Part 56
38) A 30-year-old G2P2 woman comes to the physician with fatigue, mood swings, irritability, breast tenderness, abdominal bloating, and headaches that occur monthly. The symptoms are worse just before her menses and resolve by the third day of her menstrual cycle. The symptoms interfere with her daily activities, including her proficiency at work. The patient's only current medication is a multivitamin. She uses spermicidal foam and condoms for birth control. Her menses are regular. Her sister was diagnosed with hypothyroidism and takes levothyroxine. Examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Menopausal transition
. Migraine
. Normal menstrual cycle
. Premenstrual syndrome
. Somatization
39) At a follow-up routine prenatal visit, the uterine fundus of a healthy 23-year-old pregnant woman is palpated halfway between her symphysis pubis and umbilicus. Which of the following is the most appropriate test to order at this stage of her pregnancy?
Serum human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) titer
Glucose tolerance test
Amniocentesis
Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP)
Cervical culture for group B Streptoccus (GBS)
40) A 25-year-old woman in her 15th week of pregnancy presents with uterine bleeding and passage of a small amount of watery fluid and tissue. She is found to have a uterus that is much larger than estimated by her gestational dates. Her uterus is found to be filled with cystic, avascular, grapelike structures that do not penetrate the uterine wall. No fetal parts are found. Immunostaining for p57 was negative in the cytotrophoblasts and villi mesenchyme. Which of the following is the best diagnosis?
Partial hydatidiform mole
Complete hydatidiform mole
Invasive mole
Placental site trophoblastic tumor
. Choriocarcinoma
41) A 24-year-old woman delivered a healthy baby by vaginal delivery at 36 weeks gestation. She had a prolonged premature rupture of the membranes, and mid forceps application was required during delivery. On the second postpartum day she complained of fever and chills. She cannot breast-feed because her "nipples are tender". Her temperature is 38.5C (101.3F), blood pressure is 120/55 mmHg and pulse is 92/min. Bimanual examination shows tender uterus and foul-smelling lochia. Her nipples are cracked but without surrounding erythema or warmth. Physical examination otherwise shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Normal postpartum
Puerperal mastitis
Endometritis
Deep venous thrombosis
Aspiration pneumonia
42) A 20-year-old, G1 PO, woman at 35 weeks gestation comes to the hospital because of regular uterine contractions. She noticed a passage of clear fluid per vagina for the past 24 hours. She has no other symptoms. Her pregnancy thus far has been uncomplicated. Her temperature is 38.2 C (100.7 F), blood pressure is 120/68 mmHg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 17/min. Speculum examination shows a closed cervix and clear fluid pooling in the vaginal fornix. The pH of the fluid is 7.5. Fetal heart monitoring shows a rate of 165/min and uterine contractions occurring every 3-4 minutes. Initial laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin: 10.2 g/L; Platelets: 198,000/mm3; Leukocyte count: 18,500/mm3; Neutrophils: 86%; Lymphocytes: 14%. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Abruptio placenta
Intraamniotic infection
Urinary tract infection
Trichomonas vaginitis
Normal labor
43) A 37-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of infertility. She and her 39-year-old husband have not been able to conceive after 13 months of unprotected and frequent intercourse. She has 28-day regular menstrual cycles. The patient had a pregnancy with her husband at age 31. She has no other genitourinary complaints such as menorrhagia, dyspareunia or pelvic pain. She has no previous history of sexually transmitted diseases or abdominal surgery. The patient does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. She is an aerobics instructor and teaches 230-minute classes daily. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg and pulse is 84/min. Her body mass index is 23 kg/m2. Complete physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
Adrenal hyperplasia
Decreased ovarian reserve
Intense exercise
Premature ovarian failure
Uterine leiomyomas
44) A 20-year-old, G1PO, woman at 35 weeks gestation comes to the hospital because of regular uterine contractions and passage of clear fluid per vagina. She has no other symptoms. Her pregnancy thus far has been uncomplicated. Her temperature is 38.2 C (100.7 F), blood pressure is 120/68 mmHg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 17/min. Speculum examination shows a closed cervix and clear fluid pooling in the vaginal fornix. The pH of the fluid is 7.5. Fetal heart monitoring shows a rate of 165/min and uterine contractions occurring every 3-4 minutes. Initial laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 10.2 g/L; Platelets 198,000/mm3; Leukocyte count 18,500/mm3; Neutrophils 86%; Lymphocytes 14%. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Abruptio placenta
Intraamniotic infection
Urinary tract infection
Trichomonas vaginitis
Normal labor
45) A 40-year-old G3P3 comes to your office for a routine annual GYN examination. She tells you that she gets up several times during the night to void. On further questioning, she admits to you that during the day she sometimes gets the urge to void, but sometimes cannot quite make it to the bathroom. She attributes this to getting older and is not extremely concerned, although she often wears a pad when she goes out in case she loses some urine. This patient is very healthy otherwise and does not take any medication on a regular basis. She still has regular, monthly menstrual periods. She has had three normal spontaneous vaginal deliveries of infants weighing between 7 and 8 lb. An office dipstick of her urine does not indicate any blood, bacteria, WBCs, or protein. Her urine culture is negative. Based on her office presentation and history, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Urinary stress incontinence
. Urinary tract infection
Overflow incontinence
Bladder dyssynergia
Vesicovaginal fistula
46) An 18-year-old G0 comes to see you complaining of a 3-day history of urinary frequency, urgency, and dysuria. She panicked this morning when she noticed the presence of bright red blood in her urine. She also reports some midline lower abdominal discomfort. She had intercourse for the first time 5 days ago and reports that she used condoms. On physical examination, there are no lacerations of the external genitalia, there is no discharge from the cervix or in the vagina, and the cervix appears normal. Bimanual examination is normal except for mild suprapubic tenderness. There is no flank tenderness, and the patient’s temperature is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chlamydia cervicitis
. Pyelonephritis
. Acute cystitis
. Acute appendicitis
. Monilial vaginitis
47) A 17-year-old teenage girl presents to your office with a 10-month history of lower abdominal pain that radiates to the upper thighs and back. The pain is colicky in nature and usually starts a few hours prior to menses, lasting 3-4 days. Menses have occurred at regular 28-day intervals over the past 2 years. She has no inter-menstrual bleeding. She became sexually active 6-months ago and does not use contraception. Physical examination shows healthy external genitalia and well-developed secondary sexual characteristics; the uterus is normal in size and freely mobile. Examination shows no other abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her pelvic pathology?
