7Year/Biomedecal Sciences/Final exam
1. The smallest bone of the skull is:
Zygoma
Lacrimal
Palatine
Mandible
2. How many foramens are in the mandible:
2 foramens, Mandibular and infra-orbital foramens
2 foramens, Mandibular and Incisive foramens
2 foramens, Mandibular and Mental foramens
2 foramens, Mental and Incisive foramens
3. The most fragile bone of the face is:
Palatine bone
Mandible
Lacrimal Bone
Maxilla
4. Zygomatic arch is formed by:
Temporal and Maxilla
Zygoma and temporal
Zygoma and Maxilla
Temporal, Zygoma and Maxilla
5. Meninges is formed by:
Pia Mater
Dura Mater
Arachnoid Mater
All of them
6. Subarachnoid Space is:
Above Pia Mater
Below Arachnoid Mater
Between Dura and Arachnoid Maters
Between Arachnoid and Pia Maters
7. Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) is in:
Dura Mater
Subarachnoid space
Extradural Space
Pia Mater
8. Artery supplies cranial dura mater is:
Middle meningeal artery
Anterior meningeal artery
Posterior meningeal artery
Internal Carotid artery
9. The following sensory nerves are:
Olfactory, Optic, and Vestibulocochlear
Trigeminal, Facial, Glossopharyngeal and Vagus
Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducens, Accessory and Hypoglossal
Accessory and Hypoglossal
10. The following motor nerves are:
Olfactory, Optic and Vestibulocochlear
Trigeminal, Facial, Glossopharyngeal and Vagus
Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducens, Accessory, and Hypoglossal
Accessory and Hyphoglossal
11. Division 3 of CN V is running from:
Superior orbital fissure
Foramen Rotundum
Foramen Ovale
Inferior orbital fissure
12. Division 1 of CN V is running from:
Superior orbital fissure
Foramen Rotundum
Foramen Ovale
Infra-orbital foramen
13. Orbit and eye are innervated by:
Abducens nerve
Trochlear nerve and Oculomotor nerve
C. Optic nerve and ophthalmic nerve
Abducens, Trochlear, Oculomotor, Optic and Ophthalmic nerve
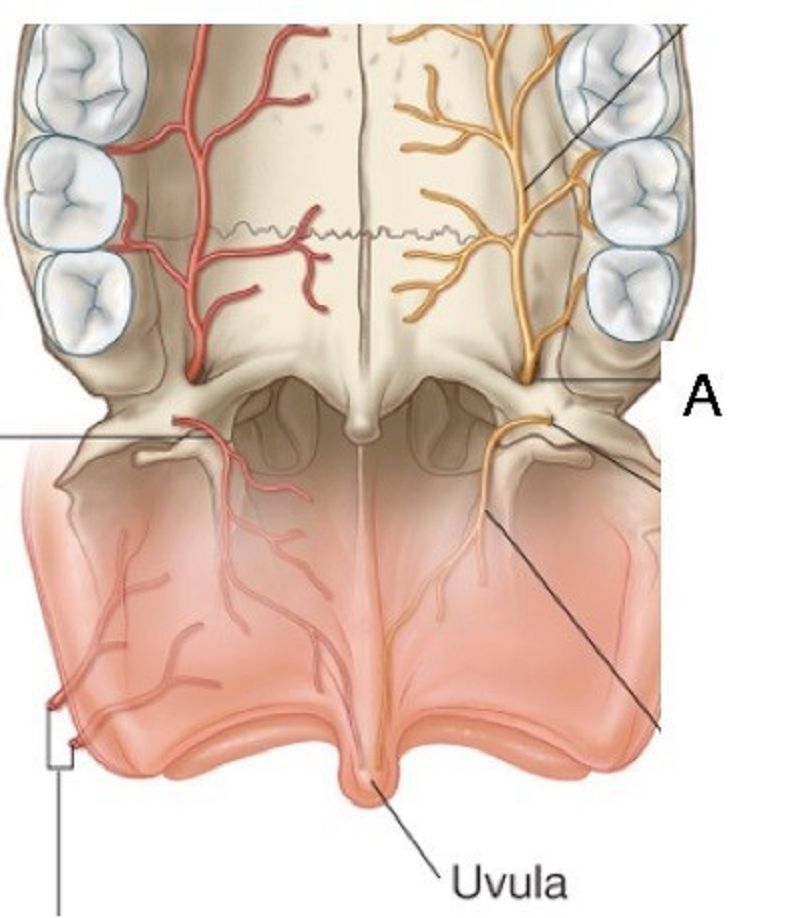
14. A is……………………………..
Greater palatine foramen
Lesser palatine foramen
Nasopalatine foramen
Greater palatine nerve
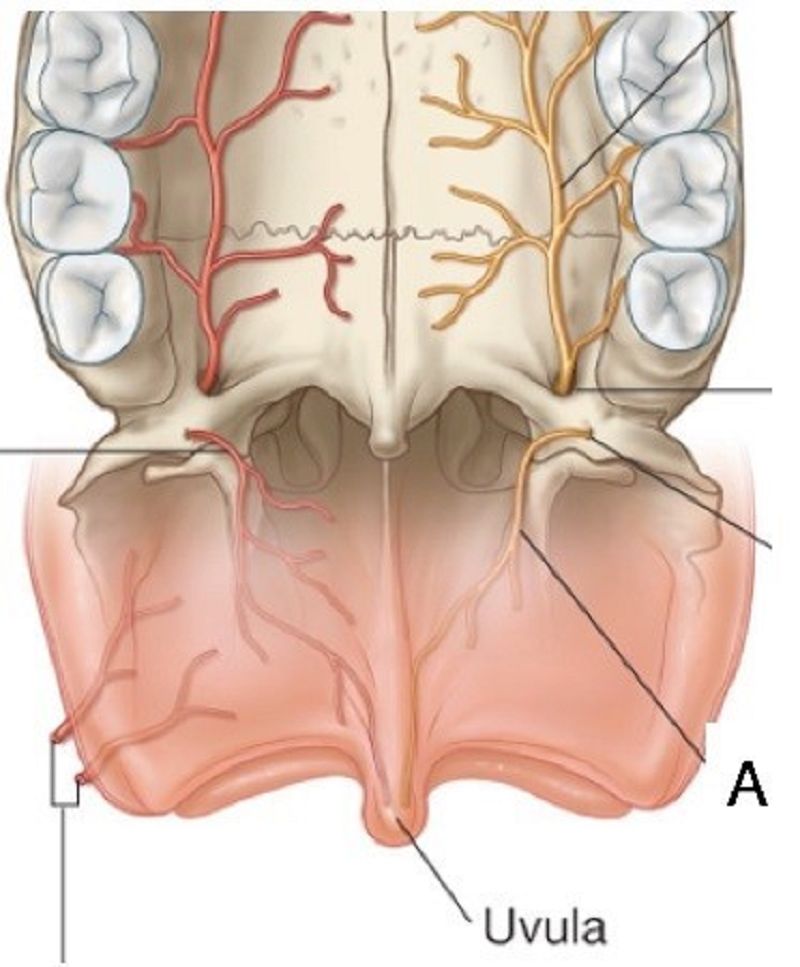
15. A is……………………………..
Incisive fossa
Nasopalatine nerve
Lesser palatine nerve
Greater palatine nerve
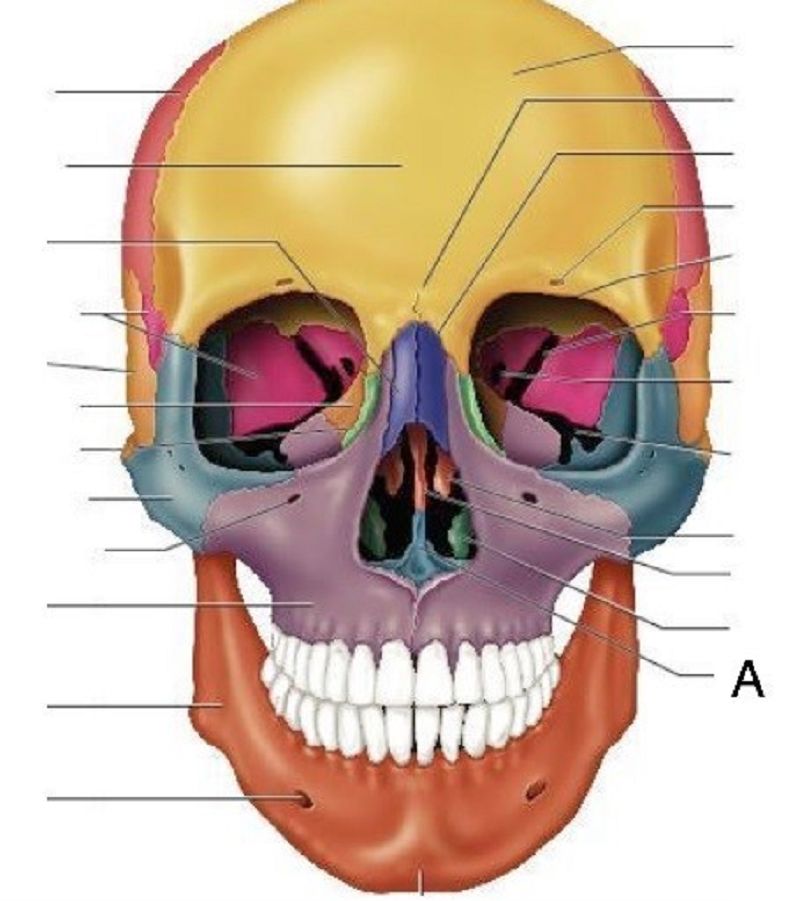
16. A is……………………………..
Nasal bone
Vomer
Mandible
Palatine bone
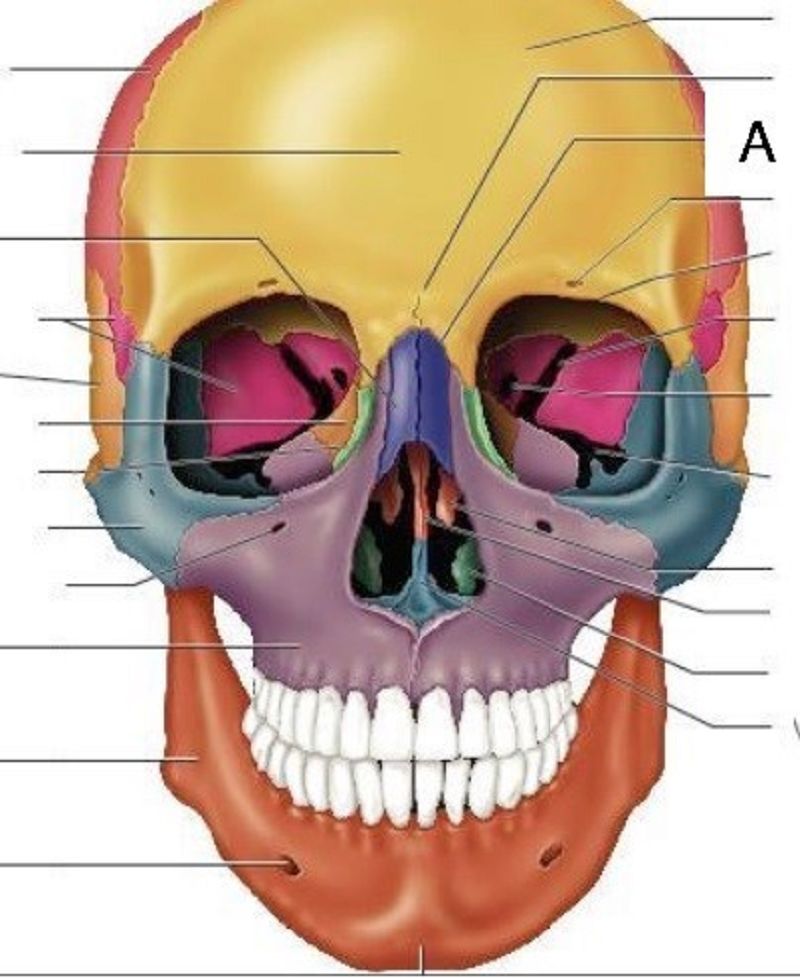
17. A is……………………………..
Nasal bone
Lacrimal bone
Ethmoid bone
Sphenoid bone
18. Pathway between nasal cavity and nasopharynx is called
Nares (nostrils)
Choanae (posterior nasal apertures)
Nasopharyngeal isthmus
Oropharyngeal isthmus
19. The anterior openings to the nasal cavities are
Nares (nostrils)
Choanae (posterior nasal apertures)
Nasopharyngeal isthmus
Oropharyngeal isthmus
20. Boundary between oral cavity and oropharynx is
Nares (nostrils)
Choanae (posterior nasal apertures)
