Q1
1) A 48-year-old woman develops constipation postoperatively and self-medicates with milk of magnesia. She presents to clinic, at which time her serum electrolytes are checked, and she is noted to have an elevated serum magnesium level. Which of the following represents the earliest clinical indication of hypermagnesemia?
. Loss of deep tendon reflexes
. Flaccid paralysis
. Respiratory arrest
. Hypotension
. Stupor
2) A football player is tackled, and he develops severe knee swelling and pain. On physical examination with the knee flexed at 90 degrees, the leg can be pulled anteriorly, like a drawer being opened. A similar finding can be elicited with the knee flexed at 20 degrees by grasping the thigh with one hand, and pulling the leg with the other. Which of the following is the most likely injured structure?
. Anterior cruciate ligament
. Lateral collateral ligament
. Medial collateral ligament
. Medial meniscus
. Posterior cruciate ligament
3) A 45-year-old woman with Crohn disease and a small intestinal fistula develops tetany during the second week of parenteral nutrition. The laboratory findings include: Na: 135 mEq/LK: 3.2 mEq/LCl: 103 mEq/LHCO3: 25 mEq/LCa: 8.2 mEq/LMg: 1.2 mEq/LPO4: 2.4 mEq/LAlbumin: 2.4An arterial blood gas sample reveals a pH of 7.42, PCO2 of 38 mm Hg, and PO2 of 84 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s tetany?
. Hyperventilation
. Hypocalcemia
. Hypomagnesemia
. Essential fatty acid deficiency
. Focal seizure
4) A 42-year-old, right-handed man has had a history of progressive speech difficulties and right hemiparesis for 5 months. He has had progressively severe headaches for the past 2 months, which are worse in the mornings. At the time of admission, he is confused and vomiting, and has blurred vision, papilledema, and diplopia. Shortly thereafter, his blood pressure increases to 190/110 mm Hg, and he develops bradycardia. Which of the following is most likely the significance of the hypertension and the bradycardia?
. The brain tumor has produced tentorial herniation
. The brain tumor is pressing on the hypothalamus
. The chronic subdural hematoma has ruptured
. The genesis of his symptoms is aortic dissection
. There is a near-terminal increase in intracranial pressure
5) A 19-year-old man sustains multiple injuries in a high-speed automobile collision. There is a pneumothorax on the left, for which he has a chest tube placed. Over the next several days, a large amount of air drains continuously through the tube (a large "air leak"), and daily chest x-rays show that his collapsed left lung is not expanding. The patient is not on a respirator. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
. Air embolism
. Injury to the lung parenchyma
. Injury to a major bronchus
. Insufficient suction being applied to the chest tube
. Tension pneumothorax
6) A 23-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room from a halfway house, where she apparently swallowed a handful of pills. The patient complains of shortness of breath and tinnitus, but refuses to identify the pills she ingested. Pertinent laboratory values are as follows:Arterial blood gases: pH 7.45, PCO2 12 mm Hg, PO2 126 mm Hg.Serum electrolytes (mEq/L): Na+ 138, K+ 4.8, Cl− 102, HCO3− 8.An overdose of which of the following drugs would be most likely to cause the acid–base disturbance in this patient?
. Phenformin
. Aspirin
. Barbiturates
. Methanol
. Diazepam (Valium)
7) A middle-aged man with symptomatic carotid stenosis underwent a carotid endarterectomy on the right side. The area of significant stenosis extended from die carotid bifurcation up into the internal carotid, requiring a very high dissection and clamping of the vessel. The endarterectomy was done with an in situ shunt and closed with a Dacron patch. In the postoperative period, the patient has persistent difficulty swallowing solids and even more difficulty swallowing liquids. Any attempt to do so results in violent coughing and aspiration. His lips look symmetric and move normally, he speaks in a normal tone of voice without tiring, and he has no trouble breathing. When he is asked to stick his tongue out, he does so without deviation to either side. His symptoms are due to intraoperative damage of which of the following nerves?
Main trunk of the tenth (vagus) nerve
Mandibular branch of the seventh (facial) nerve
Sensory fibers of the ninth (glossopharyngeal) nerve
Superior laryngeal branch of the tenth (vagus) nerve
Trunk of the twelfth (hypoglossal) nerve
8) A 52-year-old man has been impotent ever since he had an abdominoperineal resection for cancer of the rectum. The tumor was staged as T3, NO, MO. He gets no nocturnal erections, and his impotence extends to all situations, regardless of sexual partner, and includes inability to masturbate. His erectile dysfunction is most likely due to which of the following?
Arterial vascular insufficiency
Erectile nerve damage
Psychogenic factors
Tumor invasion of the urethra
Venous incompetence
9) A 60-year-old diabetic man undergoes incision and drainage of an infected boil on his back. The wound is left open and packed daily. Week by week, the wound grows smaller and eventually heals. Which of the following terms describes the method of wound closure by the patient?
. Primary intention
. Secondary intention
. Tertiary intention
. Delayed primary closure
. Delayed secondary closure
10) A 55-year-old-woman of Asian descent goes to the emergency department because of vomiting and severe abdominal cramping of 3 days' duration. Her pain is centered on the umbilicus. She denies being exposed to a viral or bacterial illness. Her medical history includes a previous cholecystectomy and an appendectomy after which she developed an infection. Her abdomen is not tender, but hyperactive, high-pitched peristalsis with rushes coincides with palpable bowel cramping. Abdominal x-ray films taken in the supine and upright positions demonstrate a ladder-like series of distended small bowel loops. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
Adhesions
Ascaris infection
Cancer
Intussusception
Volvulus
11) A patient with a solid malignancy discusses chemotherapy with his oncologist. He is interested in the risks of the treatment. What is the primary toxicity of doxorubicin (Adriamycin)?
. Cardiomyopathy
. Pulmonary fibrosis
. Peripheral neuropathy
. Uric acid nephropathy
. Hepatic dysfunction
12) A 56-year-old woman is undergoing chemotherapy. She presents today with complaints of burning on urination and bloody urine. Which of the following agents causes hemorrhagic cystitis?
. Bleomycin
. 5-fluorouracil
. Cisplatin
. Vincristine
. Cyclophosphamide
13) A 65-year-old man undergoes a technically difficult abdominal–perineal resection for a rectal cancer during which he receives 3 units of packed red blood cells. Four hours later, in the intensive care unit (ICU), he is bleeding heavily from his perineal wound. Emergency coagulation studies reveal normal prothrombin, partial thromboplastin, and bleeding times. The fibrin degradation products are not elevated, but the serum fibrinogen content is depressed and the platelet count is 70,000/μL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his bleeding?
Delayed blood transfusion reaction
Autoimmune fibrinolysis
. A bleeding blood vessel in the surgical field
. Factor VIII deficiency
. Hypothermic coagulopathy
14) A 78-year-old man with a history of coronary artery disease and an asymptomatic reducible inguinal hernia requests an elective hernia repair. Which of the following would be a valid reason for delaying the proposed surgery?
. Coronary artery bypass surgery 3 months earlier
. A history of cigarette smoking
. Jugular venous distension
. Hypertension
. Hyperlipidemia
15) A 53-year-old woman has been intubated for several days after sustaining a right pulmonary contusion after a motor vehicle collision as well as multiple rib fractures. Which of the following is a reasonable indication to attempt extubation?
. Negative inspiratory force (NIF) of –15 cm H2O
. PO2 of 60 mm Hg while breathing 30% inspired FiO2 with a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of 10 cm H2O
. Spontaneous respiratory rate of 35 breaths per minute
. A rapid shallow breathing index of 80
. Minute ventilation of 18 L/min
16) A 74-year-old woman with a history of a previous total abdominal hysterectomy presents with abdominal pain and distention for 3 days. She is noted on plain films to have dilated small-bowel and air-fluid levels. She is taken to the operating room for a small-bowel obstruction. Which of the following inhalational anesthetics should be avoided because of accumulation in air-filled cavities during general anesthesia?
. Diethyl ether
. Nitrous oxide
. Halothane
. Methoxyflurane
. Trichloroethylene
17) A 65-year-old man has an enterocutaneous fistula originating in the jejunum secondary to inflammatory bowel disease. Which of the following would be the most appropriate fluid for replacement of his enteric losses?
. D5W
. 3% normal saline
. Ringer lactate solution
. 0.9% sodium chloride
. 6% sodium bicarbonate solution
18) A 45-year-old woman is seen with wasting of the intrinsic muscles of the hand, weakness, and pain in the wrist. Which of the following nerves has most likely been injured?
. Ulnar nerve
. Radial nerve
. Brachial nerve
. Axillary nerve
. Median nerve
19) A 68-year-old woman presents with a pigmented lesion on the trunk. Upon further examination the lesion has an irregular border, darkening coloration, and raised surface. An incisional biopsy is performed and confirms a melanoma with a thickness of 0.5 mm. The patient is scheduled for a wide local excision of the melanoma in the operating room. Which of the following is the smallest margi recommended for excision?
. 3 mm
. 5 mm
. 1 cm
. 2 cm
. 5 cm
20) A 25-year-old woman presents with a benign nevus on the right upper arm. She desires removal and undergoes a clean incision and then closure of the incision without complication. With regard to the healing process, which of the following cell types are the first infiltrating cells to enter the wound site, peaking at 24 to 48 hours?
. Macrophages
. Neutrophils
. Fibroblasts
. Lymphocytes
. Monocytes
21) A 35-year-old woman undergoes an elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy for symptomatic cholelithiasis. Which of the following wound classes best describes her procedure?
. Class I, Clean
. Class II, Clean/contaminated
. Class III, Contaminated
. Class IV, Dirty
. None of the above
22) A 65-year-old woman presents with a 1-cm lesion with a pearly border on her nose, and punch biopsy is consistent with a basal cell carcinoma. She is scheduled to undergo Mohs surgery. Which of the following is a benefit of Mohs surgery over wide local excision?
. Mohs surgery results in a smaller cosmetic defect while obtaining negative margins circumferentially.
. Mohs surgery offers a shorter operating time.
. Mohs surgery can be performed on many different types of skin cancers.
. Mohs surgery results in less recurrence and metastases.
. Mohs surgery does not depend on intraoperative evaluation of specimen margins with frozen sections.
23) A 55-year-old man presents with worsening cirrhosis. After evaluation by a hepatologist, he presents for evaluation for hepatic transplantation. He is informed that prioritization for transplantation is based on the Model of End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score, and that patients with higher MELD scores have a greater benefit from transplantation. Which of the following contributes to the MELD score?
. Platelet count
. Total bilirubin
. Albumin
. Encephalopathy
Ascites
24) A young woman who has received a transplant has posttransplant fever and malaise. Graft-versus- host disease (GVHD) is diagnosed. This has occurred most commonly with the transplantation of which of the following?
. Kidney
. Lung
. Heart
. Bone marrow
. Pancreas
25) A 55-year-old woman who has end-stage liver disease is referred to a hepatologist for evaluation. Which of the following would prevent her from being a transplantation candidate?
. Use of alcohol 3 months ago
. Two 2-cm hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) in the right lobe of the liver
. A 4-cm hepatocellular carcinoma in the right lobe of the liver
. Development of hepatorenal syndrome requiring hemodialysis
. History of breast cancer 5 years ago with no evidence of disease currently
26) A 63-year-old man with a 40-pack per year smoking history undergoes a low anterior resection for rectal cancer and on postoperative day 5 develops a fever, new infiltrate on chest x-ray, and leukocytosis. He is transferred to the ICU for treatment of his pneumonia because of clinical deterioration. Which of the following is a sign of early sepsis?
. Respiratory acidosis
. Decreased cardiac output
. Hypoglycemia
. Increased arteriovenous oxygen difference
. Peripheral vasodilation
27) A 43-year-old trauma patient develops acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and has difficulty oxygenating despite increased concentrations of inspired O2. After the positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) is increased, the patient’s oxygenation improves. What is the mechanism by which this occurs?
. Decreasing dead-space ventilation
. Decreasing the minute ventilation requirement
. Increasing tidal volume
. Increasing functional residual capacity
. Redistribution of lung water from the interstitial to the alveolar space
28) An 80-year-old man comes to the physician because of a slowly growing ulcerated mass on the glans penis. A biopsy is positive for squamous cell carcinoma. Which of the following conditions is usually present in association with this tumor?
Balanitis xerotica obliterans
Condyloma acuminatum due to human papillomavirus (HPV) type 6
Lack of circumcision
Peyronie disease
Syphilis
29) A 33-year-old woman seeks assistance because of a swelling of her right parotid gland. Biopsy is performed and reveals acinar carcinoma. You consent the patient for resection and inform her that at the very least, she will require superficial parotidectomy. Which of the following intraoperative findings would require sacrifice of the facial nerve?
. Invasion of the deep lobe of the parotid
. Invasion of the lateral lobe of the parotid.
. Proximity of the carcinoma to the facial nerve.
. Encasement of the facial nerve by carcinoma.
. The facial nerve should always be preserved regardless of intraoperative findings.
30) A college student is tackled while playing football and develops severe knee pain. When examined shortly thereafter, the knee is swollen and the patient has pain on direct palpation over the lateral aspect of the knee. With the knee flexed 30 degrees, passive adduction elicits pain on the same area, and the leg can be adducted further than in the normal contralateral leg (varus stress test). The anterior drawer test, posterior drawer test, and Lachman test are negative. Which of the following is the most likely site of injury?
Anterior cruciate ligament
Lateral collateral ligament
Lateral meniscus
Medial collateral ligament
Posterior cruciate ligament
31) A 39-year-old woman presents with generalized malaise and lymphadenopathy. Biopsy of a supraclavicular lymph node reveals non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Fortyeight hours after initiation of chemotherapy, she develops a high-grade fever and her laboratory studies demonstrate hyperkalemia, hyperphosphatemia, and hypocalcemia. Which of the following cells mediate this syndrome?
. Macrophages
. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
. Natural killer cells
. Polymorphonuclear leukocytes
. Helper T lymphocytes
32) A 33-year-old diabetic man receives a renal allograft. The physicians choose cyclosporine as one of the antirejection medications. Which of the following functions does cyclosporine A primarily inhibit?
. Macrophage function
. Antibody production
. Interleukin 1 production
. Interleukin 2 production
. Cytotoxic T-cell effectiveness
33) A 57-year-old man has end-stage heart failure due to atherosclerosis. His cardiologist refers him for evaluation for heart transplantation. Which of the following is an absolute contraindication for heart transplantation?
. Cirrhosis
. Age over 65
. Diabetes without end-organ damage
. Reversible high pulmonary vascular resistance
. History of colon cancer resected 5 years ago with no evidence of recurrence
34) A 55-year-old woman has been hospitalized because of recurrent pancreatitis, ARDS, prolonged ileus, and need for parenteral nutrition. She demonstrates weakness, lassitude, orthostatic hypotension, nausea, and fever. Which of the following abnormalities is most likely to explain these symptoms?
. Hypothermia
. Hypokalemia
. Hyperglycemia
. Hyponatremia
. Hypervolemia
35) A 25-year-old man presents to the same day surgical center for repair of an old injury to his lateral collateral ligament. The anesthesiologist wants to perform an axillary block for local pain control. If the posterior wall of the axillary artery is pierced during placement of the block, which of the following nerves will most likely be affected?
Axillary
Median
Musculocutaneus
Radial
Ulnar
36) A 72-year-old woman who is planning to undergo ventral hernia repair is on warfarin for atrial fibrillation. She is advised to cease her warfarin several days before her surgery and is hospitalized preoperatively for heparinization. During her hospital stay, she complains of severe abdominal and flank pain. Her prothrombin time (PT) is normal, but her activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) is elevated. An abdominal CT scan demonstrates a large retroperitoneal hematoma. Which of the following should be administered to reverse the effects of the heparin?
. Thrombin
. Vitamin K
. Protamine sulphate
. Aprotinin
. Platelet transfusion
37) A 24-year-old man whose father was just diagnosed with colon cancer presents to his family physician to discuss screening colonoscopy. His physician suspects that he has hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC) or Lynch syndrome and recommends screening colonoscopy beginning at age 25. Which of the following is most supportive of a clinical diagnosis of HNPCC?
. A father with colon cancer at 52 years of age
. A father and an uncle (same side of the family) with colon cancer
. A father and grandfather (same side of the family) with colon cancer
. A father and 2 uncles (same side of the family) with colon cancer
. A father, uncle, and grandfather (same side of the family) with colon cancer at 50 years of age
38) A patient requires both cardiac and renal transplantation. Preparation for the procedures has begun. How do cardiac allografts differ from renal allografts?
. Cardiac allografts are matched by HLA tissue typing and renal allografts are not.
. Cardiac allografts can tolerate a longer period of cold ischemia than renal allografts.
. One-year graft survival for cardiac allografts is substantially lower than that for renal allografts.
. Cardiac allografts are matched only by size and ABO blood type.
. Cyclosporine is a critical component of the immunosuppressive regimen for cardiac allografts but not renal allografts.
39) A patient with colon cancer has a mass in the upper lobe of his left lung 2.5 years following resection of his colon cancer and subsequent 12 months of chemotherapy. His CEA level is rising. Which of the following predicts a 5-year survival rate of greater than 20% following resection of pulmonary metastases?
. Other organ metastases are present.
. Lung lesions are solitary.
. Local tumor recurrence is found.
. The tumor doubling time is less than 20 days.
. The patient has received prior chemotherapy.
40) A 60-year-old man presents with a 6-mm basal cell carcinoma on the tip of his nose. He is scheduled to undergo excision of the tumor in the operating room with repair of the defect using skin and subcutaneous tissue from his earlobe. Which of the following terms most appropriately describes this form of reconstructive surgery?
. Split-thickness graft
. Full-thickness graft
. Composite graft
. Pedicle flap
. Free flap
41) A 45-year-old woman with breast cancer undergoes a modified radical mastectomy with lymph node dissection. Six weeks later, she returns complaining of decreased mobility of her shoulder. On physical examination, the scapula protrudes from the body when pressing her outstretched arm on the wall. Which of the following nerves was most likely injured during the operation?
Intercostal
Lateral pectoral
Long thoracic
Medial pectoral
Thoracodorsal
42) A 19-year-old college student presents with a testicular mass, and after treatment he returns for regular follow-up visits. Which of the following is the most useful serum marker for detecting recurrent disease after treatment of nonseminomatous testicular cancer?
. Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
. Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA)
. CA125
. p53 oncogene
43) A 72-year-old man undergoes resection of an abdominal aneurysm. He arrives in the ICU with a core temperature of 33°C (91.4°F) and shivering. Which of the following is a physiologic consequence of the shivering?
. Rising mixed venous O2 saturation
. Increased production of CO2
. Decreased consumption of O2
. Rising base excess
. Decreased minute ventilation
44) A 43-year-old man with a gangrenous gallbladder and gram-negative sepsis agrees to participate in a research study. An assay of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is performed. Which of the following is the origin of this peptide?
. Fibroblasts
. Damaged vascular endothelial cells
. Monocytes/macrophages
. Activated T lymphocytes
. Activated killer lymphocytes
45) A patient sustained third-degree burns on both his arms when his shirt caught on fire while he was lighting the backyard barbecue. The burned areas are dry, white, leathery, anesthetic, and circumferential all around the arms and forearms. Which of the following parameters should be very closely monitored?
Blood gases
Body weight
Carboxyhemoglobin levels
Myoglobinemia and myoglobinuria
Peripheral pulses and capillary filling
46) A previously healthy 60-year-old man is referred for urologic evaluation of macroscopic hematuria. Urinary cytology is positive for malignant cells, and cystoscopic examination reveals an exophytic multifocal tumor. A biopsy of die tumor demonstrates papillary fronds lined by ccfls similar to transitional epithelium but showing nuclear atypia, mitoses, and necrosis. Which of the following is the most important risk factor in the U.S. For the development of this type of tumor?
Aniline dyes
Smoking
Phenacetin
Radiation
Recurrent cystitis
47) A 54-year-old woman presents to her physician for an opinion regarding additional therapy following curative resection of recently diagnosed colon cancer. She underwent uncomplicated sigmoid resection for invasive colon cancer 4 weeks ago. The pathology revealed carcinoma invading into, but not through, the muscularis propria, with one of eight positive mesenteric nodes. There was no evidence of liver metastases at the time of operation. Preoperative chest x-ray and CT scan of the abdomen showed no evidence of distant disease. Preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) level was normal. Past history is positive for diabetes and mild hypertension. Examination is unremarkable except for a healing abdominal incision. Which of the following is the correct stage of this patient’s colon cancer?
. stage 0
. stage I
. stage II
. stage III
. stage IV
48) Which of the following patients with primary hyperparathyroidism should undergo parathyroidectomy?
. A 62-year-old asymptomatic woman
. A 54-year-old woman with fatigue and depression
. A 42-year-old woman with a history of kidney stones
. A 59-year-old woman with mildly elevated 24-hour urinary calcium excretion
. A 60-year-old woman with mildly decreased bone mineral density measured at the hip of less than 2 standard deviations below peak bone density
49) A 49-year-old woman presents to her physician with dysphagia, regurgitation of undigested food eaten hours earlier, and coughing over the last 6 months. She was hospitalized 1 month ago for aspiration pneumonia and successfully treated with antibiotics. Examination reveals a thin-appearing woman with normal vital signs and unremarkable chest, heart, and abdominal examination. A UGI contrast study is performed and reveals a pharyngoesophageal (Zenker’s) diverticulum. Which of the following statements is true regarding Zenker’s diverticula?
. Cervical dysphagia is related to the size of the diverticulum.
. Pharyngoesophageal diverticula are of the pulsion type.
. Pharyngoesophageal diverticula are true diverticula.
. Pharyngoesophageal diverticula are congenital in origin.
. Upper esophageal sphincter function is usually normal.
50) A 36-year-old woman whose mother has just undergone treatment for breast cancer is asking about how this affects her and what can be done to lessen her chances of having the disease. Which of the following has the lowest risk factor for breast cancer?
. Dietary fat intake
. Paternal relative with breast cancer 1 (BRCA1) mutation
. Excessive estrogen exposure—early menarche, late menopause, nulliparity
. Previous biopsy with atypical hyperplasia
. Exposure to ionizing radiation
51) A 39-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a palpable nodule in the neck of 2 years’ duration. Her past history is pertinent for Hashimoto’s disease diagnosed 5 years ago, for which she takes thyroid hormone. She has a history of low-dose chest irradiation for an enlarged thymus gland during infancy. On examination, a 2.5-cm nodule is palpable in the left lobe of the thyroid and is firm and nontender. Which of the following portions of her history increases the risk for thyroid cancer?
. Age group of 20–40 years
. Female gender
. low-dose irradiation during infancy
. Chronicity of the nodule
. Past history of Hashimoto’s disease
52) While playing with his children, a 44-year-old man falls and lands on his right shoulder. There is immediate pain and deformity. In an uncomplicated dislocation of the glenohumeral joint, the humeral head usually dislocates primarily in which of the following directions?
. Anteriorly
. Superiorly
. Posteriorly
. Laterally
. Medially
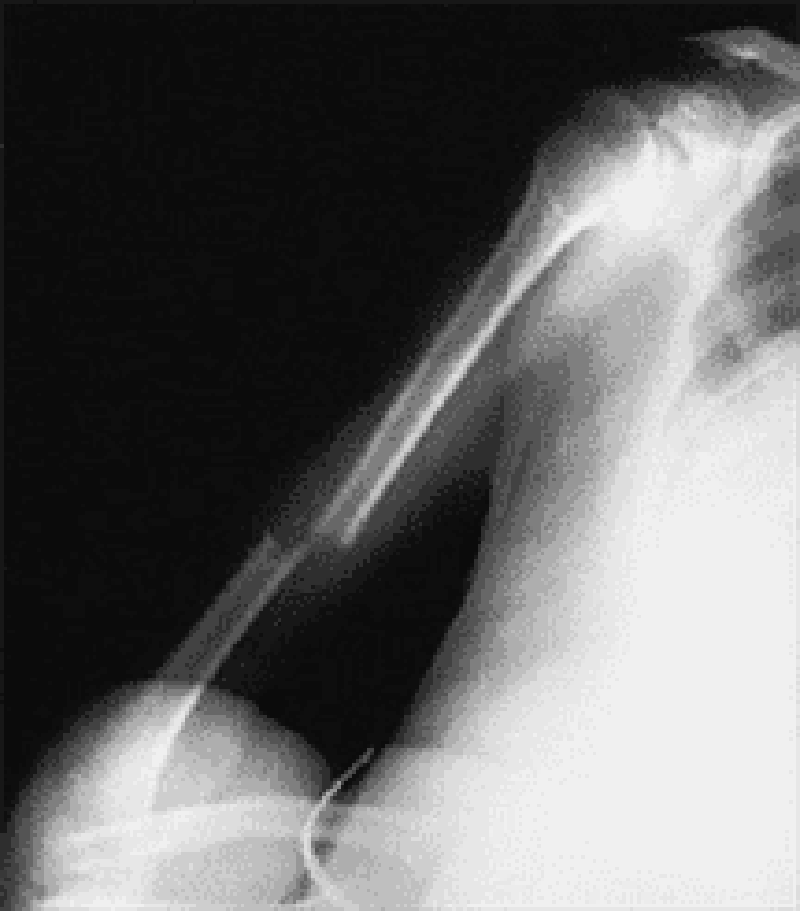
53) A 29-year-old construction worker fell 15 ft from a roof and broke his right humerus, as depicted in the accompanying radiograph. Given his injury, which of the following nerves is most at risk?
. Median nerve
. Radial nerve
. Posterior interosseous nerve
. Ulnar nerve
. Ascending circumflex brachial nerve
54) In a failed suicide gesture, a depressed student severs her radial nerve at the wrist. Which of the following is her expected disability?
. Loss of ability to extend the wrist
. Loss of ability to flex the wrist
. Wasting of the intrinsic muscles of the hand
. Sensory loss over the thenar pad and the thumb web
. Palmar insensitivity
55) A 52-year-old woman presents with hypertension, obesity, and new skin striae. You are concerned about possible Cushing syndrome. Which of the following is the most common cause of Cushing syndrome?
. Adrenocortical hyperplasia
. Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)–producing pituitary tumor
. Primary adrenal neoplasms
. Ectopic adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)–secreting carcinoid tumor
. Pharmacologic glucocorticoid use
56) A 62-year-old woman presents with invasive ductal carcinoma of the right breast. Which of the following findings would still allow her to receive breast conservation surgery (partial mastectomy)?
. Diffuse suspicious microcalcifications throughout the breast
. Multifocal disease
. Previous treatment of a breast cancer with lumpectomy and radiation
. Large tumor relative to breast size
. Persistently positive margins after multiple reexcisions of the breast cancer
57) A 56-year-old woman presents to the clinic for routine health screening. Her concern is the development of breast cancer. She has no current breast-related complaints. Past history is pertinent for fibrocystic changes with atypical ductal hyperplasia and a single fibroadenoma, both diagnosed by open biopsy 5 years ago. She smokes one pack per day and drinks one can of beer daily. Family history is positive for breast cancer in her mother, diagnosed at the age of 85. Current medications include a cholesterol-lowering agent, an antihypertensive, and HRT, which she has taken for 5 years. Physical examination is unremarkable. Mammograms show dense breasts, decreasing the accuracy of the study, but no suspicious findings were noted. Which of the following is the most common risk factor in evaluating women for breast cancer?
