Pediatrie 811-999
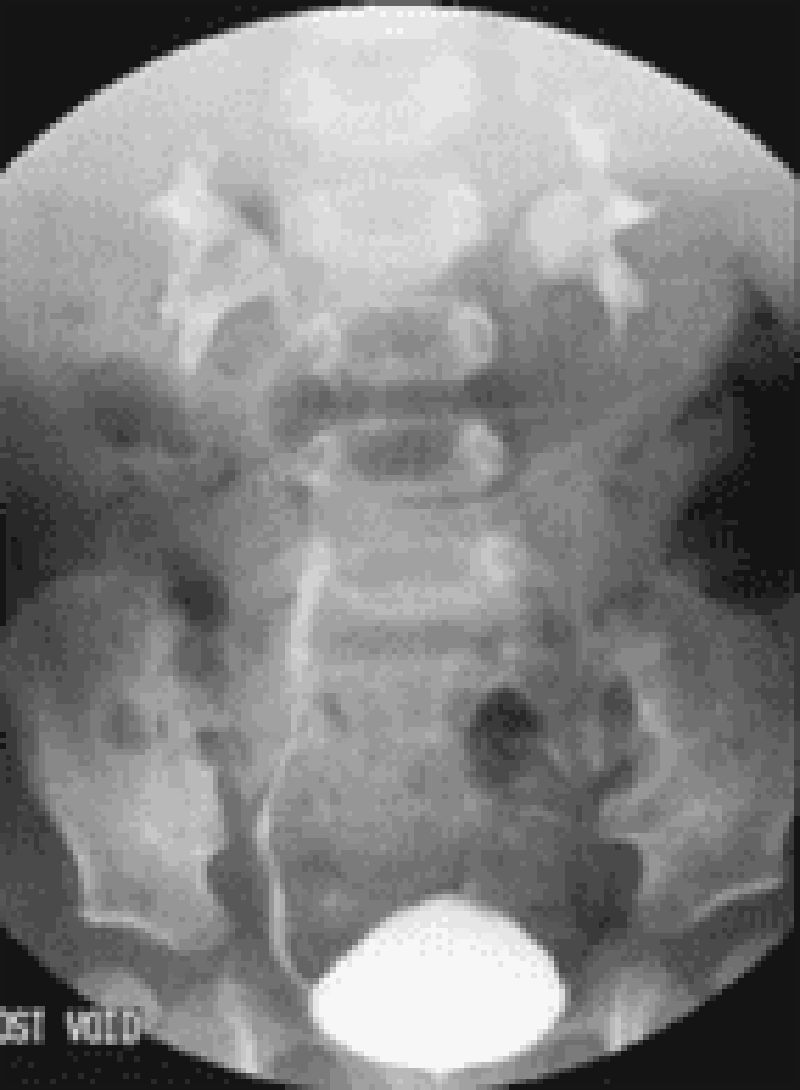
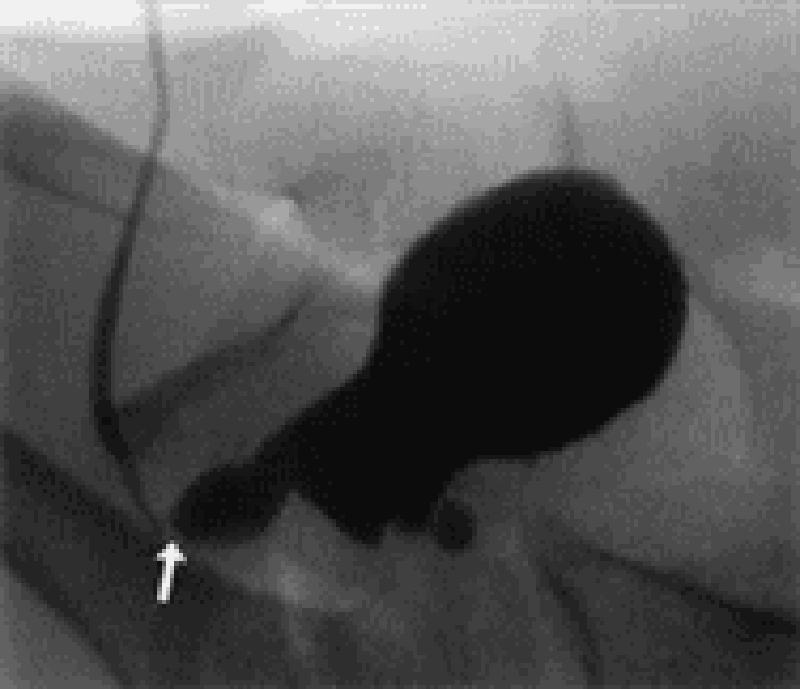
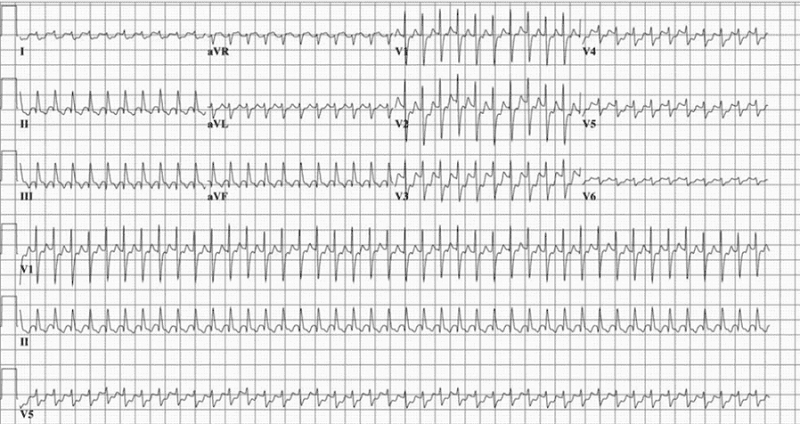
Hb 7 g/dl
WBC 7,000/mm3
Platelets 230,000/mm3 Reticulocytes Low
The peripheral smear shows normocytic normochromic RBC. What is the most likely diagnosis?


