Module Chirurgie Visce̝rale 3 (Prof. MAM Bunsocheath)

Visceral Surgery Challenge
Test your knowledge on visceral surgery with our comprehensive quiz! This quiz contains 18 questions covering a wide range of topics relevant to current practices and clinical scenarios in visceral surgical procedures.
- Multiple choice questions
- Designed for healthcare professionals and students
- Evaluate your surgical knowledge and skills
1. For the first 6 hours following a long and difficult surgical repair of a 7-cm abdominal aortic aneurysm, a 70-year-old man has a total urinary output of 25 mL since the operation. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test to evaluate the cause of his oliguria?
A. Renal scan
B. Aortogram
C. Left heart preload pressures
D. Urinary sodium concentration
E. Creatinine clearance
2. A 72-year-old man undergoes an aortobifemoral graft for symptomatic aortoiliac occlusive disease. The inferior mesenteric artery (IM A) is ligated at its aortic attachment. Twenty-four hours after surgery the patient has abdominal distention, fever, and bloody diarrhea. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic study for this patient?
A. Aortogram
B. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
C. Computed tomographic (CT) scan
D. Sigmoidoscopy
E. Barium enema
3. A 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency room complaining of redness and pain in her right foot up to the level of the midcalf. She reports that her right lower extremity has been swollen for at least 15 years, but her left leg has been normal. On physical examination, she has a temperature of 39°C (102.2°F) and the right lower extremity is nontender with nonpitting edema from the groin down to the foot. There is cellulitis of the right foot without ulcers or skin discoloration. The left leg is normal. Which of the following is the most likely underlying problem?
A. Congenital lymphedema
B. Lymphedema praecox
C. Venous insufficiency
D. Deep venous thrombosis
E. Acute arterial insufficiency
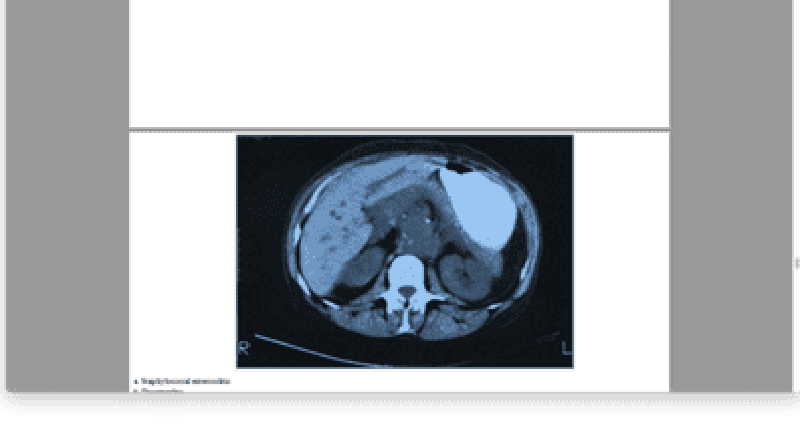
4. A 76-year-old woman presents with acute onset of persistent back pain and hypotension. A CT scan is obtained (shown below), and the patient is taken emergently to the operating room. Three days after surgery she complains of abdominal pain and bloody mucus per rectum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Staphylococcal enterocolitis
B. Diverticulitis
C. Bleeding arteriovenous (AV) malformation
D. Ischemia of the left colon
E. Bleeding colonic carcinoma
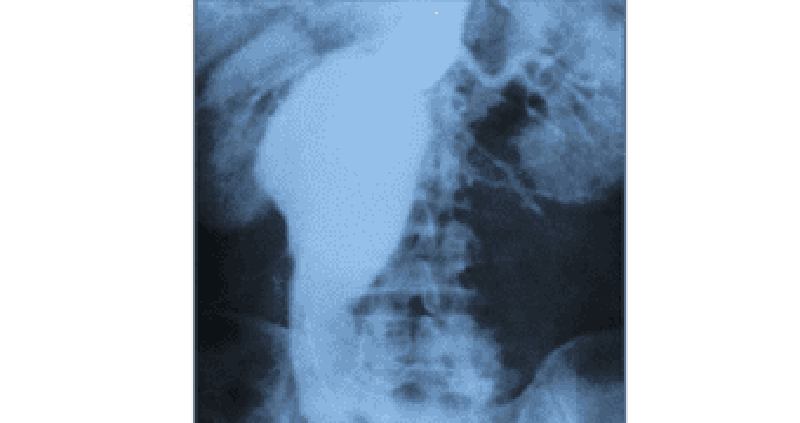
5. An 80-year-old man is found to have an asymptomatic pulsatile abdominal mass. An arteriogram is obtained (shown below). Which of the following is the most frequent and lethal complication of this condition?
