Planning 1

Site and Environmental Planning Quiz
Test your knowledge on site planning, environmental science, and geology with this comprehensive quiz! Designed for enthusiasts and professionals alike, this quiz will challenge your understanding of the principles that shape the land around us.
- Assess your grasp of critical concepts in site design
- Explore the relationship between natural science and architecture
- Engage with questions covering geology, hydrology, and sustainability
The art of arranging structures on the land and shaping the spaces between, an art linked to architecture, engineering, landscape architecture, and city planning. Site plans locate objects and activities in space and time. These plans may concern a small cluster of houses, a single building, and its grounds, or something as exclusive as a small community but in a single operation.
Site Planning
Landscape
Landscape Architecture
�the art of arranging structures on the land and shaping the spaces between; an art linked to architecture, engineering, landscape architecture, and city planning.
Landscape
Site Planning
Landscape Architecture
This process selects from a list of potential sites one that suits best the given use and requirements of the project.
SITE SELECTION PROCESS
DEVELOPMENT SUITABILITY PROCESS
Landscape
ownership of adjacent property, off-site nuisances
Existing land use
Traffic and transit
Cultural factors
The natural science that studies the Earth
GEOLOGY
GEORMORPHOLOGY
GEOLOGICAL
Produced by crystallization from a liquid.
Rocks
Sendimentary rock
Metamorphosed Rocks
branch of Geology that deals with the origin, nature, and distribution of landforms.
GEORMORPHOLOGY
GEOLOGY
Physiography
Refers to the description of landforms.
Physiography
GEORMORPHOLOGY
GEOLOGY
The term used to describe the composite sizes of particles in a soil sample
GEOMORPHOLOGY TEXTURE
SITE PLANNING REVIEW
GEOLOGY
Refers to the soil’s ability to transfer gravity water downward
Good drainage
Poor Drainage
Drainage
Means that gravity water is not readily transmitted by the soil and soil is frequently or permanently saturated and may have water standing on it caused by
Good drainage
Poor drainage
Drainage
� the rate at which water penetrates the soil surface (usually measured in cm or inches per hour
Infiltration
Permeability
Understanding slope forms for site design requires an understanding of local geologic, soil, hydrologic, and vegetative conditions.
SLOPE ANALYSIS
SLOPE FORM
Expressed graphically in terms of a slope profile, a silhouette of a slope drawn to known proportions with distance on the horizontal axis and elevation on the vertical axis
SLOPE FORM
SLOPE ANALYSIS
Angle of repose
Four basic slope forms are detectable on contour maps:
Straight S - shape concave convex
The angle at which soil can be safely inclined and beyond which it will fail.
Angle of repose
SLOPE ANALYSIS
SLOPE FORM
A map of a portion of the earth that describes the shape of the earth’s surface by contour lines.
TOPOGRAPHIC MAP
CONTOURS
SLOPE
imaginary lines that join points of equal elevation on the surface of the land above or below a reference surface such as the mean sea level.
CONTOURS
TOPOGRAPHIC MAP
SLOPE
When slopes are selected according to building type and the activities associated with it.
DESIRABLE SLOPES
SLOPE
SLOPE MAP
When rocks are broken down (weathered) into small fragments and carried by the wind, water, ice, and gravity. Energy for this process is solar and gravitational
SOIL EROSION
SLOPE
TOPOGRAPHIC MAP
The planet’s water cycle, is described by the movement of water from the oceans to the atmosphere to the continents and back to the sea.
Hydrologic cycle
SLOPE
SOIL
The upper boundary of the zone of groundwater; the top of the unconfined aquifer.
Water table
WATERSHED
AQUIFIER
A permeable geological stratum or formation that can both store and transmits groundwater in significant quantities
AQUIFIER
WATERSHED
Water table
A geographic area of land bounded by topographic features and height of land that captures precipitation, filters, and stores water and drains waters to a shared destination. Knowledge of watershed boundaries is critical to water quality and stormwater management.
Water table
WATERSHED
AQUIFIER
Plants reduce glare and reflection caused by sunlight. A light source received directly produces primary glare while reflected light is secondary glare. Plants may be used to filter or block glare by use of plants with the appropriate size, shape, and foliage density
Glare and Reflection
Erosion Control
Plants are a primary means of preventing erosion from stormwater runoff and controlling erosion during construction. Erosion is also minimized by the plant's action of intercepting rain, decreasing splash, and increased water absorption.