Nasopharyngeal isthmus
Oropharyngeal isthmus
21. The nasopharynx is anteriorly to which spinal vertebrae?
C1
C2-C3
C4-C6
C7
22. Salpingopharyngeus muscle is located
Styloid process
Cartilaginous part of auditory tube
Palatine aponeurosis of soft palate
All are correct
23. Stylopharyngeus muscle is located
Styloid process
Cartilaginous part of auditory tube
Palatine aponeurosis of soft palate
All are correct
24. Palatine tonsil is located between
Palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds
Palatoglossal and salpingopharyngeal folds
Palatopharyngeal and salpingopharyngeal folds
Salpingopalatine and salpingopharyngeal folds
25. Temporalis muscle is innervated by
Masseteric nerve
Deep temporal nerve
Pterygoid nerve
Posterior auricular nerve
26. Masseteric muscle is innervated by
Masseteric nerve
Deep temporal nerve
Pterygoid nerve
Posterior auricular nerve
27. Lateral pterygoid muscle is innervated by
Masseteric nerve
Deep temporal nerve
Pterygoid nerve
Posterior auricular nerve
28. Medial pterygoid muscle is innervated by
Masseteric nerve
Deep temporal nerve
Pterygoid nerve
Posterior auricular nerve
29. All the following are true about parotid gland, EXCEPT
Largest salivary gland
Mucous secretion
Extends from zygomatic arch down to upper neck
Deep and superficial parts
30. What are within parotid gland?
Internal carotid artery, External jugular vein and The last 4 cranial nerves
External carotid artery, Retromandibular vein and Facial nerve
Internal carotid artery, Internal jugular vein and The last 4 cranial nerves
External carotid artery, Retromandibular artery and Facial nerve
31. Parotid gland’s duct also known as
Stenson's duct
Wharton's duct
Bartholin's duct
All are incorrect
32. The opening of Stenson’s duct is at
Sublingual fold
Sublingual caruncle
Opposite upper 2nd molar teeth
Floor of mouth on sublingual fold or into submandibular duct
33. A branch of temporo-facial division of CNVII is
Temporal branch
Buccal branch
Marginal mandibular branch
Cervical branch
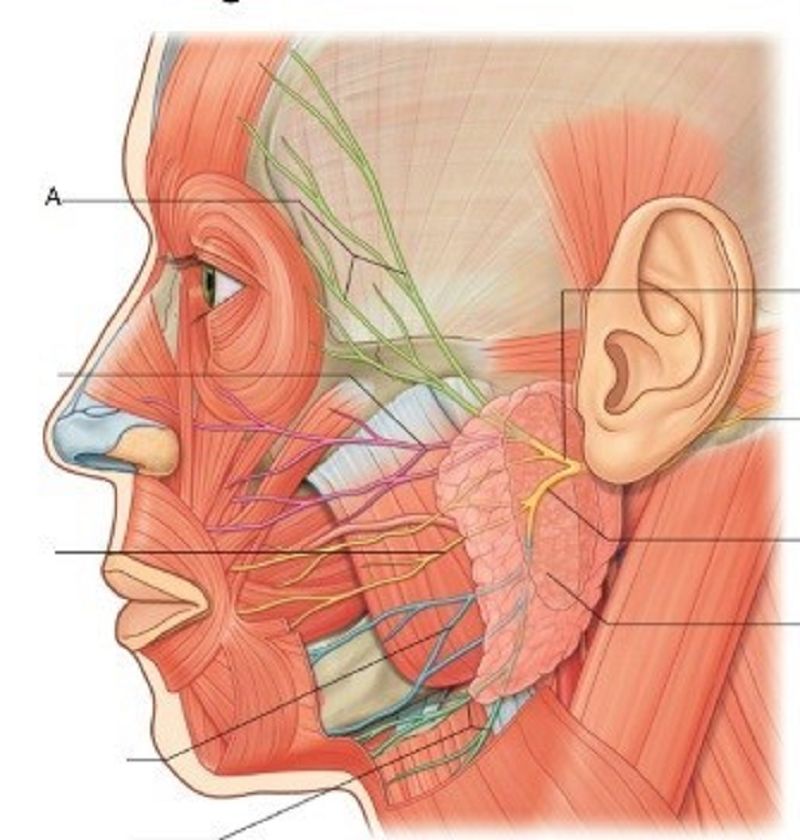
34. A is …………………………..
Temporal branches
Zygomatic branches
Buccal branches
Marginal mandibular branches
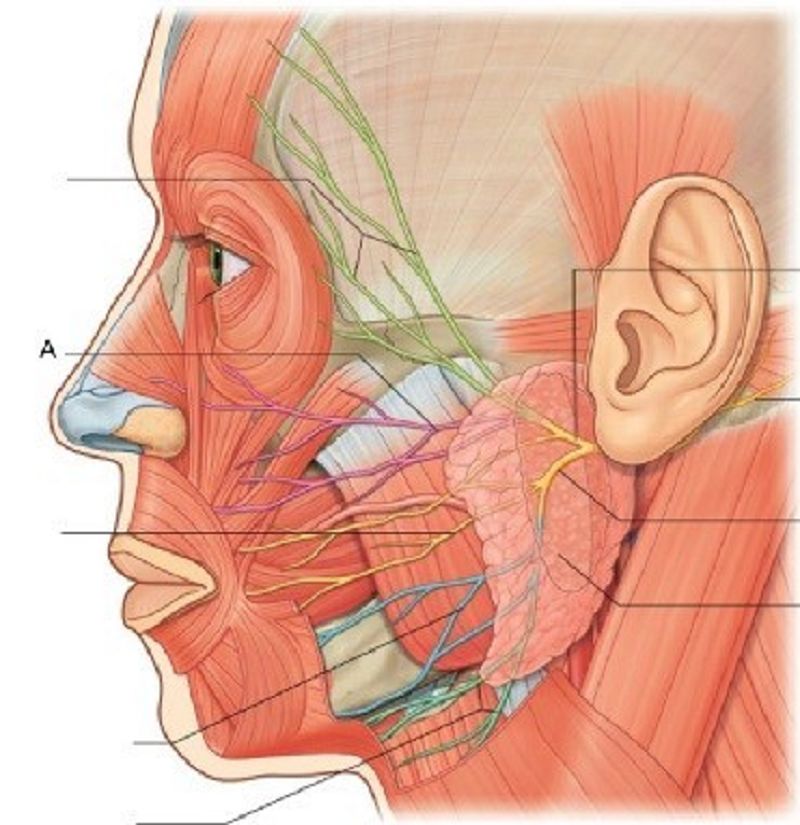
35. A is …………………………..
Temporal branches
Zygomatic branches
Buccal branches
Marginal mandibular branches
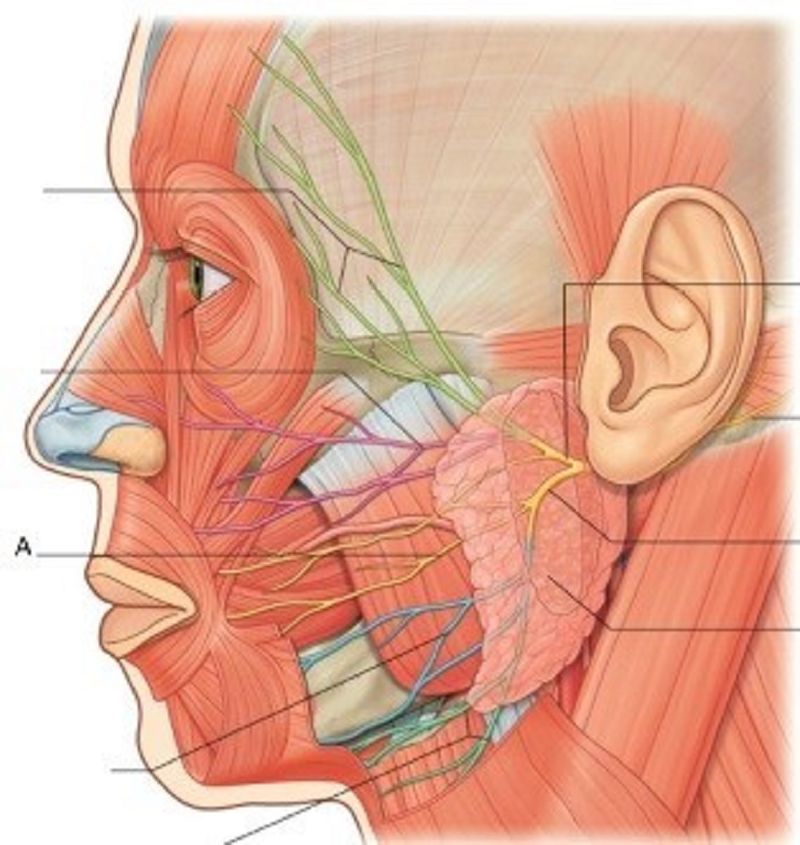
36. A is ………………………….
Temporal branches
Zygomatic branches
Buccal branches
Marginal mandibular branches
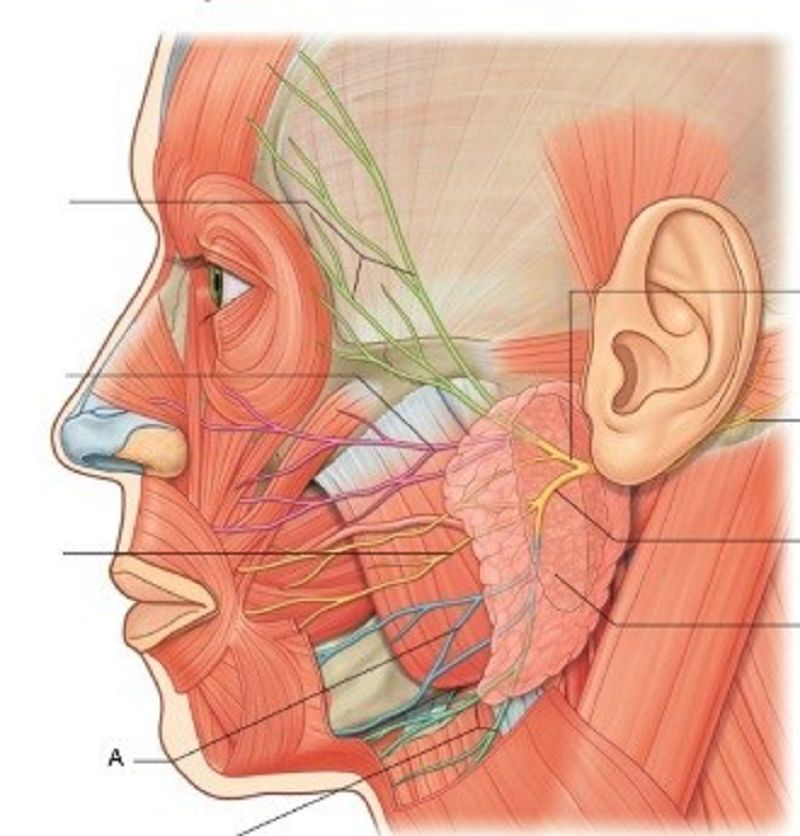
37. A is …………………………..
Temporal branches
Zygomatic branches
Buccal branches
Marginal mandibular branches
38. Muscles of facial expression are innervated by
Trochlear nerve (CN IV)
Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Abducen nerve (CN VI)
Facial nerve (CN VII)
39. Muscles of mastication are innervated by
Trochlear nerve (CN IV)
Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Abducen nerve (CN VI)
Facial nerve (CN VII)