A. Rupture
B. Acute thromboembolism
C. Dissection
D. High-output congestive heart failure
E. Myocardial infarction
6. 6. A 75-year-old man is found by his internist to have an asymptomatic carotid bruit. Which of the following is the most appropriate next test?
A. Transcranial Doppler studies
B. Doppler ultrasonography (duplex)
C. Spiral CT angiography
D. Arch aortogram with selective carotid artery injections
E. Magnetic resonance arteriogram (MRA)
7. 7. A 55-year-old man with recent onset of atrial fibrillation presents with a cold, numb, pulseless left lower extremity. He is immediately taken to the operating room for an embolectomy of the left popliteal artery. Which additional procedure should be performed along with the embolectomy?
A. Electromyography (EMG) of the leg
B. Measurement of anterior compartment pressure in the leg
C. Fasciotomy of the anterior compartment in the leg
D. Fasciotomy of all the compartments in the leg
E. Application of a posterior splint to the leg
8. A 58-year-old man presents with pain in the left leg after walking more than one block that is relieved with rest. On physical examination, distal pulses are not palpable in the left foot and there is dry gangrene on the tip of his left fifth toe. An ankle-brachial index on the same side is 0.5. Which of the patient’s symptoms or signs of arterial insufficiency qualifies him for reconstructive arterial surgery of the left lower extremity?
A. Ankle-brachial index less than 0.7
B. Rest pain
C. Claudication
D. Absent palpable pulses
E. Toe gangrene
9. A 64-year-old man with a history of a triple coronary artery bypass 2 years ago presents with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. His only medication is a thiazide diuretic. Which of the following medications would be most appropriate in the medical management of his atherosclerosis?
A. Aspirin
B. Warfarin
C. Low-dose heparin
D. High-dose heparin
E. Low-molecular-weight heparin
10. A patient who has had angina as well as claudication reports feeling light-headed on exertion, especially when lifting and working with his arms. The subclavian steal syndrome is associated with which of the following hemodynamic abnormalities?
A. Antegrade flow through a vertebral artery
B. Venous congestion of the upper extremities
C. Occlusion of the carotid artery
D. Occlusion of the vertebral artery
E. Occlusion of the subclavian artery
11. A 66-year-old woman presents with severe right lower extremity claudication. Surgery is considered, but her hypertension, smoking, and diabetes puts her at risk for associated coronary heart disease. What test is most predictive of postoperative ischemic cardiac events following surgery?
A. Exercise stress testing
B. Electrocardiography (ECG)
C. Coronary angiography
D. Dipyridamole-thallium imaging
E. Transesophageal echocardiography
12. A 60-year-old man is admitted to the coronary care unit with a large anterior wall myocardial infarction. On his second hospital day, he begins to complain of the sudden onset of numbness in his right foot and an inability to move his right foot. On physical examination, the right femoral, popliteal, and pedal pulses are no longer palpable. The left lower extremity is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
A. Duplex imaging of the right lower extremity arteries
B. CT angiogram of the right lower extremity
C. CT angiogram of bilateral lower extremities
D. Embolectomy of the right femoral artery
E. Embolectomy of the right femoral artery with exploration of the contralateral femoral artery
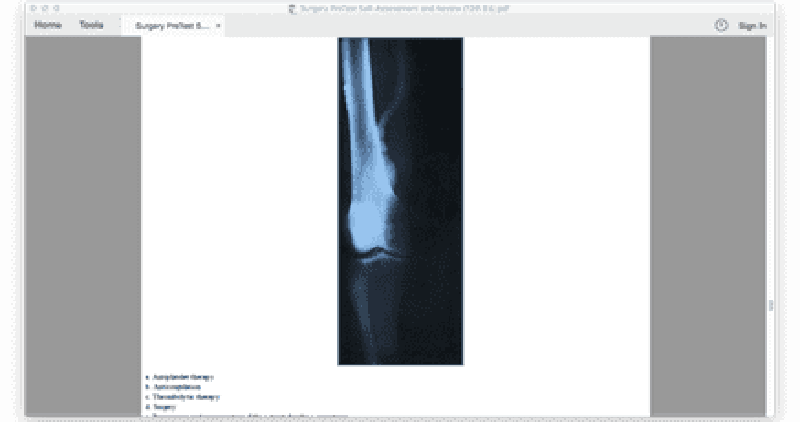
13. A 60-year-old man is found on a routine physical examination to have a 3-cm pulsatile mass in the right popliteal fossa. X-ray of the right of the right lower extremity is shown below. Which of the following is the most appropriate management of this patient?