Erosion Control
Glare and Reflection
The technology of cooling spaces through proper siting of structure and use of energy-efficient materials, with the overall objective of energy conservation.
PASSIVE COOLING
COOLING
He art of arranging structures on the land and shaping the spaces between, an art linked to architecture, engineering, landscape architecture, and city planning. Site plans locate objects and activities in space and time. These plans may concern a small cluster of houses, a single building, and its grounds, or something as exclusive as a small community but in a single operation
TRAFFIC AND TRANSIT SYSTEMS
DENSITY AND ZONING
SOCIO-ECONOMIC FACTORS:
refers to the population per unit land area
Density
DENSITY AND ZONING
SIte
The study of the community and its social and economic structures are done to determine whether there is a need, an interest, or any objections to the project
SOCIO-ECONOMIC FACTORS:
TRAFFIC AND TRANSIT SYSTEMS
DENSITY AND ZONING
Defined as the way an open space of a given site is configured according to an arrangement of elements that evoke activity or flow, both physically or SITE PLANNING REVIEW visually.
SPATIAL PATTERNS
NATURAL FEATURES
AESTHETIC FACTORS
When sites are characterized by outstanding natural features of earth, rock, water, or plant material, SITE PLANNING REVIEW these may be incorporated in the site development as natural assets of the land.
SPATIAL PATTERNS
AESTHETIC FACTORS
NATURAL FEATURES
� is a scene observed from a vantage point. A view can be a theme that may suggest and give added meaning to buildings. The full view is not always the best.
