ATAC201 - midterm prep pt.1

Mastering Semiconductor Basics
Prepare yourself for the ATAC201 midterm exam with our comprehensive quiz designed to test your knowledge of semiconductors and atomic structure. With 98 carefully crafted questions, you'll reinforce your understanding of key concepts and principles in the field.
Key features of the quiz:
- Multiple choice questions covering essential topics
- Score tracking to help you monitor your progress
- Engaging questions that challenge your comprehension
Pentavalent elements contain how many electrons in their valence shell?
Eight
Three
Five
Four
N-type semiconductors have an excess of what?
Electrons
Holes
Neutrons
Protons
The process by which atoms gain or lose electrons is called what?
Repulsion
Attraction
Ionization
Charging
What takes place initially as a result of combining N and P type semiconductors?
Repulsion
Diffusion
Attraction
Distraction
What best describes a chemcial compound?
Two or more atoms of chemical elements that have joined together to form molecules
Chemical elements that have been mixed together
The building block of which all matter is made
Chemical elements that have been mixed together with oxygen
What is the charge state of proton?
It has no charge
It has a negative electrical charge
It has a positive electrical charge
It has equal balanced state of positive and negative electrical charge
Which of the following best describes the atom?
The smallest particle of a chemical element that can exist
The smallest particle of a chemical mixture that can exist
The smallest particle of a chemical compound that can exist
The smallest particle of a element that can exist, either alone or combined with other atoms
A pure piece of Silicon or Germanium is called what type of material?
Valensic
Extrinsic
Intrinsic
Atomic
What particle spins and surrounds an atom's nucleus in a series of shells?
Grains of sand
Neutron
Electron
Proton
The purpose of adding pentavalent impurity to intrinsic materials is to
Reduce the conductivity of sillicon
Increase the number of holes
Increase the number of free electrons
Create minority carriers
The most widely used semiconductor element in electronic devices is what?
Carbon
Copper
Germanium
Silicon
The PN junction is formed by
The recombination of electrons and holes
Ionization
The boundary of a p-type and an n-type material
The collision of a proton and a neutron
What is the atomic number of Germanium?
4
2
32
8
An electronic device that operates because of the movement of electrons within a solid piece of semiconductor material is called what?
A solid-state device
A transistor
A diode
A fuse
In a silicon crystal, how many covalent bonds does a single atom form?
2
4
6
8
Holes in an n-type semiconductor are
Minority carriers that are thermally produced
Minority carriers that are produced by doping
Majority carriers that are thermally produced
Majority carriers that are produced by doping
The energy band in which free electrons exist is called what?
Valence band
First band
Conduction band
Second band
The process of adding an impurity to an intrinsic semiconductor is called
Recombination
Ionization
Doping
Atomic mixing
A trivalent impurity is added to Silicon or germanium to create
Germanium
A p-type semiconductor
A n-type semiconductor
A depletion region
When the peak output voltage is 100 V, the PIV for each diode in a center-tapped full-wave rectifier is (neglecting the diode drop)
100V
141V
200V
50V
If any capacitor is open, the ac output voltage will
Decrease
Increase
Remain the same
Equal Zero
When doping increases the number of free electrons, the semiconductor is:
Negative, or N-type
Neutral, or N-type
Positive or P-type
Base, or B-type
What is atomic number of silicon?
14
12
32
8
Which of the following best describes the Bohr model of an atom?
A central nucleus consisting of neutrons and electrons orbited by protons
A central nucleus consisting of protons and neutrons orbited by electrons
All the protons, neutrons and electrons equally spaced like raisins in a pudding
Protons and neutrons orbiting the central nucleus
What is the nucleus of an atom composed of?
Negatively charged protons and neutrons which have no charge
Positively charged protons and neutrons which have no charge
Negatively charged electrons and neutrons which are positively charged
Nothing - a sphere of empty space
What is the charge state of a Neutron?
It has an equally balanced state of positive and negative charges
It has no charge
It has a negative charge
It has a positive charge
What is a positive ion?
