Ap Bio Final Exam

AP Biology Final Exam Quiz
Test your knowledge of key concepts in AP Biology with our comprehensive final exam quiz. This quiz contains 36 multiple-choice questions that cover various topics, including biochemistry, cellular biology, genetics, and ecology.
Challenge yourself and revise what you've learned:
- Multiple-choice format
- Covers essential AP Biology topics
- Great for exam preparation
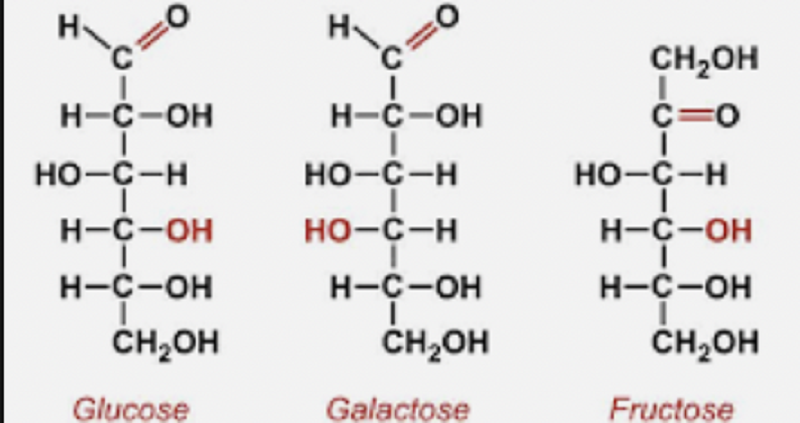
The carbohydrates glucose, galactose, and fructose have the same chemical formula (C.H..0.) but different structural formulas, as represented in the figure.Which of the following statements about glucose, galactose, and fructose is most likely true?
The carbohydrates have the same properties because they have the same number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
The carbohydrates have the same properties because they each have a single carbon-oxygen double bond.
The carbohydrates have different properties because they have different arrangements of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms.
The carbohydrates have different properties because they have different numbers of carbon-carbon bonds.
Which of the following best describes the possible structures of carbohydrates?
They only occur as disaccharides.
They occur as monomers, chains of monomers, and branched structures.
They only occur as long and branched structures.
They occur as chains of monomers that hydrogen bond with complementary chains of monomers.
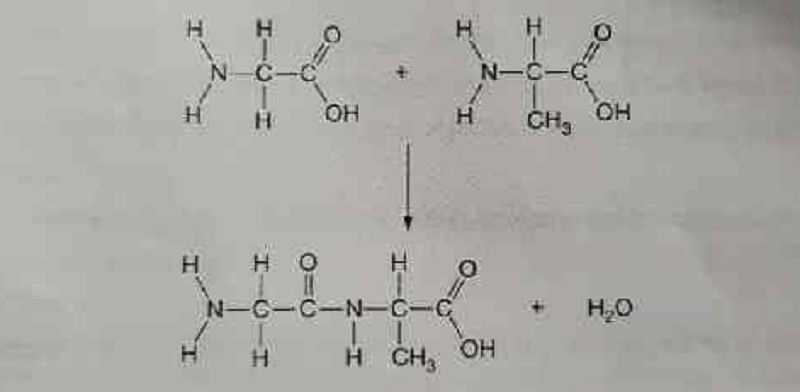
Which of the following is an accurate description of the process shown below ?
The linking of amino acids with an ionic bond as an initial step in the protein synthesis process
The formation of a more complex carbohydrate with the covalent bonding of two simple sugars
The hydrolysis of amino acids with the breaking of covalent bonds with the release of water
The formation of a covalent peptide bond in a dehydration synthesis reaction
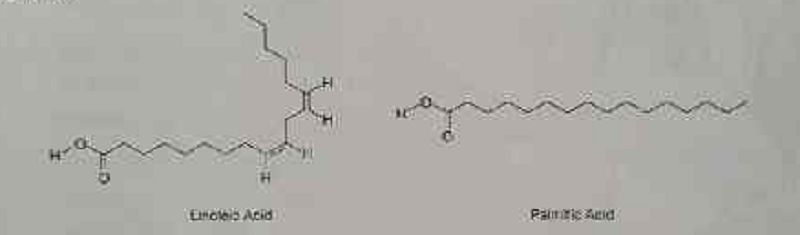
The molecular structures of linoleic acid and palmitic acid, two naturally occurring substances, are shown in the figure. Based on the molecular structures shown in the figure, which molecule is likely to be solid at room temperature?