Sodium......................130 mEq/L
Potassium..................6.1 mEq/L
Chloride....................100 mEq/L
Bicarbonate...............8 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen............10 mg/dL Creatinine.................1.0 mg/dL
Glucose....................680 mg/dL
pH....................... 7.15
pCO2.......................30 mm Hg
pO2.........................85 mm Hg
Urinalysis is positive for ketones.
Which of the following is the most appropriate initial step in management?

Nonpalpable ecchymoses of varying ages are present on the shins and arms. The laboratory findings are as follows:
Hemoglobin 12 .8 g/dl
Hematocrit 38.5% WBC 6,000/mm3
Platelets 5,000/mm3 PT 12.0 sec
PTT 30 sec
Peripheral smear shows normal morphology of the red and white blood cell lines. The platelets are reduced in number, and majority of them are increased in size. What is the most likely diagnosis?



Urinalysis: 30 red blood cells (RBCs) per high-powered field, 2+ protein Stool: Guaiac positive Platelet count: 135,000/μL
These findings are most consistent with which of the following?

Hematocrit 35%
Platelet count 350,000/mm3
Leukocyte count 17000/mm3 Segmented neutrophils 65%
Bands 10%
Lymphocytes 25%
Gram stain of fluid aspirated from the affected lymph node reveals numerous bacteria-filled segmented neutrophils. Cultures grow S. aureus. What is the most likely mechanism underlying these findings?

Urea nitrogen 50 mg/dL
Serum sodium 170 mEq/L
Serum calcium 8.5 mg/dL
Serum magnesium 1.5 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this infants seizure?
Vitamin A 3000 IU
Thiamine 1 mg
Vitamin C 75 mg
Vitamin B6 1 mg
Vitamin D 400 IU
Iron 12 mg
Fluoride 1 mg
The child is brought to the emergency department in no acute distress. Which of the following complications may occur if appropriate therapy is not undertaken?

Computed tomography scan of the head is within normal limits. Lumbar puncture shows the following:
Opening pressure 280 mm H2O
Cerebrospinal fluid glucose 40 mg/dL
Cerebrospinal fluid protein 40 mg/dL
White blood cells 3/mm3
Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
Leukocyte count 14, 500/mm3
Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L
Chest x-ray is normal limits. Abdominal imaging shows radiopaque tablets in the stomach. Intravenous normal saline is started. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
Hemoglobin 8.2 mg/dL
WBC count 14, 000.mm3
Platelet count 210, 000/mm3
Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
CT of the head shows no evidence of intracranial bleeding. Which of the following is the best initial management for this patient?