201. It is used to connect dissimilar devices such as DCE to DTE and DTE to DCE
A. Modem Cable
B. Straight-Through Cable
C. Crossover Cable
D. Gateway Cable
202. It is the general term that describes the equipment that converts the digital signals to analog signals and interfaces the data terminal equipment to the analog transmission system.
A. DTE (Data Terminal Equipment)
B. DCE (Data Communications Equipment)
C. Interface
D. Modem
203. Also known as baseband modem or line drivers. It can be use up to 40 ft or 12 m distance.
A. Short-range modem
B. Analog modem
C. Long-range modem
D. None of the choices
204. Is a modem technology that uses existing twisted pair telephone lines to transport high bandwidth data, such as multimedia and video, to service subscribers.
A. EIA RS 232C
B. DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)
C. FTTC
D. Dial Up
205. The analog signal is sampled and converted to a fixed-length, serial binary number for transmission.
A. PPM (Pulse Position Modulation)
B. PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
C. PCM (Pulse Code Modulation)
D. PAM (Pulse Amplitude Modulation)
Another term for gray code. This code is used to reduce the number of transmission errors.
A. Maximum distance code
B. Minimum distance code
C. Hamming code
D. Baudot code
An ASCII character code of 7 bits that is transmitted serially back to the transmitter every 10s until the transmitter recognizes it.
A. Acknowledge (ACK)
B. End of Transmission (EOT)
C. Start of Header (SOH)
D. Negative Acknowledge (NAK)
208. Program that runs on computers and servers that allows the computers to communicate over a network.
A. Cloud
B. Local Operating System
C. Mainframes
D. Network Operating System
209. A device used to interconnect networks; routers operate at level three, the network layer, of the OSI protocol model and can change packets from one protocol to another.
A. Virtual circuit
B. Router
C. Gateway
D. X.25 Protocol
210. Are set of channels dedicated for exchanging control information between mobile units and base stations.
A. Forward Channels
B. Control Channels
C. Reverse Channels
D. Voice Channels
250. It is the magnitude of the quantum
A. Bit
B. Resolution
C. Minimum Dynamic Range
D. Minimum Quantization
211. 30B+D has an aggregate bit rate of:
A. 1.544 kbit/s
B. 2.048 kbit/s
C. 1.544 Mbit/s
D. 2.048 Mbit/s
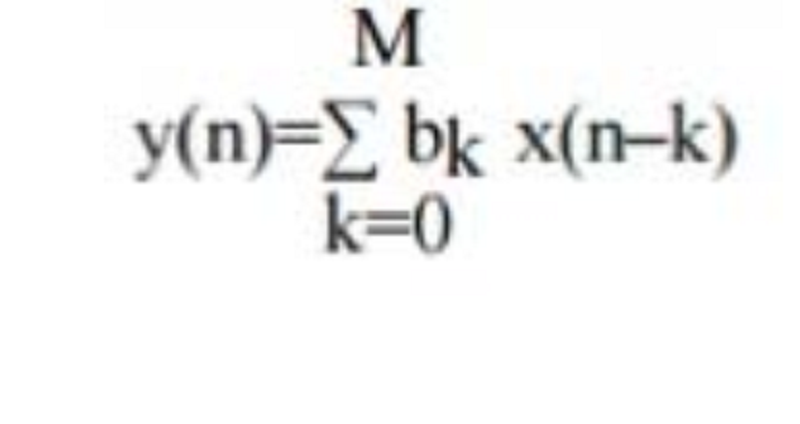
212. A filter described as:
A. IIR
B. FIR
C. RII
D. RIF
213. PLC means:
A. Philippine Logistics Commission
B. Programmable Logic Controllers
C. Positive Logic Control
D. Power Lag Circuit
214. It is a multiplexer with storage buffer and a minicomputer processor, and it may act to store and forward traffic and is used to hold program logic.
A. Hub
B. Multiplexer
C. Repeater
D. Concentrator
215. It is a two-port device which operates at the physical layer, and its job is to regenerate the signal over the same network before the signal becomes too weak or corrupted so as to extend the length to which the signal can be transmitted.
