaining of a 12-month history of inter-menstrual bleeding and heavy menses. She has had type-2 diabetes for the past 4-years, managed with glipizide and metformin. She has no family history of gynecological malignancies. She does not use tobacco or alcohol. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), and blood pressure is 126/76 mm Hg. Her BMI is 30 Kg/m2. Physical examination shows pale mucus membranes. Pelvic examination is within normal limits; no vaginal lesions are noted. Urine pregnancy test is negative. Her hemoglobin is 10.8 g/dl and platelet count is 223,000/mm3. Coagulation studies are within normal limits. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Conjugated estrogens for 3-months
Endometrial biopsy
Endometrial ablation
Cyclic progestins
Prescribe combined oral contraceptive pills
A 36-year-old woman comes to your office concerned that she might become pregnant after her partner’s condom broke during intercourse 2 days ago. She wasn’t sure what to do, but some friends of hers told her that her doctor could still give her the “morning-after” pill. Her past medical history is significant for occasional tension headaches that resolve with acetaminophen. She smokes 0.5 pack cigarettes a day. She has never had surgery, takes no medications, and is allergic to sulfa drugs. Her family history is significant for ovarian cancer. Physical examination is normal. Laboratory evaluation demonstrates a positive urine HCG test. Which of the following represents an absolute contraindication to emergency contraception in this patient?
Family history of ovarian cancer
Smoking
Pregnancy
History of headaches
Age greater than 35
A 36-year-old woman presents to the emergency room complaining of pelvic pain, fever, and vaginal discharge. She has had nausea and vomiting and cannot tolerate liquids at the time of her initial evaluation. The emergency room physician diagnoses her with pelvic inflammatory disease and asks you to admit her for treatment. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial antibiotic treatment regimen for this patient?
Doxycycline 100 mg PO twice daily for 14 days
Clindamycin 450 mg IV every 8 hours plus gentamicin 1 mg/kg load followed by 1 mg/kg every 12 hours
Ofloxacin 400 mg PO twice daily for 14 days plus Flagyl 500 mg PO twice daily for 14 days
Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM plus doxycycline 100 mg PO twice daily for 14 days
Cefoxitin 2 g IV every 6 hours with doxycycline 100 mg IV twice daily
A 36-year-old woman presents to your office for contraception. She has had three vaginal deliveries without complications. Her medical history is significant for hypertension, well-controlled with a diuretic, and a seizure disorder. Her last seizure was 12 years ago. Currently she does not take any antiepileptic medications. She also complains of stress-related headaches that are relieved with an over-the-counter pain medication. She denies any history of surgeries. She is divorced, smokes one pack of cigarettes per day, and has three to four alcoholic drinks per week. On examination, her vital signs include weight 90 kg, blood pressure 126/80 mmHg, pulse 68 beats per minute, respiratory rate 16 breaths per minute, and temperature 36.4C (97.6F). Her examination is normal except for some lower extremity nontender varicosities. She has taken birth control pills in the past and wants to restart them because they help with her cramps. Which of the following would contradict the use of combination oral contraceptive pills in this patient?
Seizure disorders
Smoking in a woman over 35 years of age
Mild essential hypertension
Varicose veins
Tension headache
A 36-year-old woman presents with palpitations, anxiety, and hypertension. Workup reveals a pheochromocytoma. Which of the following is the best approach to optimizing the patient preoperatively?
Escalating antihypertensive drug therapy with β-blockade followed by α-blockade starting at least 1 week prior to surgery
Initiation of a β-blocker 1 to 3 weeks prior to surgery
Initiation of an α-blocker at 1 to 3 weeks prior to surgery
Initiation of an α-blocker 24 hours prior to surgery
Fluid restriction 24 hours preoperatively to prevent intraoperative congestive heart failure
A 36-year-old woman who lives in the suburbs of a large city comes to your office for a tuberculin skin test. She will be volunteering in her daughter's school cafeteria and the school district requires tuberculin testing. You inject a small amount of Mycobacterium tuberculosis purified protein derivative (PPD) in the skin and 2 days later she returns for a reading. You measure 12 mm of induration. She reports no history of tuberculosis exposure and no underlying medical conditions. She has never before been tested for tuberculosis. She was born in the United States, is not a healthcare worker, and has never spent time in prison. What is the best next step in her management?