Linoleic acid , because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together.
Linoleic acid, because the presence of carbon-carbon double bonds prevents the molecules from packing closely together.
Palmitic acid, because the absence of carbon-carbon double bonds allows the molecules to pack closely together.
Palmitic acid, because the presence of carbon-carbon double bonds prevents the molecules from packing closely together.
Which of the following is responsible for water's cohesive property?
Hydrogen bond between the oxygen atoms of two adjacent water molecules
Covalent bond between the hydrogen atoms of two adjacent water molecules
Hydrogen bond between an oxygen atom from one water molecule and a hydrogen atom from an adjacent water molecule
Covalent bond between an oxygen atom from one water molecule and a hydrogen atom from an adjacent water molecule
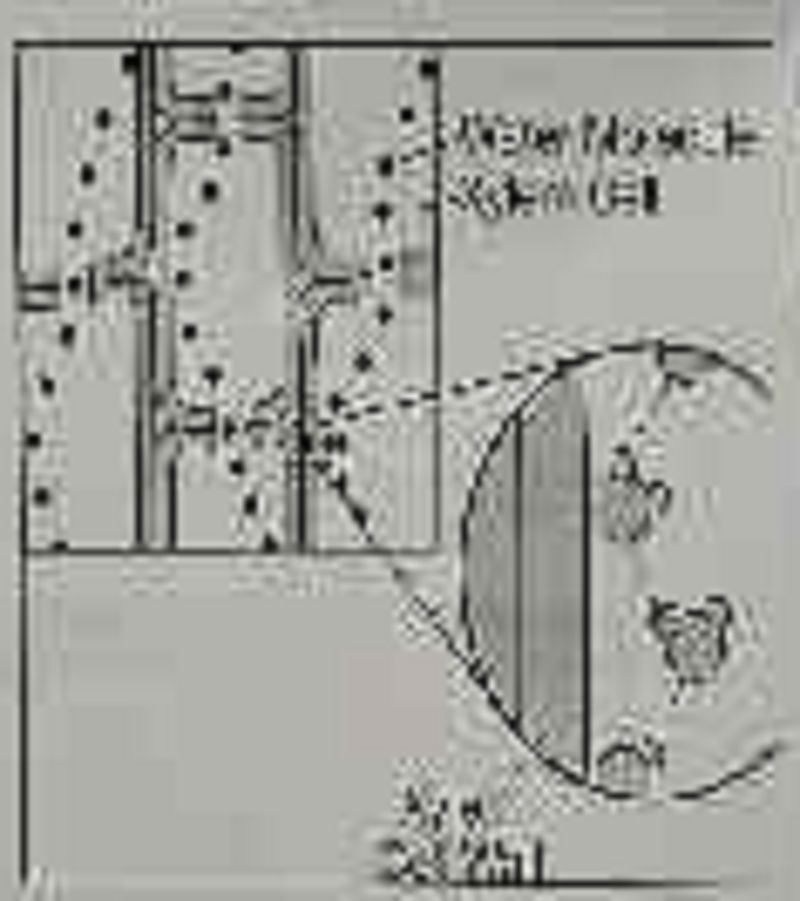
The diagram shows how water can adhere to the xylem in the stems of plants, which contributes to water movement in the plant. Which of the following best explains how water is able to move upward from the roots of a plant, through its xylem in the stem, and out to the leaves?
Water is polar, and the walls of the xylem are nonpolar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with one another but not with the xylem walls.
Water is nonpolar, and the walls of the xylem are polar. Water molecules are able to form hydrogen bonds with the xylem walls, and they are pulled up the xylem
Water and the xylem are both nonpolar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with one another but not with the xylem walls.
Water and the xylem are both polar. Water molecules have the ability to form hydrogen bonds with each other and with the walls of the xylem.