40. Which is the facial expression muscle around the eye?
Orbicularis oculi
Nasalis muscle
Frontalis muscle
Procerus muscle
41. Which is the facial expression muscle around the eye?
Corrugator supercilli
Nasalis muscle
Frontalis muscle
Procerus muscle
42. Which is the facial expression muscle around the nose?
Orbicularis oculi
Orbicularis oris
Nasalis
Mentalis
43. All are muscles around the mouth, EXCEPT
Buccinator
Orbicularis oris
Orbicularis oculi
Levator labii superioris
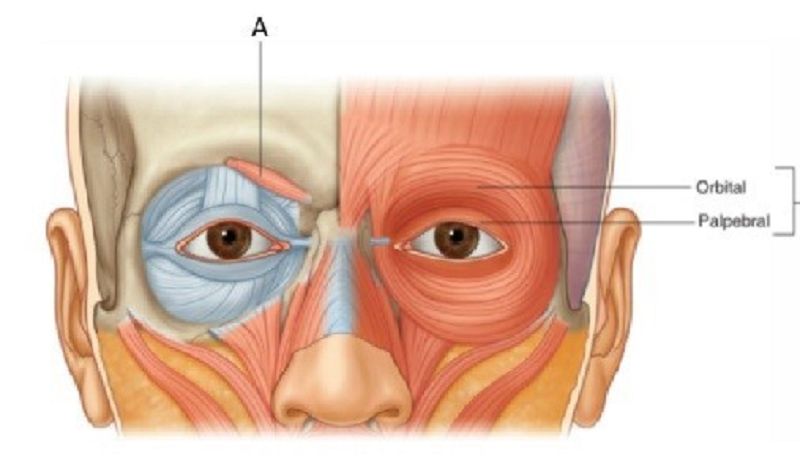
44. A is …………………………..
Orbicularis oculi
Orbicularis oris
Corrugator supercilli
Mentalis
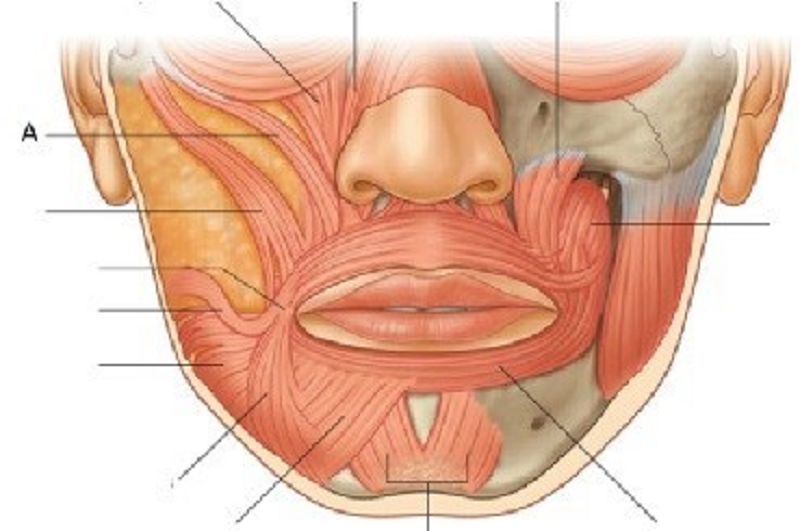
45. A is ………………………….
Levator labii superioris
Zygomaticus minor
Zygomaticus major
Depressor anguli oris
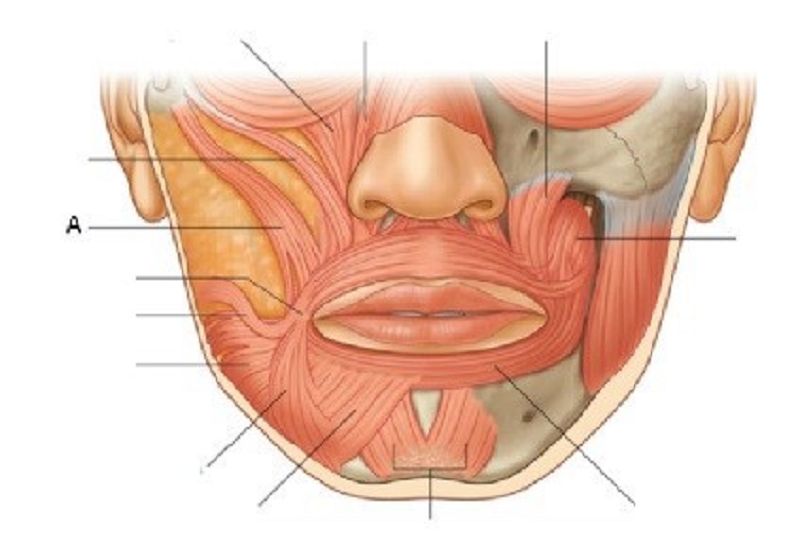
46. A is …………………………..
Levator labii superioris
Zygomaticus minor
Zygomaticus major
Depressor anguli oris
47. មនុស្សស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ ២៩ឆ្នាំមានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងផ្នែកសង្គ្រោះបន្ទាន់ ED (Emergency Department )ដោយមានរបួសផ្នែកក្រោយនៃក្បាល។អ្នកជំងឺត្អូញត្អែថាឈឺក្បាលខ្លាំង ហើយគេបានបញ្ជូនគាត់ទៅផ្នែកថត MRI បង្ហាញថាមានហូរឈាមនៅក្នុងលលាដ៏ក្បាល ហើយ ការធ្វើ CT scan បង្ហាញថាមានបែកលលាដ៏ក្បាល (Skull)។ តើសរសៃឈាមណាដែលទាក់ទងក្នុងការហើម in an epidural hematoma?
Anterior communicating artery
Posterior cerebral artery
Anterior cerebara artery
Posterior communicating artery
Middle meningeal artery
48. មនុស្សស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ ២៩ឆ្នាំមានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងផ្នែកសង្គ្រោះបន្ទាន់ ED( Emergency Department ) ដោយមានរបួស ផ្នែកក្រោយនៃក្បាល។ អ្នកជំងឺត្អូញត្អែថាឈឺក្បាលខ្លាំង ហើយគេបានបញ្ជូនគាត់ទៅ ផ្នែកថត MRI បង្ហាញថាមានហូរឈាម (Bleeding ) នៅក្នុងលលាដ៏ក្បាល ហើយ CT scan បង្ហាញថាមានបែកលលាដ៏ក្បាល។ រចនសម្ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមមាននៅក្នុង posterior cranial fossa. លើកលែងតែ EXCEPT
Occipital lobes
Jugular foramen
Cerebellum
Hypoglossal canal
Optic foramen
49. មនុស្សស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ២៩ឆ្នាំមានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងផ្នែកសង្គ្រោះបន្ទាន់ ED Emergency Departmentដោយមានរបួស ផ្នែកក្រោ យនៃក្បាល។ អ្នកជំងឺត្អូញត្អែថាឈឺក្បាលខ្លាំង ហើយគេបានបញ្ជូនគាត់ទៅ ផ្នែកថត MRI បង្ហាញថាមានហូរឈាម (Bleeding ) នៅក្នុងលលាដ៏ក្បាល ហើយ CT scan បង្ហាញ ថាមានបែកលលាដ៏ក្បាល។ សួរថាតើ Cranial nuclei នៃ Thalamus ដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធទៅនឹង Mediating facial sensation និងការឈឺចាប់ណាខ្លះ?
Ventral posterior medial nuclei (PM)
Ventral anterior nucleus
Lateral geniculate. nucleus
Ventral posterior lateral nuclei
Ventral lateral nuclei
50. មនុស្សស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ ២៩ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងផ្នែកសង្គ្រោះបន្ទាន់ដោយមានរបួស ផ្នែកក្រោយនៃក្បាល។ អ្នកជំងឺត្អូញត្អែថាឈឺក្បាលខ្លាំង ហើយគេបានបញ្ជូនគាត់ទៅ ផ្នែកថត MRI បង្ហាញថាមានហូរឈាមនៅក្នុងលលាដ៏ក្បាល ហើយ CT scan បង្ហាញថាមាន បែកលលាដ៏ក្បាល។ សួរថាតើ Cranial nuclei of the thalamus ណាខ្លះដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធទៅនឹង mediating facial senation and pian? ទាំងអស់នៅខាងក្រោមនេះគឺជា Brainstem nuclei ពាក់ព័ន្ធទៅនឹងមុខងារនៃ Crania nerve លើកលែងតែ
Superior salivatory nucleus
Nucleus ambiguus
Nucleus of the sotitary tract
Ventromedial nucleus
Inferior salivatary nucleus
51. សួរថាតើ Germ Layer ណាមួយដែលក្លាយបញ្ចូលទៅនឹងប្រព័ន្ធ epithelial lining of the cardio vascula
Mesoderm
Endoderm
Ectoderm
All of the above
None of the above
52. ចំពោះការតផ្ជាប់ Tissue attachments ណាមួយនៃខាងក្រោមនេះដែលត្រឹមត្រូវ?
Tendons form attachments between bone and bone.
Aponeuroses are merely sheetlike layers of tendon.
Neary all connective tissue is of neural crest origin, with head and neck regions of connective tissue being of mesodermal origin.
Ligaments form attachments between muscle and bone.
None of the above are correct.
53. បើកាលណាមានការប៉ះពាល់ដល់រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធឆ្អឹងខាងក្រោមនេះ វានឹងធ្វើអោយមានការប្តូរចលនានៃអណ្តាត លើកលែងតែៈ
Genial tubercles
Hamulus
Hyiod bone
Styliod process
None of the above
54. នៅផ្ទៃខាងលើសន្លាក់នៃ Mandibular condyle មានគ្របទៅដោយៈ
Dense fibrocartilage
Loose connective tissue.
Elastic cartilage
Hyaline cartilage
None of the above
55. សន្លាក់ disc នៃ Tempora-mandibular joint តផ្ជាប់ទៅនឹង Condyle ដោយសារៈ
Stylomandibular ligament
Collateral ligament
Temporomandibular ligament
Sphenomandibular ligament
None of the above
56. តើទិសណាដែល articulating disc of the temporomandibular joint ធ្វើចលនាខ្លាំងជានិច្ចៈ
Anteromedially
Laterally
Inferiorly
Superiorly
Posteromedially
57. តើ pituitary gland ស្ថិតនៅពីលើនៃ Sinus ណា ?
Frontal
Maxillary
Anterior ethmoid
Posterior ethmoid
Sphenoid
58. មនុស្សប្រុសម្នាក់មានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងបន្ទប់ព្យាបាលធ្មេញរបស់អ្នក ដោយចង់ដកធ្មេញ ខុសជួរលេខ១៧។ ទន្តបណ្ឌិតព្យាយាមដកធ្មេញនេះ ដោយប្រើដង្កាប់ Mandibular cowhorn forceps។ ធ្មេញបានដករួចហើយ ដោយគ្មានផលវិបត្តិភ្លាមៗទេ។ បើកាលណា អ្នកជំងឺត្អូញត្អែរថា មានការផ្លាស់ប្តូររស់ជាតិ2/3 នៃអណ្តាតរបស់គាត់។ តើរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធណាមួយដែលធ្វើ អោយមានការប៉ះពាល់ក្រោយពីការដកធ្មេញ។
Buccal nerve
Lingual nerve
Middle superior alveolar nerve
Hypoglossal nerve
Inferior alveolar nerve
59. មនុស្សប្រុសម្នាក់អាយុ ២២ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងបន្ទប់ព្យាបាលធ្មេញរបស់អ្នក ដោយចង់ដកធ្មេញខុសជួរ លេខ ១៧។ ទន្តបណ្ឌិតព្យាយាមដកធ្មេញនេះ ដោយប្រើ ដង្កាប់ Mandibular cowhorn។ ធ្មេញដករួចហើយ តែគ្មានផលវិបតិ្តភ្លាមៗនោះទេ។ មុនការដក ធ្មេញ ប្រសិនបើ Infection បានកកើតនៅចុងឬស (at the root apices) នៃធ្មេញ លេខ១៧។ សួរ ថាតើ Infection ឆ្លងកាត់ខ្លាំងជាងគេនៅ facial plane ណា?
Sublingual
Parapharyngeal.
Masticator
Submandibular
Parotid
60. មនុស្សប្រុសម្នាក់អាយុ ២២ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងបន្ទប់ព្យាបាលធ្មេញរបស់អ្នក ដើម្បីដកធ្មេញលេខ១៧ ដែលខុសជួរ ។ ទន្តបណ្ឌិតបានដកធ្មេញ ដោយប្រើ ដង្កាប់ Mandibular cowhorn fosceps។ ធ្មេញបានដករួចហើយ ដោយគ្មាន គុណវិបតិ្តភ្លាមៗនោះទេ។ ការសង្រ្គោះបន្ទាន់ទៅលើអ្នកជំងឺដោយមានការថប់ដង្ហើម(air way obstruction)។ តើគេធ្វើការធ្វើវះកាត់ដើម្បីអោយអ្នកជំងឺដកដង្ហើមបាន (Cricothyrotomy) គឺធ្វើការកាត់ (incising) រវាង
Hyoid bone and thryroid cartilage
Cartilaginous rings of trachea
Thyroid cartilage and criciod cartilage
Thyroid gland
Left 3rd and intercostal muscles, laterally
61. កាលណាធ្វើ IDB (inferior alveolar nerve block) ម្ជុលបានចាក់ចូលយ៉ាងជ្រៅដល់ផ្នែកខាង ក្រោយ។ សួរថាតើរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធណាមួយដែលរងគ្រោះ?
Buccinator
Lateral pterygoid
Medial pterygoid
Mylohyoid
Parotid gland
62. តើរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធណាដែលប្រសព្វគ្នាជាមួយ Pterygomandibular raphe?
Superior pharyngeal constrictor and mylohyoid
Medial pterygoid and mylohyoid
Buccinator and superior pharyngeal constrictor
Buccinator and mylohyoid
Medial pterygoid and superior pharyngeal constrictor
63. មនុស្សស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ ៥៥ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅបន្ទប់ព្យាបាលធ្មេញ ដើម្បីធ្វើ Deep scaling and root planing ជាផ្នែកនៃការព្យាបាល periodontitis ។ ដោយសារមាន pocket ធំនិងជ្រៅ ព័ទ្ធជុំវិញធ្គាមស្តាំខាងក្រោម ការចាក់ថ្នាំស្ពឹកនៅផ្នែកនេះជាការចាំបាច់ដើម្បី Scale នឹង plane the roots។ ជាលំដាប់ ការធ្វើ IDB នៅផ្នែកនេះ តើត្រូវស្ទាបរករចនាសម្ព័ន្ធណាមុនការ ធ្វើ IDB?
Lingula
Coronoid notch.
Antilingula
Angle of the mandible
External oblique ridge of the mandible
64. មនុស្សស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ ៥៥ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅបន្ទប់ព្យាបាលធ្មេញ ដើម្បីធ្វើ Deep scaling and root planing ដែលជាផ្នែកនៃការព្យាបាល periodontitis ។ ដូចគ្នាទៅនឹងករណី ដែល មានជំងឺ Periodontal គឺ periodontal attachment បាត់បង់យ៉ាងជាក់ច្បាស់។ សួរថាតើ Pricipal collagen fibers of the PDL ណាដែលរត់ពី Cementum ទៅភ្ជាប់ alveolar bone?
Horizontal
Apical
Interradicular
Transseptal
Oblique
65. មនុស្សស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ ៥៥ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅបន្ទប់ព្យាបាលធ្មេញ ដើម្បីធ្វើ Deep scaling នឹង root planing ដែលជាផ្នែកក្នុងការព្យាបាល periodontitis ។សួរថា តើ Principal collagen fibers of the PDL នៅរវាង Type of collagen ណា?
Type I only
Type II only
Type III only
Type I and III
Type II and III
66. មនុស្សស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ ៥៥ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅបន្ទប់ព្យាបាលធ្មេញ ដើម្បីធ្វើ Deep scaling នឹង root planing ដែលជាផ្នែកក្នុងការព្យាបាល periodontitis ។ សួរថា តើ Cell ណា ដែលសំបូរខ្លាំង ដើម្បីសុខភាព Periodontal ligament?
