FSc PHYSICS - Vectors and Equilibrium (SMART INSTITUTE)

FSc Physics Vector and Equilibrium Quiz
Test your knowledge of vectors and equilibrium with this comprehensive quiz designed for FSc Physics students. Dive into concepts ranging from coordinate systems to torque and equilibrium conditions.
You'll encounter questions that challenge your understanding of:
- Vector operations and properties
- Torque and its applications
- Conditions for equilibrium in various systems

1. Rectangular coordinate system is also called
Polar coordinate system
Cartesian coordinate system
Cylindrical coordinate system
Spherical coordinate system
2. The direction of a vector in space is specified by
One angle
Two angle
Three angle
No angle
3. Addition of vector obeys
Commutative law
Distributive law
Associative law
All given laws in a , b and c
4. A vector can be multiplied by a number. The number may be
Dimensionless
Dimensional scalar
Negative
All a, b and c are correct
5. Unit vector n^ is along
X-axis
Normal on a surface
Y-axis
Z-axis
6. Cosθ i^ + Sinθ j^ is a
Vector
Position vector
Vector in the direction at angle with x-axis
Unit vector in the direction at angle with x-axis
7. Maximum number of rectangular components are
One
Two
Three
Infinite
8. Maximum number of components of a vector may be
One
Two
Three
Infinite
9. Which one is not correct for a vector A= 2 i^ + 2 j^
Has direction θ=45 with x-axis
Has magnitude 2
Has magnitude 2 and direction θ=45 with y-axis
Has magnitude -2
10. The resultant of two forces of equal magnitudes is also equal to the magnitude of the forces. The angle between the two forces is
30'
60'
90'
120'
11. What is the angle that the given vector makes with y-axis A=2 i^+√ 12 j^
30'
60'
90'
120'
12. In which quadrant the two rectangular components of a vector have same sign?
1st
2nd
Both 1st and 3rd
Fourth
13. Two vectors A and B are making angle with each other. The scalar projection of vector B on vector A is written as
A.B/A
A.B/B
A.cos θ
Both a and b are correct
14. Two vectors are A = 3i^+2j^ -k^& B = 3i^-2j^ +k^ , then
B is anti parallel to A
B is negative vector of A
B has negative magnitude
B is perpendicular to A
15. If A=B, which of the following is not correct
A.B = A^ B^
|A| = |B|
|A^| = |B^|
AB^ = BA^
16. i^ . (j^ x k^) is equal to
1
I^
J^
K^
17. Which one is not a correct relation?
AxB = -BxA
|AxB| = -|BxA|
AxB = AB Sinθ n^
BxA = AB Sinθ(-n^)
18. The direction of vector product is given by
Head to tail rule
Right hand rule
Left hand rule
Triangular rule
19. If east, west, north, south, up and down are representing the direction of unit vectors, then east x south has direction along
West
North
Down
Up
20. Null vector is a vector which has
Zero magnitude
No specified direction
Both a and b are correct
Both a and b are not correct
21. Which one is a unit vector?
3 i^ + 3 j^ + 3 k^
1/3 i^ + 1/3 j^ +1/ 3 k^
3 / 3 i^ + 3 / 3 j^ + 3 / 3 k^
Both b and c are correct
22. Angle between two vectors A and B can be determined by
Their dot product
Their cross product
Head to tail rule
Right hand rule
23. The magnitude of cross product is equal to the dot product. The angle between the two vectors is
30'
45'
60'
180'
24. Torque is defined as
Turning effect of force
Cross product of position vector and force
Product of force and moment arm
All a, b and c are correct
25. The dimension of torque is
[ML2T-2]
[MLT-2]
[ML2T]
[ML-2T-2]
26. SI unit of torque is
N.m
Joule
Both a and b are correct
Neither a nor b is correct
27. Torque acting on a body determines
Acceleration
Linear acceleration
Angular acceleration
Direction of motion of the body
28. A body in equilibrium
Always at rest
Always in uniform motion
May be at rest or in uniform motion
May be at rest or in motion
29. A body will be in complete equilibrium when it is satisfying
Ist condition of equilibrium
2nd condition of equilibrium
Both Ist and 2nd condition of equilibrium
Impossible
30. Which one is not a type of dynamic equilibrium?
Rotational equilibrium
Translational equilibrium
Static equilibrium
Both a and c are correct answer.