. Ureteric stone
. Pelvic infection
. Abnormal myometrial growth
. Increased prostaglandins
. Ectopic endometrial implants
48) You have diagnosed a healthy, sexually active 24-year-old female patient with an uncomplicated acute urinary tract infection. Which of the following is the likely organism responsible for this patient’s infection?
Chlamydia
. Pseudomonas
. Klebsiella
. Escherichia coli
. Candida albicans
49) A 15-year-old girl is being evaluated for primary amenorrhea. She has no other symptoms. She has not been sexually active. She has no other medical problems and does take any medication. Her family history is unremarkable. On examination, you note fully developed breasts and absent axillary and pubic hair. External genitalia have a normal appearance, but the vagina is abnormally short and blind ended. Initial work-up reveals no uterus on ultrasound, a testosterone level of 400 ng/dl (Normal is 20-80 for a female), and a 46 XY karyotype. Which of the following events is most likely to have caused the absence of in utero development of the internal reproductive organs?
Absence of mullerian inhibiting factor
Presence of mullerian inhibiting factor
Agenesis of Wolffian ducts
Agenesis of mullerian ducts
Testosterone surge
50) A previously healthy 50-year-old gravida 5, para 4, Caucasian woman comes to the physician complaining of passing small amounts of urine while sneezing or coughing for the past five months. She denies any episodes of weakness, numbness or fecal incontinence. There is no history of dysuria, increased frequency of urination, or hematuria. Her symptoms are progressively getting worse. Her other medical problems include diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosed 3 years ago, treated with glyburide 2.5mg/day. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs, and has no known drug allergies. She mentions that she is an avid jogger, but her problem causes her significant embarrassment. She now has to wear absorbent pads while jogging. Her vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, the abdomen is soft. Neurological examination is within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a cystocele. The patient's labs reveal: Urine: Specific gravity: 1.020, Blood: negative, Glucose: negative, Leukocyte esterase: negative, Nitrites: negative, WBC: 5-10/hpf, Bacteria: none. Random blood sugar is 120 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Detrusor instability
Interstitial cystitis
Overflow incontinence due to detrusor weakness
Overflow incontinence due to medication
Pelvic floor muscle weakness
51) A 34-year-old primigravida develops severe postpartum bleeding requiring aggressive volume resuscitation and transfusion of 5 units of packed red blood cells. Her pregnancy was complicated by mild hypertension and trace proteinuria that was treated with low-dose methyldopa. Her mother suffered from premature menopause and severe osteoporosis. Seven days after giving birth, she has failed to lactate. Her urinalysis is insignificant and her blood pressure has ranged from 95 to110 mmHg systolic and 69 to 75 mmHg diastolic. Fundoscopy shows no retinal changes. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
. Inhibin
. Progesterone
. Aldosterone
. Prolactin
. Oxytocin
52) A 35-year-old African-American marathon runner presents to the gynecologist complaining of secondary amenorrhea that developed three months ago. Her cycles are normally 28 days long, and her menses last three to five days with moderate flow. One year ago, the woman adopted a vigorous exercise regimen that lasted between three and five hours every day. Since then, her BMI has declined from 23.4 to 16.5 Kg/m2. She has been winning many local races and is considering increasing the difficulty of her exercise regimen, but would like to address the issue of her amenorrhea first. Physical examination reveals a thin woman with well-defined musculature but is otherwise unremarkable. Pregnancy test is negative. What is the most likely etiology of her amenorrhea?
. Kwashiorkor
. Testosterone deficiency
. Estrogen deficiency
. Progesterone deficiency
. Prolactin excess
53) A 26-year-old primigravid woman at 32 weeks gestation comes to the physician because of swelling of her hands and feet. Her previous prenatal check-up was normal. Blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg, and five minutes later following lateral rest her blood pressure is 140/95 mmHg. Physical examination shows 2+ pitting edema of the legs and a macular eruption on the cheekbones. Optic fundi show no abnormalities. Laboratory studies are as follows: Urinalysis: 4+ protein, RBC casts, Urine protein: 8 g/24hr, Uric acid: 5 mg/dl, BUN: 28 mg/dl, Serum creatinine: 2.1 mg/dl, Serum electrolytes, liver function tests and coagulation studies are within normal limits. A serum antinuclear antibody (ANA) test is positive in high titers Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pregnancy induced hypertension
. Chronic hypertension with superimposed pre-eclampsia
. Glomerulonephritis
. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
. HELLP syndrome
54) A 28-year-old G1P0 presents to your office at 18 weeks gestational age for an unscheduled visit secondary to right-sided groin pain. She describes the pain as sharp and occurring with movement and exercise. She denies any change in urinary or bowel habits. She also denies any fever or chills. The application of a heating pad helps alleviate the discomfort. As her obstetrician, what should you tell this patient is the most likely etiology of this pain?