Lymphocytes
Neutrophils
Osteoblasts
Cementobasts
Fibroblasts
67. "មនុស្សប្រុសម្នាក់អាយុ ២៦ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅផ្នែកសង្រ្គោះបន្ទាន់ ដោយរងនូវការ វាយនឹងរនុក។ គាត់បានបញ្ជាក់ថា គាត់ត្រូវបានគេដាល់ចំភ្នែកស្តាំ ហើយត្អួញត្អែពីការ ឈឺក្បាល។ ទន្តបណ្ឌិងកត់សំគាល់ថា មានហើមនៅភ្នែកស្តាំរបស់អ្នកជំងឺ ជាងនេះទៀតបានត្អូញត្អែថា ពេលស្ទាប មានការឈឺមួយចំហៀងមុខផ្នែក Infero-lateral នៃភ្នែកស្តាំ (ធ្វើអោយមានការព្រួយបារម្ភបន្តិច) ឆ្អឹងនិមួយៗនៅខាងក្រោមគឺជាផ្នែកនៃ orbit លើកលែងតែៈ"
Frontal
Zygoma
Ethmoid
Lacrimal
Temporal
68. មនុស្សប្រុសម្នាក់អាយុ ២៦ឆ្នាំ មានវត្តមាននៅផ្នែកសង្រ្គោះបន្ទាន់ ដោយរងនូវការវាយ នឹងរនុក។ គាត់បានបញ្ជាក់ថា គាត់ត្រូវបានគេដាល់ចំភ្នែកស្តាំ ហើយធ្វើអោយឈឺក្បាល។ ទន្តបណ្ឌិតមានសំគាល់ថា មានហើមនៅរង្វង់ភ្នែកស្តាំ(periorbital edema) ហើយគាត់បានត្អូញត្អែថា ពេលស្ទាបមានការឈឺមួយចំហៀងមុខនៅផ្នែក Infero-lateral នៅភ្នែកស្តាំរបស់គាត់។ សួរថាតើ Artery ធំចំបងណាដែលផ្តល់ឈាម ដើម្បីចិញ្ចឹម orbit នឹងភ្នែក?
Facial
Ophthalmic
Maxillary
Transverse facial
Infraorbital
69. មនុស្សប្រុសម្នាក់អាយុ ២៦ឆ្នាំមានវត្តមាននៅបន្ទប់សង្រ្គោះបន្ទាន់ ដោយរងនូវការវាយនឹង រនុក ។ គាត់បានបញ្ជាក់ថា គាត់ត្រូវបានវាយយ៉ាងដំណំនៅចំភ្នែកស្តាំ ហើយមានការឈឺ ក្បាល។ យើងបានកត់សំគាល់ថា មានការហើមនៅរង្វង់ភ្នែកស្តាំ ហើយអ្នកជំងឺបានត្អូញត្អែថា ពេលស្ទាប មានការឈឺមួយចំហៀងមុខ នៅ Infero-lateral នៃភ្នែកស្តាំ។តើសាច់ដុំណាមួយ ដែលមានកំណើតពីលើ Zygamatic Process of Maxilla (superfi-ciallyn ) និង Zygamatic arch ( Deep)
Lateral pterygoid
Temporalis
Buccinator
Masseter
Medial pterygoid
70. មនុស្សម្នាក់អាយុ២៦ឆ្នាំមានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងបន្ទប់សង្រ្គោះបន្ទាន់ដោយរងនូវការវាយនឹង រនុក ។ គាត់បានបញ្ជាក់ថាគាត់ត្រូវគេវាយយ៉ាងដំណំចំភ្នែកស្តាំ ហើយបានត្អួញត្អែថា មានការឈឺក្បាល។ យើងកត់សំគាល់ឃើញមានការហើមនៅរង្វង់ភ្នែកស្តាំ និងជាងនេះទៅទៀត បានត្អួញត្អែរថា កាលណាគេស្ទាប មានការឈឺមួយចំហៀងមុខនៅម្តុំ Infero-Lateral ភ្នែកស្តាំ។ តើ Superior orbital fissure ស្ថិតនៅរវាងឆ្អឹងណាខ្លះ?
Lesser wing of sphenoid and frontal
Ethmoid and maxilla
Greater wing of sphenoid and maxilla
Greater wing of sphenoid and lesser wing of sphenoid
Lesser wing of sphenoid and ethmoid
71. តើសាច់ដុំ platysma មានការគ្រប់គ្រងដោយសរសៃរប្រសាទណា?
Trigeminal
Facial
Glossopharyngeal
Spinal accessory
Vagus
72. តើ layer of fascial ណាដែលមាន Lymphatic vessels នៅក្នុងក?
Pretracheal
Prevertebral
Subcutaneous
Investing
Nun of the above
73. តើ ឆ្អឹងcartilage ណាដែលមានសមត្ថភាព Calcify ?
Fibrocartilage
Hyaline
Elastic
Elastic and Hyaline
Hyaline and Fibrocartilage
74. The one-cell thick layer ស្រទាប់ក្រាស់នៃក្រុមកោសិកាមួយ នៃ Osteoprogenitor cell ដែលមាននៅផ្ទៃខាងក្នុងនៃឆ្អឹងគឺ
Endosteum
Haversian canal
Volkmann canal
Lacuna.
Periosteum
75. តើ Type of syndesmosis ណាដែលមានដូចតទៅៈ
Tooth in socket
Cranial sutures
Temporomandibular joint
Epiphyseal plate of long bones
Connection between radius and ulna
76. តើ Granulocyte ណាមាននៅខាងក្រោមនេះ?
T cell
Marcrophage
Platelet
Neutrophil
B cell
77. តើ Nuclei ណាដែលត្រួតពិនិត្យដំបូងនៃការលាប?
Subperior Salivatory
Nucleus ambiguus
Inferior Salivatory
Facial Nucleus
Nucleus of the solitary tract
78. ទាក់ទង់ទៅនឹងក្នុងមាត់ តើ Layer of mucosa interdigitates ដែលរឹត?
Stratum granulosum
Papillary layer of lamina propria
Stratum corneum
Reticular layer of lamina propria
Stratum spinosum
79. ការលូតលាស់ cell នៃរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធធ្មេញ លេចចេញពីៈ
Inner enamel epitphelium
Dental follicle
Dental papilla
Dental follicle and papilla
Inner enamel epitphelium and Dental papilla
80. ពេលណាដែល Ameloblasts ចាប់ផ្តើមបញ្ចេញនៅ Enamel matrix?
During the cap stage
After the odontoblasts form dentin
Before the odontoblasts form dentin
After root formation begins
Before cap stage
81. តើ cribiform plate បានស្ថិតនៅជាឆ្អឹងណា?
Sphenoid
Ethoid
Frontal
Maxilla
Vomer
82. ឧបមាថាត្រូវចាក់ថ្នាំស្ពឹកជាចាំបាច់នៅ anterior palatal mucosa ។ តើ Nerve ណាដែលគ្រប់គ្រងនៅផ្នែកនេះ?
Nasopalatine
Middle superior alveolar
Posterior superior alveolar
Maxillary
Lesser palatine
83. Stylomandibular ligament មានដើមកំណើតភ្ជាប់មកពីឆ្អឹងណា?
Temporal
Sphenoid
Occipital
Maxilla
Parietal
84. ឆ្អឹងនិមួយៗសុទ្ធតែជាគូរៗ លើកលែងតែៈ
Occipital
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Frontal
None of the above
85. សូមមើលការតភ្ជាប់នៃសាច់ដុំ Mylohyoid? សួរថា មួយណាដែលត្រឹមត្រូវ?
វាតភ្ជាប់ ខាងលើទៅនឹងគែមកណ្តាលនៃឆ្អឹងធ្គាមក្រោម ហើយខាងក្រោមតភ្ជាប់ស្នែងតូចនៃឆ្អឹង hyoid.
វាតភ្ជាប់ខាងលើទៅនឹងគែមកណ្តាលនៃឆ្អឹងធ្គាមក្រោម ហើយខាងក្រោមតភ្ជាប់ ស្នែងធំនៃឆ្អឹង hyoid.
វាតភ្ជាប់ ខាងលើទៅនឹងគែមកណ្តាលនៃឆ្អឹងក្រោម ហើយខាងក្រោមតភ្ជាប់ ដងខ្លួននៃឆ្អឹង hyoid
វាតភ្ជាប់ ខាងលើទៅនឹងគែមខាងនៃឆ្អឹងធ្គាមក្រោម ហើយខាងក្រោមតភ្ជាប់ ដងខ្លួននៃឆ្អឹង hyoid
86. តើ Nerve ណាទៅគ្រប់គ្រង digastric muscle ( innervates the anterior Belly of the digastric muscle?)
Inferior alveolar nerve
Mental nerve
Mylohyoid nerve
Auriculotemporal nerve
Facial nerve
87. The infrahyoid musculature នៃក ទទួលនូវសរសៃចលនាពីៈ
C4-C6
ansa cervicalis
Leesser occipital nerve
Greater occipital nerve
C6- C8
88. នៅខាងក្រោមនេះទាំងអស់សុទ្ធជាមែកធាងនៃ External carotid artery លើកលែងតែៈ
Ophthalmic artery
Ascending pharyngeal artery
Superior thyroid artery
Posterior aurcular artery
Occipital artery
89. Crista galli គឺជាឆ្អឹងរីកលើនៃឆ្អឹងណា?
Sphenoid
Ethmoid
Vomer
Frontal
Maxilla
90. និយាយអំពី Hypothetically, កាលណាគេរៀបចំធ្វើ Cavity មួយនៅលើ Crown នៃ ធ្មេញស្រុកមួយ អ្នកត្រូវកាត់ជាដំបូងនូវ Enamel ហើយចូលទៅដល់ Dentin។ តើរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធដំបូងណាមួយដែលត្រូវប៉ះពាល់?
Circumpulpal dentin
Mantle dentin
Odontoblasts
Radicular dentin
Circumpulpal and radicular dentin
91. ធ្មេញមួយបានដកមកហើយ ហើយឬសមួយបានបាក់នៅក្នុង Alveolus ។ តើឬសធ្មេញណាដែលអាចធ្វើអោយរបួសដល់ Maxillary Sinus?:
Buccal root of the maxillary 1st premolar
Root of the maxillary canine
Root of the maxillary lateral incisor
Lingual root of the maxillary 1st molar
Lingual root of the maxillary 1st premolar
92. ឆ្អឹងទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមនេះតភ្ជាប់ជាមួយ Zygoma លើកលែងតែៈ:
Temporal
Maxilla
Frontal
Sphenoid
Parietal
93. ក្មេងស្រីម្នាក់អាយុ ១៨ឆ្នាំមានវត្តមាននៅផ្នែកសង្រ្គោះបន្ទាន់ ត្អូញត្អែរយ៉ាងខ្លាំង ដោយចង្កាជាប់មិនអាចធ្វើចលនាបាន អ្នកបានសន្និដ្ឋានថា ជា Luxation នៃ Mandible។ តើទិសដៅណាដែល Mandible condyle ត្រូវធ្វើចលនាបានល្អធម្មតាវិញ?:
Posterior and superior
Posterior and inferior
Lateral and inferior
Anteriorly
Medially
94. តើ the inferior alveolar artery កើតចេញមកពី Artery ណា?
Meddle meningeal
Facial
External carotid
Maxillary
Buccal
95. តើ attachment of epithelium តភ្ជាប់ទៅជាលិកាណា?
Hemidesmosome
Zonula adherens
Zonula occludens
Desmosome
Gap junction
96. A-gamma fibers មានមុខងារនៅក្នុង
Touch sensation
Muscle spindle apparatus
Pressure sensation
Temperature sensation
Sharp pain sensation
97. The submaxillary ganglion បានទទួល Presynap-tie efferent innervation ពី Nerve ណា?
Inferior alveolar
Facial
Buccinator
Maxillary
Lingual
98. សាច់ដុំនិមួយៗបានទទួលនូវ motor innervation ពី Facial Nerve លើកលែងតែៈ
Risorius
Masseter
Orbicularis oris.
Mentalis
Buccinator
99. The jaw-jerk reflex ទាក់ទង efferent signals ពី Cranial nerves?
V-1
V-3
VII
V-2
IX
100. ជាធម្មតា the esophagus មាន epithelium ប្រភេទណា?
Nonkeratinized stratified squamous
Columnar
Keratinized stratified squamous
Cuboidal
Pseudostratified squamous
101. Spem ប្រមូលទុកក្នុងៈ
Epididymis
Urethra
Testis
Seminiferous tubules
Prostate gland
102. ខាងក្រោមនេះជាមុខងារមួយៗរបស់ស្បែក លើកលែងតែៈ
Sensation of touch, pain , and pressure
Synthesis of vitamin E from ultraviolet light
Excretion via sweat glands
Homeostatic regulation of body temperature
Protection against physical and chemical stresses
103. 1/3 នៃផ្នែកក្រោយអណ្តាតបានបង្ហូរចេញ tymphatiel តម្រង់ចូលទៅក្នុងៈ
Deep cervical nodes
Submental nodes
Submandibular nodes
Rectopharyngeal nodes
Subpraclavicular nodes
104. ទាក់ទងទៅនឹង bone marrow នៃឆ្អឹងថ្គាមលើនិងក្រោម តើឃ្លាណាមួយដែលខុស ?
It is contained within the medullary spaces of spongy bone.
Red marrow contain fatty cells and is the predominant marrow type in the mandibular ramus and condyles.
Red marrow contains hematopoietic cells.
Yellow marrow contains fatty cells.
Yellow marrow is the predominant marrow type in the maxilla and mandible.
105. តើ combination of epithelium ណាមួយ ដែលមាននៅក្នុងរន្ធច្រមុះ?
Stratified squamous, pseudostratified ciliated columnar, olfactory.
Simple squamous, olfactory, simple columnar.
Stratified squamous, olfactory, stratified columnar.
Simple cuboidal, simple squamous, simple columnar.
Stratified columnar, simple squamous, simple columnar.
106. អ្នកជំងឺម្នាក់មានវត្តមាននៅចំពោះមុខអ្នក ដោយមានការប៉ះទង្គិចនៅចង្កា យើងពិនិត្យឃើញថា ផ្នែកខាងមុខអណ្តាតមានការដាច់ ហើយហូរឈាមយ៉ាងខ្លាំង។ សរសៃនិមួយៗ សុទ្ធនាំឈាមទៅផ្គត់ផ្គង់អណ្តាតលើកលែងតែៈ
Facial artery
Ascenting pharyngeal artery
Lingual artery
Superior laryngeal artery
External carotid artery
107. "អ្នកជំងឺម្នាក់ មានវត្តមាននៅចំពោះមុខអ្នក ដោយមានការប៉ះទង្គិចនៅចង្កា។គេកត់សំគាល់មានការដាច់នៅផ្នែកខាងមុខនៃអណ្តាត ហើយមានការហូរឈាមយ៉ាង អ្នកខ្លាំង។ សាច់ដុំមួយៗសុទ្ធតែទទួលគ្រោះថ្នាក់ លើកលែងតែៈ"
Longitudinal
Styloglossus
Hyoglossus
Transverse
Palatoglossus
108. តើ Combinations of cranial nerves ណា ដែលផ្គត់ផ្គង់ motor innervation ដល់អណ្តាតៈ
VII, X
X, XII
VII, XII
V, XII
VII, IX.