A. Antiplatelet therapy
B. Anticoagulation
C. Thrombolytic therapy
D. Surgery
E. Reassurance and reexamination if the patient develops symptoms
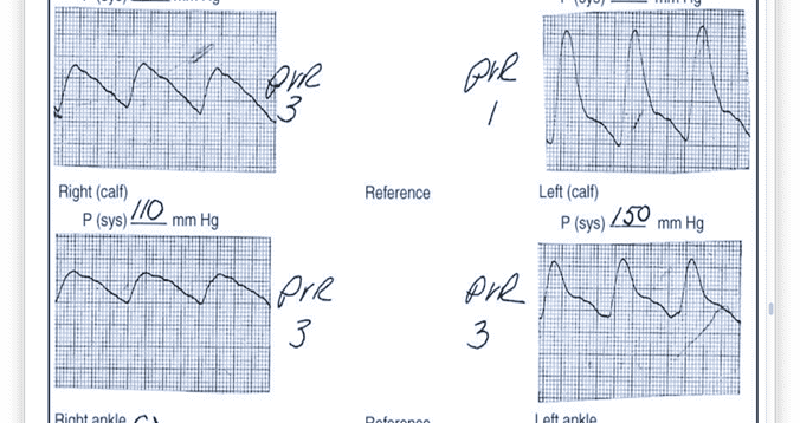
14. A 65-year-old male cigarette smoker reports onset of claudication of his right lower extremity approximately 3 weeks previously. He can walk 3 blocks before the onset of claudication. Physical examination reveals palpable pulses in the entire left lower extremity, but no pulses are palpable below the right groin level. Noninvasive flow studies are obtained and are pictured here. What is the level of the occlusive process in this patient?
A. Right anterior tibial artery
B. Right superficial femoral artery
C. Right profunda femoris artery
D. Right external iliac artery
E. Right internal iliac artery
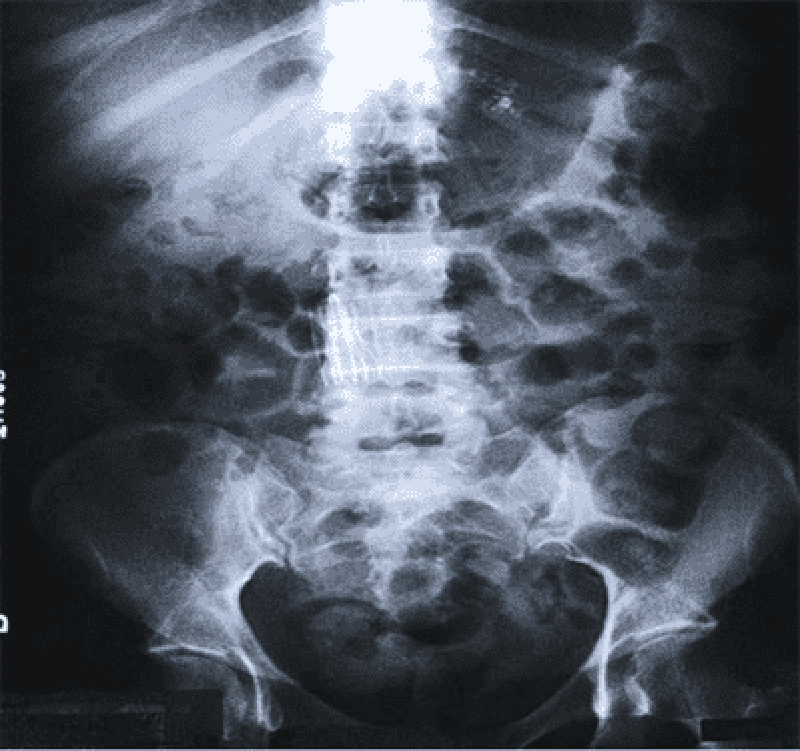
15. A 56-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for a routine checkup. She states that she was recently hospitalized for surgery and was told she had some metal placed in a large blood vessel to prevent blood clots from moving to her lungs. An abdominal x-ray is shown here. Which of the following is the most appropriate indication for placement of this device?