View
Vista
is a confined view, usually directed toward a terminal or dominant feature. It has three components: a viewing station, a view, and a foreground. A view is usually better if enframed or seen through an appropriate screen
View
Vista
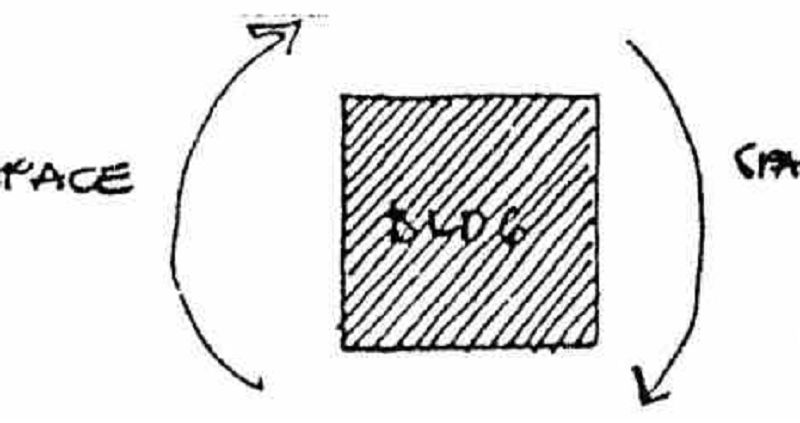
Enclosed within space
ISOLATED BUILDING
ENCLOSED SPACE
BUILDING ENCLOSING SPACE AND SPACE ENCLOSING BUILDING
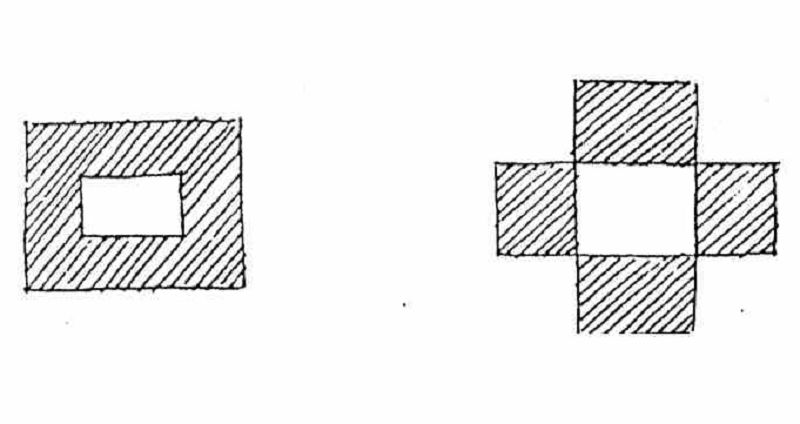
Interior space becomes cohesive therefore no elements to alienate buildings
ISOLATED BUILDING
BUILDING ENCLOSING SPACE AND SPACE ENCLOSING BUILDING
ENCLOSED SPACE
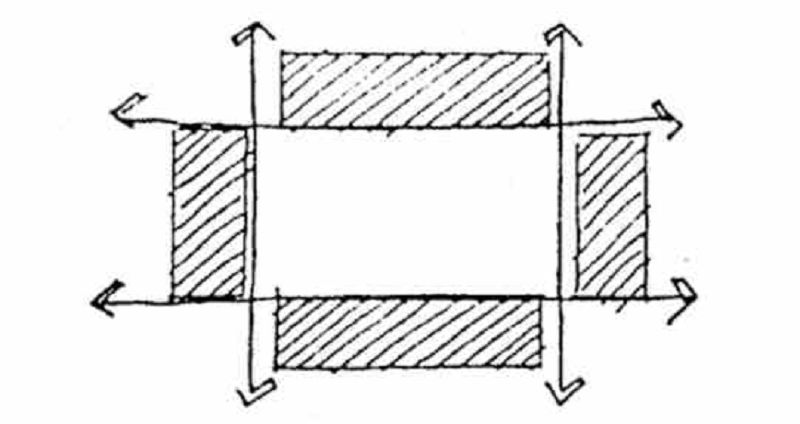
Isolated but cut-up with traffic lines
ENCLOSED SPACE
SPACE COHESIVE:
UNDER/ OVER PASS
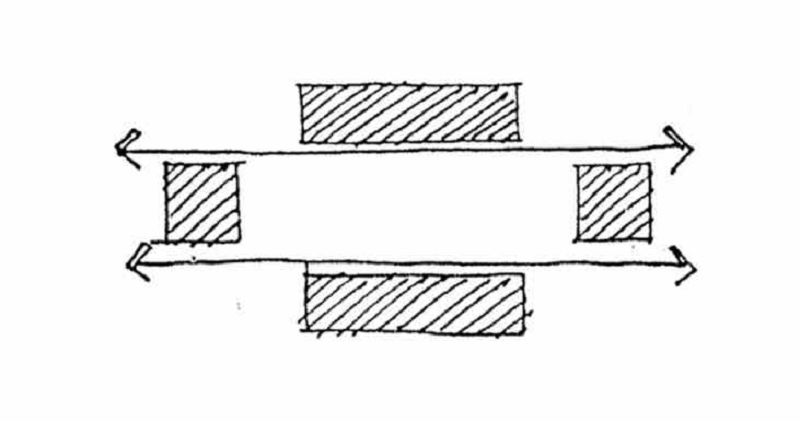
Less Isolated
SPACE COHESIVE:
UNDER/ OVER PASS
BUILT-UP CORNERS:

Unified isolated buildings
BUILT-UP CORNERS:
UNDER/ OVER PASS
MONUMENT/ STATUE/ FOUNTAIN:
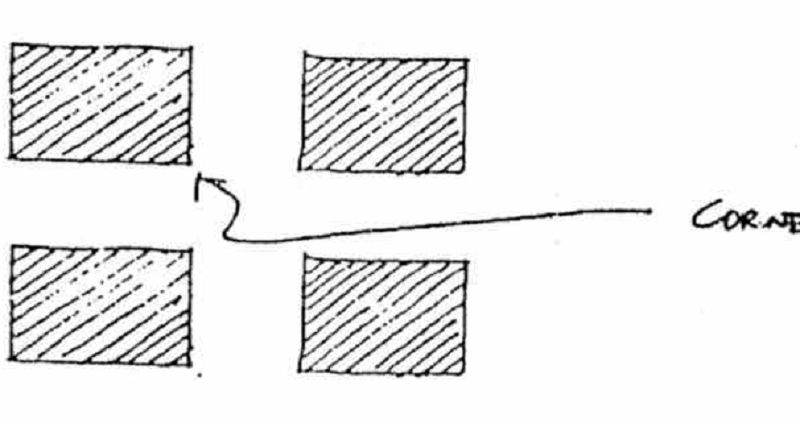
Corners are built-up making the design of buildings restricted since a similar shape must be adopted to hold the design together
BUILT-UP CORNERS:
MONUMENT/ STATUE/ FOUNTAIN:
TERMINAL POINTS
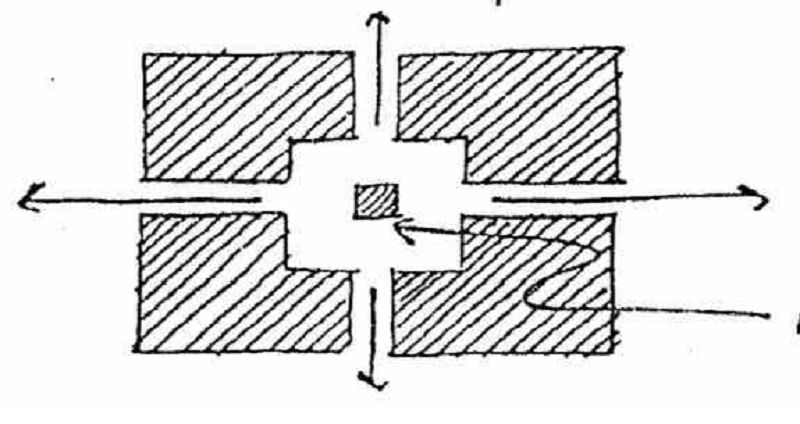
Introducing a monument/ statue/ fountain creates a visual identity for the space
MONUMENT/ STATUE/ FOUNTAIN:
TERMINAL POINTS
TERMINAL POINTS
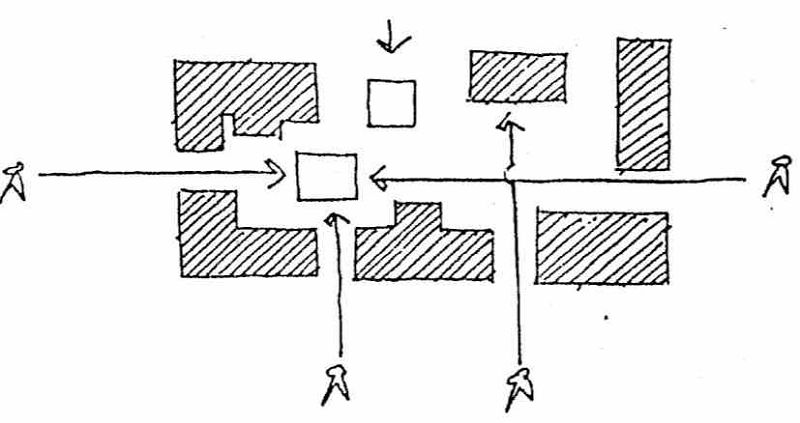
Use of terminal points is essential in siting a building such as the Piazza San Marco in Venice
TERMINAL POINTS
BUILT-UP CORNERS:
UNDER/ OVER PASS
A checklist of information or data pertaining to a site. The kind of data that would be required in some rather normal example of site planning. Such a list would be drawn up after an initial analysis of the problem. To guide the first survey, information would be gathered continuously as the problem develops.
Survey
Checklist
Form
Building design should integrate very nicely with the natural environment and make the best use of the existing site conditions.
Site Planning
Building Orientation
The Building Form
Developed with respect to the topographical contours where to minimize the area of cutting solid and in return filling back of soil to the site and to minimize the disturbance of the construction to the existing trees and landscape where digging up of soil and cutting off of tress were minimized.
The Building Form
Site Planning
Building Orientation
Elements placed in a landscape or streetscape for comfort, convenience, information, circulation control, protection, and user enjoyment, I.e. bollards, benches, signage, lighting, tree grates, utility boxes, etc.
Building Orientation
The Building Form
SITE FURNITURE
a major objective in the design and placement of site furniture elements. It should respond to the character of a site as well as to its existing and proposed function.
Appropriateness
Design Objectives
Response to setting
Design should respond to the essential identity or inherent character or a place.
Response to setting
Appropriateness
Design Objectives
If the central purpose of planning is to create for any person or group of persons an environment suited to their needs, then climate must a first consideration.