. Round ligament pain
. Appendicitis
. Preterm labor
. Kidney stone
. Urinary tract infection
55) A 30-year-old G2P1001 patient comes to see you in the office at 37 weeks gestational age for her routine OB visit. Her first pregnancy resulted in a vaginal delivery of a 9-lb 8-oz baby boy after 30 minutes of pushing. On doing Leopold maneuvers during this office visit, you determine that the fetus is breech. Vaginal examination demonstrates that the cervix is 50% effaced and 1 to 2 cm dilated. The presenting breech is high out of the pelvis. The estimated fetal weight is about 7 lb. The patient denies having any contractions. You send the patient for a sonogram, which confirms a fetus with a double footling breech presentation. There is a normal amount of amniotic fluid present and the head is hyperextended in the “stargazer” position. Which of the following is the best next step in the management of this patient?
. Allow the patient to undergo a vaginal breech delivery whenever she goes into labor.
. Send the patient to labor and delivery immediately for an emergent cesarean section.
. Schedule a cesarean section at or after 41 weeks gestational age.
. Schedule an external cephalic version in the next few days.
. Allow the patient to go into labor and do an external cephalic version at that time if the fetus is still in the double footling breech presentation.
56) A 33-year-old woman presents to the physician because of a malodorous vaginal discharge that has been present for the past 3 days. She has no vaginal or vulvar irritation, and has no urinary complaints. Pelvic examination demonstrates a copious, gray discharge with a pH of 5.0. When 1 drop of potassium hydroxide (KOH) is added to a sample of the discharge there is an intense amine odor. A normal saline wet preparation is performed that demonstrates epithelial cells whose borders and nuclei are obscured by the presence of bacteria. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Candida albicans
Chlamydia trachomatis
Gardnerella vaginalis
Lactobacillus species
Trichomonas vaginalis
57) A 32-year-old woman is brought to the operating room for diagnostic laparoscopy because of chronic pelvic pain and chronic right upper quadrant pain. She has had these pains for the past 2 years. Her bowel and bladder function are normal. Past medical history is significant for two episodes of gonorrhea. She drinks one beer per day. Laboratory studies show: Urine hCG: negative, Haematocrit: 39%, leukocyte count: 8,000/mm3, platelet count: 200,000/mm3, AST: 12U/L, ALT:14U/L. Intraoperatively, the patient is noted to have dense adhesions involving her fallopian tubes, ovaries, and uterus. The fallopian tubes themselves appear clubbed and occluded. A survey of her upper abdomen is remarkable for perihepatic adhesions extending from the liver surface to the diaphragm. The liver otherwise appears unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for her right upper quadrant pain?
Alcoholic cirrhosis
Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
Hepatitis
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
58) A 22-year-old primigravid woman at 10 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department because of vaginal bleeding and lower abdominal pain. She was cleaning the house when she suddenly started feeling colicky pain in the suprapubic area. The pain did not subside after resting, and a few minutes later a tissue-like substance passed through her vagina along with moderate bleeding. The pain subsequently ceased, but she still has mild discomfort. Her temperature is 37.0 C (98.7 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows a closed cervix and blood pooled in the vaginal vault. Ultrasonogram shows a vacant uterine cavity and free adnexae. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Incomplete abortion
Molar pregnancy
Inevitable abortion
Ectopic pregnancy
Complete abortion
59) A 26-year-old Caucasian female calls your office with a question about levothyroxine dosage during pregnancy. She is contemplating her first pregnancy very soon. You have been following her for primary hypothyroidism for several years. Her thyroid functions have been stable on a daily levothyroxine dose of 100μg. Her TSH level three months ago was 2.0 μU/ml (0.35 - 5.0 μU/ml is normal). What would be the most appropriate answer to this patient's question?
. Ask her to increase her levothyroxine dose before becoming pregnant
. She is most likely to increase her levothyroxine dose during pregnancy
. Her levothyroxine dose will not change after she becomes pregnant
. She is most likely to decrease her levothyroxine dose during pregnancy
. Levothyroxine is contraindicated in pregnancy and she has to switch to liothyronine (T3)
60) A 50-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of severe insomnia, hot flashes, and mood swings. She also states that her mother had a hip fracture at 65 years of age. She is afraid of developing osteoporosis and having a similar incident. Her last menstrual period was six months ago. Her past medical history is significant for hypothyroidism diagnosed seven years ago. She takes L-thyroxine and the dose of the hormone has been stable for the last several years. Her blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and her heart rate is 75/min. Serum TSH level is normal. You consider estrogen replacement therapy for this patient. Which of the following is most likely concerning estrogen replacement therapy in this patient?
. The level of total thyroid hormones would decrease
. The metabolism of thyroid hormones would decrease
. The requiren1ent for L-thyroxine would increase
. The volume of distribution of thyroxine would decrease
. The level of TSH would decrease
61) A previously healthy 50-year-old gravida 5, para 4, Caucasian woman comes to the physician complaining of passing small amounts of urine while sneezing or coughing for the past five months. She denies any episodes of weakness, numbness or fecal incontinence. There is no history of dysuria, increased frequency of urination, or hematuria. Her symptoms are progressively getting worse. Her other medical problems include diabetes mellitus type 2 diagnosed 3 years ago, treated with glyburide 2.5mg/day. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs, and has no known drug allergies. She mentions that she is an avid jogger, but her problem causes her significant embarrassment. She now has to wear absorbent pads while jogging. Her vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, the abdomen is soft. Neurological examination is within normal limits. Pelvic examination shows a cystocele. The patient's labs reveal: Urine Specific gravity: 1.020, Blood: negative, Glucose: negative, Leukocyte esterase: negative, Nitrites: negative, WBC: 5-10/hpf, Bacteria: none. Random blood sugar is 120 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Detrusor instability
Bladder irritation from a neoplasm
Interstitial cystitis
Overflow incontinence due to detrusor weakness
Pelvic floor muscle weakness
62) A 28-year-old, G2 P1 woman presented to the hospital at 34weeks gestation because of midepigastric and right upper quadrant pain associated with nausea and vomiting. She has been closely followed for mild hypertension and mild proteinuria (250 mg/24hr) on an outpatient basis since the 28th week of gestation. Her previous pregnancy was without incident. Her temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), blood pressure is 160/94 mmHg and pulse is 80/min. Physical examination shows epigastric and right upper quadrant tenderness; her bowel sounds are slightly reduced. The extremities have 2+ edema. Fetal heart sounds are audible on Doppler. Laboratory studies show: Hb: 8.2g/dl, Platelets: 96,000/mm3, Prothrombin time: 12.4 sec, Partial thromboplastin time: 23.6 sec, Serum creatinine: 1.1 mg/dl, Total bilirubin: 2.6 mg/dl, Direct bilirubin: 0.8 mg/dl, Alkaline phosphatase: 120 U/L, Aspartate aminotransferase: 308 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase: 265 U/L, Lipase: 53 U/L. Peripheral blood smear shows numerous red blood cell fragments. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. HELLP syndrome
. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
. Viral hepatitis
. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
63) A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, comes to the physician for a prenatal checkup. According to the last menstrual period and an ultrasonography performed at 16 weeks gestation, she is at 30 weeks gestation. She missed two antenatal appointments. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Examination shows a fundal height of 26cm (9.8in). Fetal heart tones are heard by Doppler. Repeat ultrasonogram shows a biparietal diameter consistent with dates and an abdominal circumference below the 10th percentile. Which of the following could most likely be responsible for the observed fetal findings?