. Fibrocystic changes with atypical ductal hyperplasia
. Alcohol consumption
. Positive family history
. HRT
. age
58) A patient who has had angina as well as claudication reports feeling light-headed on exertion, especially when lifting and working with his arms. The subclavian steal syndrome is associated with which of the following hemodynamic abnormalities?
. Antegrade flow through a vertebral artery
. Venous congestion of the upper extremities
. Occlusion of the carotid artery
. Occlusion of the vertebral artery
. Occlusion of the subclavian artery
59) While working at a bookbinding shop, a young man suffers a traumatic amputation of his index finger. The finger was cleanly severed at its base. The patient and the finger are brought to a first-aid station, from which both are to be transported to a highly specialized medical center for replantation to be done. Which of the following is the correct way to prepare and transport the severed finger?
. Dry the finger of any traces of blood and place it in a cooler filled with crushed ice
. Freeze it as quickly as possible, and transport it immersed in liquid nitrogen
. Immerse it in cold alcohol for the entire trip
. Paint it with antiseptic solution and place it on a bed of dry ice
. Wrap it in a moist gauze, place it on a plastic bag, and place the bag on a bed of ice
60) A 27-year-old basketball player jumps to block a shot with his right hand. As his hand contacts the ball, he feels severe pain in his right shoulder. He presents to the emergency department with continuing shoulder pain. You note that he holds his right arm in slight external rotation, supporting its weight with his left hand. On physical examination, he resists internal rotation of his right arm. Which of the following nerves is most likely to be injured in this patient?
. Radial
. Ulnar
. Musculocutaneous
. Axillary
. Long thoracic
61) A 23-year-old male is found at the scene of a motor vehicle accident with bilateral lower extremity fractures. You also note extensive abdominal bruising and scalp lacerations. At the scene, the patient's blood pressure is 80/60 mmHg and his heart rate is 120/min. He is given 2 liters of IV fluids wide open. On the way to the hospital he becomes progressively drowsy, and he develops progressive weakness on the right side of his body. This patient is also likely to show deficits in the functioning of which of the following nerves?
. Abducens
. Oculomotor
. Glossopharyngeal
. Trigeminal
. Accessory
62) A 34-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motorbike accident. Examination shows a hematoma on the forehead and bleeding from his leg. His pupils are bilateral round and eactive; he has papilledema. He responds to pain, has decorticated posture and speaks incoherently. After the initial resuscitation you start the treatment with intravenous fluids, hyperventilation, head elevation and intravenous mannitol. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of hyperventilation in this patient?
. Hyperventilation acts as stimuli to brain and helps to arouse the patient
. Hyperventilation corrects hypoxia
. Hyperventilation helps to wash out the carbon dioxide
. Hyperventilation causes vasoconstriction and helps to reduce his bleeding
. Hyperventilation causes vasoconstriction and thus decreases the cerebral blood flow
63) A 40-year-old female is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident in which she was the front seat passenger. She reports hitting her head against the windshield and hurting her right leg. She appears completely alert and oriented. Glasgow Coma Scale = 15/ 15. Her pupils are equal and reactive to light. There is a bruise over the right forehead, but no tenderness is present on palpation of the cranial bones. Examination of the right leg reveals a hematoma over the thigh. Knee extension on the right is markedly reduced when compared to the left. Sensory examination reveals decreased sensory perception to both sharp and dull stimuli over the right lower medial leg. All other dermatomes are intact. What nerve injury is most likely present in this patient?
. Femoral nerve
. Tibial nerve
. Obturator nerve
. Common peroneal nerve
. Fibular nerve
64) A 74-year-old woman is admitted with upper gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. She is started on H 2 blockers, but experiences another bleeding episode. Endoscopy documents diffuse gastric ulcerations. Omeprazole is added to the H2 antagonists as a therapeutic approach to the management of acute gastric and duodenal ulcers. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of omeprazole?
. Blockage of the breakdown of mucosa-damaging metabolites of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
. Provision of a direct cytoprotective effect
. Buffering of gastric acids
. Inhibition of parietal cell hydrogen potassium ATPase (adenosine triphosphatase)
. Inhibition of gastrin release and parietal cell acid production
65) A 38-year-old woman who underwent total thyroidectomy for multinodular goiter 6 months ago presents with persistent hoarseness. Which of the following nerves was most likely injured during her operation?
. Superior laryngeal nerve
. Bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerves
. Unilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve
. Hypoglossal nerve
. Marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve
66) A 52-year-old man with a family history of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1) has an elevated gastrin level and is suspected to have a gastrinoma. Which of the following is the most likely location for his tumor?
. Fundus of the stomach
. Antrum of the stomach
. Within the triangle formed by the junction of the second and third portions of the duodenum, the junction of the neck and body of the pancreas, and the junction of the cystic and common bile duct Q
. Tail of the pancreas
. Within the triangle formed by the inferior edge of the liver, the cystic duct, and the common hepatic duct
67) A 73-year-old woman presents to the emergency room complaining of severe epigastric pain radiating to her back, nausea, and vomiting. CT scan of the abdomen demonstrates inflammation and edema of the pancreas. A right upper quadrant ultrasound demonstrates the presence of gallstones in the gallbladder. Which of the following is an important prognostic sign in acute pancreatitis according to Ranson’s criteria?
. Amylase level
. Age
. Total bilirubin level
. Albumin level
. Lipase level
68) A 24-year-old man presents to the emergency room with abdominal pain and fever. CT scan of the abdomen reveals inflammation of the colon. He is referred to a gastroenterologist to be evaluated for inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn disease versus ulcerative colitis). Which of the following indications for surgery is more prevalent in patients with Crohn disease?
. Toxic megacolon
. Massive bleeding
. Fistulas between the colon and segments of intestine, bladder, vagina, urethra, and skin
. Intractable disease
. Dysplasia or carcinoma
69) A newborn has a midline defect in the anterior abdominal wall. The parents ask what, if anything, should be done. Spontaneous closure of which of the following congenital abnormalities of the abdominal wall generally occurs by the age of 4?
. Umbilical hernia
. Patent urachus
. Patent omphalomesenteric duct
. Omphalocele
. Gastroschisis
70) A neonate is found to have an imperforate anus. As the pediatric surgeon you recommend studies to search for other anomalies. Which of the following is an associated abnormality?
. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
. Hydrocephalus
. Duodenal atresia
. Congenital heart disease
. Corneal opacities
71) A 45-year-old man is examined for a yearly executive physical. A mass is palpated in the rectum, and a biopsy suggests carcinoid. Which of the following findings is most likely to be associated with the carcinoid syndrome?
Tumor < 2 cm
. Tumor < 2 cm with ulceration
. Tumor > 2 cm
. Involvement of regional lymph nodes
. Hepatic metastases
72) A 31-year-old biker is involved in a motor vehicle accident after attending a party where he drank a lot of soda drinks. He describes a direct blow to his lower abdomen and pelvis during the accident. He complains of diffuse abdominal pain that refers to his left shoulder. Which of the following injuries most likely accounts for this patient's current symptoms?
. Bladder neck
. Bladder dome
. Anterior bladder wall
. Pseudomembranous urethra
. Anterior urethra
73) Your hospital is conducting an ongoing research study involving the hormonal response to trauma. Blood is drawn regularly (with Institutional Review Board [IRB] approval) for various studies. Which of the following values are likely to be seen after a healthy 36-year-old man is hit by a bus and sustains a ruptured spleen and a lacerated small bowel?
. Increased secretion of insulin
. Increased secretion of thyroxine
. Decreased secretion of vasopressin (antidiuretic hormone [ADH])
. Decreased secretion of glucagon
. Decreased secretion of aldosterone
74) A 45-year-old man was an unhelmeted motorcyclist involved in a high-speed collision. He was ejected from the motorcycle and was noted to be apneic at the scene. After being intubated, he was brought to the ER, where he is noted to have a left dilated pupil that responds only sluggishly. What is the pathophysiology of his dilated pupil?
. Infection within the cavernous sinus
. Herniation of the uncal process of the temporal lobe
. Laceration of the corpus callosum by the falx cerebri
. Occult damage to the superior cervical ganglion
. Cerebellar hypoxia
75) A 25-year-old man comes to the physician because of a mass in his mouth. He has had the lump for many years. He denies weight loss. He was in a motor vehicle accident several years ago and sustained a concussion of the brain. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. Physical examination shows a nontender 2 x 2-cm mass located on the hard palate of the mouth that is immobile and has a bony hard consistency. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's oral finding?
. Congenital
. Infectious
. Neoplastic
. Traumatic
. Vascular
1) A 32-year-old female presents with intermittent blood staining of her bra from her left breast. She has not felt any lumps on either breast. Physical examination shows no breast mass or axillary lymphadenopathy. Ultrasonogram of the breast is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Fibrocystic changes
. Fibroadenoma
. Intraductal papilloma
. Ductal carcinoma in situ
. Hyperprolactinemia
2) A 68-year-old man is brought to the emergency department following a high-speed automobile accident. He is alert and complains of chest pain and mild back pain. His blood pressure is 80/60 mm Hg. Chest x-ray shows a widened mediastinum, tracheal deviation, bronchial displacement, and loss of the aortic knob. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Cardiac tamponade
. Myocardial contusion
. Pulmonary contusion
. Tension pneumothorax
. Traumatic aortic rupture
3) A 35-year-old man comes to the physician because of persistent dull perineal pain and dysuria for 6 months. The patient denies urinary tract infections or urethral discharge. His temperature is 37 C (98.6 F). On digital rectal examination, the prostate is slightly tender and boggy but not enlarged or indurated. Urinalysis is normal. Expressed prostatic secretions show the following: Leukocytes 30 cells/high power field Bacteria None Cultures of prostatic secretion and urine are negative for bacteria. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute cystitis
Acute prostatitis
Chronic bacterial prostatitis
Chronic nonbacterial prostatitis
Prostatodynia
4) A 56-year-old man has been having bloody bowel movements on and off for the past several weeks. He reports that the blood is bright red, it coats the outside of the stools, and he can see it in the toilet bowl even before he wipes himself. When he does so, there is also blood on the toilet paper. After further questioning, it is ascertained that he has been constipated for the past 2 months and that the caliber of the stools has changed. They are now pencil thin, rather the usual diameter of an inch or so that was customary for him. He has no pain. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anal fissure
. Cancer of the cecum
. Cancer of the rectum
. External hemorrhoids
. Internal haemorrhoids
5) A front-seat passenger in a car involved in a head-on collision relates that he hit the dashboard with his knees, however, he is specifically complaining of severe pain in his right hip, rather than knee pain. He lies in the stretcher in the emergency department with the right lower extremity shortened, adducted, and internally rotated. Which of the following is the most likely injury?
. Femoral neck fracture
. Fracture of the shaft of the femur
. Intertrochanteric fracture
. Posterior dislocation of the hip
. Posterior dislocation of the knee
6) An 81-year-old man with Alzheimer disease who lives in a nursing home undergoes surgery for a fractured femoral neck. On the 5th postoperative day, it is noted that his abdomen is grossly distended and tense, but not tender. He has occasional bowel sounds. The rectal vault is empty on digital examination, and there is no evidence of occult blood. X-ray films show a few distended loops of small bowel and a much distended colon. The cecum measures 9 cm in diameter, and the gas pattern of distention extends throughout the entire large bowel, including the sigmoid and rectum. No stool is seen in the films. Other than the abdominal distention, and the ravages of his mental disease, he does not appear to be ill. Vital signs are normal for his age. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Fecal impaction
. Mechanical intestinal obstruction
. Ogilvie syndrome
. Paralytic ileus
. Volvulus of the sigmoid colon
7) A 55-year-old, HIV-positive man has a fungating mass growing out of the anus. He can feel it when he wipes himself after having a bowel movement, but it is not painful. For the past 6 months, he has noticed blood on the toilet paper, and from time to time there has also been blood coating the outside of the stools. He has lost weight, and he looks emaciated and ill. On physical examination, the mass is easily visible. It measures 3.5 cm in diameter, is fixed to surrounding tissues, and appears to grow out of the anal canal. He also has rock-hard, enlarged lymph nodes on both groins, some of them as large as 2 cm in diameter. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Adenocarcinoma of the rectum
. Condyloma acuminata of the anus
. External hemorrhoids
. Rectal prolapse
. Squamous cell carcinoma of the anus
8) A 79-year-old man with atrial fibrillation develops an acute abdomen. When seen 2 days after the onset of the abdominal pain, he has a silent abdomen, with diffuse tenderness and mild rebound. There is a trace of blood on the rectal examination. He also has acidosis and looks quite sick. X-ray films show distended small bowel and distended right colon, up to the middle of the transverse colon. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute pancreatitis
. Mesenteric ischemia
. Midgut volvulus
. Perforated viscus
. Primary peritonitis
9) After a grand mal seizure, a 32-year-old epileptic woman notices pain in her right shoulder, and she cannot move it. She goes to a minor emergency clinic, where she has a limited physical examination and anteroposterior (AP) x-ray films of her shoulder. The films are read as negative, and she is diagnosed as having a sprain and given pain medication. The next day, she still has the same pain and is unable to move her arm. She comes to the emergency department holding her arm close to her body, with her hand resting on her anterior chest wall. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acromioclavicular separation
. Anterior dislocation of the shoulder
. Articular cartilage crushing
. Posterior dislocation of the shoulder
. Torn teres major and minor muscles
10) A 54-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after a head-on automobile accident. On arrival, she is breathing well. She has multiple bruises over the chest and multiple sites of point tenderness over the ribs. X-ray films show multiple rib fractures on both sides, but the lung parenchyma is clear, and both lungs are expanded. Two days later she is in respiratory distress, and her lungs "white out" on repeat chest x-ray films. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Flail chest
Myocardial contusion
Pulmonary contusion
Tension pneumothorax
Traumatic rupture of the aorta
11) A previously healthy 55-year-old man undergoes elective right hemicolectomy for a stage I (T2N0M0) cancer of the cecum. His postoperative ileus is somewhat prolonged, and on the fifth postoperative day his nasogastric tube is still in place. Physical examination reveals diminished skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, and orthostatic hypotension. Pertinent laboratory values are as follows:Arterial blood gases: pH 7.56, PCO2 50 mm Hg, PO2 85 mm Hg.Serum electrolytes (mEq/L): Na+ 132, K+ 3.1, Cl- 80; HCO3- 42.Urine electrolytes (mEq/L): Na+ 2, K+ 5, Cl- 6What is the patient’s acid– base abnormality?
. Uncompensated metabolic alkalosis
. Respiratory acidosis with metabolic compensation
. Combined metabolic and respiratory alkalosis
. Metabolic alkalosis with respiratory compensation
. Mixed respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
12) A 65-year-old man undergoes a low anterior resection for rectal cancer. On the fifth day in hospital, his physical examination shows a temperature of 39°C (102°F), blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg, pulse of 110 beats per minute and regular, and respiratory rate of 28 breaths per minute. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen reveals an abscess in the pelvis. Which of the following most accurately describes his present condition?
. Systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS)
. Sepsis
. Severe sepsis
. Septic shock
. Severe septic shock
13) A 24-year-old man comes to the physician 24 hours after sustaining an injury to the right knee while playing soccer. He can walk, but he limps on the right side. He reports that he was hit by another player on the lateral side of his right knee, but did not feel a snap or pop at the time of the accident. On examination, the right knee appears normal, but palpation elicits tenderness along the medial aspect of the joint line. Increased laxity is observed when a valgus stress is applied to the knee flexed at 30 degrees, but not when the knee is in full extension. Lachman's test and posterior drawer tests are negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Meniscus injury
Sprain of the lateral collateral ligament
Sprain of the medial collateral ligament
Tear of the anterior cruciate ligament
Tear of the posterior cruciate ligament
14) A 35-year-old man had a splenectomy 8 days ago, following a motor vehicle accident. He is now complaining of left shoulder pain. His temperature is 39.0C (102.2F), blood pressure is 110/80 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 30 min and shallow, Physical examination shows clear lungs with equal breath sounds bilaterally and mild tenderness to palpation in the left upper quadrant with a well- healing midline laparotomy incision. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 15 g/dL, Hematocrit 45%, Leukocyte counts 15,000/mm3.A chest x-ray film shows no infiltrates or effusions. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Left clavicle fracture
Left lower lobe pneumonia
Post-splenectomy sepsis
Subphrenic abscess
Subphrenic hematoma
15) A 27-year-old man is shot point blank with a .22-caliber revolver. The entrance wound is in the anterior chest wall, just to the left of the sternal border, at the level of the 4th intercostal space. There is no exit wound. He is diaphoretic, cold, shivering, and anxious, and is asking for a blanket and a drink of water. His blood pressure is 65/40 mm Hg, and his pulse is 145/min and barely perceptible. He has large, distended veins in his neck and forehead. He is breathing adequately and has bilateral breath sounds. He is neurologically intact. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Extrinsic cardiogenic shock due to pericardial tamponade
Extrinsic cardiogenic shock due to tension pneumothorax
Hemorrhagic shock
Intrinsic cardiogenic shock due to myocardial damage
Vasomotor shock
16) A 61-year-old alcoholic man presents with severe epigastric pain radiating to his back. His amylase and lipase are elevated, and he is diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. Over the first 48 hours, he is determined to have 6 Ranson’s criteria, including a PaO2 less than 60 mm Hg. His chest x-ray reveals bilateral pulmonary infiltrates, and his wedge pressure is low. Which of the following criteria must be met to make a diagnosis of adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)?
. Hypoxemia defined as a PaO2/FiO2 ratio of less than 200
. Hypoxemia defined as a PaO2 of less than 60 mm Hg
A pulmonary capillary wedge pressure greater than 18 mm Hg
. Lack of improvement in oxygenation with administration of a test dose of furosemide
. Presence of a focal infiltrate on chest x-ray
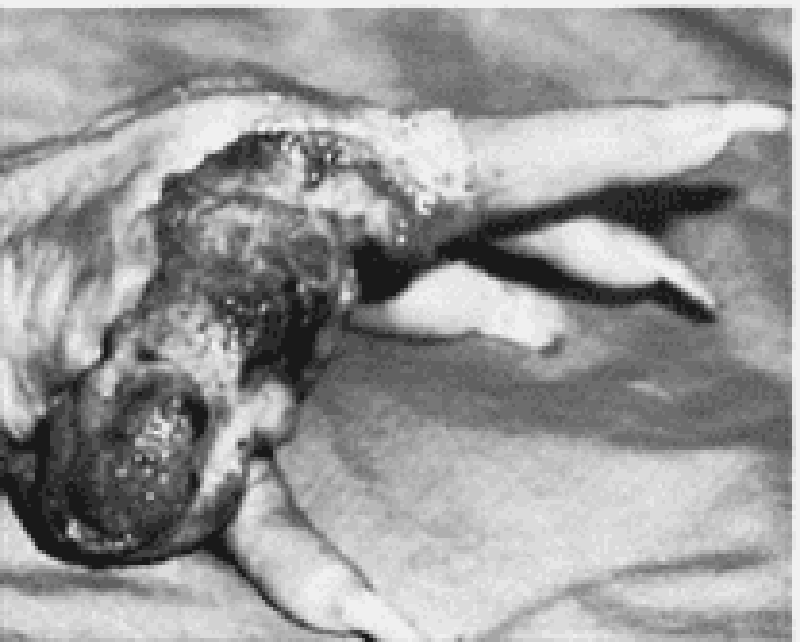
17) A 60-year-old woman presents with the skin lesion shown here. She reports a history of a burn injury to the hand while cooking a few years ago. She reports the wound has never healed completely. You are concerned about the skin lesion and perform a punch biopsy. Which of the following is the most accurate diagnosis given the patient’s history?
. Basal cell carcinoma
. Malignant melanoma
. Erythroplasia of Queyrat
. Bowen disease
. Marjolin ulcer
18) A 31-year-old accounting student presents with a persistent headache that began approximately 4 months ago. The headache has been gradually increasing in intensity, and is worse in the mornings. Thinking that she might need new glasses, she sought help from her optometrist, who discovered that she has bilateral papilledema and sent her in for medical evaluation. On direct questioning, she admits to repeat vomiting for the past 3 weeks, with no heaving, straining, or preceding nausea. "I would just open my mouth, and the stuff would hit the wall," she explains. She denies any other neurological symptoms. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Brain abscess
Brain tumor
Chronic subdural hematoma
Multiple sclerosis
Subarachnoid bleeding
19) A brain-dead potential donor has become available. You must plan for the dispersal of the thoracic organs. Which of the following will necessitate a heart-lung transplant?
. Primary pulmonary hypertension
. Cystic fibrosis
. End-stage emphysema
. Idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy with long-standing secondary pulmonary hypertension
. End-stage pulmonary fibrosis secondary to sarcoidosis
20) A 55-year-old woman who has end-stage liver disease is referred to a hepatologist for evaluation. Which of the following would prevent her from being a transplantation candidate?
. Use of alcohol 3 months ago
. Two 2-cm hepatocellular carcinomas (HCCs) in the right lobe of the liver
. A 4-cm hepatocellular carcinoma in the right lobe of the liver
. Development of hepatorenal syndrome requiring hemodialysis
. History of breast cancer 5 years ago with no evidence of disease currently
21) A 55-year-old woman requires an abdominoperineal operation for rectal cancer. She has a history of stable angina. Which of the following clinical markers is most likely to predict a cardiac event during her noncardiac surgery and should prompt further cardiac workup prior to her operation?
. Abnormal electrocardiogram
. Prior stroke
. Unstable angina
. Uncontrolled hypertension
. Her age
22) An 18-year-old man was traveling at a high speed when his car slammed into a wall. He is brought into the emergency department by ambulance. His blood pressure is 60/40 mmHg, pulse is 115/min and weak, respirations are 18/min, and central venous pressure is 2 cmH2O. He is responsive only to painful stimuli. Breath sounds are equal bilaterally, and cardiac auscultation reveals only tachycardia. The abdomen is soft, nondistended, and nontender with active bowel sounds. A chest x-ray film shows a widened mediastinum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cardiac contusion
Cardiac tamponade
Flail chest
Ruptured thoracic aorta
Tension pneumothorax
23) A 22-year-old woman is taken to the emergency department after she injures her foot. She had been standing on a chair changing a light bulb, when she accidentally stepped off the chair backward. She heard a cracking sound when she fell and developed pain and swelling behind the ankle. Her symptoms worsened when she tried to descend the stairs in her house. Physical examination demonstrates marked swelling behind her ankle, and her pain is exacerbated by plantar flexion and dorsiflexion of the hallus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anterior Achilles tendon bursitis
Calcaneal spur syndrome
Epiphysitis of the calcaneus
Fracture of the posterolateral talar tubercle
Posterior tibial nerve neuralgia
24) A 60-year-old man complains of anal itching and discomfort, particularly toward the end of the day. He works as a salesman in a department store, where he has to be on his feet all day. When he goes home in the evening, he finds himself sitting sideways to avoid the discomfort. He has no fever, rectal bleeding, or soiling of his underwear, and he has never had surgery in that area. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anal fissure
External hemorrhoids
Fistula in ano
Internal hemorrhoids
Perirectal abscess
25) A 71-year-old man develops dysphagia for both solids and liquids and weight loss of 60 lb over the past 6 months. He undergoes endoscopy, demonstrating a distal esophageal lesion, and biopsies are consistent with squamous cell carcinoma. He is scheduled for neoadjuvant chemoradiation followed by an esophagectomy. Preoperatively he is started on total parenteral nutrition, given his severe malnutrition reflected by an albumin of less than 1. Which of the following is most likely to be a concern initially in starting total parenteral nutrition in this patient?
. Hyperkalemia
. Hypermagnesemia
. Hypoglycemia
. Hypophosphatemia
. Hypochloremia
26) A 38-year-old woman who underwent a cadaveric renal transplant 8 years ago presents with fevers, fatigue, and weight loss. Evaluation included CT scans of the head, neck, chest, abdomen, and pelvis; she is noted to have diffuse lymphadenopathy and pulmonary nodules. A biopsy and histologic examination of a lymph node is performed. Which of the following viruses is most likely to be present in the lymph node?
. Cytomegalovirus
. Human papillomavirus
Human herpesvirus 8
. Epstein-Barr virus
. Coxsackie virus
27) An elderly diabetic woman with chronic steroid-dependent bronchospasm has an ileocolectomy for a perforated cecum. She is taken to the ICU intubated and is maintained on broad-spectrum antibiotics, renal dose dopamine, and a rapid steroid taper. On postoperative day 2, she develops a fever of 39.2°C (102.5°F), hypotension, lethargy, and laboratory values remarkable for hypoglycemia and hyperkalemia. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for her deterioration?
. Sepsis
. Hypovolemia
. Adrenal insufficiency
. Acute tubular necrosis
. Diabetic ketoacidosis
28) On postoperative day 5, an otherwise healthy 55-year-old man recovering from a partial hepatectomy is noted to have a fever of 38.6°C (101.5°F). Which of the following is the most common nosocomial infection postoperatively?
. Wound infection
. Urinary tract infection
. Pneumonia
. Intra-abdominal abscess
. Intravenous catheter-related infection
29) A 42-year-old man has had a rocky course for the 3 days following a bowel resection for intestinal perforation due to inflammatory bowel disease. His CVP had been 12 to 14 but is now 6, in the face of diminished blood pressure and oliguria. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of his hypotension?
. Pulmonary embolism
. Hypervolemia
. Positive-pressure ventilation
. Pneumothorax
. Gram-negative sepsis
30) Acute renal failure occurs following aortic angiography in a 72-year-old man. His weight has been rising, his lungs show rales at both bases, and he is dyspneic. His fractional excretion of sodium is greater than 1. He has eosinophilia on his peripheral smear, an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and proteinuria with microscopic hematuria. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his renal failure?
. Hypovolemia
. Renal artery cholesterol embolism
. Acute tubular necrosis
. Cardiogenic shock
. Aortic dissection
31) A 26-year-old man is resuscitated with packed red blood cells following a motor vehicle collision complicated by a fractured pelvis and resultant hemorrhage. A few hours later the patient becomes hypotensive with a normal central venous pressure (CVP), oliguric, and febrile. Upon examination, the patient is noted to have profuse oozing of blood from his intravenous (IV) sites. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hypovolemic shock
. Acute adrenal insufficiency
. Gram-negative bacteremia
. Transfusion reaction
. Ureteral obstruction
32) A 72-year-old man undergoes a subtotal colectomy for a cecal perforation due to a sigmoid colon obstruction. He has had a prolonged recovery and has been on total parenteral nutrition (TPN) for 2 weeks postoperatively. After regaining bowel function, he experienced significant diarrhea. Examination of his abdominal wound demonstrates minimal granulation tissue. He complains that he has lost his taste for food. He also has increased hair loss and a new perioral pustular rash. Which of the following deficiencies does he most likely have?
. Zinc
. Selenium
. Molybdenum
. Chromium
. Thiamine
33) A patient develops a fever and tachycardia during a blood transfusion after a redo coronary artery bypass procedure. The nurse subsequently discovers that there was a mix-up in the cross-match because of a labeling error. Which of the following is diagnostic in a patient with an immediate hemolytic reaction secondary to a blood transfusion?
. Serum haptoglobin above 50 mg/dL
. Indirect bilirubin greater than 5 mg/dL
. Direct bilirubin greater than 5 mg/dL
. Positive Coombs test
. Myoglobinuria
34) An obese 50-year-old woman undergoes a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In the recovery room, she is found to be hypotensive and tachycardic. Her arterial blood gases reveal a pH of 7.29, PaO2 of 60 mm Hg, and PaCO2 of 54 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s problem?