CLIMATE DESIGN
Design Objectives
Appropriateness
Suitable for various types of topography, each with its own practicality, functionality, and charm. The problem is choosing the type of street pattern for a particular site. One that would give utmost performance.
Street Patterns
CLIMATE DESIGN
Design Objectives
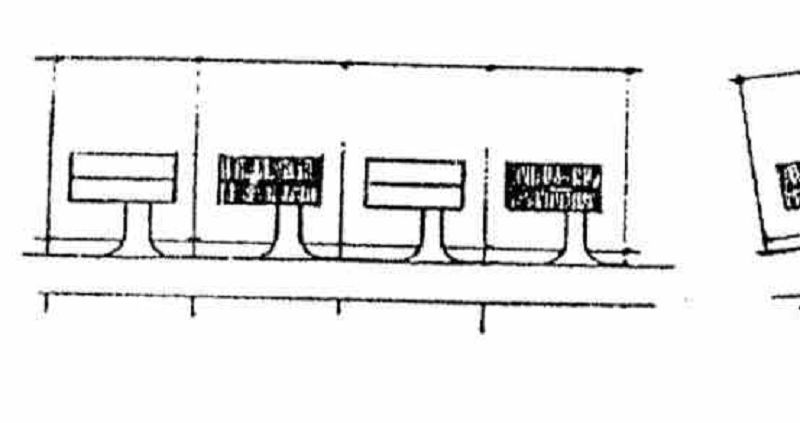
Linear or Street Ribbon. A straight road used to connect one community to another. Crossings are few and far between.
GEOMETRIC
GRIDIRON
RADIAL
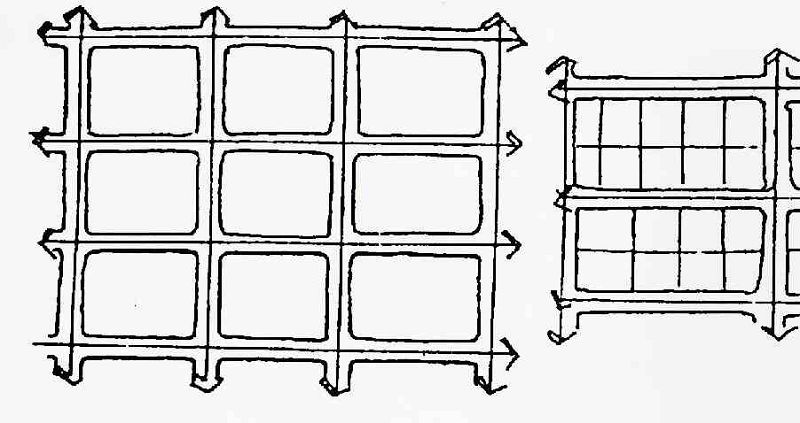
Site is divided into square or rectangular blocks. Advantages: blocks and services are easy to layout. Disadvantages: causes traffic congestion due to the frequent crossings created.
RADIAL
GRIDIRON
MEANDERING
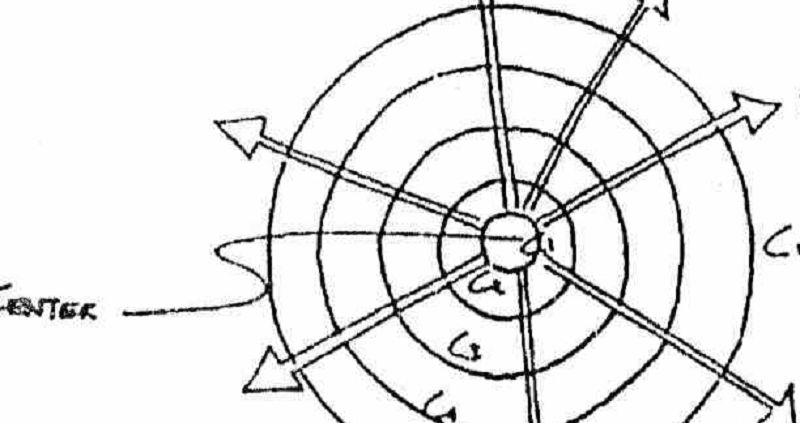
Use of circumferential and radial roads to connect the center of the city to the outskirts a ripple manner.