109. តើប្រភេទរសជាតិណាដែលបាត់បង់ខ្លាំង នៅពេលដែលចុងអណ្តាតមានការប៉ះទង្គិច?
Sweet
Salt
Bitter
Sour
None of the above
110. តើ formation ណាដែលមិនបានផ្លាស់ប្តូរនៅក្នុង compete bilateral paratal clefting?
Lip
Primary palate
Alveolar process
Inferior nasal turbinate/concha
Secoondary palate
111. តើតាមបែបលក្ខណៈណាដែលពន្លកធ្មេញលេចឡើង?
Elongation of cervical loop and formation of HERS.
Fusion of REE and oral epithelium.
Disappearance of the enamel knot.
Formation of the enamel organ.
Mergin of the OEE with the IEE.
112. គេសង្កេតឃើញថា អ្នកជំងឺម្នាក់មានការផ្លាស់ប្តូរនូវ hemostasis Malfunctionតើវាអាចបណ្តាលមកពីមូលហេតុអី្វ?
Monocytes
B cells
Megakaryocytes
Erythroblasts
Granulocytes
113. ប្រសិនបើអ្នកជំងឺម្នាក់មានកំរិតខ្ពស់នូវ bile pigment ដែលបញ្ចេញដោយថ្លើមតើវាបានបង្កើនឡើងនូវការបំផ្លាញនៃ causative factor ណា?
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Erythrocytes
Platelets
Macrophages
114. ឃ្លាខាងក្រោមនៃ Gingival crevicular fluid. ពិតជាត្រូវឬ?
It is comprised mostly of PMNs and leukocytes.
It lacks plasma proteins and epithelial cells.
It is contained mostly within the vestibule of the buccal mucosa.
It lacks function in immune defense.
It is not located within the gingival sulcus.
115. តើរោគវិនិច្ឆ័យណាមួយ បញ្ជាក់យ៉ាងច្បាស់នៃអ្នកជំងឺក្មេងម្នាក់ដែលមានbrownish pigmentation and mottling of his dentition?
Conginatal syphilis.
Nutritional deficiency.
Fluorosis.
Hypocalcification.
Hypomineralization.
116. សកម្មភាពមិនត្រឹមត្រូវនៃសរសៃលលាដ៏ក្បាលណាមួយ ដែលជះឥទ្ធិពលដល់ efferent output of the gag reflex?
CN XII
CN V
CN IX
CN VII
CN X
117. Vein និមួយៗតែងតែនាំ deoxygenated blood លើកលែងតែៈ
Hepatic vein
Superior vena cava
inferior vena cava
Pulmonary vein
Coronary sinus
118. តើសាច់ដុំណាមួយដែលកាត់ Maxillary artery ជាបីផ្នែកផ្សេងៗគ្នា?
Lateral pterygoid
Masseter
Posterior belly of digastric
Stylohyoid
Anterior belly of digastric
119. រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធនិមួយៗទទួលឈាមពី External carotid លើកលែងតែៈ
Thyroid
Brain
Salivary glands
Teeth
Jaw bones
120. តើឆ្អឹងណាមួយដែល Vestibulocochlear nerve គ្រប់គ្រងច្រើនជាងគេ?
Parietal
Occipital
Temporal
Frontal
Maxilla
121. តើ Arteries ណាមួយ ដែលទៅផ្គត់ផ្គង់ Maxillary Canines and Incisors?
Pterygoid
Sphenopalatine
Descenting palatine
Infraorbital
Pharyngeal
122. Dentin ដែលមានអាយុចាស់(ក្រិន) តើប្រភេទណាដែលគេប្រទះ?
Increased dentinal tubule diameter.
Decreased reparative dentin.
Decreased dead tracts.
Decreased sclerrotic dentin.
Increased deposition of peritubularl dentin.
123. អ្នកជំងឺម្នាក់អាយុ ១៧ឆ្នាំមានវត្តមាននៅក្នុងបន្ទប់ព្យាបាលរបស់អ្នក បានសួរថា តើហេតុ អី្វបានជាធ្មេញរបស់គាត់ពណ៍ Brownish –gray ឆ្នូតកាត់ទទឹងនៅលើធ្មេញ អ្នកសង្ស័យថា ប្រហែលអ្នកជំងឺត្រូវបានគ្រូពេទ្យព្យាបាលអោយលេបថ្នាំណាមួយ នៅក្នុងរវាងអាយុប៉ុន្មាន?
5
10
11
14
17
124. តើការខ្វះខាតដ៏តិចបំផុតនៃ Vitamin ណា?ដែលប៉ះពាល់ដល់រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ Enamel ?
A
B
C
K
Calcium
125. តើប្រភេទ Epithelium ណាដែលគេប្រទះឃើញច្រើនជាងគេ ដែលវាពាស Body cavities?
Simple columnar
Simple squamous
Transitional
Stratifies squamous
Pseudostratified columnar
126. តើ basement membrane ណាដែលត្រូវ?
Lamina lucida is electron dense.
Lamina densa is a product of the connective tissue.
Type IV collagen is typically found in the basal lamina.
Reticular lamina contains anchoring fibrils.
It does not have a filtering function.
127. តើប្រភេទ Oral epithelium ណាដែលធ្វើ Keratinized?
Sulcular epithelium
Alveolar mucosa
Junctional epithelium
Attached gingiva
Gingival col
128. ណាមួយដែលមាន Organic Composition ទាបខ្លាំង?
Cementum
Dentin
Pulp
Enamel
Alveolar bone
129. បន្ទប់សរសៃធ្មេញ (Pulpal Chamber)ដែលមានអាយុច្រើន ឃ្លានិមួយៗខាងក្រោមត្រឹមត្រូវលើកលែងតែៈ
Decreased collagen content
Decreased size of apical foramen
Decreased sensitivity
Decreased cellularity
Increased calcification
130. ផ្នែកណាមួយនៃធ្មេញ ឬរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធសំរាប់ចលនា Orthodontic?
Enamel
Cementum
Dentin
Epithelial attachment
Alveolar bone
131. តើ Nerve ប្រភេទណាដែលបានបញ្ចប់នៅក្នុង periodontal ligament?
Coiled
Spindle
Free
Meissner
Ruffini
132. ណាមួយដែលជាសំពាធនៃ Interdental gingiva ដែលបានផ្ជាប់ lingual នឹង facial Papillae?
Gingival col
Alveolar mucosa
Attached gingiva
Mucogingival junction
Interdental papilla
133. តើណាមួយដែលមិនពិត បញ្ជាក់ពី primary palate?
It can be involved in facial clefting
It contains the incisive foramen
It Usually contains no teeth
It is mesenchymal in origin
It is formed by fusion of two metian nasal processes
134. តើណាមួយដែលបានបង្ហាញយ៉ាងច្បាស់នូវ circumpulpal dentin?
Most is produced in the form of intertubular dentin.
It is the initial 150 µm of dentin laid down.
It lacks hydroxyapatite.
It forms before mantle dentin.
It lacks dead tracts
135. ក្នុងកំឡុងពេលនៃ Amelogenesis តើ Enamel បានថយចុះក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃជាមធ្យមប៉ុន្មាន?
0.04 µm
1mm
0.1mm
4 µm
4mm
136. ក្នុងរយៈពេល odontogenesis កោសិកាណាដែលបញ្ជាក់ពីប្រភេទធ្មេញដែលត្រូវកកើត?
Mesoderm
Mesenchyme
Ectomesenchyme
Endoderm
Ectoderm
137. ទំហំនៃស្បែកដែលគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ parotid gland ទទួលនូវ sensory innervation ពីសរសៃប្រសាទណា?
Transverse cervical
Superficial temporal
Long buccal
Lesser occipital
Great auricular
138. ឆ្អឹង Temporal ភ្ជាប់ជាមួយឆ្អឹងដូចខាងក្រោមលើកលែងតែៈ
Parietal
Occipital
Zygoma
Ethmoid
Sphenoid
139. The embryological stomodeum គឺគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយ
Endoderm
Mesoderm
Neural crest
Ectoderm
Ectomesenchyme
140. ការបង្កើននូវ Vitamin D វាមាននៅកន្លែងណា?
Large intestine
Kidney
Spleen
Liver
Epidermis
141. Serum មាននៅក្នុងចំនុចខាងក្រោមលើកលែងតែ
Electrolytes
Fibrinogen
Immunglobulins
Water
Albumin
142. ណាមួយនៃឃ្លាខាងក្រោមដែលត្រូវនឹងបេះដូង?
The pericardium contains cardiac muscle.
The endocardium has a layer of simple squamous endothelium.
The innermost layer of the heart is pericardium.
Normally the thickest portion of the heart is the endocardium.
A layer of columnar epithelium surrounds the pericardium.
143. ណាមួយនៃឃ្លាខាងក្រោមដែលត្រូវនឹង Platelets?
They range 200,000-400,000 per mm3 blood.
They are involved in immunoregulation.
They average lifespan is upward of 120 days.
They are nucleated.
They function in blood gas trasport.
144. ណាមួយនៃឃ្លាខាងក្រោមគឺជាកន្លែងនៃ B-cell maturation?
Lymph nodes
Blood
Thymus
Bone marrow
Target tissue
145. Thyroxine ផលិតចេញពីៈ
Follicular cells
Outer cortex of adrenals
Pars distalis
Pars intermedia.
Parafollicular cells
146. មួយណានៃ blood elements ខាងក្រោមនេះដែលជា fragment នៃ megakaryocytic cytoplasm?
Platelet
Normoblast
Erythrocyte
Promyelocyte
Proerythroblast
147. ណាមួយដែលជាសាច់ដុំចំបងក្នុងការធ្វើចលនា retracting and elevating the mandible?
Masseter
Digastric
Mylohyoid
Temporalis
Lateral pterygoid
148. សរសៃដែលផ្តល់ឈាមដល់ walls of large arteries ជាទូទៅត្រូវបានគេស្គាល់ថាជាៈ
Arterioles
Capillaries
Vasa vasorum
Metarterioles
Glomus
149. រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធមួយដែល Calcified នៃធ្មេញមិនអាចបន្តលូតលាស់ក្រោយពីបានដុះចេញមកគឺៈ
Enamel
Dentin
Cementum
Ligament
True denticle
150. ណាមួយដែលជាផ្នែកទីមួយកកើតឡើងនៃ Dentin
Circumpulpal
Intertubular
Transparent
Reparative
Mantle
151. ណាមួយដែលកំណត់ផ្នែកខាងក្រោយនៃ oral cavity នឹងផ្នែកខាងមុខនៃ fauces?
Tonsil
Soft palate
Dorsum of the tongue
Palatopharyngeal arch
Palatoglossal arch
152. តើfiber groups PDL (ជាលិកាជុំវិញធ្មេញ) ណាមួយដែលទាក់ទងនឹងcentral incisor លើកលែងតែមួយ ?
Apical
Oblique
Horizontal
Alveolar crest
Interradicular
153. តើសារធាតុខាងក្រោមណាមួយមិនមែនអរមូន Peptide hormone?
PTH
Insulin
GH
Aldosterone
ADH
154. តើសសៃឈាមប្រភេទណាមួយខាងក្រោមដែលទទួលបន្ទុកផ្នែកធំបំផុតនៃ vascular resistance ?
Arteries
Arterioles
Capillaries
Venules
Veins
155. សារធាតុទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមជារបស់ Carbonic anhydrase លើកលែងតែ
ជាទូទៅវាមានអាតូម Zinc នៅកណ្តាល
ប្រតិកម្មបំលែងពី Carbon dioxide and bicarbonate
បង្កើនល្បឿនប្រតិកម្មគួរ
មានសកម្មភាពខ្លាំងនៅក្នុង Platelets
មាននៅក្នុង Osteoclastic activity
156. បរិមាណទឹកនៅក្រៅកោសិកាមានចំនួនប៉ុន្មានធៀបនឹងបរិមាណទឹកក្នុងខ្លួនសរុប ?
25%
33%
50%
66%
75%
157. តើប្រភេទ cartilage ខាងក្រោមណាមួយ may calcify ?