Chromosomal abnormalities
Intrauterine infection
Hypertension
Gross fetal anomalies
Inaccurate dates
64) While you are on call at the hospital covering labor and delivery, a 32-year-old G3P2002, who is 35 weeks of gestation, presents complaining of lower back pain. The patient informs you that she had been lifting some heavy boxes while fixing up the baby’s nursery. The patient’s pregnancy has been complicated by diet-controlled gestational diabetes. The patient denies any regular uterine contractions, rupture of membranes, vaginal bleeding, or dysuria. She denies any fever, chills, nausea, or emesis. She reports that the baby has been moving normally. She is afebrile and her blood pressure is normal. On physical examination, you note that the patient is obese. Her abdomen is soft and nontender with no palpable uterine contractions. No costovertebral angle tenderness can be elicited. On pelvic examination her cervix is long and closed. The external fetal monitor indicates a reactive fetal heart rate strip; there are rare irregular uterine contractions demonstrated on the tocometer. The patient’s urinalysis comes back with trace glucose, but is otherwise negative. The patient’s most likely diagnosis is which of the following?
. Labor
. Musculoskeletal pain
. Urinary tract infection
. Chorioamnionitis
. Round ligament pain
65) A 29-year-old G3P2 presents to the emergency center with complaints of abdominal discomfort for 2 weeks. Her vital signs are: blood pressure 120/70 mm Hg, pulse 90 beats per minute, temperature 36.94C, respiratory rate 18 breaths per minute. A pregnancy test is positive and an ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis reveals a viable 16-week gestation located behind a normal-appearing 10×6×5.5 cm uterus. Both ovaries appear normal. No free fluid is noted. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
. Ectopic ovarian tissue
Fistula between the peritoneum and uterine cavity
. Primary peritoneal implantation of the fertilized ovum
. Tubal abortion
. Uterine rupture of prior cesarean section scar
66) A 32-year-old G2P1 at 28 weeks gestation presents to labor and delivery with the complaint of vaginal bleeding. Her vital signs are: blood pressure 115/67 mm Hg, pulse 87 beats per minute, temperature 37.0C, respiratory rate 18 breaths per minute. She denies any contraction and states that the baby is moving normally. On ultrasound the placenta is anteriorly located and completely covers the internal cervical os. Which of the following would most increase her risk for hysterectomy?
. Desire for sterilization
Development of disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC)
. Placenta accreta
. Prior vaginal delivery
. Smoking
67) A 29-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of constant, severe lower abdominal pain. She also complains of fever and chills. Three weeks ago she had an intrauterine device (IUD) placed for contraception. Her temperature is 38.3 C (101 F), blood pressure is 110/76 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 16/min. She has bilateral lower quadrant abdominal tenderness. On pelvic examination, she has cervical motion tenderness and bilateral adnexal tenderness. A urinalysis is negative. A pelvic ultrasound is negative, with normal uterus and adnexae and no free fluid. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Appendicitis
Hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
Ovarian torsion
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Pyelonephritis
68) A 32-year-old G5P1 presents for her first prenatal visit. A complete obstetrical, gynecological, and medical history and physical examination is done. Which of the following would be an indication for elective cerclage placement?
. Three spontaneous first-trimester abortions
. Twin pregnancy
Three second-trimester pregnancy losses without evidence of labor or abruption
History of loop electrosurgical excision procedure for cervical dysplasia
Cervical length of 35 mm by ultrasound at 18 weeks
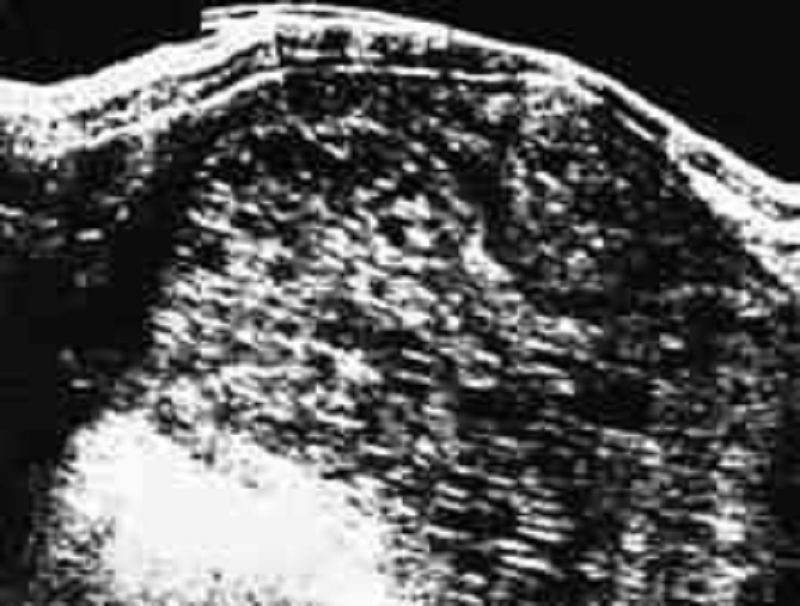
69) A 19-year-old primigravida is expecting her first child; she is 12 weeks pregnant by dates. She has vaginal bleeding and an enlarged-for-dates uterus. In addition, no fetal heart sounds are heard. The ultrasound shown below is obtained. Which of the following is true regarding the patient’s diagnosis?