Isoniazid, rifampin and pyrazinamide for 8 weeks
Isoniazid with pyridoxine for 9 months
Chest X-ray
Isoniazid for 6 months
Observation
A 36-year-old woman, 20 weeks pregnant, presents with a 1.5-cm right thyroid mass. FNA is consistent with a papillary neoplasm. The mass is cold on scan and solid on ultrasound. Which of the following methods of treatment is contra-indicated in this patient?
Total thyroidectomy with lymph node dissection
Right thyroid lobectomy
131I radioactive ablation of the thyroid gland
Subtotal thyroidectomy
Total thyroidectomy
A 36-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 16 weeks' gestation undergoes amniocentesis for evaluation of Down syndrome. She has no past medical history. Immediately after the procedure she becomes breathless, cyanotic and loses consciousness. Minutes later, she experiences a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. A generalized purpuric rash is noted. Her blood pressure is 90/50 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 26/min. Oxygen saturation is 75% on 100% facemask. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Intubation and mechanical ventilation
Administer intravenous diazepam
Low molecular weight heparin
Immediate induction of labor
Intravenous fluids
A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 3, is 2 days status post cesarean section for dystocia when she begins wandering the hallways of the hospital at 2 AM. She is extremely confused and thinks that she is at the police station. She states that she cannot sleep, feels very anxious, and wants to hurt her baby. Her prenatal course was unremarkable. She has no medical problems and had never had surgery. She has been taking Tylenol with codeine postpartum for incisional pain. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management?
Fluoxetine
Supervised visit to the nursery
Psychiatric hospitalization
Morphine
Naloxone
A 37-year-old healthy Caucasian male is seen in your office for a routine physical examination. He denies any symptoms or illness. He says he smokes a pack a day and drinks one to two beers every weekend. He has no allergies. Examination is unremarkable. The EKG reveals normal sinus rhythm with a heart rate of 72; there are frequent premature atrial beats present. The blood pressure is 120/65mm Hg. The next step in his management is:
Complete electrophysiological study
Observation
Digoxin
Lidocaine
Order potassium levels
A 37-year-old male is brought to the emergency department immediately after being smashed in a hydraulic press at a local factory. He is alert and oriented. Despite 10mg of IV morphine given by the paramedics, he is crying with pain. His blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 18/min. apparently, his left humeral shaft is fractured and the left arm is severely deformed being bent medially 90 degrees. Left radial artery pulse sensation and muscle strength in the left forearm are decreased compared to the right side. His right leg is shortened and externally rotated. Deformity of the right thigh is noted. Pedal pulses are symmetric. He has pain in the left anterior chest on anteroposterior sternal compression, but breath sounds are normal. Physical examination otherwise shows no abnormalities. The paramedics have placed 2 peripheral intravenous lines and immobilized the fractured limbs. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Gentle traction of the right leg to attempt alignment of the fragments of the femur
Gentle traction of the left forearm to attempt alignment of the fragments of the humerus
Induction of general anesthesia for operative reduction of the fractures
X-ray of the left arm, right leg and chest
Repeat 10 mg morphine
A 37-year-old man comes to his primary care physician for the evaluation of slightly pruritic skin lesions around his anus. He denies fever, malaise, and anorexia. He is sexually active with multiple male partners and occasionally uses condoms. He has never been tested for HIV or other sexually transmitted diseases. He has no drug allergies. Examination shows skin-colored, verrucous, papilliform lesions around his anus. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
Podophyllin
Erythromycin
Doxycycline
Tetracycline
Penicillin
A 37-year-old obese man returns to his doctor for a follow-up visit. One month ago, he was diagnosed with type II diabetes mellitus and was started on metformin. His fasting glucose is 122 mg/dl, and his blood pressure is 145/85 mm Hg. The patient looks rather dejected and admits it has been difficult to come to terms with his diagnosis. He has tried to exercise, watch his diet, and quit smoking as was suggested, but lately he has been feeling unmotivated and without energy. He admits to feeling sad and guilty about his weight, but is not sure he will be able to do anything about it. He continues to smoke despite attempts to cut back, and has been spending much of the day in bed watching television or sleeping. He has withdrawn from friends and family and took the last two weeks off from work, as he did not feel "up to going." Which of the following would be the best medication to prescribe at this time?