. Acute pulmonary embolism
. Carbon dioxide (CO2) absorption from induced pneumoperitoneum
. Alveolar hypoventilation
. Pulmonary edema
. Atelectasis from a high diaphragm
35) Approximately 6 weeks following a kidney transplant, a 59-year-old woman develops fever, malaise, and myalgias and is found to have a cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Which of the following is a potential sequela of CMV infection?
. Pyelonephritis
. Gastrointestinal (GI) ulceration and haemorrhage
. Cholecystitis
. Intra-abdominal abscess
. Parotitis
36) A 24-year-old woman develops moderate, generalized abdominal pain of sudden onset and shortly thereafter faints. At the time of evaluation in the emergency department, she has regained consciousness, is pale, and has a blood pressure of 95/70 mm Hg and a faint pulse rate of 90/min. The abdomen is mildly distended and tender, with normal bowel sounds. Her hemoglobin is 7 g/dL. There is no history of trauma, but it is suspected that she might be bleeding into her abdomen, and a diagnostic peritoneal lavage is performed. The study shows that there is free blood in the peritoneal cavity. She denies the possibility of pregnancy because she has been on birth control pills since the age of 14 and has never missed taking them. Pelvic examination is normal, and a pregnancy test is negative. At laparotomy, the surgeons are likely to find which of the following?
Bleeding ovarian follicle
Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm
Ruptured ectopic pregnancy
Ruptured hepatic adenoma
Ruptured hepatic artery aneurysm
37) A 42-year-old man is undergoing chemotherapy after resection of a cecal adenocarcinoma with positive lymph nodes. You are asked to see him regarding a potential surgical complication. Which of the following potentially operable complications is a common occurrence among patients receiving systemic chemotherapy?
. Acute cholecystitis
. Perirectal abscess
. Appendicitis
. Incarcerated femoral hernia
. Diverticulitis
38) A 30-year-old previously healthy man presents with refractory hypertension on four medications. Urinalysis is positive for metanephrines. He was adopted as an infant and therefore does not know his family history. Which of the following inherited syndromes is not associated with this disease?
. MEN2A
MEN2B
. von Hippel-Lindau disease
. Neurofibromatosis I
. Neurofibromatosis II
39) A 55-year-old man is diagnosed with benign prostatic hyperplasia. The patient declines pharmacologic treatment and elects to undergo transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP). Which of the following is the most common complication of this procedure?
Bladder neck contracture
Impotence
Incontinence
Recurrence of symptoms
Retrograde ejaculation
40) A 22-year-old healthy African-American woman presents with a recurrent growth on her right thigh. She has a childhood history of a third-degree scald burn to the same area that did not require skin grafting. The growth was completely removed 2 years ago. On physical examination there is a 5 cm × 2 cm, raised, irregularly shaped purple lesion with a smooth top. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Angiosarcoma
. Malignant melanoma
. Squamous cell carcinoma
. Kaposi sarcoma
. Keloid
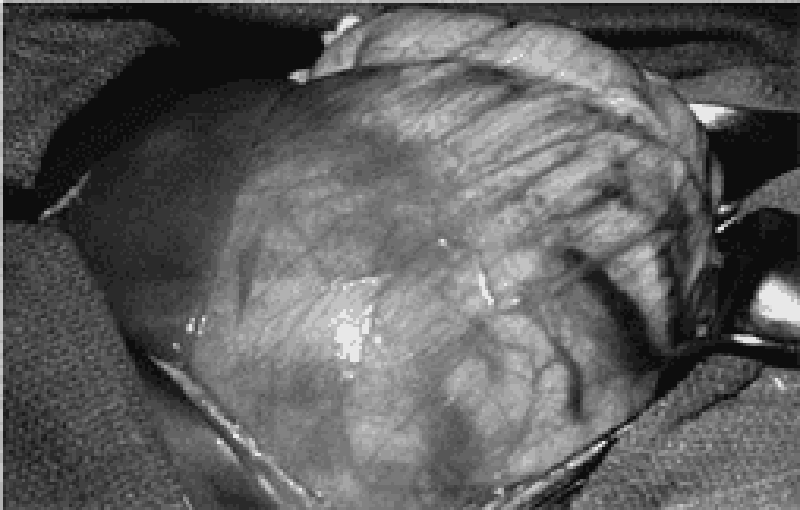
41) A mother notices an abdominal mass in her 3-year-old son while giving him a bath. There is no history of any symptoms, but the boy’s blood pressure is elevated at 105/85 mm Hg. Metastatic workup is negative and the patient is explored. The mass shown here is found within the left kidney. Genetic testing reveals deletion of 2 genes on chromosome band 11p13. Which of the following anomalies in addition to the identified tumor is associated with these chromosomal deletions?
. Cardiac anomalies
. Hemihypertrophy
. Hypoglycemia
. Macroglossia
. Aniridia
42) A 61-year-old man with severe three-vessel coronary disease and diabetes mellitus is scheduled for abdominal surgery. The patient has a long history of coronary disease and had a q-wave myocardial infarction 2 years ago. He has had type 1 diabetes mellitus for 12 years. His medications include atenolol, insulin, and captopril. His last hemoglobin Alc, 3 months ago, was 9.2%. Which of the following is the most predictive of a perioperative complication in this patient?
Poor exercise tolerance
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) on ECG
Recent myocardial infarction (MI)
Recent shortness of breath
Use of a beta blocker in the preoperative period
43) A 30-year-old man with a history of Crohn disease develops an enterocutaneous fistula and is placed on total parenteral nutrition through a right subclavian central venous catheter. After 5 days, the patient develops a fever and leukocytosis; CT scan of the abdomen reveals no intra-abdominal abscess. The subclavian catheter insertion site is inspected and noted to be erythematous and painful. Blood cultures are positive. Which of the following organisms is the most likely cause of his fever?
. Coagulase-positive staphylococci
. Coagulase-negative staphylococci
. Group A Streptococcus
. Enterococcus
. Escherichia coli
44) A 32-year-old woman has an episode of upper gastrointestinal bleeding after a night of heavy alcoholic intake followed by ingestion of multiple aspirin tablets for the hangover. There was no prior vomiting until the time when she felt nauseated, went to the bathroom, and "filled the wash basin with vomiting of bright red bloody fluid." When she arrives in the emergency department, an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy is promptly performed, which confirms a diagnosis of acute erosive gastritis. She has no duodenal ulcer and no esophageal varices. Gastric lavage with ice-cold saline is performed and the bleeding stops. Laser photocoagulation or electrocautery are not used, neither is pitressin infused. She remains hemodynamically stable throughout the procedure, and she has normal hemoglobin. She is sent home 2 hours later. Four hours after discharge, she returns complaining of severe, constant chest pain. She is in acute distress, has a temperature of 39.0C (102.2F), is having chills, and looks quite ill. Physical examination is remarkable for the presence of crepitation to palpation in the upper chest and lower neck, and chest x-rays confirm the presence of air in the mediastinum and the subcutaneous tissues. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Boerhaave syndrome
Dissecting thoracic aortic aneurysm
Gastric perforation
Iatrogenic esophageal perforation
Myocardial infarction
45) A 71-year-old man is involved in a minor automobile accident on the road between Guadalajara and Lake Chapala in Mexico. The man is an American citizen who at the age of 65 years retired to a lakeside home in that area. Although he is asymptomatic, he decides to return to the United States to be "thoroughly checked." He is admitted to a veteran's hospital in south Texas, where he undergoes a CT scan of his abdomen. There are no signs of traumatic injuries, but the scan reveals the presence of four simple, thin walled cystic structures, approximately 1 cm in diameter, scattered throughout both lobes of his liver. They have no septations. There are no cysts in the kidneys or pancreas. The man is completely asymptomatic and afebrile. Liver function tests are normal, as is his white blood count and differential. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Amebic abscesses
Cystadenocarcinoma of the liver
Hydatid cysts
Polycystic liver disease
Simple liver cysts
46) A 78-year-old man comes to the physician because of a bloody urethral discharge for 3 days. He has had increasing frequency of urination and hesitancy for the past 2 years, but these symptoms have never been severe enough to require medical attention. Digital rectal examination reveals a slightly enlarged and firm prostate. Expressed prostatic secretions are negative for bacteria and leukocytes. Collection of clean-catch urine in separate aliquots reveals initial hematuria, with blood present in the first 5 mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Gonococcal infection
Nonbacterial prostatitis
Prostatic carcinoma
Testicular cancer
Urethral carcinoma
47) A 19-year-old man sustains severe lower-extremity trauma, including a femur fracture and a crush injury to his foot. He requires vascular reconstruction of the popliteal artery. On the day after surgery, he becomes dyspneic and hypoxemic and requires intubation and mechanical ventilation. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of his decompensation?
. Aspiration
. Atelectasis
Fat embolism syndrome
Fluid overload
. Pneumonia
48) An 18-year-old gang member is stabbed in the back, just to the right of the midline. Physical examination shows paralysis and loss of proprioception distal to the injury on the right side, and loss of pain perception distal to the injury on the left side. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Posterior cord syndrome
Hemisection of the spinal cord
Complete transection of the spinal cord
Central cord syndrome
Anterior cord syndrome
49) A 14-year-old girl has a firm, movable, rubbery mass in her left breast. The mass was first noticed 6 months ago and has since grown to about 6 cm in diameter. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Intraductal papilloma
Giant juvenile fibroadenoma
Fibrocystic disease (mammary dysplasia)
Cystosarcoma phyllodes
Cancer of the breast
50) A 3-week-old infant is brought in because of 2 days of protracted bilious vomiting. He looks acutely ill, and plain x-rays show two large air fluid levels in the upper abdomen, the larger one on the left side and a smaller one on the right side. The radiologist describes the finding as a "double bubble sign." He also reports that there is intraluminal gas distal to those two air fluid levels, but that it is sparse and does not outline distended loops. Which of the following is the most likely tentative clinical diagnosis?
Necrotizing enterocolitis
Meconium ileus
Malrotation
Intestinal atresia
Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
51) A 16-year-old boy is persuaded by his older brother to accompany him and his friends on a beer- drinking binge. This is the first such experience for the boy, and it leads to the development of severe colicky left flank pain. When rescued by his parents, he is diaphoretic and doubled up in pain. He relates that he began to urinate frequently and profusely after the third or fourth beer and that the pain seized him shortly thereafter. He is tender to fist percussion over the left costovertebral angle but is afebrile. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Vesicoureteral reflux
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Low implantation of one ureter
Bladder calculi
Ureteral stone
52) A 53-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife because of headache and visual changes. Approximately 3 hours ago, he had the acute onset of an extremely severe posterior headache that was non-radiating but was associated with nausea and vomiting. This headache subsided, but over the past hour he has developed mild neck stiffness and pain on flexion of his neck. The patient is not cooperative, so no additional history is known; however, his wife states that he was feeling well until recently and has no allergies. The patient appears moderately uncomfortable and is complaining of the worst headache he has ever experienced. Which of the following is the most likely cause for his symptoms?
Thalamic bleed
Ruptured berry aneurysm
Putamenal bleed
Cerebellar bleed
Arteriovenous malformation
53) A 72-year-old man has a 4-cm hard mass in the left supraclavicular area. The mass is movable and nontender and has been present and steadily growing for the past 3 months. On direct questioning the only additional findings include a 20-pound weight loss and a vague feeling of epigastric discomfort over the past 2 months. Physical examination shows evidence of the weight loss but no other significant findings in the abdominal examination. The supraclavicular mass are obvious, but no other masses can be felt anywhere else in the neck, axillas, or groins. There is occult blood in the stool, and his hemoglobin is 10.5 g/dL. Which of the following would a biopsy of the supraclavicular mass most likely reveal?
Metastatic thyroid cancer
Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
Metastatic gastric cancer
Lymphoma
Chronic inflammation
54) A 6-year-old boy has insidious development of limping with decreased motion in one hip. He complains occasionally of knee pain on that side. He walks into the office with an antalgic gait. Examination of the knee is normal, but passive motion of the hip is guarded. The child is afebrile, and the parents indicate that his gait and level of activity were completely normal all his life until this recent problem. He has not had a recent febrile illness. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
Septic hip
Hematogenous osteomyelitis of the femoral head
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
Avascular necrosis of the capital femoral epiphysis
55) A patient involved in a car accident sustains burst fractures of several thoracic vertebral bodies. At the time of admission, he has no neurologic function at all below the level of the injury and he has flaccid sphincters. After a few days, there is partial recovery of function; the remaining deficits are loss of motor function and loss of pain and temperature sensation on both sides distal to the injury, with preservation of vibratory and positional senses. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Spinal shock
Cord hemisection
Complete cord transection
Central cord syndrome
Anterior cord syndrome
56) A 51-year-old man is undergoing abdominal surgery and becomes hypotensive while under general anesthesia. The patient had been doing well during most of the procedure but now has a blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. His past medical history is significant for coronary artery disease and diabetes mellitus. A pulmonary artery catheter placed prior to the procedure gives the following data: Central venous pressure 10 mmHg, Pulmonary artery pressure 60/30 mmHg, Pulmonary capillary occlusion 24 mm Hgpressure Cardiac output 2.3 L/min. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute left heart failure
Acute mitral regurgitation
Acute right heart failure
Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
Sepsis syndrome
57) A 62-year-old man complains of perineal discomfort and reports that there are streaks of fecal soiling in his underwear. Four months ago, he had a perirectal abscess drained surgically. Physical examination shows a perineal opening in the skin lateral to the anus, and a cord-like tract can be palpated going from the opening toward the inside of the anal canal. Brownish purulent discharge can be expressed from the tract. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anal fissure
Anorectal carcinoma
. Fistula-in-ano
Pilonidal cyst
Thrombosed hemorrhoids
58) A 50-year-old woman with a history of essential hypertension presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of a severe headache, nausea and vomiting, and photophobia. On examination, her BP is 160/100 mmHg. She is mildly confused and has nuchal rigidity, without focal neurologic signs. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. meningitis
Ruptured cerebral aneurysm
hemorrhagic stroke
ischemic cerebrovascular accident
transient ischemic attack
59) A 72-year-old man of Norwegian ancestry has a contracted hand that can no longer be extended and placed flat on a table. The problem developed gradually, over many years. He complains of no pain or neurologic abnormalities and, to the extent that the deformity allows, can move his fingers at will. Physical examination demonstrates the deformity described and in addition shows the presence of palpable fascial nodules. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Carpal tunnel syndrome
De Quervain tenosynovitis
Dupuytren contracture
Palmar tenosynovitis
Rheumatoid arthritis
60) A previously healthy 28-year-old woman develops significant postpartum hemorrhage, with a rapid drop in hematocrit to 18%. Despite aggressive IV fluid resuscitation, the patient has a persistent tachycardia, labile systolic blood pressure, and poor urine output. Ongoing resuscitation includes emergency transfusion with 2 units of O-negative packed red blood cells. During transfusion of the second unit, the patient develops chills, fever, vomiting, and hypertension. These symptoms are most likely the result of which of the following?
. A febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reaction
an anaphylactic transfusion reaction .
ABO incompatibility with acute hemolytic transfusion reaction
Delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction
acute bacterial infection transmitted in the blood product
61) A 45-year-old woman underwent elective surgery for an inguinal hernia. In the postoperative recovery room, she developed nausea, vomiting, and acute abdominal pain. She has a history of systemic lupus erythematosus, pernicious anemia, type 1 diabetes, chronic low back pain, and uterine fibroids. Her preoperative medications include monthly vitamin B-12 injections, insulin, prednisone, hydroxychloroquine, and acetaminophen. Her blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg and heart rate is 110/min. Initial laboratory studies show blood glucose of 50 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
. Postoperative bleeding
. Diabetic ketoacidosis
Intra-abdominal abscess
Intestinal obstruction
. Adrenal insufficiency
62) A 45-year-old woman, who wears high-heeled, pointed shoes, complains of pain in the forefoot after prolonged standing or walking. Occasionally, she also experiences numbness, a burning sensation, and tingling in the area. Physical examination shows no obvious deformities and a very tender spot in the third interspace, between the third and fourth toes. There is no redness, limitation of motion, or signs of inflammation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Gout
Hallux rigidus
Metatarsophalangeal articulation pain
. Morton's neuroma
Plantar fasciitis
63) A 45-year-old man presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a skin lesion on his abdomen. He states that the lesion has been present for 1 year, but has recently enlarged over the last 2 months. The mass is nontender, and he is otherwise asymptomatic. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals a 3-cm, pigmented, irregular skin lesion located in the left lower quadrant of the abdomen, as shown in Figure 6-12. Heart, lung, and abdominal examination are normal. There are no palpable cervical, axillary, or inguinal lymph nodes. Chest x-ray and liver function tests are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Squamous cell carcinoma
basal cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma
. melanoma
keratoacanthoma
64) A 58-year-old man presents with pain in the left leg after walking more than one block that is relieved with rest. On physical examination, distal pulses are not palpable in the left foot and there is dry gangrene on the tip of his left fifth toe. An ankle-brachial index on the same side is 0.5. Which of the patient’s symptoms or signs of arterial insufficiency qualifies him for reconstructive arterial surgery of the left lower extremity?
. Ankle-brachial index less than 0.7
Rest pain
. Claudication
. Absent palpable pulses
Toe gangrene
65) An 84-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of 1 hour of severe back pain. He also had syncope that lasted <1 minute. Before arriving at the hospital, he had an episode of gross hematuria, which he has never had before. He also complains of some shortness of breath. He denies chest pain, cough, nausea, vomiting, headache, and neck pain. His blood pressure is 72/55 mm Hg and pulse is 112/min and regular. His pulse oximetry shows 92% on room air. His ECG shows sinus tachycardia with prominent horizontal ST segment depression in the anterior chest leads. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture
Acute mesenteric ischemia
Acute myocardial infarction
. Massive pulmonary embolism
Nephrolithiasis with renal colic
66) A 54-year-old man comes to the physician because of edema of his right ankle. He reports heaviness and cramping in the same leg that is worse after a long day at work. The swelling is usually reduced significantly when he wakes up in the morning and worsens progressively throughout the day. He denies any other symptoms. He has no significant medical problems except hypertension, for which he takes atenolol. His temperature is 36.7° C (98° F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. JVP is normaL Lungs are clear to auscultation. There are no murmurs. There is no hepatosplenomegaly. Examination shows edema of the right ankle. Doppler examination of the leg shows no evidence of thrombosis. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his edema?
. Lymphatic obstruction
Reduced diastolic filling of the heart
Increased urinary loss of protein
Venous valve incompetence
Impaired cardiac contraction
67) A 68-year-old man presents to the physician’s office complaining of progressive dysphagia over the last 3 months associated with mild chest discomfort. He reports a 15-lb weight loss, a 30 pack-year smoking history, and occasional alcohol intake. The physical examination, including vital signs, is unremarkable. A chest x-ray was normal, and a barium esophagogram shows an irregular filling defect in the distal third of the esophagus with distortion and narrowing of the lumen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Esophagitis with stricture
Esophageal carcinoma
Lung carcinoma with invasion into the esophagus
lymphoma
Achalasia
68) A 29-year-old man presents with a 2-day history of severe left-sided scrotal pain and swelling. He is sexually active and has had "many" sexual partners. His temperature is 38.2 C (100.8 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. Examination shows unilateral intrascrotal tenderness and swelling. Testicular support makes the pain less intense. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Epididymitis
Prostatitis
Testicular torsion
Urethritis
Varicocele
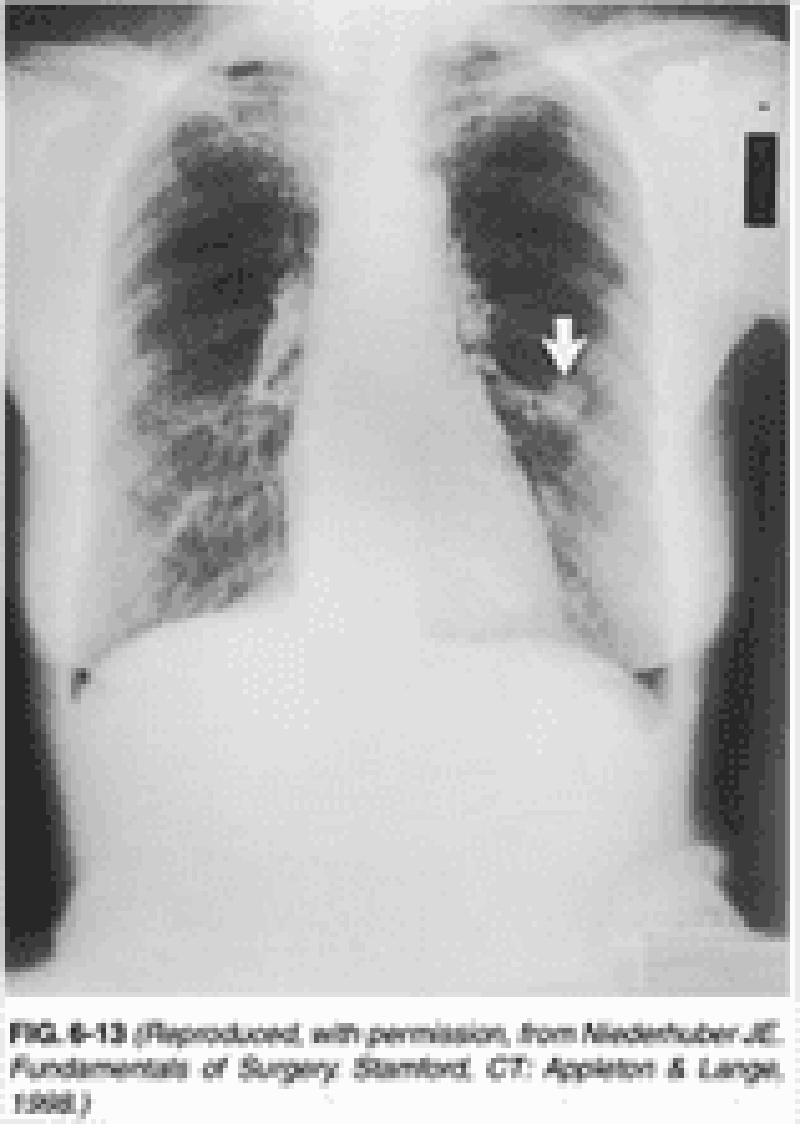
69) A 65-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for her yearly physical examination. She has no complaints except for a recent 10-lb weight loss. Past history is pertinent for a 40 pack-year smoking history, hypertension, asthma, and hypothyroidism. Examination reveals a thin woman with normal vital signs and unremarkable heart and abdominal examinations. Lung examination reveals mild wheezing and a few bibasilar rales. A chest x-ray is obtained and is shown in Figure 6-13. A chest x-ray obtained 3 years ago was normal. Yearly laboratory tests including a CBC, electrolytes, and lipid panels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Small cell lung cancer
. tuberculosis
. Nonsmall cell lung cancer
. hamartoma
abscess
70) A 24-year-old man comes to the physician because of 1 week of abdominal pain. It is localized in the right lower quadrant and somewhat exacerbated by motion. Over the past 2 days, it has radiated to the back. He initially had two episodes of vomiting but now just has decreased appetite. He had one episode of diarrhea 1 day ago. He denies urinary frequency. His other medical problems include mild intermittent asthma and gastroesophageal reflux disease. He traveled to Mexico for 5 days 1 month ago and did not have any gastrointestinal symptoms during his stay there. His mother was diagnosed with colon cancer at the age of 49 years. His temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F), blood pressure is 122/77 mm Hg, and pulse is 109/min and regular. Physical examination reveals prominent tenderness in the right lower quadrant, without rebound. Flexion of the right hip against resistance elicits significant abdominal pain. Laboratory results show:WBC count 16,000/mmHemoglobin 14.2 g/dlPlatelet count 620,000/mmPotassium 4.5 mEq/LCreatinine 1.0 mg/dlWhich of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Appendiceal perforation
. Colonic malignancy
. Complicated pyelonephritis
. Inflammatory bowel disease
Parasitic colitis
71) A 35-year-old woman is involved in a motor vehicle crash, sustaining a severe pelvic fracture, with disruption of the pelvic ring. In the trauma resuscitation room, she is confused and tachypneic, with a blood pressure of 90 mmHg systolic and a heart rate of 130/min. Laboratory investigations include serum electrolyte analysis, revealing a sodium of 139, a chloride of 103, and a bicarbonate of 14 meq/L. This patient demonstrates which of the following?
Nonanion gap metabolic acidosis
. Anion gap metabolic acidosis
metabolic alkalosis
. Respiratory acidosis
. Normal serum electrolytes
72) A 1-day-old infant with Down syndrome, feeding intolerance, bilious vomiting, and a double bubble on plain radiographs (Figure 6-18). Which one is the most likely diagnostic?
. Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
. Annular pancreas
. Duodenal atresia
. Midgut volvulus
Intussusception
73) A 43-year-old man develops excruciating abdominal pain at 8:23 PM (he looked at his watch when the pain "hit him"). When seen in the emergency department about 30 minutes later, he has a rigid abdomen, lies motionless on the examination table, has no bowel sounds, and is obviously in great pain, which he describes as constant and encompassing the entire abdomen. There is very severe pain when deep palpation of the abdomen is attempted in any of the four quadrants. However, the examining hand cannot make much of an indentation because of the impressive muscle guarding. When the attempt is aborted, he manifests severe rebound tenderness. X-ray films show free air under both diaphragms. Which of the following does this man most likely have?
. Acute abdomen, the nature of which cannot yet be defined
Acute inflammatory process affecting an intra-abdominal viscera
. Acute obstruction of an intra-abdominal viscera
. Ischemic process affecting intra-abdominal organs
. Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract
74) A 56-year-old woman presents for evaluation of a murmur suggestive of mitral stenosis and is noted on echocardiography to have a lesion attached to the fossa ovalis of the left atrial septum. The mass is causing obstruction of the mitral valve. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Endocarditis
. Lymphoma
Cardiac sarcoma .