. The most common chromosomal makeup of a partial or incomplete mole is 46XX, of paternal origin
. Older maternal age is not a risk factor for hydatidiform mole
. Partial or incomplete hydatidiform mole has a higher risk of developing into choriocarcinoma than complete mole
. Vaginal bleeding is a common symptom of hydatidiform mole
. Hysterectomy is contraindicated as primary therapy for molar pregnancy in women who have completed childbearing
70) A 32-year-old female presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago and her pregnancy test is positive. On examination she is tachycardic and hypotensive and her abdominal examination findings reveal peritoneal signs, a bedside abdominal ultrasound shows free fluid within the abdominal cavity. The decision is made to take the patient to the operating room for emergency exploratory laparotomy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
Hydatidiform mole
Incomplete abortion
Missed abortion
Torsed ovarian corpus luteal cyst
71) A 19-year-old woman comes to the emergency department and reports that she fainted at work earlier in the day. She has mild vaginal bleeding. Her abdomen is diffusely tender and distended. In addition, she complains of shoulder and abdominal pain. Her temperature is 37.2C, pulse rate is 120 beats per minute, and blood pressure is 80/42 mm Hg. Which of the following is the best diagnostic procedure to quickly confirm your diagnosis?
. Computed tomography of the abdomen and pelvis
. Culdocentesis
. Dilation and curettage
. Posterior colpotomy
. Quantitative β-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG)
72) A 22-year-old G1P0 woman who is 10 weeks pregnant with twins presents to the emergency department because of vomiting and dizziness. She has had “morning sickness” for the past month and would vomit once or twice a day. However, over the past week, she has been vomiting multiple times a day, and she has been unsuccessful at “keeping anything down” for the past 2 days. She denies fever or change in her bowel movements; her last bowel movement was that morning and was well formed. She has otherwise been healthy. Physical examination reveals a tired-appearing, pale woman with poor skin turgor; otherwise her examination is unremarkable. Her blood pressure is 110/75 mm Hg lying down and 90/45 mmHg sitting up. Her pulse is 80/min lying down and 115/min sitting up. Her respiratory rate is 24/min, and her temperature is 37.2C (99.0F). Her original blood work results are: WBC count: 14,000/mm3, Platelet count: 350,000/mm3, Na+: 150 mEq/L, K+: 4 mEq/L, Cl-: 88 mEq/L, HCO3-: 26 mEq/L, Hemoglobin: 15 g/dL, Hematocrit: 40%, Aspartate aminotransferase: 80 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase: 85 U/L. What is this woman’s most likely diagnosis?
Acute viral hepatitis A
Food poisoning with Salmonella
Hyperemesis gravidarum
Preeclampsia
Viral gastroenteritis
73) A 58-year-old woman with stage II epithelial ovarian cancer undergoes successful surgical debulking followed by chemotherapy with carboplatin and radiation therapy. Subsequently, she develops non-pitting edema of both legs and pain and numbness in her legs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her pain and numbness?
Nerve damage caused by the pelvic lymphadenectomy
Lymphedema
Carboplatin therapy
Radiation therapy
Recurrent ovarian cancer
74) A 26-year-old black gravida 2, para 1, at 32 weeks' gestation presents to the physician for a prenatal visit. Her prenatal course has been remarkable for hyperemesis gravidarum in the first trimester. She also had a urine culture in the first trimester that grew out Group B Streptococcus. She has had type 1 diabetes for the past 2 years and has had good control of her blood glucose levels during this pregnancy. Her first pregnancy resulted in a low transverse cesarean section for dystocia. Other than insulin, she takes no medicines and has no known drug allergies. After a routine prenatal visit, the physician sends her to the antepartum fetal testing unit to undergo a non-stress test (NST). Which of the following characteristics makes this patient a good candidate for antepartum fetal testing with an NST?
Black race
Diabetes mellitus
Group B Streptococcus urine culture
History of cesarean section
Hyperemesis gravidarum
75) A 39-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office with a palpable nodularity in the right breast. Pathologically, the lesion is composed of ducts distended by pleomorphic cells with prominent central necrosis. The lesion does not extend beyond the ductal basal membrane. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Paget disease
. Comedocarcinoma
Medullary carcinoma
Sclerosing adenosis
Mammary duct ectasia
76) A 32-year-old female presents to your office complaining of a small amount of vaginal discharge. Wet mount preparation of the discharge shows few leukocytes. Application of KOH solution to the discharge yields a strong fishy odor. The most likely diagnosis is:
Gonorrhea infection
Chlamydia infection
Bacterial vaginosis
Fungal infection
Trichomonas infection
77) A 50-year-old woman presents with fatigue, insomnia, hot flashes, night sweats, and absence of menses for the last 5 months (secondary amenorrhea). Her urine hCG test is negative. Laboratory tests reveal decreased serum estrogen and increased serum FSH and LH levels. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this individual’s clinical signs and symptoms?