Elastic
Hyaline & Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage
All of the above
158. ទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមជា Key Enzyme ក្នុងការសំយោគ DNA លើកលែងតែ
Polymerase
Exonuclease
Aminotransferase
Topoisomerase
Helicase
159. ទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមជាជាលិកាដែលទាក់ទងក្នុង Feedback axis with the Hypothalamus លើកលែងតែ
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Pituitary
Adrenal
Testicular
160. ទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមជាចំលើយត្រូវនឹង somatic nervous system លើកលែងតែ
វាមានសសៃទាំង ១២(12 Cranial Nerves)
វាបញ្ជូនការឈឺចាប់និងកំដៅ
ផ្តល់វិញ្ញាណដល់ Skeletal muscle
វាមានរយៈពេលខ្លីនៃpreganglionic motor neurons
ទាំងអស់ខាងលើជាចំលើយត្រូវទាក់ទងនឹង Somatic nervous system
161. ទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមជាចំលើយត្រូវទាក់ទងនឹង Pulmonary circulation ប្រៀបធៀបនឹង System circulation លើកលែងតែ
វាមានResistanceខ្ពស់ជាង
វាមានCompliance ខ្ពស់ជាង
វាមានសំពាធឈាមទាបជាង
វាមានការស្រដៀងទៅនឹងកំរិតឈាមហូរ
វាដឹកនាំDeoxygenated ឆ្លងកាត់ pulmonary artery
162. Aldosteroneគឺបង្កើតនៅpathwayដើមី្បបញ្ចេញអរម៉ូនអ្វី?
Renin
ADH
Vasopressin
Erythropoietin
ACTH
163. ទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមជាចំលើយត្រូវទាក់ទងនឹងplasma membranes លើកលែងតែ
Selectively permeable
Function as barriers
Symmetrical
Contain cholesterol
Have a hydrophobic inner layer
164. ជាទូទៅ អត្រាប្រតិកម្មនឹងកើនឡើងជាលទ្ធផលនៃកត្តាខាងក្រោមលើកលែងតែ
ការបង្កើនសីតុណ្ហភាព
ការបង្កើនកំហាប់អង់ស៊ីម
ការបង្កើនកំលាំងប្រតិកម្ម
ការបង្កើនកំហាប់Substrate
ការបន្ថយកំលាំងប្រតិកម្ម
165. ទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមជា Zymogens លើកលែងតែ
Clotting factor I
Calmodulin
Trypsinogen
Clotting factor
Procollagen
166. Hyperventilation ជាលទ្ធផលនៅក្នុង ទាំងអស់ខាងក្រោមលើកលែងតែ
Increased PO2
Hypocapnia
Decrease cerebral blood flow
Increased PCO2
Respiratory alkalosis
167. មុខងាររបស់ថ្នាំស្ពឹក LA function by
Activating Na+ channels
Blocking Na+ cannels
Activating K+ channels
Blocking K+ channels
មិនត្រឹមត្រូវទាំងអស់
168. តើចំលើយមួយណាខាងក្រោមដែលទាក់ទងនឹងOsteonecrosis of the jawsថ្គាម?
Pamidronate
Zolendronate
Alendronate
ចំលើយទាំងអស់ខាងលើត្រឹមត្រូវ
ខាងលើខុសទាំងអស់
169. Insulin ផលិតមកពីក្រពេញមួយណា?
Mecrocrin
Acinar
Tubular
Mecrocrin and Acina
None of the above
170. ចំនួនសរុបនៃការដឹកនាំអុកស៊ីសែននៅក្នុងចរន្ធឈាមកើតឡើងដោយសារ
Bicarbonate
Dissolved O2
Dissolved O2 &Bound to haemoglobin
ត្រូវទាំងអស់
171. តើខាងក្រោមណាមួយមិនមែនមានក្នុងplasma membranes
Sphinogomyelin
Cholesterol
G proteins
Collagen
Arachidonic acid
172. តើផ្នែកណាមួយជាអ្នកបញ្ជូនការឈឺចាប់និងកំដៅ?
Dorsal column pathway
Anterior spinothalamic tract (of the antero-lateral pathway)
Lateral spinothalamic tract ( of the antero-lateral pathway)
Corticospinal tract (of the pyramidal system)
Medial lemniscal pathway
173. តើសាច់ដុំខាងក្រោមណាមួយមិនទាក់ទងនឹងការលេប Swallowing
Salpingopharyngeus
Levator veli palatine
Palatopharyngeus
Tensor veli palatine
Inferior pharyngeal constrictor
174. រណ្តៅដកធ្មេញថ្មីនឹងបំពេញដោយឆ្អឹងថ្មីនៅពីរបីខែបន្ទាប់ តើឆ្អឹងប្រភេទណាមួយ នឹងកើតឡើងនៅអំឡុងពេលនោះ
Intramembranous
Endochodral
Intermembranous
Intramembranous and Endochodral
ខាងលើខុសទាំងអស់
175. Epinephrine គឺជាស្រលាយណានៃAmino acids ខាងក្រោម
Histidine
Serin
Glycine
Tryptophan
Phenylalanine
176. តើ Receptorsខាងក្រោមណាមួយដែលទទួលបន្ទុកធំជាងគេលើ detecting stretch?
Free nerve endings
Meissner corpuscles
Ruffini corpuscles
Pacinian corpuscles
Merkel discs
177. ADH ផលិតនៅក្នុងរចនាសម្ព័ន្ធណា?
Hypothalamus
Anteroir pituitary
Posterior pituitary
Adrenal medulla
Adrenal cortex
178. តើសរីរាង្គខាងក្រោមប្រភេទណាមួយដែលបញ្ចេញ អាស៊ីតច្រើន?
Bile
Pancreatic
Gastric
Intestinal
179. ប្រភេទ Amino acid សំខាន់មាននៅក្នុង collagen ជាប្រភេទមួយណាខាងក្រោម?
Apartate
Proline
Glycine
Lysine
Glutamine
180. Hematopoiesis កើតឡើងជាចំបងលើជាលិកាមួយណា?
Lymph nodes
Red marrow
Yellow marrow
Spleen
Thymu
181. មុខងារ Na+ /K+ pump តាមរយៈការសំរួលភាពបន្សាយ ព្រោះវាត្រូវការ ATP
ហេតុផលនិងប្រយោគទាំងពីរគឺត្រឹមត្រូវនិងស៊ីចង្វាក់ទាក់ទងគ្នា
ហេតុផលនិងប្រយោគទាំងពីរគឺត្រឹមត្រូវតែមិនស៊ីចង្វាក់ទាក់ទងគ្នា
ប្រយោគត្រឹមត្រូវតែហេតុផលមិនត្រឹមត្រូវ
ប្រយោគមិនត្រឹមត្រូវតែហេតុផលត្រឹមត្រូវ
ប្រយោគនិងហេតុផលមិនត្រឹមត្រូវ
182. បុគ្គលម្នាក់ដែលបានលេបថ្នាំPrednisoneរយៈពេលច្រើនខែភាគច្រើននឹងកើតមានបញ្ហាណាមួយខាងក្រោម
Addison disease
Cushing disease
Cushing syndrome
Plummer disease
Myxedema
183. តើសសៃវិញ្ញាណណាមួយដេលបញ្ជូន រស់ជាតិទៅខួរក្បាល?
VII
VII &IX
X
ត្រូវទាំងអស់
184. ការសំយោគDNA កើតឡើងនៅក្នុងដំណាក់កាលណានៃកោសិកា
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Interphase
185. រោគលឿង(Jaundice)បង្កលើងដោយកំរិតឈាមកើននៃ
Bilirubin
Bile
Hemoglobin
Cholesterol
Cholecystokinin
186. តើខាងក្រោមណាមួយមានសារៈសំខាន់regulating serum Calcium levels
PTH
Calcitonin
Vitamin D
Hydroxyapatite
មិនត្រឹមត្រូវទាំងអស់
187. ក្នុងខ្លួនមនុស្ស Fatty acids អាចបំលែងទៅជា Glucose ហើយ Glucose អាចបំលែងជា fatty acid
ឃ្លាទាំងពីរត្រឹមត្រូវ
ឃ្លាទាំងពីរមិនត្រឹមត្រូវ
ឃ្លាទី១ត្រូវ ឃ្លាទី២ខុស
ឃ្លាទី១ខុស ឃ្លាទី២ត្រូវ
188. Taste Buds មានឃើញនៅលើ Papillae ខាងក្រោមលើកលែងតែៈ
Fungiform
Filiform
Vallate
Foliate
មិនត្រូវទាំងអស់
189. Reverse transcriptase
Synthesizes a complementary strand of RNA from DNA
Synthesizes a complementary strand of DNA from RNA
Ligates each anticodon to tRNA
Copies cellular RNA
Copies cellularDNA
190. Hematocrit is defined as
The concentration of hemoglobin within erythrocytes
The percentage of erythrocytes in blood plasma volume
The number of erythrocytes in blood volume
The percentage of hemoglobin in blood volume
191. ជម្ងឺខាងក្រោមនេះវាបង្កលើសកំរិត thyroid លើកលែងតែ
Grave disease
Plummer disease
Hashimoto thyroiditis
Cretinism
Toxic multinodular goiter
192. តើមួយណាជាAntibiotic inhibits bacterial protein synthesis
Amoxicillin
Doxycycline
Metronidazole
Cephalexin
Ciprofloxacin
193. Mandible មានតែឆ្អឹង cortical bone ហើយ Maxillaមានតែឆ្អឹង cancellouse bone
ឃ្លាទាំងពីរត្រឹមត្រូវ
ឃ្លាទាំងពីរមិនត្រឹមត្រូវ
ឃ្លាទី១ត្រូវ ឃ្លាទី២ខុស
ឃ្លាទី១ខុស ឃ្លាទី២ត្រូវ
194. តើមួយណាមាននាទីសំខាន់សំរាប់
Alanine
Leucine
Glutamate
Methionine
Valine
195. ឃ្លាទី១ Eeccrine sweat ត្រួតពិនិត្យដោយ cholinergic neurons ឃ្លាទី២ Apocrine sweat glands ផលិតដោយ pheromones
ឃ្លាទាំងពីរត្រឹមត្រូវ
ឃ្លាទាំងពីរមិនត្រឹមត្រូវ
ឃ្លាទី១ត្រូវ ឃ្លាទី២ខុស
ឃ្លាទី១ខុស ឃ្លាទី២ត្រូវ
196. All of the followings would likely result in an individual with severe anemia EXCEPT
Fatigue, Folic acid, Vitamin E
Cyanosis, Biotin
Hypoxia
Increase cardiac output
Pulmonary vasoconstriction
Folic acid
197. ខាងក្រោមនេះជាវីតាមីនរលាយក្នុងទឹក(Water-soluble vitamin)លើកលែងតែៈ
Vitamin B6
Vitamin C
Na+ Channel closure
K+ channel closure
Ca+ channel opening
198. ខាងក្រោមណាមួយជា Transient cessation of breathing
Hypoventilation
Dyspnea
Hypocapnia
Apnea
Hyperapnea
199. Beta-2 adrenergic agonistsបង្កឡើងដោយខាងក្រោមណាមួយ
Vascular smooth muscle vasoconstriction
Bronchodilation
Miosis
Increase heart rate
GI relaxation
200. តើខាងក្រោមណាមួយមាន LOWEST organic composition
Cementum
Dentin
Pulp
Enamel
ត្រឹមត្រូវទាំងអស់
201. តើសារធាតុណាមួយដែលធ្វើឲ្យ pernicious anemia
Cobalt
Iodine
Magnesium
Manganese
Zinc
202. ខាងក្រោមណាមួយជា impair odontogenesis
Cephalexin
Amoxicillin
Doxycycline
Clindamycin
មិនត្រឹមត្រូវទាំងអស់
203. ទាំងអស់ជា smooth muscle cellsលើកលែងតែ
They have only one nucleus
They are typically very long
Their myofibrils are not striated
They have an extensive SR
They do not have T tubules
204. អរម៉ូនដែលប៉ះពាល់លើស្រ្តីបង្កើតដោយក្រពេញណាមួយខាងក្រោមៈ
Adrenal medulla
Anterior pituitary
Posterior pituitary
Anterior pituitary and Posterior pituitary
ត្រឹមត្រូវទាំងអស់
205. ដោយផ្អែកទៅលើមេកានិច Frank – Starling តើចំលើយមួយណាខាងក្រោម ដែលមានសារះ សំខាន់ក្នុងការកត់សំគាល់ ក្នុង Cardiac Output ?
ចំណុចបញ្ចប់ នៃ Diastolic Volume
Stroke Volume
ចង្វាក់បេះដូង
ការប្រើប្រាស់ Oxygen
សំពាធនៃ Systolic intraventricular
206. នៅក្នុងឈាម Carbon dioxide ជា
CO2 ដែលអាចរលាយ
Bicarbonate
Carbaminohemoglobin
CO2 ដែលអាចរលាយ& Bicarbonate
207. តើជាលិកាណាខ្លះខាងក្រោម មាន Post – ganglionic sympathetic neurons ដែលជា Cholinergic ?
Sebaceous glands
Skeletal muscle vasculature
Sweat glands
Skeletal muscle vasculature and Sweat glands
All of the above
208. ខាងក្រោមនេះ ជារចនាសម្ព័ន Anatomic ដែលបញ្ចេញ អ៊រម៉ូនដែលអាចធ្វើអោយកំរិតជាតិស្ករក្នុង ឈាមឡើងខ្ពស់ លើកលែងតែ
Pituitary Gland ផ្នែកខាងមុខ
Adrenal medulla
Adrenal Cortex
Pancreatic Alpha Cell
Pancreatic Delta Cell
209. Sickle cell anemia គឺកើតឡើងដោយ Mutation ប្រភេទអ្វី?
Non sense mutation
Transition mutation
Repeat mutation
Transverse mutation
Missense mutation
210. Hypoglycemia គឺជាលទ្ធផលនៃការបញ្ចេញដោយលើសលប់
Glucose
Insuline
Glucagon
Cyclic-AMP
Epinephrine
211. កំហាប់ Fluoride ក្នុងសារធាតុរាវក្នុងខ្លួនយើង ត្រូវការសំរបសំរួលជាចំបង ដោយសកម្មភាពរបស់អ៊រម៉ូន
Bone resorption និង ការបញ្ចេញរបស់ Kidney tubular
Simple skeletal exchange and resorption of bone
Skeletal uptake and soft tissue deposition
Skeletal uptake and renal excretion
212. តើវីតាមីនខាងក្រោមនេះណាមួយដែលមានភាពទាក់ទងខ្លាំងជាងគេចំពោះការបាត់បង់ឆ្អឹង ក្នុងវ័យចំណាស់?