A. Multiplexer
B. Hub
C. Concentrator
D. Repeater
216. It is basically a multiport repeater which connects multiple wires coming from different branches.
A. Router
B. Bridge
C. Gateway
D. Hub
217. Two nodes on an Ethernet LAN using coaxial cable are 200 m apart. How long will it take the stations to detect a collision?
A. 995 ns
B. 2 µs
C. 995 us
D. 2 ns
218. It is a two-port device which operates at data link layer. It is a repeater, with add on functionality of filtering content by reading the MAC addresses of source and destination.
A. Router
B. Gateway
C. Hub
D. Bridge
219. It is a multiport bridge which operates at data link layer. It can perform error checking before forwarding data that makes it very efficient as it does not forward packets that have errors.
A. Switch
B. Bridge
C. Hub
D. Gateway
220. It is a device like a switch, but operates in the network layer, that routes data packets based on their IP addresses.
A. Gateway
B. Router
C. Hub
D. Bridge
221. It is a passage to connect two networks together that may work upon different networking models. It is generally more complex than switch or router.
A. Router
B. Gateway
C. Bridge
D. Hub
222. It is when the input analog waveform is sampled by a sampling pulse with an output sampled waveform obtaining the shape of the input analog waveform.
A. Quantization
B. Natural Sampling
C. Sample and Hold
D. Flat Top Sampling
223. It states that for a sample to be reproduced accurately in a PCM receiver, each cycle of the analog input signal must be sampled at least twice.
A. All of the choices
B. Hartley’s Theorem
C. Nyquist Sampling Theorem
D. Shannon sampling Theorem
224. This is the ratio of the transmission but rate to the minimum bandwidth required for a particular modulation scheme
A. Bit error rate
B. Bandwidth efficiency
C. Carrier recovery
D. Probability of error
225. Is the binary sum of all the binary information sent in the block.
A. Vertical Redundancy Check
B. Check Sum
C. Longitudinal Redundancy Check
D. Cyclic Redundancy Check
226. Interconnects memory cards carried by people and in computers that are in close proximity to each other.
A. BAN
B. PAN
C. MAN
D. WAN
227. An IBM system for transferring data between IBM mainframes and other computers
A. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
B. Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
C. System Network Architecture
D. Open Systems Interconnection model
228. Is a globally accepted standard for digital cellular communications systems.
A. GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)
B. AMPS (Advance Mobile Phones Service)
C. MTS (Mobile Telephone Service)
D. IMTS (Improved Mobile Telephone Service
229. ISDN ready equipments are known as:
A. TE1
B. TE2
C. NT1
D. NT2
230. Which of the following filter has a limited or finite memory requirements?
A. IIR
B. FIR
C. RII
D. RIF
231. It is the first level protocol standard as well as an electrical standard specifying handshaking and functions between the DTE and DCE.
A. Firewire
B. IEEE 488 BUS
C. EIA RS 232C
D. USB
232. It is used to transfer data between two devices at 8 or more bits at a time and also known as serial-by-word interface.
A. USB
B. Serial Interface
C. Centronics Parallel Interface
D. Parallel Interface
233. Is used for asynchronous transmission of data between DTE and the DCE.
A. IEEE 488 BUS
B. USRT (Universal Synchronous Receiver/Transmitter)
C. EIA RS 232C
D. UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter)
234. It is a transparent switch that is used for making a standard telephone call on public telephone network.
A. Transactional switch
B. Packet Switching
C. Circuit Switching
D. Message Switching
235. It is also known as hold-and-forward network in which the data are divided into smaller segment known as packets prior to transmission through the network.
A. Message Switching
B. Packet Switching
C. Transactional switch
D. Circuit Switching
236. Is a switch that does nothing more than interconnect the source and destination terminal equipment. A circuit adds no value to the circuit.
A. Packet Switching
B. Transparent Switch
C. Transactional switch
D. Message Switching
237. Occurs when the magnitude of the sample exceeds the highest quantization interval.
A. Aperture distortion
B. Overload distortion
C. Quantization Error
D. Aliasing
238. This is a theoretical expectation of the bit error rate for a given system.
A. Bit error rate
B. Bandwidth efficiency
C. Carrier recovery
D. Probability of error
239. When the entire message has been sent, the transmitting computer will send ______________.
A. Acknowledge (ACK)
B. End of Transmission (EOT)
C. Start of Header (SOH)
D. Negative Acknowledge (NAK)
240. A link between computers in which each recognizes a software connection to the other; the physical connection is not continuous but consists of packets routed as transmitted.