. 17-hydroxylase deficiency of the adrenal cortex
. Prolactin-secreting tumor of the anterior pituitary
. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone–secreting tumor of the hypothalamus
. Menopause
. Menarche
78) A 39-year-old woman presents with new onset of a bloody discharge from her right nipple. Physical examination reveals a 1-cm freely movable mass that is located directly beneath the nipple. Sections from this mass reveal multiple fibrovascular cores lined by several layers of epithelial cells. Atypia is minimal. The lesion is completely contained within the duct and no invasion into underlying tissue is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Benign phyllodes tumor
. Ductal papilloma
. Intraductal carcinoma
. Paget disease
. Papillary carcinoma
79) A 48-year-old woman presents with a 1.5-cm firm mass in the upper outer quadrant of her left breast. A biopsy from this mass reveals many of the ducts to be filled with atypical cells. In the center of these ducts there is extensive necrosis. No invasion into the surrounding fibrous tissue is seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Colloid carcinoma
. Comedocarcinoma
. Infiltrating ductal carcinoma
. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma
. Lobular carcinoma in situ
80) A 51-year-old woman presents with an ill-defined, slightly firm area in the upper outer quadrant of her right breast. The clinician thinks this area is consistent with fibrocystic change, but a biopsy from this area has a focus of lobular carcinoma in situ. Which of the following histologic features is most characteristic of this lesion?
. Expansion of lobules by monotonous proliferation of small cells
. Large cells with clear cytoplasm within the epidermis
. Large syncytium-like sheets of pleomorphic cells surrounded by aggregates of lymphocytes
. Small individual malignant cells dispersed within extracellular pools of mucin
. Small tumor cells with little cytoplasm infiltrating in a single-file pattern
81) A 46-year-old woman presents with a 4-month history of a discharge from the nipple. An excisional biopsy of the nipple area reveals infiltration of the nipple by large cells with clear cytoplasm. These cells are found both singly and in small clusters in the epidermis and are PAS-positive and diastase resistant. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ductal papilloma
. Eczematous inflammation
. Mammary duct ectasia
. Paget disease
. Phyllodes tumor, malignant
82) A 59-year-old woman who had been diagnosed with infiltrating ductal carcinoma 2years prior presents with pain of her right breast. The breast is swollen, tender on palpation, and is diffusely indurated with a “peau d’orange” appearance. Multiple axillary lymph nodes are palpable in the lower axilla. A skin biopsy from her breast reveals extensive invasion of dermal lymphatics. What is the best diagnosis?
. Angiosarcoma
. Comedocarcinoma
. Duct ectasia
. Inflammatory carcinoma
. Sclerosing adenosis
83) A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician's office for evaluation of a vulvar ulcer that she noticed two days ago. Initially she had a small painless papule that later became ulcerated. Upon further questioning she reluctantly admits to using sex to obtain drugs. She also reports using oral contraceptives to prevent pregnancy. On vulvar examination there is a 2-cm ulcer with a non-exudative base and a raised, indurated margin. Painless bilateral inguinal lymphadenopathy is present. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Syphilis
. Chancroid
. Herpes genitalis
. Granuloma inguinale
. Basal cell carcinoma
84) A 23-year-old woman who is 26 weeks pregnant presents to the emergency department with sudden onset severe shortness of breath and inability to lie flat. She recently emigrated from Eastern Europe. Her medical history is significant for recurrent sore throats requiring tonsillectomy as a child. Presently, her blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg and her heart rate is 120/min. An EKG rhythm strip suggests atrial fibrillation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
. Constrictive pericarditis
. Mitral stenosis
. Myocardial infarction
. Aortic insufficiency
85) A 47-year-old woman presents to your office with complaints of lower abdominal pain, nocturia, urinary urgency and frequency relieved with urination. She states the symptoms have been worsening this past month and she recently experienced dyspareunia. She is sexually active with her husband, but this is causing her a great amount of pain. She has four children and had uncomplicated pregnancies. She denies fevers or chills. On examination, she has diffuse lower abdominal pain with no rebound or guarding. Her external genitalia appear normal. On bimanual examination, palpation of the anterior vaginal wall elicits extreme pain. No cervical motion tenderness is present. No other abnormalities are noted. A urinalysis is negative. The most likely diagnosis is:
. Urinary tract infection
. Stress incontinence
. Cystocele
. Interstitial cystitis
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
86) A 22-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 39 weeks gestation is admitted to the hospital for delivery. She has had regular and painful uterine contractions occurring every 3 minutes for the past 10 hours. Her pregnancy has been uncomplicated. She had a normal vaginal delivery for her first pregnancy and required an episiotomy. A recent ultrasound at 37 weeks gestation showed a fetus in a cephalic presentation with an estimated fetal weight of 3,400 g (7.5 lb). Examination shows the cervix is soft, 50% effaced and 2 cm dilated. She is given epidural anesthesia per her request. Eight hours later, her cervix has not significantly changed, and uterine contractions are occurring every 5 minutes. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her current condition?