Vitamin A
Niacin
Thiamine
Vitamin D
Vitamin E
213. ដោយមិនរាប់បញ្ចូលប្រសិទ្ធភាពនៃថ្នាំ Apnea ដែលកើតឡើងបន្ទាប់ពី មាន Hyperventilation លើអ្នកជំងឺ ដែលទទួលថ្នាំស្ពឹកហើយគឺ ជាលទ្ធផលនៃ
ការធ្លាក់ចុះកំរិត Oxygen
ការកើនឡើងលំហូរឈាមក្នុង Cerebral
ការធ្លាក់ចុះ តង់សុងរបស់Carbon dioxide
ការកើនឡើង កំហាប់ អីយុង Hydrogen
ការធ្លាក់ចុះ Oxydation oxygenation of carotid bodies
214. Anemia ជារើយៗមានការទាក់ទងនិងការខ្វះ
Vitamin A and D
Vitamin C and D
Vitamin E and K
Vitamin B12 and folic acid
Thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin
215. ខាងក្រោមនេះគឺជាមុខងារសំខាន់របស់ទឺកមាត់ លើកលែងតែ មួយ គឺ
ផ្តល់សកម្មភាព Buffering
Facilitates deglutition
Initiates protein digestion
ការពារ មិនអោយមាន Demineralization
ធើ្វអោយមានរស់ជាតិ
216. បុរសអាយុ៣០ឆ្នាំម្នាក់ មកកាន់ការិយាល័យរបស់អ្នកដើម្បី ទទួលការព្យាបាលធេ្មញ។ គាត់បាន ត្អូញត្អែរពីការបែកញើសពេលយប់និងអស់កំលាំង ល្ហិនល្ហៃ។ ក្នុងការពិនិត្យ អ្នកបានកត់សំគាល់នូវការ ការឡើង ធំ ច្រើនកន្លែង និងហើម នូវ Node ដោយការប៉ះ នៅតំបន់ Cervical និង Sub mandibular ។ សប្តាហ៍ក្រោយមក Node ទាំងនោះមានការរីកទំហំកាន់តែធំ ដែលធ្វើអោយអ្នកសំរេចចិត្ត បញ្ចូល គាត់ ទទួលការធ្វើ Biosy លើ Node នោះ។ តើជំងឺខាងក្រោមនេះ ណាខ្លះដែលបង្ហាញ ពី Reed – Sternberg cell ក្នុងពេល ធើ្វ Cytological Exam ?
Non – Hodgkin Lymphoma
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Hodgkin lymphoma
Multiple myeloma
217. បុរសអាយុ៣០ឆ្នាំម្នាក់ មកកាន់គ្លីនិកធ្មេញរបស់អ្នកដើម្បី ទទួលការព្យាបាលធេ្មញ។ គាត់បាន ត្អូញត្អែរពីការបែកញើសពេលយប់និងអស់កំលាំង ល្ហិនល្ហៃ។ ក្នុងការពិនិត្យ អ្នកបានកត់សំគាល់នូវការ ការឡើង ធំ ច្រើនកន្លែង និងហើម នូវ Node ដោយការប៉ះ នៅតំបន់ Cervical និង Sub mandibular ។ សប្តាហ៍ក្រោយមក Node ទាំងនោះមានការរីកទំហំកាន់តែធំ ដែលធ្វើអោយអ្នកសំរេចចិត្ត បញ្ចូល គាត់ ទទួលការធ្វើ Biosy លើ Node នោះ។ ប្រយោគខាងក្រោមនេះ គឹមានលក្ខណះត្រឹមត្រូវ នៃ Cell – immediate Immunity លើកលែង តែ
វាជាការឆ្លើយតបរបស់ Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
វាជាការប្រឆាំង នឹង Parasite
វាសំខាន់នៅក្នុង Transplant Recjection
វាជាប់ទាក់ទងនឹង NK Cell និង Macrophage
Hemophilia C
218. បុរសអាយុ១៧ឆ្នាំមា្នក់ មកកាន់ការិយាល័យអ្នក ក្នុងគោលបំណងដកធ្មេញ ថ្គាមធំទី៣ ទាំង៤ ចេញ។ គាត់ មិនបានផ្តល់ពី Medical History និងក្រោយមកអ្នកចាប់ផ្តើម ការពិនិត្យមុនពេលដកធ្មេញ។ នៅពេលកំពុងចាប់ផ្តើម Intra – venous line ដៃរបស់គាត់ទទួលការមុតដោយចៃដន្យ បន្ទាប់មក គាត់ ចាប់ផ្តើមមានការឈាមខ្លាំង។ តើ ជំងឹ Secondary hemostatic ខាងក្រោមនេះមួយណាដែលអាច មាន
Von Willebrand disease
Hemophilia A
Bernard – Soulier syndrome
Thrombocytopenia
Hemophilia C
219. បុរសអាយុ១៧ឆ្នាំមា្នក់ មកកាន់គ្លីនិកធ្មេញ ក្នុងគោលបំណងដកធ្មេញ ថ្គាមធំទី៣ ទាំង៤ ចេញ។ គាត់ មិនបានផ្តល់ពីMedical History និងក្រោយមកអ្នកចាប់ផ្តើម ការពិនិត្យមុនពេលដកធ្មេញ។ នៅពេលកំពុងចាប់ផ្តើម Intra – venous line ដៃរបស់គាត់ទទួលការមុត ដោយចៃដន្យ បន្ទាប់មក គាត់ ចាប់ផ្តើមមានការឈាមខ្លាំង។ ប្រយោគខាងក្រោមទាំងនេះមានភាពត្រឹមត្រូវ ក្នុងការបរិយាយពី ជំងឺ Von Willebrand លើកលែងតែ
វាជាការប៉ះពាល់ ដល់ចំនួន Platelet ( Qualitative Platelet defect)
vWF ផ្តល់អោយមានការស្អិតជាប់ នៃ Platelets នឹង Collagen
វាប៉ះពាល់ដល់ Pletelet plug និង Coagu-lation cascade.
vWF functions independent of factor VIII
វាជា ជំងឺAutosomal dominant disorder
220. "បុរសអាយុ១៧ឆ្នាំមា្នក់ មកកាន់គ្លីនិកធ្មេញអ្នក ក្នុងគោលបំណងដកធ្មេញ ថ្គាមធំទី៣ ទាំង៤ ចេញ។ គាត់ មិនបានផ្តល់ពីMedical History និងក្រោយមកអ្នកចាប់ផ្តើម ការពិនិត្យមុនពេលដកធ្មេញ។ នៅពេលកំពុងចាប់ផ្តើម Intra – venous line ដៃរបស់គាត់ទទួលការ មុតដោយចៃដន្យ បន្ទាប់មក គាត់ ចាប់ផ្តើមមានការឈាមខ្លាំង។ តើប្រយោគ ខាងក្រោមណាមួយមានលក្ខណះត្រឹមត្រូវ ដែលទាក់ទងនឹង ការខ្វះ Vitamin K ?"
បង្កើនសកម្មភាព នៃ Clotting factors II VII IX X
ថយចុះ PT
មិនមានការផ្លាស់ប្តូរ PTT
បង្កឡើងដោយ ការបាត់បងសកម្មភាពក្នុងការស្រូបយកខ្លាញ
ចំនួន Platelet មិនធម្មតា
221. បុរសអាយុ១៧ឆ្នាំមា្នក់ មកកាន់គ្លីនិកធ្មេញអ្នក ក្នុងគោលបំណងដកធ្មេញ ថ្គាមធំទី៣ ទាំង៤ ចេញ។ គាត់ មិនបានផ្តល់ពីMedical History និងក្រោយមកអ្នកចាប់ផ្តើម ការពិនិត្យមុនពេលដកធ្មេញ។ នៅពេលកំពុងចាប់ផ្តើម Intra – venous line ដៃរបស់គាត់ទទួលការមុតដោយចៃដន្យ បន្ទាប់មក គាត់ ចាប់ផ្តើមមានការឈាមខ្លាំង។ ប្រយោគខាងក្រោមនេះពិតជាមានលក្ខណះត្រឹមត្រូវ ចំពោះការជាសះស្បើយនៃមុខ របួសលើកលែងតែ
secondary intention wound healing occurs when a sizeable gap exists between margins.
a large extraction socket heals by primary intention.
the inflammatory stage occurs immedi- ately after tissue injury.
contact inhibition occurs when migrating epithelial wound margins meet.
healing by primary intention occurs at a faster rate than secondary intention.
222. បុរសអាយុ១៧ឆ្នាំមា្នក់ មកកាន់គ្លីនិកធ្មេញអ្នក ក្នុងគោលបំណងដកធ្មេញ ថ្គាមធំទី៣ ទាំង៤ ចេញ។ គាត់ មិនបានផ្តល់ពីMedical History និងក្រោយមកអ្នកចាប់ផ្តើម ការពិនិត្យមុនពេលដកធ្មេញ។ នៅពេលកំពុងចាប់ផ្តើម Intra – venous line ដៃរបស់គាត់ទទួលការមុតដោយចៃដន្យ បន្ទាប់មក គាត់ ចាប់ផ្តើមមានការឈាមខ្លាំង។ ខាងក្រោមនេះជា Topical antibiotic លើកលែងតែ
Neomycin
Bacitracin
Polymyxin B
Ofloxacin
all of the above are topical antibiotics
223. តើបាក់តេរីខាងក្រោមណាមួយជា Gram positive Cooci ដែលតែងតែបង្ករោគលើ ស្បែកនិង បង្កជាបូស?
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus bovis
Streptococcus viridians
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Actinomyces israelii
224. ស្ត្រីអាយុ ៥៥ឆ្នាំម្នាក់មកកាន់គ្លីនិកធ្មេញរបស់អ្នក ដើម្បីព្យាបាល Burning mouth ស្ងួតភ្នែក និងមានរមាស់លើមុខរបស់គាត់ ។អ្នកបានពិនិត្យក្នុងមាត់ឃើញមាន Multiple carious lesions និង ការខ្វះទឹកមាត់។ បន្ទាប់មក អ្នកក៏សំរេចចិត្ត យកឈាម របស់គាត់ទៅមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍ដើម្បី ធ្វើ Immunologic marker ជាមុន មុននឹងចាប់ផ្តើមការព្យាបាល។ ឧទាហរណ៍ថាលទ្ធផលនៃការពិសោធន៍បង្ហាញពីantinuclear antibodies ។ តើជំងឺខាងក្រោមណាមួយ ដែលមានរោគសញ្ញានេះ?
Reiter syndrome
Behcet syndrome
Scleroderma
Ankylosing spondylitis
SjÖgren syndrome
225. ស្ត្រីអាយុ ៥៥ឆ្នាំម្នាក់មកកាន់គ្លីនិកធ្មេញរបស់អ្នក ដើម្បីព្យាបាល Burning mouth ស្ងួតភ្នែក និងមានរមាស់លើមុខរបស់គាត់ ។អ្នកបានពិនិត្យក្នុងមាត់ឃើញមាន Multiple carious lesions និង ការខ្វះទឹកមាត់។ បន្ទាប់មក អ្នកក៏សំរេចចិត្ត យកឈាម របស់គាត់ទៅមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍ដើម្បី ធ្វើ Immunologic marker ជាមុន មុននឹងចាប់ផ្តើមការព្យាបាល។ តើប្រយោគខាងក្រោមនេះមួយណាដែល មិនត្រឹមត្រូវ យោងទៅតាម Stephan curve?
Nonfermentable carbohydrates បង្កអោយ ការធ្លាក់ចុះ យ៉ាងឆាប់រហ័ស នៃ pH របស់ទឺកមាត់
វាត្រូវការ៤០នាទី ក្នុងការត្រលប់មកកាន់ pH ធម្មតាវិញបន្ទាប់ ញុំាស្ករហើយ"
Sucrose មានការប៉ះពាល់ខ្លាំង ដល់ pH របស់ទឹកមាត់
pH ធម្មតារបស់ ទឹកមាត់ គឺប្រហែល 7.0
Enamel អាច Demineralize នៅ pH 5.5
226. ស្ត្រីអាយុ ៥៥ឆ្នាំម្នាក់មកកាន់គ្លីនិកធ្មេញរបស់អ្នក ដើម្បីព្យាបាល Burning mouth ស្ងួតភ្នែក និងមានរមាស់លើមុខរបស់គាត់ ។អ្នកបានពិនិត្យក្នុងមាត់ឃើញមាន Multiple carious lesions និង ការខ្វះទឹកមាត់។ បន្ទាប់មក អ្នកក៏សំរេចចិត្ត យកឈាម របស់គាត់ទៅមន្ទីរពិសោធន៍ដើម្បី ធ្វើ Immunologic marker ជាមុន មុននឹងចាប់ផ្តើមការព្យាបាល។ តើភ្នាក់ងារកាត់បន្ថយ Plaque ខាងក្រោមនេះណាមួយ មានជាតិ អាល់កុល ច្រើនជាងគេ?
Total ( Sodium fluoride triclosan)
Gel-Kem ( Stannous fluoride)
Listerine (phenolic/ essential oil compound)
Peridex (Chlorhexidine gluconate)
Scope (cetylpyridinium chloride)
227. The benign neoplasm that originates from squamous epithelium is called a/an?
adenoma
choriocarcinoma
chondroma
lipoma
papilloma
228. In the presence of an acute bacterial infection, laboratory tests will show an increase in?
polymorphonuclear leukocytes
plasma cells
lymphocytes
monocytes
eosinophils
229. Mucoceles are most commonly found in the?
upper lip
lower lip
tongue
buccal mucosa
soft palate
230. The radicular or root-end cyst occurs as a result of?
trauma
pulpal necrosis
hyperparathyroidism
poorly calcified bone
231. Excessive formation of scar tissue beyond the wound margin is called?
a fibroma
a keloid
a fibro-epithelial polyp
epithelial hyperplasia
232. The term "carcinoma in situ" implies that the lesion shows?
metaplasia
early invasion of malignant cells through the basement membrane
dysplasia of cells confined within the epithelium
distant metastasis of a malignant tumor
233. Which of the following is NEVER associated with an impacted tooth?
Adeno-ameloblastoma
Odontogenic myxoma
Pindborg's tumor
Primordial cyst
Ameloblastoma
234. Which one of the following would be of greatest value in determining the etiology of an oral ulceration?
History of the oral lesion
Cytological smear
Systemic evaluation
Laboratory tests
235. A 20-year old male presents with a three-day history of an acute generalized gingivitis He has malaise, fever and bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy A blood examination reveals
Hb: 89g100ml
Platelets: 82,000mm3
Red blood cell count: 3,900,000mm3
White blood cell count: 870,000mm3
Normal Values:
Hb: 14-18g100ml
Platelets: 150,000-400,000mm3 Red blood cell count: 4-5millionmm3
White blood cell count: 5,000-10,000mm3
The most likely diagnosis is?