Bupropion
Selegiline
Venlafaxine
Fluoxetine
Modafinil
A 37-year-old obese, hypertensive female comes to the physician because of intermenstrual bleeding and heavy menses. Endometrial biopsy shows "complex hyperplasia without atypia." She has two young healthy children and does not want more children in the future. W hich of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Hysterectomy
Low dose oral contraceptives
Cyclic progestins
Estrogen replacement
Raloxifen
A 37-year-old pregnant woman has a genetic amniocentesis at 16 weeks’ gestation. A concurrent ultrasound shows normal fetal anatomy. Her prenatal course has been unremarkable. Her prenatal laboratory tests include a B negative blood type, a negative rubella antibody titer, a negative hepatitis B surface antigen, and a hematocrit of 31%. Which of the following is the most appropriate management for this woman?
Chorionic villus biopsy at the time of the amniocentesis
Administration of Rh immune globulin at the time of the amniocentesis
A follow-up ultrasound in 1 week to assess for intra-amniotic bleeding
A serologic test for the presence of hepatitis B surface antibody
Rubella immunization at the time of the amniocentesis
A 37-year-old white female presents with galactorrhea and amenorrhea for the past 7 months. She denies any headaches, visual problems, vaginal dryness or dyspareunia. She is married, has two children, and remarks that her family is "complete." She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 72/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98.6°F) and respirations are 14/min. Visual field testing is within normal limits. Pregnancy test is negative. Her serum prolactin level is 150ng/ml. Pituitary MRI shows a 6mm pituitary adenoma. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Treatment with estrogens
Monitoring by serum prolactin and MRI
Radiotherapy
Surgery
Treatment with cabergoline
A 37-year-old woman comes to the physician because of intermenstrual bleeding and heavy menses. Her other medical problems include hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. Her blood pressure is 144/86 mm Hg. Her BMI is 40 kg/m2. Physical examination shows no obvious abnormalities. Endometrial biopsy shows "complex hyperplasia without atypia." She has three young healthy children and does not want more children in the future. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Low dose oral contraceptives
Endometrial ablation
Estrogen replacement
Hysterectomy
Cyclic progestins
A 37-year-old woman comes to the physician's office because of left breast discomfort. The discomfort has been there for several months, and she recently started having breast pain before menses. Yesterday she noticed a lump in her breast. She has no family history of breast cancer. She smokes one pack of cigarettes every day. She had a baseline mammogram at age 35, which showed no abnormalities. Examination shows a smooth, soft, mobile mass palpable in the upper outer quadrant of the left breast; some diffuse nodularity is present bilaterally. Vital signs are normal. Physical examination otherwise shows no abnormalities. Fine needle aspiration of the mass shows thin greenish, non-bloody fluid; the mass disappears completely after the aspiration. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Recommend ultrasound evaluation of the aspirated cyst
Send the aspirated fluid for cytologic analysis
Reassure and reexamine her in six weeks
Prescribe oral contraceptives and reassure her
Recommend mammogram to be done as soon as possible
A 37-year-old woman has developed a 6-cm mass on her anterior thigh over the past 10 months. The mass appears to be fixed to the underlying muscle, but the overlying skin is movable. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in her management?
Above-knee amputation
Bone scan
Abdominal CT scan
Excisional biopsy
Incisional biopsy
A 37-year-old woman presents to your office with severe vertigo, postural instability, and vomiting. She also complains of "a buzzing sound" in her right ear. She has had two similar episodes over the previous year that lasted several hours and resolved spontaneously. She has no other medical problems. Her mother died of breast cancer at 55 years of age and her father is currently suffering from colon cancer. Her heart rate is 90/min and blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. Her BMI is 25.3 kg/m2. Examination reveals horizontal nystagmus. Which of the following could have prevented this patient's symptoms?
High complex carbohydrate diet
Calcium supplementation
Caloric restriction
Low salt diet
Gluten-free diet
A 37-year-old woman undergoes a lumpectomy and axillary dissection for a 3-cm infiltrating ductal carcinoma, diagnosed by core biopsies, located on the upper outer quadrant of her left breast. The pathology report of the surgical specimen is received 3 days after the operation. It indicates that all margins around the tumor are clear, and that 4 of 17 axillary lymph nodes have metastatic tumor. The tumor is reported to be estrogen and progesterone receptor negative. Which of the following should further therapy most likely include?