An atom with a net negative charge
A atom with protons orbiting the nucleus
A neutral atom that has lost a valence electron and has a net positive charge
A neutral atom that has gained an extra electron
What is a free electron?
It is a valence electron which has broken free from its parent atom
It is an electron which has no electrical charge
Only electrons in a molecule are free electrons
It is any electron in an atom
What is the maximum number of electrons that can exist in the 3rd shell of an atom?
6
8
12
18
With the proper amount of energy added, electrons may cross this band and be elevated to the outermost band of an atom’s electrons
The conduction band
The atomic band
The valence band
The forbidden band
If the atomic number of a neutral atom is 6, how many electrons does the atom have? How many protons?
3 electrons and 6 protons
6 electrons and 6 protons
6 electrons and 3 protons
12 electrons and 12 protons
Recombination is when
A crystal is formed
A positive and a negative ion bond together
A valence electron becomes a conduction electron
An electron falls into a hole
The difference between an insulator and a semiconductor is
The atomic structure
An insulator has a wider energy gap between the valence band and the conduction band
The number of free electrons
The molecular structure
Which of the following is NOT an acceptor impurity?
Arsenic
Boron
Indium
Gallium
Which of the following elements is a pentavalent dopant?
Tin
Boron
Aluminum
Arsenic
The depletion region is created by
Ionization
Diffusion
Recombination
All of the above
If the "+" lead on an ohmmeter is connected to a diode's anode and the "-" lead on the ohmmeter is connected to the diode's cathode, the measured resistance is normally ________.
Very high
0Ω
140 kΩ
Very low
If the "+" lead on an ohmmeter is connected to a diode's cathode and the "-" lead on the ohmmeter is connected to the diode's anode, the measured resistance is normally ________.
OL
0Ω
140 kΩ
Very low
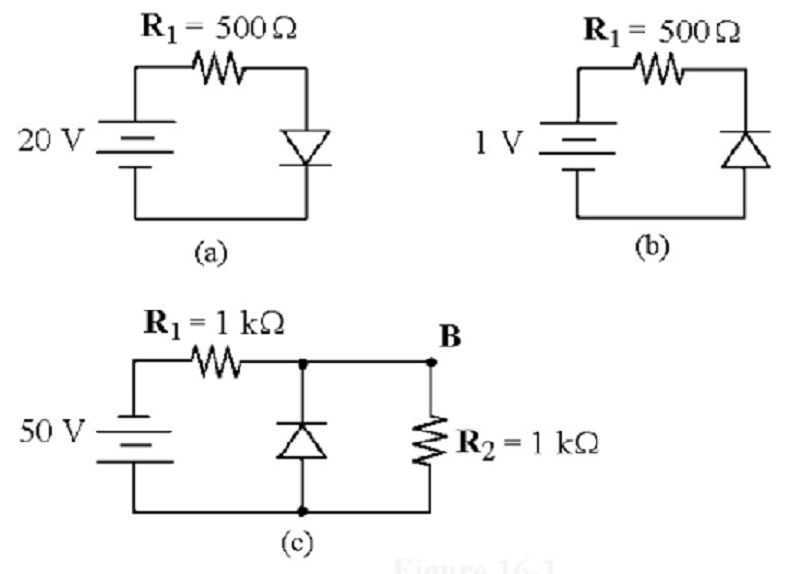
If the diode is silicon, what is the voltage across the resistor in Figure (a)?