Which of the following is most directly responsible for water's unique properties?
It contains oxygen atoms
It contains hydrogen atoms
It is an ionic compound
It has hydrogen bonds
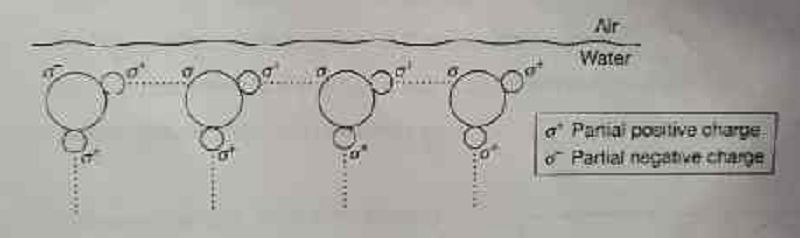
Below is a diagram of water molecules at the air-water interface at the surface of a pond.Based on the diagram, which of the following best describes how the properties of water at an air-water interface enable an insect to walk on the water's surface?
Covalent bonds between water molecules and the air above provide cohesion, which causes tiny bubbles to form under the feet of the insect.
Ionic bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide an electric charge, which attracts the feet of the insect, keeping it on the surface.
Polar covalent bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide adhesion, which supports the weight of the insect.
Hydrogen bonds between molecules at the surface of the water provide surface tension, which allows the water surface to deform but not break under the insect.
A typical bag of fertilizer contains high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium but trace amounts of magnesium and calcium. Which of the following best matches the fertilizer component with the molecule in which will be incorporated by organisms in the area?
Nitrogen will be incorporated into nucleic acids
Phosphorus will be incorporated into amino acids
Potassium will be incorporated into lipids
Magnesium will be incorporated into carbohydrates

Which statement is the most accurate description of the reaction shown to the right?
It represents monomers linked by dehydration synthesis
It represents a polypeptide chain that folds to form the tertiary structure
It represents a polypeptide chain that is denatured into the primary structure
It represents a polypeptide chain that is broken down through a hydrolysis reaction
Every amino acids consists of:
An amine group, R-group, and a central carbon
A hydroxyl side chain, a central carbon with R group, carboxyl group
An amine group, a central carbon with a variable R group, and carboxyl group
A phosphate, pentose sugar, and nitrogenous base
DNA and RNA are nucleic acids that can store biological information based on the sequence of their nucleotide monomers. Which of the following best describes a structural difference between DNA and RNA?
DNA's backbone consists of deoxyribose sugar, while RNA's backbone consist of ribose sugar
DNA's backbone consists of ribose sugar, while RNA's backbone consists of ribose sugar
DNA's backbone is more stable because of its ribose sugar
RNA's backbone is more stable because of its ribose sugar
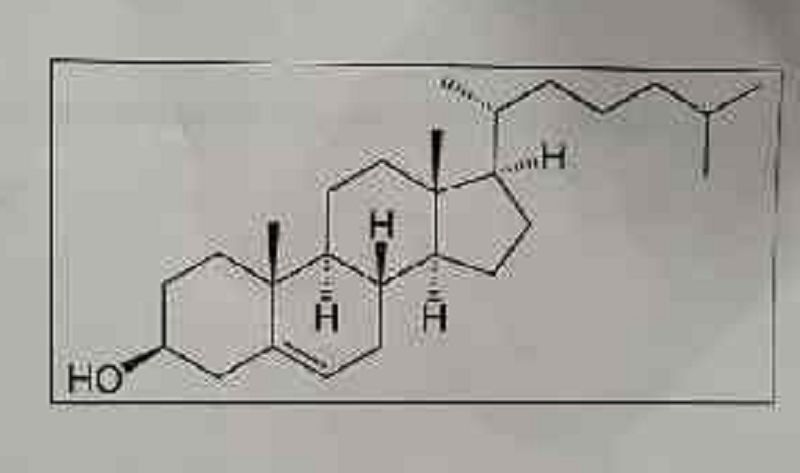
Look at the figure to the right. Which of the following statements is most likely to be true about that molecule?