Hb: 89g100ml
Platelets: 82,000mm3
Red blood cell count: 3,900,000mm3
White blood cell count: 870,000mm3
Normal Values:
Hb: 14-18g100ml
Platelets: 150,000-400,000mm3 Red blood cell count: 4-5millionmm3
White blood cell count: 5,000-10,000mm3
The most likely diagnosis is?
Thrombocytopenic purpura
Acute myelogenous leukemia
Infectious mononucleosis
Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
236. Hyperplastic lingual tonsils may resemble which of the following?
Epulis fissuratum
Lingual varicosities
Squamous cell carcinoma
Median rhomboid glossitis
Prominent fungiform papillae
237. A possible consequence for patients taking cyclosporine is?
erythematous gingivae
fibrous gingival hyperplasia
loss of soft tissue attachment
epithelial sloughing
238. A well circumscribed 3mm radiolucent lesion is present in the apical region of the mandibular second premolar The tooth responds normally to vitality tests The radiolucency is most likely?
a periapical granuloma
a periapical cyst
a chronic periapical abscess
the mental foramen
239. Physiologic (racial) pigmentation differs from melanoma because melanoma?
is macular
contains melanin
affects the gingiva
undergoes clinical changes
240. Which teeth are responsible for tearing food?
Canines
Molars
Central incisors
Premolars
241. When maxillary premolars have two roots where are they placed ?
One mesially and other distally
One buccally and other lingually
Both roots a placed lingually
Both roots a placed buccally
242. The maxillary first premolar has which of the following characteristics for differentiation from other anterior teeth ?
Greater relative faciolingual measurement as compared with the mesiodistal measurement
Broader contact area
Both contact areas are more nearly at the same level
Anterior teeth crown a longure than the maxillary premolar crown
243. When viewed from buccal aspect the form of the maxillary first premolar is ?
Rhomboidal
Trapezoidal
Rectangular
Pentagonal
244. Which statement is correct about permanent maxillary first molar ?
Crown is wider buccolingually than mesiodistally
Crown is wider mesiodistally than buccolingually
Crown is equal buccolingually than mesiodistally
Crown is equal mesiodistally than buccolingually
245. The oblique ridge is found in permanent maxillary first molar that crosses the occlusal surface obliquely. It is formed by the union of ?
Triangular ridge of distobuccal cusp and distal ridge of mesiolingual cusp
Triangular ridge of mesiobuccal cusp and distal ridge of mesiolingual cusp
Triangular ridge of distolingual cusp and distal ridge of mesiolingual cusp
Triangular ridge of distobuccal cusp and mesial ridge of mesiolingual cusp
246. When we observe from buccal aspect, in permanent mandibular first molar, the point of furcation of the two roots is located approximately?
3mm below the cervical line
4mm below the cervical line
5mm below the cervical line
2mm below the cervical line
247. Which of the following roots is the largest permanent maxillary first molar ?
Buccal root
Lingual root
Mesiobuccal root
Distobuccal root
248. When we see from the buccal aspect in the permanent maxillary first molar, the point of furcation of the two buccal roots is located approximately?
2mm below the cervical line
5mm below the cervical line
3mm below the cervical line
4mm below the cervical line
249. Crown shape from occlusal aspect of permanent mandibular first molar is?
Trapezoid
Rhomboid
Parallelogram
Pentagonal
250. Crown shape from buccal aspect of permanent mandibular first molar is?
Parallelogram
Rhomboid
Trapezoid
Pentagonal
251. Anatomical crown of tooth is?
Portion of tooth wich is covered by enamel
Portion of tooth wich is visible in mouth
Portion crown of tooth wich is visible in mouth
Portion of tooth may or may not correspond to anatomical croun
252. Clinical crown of tooth is ?
Portion crown of tooth wich is visible in mouth
Portion of tooth may or may not correspond to clinical croun
Portion of tooth wich is visible in mouth
Portion of tooth wich is covered by enamel
253. នៅពេលធ្វើ Cervical cross sectionនៅលើ Maxillary central incisor, Pulp cavity មានរាង៖
ពងក្រពើ
មូល
មូលទ្រវែង
ត្រីកោណ
254. The union of the triangular ridge of the distobuccal cusp and the distal ridge of the mesiolingual cusp of maxillary molar forms the:
Marginal ridge
Oblique ridge
Triangular ridge
Transverse ridge
255. The identifying number of permanent mandibular left second molar in the FDI numbering is:
2
17
18
37
256. Universal system នៃMaxillary central incisor គឺ:
11,21
8,9
41, 51
21, 22
257. Lingual fossa of maxillary centralស្ថិតនៅ៖:
ចន្លោះMarginal ridges
ក្រោម Cingulum
លើCingulum
ចន្លោះMarginal ridgesនិងក្រោមCingulum
258. នៅពេលធ្វើ Cervical cross sectionនៅលើ Maxillary central incisor, Pulp cavity មានរាង:
ពងក្រពើ
មូល
មូលទ្រវែង
ត្រីកោណ
259. The identifying number of permanent maxillary right second premolar in the FDI numbering is:
25
14
15
44
260. The identifying number of permanent mandibular left canine in the universal numbering system is:
3
22
33
43
261. Line angle ត្រូវបានបង្កើតឡើងដោយៈ
Surfaces ពីរប្រសព្វគ្នា
Surfaces បីប្រសព្វគ្នា
Surface មួយប្រសព្វគ្នានឹងPoint angle មួយ
Point angle មួយ ប្រសព្វគ្នា Surfaces ពីរ
262. Permanent maxillary incisors ជាទូទៅ:
មានស៊េរីចុះពីធំទៅតូចគឺទី១ធំជាងទី២
មានស៊េរីឡើងពីធំទៅតូចគឺទី១ធំជាងទី២
មានស៊េរីចុះពីតូចទៅធំគឺទី១តូចជាងទី២
មានស៊េរីឡើងពីតូចទៅធំគឺទី១ធំជាងទី២
263. លក្ខណៈបួនដែល Crowns of permanent incisors មានលក្ខណៈខុសប្លែកពី Crowns របស់Permanent teeth ដ៏ទៃទៀតរួមមាន:
Incisal edge, Mamelons,ទីតាំងនិងមុំនៃ Marginal ridges, Lingual fossa និង Cingulum
ទីតាំងនិងមុំនៃ Marginal ridges, Incisal edge, Mamelons, Lingual fossa
Mamelons, Lobes, Lingual fossa, Lingual fossa និង Cingulum
Lingual fossa , Cingulum, Incisal edge, Mamelons
264. Universal numbering system របស់ Permanent maxillary central incisor right គឺ :
11
1
9
8
265. Universal numbering system របស់ Permanent maxillary central incisor leftគឺ :
21
2
9
8
266. Root completion របស់ Permanent maxillary central incisor គឺៈ
4-5 years
10-11 years
2-3 months
3-4 months
267. The permanent mandibular second premolar មានៈ
2 Cusp
3 Cusp
1 or 2 Cusp
2 or 3 Cusp
268. From the occlusal aspect of the permanent mandibular second premolar នៅពេលមានទម្រង់ជាY type cuse ដែលមានបីCusps គឺ:
Buccal cusp > Mesiolingual cusp > Distolingual cusp
Buccal cusp > Distolingual cusp > Mesiolingual cusp
Mesiolingual cusp > Buccal cusp > Distolingual cusp
Distolingual cusp > Mesiolingual cusp > Buccal cusp
269. The most common cusp form of mandibular second premolar is:
Y type
U type
H type
U or H type
270. Eruption របស់ Permanent maxillary first molar គឺៈ
At birth
6-7 years
5 - 6 Years
6 years
271. Root completion របស់ Permanent maxillary first molar គឺៈ
6 Years
5-6 years
10 - 11 Years
9- 10 years
272. បើមើលតាម Buccal surface នៃ Permanent maxillary first molar Crown របស់វាមានរាង
Parallelogram with small uneven side occlusally
Trapezoidal with the small uneven side present cervically
Rectangular with small uneven side occlusally
Trapezoidal with small uneven side cervically
273. Anatomical landmarks នៅលើ Occlual surface crown of Permanent maxillary first molar គេសង្កេតឃើញ:
Elevations, Cusps, Marginal ridge, Tubercle, Oblique ridge
Depression, Developmental grooves, Supplemental groove, Fossa
Cusps, Marginal ridge, Tubercle, Groove
Elevations and depression
274. 3 point from Goal of complete dentistry :
Stable TMJs, Stable occlusion, and Comfort of function
Stable TMJs, No pain, and Comfort of function
Stable TMJs, Stable occlusion, and occlusion class II
Stable occlusion, No pain and Stable TMJs
275. The 5 main mastication muscles are:
Masseter, Mylohyoid, Medial Pterygoid, Lateral Pterygoid, and Digastric
Masseter, temporalis, Medial Pterygoid, Lateral Pterygoid, and Stylohyoid
Masseter, temporalis, Medial Pterygoid, Lateral Pterygoid, and Digastric
Masseter, Mylohyoid, Medial Pterygoid, Lateral Pterygoid, and Stylohyoid
276. The Chewing cycle consists of 3 phase in order:
Opening, closing, and occlusal or intercuspal phase
Occlusal or intercuspal, opening, and close
Opening, occlusal, and intercuspal phase
All are correct
277. What are the three restoring function of a complete denture?
Aesthetic, mastication, sound
Mastication, Phonetic, speech
Sound, speech, aesthetic
Aesthetic, mastication, Phonetic.
278. What is a complete denture?
The replacement of all natural teeth in the mandible
The replacement of all natural teeth in the maxilary
The replacement of some natural teeth in the maxillay and mandible
The replacement of all natural teeth in the arch and their associated parts by artificial substitutes
279. What is phonetic function in complete denture?
One of the most important functions of a complete denture to restore the sound of the patient
One of the most important functions of a complete denture to restore the speech of the patient.
One of the most important functions of a complete denture to restore the sound of a denture
One of the most important functions of a complete denture to restore the speech of a denture
280. What is denture border?
Denture border is margin of denture base at junction of the polishing surface and occlusal surface
Denture border is margin of denture base at junction of the polishing surface and impression surface.
Denture border is margin of denture base at junction of the impression surface and occlusal surface
Denture border is margin of denture base at junction of the polishing surface, occlusal surface, and polishing surface
281. What are three the type of morphology of denture teeth?
Anatomy teeth, semi-anatomy teeth, resin teeth
Anatomy teeth, semi-anatomy teeth, porcelain teeth
Anatomy teeth, non-anatomy teeth, composite teeth
Anatomy teeth, semi-anatomy teeth, non-anatomy teeth.
282. What are the limiting structures in maxillary in complete denture?
Labial frenum, labial vestibule, buccal frenum, buccal vestibule, hamular notch, and posterior palatal seal area.
Labial frenum, labial vestibule, buccal frenum, buccal vestibule, Lingual frenum, and posterior palatal seal area
Lingual frenum, labial vestibule, buccal frenum, buccal vestibule, hamular notch, and posterior palatal seal area
Labial frenum, labial vestibule, buccal frenum, buccal vestibule, hamular notch, and toris palatin
283. What are the supporting structures?
Hard palate, postero-lateral slopes of the residual alveolar ridge, toris palatin, maxillary ridge, alveolar tubercle, tuberosity
Hard palate, postero-lateral slopes of the residual alveolar ridge, rugae, maxillary tuberosity, alveolar tubercle.
Hard palate, tissue, rugae, maxillary tuberosity, alveolar tubercle.
Hard palate, frenum, postero-lateral slopes of the residual alveolar ridge, rugae, maxillary tuberosity
284. What are the relief areas?
Incisive papilla, cispid eminence, mid-palatine raphe, and fovea palatine.
Incisive canal, canine eminence, mid-palatine raphe, and fovea palatine
Incisive papilla, cispid eminence, tuberosity, and fovea palatine
Incisive papilla, cispid eminence, toris palatine, and fovea palatine
285. Where is vibration line?
Located between the movable and immovable tissues of the soft palate
Located in front of the movable tissues of the soft palate
Located behind the movable tissues of the soft palate
Located in front the immovable tissues of the soft palate
286. A bulbus extension of the residual ridge in the second and third molar region. What is it called?
Rugae
Incisive Papilla
Fovea Palatina
Maxillary Tuberosity
{"name":"7Year\/Biomedecal Sciences\/Final exam", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1. The smallest bone of the skull is:, 2. How many foramens are in the mandible:","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/92-4488133/greater-palatine-foramen.jpg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Quiz about me
100
Do you have any recommendations in new papers today?
100
Test Your Knowledge: Soil and Science
5226
Dusty
2211125
Free Research Methods Knowledge Assessment
201030714
Marriage Between Different Social Groups: Sociology
201068313
Amplification II
15822366
Sterile Processing: Test Your CSSD Skills Free
201054521
Spiderman: How Well Do You Know Spider-Man Trivia?
201053208
Free Mental Health Trivia
201031083
Do I Have Leukemia? Challenge Your Knowledge
201025497
External Anatomy of the Spinal Cord: Test Your Knowledge
201097203