. Cardiac myxoma
. Metastatic cancer to the heart
75) A 54-year-old man presents to the emergency department on transfer from another hospital at the request of the family. He was admitted to the outside hospital 2 weeks ago with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. He was treated with antibiotics, NG tube decompression, and TPN without significant improvement. He developed jaundice 2 days ago. His past history is pertinent for a 40 pack- year smoking history, chronic alcohol abuse, and diabetes. Examination reveals a mildly jaundiced patient with vital signs of temperature 100°F, pulse rate 95/min, and BP 110/60 mmHg. Cardiac examination is unremarkable, lung examination reveals decreased breath sounds at the bases bilaterally, and abdominal examination reveals fullness in the epigastrium with tenderness and voluntary guarding. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. hepatitis A
. hemolysis
. pancreatitis
. Liver metastases
. cirrhosis
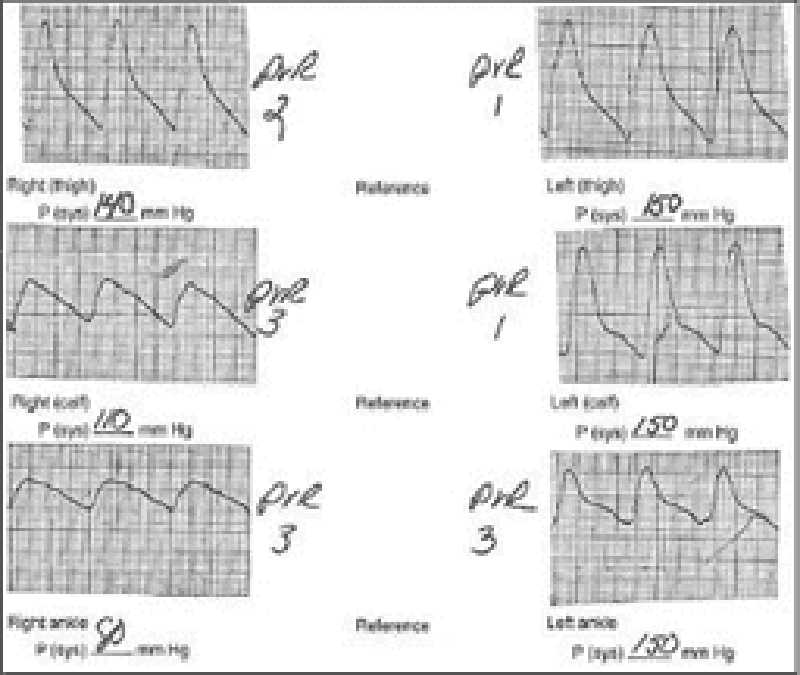
76) A 65-year-old male cigarette smoker reports onset of claudication of his right lower extremity approximately 3 weeks previously. He can walk 3 blocks before the onset of claudication. Physical examination reveals palpable pulses in the entire left lower extremity, but no pulses are palpable below the right groin level. Non-invasive flow studies are obtained and are pictured here. What is the level of the occlusive process in this patient?
. Right anterior tibial artery
Right superficial femoral artery
Right profunda femoris artery
Right external iliac artery
Right internal iliac artery
77) A 5-week-old infant presents with a 1-week history of progressive nonbilious emesis, associated with a 24-hour history of decreased urine output. The infant continues to be active and eager to feed. On examination, the infant has a sunken fontanelle and decreased skin turgor. The abdomen is scaphoid, and with a test feed, there is a visible peristaltic wave in the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Viral gastroenteritis
. Gastroesophageal reflux
. Urinary tract sepsis
. Pyloric stenosis
milk protein allergy
78) A 5-week-old infant presents with a 1-week history of progressive nonbilious emesis, associated with a 24-hour history of decreased urine output. The infant continues to be active and eager to feed. On examination, the infant has a sunken fontanels and decreased skin turgor. The abdomen is scaphoid, and with a test feed, there is a visible peristaltic wave in the epigastrium. The diagnosis is best confirmed by which of the following?
. Abdominal ultrasound
. Careful clinical examination with palpation of an epigastric mass
UGI contrast study
. Surgical exploration
. endoscopy
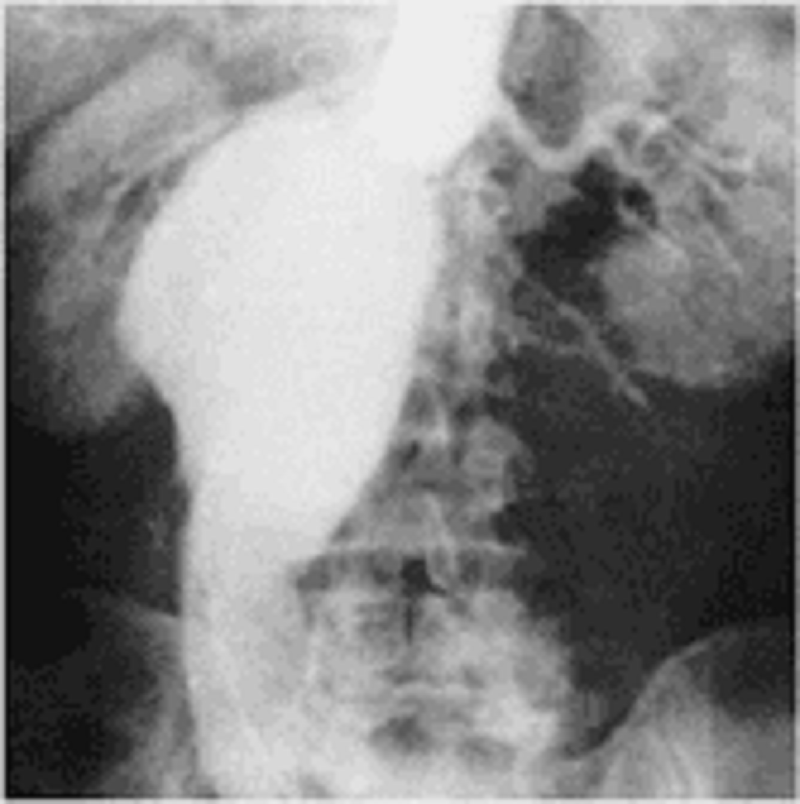
79) An 80-year-old man is found to have an asymptomatic pulsatile abdominal mass. An arteriogram is obtained (shown below). Which of the following is the most frequent and lethal complication of this condition?
Rupture
. Acute thromboembolism
. Dissection
High-output congestive heart failure
. Myocardial infarction
80) An older, overweight man complains of disabling, sharp heel pain every time his foot strikes the ground. The pain is worse in the mornings, preventing him from putting any weight on the heel. X-ray films show a bony spur matching the location of his pain, and physical examination shows exquisite tenderness to direct palpation right over that heel spur. Furthermore, when the ankle is dorsiflexed, the entire inner border of the fascia is tender to palpation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Epiphysitis of the calcaneus
Fracture of the posterolateral talar tubercle
Plantar fasciitis
Posterior Achilles tendon bursitis
Posterior tibial nerve neuralgia
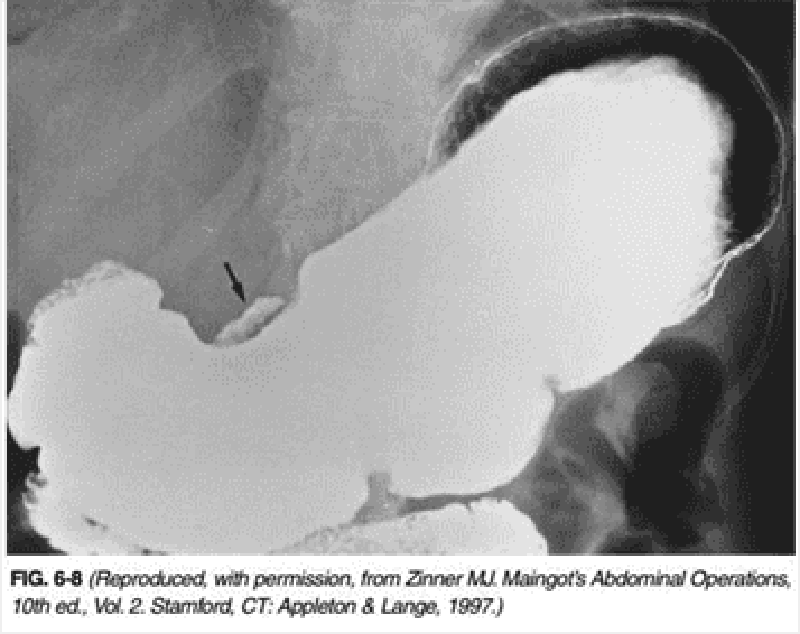
81) A 65-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office with a 6-month history of epigastric discomfort, poor appetite, and 10-lb weight loss. Past history is pertinent for hypertension, diabetes, a 30 pack-year smoking history, and occasional alcohol intake. Examination is unremarkable except for mild epigastric tenderness to deep palpation. An abdominal ultrasound reveals cholelithiasis, and one view of a UGI x-ray series is shown in Figure 6-8. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cholecystoenteric fistula
. Duodenal ulcer
. Gastric ulcer
. Gastric diverticulum
. Duodenal diverticulum
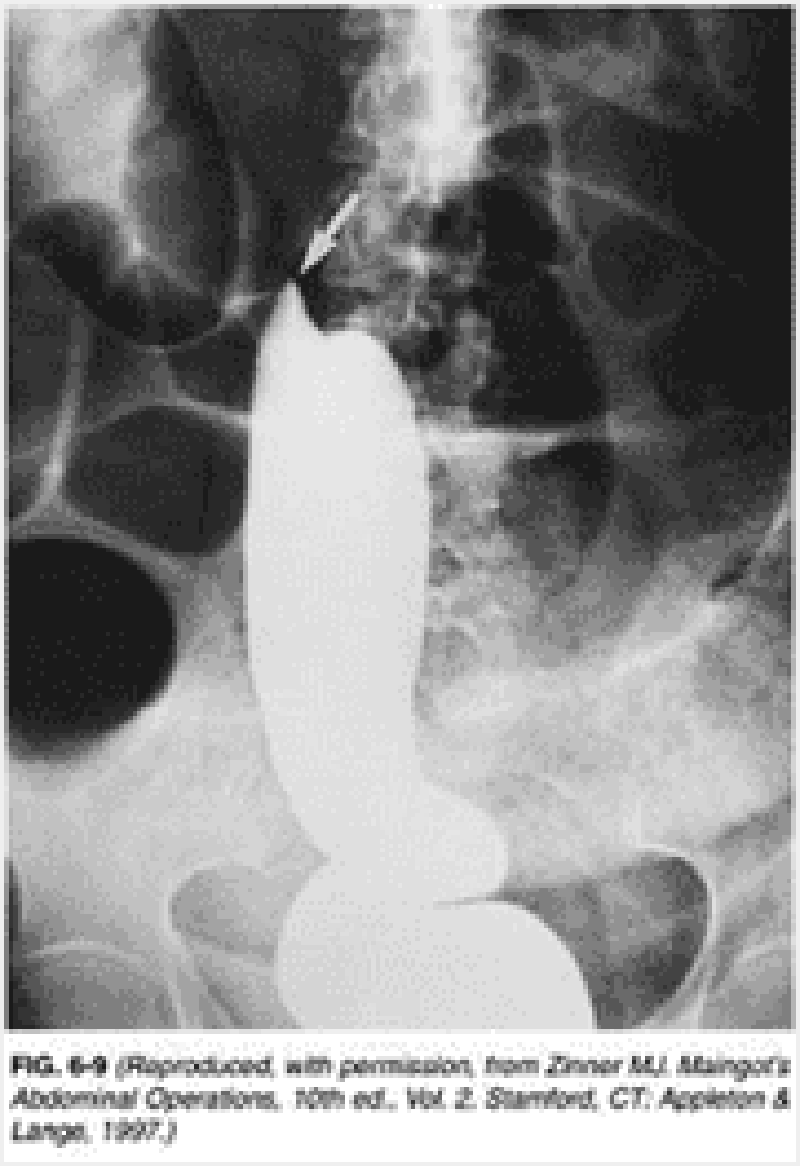
82) A 75-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from a nursing home for abdominal pain, distention, and obstipation over the last 2 days. Past history is pertinent for stroke, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and chronic constipation. Examination reveals a temperature of 98.6°F, pulse rate 90/min and irregularly irregular, and BP 160/90 mmHg. Heart examination reveals irregularly irregular rhythm with no murmurs; lung examination reveals few bibasilar rales; and abdominal examination reveals a distended, tympanic abdomen with mild tenderness and no rebound tenderness. Plain abdominal x-rays reveal dilated loops of bowel, and a barium enema is obtained and shown in Figure 6-9. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ischemic colitis with stricture
diverticulitis with obstruction
cecal volvulus
. Sigmoid volvulus
Colon cancer with obstruction
83) A 63-year-old man is seen because of facial swelling and cyanosis, especially when he bends over. There are large, dilated subcutaneous veins on his upper chest. His jugular veins are prominent even while he is upright. Which of the following conditions is the most likely cause of these findings?
Histoplasmosis (sclerosing mediastinitis)
. Substernal thyroid
. Thoracic aortic aneurysm
Constrictive pericarditis
. Bronchogenic carcinoma
84) A 55-year-old woman presents with a 6-month history of weight loss, abdominal cramps, and intermittent nonbloody diarrhea. On examination, her abdomen is mildly distended and there is a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant. Stool cultures yield normal fecal flora. CT scan with oral contrast demonstrates an inflammatory mass in the right lower quadrant, with thickening of the terminal ileum and ileocecal valve. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ulcerative colitis
. appendicitis
Crohn’s disease
Irritable bowel syndrome
. Lactose intolerance
85) A 65-year-old woman has had pain in her right shoulder and has been treated with analgesics without relief. The CXR reveals a mass in the apex of the right chest. A transthoracic needle biopsy documents carcinoma. Superior pulmonary sulcus carcinomas (Pancoast tumors) are bronchogenic carcinomas that typically produce which of the following clinical features?
. Atelectasis of the involved apical segment
. Horner syndrome
Pain in the T4 and T5 dermatomes
. Nonproductive cough
Hemoptysis
86) A 45-year-old woman presents with hypertension, development of facial hair, and a 7-cm suprarenal mass. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Myelolipoma
Cushing disease
Adrenocortical carcinoma
Pheochromocytoma
Carcinoid
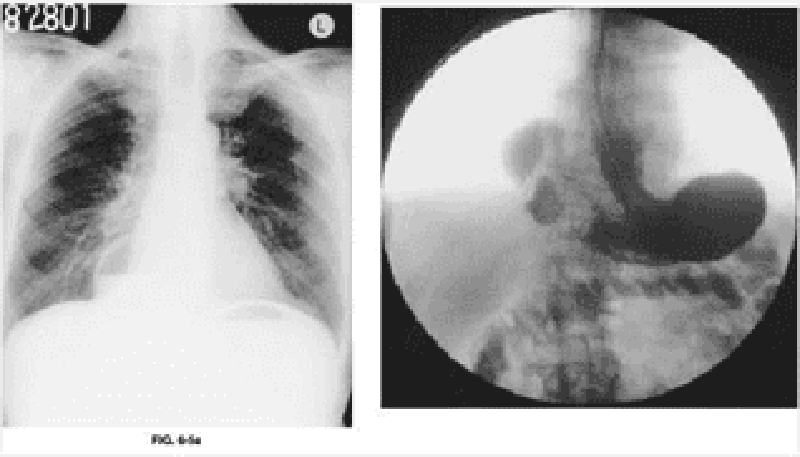
87) An 85-year-old man presents to the emergency room with an acute onset of midepigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and hiccups starting 2 days ago. He is unable to keep any food down. Past history is pertinent for a long-standing hiatal hernia, hypertension, and diet-controlled diabetes. Examination reveals vital signs of pulse rate 82/min, BP 100/52 mmHg, respiratory rate 16/min, and temperature 97.2°F. The patient is in no acute distress, but has epigastric tenderness without guarding. Laboratory analysis revealed a hematocrit of 46 and a normal white blood cell (WBC) count. A chest x-ray is shown in Figure 6-5a. A fluoroscopically guided NG tube was placed using contrast, and his stomach was decompressed. After adequate fluid and electrolyte resuscitation, an upper gastrointestinal (UGI) contrast study was obtained and is shown in 6-5b. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Sliding hiatal hernia
. Hernia of Bochdalek (posterorlateral congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
. Hernia of Morgagni (parasternal congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
. Paraesophageal hernia
. Eventration of the diaphragm (central diaphragm)
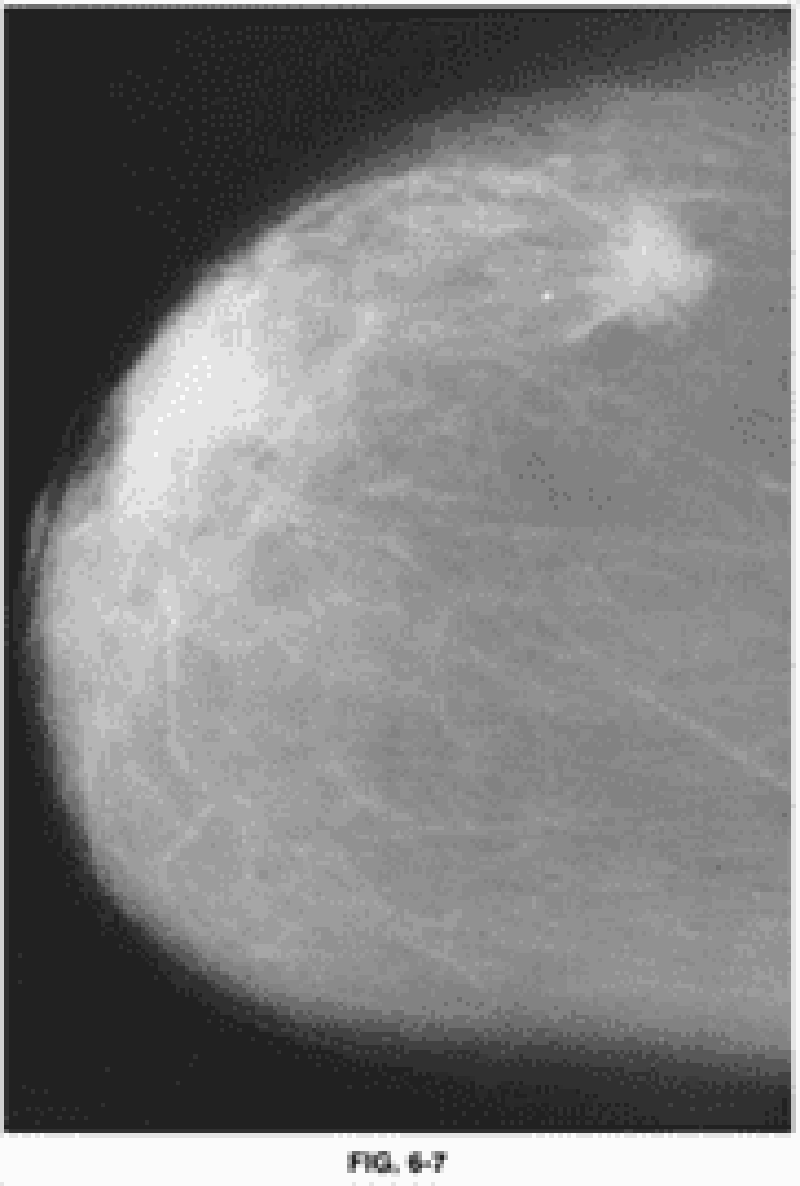
88) An 83-year-old woman presents to a mammographic facility for a screening mammogram. The technician notices a mass in the lateral right breast. The patient denies any breast pain, nipple discharge, skin changes, or breast trauma. A right breast CC view is shown in Figure 6-7. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Papilloma
invasive carcinoma
Cystosarcoma phyllodes
DCIS
fat necrosis
89) A 56-year-old man develops slow, progressive paralysis of the facial nerve on one side. It took several weeks for the full-blown paralysis to become obvious, and it has been present now for 3 months. It affects both the forehead and the lower face. He has no pain anywhere, and no palpable masses by physical examination. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bell's palsy
. Facial nerve tumor
. Hemorrhagic stroke
. Parotid gland cancer
. Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland
90) A 28-year-old man with a past history of bilateral orchiopexy for cryptorchidism presents with a painless, unilateral right scrotal enlargement. On examination, there is a palpable right testicular mass and enlarged inguinal nodes. Scrotal ultrasonography demonstrates heterogeneity of the testis, with an associated hydrocele. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated right-sided retroperitoneal adenopathy. CT scan of the chest is normal. Which of the following would help confirm the diagnosis?
Transscrotal needle biopsy
transscrotal aspiration of the hydrocele for cytology
radical orchiectomy through an inguinal incision
transscrotal exploration and orchiectomy
laparotomy with pelvic and retroperitoneal node dissection
91) A 45-year-old woman complains to her primary care physician of nervousness, sweating, tremulousness, and weight loss. The thyroid scan shown here exhibits a pattern that is most consistent with which of the following disorders?
Hyper secreting adenoma
Graves’ disease
Lateral aberrant thyroid
Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
Medullary carcinoma of thyroid
92) The unrestrained front-seat passenger in a car that crashes sustains closed comminuted fractures of both femoral shafts. Shortly after admission, he develops a blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg, a pulse rate of 110/min, and a venous pressure of zero. He becomes pale, cold, and clammy, but the rest of his physical examination and x-ray films of the chest and pelvis are unremarkable. A sonogram of the abdomen done in the emergency department is likewise negative. Which of the following is the most likely reason for the low blood pressure?
. Blood loss at the fracture sites
. Fat embolism
. Neurogenic shock from pain
. Unrecognized intracranial bleeding
. Unrecognized pericardial tamponade
93) A 24-year-old patient with known neurofibromatosis type 2 undergoes an MRI for ringing in his ears. The MRI demonstrates lesions in bilateral auditory canals. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Gangioneuroma
. Schwannoma
. Ependymoma
. Meningioma
. Pituitary adenoma
94) A40-year-old man with a history of alcohol abuse presents after an episode of binge drinking. He is complaining of epigastric pain, radiating to the back, associated with nausea and vomiting. On examination, he has marked tenderness in the epigastrium, with guarding, decreased bowel sounds, and moderate abdominal distention. Laboratory findings include leukocytosis and increased serum amylase and lipase. Abdominal roentgenograms demonstrate several dilated bowel loops in the upper abdomen. Select the most likely diagnosis?
. gastroenteritis
. Acute appendicitis
. Sigmoid diverticulitis
. Acute pancreatitis
. Acute cholecystitis
95) A 65-year-old man presents with a 4-day history of worsening lower abdominal pain and constipation. On examination, he is febrile (38.5°C) and has lower abdominal tenderness that is most intense in the midline and left lower quadrant associated with a palpable fullness. Laboratory findings demonstrate a moderate leukocytosis and abdominal roentgenograms show an ileus pattern. Select the most likely diagnosis?
. gastroenteritis . Regional enteritis
. Regional enteritis
. Acute appendicitis
. Perforated peptic ulcer
. Sigmoid diverticulitis
96) A 65-year-old man presents to the physician’s office with complaints of abdominal discomfort and jaundice for the past 3 weeks. Past history is pertinent for 30 pack-year smoking history, occasional alcohol intake, and a 5.5-mm ulcerating melanoma removed from his back 21/ 2 years ago. Examination reveals a mildly jaundiced patient with normal vital signs and a slightly distended abdomen with mild right upper quadrant tenderness and significant hepatomegaly. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. hepatitis A
. hemolysis
. choledocholithiasis
. Liver metastases
. cirrhosis
97) A 30-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of severe epigastric pain and vomiting 3 hours ago. He reports a 6-month history of chronic epigastric pain occurring nearly every day and relieved by antacids. On examination, he appears sweaty and avoids movement. Vital signs reveal a temperature of 100°F, BP of 100/60 mmHg, pulse rate of 110/min, and respiratory rate of 12/min. The remainder of his examination reveals diminished bowel sounds and a markedly tender and rigid abdomen. A chest x-ray and abdominal films reveal pneumoperitoneum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. small-bowel obstruction
. Dead bowel
. Perforated colon carcinoma
. Perforated duodenal ulcer
. Perforated gastric ulcer
98) A 15-year-old otherwise healthy female high school student begins to notice galactorrhea. A pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is a frequently associated physical finding?
. Gonadal atrophy
. Bitemporal hemianopsia
. Exophthalmos and lid lag
. Episodic hypertension
. Buffalo hump
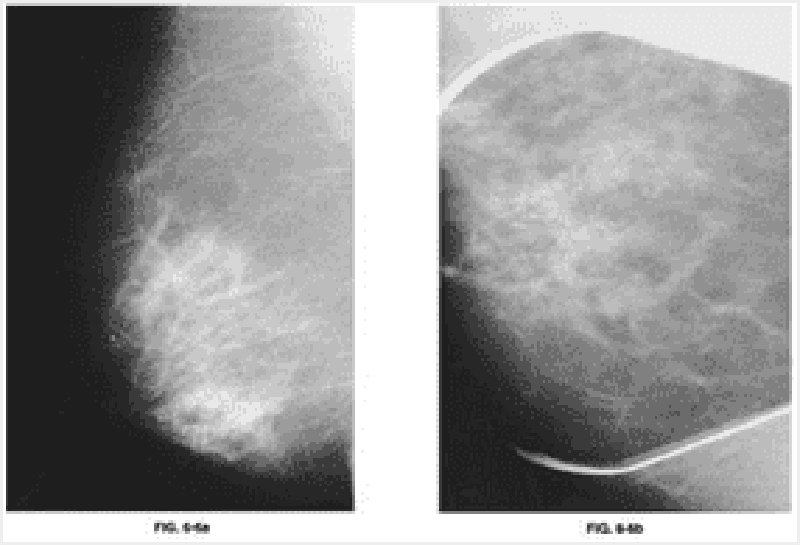
99) A 65-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of an abnormal screening mammogram. She denies any breast masses, nipple discharge, pain, or skin changes. Past history is pertinent for hypertension. Family history is positive for postmenopausal breast cancer in a sister. She has a normal breast examination and no axillary adenopathy. The remainder of her examination is unremarkable. An MLO view of the right breast is shown in Figure 6-6a along with a magnification view of the craniocaudal (CC) film (Figure 6-6b). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Milk of calcium
. LCIS with or without an invasive component
. DCIS with or without an invasive component
. Involuting fibroadenoma
. Phyllodes tumor
100) A 76-year-old man is undergoing an abdominoperineal resection for rectal cancer. During the surgery, unexpected severe bleeding is encountered, and the patient is hypotensive on and off for almost an hour. The anesthesiologist notes ST depression and T-wave flattening on the ECG monitor. Which of the following are the most likely diagnosis and the expected mortality?
. Intraoperative air embolus, 100%
. Myocardial infarction, 5% to 10%
. Myocardial infarction, 50% to 90%
. Pulmonary embolus, 5% to 10%
. Pulmonary embolus, 50% to 90%
101) A 72-year-old woman has a red, swollen breast. She states that the condition has been present for at least several weeks, perhaps a month or two. She has no pain or fever. The skin over the area looks like orange peel. The area is not warm to the touch, but on physical examination there is fullness to the entire breast, with no discrete mass. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Chronic cystic mastitis
. Inflammatory cancer of the breast
. Normal menopausal involutionary changes
. Pyogenic breast abscess
. Tuberculous or fungal breast abscess
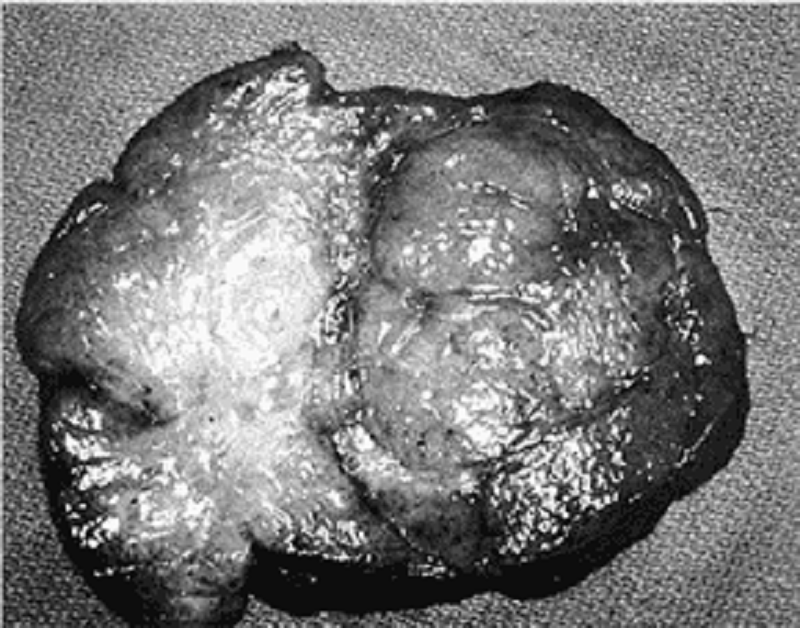
102) A 14-year-old black girl has her right breast removed because of a large mass. The tumor weighs 1400 g and has a bulging, very firm, lobulated surface with a whorl-like pattern, as illustrated here. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Cystosarcoma phyllodes
. Intraductal carcinoma
. Malignant lymphoma
. Fibroadenoma
. Juvenile hypertrophy
103) A 51-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office with a 2-month history of a right breast blood tinged nipple discharge. Past history is unremarkable. Family history is positive for postmenopausal breast cancer in a maternal grandmother. Examination reveals no palpable masses or regional adenopathy, but a serous discharge is easily elicited from a single duct in the right breast. Bilateral mammograms show no abnormalities. Cytology from the discharge was not diagnostic. A ductogram was ordered, and the results are shown: Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Invasive carcinoma
. Intraductal carcinoma
. Intraductal papilloma
. Fibrocystic disease
. Duct ectasia
104) An 18-year-old football player is seen in the emergency ward with severe knee pain incurred after being hit by a tackler while running. Which of the following findings on physical examination is most sensitive for an anterior cruciate ligament injury?