31. Three coplanar forces acting on a body keep it in equilibrium. They should therefore be
Concurrent
Non concurrent
Parallel
Non parallel
32. Which of the following pairs does not have identical dimensions ?
Torque and energy
Momentum and impulse
Energy and work
Mass and moment of inertia
33. A central force is that which
Can produce torque
Can not produce torque
Some time can produce torque some time can not
Has no relation with torque
34. It is easier to turn a steering wheel with both hands than with a single hand because
Accelerating force increases on the wheel
Two forces act on the wheel
Two hands provide firm grip
Couple acts on the wheel
35. The cross product i^ x j^ is equal to
0
1
I^
K^
36. The unit vector in the direction of vector A = 2 i^ -2j^ + k^ is
2i^ - 2j^ + k^
(2i^ - 2j^ +k^)/9
(2i^ - 2j^ +k^)/3
(2i^ - 2j^ +k^)/5
37. The magnitude of i^. (j^ x k^) is
0
1
-1
I^
38. In which quadrant, only value of tan will be positive?
First
Second
Third
Both first and third
39. If A=Ax i^ + Ay j^ + Az K^ B = Bx i^ + By j^ + Bz K^ then
A. B = Ax Bx + Ay By + Az Bz
A. B = Ax By + Ay Bz + Az By
A. B = Ay Bz + Az By + Az Bx
A. B = Ax Bz + Ay By + Az Bx
40. The cross product of two vectors is a negative vector when
They are parallel vectors
They are anti parallel vectors
They are perpendicular vector
They are rotated through 270
41-If the position vector r and force F lies in x-z plane. Then direction of the torque
Along Y-axis
Along Z-axis
Along X-axis
Along x-y plane
42-A body weighing 500N is sitting on a see-saw at a point 2m away from the pivot. What should be the force acting on the other side of the pivot at a point 4m away to balance:
3000 N
1000 N
250 N
750 N
43-If a nut and bolt are difficult to turn, it may be easier to turn the nut by using a longer spanner. This is because the longer spanner gives:
A large moment of force
Less friction
A smaller moment of force
More friction
44-It is easier to turn a steering wheel with both hands than with a single hand because
Accelerating force increases on the wheel
Two hands provide firm grip
Two forces act on the wheel
Couple acts on the wheel
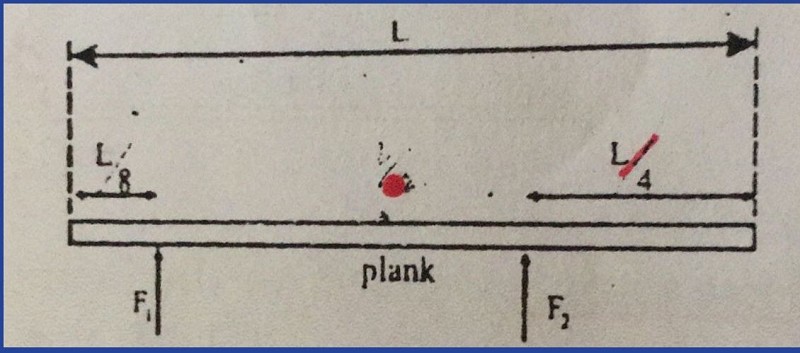
45-A heavy uniform plank of length L is supported by two force F1 and F2 at points distant L/8 and L/4 from its ends as shown in the diagram. What is the ratio of F1 and F2?
2:5
3:5
5:8
2:3
46-If direction of the applied force F is reversed then:
The magnitude of torque remains unchanged
There is change in magnitude and direction of the the torque
The magnitude and direction of the torque remains constant
The magnitude of torque remains same but the direction reverses
47-The direction of the torque τ=r x F is found out by:
Left hand rule
Head to tail rule
Knowing the direction of r
Right hand rule
48-Torque produced by a force depends upon:
Magnitude of the force and angular velocity
Magnitude of the force and displacement
Magnitude of the force and moment arm
Force and acceleration of the body
49-What is not true of two forces that give rise to a couple?
They act in opposite directions
They both act at the same point
They both act on the same body
They both have the same magnitude
50-The angle between r x F and -F x r is:
180'
60'
45'
0'
{"name":"FSc PHYSICS - Vectors and Equilibrium (SMART INSTITUTE)", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of vectors and equilibrium with this comprehensive quiz designed for FSc Physics students. Dive into concepts ranging from coordinate systems to torque and equilibrium conditions.You'll encounter questions that challenge your understanding of:- Vector operations and properties- Torque and its applications- Conditions for equilibrium in various systems","img":"https:/images/course1.png"}
More Quizzes
Physics quiz online
10513
Physics
1587
Structural Design Survey
20100
840
A Nightmare on Elm Street - Test Your Freddy Facts
201028746
Code of Conduct - Free Ethics Knowledge Check
201020927
Bible IQ Test - Old Testament Trivia (Free Online)
201023730
Hard Avatar: The Last Airbender Trivia - Free
201022355
Misplaced and Dangling Modifiers - Free Practice
201022215
Transformers - Ultimate Movie Trivia Challenge
201021675
Delta Dental CAMBRA - Caries Risk Assessment (Free)
201024774
Birthday for Friends - Who Will Show Up for You?
201019416