The molecule is most likely a type of enzyme
The molecule is most likely a type of steroid
The molecule is most likely a type of disaccharide
The molecule is most likely a fragment of RNA

The sequences for two short DNA fragments are shown above. Which of the following is one way in which these two segments differ?
Segment 1 would not code for RNA because both strands have T, a base not found in RNA
Segment 1 would denature at a lower temperature than segment 2 because A-T base pairs have two hydrogen bonds whereas the G-C base pairs have three
Segment 1 would be more water soluble because it has more phosphate groups
Segment 1 must be from a prokaryote because it has more A-T base pairs.
A section of double-stranded DNA is composed of 35% adenine bases. What is the percentage of cytosine bases in the section of DNA?
20%
35%
15%
30%
Which of the following DNA fragments is the correct complementary strand for the following template? 5" ATAGCTA 3"
5" TATCGAT 3'
3" TATCGAT 5*
5" UAUCGAU 3"
3" UAUCGAU 5"
All eukaryotic cells contain at least one Golgi complex, typically located in the cytoplasm and near the endoplasmic reticulum. Which of the following best describes a process that occurs within the Golgi complex?
Enzymatic modification of newly synthesized integral membrane proteins
Synthesis of cytosolic proteins based on the nucleotide sequences of mRNAs
Degradation of protein by hydrolytic enzymes contained within the complex
Synthesis of various types of lipids
Which of the following organelles contains hydrolytic enzymes associated with the intracellular digestion of macromolecules?
Centrioles
Lysosomes
Peroxisomes
Nucleolus
The figure to the right illustrates a eukaryotic cell. Which of the following best describes how the three structures indicated by the arrow work together?
To synthesize lipids and modify toxic substances in order to render them harmless
To synthesize and isolate proteins for secretion or for use in the cell
To catabolize nutrients and produce ATP for intracellular energy storage
To synthesize all ribosomal proteins
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells generally have which of the following features in common?
A membrane bound nucleus
A cell wall made of cellulose
Ribosomes
Flagella or cilia that contains microtubules
The primary function of the kidney is to exchange molecules across a membrane between the blood and the urine. One type of kidney cell has a basic rectangular shape, except for a single surface, which is lined with tiny, finger-like projections that extend into the surrounding extracellular space. Which of the following best explains the advantage these projections provide the cell?
The projections increase the volume of the cell without affecting the surface area, which increases the metabolic needs of the cell
The projection increases the surface area-to-volume ratio of the cell, which allows for more efficient nutrient exchange with the environment
The projections increase the speed at which the individual molecules can move, resulting in faster nutrient exchange with the environment
The projections increase the selectivity of the membrane because the small size of the projections limits the number of transport proteins that can be embedded in the membrane
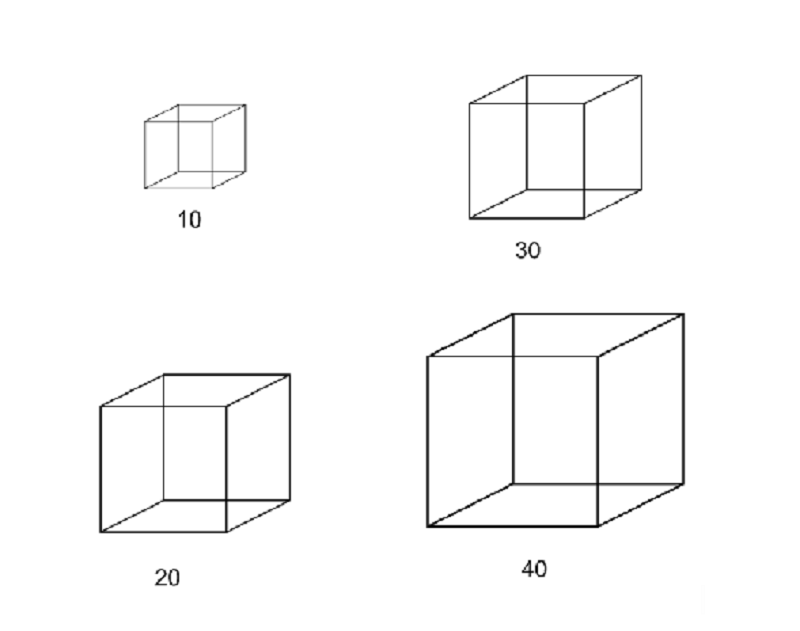
Simple cuboidal epithelial cells line the ducts of certain human exocrine glands. Various materials are transported into or out of the cells by dlifusion. (The formula for the surface area of a cube is 6 X S?, and the formula for the volume of a cube is S", where S= the length of a side of the cube.) Which of the following cube-shaped cells would be most efficient in removing waste by diffusion?