0 V
20 V
19.3 V
0.7 V
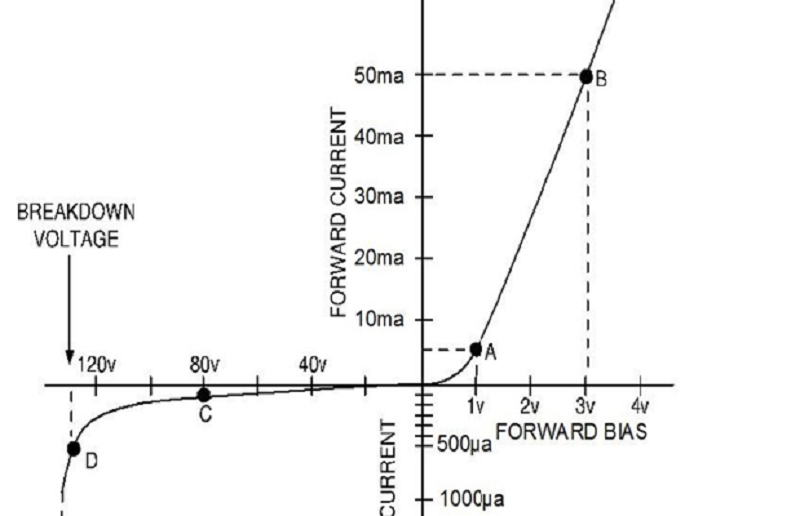
In the I-V graph below, what is the approximate value of the Peak Inverse Voltage (PIV)?
0.6 V
3 V
- 80 V
- 130 V
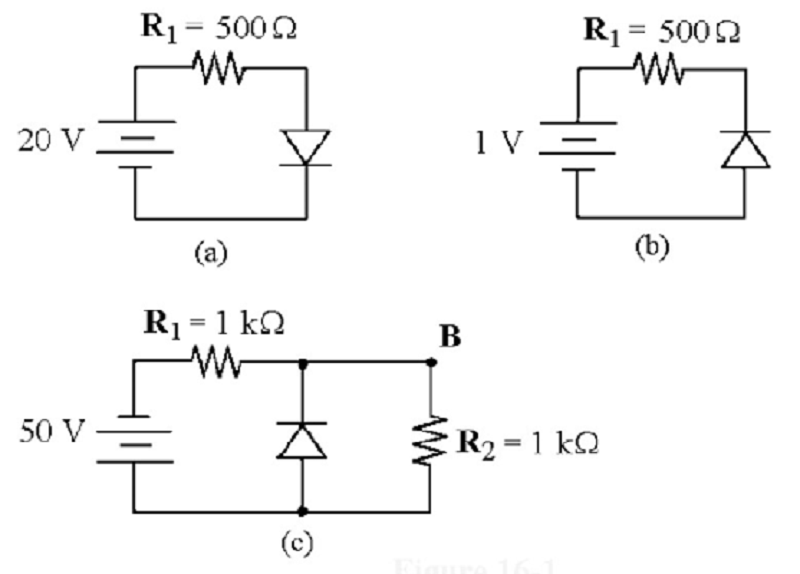
What is the voltage across the silicon diode in Figure (b)?
1.0 V
0.3 V
0.7 V
- 0.7 V
In a light emitting diode, what determines the color of the light?
The value of the voltage source
The chemical makeup of the diode and the light's wavelength
The color of the paint on the lens
The value of the current in the circuit
In a diode, the voltage at which a sudden increase in current occurs is known as what?
The breakdown voltage
The breakthrough voltage
The break-up voltage
The washout voltage
When a silicon diode is open, a DMM will generally indicate what?
0.3 Ω
0.7 Ω
0 Ω
OL
During the ____ stage of a power supply, the incoming AC voltage is changed to pulsating DC
Rectifier
Doping
Atomic mixing
Ionizing
When a 60 Hz sinusoidal voltage is applied to the input of a half-wave rectifier, what is the output frequency?
60 Hz
0 Hz
120 Hz
30 Hz
A half-wave rectifier circuit is so called because
Only one half of the input AC signal is used in its operation
Only one diode is used in the circuit
Only one of two diodes is used in the circuit
Only two of four diodes are used in the circuit
A half-wave rectifier circuit uses how many diodes?
One
Two
Three
Four
If the peak voltage of a pulsating DC waveform is 10 V, what is the value of VAVG ?