. Excessive valgus laxity of the knee
. Excessive varus laxity of the knee
. Locked knee
. Positive Lachman test
. Positive posterior drawer test
105) A 30-year-old man presents with sudden onset of severe epigastric pain 6 hours ago. Examination reveals a low-grade fever, tender abdomen throughout, with rigidity of the abdominal usculature. Abdominal roentgenograms show pneumoperitoneum. Select the most likely diagnosis?
. gastroenteritis
. Regional enteritis
. Acute appendicitis
. Perforated peptic ulcer
. Sigmoid diverticulitis
106) A 40-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with a 3-day history of worsening abdominal pain, with nausea and vomiting. Examination reveals a low-grade fever and abdominal tenderness in the right upper quadrant with guarding, especially during inspiration. Laboratory findings include a mild leukocytosis and a slightly elevated bilirubin. Select the most likely diagnosis?
. gastroenteritis
. Regional enteritis
. Acute appendicitis
. Perforated peptic ulcer
. Acute cholecystitis
107) A 3-year-old boy presents to the physician’s office with an asymptomatic neck mass located in the midline, just below the level of the thyroid cartilage. The mass moves with deglutition and on protrusion of the tongue. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Thyroid carcinoma
. Cystic hygroma
. Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
. Thyroglossal duct cyst
. lipoma
108) A 60-year-old otherwise healthy woman presents to her physician with a 3-week history of severe headaches. A contrast CT scan reveals a small, circular, hypodense lesion with ringlike contrast enhancement. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Brain abscess
. High-grade astrocytoma
. Parenchymal hemorrhage
. Metastatic lesion
. Toxoplasmosis
109) A 39-year-old man presents to his physician with the complaint of loss of peripheral vision. Which of the following findings are demonstrated by the subsequent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, shown here?
. Cerebral atrophy
. Pituitary adenoma
. Optic glioma
. Pontine hemorrhage
. Multiple sclerosis plaque
110) A 50-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a right neck mass. The mass has been present for 3 years and is painless. On examination, a nontender, firm, 2.5-cm mass is noted slightly below and posterior to the angle of the mandible on the right. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Carotid artery aneurysm
. Mixed parotid tumor (pleomorphic adenoma)
. Laryngeal carcinoma
. Parathyroid adenoma
. Branchial cleft cyst
111) A 35-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a left neck mass discovered 1 month ago on a routine physical examination. On examination, the mass measures 2 cm and is located anterolateral to the larynx and trachea. It is nontender and moves with swallowing. Past history is pertinent for a 15 pack-year smoking history and occasional alcohol intake. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Thyroid carcinoma
. Cystic hygroma
. Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
. Thyroglossal duct cyst
. lipoma
112) A 55-year-old man presents to the physician’s office with complaints of hoarseness and left neck fullness for the past month. On examination, a firm, movable, left submandibular mass is noted. Past history is pertinent for a 30 packyear smoking history with occasional alcohol intake. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Thyroid carcinoma
. Cystic hygroma
. Acute suppurative lymphadenitis .
. Thyroglossal duct cyst
. Laryngeal carcinoma
113) A 76-year-old woman presents with acute onset of persistent back pain and hypotension. A CT scan is obtained (shown below), and the patient is taken emergently to the operating room. Three days after surgery she complains of abdominal pain and bloody mucus per rectum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Staphylococcal enterocolitis
. Diverticulitis
. Bleeding arteriovenous (AV) malformation
. Ischemia of the left colon
. Bleeding colonic carcinoma
114) A 50-year-old man presents to the emergency department for increasing abdominal distention and jaundice over the last 4–6 weeks. Examination reveals mild jaundice, spider angiomas, and ascites. Enlarged veins are noted around the umbilicus. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. hepatitis A
. Pancreatic carcinoma
. Liver metastases
. cirrhosis
. pancreatitis
115) A 75-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his family for evaluation of jaundice. He complains of pruritus of 2 weeks’ duration and a recent 10-lb weight loss. On examination, he is deeply jaundiced and has a nontender, globular mass in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen that moves with respiration. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Choledochal cyst
. Pancreatic carcinoma
. Liver metastases
. cirrhosis
. pancreatitis
116) A 75-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from the nursing home for jaundice and mental confusion. The nursing home notes state that she has become less responsive and has developed jaundice over the last 2 weeks. Past history is pertinent for hypertension, diabetes, and prior colon resection for cancer at age 55. Examination reveals mild jaundice with vital signs of temperature 101.5°F, pulse rate 110/min, and BP 100/60 mmHg. She does not respond to verbal commands, but withdraws to pain. Abdominal examination reveals tenderness in the epigastrium and right upper quadrant. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. hepatitis A
. hemolysis
. choledocholithiasis
. Biliary stricture
. Choledochal cyst
117) An 18-year-old man is admitted to the ER following a motorcycle accident. He is alert and fully oriented, but witnesses to the accident report an interval of unresponsiveness following the injury. Skull films disclose a fracture of the left temporal bone. Following x-ray, the patient suddenly loses consciousness and dilation of the left pupil is noted. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. A ruptured berry aneurysm
. An acute subdural hematoma
. An epidural hematoma
. An intra-abdominal hemorrhage
. A ruptured arteriovenous malformation
118) A trauma patient with a closed-head injury is being monitored in the neurosurgical intensive care unit (ICU). His ICP measurement is seen to rise precipitously. An acute increase in ICP is characterized by which of the following clinical findings?
. Respiratory irregularities
. Decreased blood pressure
. Tachycardia
. Papilledema
. Compression of the fifth cranial nerve
119) A term infant is born at a small community hospital by caesarean section for failure to progress. The infant is noted to have the following abnormality at birth. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Umbilical hernia
. omphalitis
. omphalocele
. gastroschisis
. Traumatic evisceration
120) A 45-year-old man presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a posterior neck mass. The mass has been present for years, but has slowly enlarged over the last 2 years. Examination reveals a subcutaneous mass that is soft, nontender, and movable. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Thyroid carcinoma
. Cystic hygroma
. Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
. Thyroglossal duct cyst
. lipoma
121) A 6-year-old boy presents to the emergency department with a cough, sore throat, and malaise of 4 days’ duration. Examination reveals a temperature of 101.5°F, erythematous pharynx, and a tender right neck mass with overlying erythema. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Thyroid carcinoma
. Cystic hygroma
. Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
. Thyroglossal duct cyst
. lipoma
122) An 18-month-old girl is brought to the physician’s office for evaluation of left neck mass. Examination reveals a 2-cm soft, nontender, fluctuant mass in the left lateral neck. This is located at the anterior border of the sternomastoid, midway between the mastoid and clavicle. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Thyroid carcinoma
. Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
. Thyroglossal duct cyst
. lipoma
. Branchial cleft cyst
123) A 55-year-old-woman presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of mammographic findings on a screening mammogram. She denies any breast masses, nipple discharge, pain, or skin changes. Past history is pertinent for insulin-dependent diabetes. Family history is positive for postmenopausal breast cancer in her mother. She has a normal breast examination and no axillary adenopathy. A mediolateral oblique (MLO) view of the right breast is shown: Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Milk of calcium
. Lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) with or without an invasive component
. Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) with or without an invasive component
. Involuting fibroadenoma
. Phyllodes tumor
124) A 6-year-old boy is brought into the emergency room by his mother for walking with a limp for several weeks. On examination, the patient has tenderness over his right thigh without evidence of external trauma. An x-ray of the pelvis shows a right femoral head that is small and denser than normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis (SCFE)
. Legg-Calve-Perthes (LCP) disease
. Dysplasia of the hip
. Talipes equinovarus
. Blount disease
125) A 45-year-old man presents to the physician’s office complaining of dysphagia and retrosternal pressure and pain of 2-year duration. The symptoms have worsened over the last 3 months. He has a 30 pack-year smoking history and drinks beer on weekends. Vital signs include a BP of 150/90 mmHg, pulse rate of 90/min, and respiratory rate of 12/min, with a normal temperature. Examination reveals a thin man with a normal heart, lung, and abdomen examination. An esophagogram reveals a 6-cm, smooth, concave defect in the midesophagus with sharp borders. Esophagoscopy reveals intact overlying mucosa and a mobile tumor. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Esophageal carcinoma
. Bronchogenic carcinoma with invasion of the esophagus
. Benign esophageal polyp
. leiomyoma
. lymphoma
126) During the performance of a supraclavicular node biopsy under local anesthesia, a hissing sound is suddenly heard, and the patient suddenly dies. At the time of the catastrophic event, the target node was under traction, and the final cut was being made blindly behind it to free it up completely. The patient, an otherwise healthy 24-year-old man, was inhaling at that moment. Which of the following most likely caused this patient's death?
. Arterial injury with air embolization
. Major vein injury with air embolism
. Sudden pneumothorax with lung collapse
. Sympathetic discharge
. Tracheal injury
127) A 42-year-old man presents with a solitary lung lesion. At the time of operation on this patient, a firm, rubbery lesion in the periphery of the lung is discovered. It is sectioned in the operating room to reveal tissue that looks like cartilage and smooth muscle. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Fibroma
. Chondroma
. Osteochondroma
. Hamartoma
. Aspergilloma
128) A 55-year-old man presents with fever and pain in the perineal region. Upon further questioning he also complains of frequency, urgency, dysuria, and a decreased urinary stream. On physical examination his abdomen is soft, nondistended, and nontender. Digital rectal examination demonstrates exquisite tenderness on the anterior aspect. Laboratory examination reveals leukocytosis and findings on urinalysis are consistent with a bacterial infection. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
. Prostatitis
. Pyelonephritis
. Nephrolithiasis
. Urinary tract infection
129) A previously healthy 45-year-old man presents with a 9-month history of a slow-growing, painless right neck mass. He is a nonsmoker and has no significant past medical history. On examination, there is a nontender, discrete, 3-cm mass over the angle of the right mandible. Facial muscle function and sensation are normal. An oropharyngeal examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Metastatic carcinoma
. Infectious parotitis
. Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid
. Hodgkin’s disease
. Reactive cervical lymphatic hyperplasia
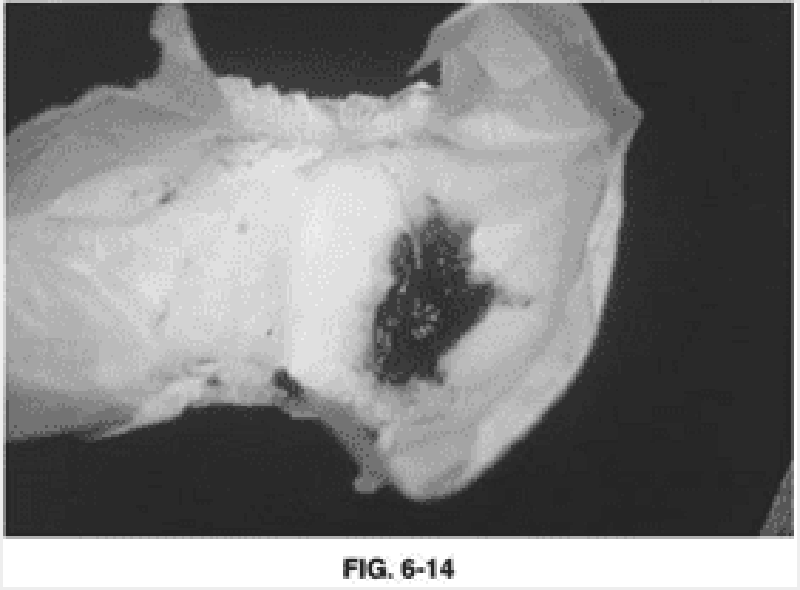
130) A 10-month-old infant presents to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of low-grade fever and anorexia. The parents report several episodes in which the child has been suddenly inconsolable and crying, followed by periods of lethargy. He has had nonbilious vomiting and several loose stools. On examination, the infant is pale and mildly dehydrated. His abdomen is soft and nondistended, with fullness to palpation in the right upper quadrant. The child passed another stool in the emergency department (see Figure 6-14). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. gastroenteritis
. intussusception
. Midgut volvulus
. Meckel’s diverticulum
. Juvenile rectal polyp
131) In a 6-month-old previously healthy male infant, an abnormality is revealed during a routine diaper change, as illustrated in Figure 6-19. The parents have noted this finding on and off on several occasions over the last month. On each occasion, the child has been feeding well, and is content and playful. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Noncommunicating hydrocele
. Inguinal adenitis
. Reducible inguinal hernia
. Incarcerated inguinal hernia
. Undescended testes
132) A young mother complains of pain along the radial side of the wrist and the first dorsal compartment. She relates that the pain is often caused by the position of wrist flexion and simultaneous thumb extension that she assumes to carry the head of her baby. On physical examination, the pain is reproduced by asking her to hold her thumb inside her closed fist, and then forcing the wrist into ulnar deviation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute and chronic bursitis
. Carpal tunnel syndrome
. Hairline unrecognized fracture of the carpal navicular (scaphoid) bone
. Palmar fascial contracture (Dupuytren's contracture)
. Tenosynovitis of the abductor or extensor tendons of the thumb (De Quervain's tenosynovitis)
133) A 10-day-old infant presenting with bilious vomiting, paucity of gas on plain radiographs, and duodenal obstruction on UGI contrast study (Figures 6-15 and 6-16). Which one is the most likely diagnostic?
. Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
. Annular pancreas
. Duodenal atresia
. Midgut volvulus
. intussusception
134) A neonate with bile-stained vomiting, abdominal distention, dilated loops of bowel on plain radiographs, and a small-caliber colon on contrast enema (Figure 6-17). Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
. Annular pancreas
. Duodenal atresia
. Midgut volvulus
. Jejunal atresia
135) A 67-year-old man has had an indolent, unhealing ulcer at the heel of the right foot for several weeks. The patient began wearing a new pair of shoes shortly before the ulcer started and noticed a blister as the first anomaly at the site where the ulcer eventually developed. He indicates that neither the blister nor the ulcer ever gave him any pain. The ulcer is 3.5 cm in diameter, the ulcer base looks dirty, and there is hardly any granulation tissue. The skin around the ulcer looks normal. The patient has no sensation to pin prick anywhere in that foot. Peripheral pulses are weak but palpable. He is obese and has varicose veins, high cholesterol, and poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus. Which of the following most accurately characterizes the ulcer?
. Diabetic ulcer due to trauma, neuropathy, and microvascular disease
. Ischemic ulcer due to arteriosclerosis
. Ischemic ulcer due to embolization
. Neoplastic in nature, probably squamous cell carcinoma
. Stasis ulcer due to venous insufficiency
136) A 40-year-old previously healthy man presents with sudden onset of severe abdominal pain that radiates from the right loin (flank) to groin. This pain is associated with nausea, sweating, and urinary urgency. He is distressed and restless, but an abdominal examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Torsion of the right testicle
. pyelonephritis
. appendicitis
. Right ureteral calculus
. Acute urinary retention
137) A 4-year-old previously healthy girl presents to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of rectal bleeding and dizziness. She has no other gastrointestinal symptoms. On examination, she appears pale. Her heart rate is 140 beats/min, and she has a 20 mmHg postural drop in systolic blood pressure. The child’s abdomen is nondistended and nontender, and fresh blood and clots are in the rectal vault on rectal examination. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. A bleeding Meckel’s diverticulum
. Juvenile rectal polyp
. hemorrhoids
. An anal fissure
. intussusception
138) A 21-year-old previously healthy woman presents with abdominal pain of 48-hour duration. The pain was initially periumbilical and on progression became localized in the right lower quadrant. The woman had nausea and an appetite. She denied dysuria. Her last menstrual period was 2 weeks earlier. On examination, she was febrile (temperature 38.2°C), and was found to have localized tenderness in the right lower quadrant with guarding. Rectal examination was normal. Laboratory examination demonstrated mild leukocytosis. Select the most likely diagnosis?
. gastroenteritis
. Regional enteritis
. Acute appendicitis
. Perforated peptic ulcer
. Sigmoid diverticulitis
139) A 25-year-old woman presents to the emergency room complaining of redness and pain in her right foot up to the level of the midcalf. She reports that her right lower extremity has been swollen for at least 15 years, but her left leg has been normal. On physical examination, she has a temperature of 39°C (102.2°F) and the right lower extremity is nontender with nonpitting edema from the groin down to the foot. There is cellulitis of the right foot without ulcers or skin discoloration. The left leg is normal. Which of the following is the most likely underlying problem?
. Congenital lymphedema
. Lymphedema praecox
. Venous insufficiency
. Deep venous thrombosis
. Acute arterial insufficiency
140) A blond, blue-eyed, 69-year-old sailor has a non-healing, indolent, 1.5-cm ulcer on the lower lip, arising from the vermilion border. The ulcer has been present and growing for the past 8 months. He is a pipe smoker, but has no history of alcohol or drug abuse. Physical examination shows "weather-beaten" facial skin, but no other ulcers. There are no enlarged lymph nodes in his neck. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Adenocarcinoma
. Basal cell carcinoma
. Benign ulceration due to chronic trauma
. Invasive malignant melanoma
. Squamous cell carcinoma
141) A 30-year-old woman presents with hypertension, weakness, bone pain, and a serum calcium level of 15.2 mg/dL. Hand films below show osteitis fibrosa cystica. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
. Sarcoidosis
. Vitamin D intoxication
. Paget disease
. Metastatic carcinoma
. Primary hyperparathyroidism
142) A 65-year-old man presents to the emergency department with an abrupt onset of excruciating chest pain 1 hour ago. The pain is localized to the anterior chest, but radiates to the back and neck. On examination, the patient is afebrile, with a BP of 210/110 mmHg, pulse rate of 95/min, and a respiratory rate of 12/min. He appears pale and sweaty. Unequal carotid, radial, and femoral pulses are noted. An electrocardiogram (ECG) shows nonspecific ST-T segment changes. Chest x-ray shows a slightly widened mediastinum and normal lung fields. Which of the following is the preferred modality in establishing the diagnosis?
. Transcutaneous echocardiography
. Transesophageal echocardiography
. CT scan
. Coronary angiography
. aortography
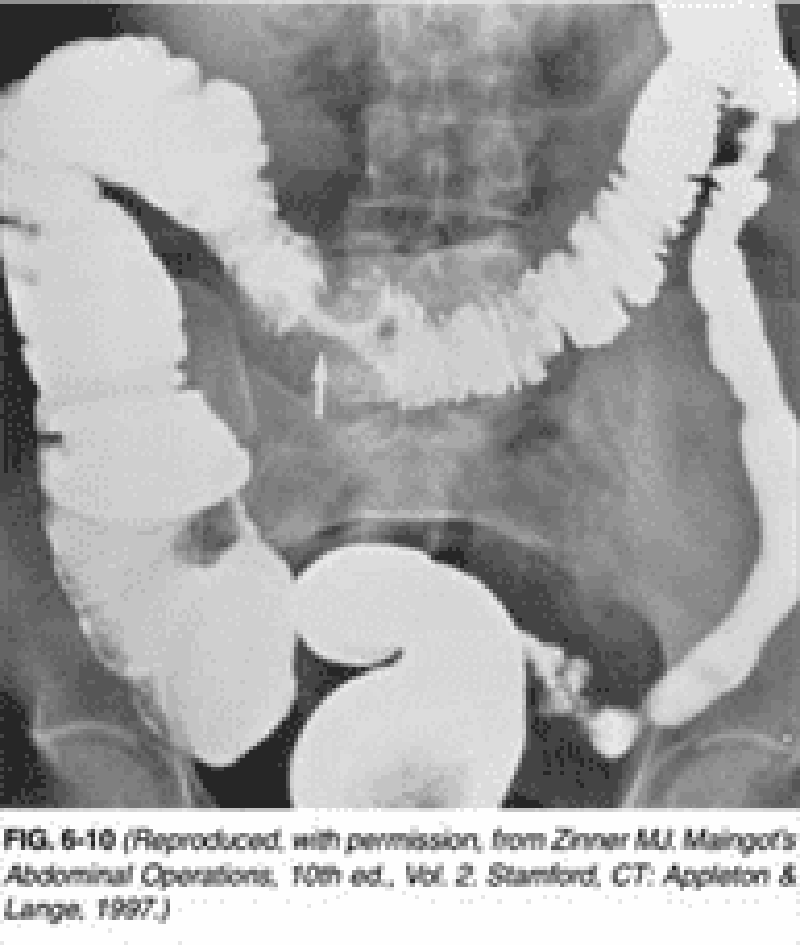
143) A 65-year-old man presents to the physician’s office for his yearly physical examination. His only complaint relates to early fatigue while playing golf. Past history is pertinent for mild hypertension. Examination is unremarkable except for trace hematest-positive stool. Blood tests are normal except for a hematocrit of 32. A UGI series is performed and is normal. A barium enema is performed, and one view is shown in Figure 6-10. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Diverticular disease
. Colon cancer
. lymphoma
. Ischemia with stricture
. Crohn’s colitis with stricture
144) An elderly man is involved in a rear end automobile collision in which he hyperextends his neck. He develops paralysis and burning pain of both upper extremities, while maintaining good motor function in his legs. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anterior cord syndrome
. Central cord syndrome
. Posterior cord syndrome
. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
. Spinal cord hemisection
145) A 53-year-old woman presents with weight loss and a persistent rash to her lower abdomen and perineum. She is diagnosed with necrolytic migrating erythema and additional workup demonstrates diabetes mellitus, anemia and a large mass in the tail of the pancreas. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Verner-Morrison syndrome (VIPoma)
. Glucagonoma
. Somatostatinoma
. Insulinoma
. Gastrinoma
1) A 25-year-old previously healthy man is scheduled for elective inguinal hernia repair under general anesthesia. After induction of anesthesia and initial inguinal incision, the patient develops tachycardia, muscle rigidity, fever of 38.5°C, and elevated end-tidal carbon dioxide. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. pneumonia
. atelectasis
. Urinary tract infection
. Myocardial infarction
. Malignant hyperthermia
2) A 55-year-old man presents to the emergency department with left lower quadrant abdominal pain. The pain has been present for 1 week, but has increased in intensity over the last 2 days associated with nausea, constipation, and dysuria. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals a temperature of 101°F, pulse rate of 95/min, BP of 130/70 mmHg, and normal heart and lung examinations. Abdominal examination reveals fullness and marked tenderness in the left lower quadrant, with voluntary guarding and decreased bowel sounds. Laboratory tests reveal a WBC count of 18,000 with a left shift and 20–50 WBCs in the urinalysis. A CT scan of the abdomen reveals a thickened sigmoid colon with pericolonic inflammation. He is admitted to the hospital for treatment. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Colon cancer with contained perforation
. Ischemic colitis
. Pseudomembranous colitis
. diverticulitis
. pyelonephritis
3) A 56-year-old woman has been treated for 3 years for wheezing on exertion, which was diagnosed as asthma. Chest radiograph, shown here, reveals a midline mass compressing the trachea. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lymphoma
. Neurogenic tumor
. Lung carcinoma
. Goiter
. Pericardial cyst
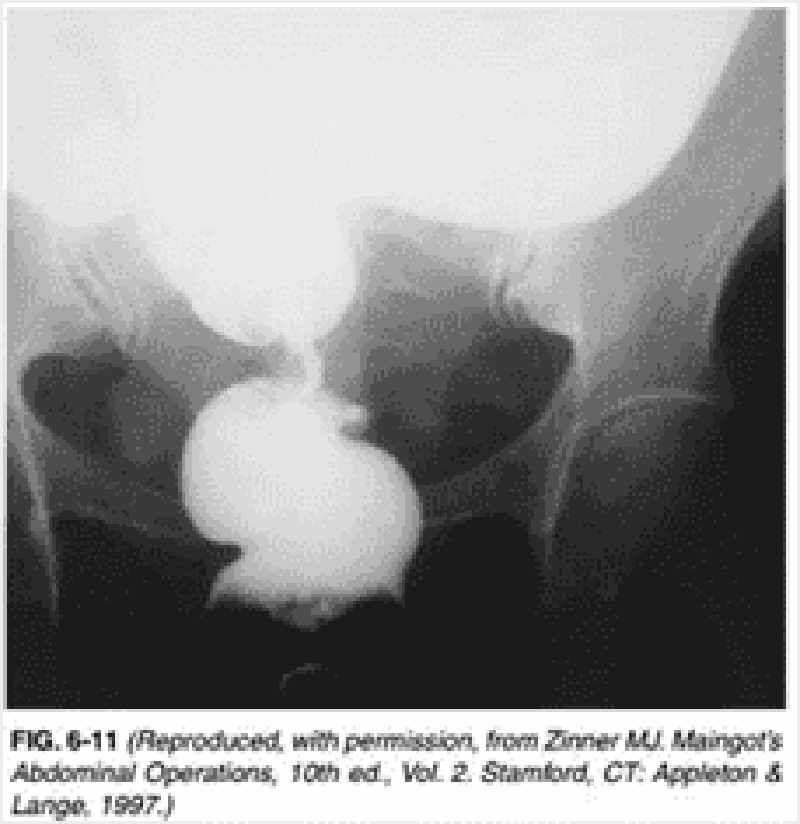
4) A 62-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office with complaints of constipation. She has had constipation for the last 6 months, which has worsened over the last month, associated with mild bloating. She noted that her stool has become “pencil thin” in the last month, with occasional blood, but she continues to have bowel movements daily. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals normal vital signs and heart and lung examination. Abdominal examination reveals mild fullness, especially in the lower quadrants. Rectal examination shows no rectal masses, but the stool is hematest positive. A barium xray is obtained, and one view is shown in Figure 6-11. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Crohn’s disease
. Ischemia with stricture
. Rectal carcinoma
. Sigmoid volvulus
. Diverticulitis with colovesical fistula
5) A 25-year-old man was admitted to the ICU with severe head injury with a basal skull fracture. Eighteen hours after the injury, he developed polyuria. Urine osmolality was 150 mOsm/Land serum osmolality was 350 mOsm/L. IV fluids were stopped, and 1 hour later urine output and urine osmolality remained unchanged. Five units of vasopressin were administered intravenously, and urine osmolality increased to 300mOsm/L. Select the most likely diagnosis of the patients with polyuria?