10
30
20
40
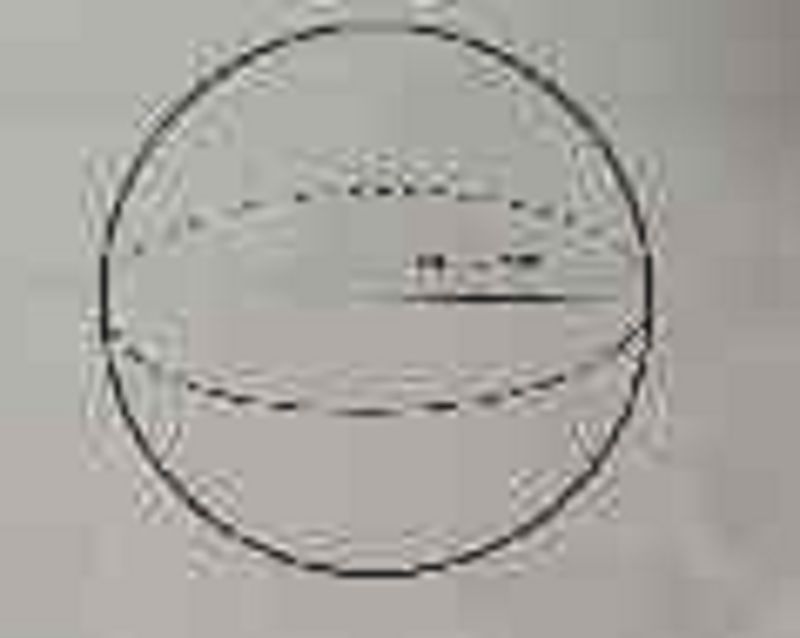
What is the surface area-to-volume ratio of the following shape:
0.4
0.067
25
15
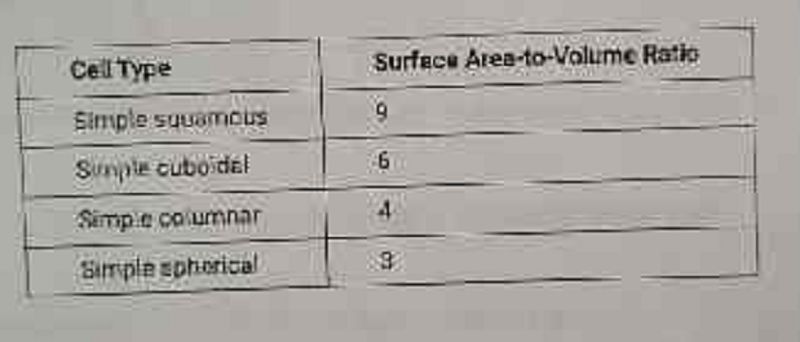
A student calculated the average surface area-to-volume ratio of four different types of human epithelial cells. The results are shown in the table below.Based on the data, which type of cell would be best suited for the lining of the alveoli of the lungs, where diffusion of carbon dioxide and oxygen occur very rapidly?
Simple Squamous
Simple Cuboidal
Simple Columnar
Simple Spherical
Which of the following components of the cell membrane is responsible for active transport?
Phospholipid
Protein
Cholesterol
Phosphate
The active transport pump used to move sodium ions across the membranes of gill cells in a freshwater fish has each of the following characteristics EXCEPT:
It uses osmosis to carry sodium ions into the cell
It requires energy
It has a specific binding site for sodium
It has a specific binding site for ATP
Which of the following statements is true regarding the movement of substances across cell membranes?