0.637 V
6.37 V
0.707 V
7.07 V
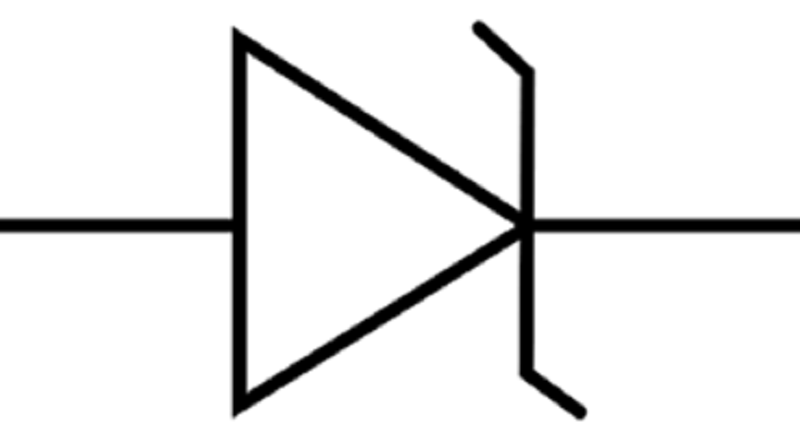
What type of diode is shown in the picture?
Zener diode
Photodiode
Varactor diode (varicap)
PN junction diode
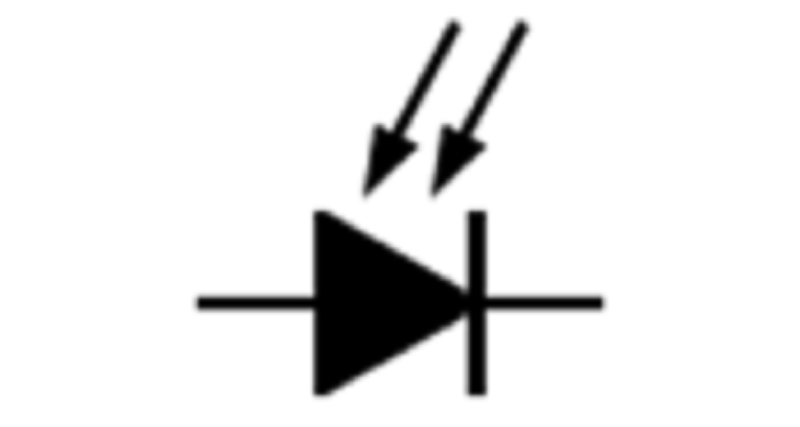
What type of diode is shown in the picture?
Zener diode
Varactor diode (varicap)
Photodidoe
PN junction diode
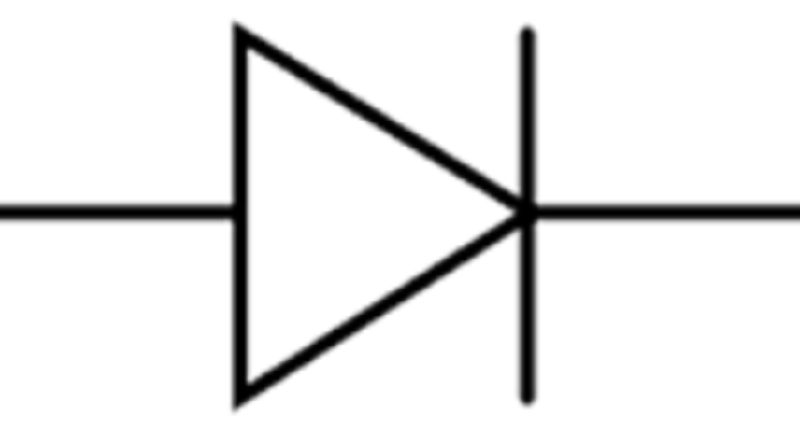
What type of diode is shown in the picture?
Zener diode
Varactor diode (varicap)
Photodiode
PN junction diode
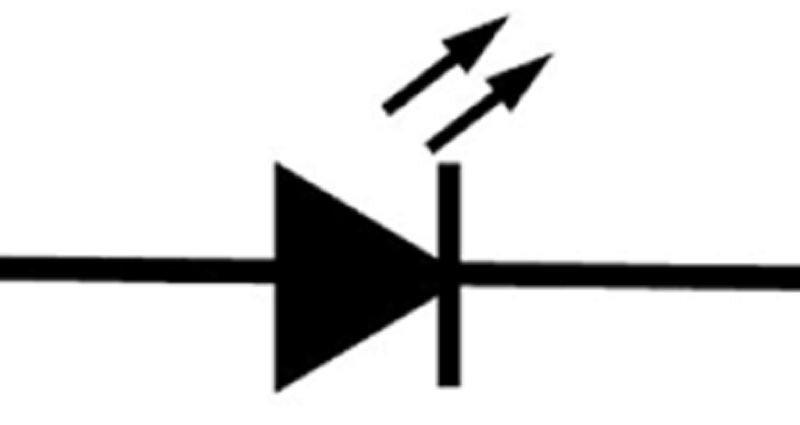
What type of diode is shown in the picture?