. Central diabetes insipidus (DI)
. nephrogenic DI
. Water intoxication
. Solute overload
. Diabetes mellitus
6) A 70-year-old man was admitted to the ICU with severe pancreatitis. During his ICU course, he underwent several CT scans with IV contrast and was also treated with an aminoglycoside for a urinary tract infection. The patient required a prolonged course of TPN, and developed Candida sepsis treated with amphotericin. He subsequently developed polyuria with urine osmolality of 250mOsm/L and serum osmolality of 350 mOsm/L. After receiving 5 units of vasopressin intravenously, there is no change in urine osmolality or urine output. Select the most likely diagnosis of the patients with polyuria?
. Central diabetes insipidus (DI)
. nephrogenic DI
. Water intoxication
. Solute overload
. Diabetes mellitus
7) A 42-year-old man describes intermittent episodes of severe, crushing chest pain that extends to the back and the jaw and last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. Many times the pain is accompanied by dysphagia and triggered by the ingestion of very cold or very hot liquids. However, sometimes the pain occurs for no apparent reason. There is no history of regurgitation, and, although the problem has been present for many years, there has been no progression of the symptoms. Repeated ECGs and cardiac enzymes have always been negative. Barium swallow shows an area of "corkscrew" appearance. Manometry shows that about one half of wet swallows produce repetitive simultaneous esophageal contractions of the esophageal body, and that the lower esophageal sphincter has normal pressures and exhibits normal relaxation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Achalasia of the esophagus
. Cancer of the lower esophagus
. Diffuse esophageal spasm
. Nutcracker esophagus
. Zenker's diverticulum
8) A 29-year-old man presents to the ER with persistent vomiting and abdominal pain for the last 24 hours. The pain is crampy, diffuse, and has been getting worse. He had a normal bowel movement two days ago and denies diarrhea. The emesis appears green without blood or coffee grounds. He has not eaten since the onset of the pain due to nausea. On exam, his temperature is 36.8° C (98.2° F}, pulse is 91/min, and blood pressure is 116/75 mmHg while sitting and 94/65 mmHg while standing. His abdomen is distended with hyperactive bowel sounds. Percussion reveals tympany and he is diffusely tender to palpation. There is no rebound tenderness or guarding. Laboratory studies reveal:WBC count 9,600/mm3Hematocrit 45%Sodium 147 mEq/LPotassium 3.1 mEq/LCreatinine 1.0 mg/dLAST 20 U/LALT 12 U/LBilirubin 0.8 mg/dLWhich of the following historical findings would you most expect in this patient?
. High alcohol consumption
. Occasional black or tarry stool
. Appendectomy six months ago
. Fatty food intolerance
. Recent weight loss
9) A 63-year-old obese female undergoes an elective cholecystectomy after two episodes of acute calculous cholecystitis. Three days after surgery, her blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg, her heart rate is 90/min, and her arterial oxygen saturation is 91 % on room air. She is afebrile. Which of the following would most likely increase her functional residual lung capacity?
. Inhaled albuterol
. Sequential compression devices to her lower extremities
. Elevation of the head of the bed
. Decreasing the dose of her postoperative opioids
. Postoperative benzodiazepines
10) A 62-year-old woman had an abdominal hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy 3 days ago. She had an indwelling bladder catheter during the procedure, which was removed in the recovery room. She has been voiding at will since then. She also had compression pneumatic stockings on both lower extremities during the operation. She began ambulation on the 1st postoperative day, and has been as active as possible under the circumstances, including faithful adherence to a prescribed program of incentive spirometry. On the evening of the 3rd postoperative day, she spikes a fever, with a temperature to 39.4C (103F). Which of the following is the most likely source of the fever?
. Atelectasis
. Deep thrombophlebitis
. Intra-abdominal abscess
. Urinary tract infection
. Wound infection
11) A 44-year-old male is found unresponsive and hypotensive at the scene of a high-speed motor vehicle accident. He is intubated and immediately rushed to the emergency department. The passenger in his car is pronounced dead at the scene. Physical examination in the ED shows large bruises over the entire chest wall and collapsed neck veins bilaterally. Lung exam reveals decreased breath sounds on the left side. Chest x-ray shows a large left hemothorax and a widened, rightward deviating mediastinum. The most likely diagnosis is?
. Aortic injury
. Diaphragm rupture
. Myocardial contusion
. Esophageal rupture
. Myocardial rupture
12) An 85-year-old male is placed on mechanical ventilation after a complicated elective hernia repair. After five days of endotracheal intubation with mechanical ventilation, the ratio of the rate of carbon dioxide produced to the rate of oxygen uptake is 1.05. What is the best explanation for these findings?
. Sepsis
. Pulmonary atelectasis
. High inspired oxygen fraction
. Carbohydrate excess in the diet
. High-protein tube feeding
13) A 75-year-old woman is admitted to the hospital from a nursing home for abdominal pain and pneumonia. She was noted to be short of breath with increasing cough for 2 days before admission. Treatment, consisting of supplemental oxygen, IV antibiotics, and pulmonary toilet, is instituted, with improvement within 2 days. On the third hospital day, her abdominal pain worsens. Examination reveals a mildly distended abdomen with bowel sounds but no signs of peritonitis. Remainder of examination reveals a tender bulge in the medial left thigh below the inguinal ligament. Gentle pressure causes more pain but does not change the size or shape of the bulge. Abdominal films show a nonspecific bowel gas pattern. Laboratory analysis shows a WBC of 13,000, decreased from 18,000 at the time of admission. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Incarcerated direct inguinal hernia
. Incarcerated femoral hernia
. Incarcerated indirect inguinal hernia
. Femoral artery aneurysm
. Lymph node with abscess
14) A 66-year-old woman picks up a bag of groceries out of the supermarket cart to place it in the trunk of her car. As she does so, she feels sharp, sudden pain in the middle of her arm, and her humerus suddenly breaks. She arrives at the emergency department cradling her arm; the deformity leaves no doubt that the bone is broken. Which of the following is the most likely reason for the fracture?
. Bony metastasis to the humerus from breast cancer
. Primary malignant bone tumor
. Osteoporosis
. Osteomalacia from nutritional deficiency
. Osteitis fibrosa cystica from parathyroid disease
15) An 18-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of dull aching and fullness of the scrotum. Examination shows soft left-sided scrotal swelling; transillumination testing is negative. The scrotal swelling increases when the patient performs the Valsalva maneuver. The physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Hypoalbuminemia
. Cystic dilations of the efferent ductules
. Testicular neoplasia
. Fluid in the tunica vaginalis
. Dilatation of pampiniform plexus
16) A 72-year-old man underwent surgical repair of an aneurysm of the infrarenal aorta. He received perioperative prophylaxis with a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. On the first postoperative day he complains of progressive abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. His temperature is 38.5° C (101° F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 22/min. His abdomen is mildly distended and tender to palpation. The tenderness is mostly in the left lower quadrant without rebound. Femoral pulses are full and symmetric. His white blood cell count is 12,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pseudomembranous colitis
. Perforation of the colon
. Ischemia of the bowel
. Aortoenteric fistula
. Invasive infectious diarrhea
17) A 32-year-old male comes to the emergency department because of a 3 day history of increasing lower abdominal pain, mild diarrhea and rectal pain on defecation. Ten days ago he had right lower quadrant (RLQ) pain for about 24 hours that resolved spontaneously. Since then, he has had malaise and low-grade fever. His temperature is 38.7°C (101.6°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse is 11 0/min and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows lower abdominal tenderness without rebound. No masses are palpable, and bowel sounds are decreased. Rectal examination shows a very tender, boggy and fluctuant bulging mass on palpation with the tip of the finger anteriorly. Laboratory studies show:Complete blood count Hemoglobin14.0 g/LPlatelets270,000/mm3Leukocyte count15,500/mm3His current condition is most likely a complication of?
. Anorectal abscess
. Colon cancer
. Acute diverticulitis
. Acute appendicitis
. Invasive diarrhea
18) A 44-year-old man complains of vague right upper abdominal discomfort that he has had for about 1 month. He describes no other symptoms, and, except for enucleation of one eye at age 21 "for a tumor," he has been in excellent health all his life. He exercises regularly and neither smoke nor drinks. The only findings on physical examination include the artificial eye and a tender, enlarged, and nodular liver. CT scan of the upper abdomen demonstrates multiple masses within the liver. Which of the following will most likely be found on biopsy of these masses?
. Metastatic malignant melanoma
. Metastatic sarcoma
. Metastatic retinoblastoma
. Primary hepatocellular carcinoma
. Metastatic prostatic cancer
19) A previously healthy, intoxicated, 19-year-old man is driving a car without using a seat belt. He crashes the car into the back of a parked truck. In the process he slams his abdomen into the steering wheel and ruptures his spleen. Which of the following is the most important problem associated with this type of injury?
. Bacteremia
. Peritonitis
. Internal blood loss
. External blood loss
. Electrolyte abnormalities
20) A 27-year-old immigrant from El Salvador has a 14 × 12 × 9 cm mass in her left breast. It has been present for 7 years and has slowly grown to its present size. The mass is firm, nontender, rubbery, and completely movable, and it is not attached to the overlying skin or the chest wall. There are no palpable axillary nodes or skin ulceration. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Breast cancer
. Mammary dysplasia
. Intraductal papilloma
. Cystosarcoma phyllodes
. Chronic cystic mastitis
21) A 63-year-old man, who weighs 65 kg, is in his 2nd postoperative day after an abdominoperineal resection for cancer of the rectum. An indwelling Foley catheter was left in place after surgery. The nurses are concerned because, even though his vital signs have been stable, his urinary output in the past 2 hours has been zero. In the preceding 3 hours, they had collected 56 mL, 73 mL, and 61 mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute renal failure
. Plugged or kinked catheter
. Dehydration
. Damage to the ureters during the operation
. Damage to the bladder during the operation
22) A 55-year-old woman falls in the shower and hurts her right shoulder. She shows up in the emergency department with her arm held close to her body, but the forearm rotated outward as if she were going to shake hands. She is in pain and will not move the arm from that position. Her shoulder looks "square" in comparison with the rounded unhurt opposite side, and there is numbness in a small area of her shoulder over the deltoid muscle. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acromioclavicular separation
. Scapular fracture
. Posterior dislocation of the shoulder
. Fracture of the upper end of the humeral shaft
. Anterior dislocation of the shoulder
23) A 68-year-old man is brought to the emergency department with excruciating back pain that began suddenly 45 minutes ago. The pain is constant and is not exacerbated by sneezing or coughing. He is diaphoretic and has a systolic blood pressure of 90 mm Hg. There is an 8 cm pulsatile mass deep in his epigastrium, above the umbilicus. A chest x-ray film is unremarkable. Two years ago, he was diagnosed with prostatic cancer and was treated with orchiectomy and radiation. At that time, his blood pressure was normal, and he had a 6-cm, asymptomatic abdominal aortic aneurysm for which he declined treatment. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Dissecting thoracic aortic aneurysm
. Rupturing abdominal aortic aneurysm
. Metastatic tumor to the lumbar spine
. Herniated disc
. Fracture of lumbar pedicles with cord compression
24) An out-of-shape, recently divorced, 42-year-old man is trying to impress a young woman by challenging her to a game of tennis. In the middle of the game, a loud "pop" (like a gunshot) is heard, and the man falls to the ground clutching his ankle. He limps off the court with pain and swelling in the back of the lower leg. Although he can still weakly plantar-flex his foot, he seeks medical help the next day because of persistent pain, swelling, and limping. He can put weight on that foot with no exacerbation of the pain, but the motion of taking a step is painful. Which of the following would be the most likely finding on physical examination?
. Tapping on the calcaneus is extremely painful
. There is crepitation and grating by direct palpation over either malleoli
. There is a gap in the Achilles tendon easily felt by palpation
. The ankle joint can be adducted farther in than the normal contralateral side
. The ankle joint can be abducted farther out than the normal contralateral side
25) A 27-year-old man sustained penetrating injuries of the chest and abdomen when he was repeatedly stabbed with a long ice-pick. At the time of admission, he had a right pneumothorax, for which a chest tube was placed prior to undergoing a general anesthetic for exploratory laparotomy. The operation revealed no intraabdominal injuries and was terminated sooner than had been anticipated. The patient remained intubated, waiting for the anesthetic to wear off. Because he was not moving enough air, he was placed on a respirator. Then, he suddenly went into cardiac arrest and died. All through this time he had been hemodynamically stable, and never had any signs of hypotension or arrhythmias. Which of the following was the most likely cause of the cardiac arrest?
. Air embolism
. Tension pneumothorax
. Pulmonary embolus
. Myocardial infarction
. Fat embolism
26) A 13-year-old, obese boy complains of persistent knee pain for several weeks. The family brings him in because he has been limping. He sits in the examining table with the sole of the foot on the affected side pointing to the other leg. Physical examination is normal for the knee, but shows limited hip motion. As the hip is flexed, the leg goes into external rotation and cannot be rotated internally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Avascular necrosis of the femoral head
. Tibial torsion with foot inversion
. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
. Osteogenic sarcoma of the lower femur
. Developmental dysplasia of the hip
27) A 72-year-old man comes in complaining of persistent and nagging low back pain that he has had for several weeks. The pain seems to be increasing in intensity, is worse at night, is unrelieved by rest or positional changes, and is not exacerbated by coughing, sneezing, or straining to have a bowel movement. He is a chronic smoker, and for the past 3 months has had persistent cough with occasional bloody streaked sputum, as well as a 20-pound weight loss. On physical examination, he is distinctly tender to palpation at a particular spot over his lower thoracic spine. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ankylosing spondylitis
. Primary malignant bone tumor
. Multiple myeloma
. Metastatic tumor to the thoracic spine
. Herniated disk
28) The unrestrained front-seat passenger in a car that crashed at high speed arrives at the emergency department with signs of moderate respiratory distress. Physical examination shows no breath sounds at all on the left hemithorax. Percussion is unremarkable, and his vital signs are normal. A chest x-ray film shows a collapsed left lung and multiple air-fluid levels filling the left pleural cavity. A nasogastric tube that had been placed prior to taking the film shows the tube reaching the upper abdomen and then curling up into the left chest. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Blow out of pulmonary blebs
. Major injury to the tracheobronchial tree
. Left diaphragmatic rupture
. Esophageal rupture or perforation
. Left hemopneumothorax
29) A 67-year-old man shows up in the emergency department because he has not been able to void for the past 12 hours. He feels the need to, but he cannot do it. He gives a history that, for several years now, he has been getting up four or five times a night to urinate. It would take him a considerable time to get the urinary stream going, and the stream lacked force and often ended in a dribble. Because of a cold, 2 days ago he began taking an antihistamine, taking a decongestant, and drinking plenty of fluids. Physical examination shows a palpable, smooth, round mass arising from the pubis and reaching about half way toward the umbilicus. The mass is dull to percussion, and pushing on it accentuates the feeling of needing to void. Rectal examination reveals a large, boggy, non-tender prostate gland without nodules. This a classic presentation for which of the following acute conditions?
. Bacterial prostatitis
. Urinary retention in a patient with prostatic cancer
. Urinary retention in a patient with benign prostatic hypertrophy
. Renal failure
. Cystitis in a patient with bladder cancer
30) Several months after sustaining a crushing injury to his arm, a patient complains bitterly about constant, burning, agonizing pain in that arm, that does not respond to the usual analgesic medications. The pain in his arm is aggravated by the slightest stimulation of the area, such as rubbing from the shirt sleeves. The arm is cold, cyanotic, and moist, but it is not swollen. Pulses at the wrist are normal, and neurologic function of the three major nerves is intact. Which of the following is most appropriate to provide diagnostic confirmation of the nature of the problem and eventual therapy?
. Angiogram and subclavian vein bypass
Sympathetic block and surgical sympathectomy
. Cervical spine x-rays and cervical rib resection
. Doppler studies and arterial reconstruction
. Doppler studies and fasciotomy
31) A 57-year-old alcoholic man is being treated for acute hemorrhagic pancreatitis. He was in the intensive care unit for 1 week, where he required chest tubes for pleural effusions and was on a respirator for several days. Eventually, he improved sufficiently to be transferred to the floor. Three days after leaving the unit, and about 2 weeks after the onset of the disease, he spikes a fever and develops leukocytosis. Which of the following developments do these recent findings most likely suggest?
. Chronic pancreatitis
. Subphrenic abscess
. Pelvic abscess
. Pancreatic pseudocyst
. Pancreatic abscess
32) A 33-year-old woman is involved in a high-speed automobile collision. She arrives at the emergency department gasping for breath. Her lips are cyanotic and she has flaring nostrils. There are bruises over both sides of the chest, and tenderness suggestive of multiple rib fractures. Her blood pressure is 60/45 mm Hg, pulse is 160/min and feeble and central venous pressure is 25 cm H2O. Her neck and forehead veins are distended. She is diaphoretic and has a hint of subcutaneous emphysema in the lower neck and upper chest. Her left hemithorax has no breath sounds and is hyper resonant to percussion. The trachea is deviated to the right, as are the heart sounds. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Air embolism from tracheobronchial injuries
. Tension pneumothorax caused by lung punctured by broken ribs
. Massive mediastinal bleeding from ruptured aorta
. Massive intrapleural bleeding from torn intercostal vessels
. Flail chest due to multiple rib fractures
33) A 32-year-old male is rushed to the emergency room after a motor vehicle accident. He was driving 55 mph when he suddenly lost control of his vehicle and hit a tree. He was wearing a seat belt. On physical examination, the patient appears scared and complains of moderate chest and abdominal discomfort. His voice is soft. His blood pressure is 190/ 100 mmHg and his heart rate is 100/min. The pupils are symmetric and reactive to light and the trachea is midline. You note bruising over the chest and upper abdomen. No penetrating injuries are evident. Which of the following injuries is most likely in this patient?
. Esophageal rupture
. Pulmonary contusion
. Aortic rupture
. Vagus nerve disruption
. Tracheobronchial disruption
34) A 23-year-old male is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident (MVA) where he was the unrestrained driver. The patient was found unresponsive at the scene and was intubated by paramedics. He receives 2.5L of normal saline over the 20 minutes before he reaches the ED. His blood pressure there is 70/30 mmHg and his heart rate is 120/min. On physical examination, he responds to strong vocal and tactile stimuli by opening his eyes. His pupils are equal and reactive to light. There are multiple bruises over the anterior chest and upper abdomen. His neck veins are flat, trachea is midline and extremities are cold. Cardiac monitoring shows sinus tachycardia. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current condition?
. Impaired myocardial contractility
. Loss of vascular tone
. Air embolism
. Loss of intravascular volume
. Ventricular filling restriction
35) A 33-year-old male falls while riding his bicycle in the park, and presents to the emergency department. Physical examination reveals upper abdominal bruises. His abdomen is non-distended, soft, and mildly tender in the epigastrium. Abdominal CT scan does not reveal any abnormalities. The patient is sent home with analgesic medications. He returns one week later with fever, shaking chills, poor appetite and deep abdominal pain Which of the following is most likely related to this patient's symptoms?
. Spleen rupture
. Meckel diverticulitis
. Small bowel necrosis
. Pancreatic laceration
. Stomach perforation
36) A 36-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with severe epigastric pain and right shoulder pain of about two hours duration. She also reports having one episode of emesis. When asked about her diet, she explains that she unintentionally fasted yesterday and had a large meal two hours ago. Her past medical history is significant for frequent heartburn for which she takes ranitidine. Several hours after presenting, the patient's pain resolves completely. Which of the following best explains this episode?
. Viscus distention
. Vascular obstruction
. Mucosal inflammation
. Peritoneal irritation
. Acid hypersecretion
37) A 74-year-old male is undergoing elective abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. He is given two units of packed red blood cells during the surgery. He develops fever and chills one hour after finishing the surgery and transfusion. He received one dose of prophylactic antibiotics before surgery. He had coronary bypass grafting two months ago. His temperature is 38.5C (101.3F), blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination shows a mildly tender wound; there is no redness. The lungs are clearto auscultation. He has a Foley catheter and right subclavian central venous access, each placed at the time of surgery. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his fever?
. Nosocomial pneumonia
. Catheter associated infection
. Urinary tract infection
. Transfusion reaction
. Drug fever
38) A 55-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of chronic pain in his buttock, hip and thigh muscles. The aching pain is present in both legs and usually is associated with walking. He has multiple medical problems and takes several medications. He has a 30 pack year smoking history. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 150/88 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. Examination shows decreased femoral, popliteal and dorsalis pedis pulses in both legs. Which of the following additional complaints is most likely in this patient?
. Snoring
. Impotence
. Ankle swelling
. Anorexia
. Headache
39) A 23-year-old male is brought to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. He was an unrestrained driver. He was found unresponsive at the scene of the accident, and was intubated by the paramedics. He has received 2L of normal saline over the last 20 minutes. His blood pressure is 80/40 mmHg, and heart rate is 120/min. He responds to strong vocal and tactile stimuli by opening his eyes. His pupils are equal and reactive to light. His neck veins are distended. There are multiple bruises involving the anterior chest and upper abdomen. His chest x-ray shows a small, left-sided pleural effusion and normal cardiac contours. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lung contusion
. Bronchial rupture
. Pericardial tamponade
. Esophageal rupture
. Aortic rupture
40) A 65-year-old male comes to the ER because of sudden onset severe pain in his right leg. He says he has never previously had pain in his leg and denies any recent trauma, fever or chills. He recently suffered an acute anterior wall myocardial infarction that resulted in cardiogenic shock and is currently undergoing cardiac rehabilitation. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min (regular) and respirations are 16/min. His lungs are clear to auscultation. His heart rate is regular with no murmurs. Below the knee the right leg is cool to touch and appears pale. The dorsalis pedis pulse is not palpable while the popliteal pulses are full. Pulses are normal in the contralateral extremity. Neurologic examination shows numbness over the dorsum of the leg and foot. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Nerve compression
. Arterial vasculitis
. Venous thrombosis
. Arterial embolism
. Arterial thrombosis
41) An 88-year-old male complains of severe right calf pain several hours after undergoing a right femoral artery embolectomy. He also complains of a burning sensation in his posterior right leg. He has a long history of atrial fibrillation and hypertension. His past medical history also includes stroke, bleeding duodenal ulcer, diabetes mellitus and diabetic nephropathy. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 160/70 mm Hg and his heart rate is 100 per minute and irregular. His right calf is swollen, tense and exquisitely tender; the pain is worsened by passive extension of the right knee. Dorsalis pedis and posterior tibial pulses are palpable in the bilateral lower extremities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Recurrent embolism
. Anaerobic infection
. Bone infarction
. Soft tissue swelling
. Venous thrombosis
42) A 62-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision where he suffered serious burns. On physical examination there are second degree burns covering both upper extremities and third degree burns over the anterior aspects of both lower extremities. On day three of his hospitalization, the patient develops tachycardia and decreased urine output. His blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, temperature is 95°F (35°C), and respirations are 26/min. Laboratory analysis reveals: Blood glucose 230 mg/dL, WBC 16,000/mm3, Platelets 80,000/mm3. Which of the following is the best explanation for this patient's current condition?
. Myocardial injury
. Renal glomerular injury
. Bacterial infection
. Immune reaction to heterologous proteins
. Extensive protein breakdown
43) A 36-year-old male presents with firm, non-tender swelling of his right cheek. He tells you that he had similar swelling at that site two years ago and was diagnosed with a tumor, which was subsequently removed without complication. Examination reveals fullness of the parapharyngeal space on the right side. Repeat surgery in this patient is most likely to result in which of the following complications?
. Hoarseness
. Jaw asymmetry
. Tongue palsy
. Facial droop
. Tic douloureux
44) A 43-year-old male complains of right shoulder pain and weakness after falling on his outstretched hands two days ago. He denies any swelling or shoulder deformity. You passively abduct both his arms above his head and then ask him to bring his arms down slowly in an adducting motion. The right arm drops rapidly at the midpoint of its descent. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Biceps tendon tear
. Humoral neck fracture
. Rotator cuff tear
. Lower brachial trunk injury
. Long thoracic nerve injury
45) A 32-year-old female presents with intermittent blood staining of her bra from her left breast. She has not felt any lumps on either breast. Physical examination shows no breast mass or axillary lymphadenopathy. Ultrasonogram of the breast is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Fibrocystic changes
. Hyperprolactinemia
. Ductal carcinoma in situ
. Intraductal papilloma
. Fibroadenoma
46) A 31-year-old male presents to your office with pain and swelling over his coccyx. He has never had symptoms like this before. His past medical history is significant for an appendectomy two years ago and acute pyelonephritis one year ago. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Perianal abscess
. Bowen's disease
. Suppurative hidradenitis
. Crohn's disease
. Pilonidal disease
47) An 18-year-old male comes to the physician's office because of dull aching and fullness of the scrotum. Examination shows soft testicular swelling; transillumination testing is negative. The scrotal swelling increases when the patient performs the Valsalva maneuver. The physical examination is otherwise unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Hypoalbuminemia
. Cystic dilations of the efferent ductules
. Testicular neoplasia
. Fluid in the tunica vaginalis
. Dilatation of pampiniform plexus
48) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He is in no distress and is admitted for observation. Two hours after admission, he develops tachypnea and tachycardia. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 110/66 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows bruises on the right side of the chest, but palpation of the ribs does not elicit pain or suspicion for rib fractures. Breath sounds are decreased on the right side. ABG on 6 liters of oxygen shows PO2 of 60 mm Hg, PCO2 of 32 mm Hg, and pH of 7.42. An x-ray film of the chest shows a patchy irregular alveolar infiltrate in the right middle and lower lobes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Adult respiratory distress syndrome
. Pulmonary contusion
. Hemothorax
. Fat embolism
. Aspiration pneumonia
49) A 31-year-old male is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision as an unrestrained passenger. He was given 3L of normal saline in the ambulance on his way to the hospital and has been receiving 5 L/min of oxygen by nasal cannula. He is agitated and moves all four extremities spontaneously. His blood pressure is 85/55 mmHg and his heart rate is 120/min. His respiratory rate is 30/min. His pupils are symmetric and reactive to light. His neck veins are flat and his trachea is shifted slightly to the right. Over the left hemithorax, breath sounds are absent and there is dullness to percussion. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely?
. Tension pneumothorax
. Diaphragmatic rupture
. Hemothorax
. Lung atelectasis
. Lung contusion
50) A 45-year-old policeman presents to your office complaining of tiredness and sleepiness. He says that his job seems tiring to him recently. It is difficult for him to get up in the morning and go to work. He goes to bed early because he feels tired and sleepy. Two months ago, he was investigating a case of massive murder. He slipped on the blood on the floor, fell and hit his head. He also describes recent abdominal pain that is constant and gnawing, interfering with his sleep. His appetite is poor, and he lost 15 pounds over the last month. Physical examination is significant only for tenderness and fullness in the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Duodenal ulcer
. Chronic subdural hematoma
. Post-traumatic stress disorder
. Pancreatic cancer
. Major depressive episode
51) A 54-year-old female with a 30 pack-year smoking history undergoes cholecystectomy after an episode of biliary pancreatitis. On the third postoperative day, she complains of discomfort in the upper abdomen. Though she is breathing comfortably, her oxygen saturation is 90%, compared with 98% yesterday. Her blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 20/min, and temperature is 98F (36C). Arterial blood gas analysis reveals the following: pH = 7.44, p02 =64 mmHg, pC02 =34 mmHg, which of the following most likely explains the observed findings?