Lons are able to move through the phospholipid bilayer because the polar head regions of the phospholipids are charged
Water is able to move through the phospholipid bilayer because the nonpolar tail region of the phospholipids is charged
ions are unable to move through the phospholipid bilayer because the nonpolar tail region of the phospholipids is hydrophobic
Water is unable to move through the phospholipid bilayer because the polar head region of the phospholipid is charged
Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion are related in that both:
Require protein carriers
Depend on a concentration gradient
Occur in eukaryotic cells but not prokaryotic cells
Are endergonic processes and thus require the hydrolysis of ATP
Which of the following is an important difference between light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
The light-dependent reactions occur only during the day; the light-independent reactions occur only during the night.
The light-dependent reactions occur in the cytoplasm; the light-independent reactions occur in chloroplasts.
The light-dependent reactions utilize CO2 and H2O; the light-independent reactions produce CO2 and H20
The light-dependent reactions produce ATP and NADPH; the light-independent reactions use energy stored in ATP and NADPH.
It is estimated that oxygen production first evolved in photosynthetic prokaryotes approximately 2.7 billion years ago. The first photosynthetic prokaryotes are presumed to be similar to today's cyanobacteria. Which of the following best supports the claim that photosynthetic prokaryotes were responsible for the oxygen in Earth's atmosphere?
The light reactions of photosynthesis split carbon dioxide into carbon and oxygen
The light reactions of photosynthesis split water into hydrogen ions and oxygen
The Calvin cycle splits glucose into carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
The Calvin cycle splits water into hydrogen ions and oxygen.
The energy required to run the Calvin cycle reactions of photosynthesis comes from which two substances produced during the light-dependent reactions?
ATP and NADPH
H+ and ATP
H.O and CO2
O2 and NADPH
RuBisCO catalyzes the joining of carbon dioxide with RUBP during carbon fixation. In an experiment, researchers apply a toxin to a plant cell that inhibits RuBiscO. Which of the following explains the most likely effect this toxin will have on the Calvin cycle?
ATP synthase will not catalyze the formation of ATP on the thylakoid membrane
Carbon dioxide will not be converted into carbohydrates
Excited electrons will not be transferred across the electron transport chain
Carbon and oxygen will not be released after the breakdown of carbon dioxide
Oxygen consumption can be used as a measure of cellular respiration rate because oxygen is:
Necessary for ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation
Necessary to replenish glycogen levels
Necessary for fermentation to take place
Required by all living organisms
When hydrogen ions are pumped out of the mitochondrial matrix, across the inner mitochondrial membrane, and into the space between the inner and outer membranes, the result is:
Damage to the mitochondrion
The reduction of NAD
Creation of proton gradient
Lowering of the pH of the mitochondrial matrix
The reactions of glycolysis occur in the
Cytosol
Nucleus
Matrix of mitochondria
Membrane of mitochondria
Which of the following describes a metabolic consequence of a shortage of oxygen in muscle cells?
An increase in blood pH due to the accumulation of lactic acid
No ATP production due to the absence of substrate-level phosphorylation
A buildup of lactic acid in the muscle tissue due to fermentation
A decrease in the oxidation of fatty acids due to a shortage of ATP
{"name":"Ap Bio Final Exam", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of key concepts in AP Biology with our comprehensive final exam quiz. This quiz contains 36 multiple-choice questions that cover various topics, including biochemistry, cellular biology, genetics, and ecology.Challenge yourself and revise what you've learned:Multiple-choice formatCovers essential AP Biology topicsGreat for exam preparation","img":"https:/images/course5.png"}
More Quizzes
MDCAT BIOLOGY-Bioenergetics (SMART INSTITUTE)
60300
Honors Bio GP
13610
Vegan
15812
Diwali Quiz
105167
Preppy: Are You Really Preppy? Free Online
201016618
Porsche Trivia - Free 911 & 997 Turbo Challenge
201022364
Guess the YouTuber by Channel Name - Free
201023030
What's Your Name in Spanish? Free to Find Out
201018799
Glute Shape - Find Your Butt Type Free Online
201017481
Which BFB Character Are You? Free Personality
201018639
What Supernatural Creature Am I? Free Personality
201019046
Punctuating Dialogue with Questions - Free Grammar
201019216