Radiation to both breasts and tamoxifen
Radiation to the remaining left breast and systemic chemotherapy
Radiation to the remaining left breast
Antiestrogen medication (tamoxifen)
Conversion to modified radical mastectomy
A 37-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, comes to her physician for follow-up on her ectopic pregnancy. She was diagnosed with an ectopic pregnancy 7 days ago and given methotrexate. She now presents with abdominal pain that started this morning. Examination is significant for moderate left lower quadrant tenderness. Laboratory analysis shows that her beta-hCG value has doubled over the past week. Transvaginal ultrasound shows that the ectopic pregnancy is roughly the same size but there is an increased amount of fluid in the pelvis. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Expectant management
Oophorectomy
Hysterectomy
Laparoscopy
Repeat methotrexate
A 38-year-old female comes to your office with a recent episode of hemoptysis. The symptoms started one week ago with malaise, throat pain and dry cough. The cough progressed becoming productive of yellowish sputum. She started noticing speckles of red blood in her sputum as of yesterday. Her past medical history is significant for peptic ulcer disease. She has a 5 pack-year smoking history, but she quit 10 years ago. Her temperature is 98°F (36.7°C), blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg and heart rate is 87/min. Physical examination reveals scattered bilateral wheezes. Chest X-ray shows clear lung fields. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
CT scan of the chest
Observation
Sputum cytology
Sputum Gram stain and culture
Pulmonary function tests
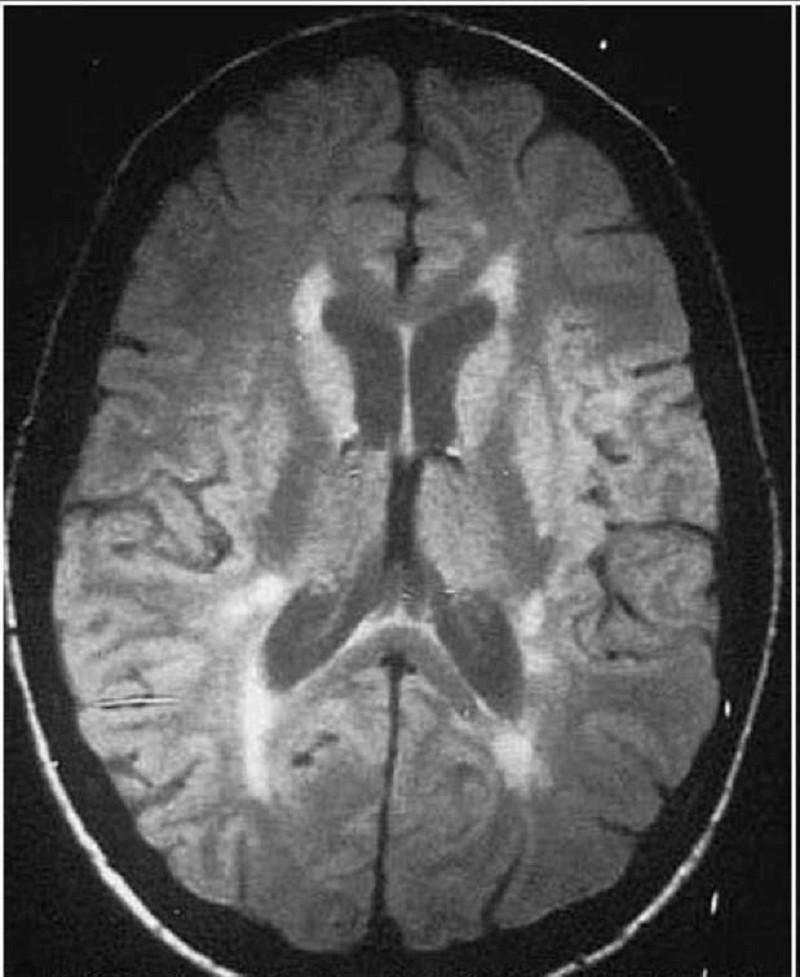
A 38-year-old female presents with one week of "shakiness" in her right arm, right leg weakness and unsteady gait. An MRI of her brain is shown below. Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient?
Aspirin and simvastatin
Argatroban
Glatiramer acetate
Tissue plasminogen activator
Broad-spectrum antibiotics
A 38-year-old G1P1 comes to see you for her first prenatal visit at 10 weeks gestational age. She had a previous term vaginal delivery without any complications. You detect fetal heart tones at this visit, and her uterine size is consistent with dates. You also draw her prenatal labs at this visit and tell her to follow up in 4 weeks for a return OB visit. Two weeks later, the results of the patient’s prenatal labs come back. Her blood type is A–, with an anti D antibody titer of 1:4. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient? . Schedule an amniocentesis for amniotic fluid bilirubin at 16 weeks
Schedule Percutaneous Umbilical Blood Sampling (PUBS) to determine fetal hematocrit at 20 weeks
Repeat the titer in 4 weeks
Repeat the titer at 28 weeks
Schedule PUBS as soon as possible to determine fetal blood type
Schedule an amniocentesis for amniotic fluid bilirubin at 16 weeks
A 38-year-old G3P2 at 40 weeks gestation presents to labor and delivery with gross rupture of membranes occurring 1 hour prior to arrival. The patient is having contraction every 3 to 4 minutes on the external tocometer, and each contraction lasts 60 seconds. The fetal heart rate tracing is 120 beats per minute with accelerations and no decelerations. The patient has a history of rapid vaginal deliveries, and her largest baby was 3200 g. On cervical examination she is 5 cm dilated and completely effaced, with the vertex at −2 station. The estimated fetal weight is 3300 g. The patient is in a lot of pain and requesting medication. Which of the following is the most appropriate method of pain control for this patient?