Zener diode
Photodiode
Light Emitting Diode (LED)
PN junction diode
What type of diode is shown in the picture?
Zener diode
Varactor Diode (varicap)
Light Emitting Diode
PN junction Diode
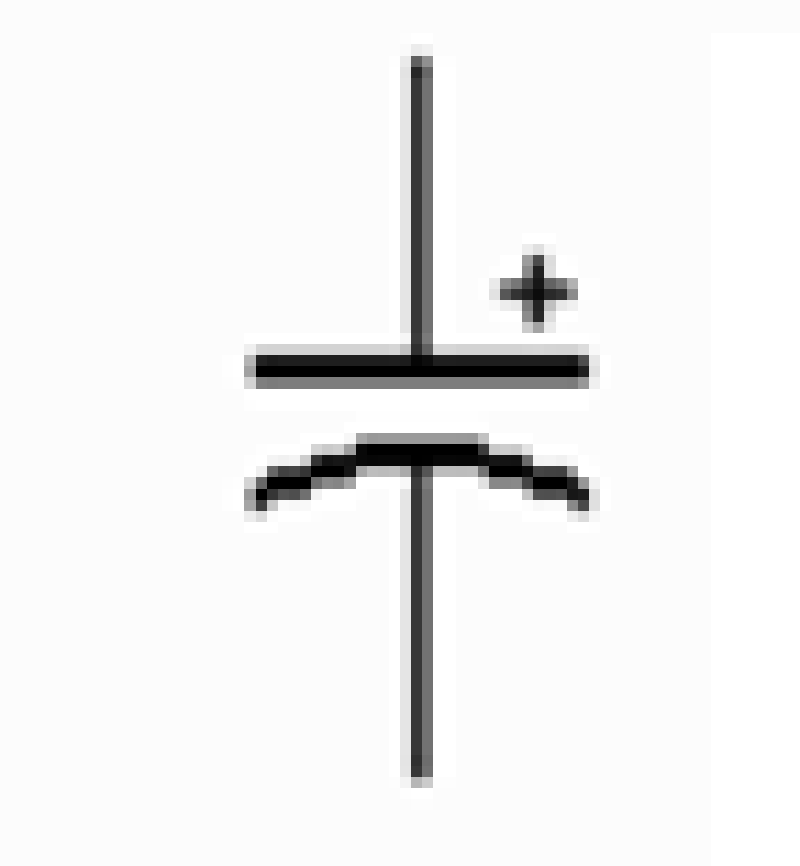
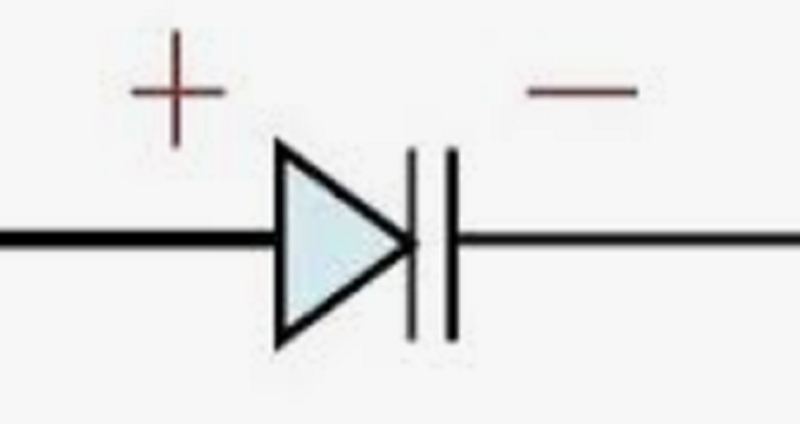
What is shown in the picture?