COMBINATION
RADIAL
MEANDERING
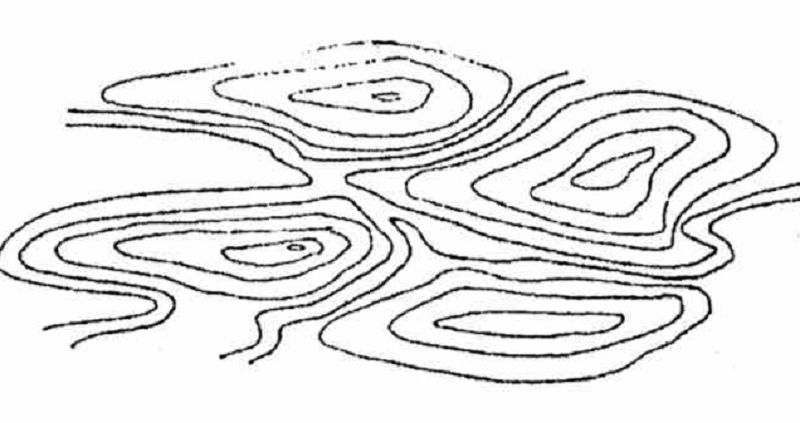
Used in highly mountainous sites. Following the contours of the topography.
MEANDERING
COMBINATION
MODIFIED GRIDS
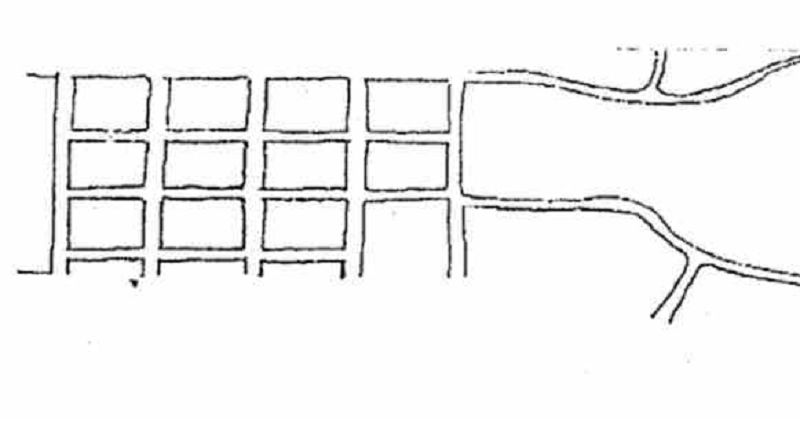
Using both the geometric and meandering street patterns. Geometric street pattern is used where the terrain is flat and meandering where the terrain is rolling.
COMBINATION
MODIFIED GRIDS
CUL-DE-SAC
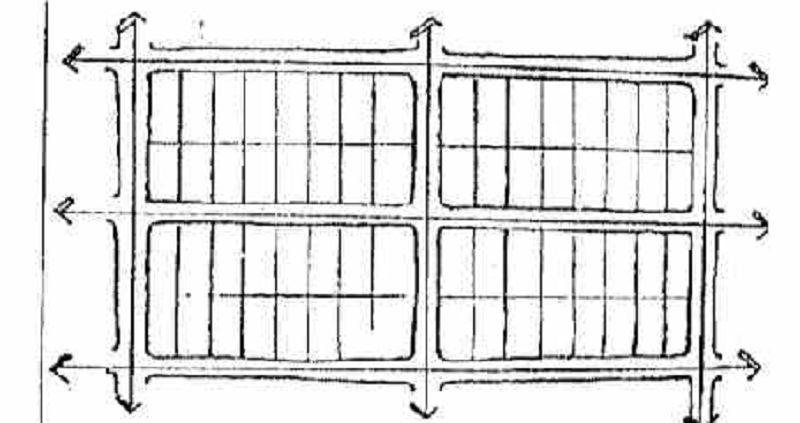
The advantage of a grid system is its ability to lay out streets in an easy and direct manner as well as the easy installation of services following the grids of the streets. One disadvantage of the grid is its relative monotony. To avoid monotonous street layout a modified grid could be used.