A. Virtual circuit
B. Router
C. Gateway
D. X.25 Protocol
241. It is where all radio-related functions are performed, and it consists of the BSC and the BTS.
A. BTS (Base Transceiver Station)
B. MS (Mobile Station)
C. BSS (Base Station System)
D. BSC (Base Station Controller)
242. To connect TE2 equipments to ISDN, a ________ is needed:
A. NT1
B. NT2
C. NT12
D. TA
243. Noise and Quantization errors are less severe in:
A. Digital filters
B. Analog filters
C. FIR
D. IIR
244. All electronics and communications equipment except consumer products installed and/or located inside buildings or in sheltered structures shall be engineered, installed, operated and maintained in such a manner that _________ shall not result when normally used and operated.
A. Shock casualty
B. Fire hazard
C. Voltage spikes
D. Both shock casualty or fire hazard
245. Is the result to the loss of data that occurs when two stations transmit at the same time on a network
A. Contention
B. Collision
C. Polling
D. None of the choices
246. It is a WAN technology with higher data rate at lower cost, however, it has bursty data and bandwidth on demand.
A. Virtual Circuit
B. ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
C. Virtual Circuit
D. Frame Relay
247. It is a high-performance, cell-oriented switching and multiplexing technology that utilizes fixed-length packets to carry different types of traffic.
A. ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mode)
B. Virtual Circuit
C. Frame Relay
D. X.25
248. It is defined by ITU-T as a service that provides transmission channels capable of supporting transmission rates greater than the primary data rate.
A. WLAN (Wireless LAN)
B. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
C. BISDN (Broadband ISDN)
D. Zigbee
249. The process of rounding off the amplitudes of flat-top samples to a manageable number of levels.
A. Filtering
B. Sampling
C. Quantizing
D. Coding
251. To transmit each character or each message multiple times until it is properly received
A. Redundancy
B. Checksum
C. Parity
D. Block
252. It handles the radio interface of the mobile station. It is the radio equipment needed to service each cell in the network.
A. BTS (Base Transceiver Station)
B. MS (Mobile Station)
C. BSS (Base Station System)
D. BSC (Base Station Controller)
253. The reference point in between TE2 and TA is:
A. R
B. S
C. T
D. U
254. Also known as Convolution Filter:
A. FIR
B. IIR
C. Butterworth
D. Chebyshev
255. A standard telephone line has a bandwidth of 3,400 Hz, what is the required signalto-noise ratio, of the channel to handle maximum channel capacity of 30 kbps?
A. 542
B. 245
C. 26
D. 452
256. It is a type of LAN that uses high frequency radio waves rather than wires to communicate and transmit data among nodes.
A. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
B. WLAN (Wireless LAN)
C. Bluetooth
D. Piconets
257. A network of Bluetooth devices.
A. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
B. Piconets
C. Bluetooth
258. A network of two or more piconets.
A. Piconets
B. Scatternet
C. Bluetooth
D. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
259 Classified as: - 802.15.4 - Low cost cable replacement technology - Close to 100M nodes in 2012 - Honeywell = HVAC systems - used for low power consumption and rely on long, multi-year battery life
A. WLAN (Wireless LAN)
B. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
C. BISDN (Broadband ISDN)
D. Zigbee
260. It was developed to provide a wireless alternative to consumers for broadband Internet connections; these connections are now dominated by cable TV and DSL.
A. UWB (Ultra Wideband)
B. Zigbee
C. Infrared PAN
D. WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access)
261. The system is deliberately restricted to a range of one meter to allow several independent infrared links to operate simultaneously in the same room.
A. NFC (Near Field Communication)
B. UWB (Ultra Wideband)
C. Infrared PAN
D. RIFD (Radio-frequency Identification)
262. This technology uses thin, inexpensive tags or labels containing passive radio circuits that can be queried by a remote wireless interrogation unit.