A. Recurrent pulmonary embolus despite adequate anticoagulation therapy
B. Axillary vein thrombosis
C. Pulmonary embolus due to DVT of the lower extremity that occurs 2 weeks postoperatively
D. DVT in a patient with patient with metastatic carcinoma
E. Pulmonary embolus in a patient with metastatic carcinoma
16. Two days after admission to the hospital for a myocardial infarction, a 65-year-old man complains of severe, unremitting midabdominal pain. His cardiac index is 1.6. Physical examination is remarkable for an absence of peritoneal irritation or distention despite the patient’s persistent complaint of severe pain. Serum lactate is 9 mmol/L (normal is < 3 mmol/L). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in this patient’s management?
A. Perform computed tomography.
B. Perform mesenteric angiography.
C. Perform laparoscopy.
D. Perform flexible sigmoidoscopy to assess the distal colon and rectum.
E. Defer decision to explore the abdomen until the arterial lactate is greater than 10 mmol/L.
17. A postoperative patient with swelling and pain in his right calf is suspected of having a deep venous thrombosis. Prior to initiating treatment with anticoagulants, he requires a confirmatory examination. Which of the following is a limitation of the duplex ultrasound in evaluating a DVT?
A. It is not very sensitive for detecting calf thrombi in symptomatic patients.
B. It is invasive.
C. It cannot differentiate between acute and chronic venous thrombi.
D. It is expensive.
E. It cannot image the proximal veins (iliac veins, IVC).
18. A 72-year-old woman with severe COPD who requires home oxygen is unable to ambulate inside her home without experiencing severe left hip pain. She was hospitalized 1 year ago for a viral pneumonia and was ventilator-dependent at that time for 6 weeks. On examination, her blood pressure is 165/80 mm Hg. She has weakly palpable bilateral femoral pulses. An angiogram demonstrates severe aortoiliac disease involving bilateral iliac vessels. Which of the following is the most appropriate vascular procedure for this patient?
A. Femorofemoral bypass
B. Axillofemoral bypass
C. Femoropopliteal bypass
D. Aortobifemoral bypass
E. Common femoral and profunda femoral endarterectomies
{"name":"Module Chirurgie Visce̝rale 3 (Prof. MAM Bunsocheath)", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on visceral surgery with our comprehensive quiz! This quiz contains 18 questions covering a wide range of topics relevant to current practices and clinical scenarios in visceral surgical procedures. Multiple choice questions Designed for healthcare professionals and students Evaluate your surgical knowledge and skills","img":"https:/images/course3.png"}
More Quizzes
Orthopedic Assessment Quiz
104520
Part 3(85)
854246
Drought : Recap Quiz
5232
What Kind of Soil Texture Are You?
14714
Twilight Teams: Are You Team Edward or Team Jacob?
201017013
Classic Cartoon - From Fred Flintstone to Bugs Bunny
201023109
Sterile Processing Practice Test - Free CRCST
201016599
Solar Weather and Climate - Free Earth Science
201019015
Area of Composite Figures - Free Geometry Practice
201015952
What Number Am I - Find Your Number Personality
201018689
Lord of the Flies - Free Ultimate LOTF Challenge
201017524
Beverly Hills 90210 - Test Your Show Knowledge
201019444