Intramuscular Demerol
General anesthesia
Local block
Epidural block
Pudendal block
A 38-year-old male with a chronic history of schizophrenia is admitted to the hospital for deterioration in his condition. He is a known patient and was stable on risperidone for the past few years. Today, the patient does not respond when spoken to and he sits motionlessly. He makes no eye contact and his face remains expressionless. Vital signs include temperature of 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure of 132/80 mm Hg, pulse of 88/min, and respirations of 14/min. Physical examination demonstrates diffuse muscle rigidity but is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following would be the most appropriate next step?
Increase risperidone dose
Continue same dose of risperidone and add clozapine
Administer lorazepam
Initiate therapy with dantrolene sodium
Replace risperidone with quetiapine
A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual examination and Pap smear. She has no complaints. She has a regular period every month. She is sexually active with her husband. She has migraine headaches and is status post a tubal ligation. She states that she uses numerous alternative medications for mood, sleep, and disease prevention. Examination, including pelvic and breast examination, is unremarkable. Which of the following is an appropriate question to ask this patient?
Why haven't you revealed your use of alternative medications before?
Why don't you stick with traditional medicines?
Does your husband know you are using these alternative medications?
Do you realize how dangerous alternative medicines are?
Which alternative medications do you use?
A 38-year-old woman complains of chronic aching pain and stiffness around the neck, shoulders, low back and hips. She fatigues easily and has been having problems with sleep. Even minor exertion worsens her pain. She has no muscle weakness, fever, malaise, weight loss or rash. She has a history of irritable bowel syndrome. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows multiple tender spots over specific points on her body. Power is 5/5 in all extremities and deep tendon reflexes are 2+. No sensory abnormalities are noted. Labs show: ESR 9 mm/hr, Hematocrit 43%, WBC count 7,000/microL, Platelet count 200,000/microL, TSH 3 microU/L, CPK 100 IU/L. Which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient?
Naproxen
Prednisone
Colchicine
Oxycodone
Amitriptyline
A 38-year-old woman has been complaining of a 2-year history of increasing dyspnea and fatigue. Physical examination reveals increased JVP and a reduced carotid pulse. Precordial examination reveals a left parasternal lift, loud P2, and right-sided S3 and S4. There are no audible murmurs. CXR reveals clear lung fields and an ECG shows evidence of right ventricular hypertrophy. Pulmonary fun
Corticosteroids
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Alpha-adrenergic blockers
Calcium channel blockers
Nitrates
A 38-year-old woman is 10 weeks pregnant with her second pregnancy and is found to have blood pressures exceeding the 150 to 160 mm Hg systolic range and 100 to 110mm Hg diastolic range at her first prenatal visit. She has no other medical problems. She had a cholecystectomy at the age of 20. She takes no medications and is allergic to sulfa drugs. Her family history is significant for hypertension on both her maternal and paternal sides. Physical examination is normal, including an obstetrical ultrasound demonstrating a 10-week intrauterine pregnancy. The patient is diagnosed with chronic hypertension. Which of the following should be used as first-line antihypertensive therapy for this patient?