A. Infrared PAN
B. UWB (Ultra Wideband)
C. RIFD (Radio-frequency Identification)
D. NFC (Near Field Communication)
263. It is an ultrashort-range wireless whose range is rarely more than a few inches.
A. UWB (Ultra Wideband)
B. Infrared PAN
D. NFC (Near Field Communication)
C. RIFD (Radio-frequency Identification)
264. It is a wireless communications technology that can transmit data at speeds between 40 to 60 Mbps and eventually to 1 Gbps. It transmits ultra-low power radio signals with very short electrical pulses.
A. UWB (Ultra Wideband)
B. RIFD (Radio-frequency Identification)
C. NFC (Near Field Communication)
D. Infrared PAN
265. It is the process wherein the quantized intervals assigned to the individual PAM samples are converted into binary signals.
A. Filtering
B. Sampling
C. Quantizing
D. Coding
266. It is the random, thermal noise that is present only into the input of the PAM sampler when there is no analog input signal and it is converted to a PAM sample just as if it were a signal.
A. Coding Noise
B. Quantization Noise
C. Random Noise
D. Idle Channel Noise
267. Is a system where each character transmitted contains one additional bit
A. Parity
B. Checksum
C. CRC
D. ARQ
268. Is responsible for performing call processing and subscriber-related functions
A. OSS (Operations Support Subsystem)
B. BSS (Base Station System)
C. NSS (Network & Switching Subsystem)
D. MSC (Mobile Services Switching Center)
269. It occurs when the analog input signal changes at a faster rate than the digitalto-analog converter can maintain.
A. Aliasing
B. Jitter
C. Slope Overload
D. Granular Noise
270. It is a delta modulation system where the step size of the DAC is automatically varied depending on the amplitude characteristics of the analog input signals
A. Delta Modulation PCM
B. Differential PCM
C. Adaptive Delta Modulation PCM
D. Analog to Digital Converter
271. The reference point in between NT2 and NT1 is:
A. R
B. S
C. T
D. U
272. A digital transmission line has a bandwidth of 2 MHz. With signal-to-noise of 36 dB, what is the maximum capacity the line can handle in Mbps?
A. 16
B. 42
C. 24
D. 12
273. Is a suite of protocols that allows a wide variety of computers to share the same network, and it forms a hierarchical much like the OSI model.
A. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
B. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
C. IP (Internet Protocol)
D. TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
It is a transport layer connectionoriented protocol which is responsible for providing reliable communications between hosts and processes on different hosts
A. TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
B. IP (Internet Protocol)
C. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
D. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
275. It was developed as a mechanism to facilitate the transfer of files between computers
A. VOIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol)
B. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
C. FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
D. OSI
276. The designation of each file or directory on the host computer connected to the Internet
A. WWW (World Wide Web)
B. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
C. IP address
D. URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
277. In the PCM codes, the lowest magnitude positive and negative codes have the same voltage range as all the other codes.
A. Midrise Quantization
B. Midtread Quantization
C. Level-at-a-Time Coding
D. Bit-at-a-Time Coding
278. It is a type of coding which determines each digit of the PCM code sequentially.
A. Nibble-at-a-time Coding
B. Word-at-a-Time Coding
C. Digit-at-a-time Coding
D. Byte-at-a-time Coding
279. Process of X-ORing all the characters in a particular block of transmitted data.
A. Parity
B. Cyclic Redundancy Check
C. Longitudinal Redundancy Check
D. Vertical Redundancy Check
280. It is a database used for the storage and management of subscriptions. These are permanent information.
A. AUC (Authentication Center)
B. EIR (Equipment Identity Register)
C. VLR (Visitor Location Register)
D. HLR (Home Location Register)
281. It provides the largest range of addresses available for assignment to host computers (16777214 hosts).
A. Class D Address
B. Class A Address
C. Class B Address
D. Class C Address
282. It is evenly split using two bytes for the network portion and two bytes for the host portion of the address (65634 hosts).