. Aspiration of gastric secretions
. Ventilator-associated pneumonia
. Diaphragmatic paralysis
. Bronchial wall edema and bronchospasm
. Impaired cough and deep breathing
52) A 35-year-old male presents with complaints of muscle weakness and sensory loss in his upper extremities. His medical history is significant for involvement in a motor vehicle accident seven years ago in which he sustained a whiplash cervical spine injury. Physical examination today reveals moderate wasting of the small hand muscles and impaired pain and temperature sensation in the bilateral upper extremities. Light touch, vibration, and position senses are all intact. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
. Multiple sclerosis
. Intervertebral disk prolapse
. Cervical spondylosis
. Syringomyelia
53) A 45-year-old male presents to his physician with persistent nausea and vomiting of partially digested food for the past month. He has also lost 5 lbs of weight during this period of time. His appetite is good but he feels full after a few bites. His past medical history is significant for a one-year history of type 2 diabetes and a suicide attempt 6 months ago in which he ingested acid. He drinks alcohol and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. His temperature is 36.80C (98.20 F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 16/min. Mucous membranes are dry. Examination shows succussion splash on the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Diabetic gastroparesis
. Pyloric stricture
. Duodenal hematoma
. Duodenal carcinoma
. Esophageal stricture
54) A 34-year-old male undergoes successful laparotomy for a gun-shot wound. He received 5 units of packed red blood cells during the surgery. He has been receiving incentive spirometry and ampicillin/sulbactam. However, he developed a fever of 38.7C (101.7F) on the sixth postoperative day. His blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 97/min and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows an alert, pleasant male in no acute distress. The oropharynx is clear. The lungs and heart are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is soft and non-tender, and the wound has no discharge. He has a right femoral triple lumen catheter and Foley catheter in place. Extremities have no swelling or redness. Two days later, four bottles of blood cultures grew coagulase negative Staphylococcus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his fever?
. Urinary tract infection
. Neoplastic fever
. Cerebral hemorrhage
. Clostridium difficile infection
. Catheter associated infection
55) An overweight 12-year-old boy presents with left knee pain that has been going on intermittently for the past three months. Physical activity, especially stair climbing, exacerbates the pain. The boy's mother also points out that he has been limping recently. On physical examination, his anterior left hip is moderately tender to palpation, and when he is asked to stand on his left leg, the right half of his pelvis tilts downward. Which of the following best explains this finding?
. Tensor fascia lata weakness
. Gluteus muscle weakness
. Quadriceps muscle weakness
. Quadratus lumborum weakness
. Psoas muscle weakness
56) A 23-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 4-week history of a whistling noise during respiration. She underwent a difficult rhinoplasty a few months ago. The noise is getting louder and is annoying. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Nasal septal perforation
. Nasal furunculosis
. Allergic rhinitis
. Nasal foreign body
. Nasal polyp
57) A 46-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He is unresponsive. His injuries include a basilar skull fracture, brain contusion, fractures of ribs 7-10, hemopneumothorax on the right and a pelvic fracture. After placement of a chest tube and pelvis fixation, his condition stabilized. On the fifth day of his hospital stay, he is still unresponsive with a Glasgow Coma Scale of 8. He is breathing spontaneously. Examination shows an abnormal facial reaction to abdominal palpation. Pain appears to be elicited by palpation in right upper quadrant. Bowel sounds are diminished. Rectal examination shows no abnormalities. Nasogastric tube aspiration shows retention of gastric contents. An abdominal CT scan shows gaseous distention of the small and large bowels without airfluid levels. The gall bladder is distended and pericholecystic fluid is present. Stones are not seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bowel obstruction
. Lung contusion
. Mesenteric contusion
. Pancreatitis
. Cholecystitis
58) A 77-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department because of sudden-onset intense diffuse abdominal pain followed by vomiting. Her past medical history is significant for chronic uncontrolled hypertension, cerebrovascular accident, diabetes and hyperlipidemia. She takes multiple medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her temperature is 38.30 C (1010 F), blood pressure is 180/100 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and irregular and her respirations are 22/min. She is in severe distress. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdominal examination shows severe pain to palpation and nearly absent bowel sounds. There is rigidity and rebound. Rectal examination shows heme-positive stools. EKG shows absent P waves, irregular rhythm and inverted T waves. There are no previous EKGs for comparison. An x-ray film of the chest shows cardiomegaly. Laboratory studies show: Hematocrit 49%, Leukocyte count 77,500/mm3, Troponin I normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Myocardial infarction
. Acute cholecystitis
. Bowel infarction
. Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm
. Acute pancreatitis
59) A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He is unconscious. His blood pressure is 100/50 mm Hg, pulse is 100/min, and respirations are 19/min. Examination shows bilaterally reactive and non-dilated pupils. He does not follow commands and makes inappropriate sounds. A CT scan of the head shows numerous minute punctuate hemorrhages with blurring of the gray-white matter interface. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Epidural hematoma
. Multiple sclerosis
. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
. Diffuse axonal injury
. Subdural hematoma
60) A 65-year-old man with cervical spondylosis secondary to degenerative changes in the cervical spine was admitted after being involved in a motor vehicle accident. He regained consciousness after 5 minutes. After regaining consciousness, he had complete weakness in both upper extremities but was able to move his lower extremities. Vital signs are stable. Plain x-ray films of the cervical spine show no abnormalities except those consistent with mild degenerative changes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Brown-Sequard syndrome
. Anterior spinal cord syndrome
. Posterior spinal cord syndrome
. Cerebral contusion
. Central cord syndrome
61) A 54-year-old alcoholic man comes to the emergency department because of dysphagia, drooling and a fever. He has been sick for two days and has not been able to eat. His mouth is swollen and feels hot. Examination shows a pale, febrile man who is drooling. There is redness around the entire mouth extending into the floor of the mouth. A tender, symmetric and indurated swelling with palpable crepitus is present in the submandibular area. Laboratory study shows an elevated W BC count. Which of the following is the most likely source of the oral cavity infection?
. Blood
. Tonsils
. Teeth
. Parotid gland
. Lungs
62) A 69-year-old man is evaluated after undergoing an elective repair of a rapidly expanding abdominal aortic aneurysm. The surgical procedure was complicated by a significant amount of blood loss and required multiple transfusions. In the postoperative recovery room, he had weakness in both lower extremities and developed urinary retention. Neurologic examination shows spastic paraplegia and loss of pain sensation over the lower extremities; vibratory sensation is intact. Upper extremity examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely pathophysiologic mechanism of the neurologic dysfunction?
. Spinal cord ischemia
. Conversion disorder
. Mechanical damage to the peripheral nerves
. Mechanical damage of the spinal cord
. Hematoma compressing the spinal cord
63) A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a one-week history of increasing pain in the right leg. She is an active dancer and practices 4-5 hours a day. One week ago, she felt a dull aching pain in the right middle leg; the pain has been increasing since and is particularly bad when she dances. The pain is interfering with her dancing sessions. She is afebrile and her other vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows point tenderness over the midpoint of the right leg; there are no abnormalities of the skin overlying the tender point. Knee and ankle examinations show no abnormalities. An x-ray of the lower leg shows no abnormalities. ESR is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her pain?
. Ligamentous tear
. Bone neoplasm
. Nerve entrapment
. Bone infection
. Stress fracture
64) A 32-year-old male comes to the emergency department because of a 3 day history of increasing lower abdominal pain, mild diarrhea and rectal pain on defecation. Ten days ago he had right lower quadrant (RLQ) pain for about 24 hours that resolved spontaneously. Since then, he has had malaise and low-grade fever. His temperature is 38.70C (101.60F), blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows lower abdominal tenderness without rebound. No masses are palpable, and bowel sounds are decreased. Rectal examination shows a very tender, boggy and fluctuant bulging on palpation with the tip of the finger anteriorly. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 14.0 g/L, Platelets 270,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 15,500/mm3, His current condition is most likely a complication of?
. Anorectal abscess
. Colon cancer
. Acute diverticulitis
. Acute appendicitis
. Invasive diarrhea
65) A 70-year-old male rushed to the emergency department because of bright red bleeding per rectum. He says his commode is full of blood and has never experienced any bleeding before. He has a history of constipation. He takes daily aspirin for prevention of stroke and hydrochlorothiazide for high blood pressure. His temperature is 36.50C (97.80F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min and respirations are 20/min. He is not hypoxic. Abdomen is soft, non-distended and non-tender; no masses or organomegaly are palpated; bowel sounds are normal. Rectal examination shows bright red blood and an enlarged prostate. Nasogastric tube aspirate shows non-bilious stomach contents without blood. An x-ray of the abdomen shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his bleeding?
. Colon cancer
. Peptic ulcer disease
. Diverticulosis
. Mesenteric thrombosis
. Ischemic colitis
66) An 11-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department for evaluation of an injury from jumping off a 10 ft wall, 2 days ago. He had some pain in his feet immediately following the jump, but was able to walk. The past 2 days, he has had increasing pain in his right foot with walking. He has no pain at rest. He has some "crunching" in the right foot. Physical examination shows the foot appears normal with the exception of suffusion on the plantar surface. Passive motion of the second toe and passive dorsiflexion of the foot produces pain in the middle of the foot. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Fracture of second metatarsal
. Hematoma in middle plantar space
. Metatarsophalangeal joint dislocation
. Tenosynoviitis of toe flexors
. Stress fracture of second metatarsal
67) An 18-year-old woman at 9 weeks' gestation is brought to the emergency department because of an open fracture of the tibia and fibula. She is hemodynamically stabilized and referred to the orthopedic department. She is scheduled for internal fixation of the tibia for the following day. However, before the surgery she develops severe dyspnea and confusion. Her temperature is 37.70C (99.90F), blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows numerous non- palpable petechiae in the upper part of the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Air embolism
. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
. Fat embolism
. Thromboembolism
. Amniotic fluid embolism
68) A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-month history of an ulcer on the sole of his right foot. He has had no trauma and does not remember how he got the ulcer. He states the ulcer has been difficult to heal and readily gets infected. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Examination shows the ulcer is located on the sole of his foot just below the head of the first metatarsal bone. His foot is warm and dry and appears slightly deformed. Dorsalis pedis pulses are present. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Venous hypertension
. Posterior spinal cord lesion
. Central spinal cord lesion
. Peripheral neuropathy
. Arterial spasm
69) A 7-year-old child is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a highway motor vehicle collision. He had blunt trauma to his abdomen. Vital signs are stable, except for a respiratory rate of 30 per minute. Physical examination shows bruising of the upper abdomen, abdominal distention, and tenderness. He is in moderate respiratory distress; breath sounds are decreased on the left side. Chest tube placement shows no blood or air in the pleural cavity. An x-ray film of the chest shows an elevated left hemidiaphragm. Laboratory studies show hemoglobin and hematocrit within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Tension pneumothorax
. Diaphragmatic hernia
. Laceration of the liver
. Pulmonary contusion
. Hemothorax
70) A 25-year-old motorcyclist is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a collision with an automobile. On arrival he is in obvious pain. He expresses an urge to void, but is unable to do so. Genital examination shows blood at the urethral meatus and a scrotal hematoma. Rectal examination reveals a high riding prostate. Abdominal examination is suggestive of a distended bladder. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Urethral injury
. Renal injury
. Fracture of penis
. Extraperitoneal bladder injury
. Intraperitoneal bladder rupture
71) A 43-year-old mildly overweight female complains of periodic right knee swelling and pain with physical activity for the past three months. She says that this problem started while on a hiking trip three months ago, at which point she experienced a 'popping' sensation in her right knee. She recalls that her knee was swollen the next day, and responded to over-the-counter pain killers. Recently, she has been having to limit her physical activities due to knee pain. On physical examination, there is tenderness of the anterior and medial right knee joint. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anterior cruciate ligament tear
. Anserine bursitis
. Patellar tendonitis
. Osteoarthritis
. Meniscal tear
72) A 35-year-old black man is brought to the emergency department after a motorcycle accident. He hit the street with the side of his head. He was found unconscious when the emergency medical team arrived. However, on the way to the emergency department he regains consciousness. Upon arrival he is confused and complains of a headache. His temperature is 36.9C (98.5F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows a dilated pupil on the right side, with some weakness of the left arm and leg. CT scan of the head shows a biconvex hematoma on the right side of the head. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute subdural hematoma
. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
. Intracerebral bleeding
. Basilar fracture of skull
. Acute epidural hematoma
73) A 54-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 1 0 minutes after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. On arrival, he is breathing spontaneously, is non-cyanotic and has no signs of external injury. His temperature is 37C (98.6F), blood pressure is 104/50 mm Hg, pulse is 122/min and respirations are 16/min. Examination shows bilateral round and reactive pupils of 4 mm. He is making some incomprehensible sounds. He responds to his name by opening his eyes and on applying supraorbital pressure he extends his left extremity and grasps your hand with his right hand. What is the Glasgow coma scale (GCS) in this patient?
.6
. 14
. 12
. 10
.8
74) A four-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of discomfort in the left hip and left knee that is causing him to limp. Examination shows normal knee joints bilaterally, but there is marked limitation of internal rotation and abduction of the left hip. His temperature is 37.1 C (98.6F), blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. Laboratory studies including complete blood count and basic metabolic profile show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
. Developmental dysplasia of the hip
. Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
. Hematogenous osteomyelitis
. Septic arthritis of the hip joint
75) A 65-year-old male is being evaluated for hip pain. The pain has been present for several months and is constant. He denies any weight loss or loss of appetite. His past medical history is significant only for high blood pressure. His temperature is 37.2 C (98.9 F), blood pressure is 150/88 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 12/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show: Alkaline phosphatase Elevated, Gamma glutamyl, transferase Normal, Serum calcium Normal, 2,5 (OH)2 vitamin D Normal. Bone scan shows increased uptake in several spots. This patient is at high risk of developing?
. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
. Hearing loss
. Pulmonary hemorrhage
. Renal cell carcinoma
. Carpal tunnel syndrome
76) A 78-year-old diabetic man has undergone surgical repair of a large abdominal aortic aneurysm. Postoperatively, he develops left lower quadrant abdominal pain followed by bloody diarrhea. He has a history of prostate cancer and received radiation therapy several years ago. He eats a low fiber diet. He quit smoking recently. Vital signs show a low grade fever. Examination shows tenderness in the left lower quadrant and rectal examination reveals blood in the stool. CT scan of the abdomen demonstrates thickening of the colon at the rectosigmoid junction. On colonoscopy, ulcerations are seen in the same area while the colon above and below the lesions is completely normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Acute diverticulitis
. Lnflammatory bowel disease
. Ischemic colitis
. Clostridium difficile colitis
. Radiation proctitis
77) A 34-year-old man comes to the physician after being involved in a street fight. He has a painful and swollen left arm. Neurovascular examination shows no abnormalities. An x-ray film of the arm shows a fracture of the midshaft of the humerus. Closed reduction of the facture is done and the arm is kept in a hanging cast. One hour later he has numbness of the left wrist and marked limitation of extension at the wrist. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Radial nerve injury
. Median nerve injury
. Ulnar nerve injury
. Compartment syndrome
. Brachial artery injury
78) A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after he jumped from the fourth floor of a burning building. His temperature is 36.9C (98.5F), blood pressure is 90/40, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 20/min. Examination shows a fracture of the right tibia. He is conscious and his pupils are bilaterally equal and reactive to light and accommodation. His neurological examination shows paraplegia, with loss of pain and temperature in both legs but normal proprioception. Upper extremities do not show any neurological deficits. Passive straight leg raising test is negative. A CT scan of the spine shows a burst fracture at the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Central cord syndrome
. Cauda equine syndrome
. Acute disk prolapse
. Brown Sequard syndrome
. Anterior cord syndrome
79) A 32-year-old man comes to the emergency room (ER) because of acute onset left flank pain, hematuria and vomiting. His pain is relieved with ketorolac in the ER. He has a history of abdominal pain due to Crohn disease, but that pain was always in the rightlower quadrant and was never this severe. His temperature is 36.8C (98.2F), blood pressure is 120/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 16/min. Chest auscultation is clear. Abdomen is soft and mildly tender over the left flank. He has no rebound or rigidity. Bowel sounds are decreased. A laparotomy scar is present in right lower quadrant. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Increased recycling of bile salts and fatty acids
. Recurrent bacterial infection in the kidney
. Increased parathyroid hormone activity
. Increased absorption of calcium
. Increased absorption of oxalate
80) A 54-year-old man comes to the physician because of edema of his right ankle. He reports heaviness and cramping in the same leg that is worse after a long day at work. The swelling is usually reduced significantly when he wakes up in the morning and worsens progressively throughout the day. He denies any other symptoms. He has no significant medical problems except hypertension, for which he takes atenolol. His temperature is 36.7C (98F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. JVP is normal. Lungs are clearto auscultation. There are no murmurs. There is no hepatosplenomegaly. Examination shows edema of the right ankle. Doppler examination of the leg shows no evidence of thrombosis W hich of the following is the most likely cause of his edema?
. Lymphatic obstruction
. Venous valve incompetence
. Increased urinary loss of protein
. Reduced diastolic filling of the heart
. Impaired cardiac contraction
81) A 30-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of swelling and pain in the right knee. He first experienced pain when he twisted his leg while playing football 15 days ago. He felt something 'popping' in the knee at that time but ignored it. The pain and swelling has been increasing since, and he feels sudden pain with extension of his leg. Examination shows the right knee is swollen and tender along the medial side. Full extension of the right knee is not possible due to sudden pain during terminal extension. Snapping can be felt in the right knee on tibial torsion with the knee flexed at 90 degrees. An x-ray film of the knee joint shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anterior cruciate ligament injury
. Lateral collateral ligament tear
. Medial collateral ligament tear
. Medial meniscus tear
. Posterior cruciate ligament injury
82) A 46-year-old male is brought to the emergency department after falling on his head and back during a downhill bike race and losing consciousness for 1 minute. He has severe back and abdominal pain. AP and lateral skull films show no abnormalities. Lumbar films show anterior compression wedge fractures of the bodies of L1 and L2. A brace is placed. CT scan of the abdomen shows a mild retroperitoneal bleed and splenic laceration. During the hospitalization he was treated conservatively with analgesics and supportive measures. On hospital day 3, he started to have abdominal distention, pain and nausea. His last bowel movement was 4 days ago and he is not passing gas. His abdomen is distended, tympanic and mildly tender without rebound or guarding. Bowel sounds are absent. An x-ray film of the abdomen is shown below: Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Functional constipation
. Worsening hematoma
. Peritonitis
. Large bowel obstruction
. Paralytic ileus
83) A 55-year-old male Asian immigrant presents to the physician because of recent-onset neck swelling. He also notes having several episodes of epistaxis lately. He has not sustained any trauma to the neck or nose. His past medical history is significant for syphilis and recurrent bacterial sinusitis. He drinks 2 beers daily and has a 30-pack year smoking history. He takes daily multivitamins with antioxidants. On physical examination, you note a mass in the posterior nasal cavity. Biopsy shows undifferentiated carcinoma. Which of the following is a risk factor for this cancer?
. Alcohol use
. Vitamin supplements
. Viral infection
. Bacterial infection
. Spirochete infection
84) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after falling from a tree. Examination shows tenderness and swelling over the left lower arm. An x-ray film of the arm shows a fracture of the distal end of the humerus with proximal and posterior displacement of the distal fracture segment. Closed reduction of the fracture is performed. However, postoperatively the patient complains of increasing pain in the left arm and forearm. Twelve hours postoperatively his forearm is pale and cold. There is marked pain on passive extension of the fingers. Which of the following is the potential dreaded complication of this condition?
. Malunion with alteration of carrying angle
. Volkmann ischemic contracture
. Sudeck's atrophy
. Reflex sympathetic dystrophy
. Non-union
85) A 7-year-old boy has been complaining of left hip pain for the past 8 months. Over recent weeks, he has developed a limp. When you examine his gait, you note that he takes short steps with his left leg. On physical examination, his left hip has significantly limited range of motion, and there is atrophy of the left proximal thigh muscle. X-ray of the patient's pelvis is shown below: W hich of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's condition?
. Slipped epiphysis
. Synovitis
. Muscle dystrophy
. Osteonecrosis
. Bone infection
86) A 73-year-old man comes to the physician because of right anterior thigh pain that is worse with walking. He has a history of stable angina, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and COPD with periodic exacerbations. He takes ipratropium, aspirin, metoprolol and pravastatin. He smokes 2 packs a day and drinks alcohol occasionally. Physical examination shows a small pulsatile mass in the right groin area. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Femoral vein aneurysm
. Femoral hernia
. Direct inguinal hernia
. Indirect inguinal hernia
. Femoral artery aneurysm
87) A 72-year-old man underwent surgical repair of an aneurysm of the infrarenal aorta. He received perioperative prophylaxis with a second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic. On the first postoperative day he complains of progressive abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. His temperature is 38.5C (101F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 22/min. His abdomen is mildly distended and tender to palpation. The tenderness is mostly in the left lower quadrant without rebound. Femoral pulses are full and symmetric. His white blood cell count is 12,000/mm3. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pseudomembranous colitis
. Perforation of the colon
. Ischemia of the bowel
. Aortoenteric fistula
. Invasive infectious diarrhea
88) A 51-year-old male with a history of alcoholic pancreatitis presented to the hospital because of sudden onset severe retrosternal and upper abdominal pain. He has been vomiting for the past few hours after consuming alcohol. His temperature is 38.1C (100.9F), blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 120/min and respirations are 30/min. Examination shows palpable crepitus in the suprasternal notch. Lungs are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is tender to palpation mostly in the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
. Spontaneous pneumothorax
. Mallory-Weiss tear
. Esophageal perforation
. Perforated duodenal ulcer
. Acute pancreatitis
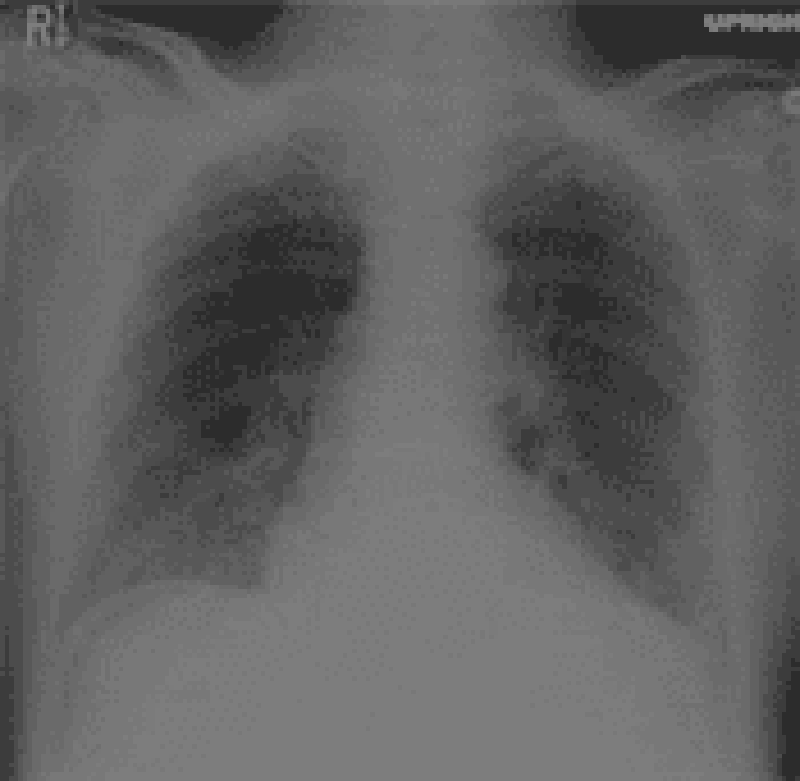
89) A 53-year-old male comes to the emergency department complaining of sudden onset intense, stabbing epigastric pain. He also vomited once and a dull, aching pain then spread through his entire abdomen. He has had nonspecific epigastric pain for several months and saw a physician one month ago. He also has a history of constipation, type II diabetes mellitus and hyperlipidemia. He has smoked one and a half packs of cigarettes daily for 26 years. He drinks 4 oz of alcohol daily. His temperature is 38.3C (100.4F), blood pressure is 160/95 mm Hg, pulse is 100/min and respirations are 26/min. The entire abdomen is tender to palpation with rebound, but there is no guarding. No masses are palpable, and Murphy's sign elicits mild pain. Rectal examination shows no abnormalities. Abdominal ultrasound performed 2 weeks ago showed stones in the gall bladder. Upright chest x-ray is shown below: Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Acute cholecystitis
. Perforated diverticulitis
. Perforated peptic ulcer
. Acute gallstone pancreatitis
. Acute alcoholic pancreatitis
90) ) A 39-year-old paleontologist complains of right-sided hip pain that makes it very difficult for him to lay on his right side while sleeping. He localizes the pain to the outer surface of his thigh. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his pain?
. Slipped femoral epiphysis
. Hip osteoarthritis
. Trochanteric bursitis
. Peripheral vascular disease
. Paget's disease
91) A 34-year-old male is involved in a high-speed highway motor vehicle collision. He is intubated by rescue workers at the accident scene. In the emergency department, the patient has decreased breath sounds on the right side, normal breath sounds on the left, and hypotension. A right-sided chest tube is placed. Physical examination reveals multiple bruises over the entire chest wall as well as subcutaneous emphysema. A few hours later, his chest x-ray shows an accumulation of air in the pleural space as well as pneumomediastinum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Myocardial contusion
. Diaphragmatic rupture
. Esophageal rupture
. Myocardial rupture
. Bronchial rupture
92) A 22-year-old primigravida woman at 33 weeks gestation is brought to the emergency department after a tonic clonic seizure. On arrival, she also has visual disturbances and a headache. She is given magnesium sulfate and hydralazine. She soon regains consciousness but cannot move her right arm; however, she can move her fingers. Her temperature is 37.2C (99F), blood pressure is 160/100 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 20/min. Examination shows her arm extended along the chest and internally rotated. There is no sensory loss on the arm, but there is an inability to externally rotate the shoulder. Deep tendon reflexes (DTR) are intact. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her inability to move her hand?