Atenolol
Magnesium sulfate
Methyldopa
Captopril
Lisinopril
A 38-year-old woman presents to the physician because of right upper quadrant pain associated with nausea and vomiting for the past 12 hours. She has had similar pain previously, usually precipitated after the ingestion of fatty foods. However, past episodes have always resolved within one to two hours. She has type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertriglyceridemia, and hypercholesterolemia. Her current medications include metformin, fenofibrate, and a statin. Her temperature is 38.3° C (101° F), blood pressure is 130/70 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 20/min. Her BMI is 32 kg/m2. Examination shows right upper quadrant tenderness. Abdominal ultrasound reveals gallstones, a thickened gallbladder wall with edema, and a normal common bile duct. Her alkaline phosphatase level is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Percutaneous trans-hepatic drainage
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography
Delayed cholecystectomy
HIDA scan
Cholecystectomy within 72 hours
A 38-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of urinary incontinence. Her symptoms are suggestive of urge incontinence. She admits to drinking several large glasses of iced tea and water on a daily basis because her mother always told her to drink lots of liquids to lower her risk of bladder infections. Urinalysis and urine culture are negative. After confirming the diagnosis with physical examination and office cystometrics, which of the following treatments should you recommend to the patient as the next step in the management of her problem?
Prescribe an anticholinergic
Schedule cystoscopy
Instruct her to eliminate excess water and caffeine from her daily fluid intake
Tell her to hold her urine for 6 hours at a time to enlarge her bladder capacity
Instruct her to start performing Kegel exercises
A 38-year-old woman presents with several months of decreased libido and a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight gain. She has not had her menstrual period for the past 3 months. Physical examination is unremarkable except that a small amount of white discharge is manually expressed from the nipples bilaterally. The serum prolactin level is 300 ng/mL. Which of the following is the most appropriate first-line treatment?
Bromocriptine
Methyldopa
Metoclopramide
Octreotide
Cortisol
A 38-year-old woman with bipolar disorder has been stable on lithium for the past 2 years. She comes to her psychiatrist’s office in tears after a 2-week history of a depressed mood, poor concentration, loss of appetite, and passive suicidal ideation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
Stop the lithium and start an antipsychotic
Start an antidepressant and continue the lithium
Stop the lithium and start an antidepressant
Start the patient on a long-acting benzodiazepine
Start the patient on a second mood stabilizer
A 38-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 8 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She has had no bleeding from the vagina or abdominal pain and no complaints. She has a long history of migraine headache and recently developed peptic ulcer disease (PUD). Examination shows a nontender 8-week sized uterus but is otherwise unremarkable. The patient is very concerned that her migraine headaches and peptic ulcer disease will make her pregnancy intolerable. Which of the following is the most appropriate response?
Pregnancy has no effect on migraines or PUD
Pregnancy is associated with improved migraines and worsened PUD
Pregnancy is associated with worsening migraines and improved PUD
Pregnancy is associated with worsening of migraines and PUD
Pregnancy is associated with improvement of migraines and PUD
A 38-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 10 weeks gestation comes to the physician's office for prenatal counseling of genetic disorders. She has a healthy 3-year-old child. Given her age, she is worried about the risk of Down syndrome, and if her baby test is positive for Down syndrome she would like to terminate the pregnancy. Ultrasonogram shows increased fetal nuchal fold lucency. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Maternal serum alpha fetoprotein levels (MSAFP)
Chorionic villus sampling
Second trimester amniocentesis
Early amniocentesis
Cordocentesis
A 34-year-old man is traveling in Southeast Asia on business. He is staying in Western-style hotels and eating food in large restaurants. He has not eaten from street vendors. One week after arrival, he develops symptoms of anorexia, nausea, and abdominal cramps followed by the sudden onset of watery diarrhea. He has no fever or chills and there is no blood or pus in the stools. Which of the following is the most appropriate therapy for his condition?
Amoxicillin
Specific antitoxin
Doxycycline
Oral rehydration only
Symptomatic therapy with loperamide
{"name":"DES C_Management (6) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 34-year-old man presents with substernal discomfort. The symptoms are worse after meals, particularly a heavy evening meal, and are sometimes associated with hot\/sour fluid in the back of the throat and nocturnal awakening. The patient denies difficulty swallowing, pain on swallowing, or weight loss. The symptoms have been present for 6 weeks; the patient has gained 20 lb in the past 2 years. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial approach?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/20-801869/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Physics: Electromagnet induction in a straight wire
940
OPERATING SYTEMS
84115
Morality of Companies
100
QUIZ 3 FINANCE PROCESS
520
Backstreet Boys - How Well Do You Know the Band?
201019092
Airport Codes - Can You Name These US Airports?
201022873
Casablanca Trivia: How Well Do You Know the Film?
201027145
Famous Painters - Name the Artist (Free)
201020306
Intercultural Communication - Intro Course Practice
15819474
I Hate My Husband - Find the Real Reasons
201022293
Axial Skeleton - Free Anatomy Practice Online
201019280
How Long Does a Short-Term Goal Take to Achieve?
201020643