. Cephalopelvic disproportion
. Early anesthesia
. Cervical dysfunction
. Perineal scar
. False labor
87) A 24-year-old gravida 2, para 1, African American woman at 12 weeks gestation comes for her first prenatal visit. Except for early morning mild headaches and nausea she has no other symptoms. Physical examination shows mild bilateral ankle edema. Blood pressure is measured twice 15 minutes apart and is 150/96 mmHg on both occasions. Blood is drawn for laboratory tests and the patient is sent home with a follow-up appointment 3 days later. She returns 3 days later and repeat blood pressure is the same. Laboratory studies show: Urinalysis: Protein: negative, Blood: negative, Glucose: trace, Ketones: negative, Leukocyte esterase: negative, Nitrites: negative, WBC: 1-2/hpf, RBC: 1-2/hpf. Chemistry panel: Serum sodium: 150 mEq/L, Serum potassium: 2.5 mEq/L, Chloride: 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate: 23 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): 14 mg/dL, Serum creatinine: 0.8 mg/dL. Ultrasonogram reveals intrauterine gestation consistent with dates; no abnormalities noted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Preeclampsia
. Chronic hypertension
. Molar pregnancy
. Transient hypertension of pregnancy
. Normal pregnancy
88) A 27-year-old primigravid woman at 30 weeks’ gestation comes to the emergency department complaining of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Earlier in the day she began to experience severe epigastric and later right upper quadrant pain. Until now her pregnancy has been uneventful and she has had regular prenatal care. Her past medical history and review of symptoms are unremarkable. On examination she is a pregnant woman in moderate distress, lying still on the hospital bed. Vital signs are: temperature 38.9 C (102.0 F), blood pressure 105/68 mm Hg, and pulse 108/min. Her abdomen is extremely tender to palpation in the right upper quadrant with guarding. There is no vaginal bleeding or discharge. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit: 36%, Leukocytes: 15,000/mm3 (88% neutrophils), Platelets: 158,000/mm3. Liver function tests, including transaminases, are normal. Prothrombin time is within normal limits. Urinalysis is unremarkable except for a few red blood cells on microscopy. X-ray is deferred out of concern for the fetus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
. Acute fatty infiltration of the liver
. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
. Luminal obstruction of the appendix from lymphoid hyperplasia or fecalith
. Pregnancy outside the uterine endometrium
. Premature separation of a normally implanted placenta
89) A 29-year-old woman comes to your office because she has been feeling depressed. She states that at times over the past several years she has regular occurrences of depression, anxiety, tearfulness, anger, and difficulty with work and social relationships. These occurrences have been increasing over the past several months. She doesn’t remember when her symptoms start or end. “It’s all a blur,” she says. She has had several urinary tract infections in her life, but otherwise has no medical problems. She takes no medications and has no drug allergies. Physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in caring for this patient?
. Have her keep a symptom calendar
. Schedule an MRI of the brain
. Schedule a pelvic ultrasound
. Start the patient on a benzodiazepine
. Start the patient on a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor
90) You examine a 28-year-old woman who is 2 days status post-cesarean delivery for a nonreassuring fetal heart rate tracing in labor. Her prenatal course was complicated by her developing acute tuberculosis in the days immediately before her delivery. When you diagnosed her with tuberculosis, she decided to hold off on therapy until after the baby was born. She was also found to be Group B Streptococcus–positive on a 36-week vaginal culture. She has a past medical history significant for chronic hepatitis B. Her past surgical history is significant for a breast reduction 4 years ago. Postpartum she is doing well, with no complaints, normal vital signs, and a normal postpartum physical examination. She wants to know if she is able to breast feed her infant. Which of the following conditions precludes this patient from breastfeeding?
. Chronic hepatitis B
. Group B Streptococcus colonization
. Status-post breast reduction
. Status-post cesarean delivery
. Untreated tuberculosis
91) A 36-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 33 weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. She has some fatigue but no other complaints. Her current pregnancy has been complicated by a Group B Streptococcus urine infection at 16 weeks. Her past obstetric history is significant for a primary, classic cesarean delivery 5 years ago for a non-reassuring fetal tracing. Two years ago, she had a repeat cesarean delivery. Past surgical history is significant for an appendectomy 10 years ago. Which of the following is the major contraindication to a vaginal birth after cesarean (VBAC) in this patient?
. Classic uterine scar
. Group B Streptococcus urine infection
. Previous appendectomy
. Prior cesarean delivery for non-reassuring fetal tracing
. Two prior cesarean deliveries
92) A 59-year-old G4P4 presents to your office complaining of losing urine when she coughs, sneezes, or engages in certain types of strenuous physical activity. The problem has gotten increasingly worse over the past few years, to the point where the patient finds her activities of daily living compromised secondary to fear of embarrassment. She denies any other urinary symptoms such as urgency, frequency, or hematuria. In addition, she denies any problems with her bowel movements. Her prior surgeries include tonsillectomy and appendectomy. She has adult-onset diabetes and her blood sugars are well controlled with oral Metformin. The patient has no history of any gynecologic problems in the past. She has four children who were all delivered vaginally. Their weights ranged from 8 to 9 lb. Her last delivery was forceps assisted. She had a third-degree laceration with that birth. She is currently sexually active with her partner of 25 years. She has been menopausal for 4 years and has never taken any hormone replacement therapy. Her height is 5 ft 6 in, and she weighs 190 lb. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg. Based on the patient’s history, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Overflow incontinence
. Stress incontinence
. Urinary tract infection
. Detrusor instability
. Vesicovaginal fistula
93) A 49-year-old G4P4 presents to your office complaining of a 2-month history of leakage of urine every time she exercises. She has had to limit her physical activities because of the loss of urine. She has had burning with urination and some blood in her urine for the past few days. Which of the following is the best next step in the evaluation and management of this patient?
. Physical examination
. Placement of a pessary
. Urinalysis with urine culture
. Cystoscopy
Office cystometrics
94) An obese 46-year-old G6P1051 with type 1 diabetes since age 12 presents to your office complaining of urinary incontinence. She has been menopausal since age 44. Her diabetes has been poorly controlled for years because of her noncompliance with insulin therapy. She often cannot tell when her bladder is full, and she will urinate on herself without warning. Which of the following factors in this patient’s history has contributed the most to the development of her urinary incontinence?
. Menopause
. Obesity
. Obstetric history
. Age
. Diabetic status
95) A 76-year-old woman presents for evaluation of urinary incontinence. She had a hysterectomy for fibroid tumors of the uterus at age 48. After complete evaluation, you determine that the patient has genuine stress urinary incontinence. On physical examination, she has a hypermobile urethra, but there is no cystocele or rectocele. There is no vaginal vault prolapse. Office cystometrics confirms genuine stress urinary incontinence. Which of the following surgical procedures should you recommend to this patient?