. Todd's paralysis
. Dislocation of acromioclavicular joint
. Posterior dislocation of shoulder joint
. Anterior dislocation of shoulder joint
. Magnesium toxicity
93) A 15-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 15-day history of painful swelling of the right knee. The swelling and redness were immediate after hitting his knee on the door, but have not subsided after 15 days of ibuprofen. He states the pain is increasing. He has no other complaints. His temperature is 37.1C (98.9F), blood pressure is 110/75 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 22/min. Laboratory studies show a normal ESR and elevated serum alkaline phosphatase. Examination shows the skin is warm and non-tender. An x-ray film of the femur and the knee joint shows an osteolytic lesion of the distal femur along with periosteal inflammation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Osteosarcoma
. Septic arthritis
. Osteoclastoma
. Chronic osteomyelitis
. Ewing's sarcoma
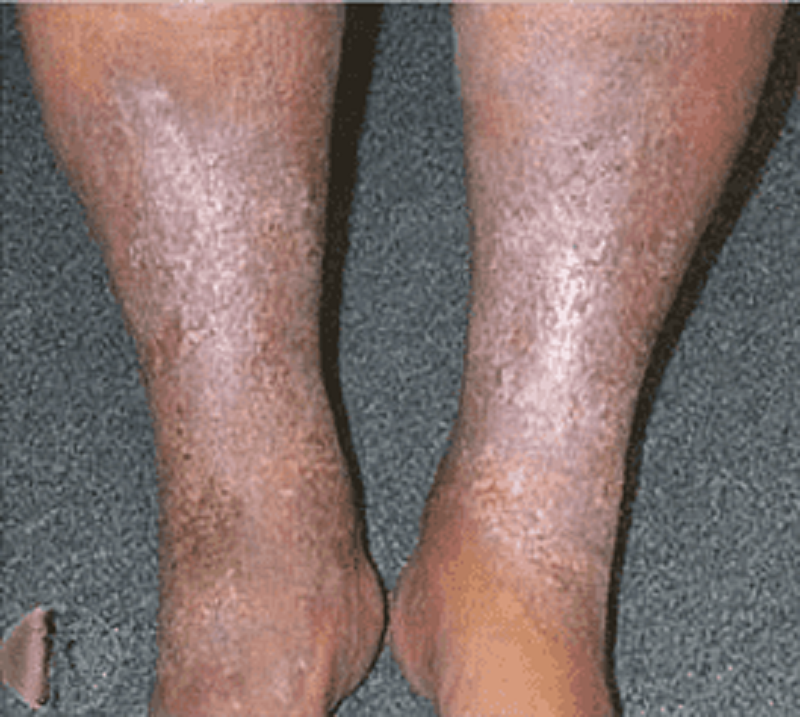
94) A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of chronic leg problems. He has had multiple medical problems and is unable to get good medical care due to lack of insurance. A photograph of his legs is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Arterial thrombosis
. Posterior spinal cord lesion
. Peripheral neuropathy
. Venous hypertension
. Arterial spasm
95) A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after he jumped from the fourth floor of a burning building. His temperature is 36.9° C (98.5° F), blood pressure is 90/40, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 20/min. Examination shows a fracture of the right tibia. He is conscious and his pupils are bilaterally equal and reactive to light and accommodation. His neurological examination shows paraplegia, with loss of pain and temperature in both legs but normal proprioception. Upper extremities do not show any neurological deficits. Passive straight leg raising test is negative. A CT scan of the spine shows a burst fracture at the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Central cord syndrome
. Cauda equine syndrome
. Acute disk prolapse
. Brown Sequard syndrome
. Anterior cord syndrome
96) A 30-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of swelling and pain in the right knee. He first experienced pain when he twisted his leg while playing football 15 days ago. He felt something popping' in the knee at that time but ignored it. The pain and swelling has been increasing since, and he feels sudden pain with extension of his leg. Examination shov1s the right knee is swollen and tender along the medial side. Full extension of the right knee is not possible due to sudden pain during terminal extension. Snapping can be felt in the right knee on tibial torsion with the knee flexed at 90 degrees. An x-ray film of the knee joint shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anterior cruciate ligament injury
. Lateral collateral ligament tear
. Medial collateral ligament tear
. Medial meniscus tear
. Posterior cruciate ligament injury
97) A 25-year-old male is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident in which he was the unrestrained driver. The emergency response team's reports indicate that his breath smelled of alcohol at the scene. En route to the hospital, the patient receives 2 liters of intravenous normal saline, and in the ED his blood pressure is 100/60 mmHg, heart rate is 120/min, and respiratory rate is 34/min. His neck veins are flat. You note multiple bruises overlying his anterior chest wall and upper abdomen. On inspiration, there is inward motion of the right side of his chest wall. His abdomen is soft and non-distended. He is put on positive pressure mechanical ventilation and his chest movements become symmetric. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Tracheobronchial disruption
. Air embolism
. Pneumothorax
. Flail chest
. Esophageal rupture
98) A 56-year-old woman is referred to you about 3 months after a colostomy subsequent to a sigmoid resection for cancer. She complains that her stoma is not functioning properly. Which of the following is the most common serious complication of an end colostomy?
. Bleeding
. Stomal prolapse
. Colonic perforation during irrigation
. Parastomal hernia
. Skin breakdown
99) A 22-year-old college student notices a bulge in his right groin. It is accentuated with coughing, but is easily reducible. Which of the following hernias follows the path of the spermatic cord within the cremaster muscle?
. Femoral
. Interparietal
. Spigelian
. Indirect inguinal
. Direct inguinal
100) An 80-year-old man with history of symptomatic cholelithiasis presents with signs and symptoms of a small-bowel obstruction. Which of the following findings would provide the most help in ascertaining the diagnosis?
. Coffee-grounds aspirate from the stomach
. A palpable mass in the pelvis
. A leukocyte count of 40,000/mL
. A pH of 7.5, PCO2 of 50 kPa, and paradoxically acid urine
. Pneumobilia
101) A 42-year-old man has bouts of intermittent crampy abdominal pain and rectal bleeding. Colonoscopy is performed and demonstrates multiple hamartomatous polyps. The patient is successfully treated by removing as many polyps as possible with the aid of intraoperative endoscopy and polypectomy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ulcerative colitis
. Crohn colitis
. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
. Familial polyposis
. Villous adenomas
102) A 35-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after a motorcycle accident. He is unconscious when the emergency medical team arrived. He regains consciousness on the way to the emergency department. Upon arrival, he is mildly confused and complains of headache and nausea. His temperature is 36.9° C (98.5° F), blood pressure is 102/60 mm Hg, pulse is 116/min, and respirations are 22/min. Pupils are equal and reactive to light. He moves all extremities on command, and deep tendon reflexes are symmetric. Head CT scan shows: Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute epidural hematoma
. Intracerebral bleeding
. Diffuse axonal injury
. Concussion
. Acute subdural hematoma
103) An 18-year-old woman at 9 weeks' gestation is brought to the emergency department because of an open fracture of the tibia and fibula. She is hemodynamically stabilized and referred to the orthopedic department. She is scheduled for internal fixation of the tibia for the following day. However, before the surgery she develops severe dyspnea and confusion. Her temperature is 37.7° C (99.9° F), blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, pulse is 11 O/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows numerous non-palpable petechiae in the upper part of the body. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Air embolism
. Acute respiratory distress syndrome
. Fat embolism
. Thromboembolism
. Amniotic fluid embolism
104) A 46-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after a fall during a downhill bike race. He lost consciousness for approximately 1 minute after the fall. He complains of severe back and abdominal pain. He has no other medical problems. Head computed tomography (CT) scan shows no intracranial bleeding. Lumbar films suggest a compression wedge fracture of the body of L2 vertebra, and a brace is placed. Abdominal CT scan shows a small retroperitoneal bleed and splenic laceration. He is conservatively treated with analgesics and supportive measures. On hospital day three, he complains of abdominal pain and nausea. His abdomen is distended, tympanic, and mildly tender, without rebound or guarding. Bowel sounds are absent. X-ray of the abdomen reveals. Which is the most likely diagnosis?
. Erosive gastritis
. Paralytic ileus
. Mesenteric ischemia
. Colonic pseudoobstruction
. Expanding retroperitoneal hematoma
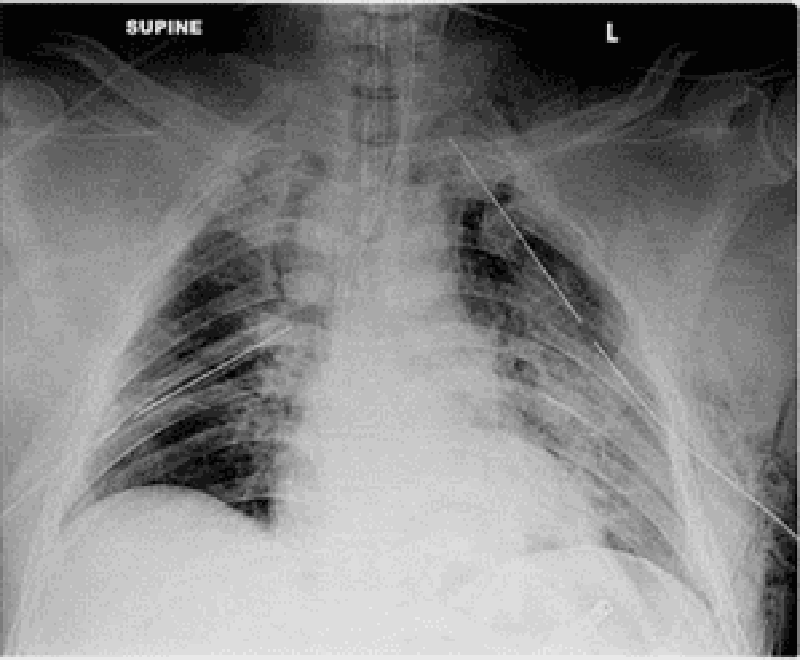
105) A 22-year-old man who was involved in a motor vehicle accident undergoes intravenous fluid resuscitation with 2 L normal saline over 20 minutes. He is in respiratory distress, with a respiratory rate of 40/min. He receives bilateral chest tubes. Endotracheal intubation is performed and mechanical ventilation is initiated due to progressive respiratory failure. His blood pressure is 92/50 mm Hg and pulse is 121/min. The patient is responsive to painful stimuli only. Pulmonary examination shows coarse breath sounds bilaterally. The chest x-ray is shown below. Which of the following most likely contributed to this patient's progressive respiratory failure?
. Diaphragmatic tear
. Tension pneumothorax
. Pulmonary edema
. Flail chest
. Esophageal rupture
106) A 48-year-old woman develops pain in the right lower quadrant while playing tennis. The pain progresses and the patient presents to the emergency room later that day with a low-grade fever, a WBC count of 13,000/mm3 and complaints of anorexia and nausea as well as persistent, sharp pain of the right lower quadrant. On examination, she is tender in the right lower quadrant with muscular spasm, and there is a suggestion of a mass effect. An ultrasound is ordered and shows an apparent mass in the abdominal wall. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute appendicitis
. Cholecystitis
. Torsion of an ovarian cyst
. Hematoma of the rectus sheath
. Cecal carcinoma
107) A 22-year-old woman presents with a painful fluctuant mass in the midline between the gluteal folds. She denies pain on rectal examination. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pilonidal abscess
. Anal fissure
. Fistula-in-ano
. Perirectal abscess
. Perianal abscess
108) A 62-year-old man has been diagnosed by endoscopic biopsy as having a sigmoid colon cancer. He is otherwise healthy and presents to your office for preoperative consultation. He asks a number of questions regarding removal of a portion of his colon. Which of the following is most likely to occur after a colon resection?
. The majority (> 50%) of normally formed feces will comprise solid material.
. The remaining colon will absorb long-chain fatty acids that result from bacterial breakdown of lipids.
. The remaining colon will absorb less water.
. Sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate will be absorbed by the colonic epithelium by an active transport process.
. Patients who undergo major colon resections suffer little long-term change in their bowel habits following operation.
109) A 40-year-old female is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident in which she was the front seat passenger. She reports hitting her head against the windshield and hurting her right leg. She appears completely alert and oriented. Glasgow Coma Scale =15/15. Her pupils are equal and reactive to light. There is a bruise over the right forehead, but no tenderness is present on palpation of the cranial bones. Examination of the right leg reveals a hematoma over the thigh. Knee extension on the right is markedly reduced when compared to the left. Sensory examination reveals decreased sensory perception to both sharp and dull stimuli over the medial side of the right lower thigh and leg. All other dermatomes are intact. What nerve injury is most likely present in this patient?
. Femoral nerve
. Fibular nerve
. Common peroneal nerve
. Obturator nerve
. Tibial nerve
110) A 28-year-old woman who is 15 weeks pregnant has new onset of nausea, vomiting, and right sided abdominal pain. She has been free of nausea since early in her first trimester. The pain has become worse over the past 6 hours. Which of the following is the most common non-obstetric surgical disease of the abdomen during pregnancy?
. Appendicitis
. Acute fatty liver of pregnancy
. Intestinal obstruction
. Pancreatitis
. Cholecystitis
111) A 30-year-old female patient who presents with diarrhea and abdominal discomfort is found at colonoscopy to have colitis confined to the transverse and descending colon. A biopsy is performed. Which of the following is a finding consistent with this patient’s diagnosis?
. The inflammatory process is confined to the mucosa and submucosa.
. Microabscesses within crypts are common.
. Superficial as opposed to linear ulcerations can be expected.
. Noncaseating granulomas can be expected in up to 50% of patients.
. The inflammatory reaction is likely to be continuous.
112) A 62-year-old man presents with a 3-month history of an enlarged lymph node in the left neck. He is a long-time smoker of cigarettes and denies fevers, night sweats, fatigue, or cough. On physical examination there is a 1.5 cm hard, fixed mass below the angle of the mandible in the left neck. Which of the following is the most likely cause of an enlarged lymph node in the neck?
. Thyroglossal duct cyst
. Branchial cleft cyst
. Carotid body tumor
. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
. Dermoid tumor
113) A 43-year-old mildly overweight female complains of periodic right knee swelling and pain with physical activity for the past three months. She says that this problem started while on a hiking trip three months ago, at which point she experienced a 'popping' sensation in her right knee. She recalls that her knee was swollen the next day, and responded to over-the-counter pain killers. Recently, she has had to limit her physical activities due to knee pain. On physical examination, there is tenderness of the anterior and medial right knee joint. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anterior cruciate ligament tear
. Anserine bursitis
. Patellar tendonitis
. Osteoarthritis
. Meniscal tear
114) A 53-year-old male is brought to the emergency room after a high-speed motor vehicle accident. He was an unrestrained driver and admits to consuming a moderate amount of alcohol before driving. In the ER, he complains of bilateral chest pain and left leg pain. His past medical history is significant for emphysema, diabetes mellitus and remote drug abuse. A traumatic fracture of the left femur is evident on physical examination. His initial arterial blood gas analysis shows a pH of 7.45, p02 of 81 mmHg and pC02 of 32 mmHg. His pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is 1OmmHg. After a 2000 ml IV fluid challenge, his p02 is 76 mmHg and his pulmonary capillary wedge pressure is 12 mmHg. Chest x-ray shows alveolar opacities over the right and left lower lobes. Hours after the accident, he complains of continued chest pain and shortness of breath. Which of the following diagnoses is most likely responsible for his shortness of breath?
. Aspiration pneumonia
. Aortic rupture
. Myocardial contusion
. Pulmonary contusion
. Hemothorax
115) A 23-year-old woman comes to the physician because of right-sided foot pain. The pain started 5 weeks ago and is sharp and localized to the forefoot. She recalls no trauma or other inciting event but is an avid runner training for a long-distance race. The pain has been worsening over the past 1 week and prevents her from doing her daily running activities. She takes no medications. She is a vegetarian and does not drink soda. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. She is not sexually active, and her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min, and respirations are 12/min. Her body mass index is 15 kg/m2. Examination reveals tenderness to palpation along the first four metatarsal bones on the dorsal surface of the right foot, normal range of motion, and no erythema or bruising. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Morton neuroma
. Tenosynovitis
. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
. Stress fracture
. Plantar fasciitis
116) An ultrasound is performed on a patient with right upper quadrant pain. It demonstrates a large gallstone in the cystic duct but also a polypoid mass in the fundus. Which of the following is an indication for cholecystectomy for a polypoid gallbladder lesion?
. Presence of clinical symptoms
. Absence of shadowing on ultrasound
. Presence of multiple small lesions
. Patient age of older than 25 years
. Size greater than 0.5 cm
117) An alcoholic man has been suffering excruciating pain from chronic pancreatitis recalcitrant to analgesics and splanchnic block. A surgeon recommends total pancreatectomy. A patient who has a total pancreatectomy might be expected to develop which of the following complications?
. Diabetes mellitus and steatorrhea
. Hypoglycemia and constipation
. Hypoglycemia and steatorrhea
. Hypoglycemia
. Diabetes mellitus and constipation
118) A 36-year-old man who was hit by a car presents to the ER with hypotension. On examination, he has tenderness and bruising over his left lateral chest below the nipple. An ultrasound examination is performed and reveals free fluid in the abdomen. What is the most likely organ to have been injured in this patient?
. Liver
. Pancreas
. Intestine
. Spleen
. Kidney
119) A 30-year-old man is stabbed in the arm. There is no evidence of vascular injury, but he cannot flex his three radial digits. Which of the following structures has he most likely injured?
. Flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitus medius tendons
. Ulnar nerve
. Thenar and digital nerves at the wrist
. Median nerve
. Radial nerve
120) A 70-year-old man presents to the ER with several fractures and a ruptured spleen after falling 20 ft. Which of the following will occur in response to the injury?
. Decreased liver gluconeogenesis
. Decreased glutamine consumption by fibroblasts, lymphocytes, and intestinal epithelial cells
. Hepatic synthesis of acute-phase reactants
. Decreased urinary nitrogen loss
. Inhibition of skeletal muscle breakdown by interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachectin)
121) A 62-year-old woman is seen after a 3-day history of fever, abdominal pain, nausea, and anorexia. She has not urinated for 24 hours. She has a history of previous abdominal surgery for inflammatory bowel disease. Her blood pressure is 85/64 mm Hg, and her pulse is 136. Her response to this physiologic state includes which of the following?
. Increase in sodium and water excretion
. Hypoglycemia
. Hyperkalemia
. Decrease in cortisol levels
. Increase in renal perfusion
122) A 46-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle collision. He is unresponsive and his injuries include a basilar skull fracture, brain contusion, fractures of ribs 7-10, hemopneumothorax on the right, and a pelvic fracture. After placement of a chest tube and pelvis fixation, his condition stabilizes. On the fifth day of his hospital stay, he is still unresponsive with a Glasgow Coma Scale of 8 and spontaneous respirations. Examination shows an abnormal facial reaction with palpation of the right upper quadrant of the abdomen and diminished bowel sounds. Rectal examination shows no abnormalities. Nasogastric tube aspiration shows retention of gastric contents. An abdominal CT scan shows gaseous distention of the small and large bowels without air-fluid levels. The gall bladder is distended with pericholecystic fluid but no gallstones. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis for this patient's abdominal findings?
. Bowel obstruction
. Lung contusion
. Mesenteric ischemia
. Pancreatitis
. Cholecystitis
123) An 18-year-old woman presents with abdominal pain, fever, and leukocytosis. With the presumptive diagnosis of appendicitis, a right lower quadrant (McBurney) incision is made and a lesion 60 cm proximal to the ileocecal valve is identified (see photo). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Intestinal duplication
. “Christmas tree” type of ileal atresia
. Ileoileal intussusception
. Meckel diverticulum
. Mesenteric cyst
124) A newborn infant born from a mother with polyhydramnios presents with excessive salivation along with coughing and choking with the first oral feeding. An xray of the abdomen shows gas in stomach and a nasogastric tube coiled in the esophagus. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Esophageal atresia
. Gastroschisis
. Omphalocele
. Esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF)
. Tracheoesophageal fistula
125) A 2-week-old infant presents with sudden onset of bilious emesis. Plain films of the abdomen show evidence of an intestinal obstruction. An upper gastrointestinal (UGI) contrast series reveals a midgut volvulus with the site of obstruction at the third portion of the duodenum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)
. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
. Anomalies of intestinal rotation and fixation
. Hirschsprung disease
. Intussusception
126) A 65-year-old woman is involved in a motor vehicle collision and sustains multiple left-sided rib fractures. Upon presentation to the ER her vital signs are stable and she is in no respiratory distress. Chest x-ray reveals fractures of ribs 4 to 7 on the left side without evidence of hemothorax or pneumothorax. She is admitted for observation and a few hours later she develops shortness of breath. A repeat chest x-ray demonstrates a well-defined infiltrate in her left lung. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Pulmonary contusion
. Cardiac tamponade
. Myocardial infarction
. Pneumonia
. Pulmonary embolus
127) Following a head-on motor vehicle collision, a 21-year-old unrestrained passenger presents to the ER with dyspnea and respiratory distress. She is intubated and physical examination reveals subcutaneous emphysema and decreased breath sounds. Chest x-ray reveals cervical emphysema, pneumomediastinum, and a right-sided pneumothorax. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Tension pneumothorax
. Pulmonary contusion
. Esophageal injury
. Tracheobronchial injury
. Open pneumothorax
128) A 35-week-term infant presents with cyanosis shortly after birth. His arterial oxygen saturation is only 30%. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Patent ductus arteriosus
. Transposition of the great vessels
. Ventricular septal defect
. Atrial septal defect
. Coarctation of the aorta
129) A 22-year-old primi-gravida woman is brought to the emergency department during the 33rd week of pregnancy after a tonic-clonic seizure. She has no history of seizure disorder and has not had any complications during her pregnancy. She is given magnesium sulfate and hydralazine. One hour later, she is lethargic and complains of persistent blurry vision and headache. She also complains of muscle pain, sore joints, and inability to move her right arm. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), blood pressure is 182/111 mm Hg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 16/min. She holds her right arm adducted and internally rotated. Examination shows no sensory loss but an inability to externally rotate the right arm. Deep tendon reflexes (DTRs) are intact bilaterally, and handgrip is preserved on both sides. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her arm weakness?
. Anterior shoulder dislocation
. Radial nerve compression
. Posterior shoulder dislocation
. Postictal (Todd) paralysis
. Magnesium toxicity
130) A 78-year-old diabetic man has undergone surgical repair of a large abdominal aortic aneurysm. Postoperatively, he develops left lower quadrant abdominal pain followed by bloody diarrhea. He has a history of prostate cancer and received radiation therapy several years ago. He eats a low fiber diet. He quit smoking recently. Vital signs show a low grade fever. Examination shows tenderness in the left lower quadrant and rectal examination reveals blood in the stool. CT scan of the abdomen demonstrates thickening of the colon at the recto-sigmoid junction. On colonoscopy, ulcerations are seen in the same area while the colon above and below the lesions is completely normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Acute diverticulitis
. Inflammatory bowel disease
. Ischemic colitis
. Clostridium difficile colitis
. Radiation proctitis
131) A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-month history of an ulcer on the sole of his right foot. He has had no trauma and does not remember how he got the ulcer. He states the ulcer has been difficult to heal and readily gets infected. He has multiple medical problems. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Examination shows the ulcer is located on the sole of his foot just below the head of the first metatarsal bone. His foot is warm and dry and appears slightly deformed. Dorsalis pedis pulses are present. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Venous hypertension
. Posterior spinal cord lesion
. Central spinal cord lesion
. Peripheral neuropathy
. Arterial spasm
132) A 43-year-old male complains of right shoulder pain and weakness after falling on his outstretched hands two days ago. He denies shoulder deformity. The physician passively abducts both his arms above his head and then asks him to bring his arms down slowly in an adducting motion. The right arm drops rapidly at the midpoint of its descent. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Biceps tendon tear
. Humeral neck fracture
. Rotator cuff tear
. Lower brachial trunk injury
. Long thoracic nerve injury
133) A 45-year-old policeman presents to your office complaining of tiredness and sleepiness. He says that his job seems tiring to him recently. It is difficult for him to get up in the morning and go to work. He goes to bed early because he feels tired and sleepy. Two months ago, he was investigating a case of mass murder. He slipped on the blood on the floor, fell and hit his head. He also describes recent abdominal pain that is constant and gnawing, interfering with his sleep. His appetite is poor, and he lost 15 pounds over the last month. Physical examination is significant only for tenderness and fullness in the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Duodenal ulcer
. Chronic subdural hematoma
. Post-traumatic stress disorder
. Pancreatic cancer
. Major depressive episode
134) A 32-year-old man comes to the emergency room (ER) because of acute onset left flank pain, hematuria and vomiting. His pain is relieved with analgesics in the ER. He has a history of abdominal pain due to Crohn disease, but that pain was always in the right lower quadrant and was never this severe. His temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F), blood pressure is 120/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 16/min. Chest auscultation is clear. Abdomen is soft and mildly tender over the left flank. He has no rebound or rigidity. Bowel sounds are decreased. A laparotomy scar is present in right lower quadrant. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Increased recycling of bile salts and fatty acids
. Recurrent bacterial infection in the kidney
. Increased parathyroid hormone activity
. Increased absorption of calcium
. Increased absorption of oxalate
135) A 36-year-old male presents with firm, non-tender swelling of his right cheek. He tells you that he had similar swelling at that site two years ago and was diagnosed with a tumor, which was subsequently removed without complication. Examination reveals fullness of the pre-auricular space on the right side. Repeat surgery in this patient is most likely to result in which of the following complications?
. Hoarseness
. Jaw asymmetry
. Tongue palsy
. Facial droop
. Tic douloureux
136) A 39-year-old paleontologist complains of right-sided hip pain that makes it very difficult for him to lie on his right side while sleeping. He localizes the pain to the outer surface of his thigh. He was recently diagnosed with hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes hydrochlorothiazide and atorvastatin. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 15 years. He does not use alcohol or illicit drugs. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his pain?
. Slipped femoral epiphysis
. Hip osteoarthritis
. Trochanteric bursitis
. Peripheral vascular disease
. Paget's disease
137) A 65-year-old male is being evaluated for hip pain. The pain has been present for several months and is constant. He denies any weight loss or loss of appetite. His past medical history is significant only for high blood pressure. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), blood pressure is 150/88 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 12/min. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show: Alkaline phosphatase Elevated, Gamma glutamyl transferase Normal, Serum calcium Normal, 25, (OH)2 vitamin D Normal. Bone scan shows increased uptake in several spots. This patient is at the highest risk of developing?
. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
. Hearing loss
. Pulmonary hemorrhage
. Renal cell carcinoma
. Carpal tunnel syndrome
138) A 25-year-old motorcyclist is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a collision with an automobile. On arrival he is in obvious pain. He expresses an urge to void, but is unable to do so. Genital examination shows blood at the urethral meatus and a scrotal hematoma. Rectal examination reveals a high-riding prostate. Abdominal examination is suggestive of a distended bladder. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Urethral injury
. Renal injury
. Fracture of penis
. Extraperitoneal bladder injury
. Intraperitoneal bladder rupture
{"name":"Q1", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1) A 48-year-old woman develops constipation postoperatively and self-medicates with milk of magnesia. She presents to clinic, at which time her serum electrolytes are checked, and she is noted to have an elevated serum magnesium level. Which of the following represents the earliest clinical indication of hypermagnesemia?, 2) A football player is tackled, and he develops severe knee swelling and pain. On physical examination with the knee flexed at 90 degrees, the leg can be pulled anteriorly, like a drawer being opened. A similar finding can be elicited with the knee flexed at 20 degrees by grasping the thigh with one hand, and pulling the leg with the other. Which of the following is the most likely injured structure?, 3) A 45-year-old woman with Crohn disease and a small intestinal fistula develops tetany during the second week of parenteral nutrition. The laboratory findings include: Na: 135 mEq\/LK: 3.2 mEq\/LCl: 103 mEq\/LHCO3: 25 mEq\/LCa: 8.2 mEq\/LMg: 1.2 mEq\/LPO4: 2.4 mEq\/LAlbumin: 2.4An arterial blood gas sample reveals a pH of 7.42, PCO2 of 38 mm Hg, and PO2 of 84 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s tetany?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/11-507181/123.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Which Ezel Are You?
13622
Groups Comms
320
Tool Name Practice
9418
Latihan KB 2 - Perbandingan Berbalik Nilai
520
What Prom Dress Should I Wear: Find Your Ideal Style
201023767
Sound and Fury Deaf Movie - Test Your Documentary IQ
201056695
Ultimate Elizabeth Gaskell Films - Test Your Film IQ
201037425
Take the Friends With Benefits - Are You FWB Material?
201027738
Challenge Your SAT Root Word of Dem Knowledge Now!
201036313
Jazz Combo
15825447
Weight Unit Conversion: Can You Convert Kg to Lbs?
201074361
Free Chemical Equation: Balance It Right
201025221