MODIFIED GRIDS
CUL-DE-SAC
LOOPS
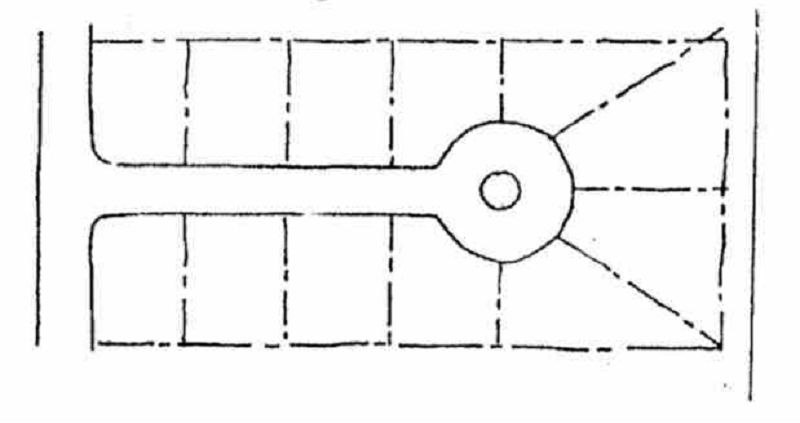
The grouping of houses presents a far less difficult problem that that of the straight street. A cul-de-sac is shaped so that the fronting houses automatically create an enclosed space.
CUL-DE-SAC
LOOPS
MODIFIED GRIDS
(major arterials: highways, bi-ways, expressways, super highways, freeways, motorways, autobahns, etc.)
Major roads
Secondary roads
Collector streets
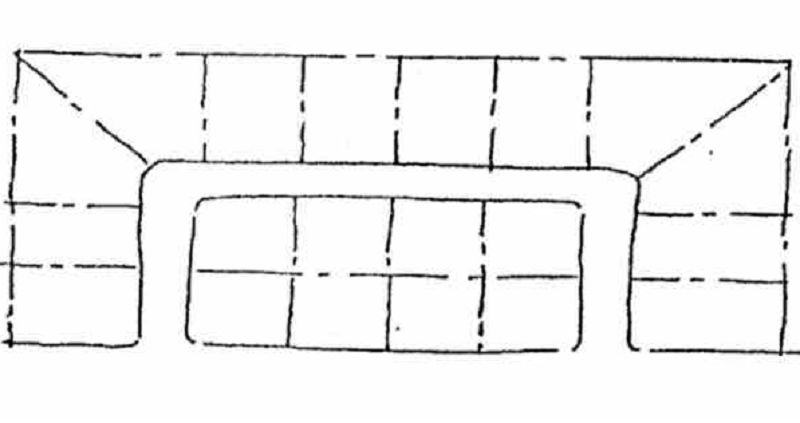
Good opportunities exist for varied and interesting house groups on lots flanking looped streets. One disadvantage of loops is the eventual narrowness of certain lot frontages especially along the curvature of the loop.
LOOPS
MODIFIED GRIDS
CUL DE SAC
Involves the remodeling of existing land form to facilitate the functions and circulation of the site.
SITE GRADING
SITE SELECTION
SITE CHECKLIST
{"name":"Planning 1", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on site planning, environmental science, and geology with this comprehensive quiz! Designed for enthusiasts and professionals alike, this quiz will challenge your understanding of the principles that shape the land around us.Assess your grasp of critical concepts in site designExplore the relationship between natural science and architectureEngage with questions covering geology, hydrology, and sustainability","img":"https:/images/course7.png"}
More Quizzes
Item 505
10518
Item 505 - Riprap and Grouted Riprap
10525
Legit Or Not?
40200
Wijsbegeerte
41200
Fairy Tale Trivia - Free Questions & Answers
201018247
Dispensary Questions - Free Cannabis Knowledge Test
201016279
Fiberoptic Bronchoscope - Airway Anatomy & Management
201022478
Which Statement Describes HSRP? - CCNA Redundancy
201020621
ServiceNow CSA Mock Test - Free Practice Questions
201017344
Which Cinderella Story Character Are You? Free
201017955
GTA San Andreas - Ultimate Trivia Challenge
201017279
Parental Anxiety - Free Coping Skills Assessment
201018631