. Kelly plication
. Anterior and posterior colporrhaphy
. Burch procedure
. Abdominal sacral colpopexy
. Le Fort colpocleisis
96) A patient presents to your office approximately 2 weeks after having a total vaginal hysterectomy with anterior colporrhaphy and Burch procedure for uterine prolapse and stress urinary incontinence. She complains of a constant loss of urine throughout the day. She denies any urgency or dysuria. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this complaint?
. Failure of the procedure
. Urinary tract infection
. Vesicovaginal fistula
. Detrusor instability
. Diabetic neuropathy
97) A 90-year-old G5P5 with multiple medical problems is brought into your gynecology clinic accompanied by her granddaughter. The patient has hypertension, chronic anemia, coronary artery disease, and osteoporosis. She is mentally alert and oriented and lives in an assisted living facility. She takes numerous medications, but is very functional at the current time. She is a widow and not sexually active. Her chief complaint is a sensation of heaviness and pressure in the vagina. She denies any significant urinary or bowel problems. On performance of a physical examination, you note that the cervix is just inside the level of the introitus. Based on the physical examination, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Normal examination
. First-degree uterine prolapse
. Second-degree uterine prolapse
. Third-degree uterine prolapse
. Complete procidentia
98) A 52-year-old woman comes to the physician because of hot flashes. Her last menstrual period was 1 year ago. Over the past year, she has noted a persistence of her hot flashes, which come several times each day and are associated with a feeling of heat and flushing. They also awaken her at night and interfere with her sleep. She has no medical problems, takes no medications, and has no known drug allergies. She has a family history of cardiovascular disease and she does not smoke. Physical examination is unremarkable. She is started on estrogen and medroxyprogesterone acetate (Provera). The addition of a progestin is most likely to decrease her risk of which of the following?
. Breast cancer
. Breast pain
. Endometrial cancer
. Mood changes
. Weight gain
99) A previously healthy 21-year-old woman has a profuse, malodorous vaginal discharge. Examination shows a greenish gray "frothy" discharge with a "fishy" odor and petechial lesions on the cervix. There is no cervical motion tenderness. Her temperature is 37.5 C (99.4 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 16/min. Microscopic evaluation of the discharge is most likely to show which of the following?
. "Clue cells"
. Gram-negative diplococci
. Gram-positive diplococci
. Motile, flagellated organisms
. Pseudohyphae or hyphae
100) A 26-year-old nulligravid woman comes to the emergency department because of severe right lower quadrant pain. She states that the pain started last night. This morning she was awakened from sleep with severe pain in the same area. During the episode of pain, she also had nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. On admission to the emergency department she required 5 mg of morphine to control her pain. Examination is significant for right lower quadrant tenderness and a tender right adnexal mass on pelvic examination. Urine hCG is negative. Urinalysis is negative. Transvaginal ultrasound reveals an 8 cm right ovarian mass. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Appendicitis
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Nephrolithiasis
. Ovarian torsion
. Pelvic inflammatory disease
101) A 21-year-old woman comes to the physician because of abdominal pain. She states that the pain is in her right lower quadrant and has been getting worse over the past 3 months. She has no other symptoms and a normal appetite. Examination demonstrates mild right lower quadrant abdominal tenderness. Pelvic examination reveals mild right adnexal enlargement and tenderness. Urine human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is negative. A pelvic ultrasound is obtained that shows a 4-centimeter, heterogeneous hyperechoic lesion in the right adnexa with cystic areas. On transvaginal ultrasound, hair and calcifications are demonstrated within the cystic areas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Appendicitis
. Benign cystic teratoma (dermoid)
. Corpus luteum cyst
. Ectopic pregnancy
. Tubo-ovarian abscess
102) A 27-year-old has just had an ectopic pregnancy. Which of the following events would be most likely to predispose to ectopic pregnancy?
. Previous cervical conization
. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
. Use of a contraceptive uterine device (IUD)
. Induction of ovulation
. Exposure in utero to diethylstilbestrol (DES)
{"name":"Part 56", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"38) A 30-year-old G2P2 woman comes to the physician with fatigue, mood swings, irritability, breast tenderness, abdominal bloating, and headaches that occur monthly. The symptoms are worse just before her menses and resolve by the third day of her menstrual cycle. The symptoms interfere with her daily activities, including her proficiency at work. The patient's only current medication is a multivitamin. She uses spermicidal foam and condoms for birth control. Her menses are regular. Her sister was diagnosed with hypothyroidism and takes levothyroxine. Examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?, 39) At a follow-up routine prenatal visit, the uterine fundus of a healthy 23-year-old pregnant woman is palpated halfway between her symphysis pubis and umbilicus. Which of the following is the most appropriate test to order at this stage of her pregnancy?, 40) A 25-year-old woman in her 15th week of pregnancy presents with uterine bleeding and passage of a small amount of watery fluid and tissue. She is found to have a uterus that is much larger than estimated by her gestational dates. Her uterus is found to be filled with cystic, avascular, grapelike structures that do not penetrate the uterine wall. No fetal parts are found. Immunostaining for p57 was negative in the cytotrophoblasts and villi mesenchyme. Which of the following is the best diagnosis?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/11-503381/share-pdf---adobe-acrobat-pro-dc.jpg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Sexual Harassment Quiz
210
Chem 30A Practice Quiz
1059
PUBLIC ENTERPRISES AND COOPERATIVE SOCIETIES
42210
Just for Fun
201028
Oxymoron: Can You Spot the Examples?
201018958
Cyber Security for Employees - Free Online
201018180
Pathological Liar Test - What Type of Liar Are You?
201020596
Borderlands 2 - Test Your Vault Hunter Knowledge
201029066
Sci‑Fi Trivia - Test Your Knowledge for Free
201017483
Dial Caliper Reading Test - Free Practice
201017557
Which Prefix Indicates a Secure Webpage? Free
201019530
Rice Purity Test - Free Online to Score Yourself
201020946