A. Class A Address
B. Class B Address
C. Class D Address
D. Class C Address
283. It uses three bytes for the network portion and one byte for host dentification (254 hosts)
A. Class C Address
B. Class B Address
C. Class A Address
D. Class D Address
284. It is a single integrated-circuit chip that performs every function of a PCM encoder and decoder.
A. Formant Vocoder
B. Codec
C. Vocoders
D. Channel Vocoder
285. Digital channel vocoders that use bandpass filter to separate waveform into narrower sub-bands.
A. Vocoders
B. Formant Vocoder
C. Linear Predictive Coder
D. Channel Vocoder
286. Is any interconnection of two or more stations that wish to communicate.
A. Mesh
B. Link
C. Network
287. It is a unit that provides authentication and encryption parameters that verify the user's identity and ensure the confidentiality of each call.
A. AUC (Authentication Center)
B. EIR (Equipment Identity Register)
C. VLR (Visitor Location Register)
D. HLR (Home Location Register)
288. A software program or hardware device designed to prevent unauthorized access to computers or networks.
A. Antivirus
B. Virus
C. Trojan
D. Firewal
289. Is a general term for the internet. It is a massive unseen networking infrastructure that is constantly changing and has never been mapped.
A. Drive
B. Cloud
C. Ether
D. Net
The input voltage of a compander with a maximum voltage range of 1V and a µ of 255 is 0.25. What are the output voltage and gain?
A. 4
B. 3
C. 2
D. 1
291. Is a company set up especially to tap into the internet.
A. Internet Backhaul
B. Internet Cafe
C. Internet Backbone
D. ISP (Internet Service Provider)
292. Is a collection of high-speed data lines that connect major computer systems located around the world.
A. Internet Backhaul
B. Internet Cafe
C. Internet Backbone
D. ISP (Internet Service Provider)
293. It causes crosstalk between channels that occupy adjacent time slots in a timedivision-multiplexed carrier system.
A. Intersymbol Interference
B. Near end crosstalk
C. Far end crosstalk
D. Jitter
294. It the binary pulse is maintained for the entire bit time.
A. NRZ (Non-return to Zero)
B. Bipolar Transmission
C. RZ (Return to Zero)
D. Unipolar Transmission
295. It is the process of simultaneously transmitting two or more individual signals over a single communications channel
A. Multiple Access
B. Multiplexing
C. Multitasking
D. Modulation
296. It is a form of multiplexing wherein two data channels modulate the same frequency that has been shifted 90 deg in phase.
A. FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing)
B. SDM (Space Division Multiplexing)
C. PDM (Phase Division Multiplexing)
D. TDM (Time Divisison Multiplexing)
297. It uses an 8-kHz sample rate and and eight-bit PCM code, which produces a 64 kbps PCM line speed.
A. DS-2
B. DS-0
C. DS-1
D. DS-1C
298. It is the basic building block of the FDM hierarchy, and was originally intended for the analog voice transmission.
A. Voice Channel
B. Message Channel
C. Signaling Channel
D. Control Channel
299. Refers to data or information signal whether it is binary or analog voice or video. The digital data is applied directly to the medium
A. Information
B. Baseband
C. Symbol
D. Broadband
300. It is the nth generation mobile phone technology. It is an IP based solution that will provide much faster access to the Internet.
A. 3G Technology
B. 4G Technology
C. 5G Technology
D. 2G Technology
{"name":"201. It is used to connect dissimilar devices such as DCE to DTE and DTE to DCE", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"201. It is used to connect dissimilar devices such as DCE to DTE and DTE to DCE, 202. It is the general term that describes the equipment that converts the digital signals to analog signals and interfaces the data terminal equipment to the analog transmission system., 203. Also known as baseband modem or line drivers. It can be use up to 40 ft or 12 m distance.","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/99-4860076/123.png?sz=1200-00000000001000005300"}
More Quizzes
Do you have any recommendations in new papers today?
100
How much do you know about indie?
1050
Tranche 3
251232
FTE quiz
12616
Ultimate FC Barcelona: Test Your Barça Knowledge!
201028847
Free Unit 3 Vocab Workshop Level F Answers
201024695
Will I Pass My Exam? Free to Test Your Readiness
201027454
Special Topics in Information Studies
15820066
Introduction to Applied Microeconomics
15823204
Find Your Match: Explore The Selection Characters Now
201026453
Master Covalent Bond: Can You Ace Every Question?
201032613
Which Anastasia Characters Are You? Take the Now
201024108