Zener diode
Varactor diode (varicap)
PN junction diode
Electrolytic
Electrolytic capacitors are ________ components due to their asymmetrical construction and must be operated with a higher potential on the anode than on the cathode at all times (+ve to +ve, -ve to -ve)
Polarized
Doped
Thermally produced
Ionized
The majority carriers in an n-type semiconductor are?
Conduction electrons
Conduction protons
Insulation neutrons
Insulation holes
If reverse-bias voltage is applied to PN junction, the size of its depletion region increases as
The charge particles on both sides move away from the junction
The charge particles on both sides stay in the junction
The charge particles on both sides move toward the N side
The charge particles on both sides move toward the P side
Each atom in a silicon crystal has
Valence electrons; four of its own and four shared
Valence electrons; fourteen of its own and fourteen shared
Valence electrons; sixteen of its own and sixteen shared
Valence electron; one of its own and one hared
Electron-holes pairs are produced by
Ionization
Thermal energy
Recombination
Doping
Forward biasing occurs when
The negative terminal of a external battery is connected to the N-type material and the positive terminal to the p-type material
The positive terminal of a battery is connected to the N-type material and the positive terminal to the p-type material
The negative terminal of a battery is connected to the P-type material and the positive terminal to the N-type material
The neutral terminal of a battery is connected to the P-type material and the positive terminal to the N-type material
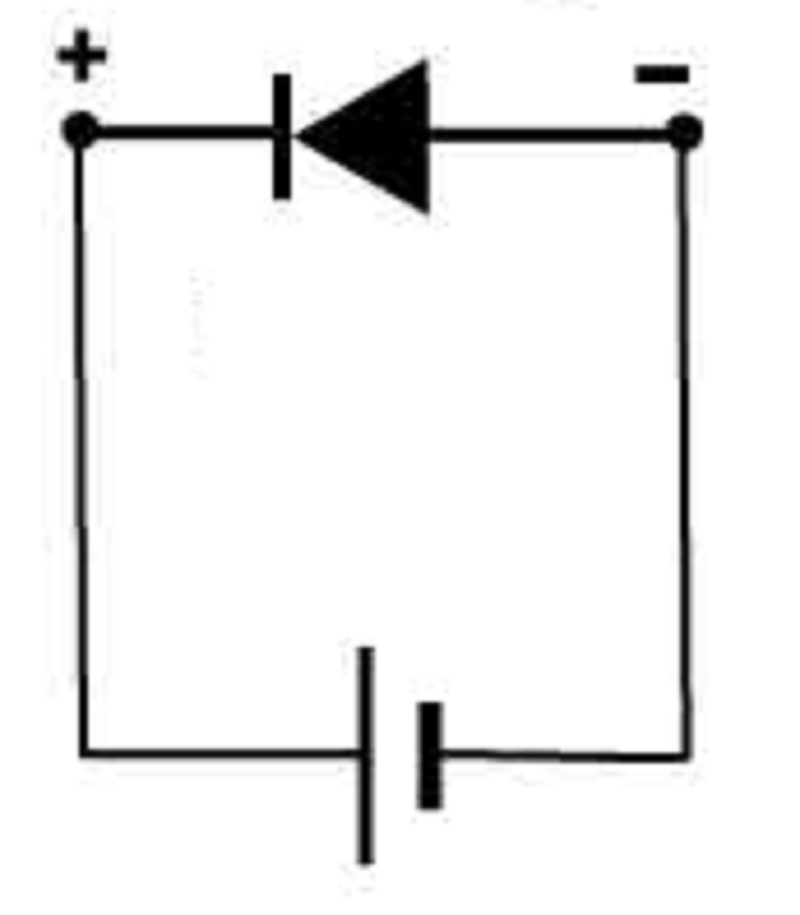
The anode terminal of the voltage source is connected to the N-type pin, and the cathode terminal of the voltage source is connected to the P-type pin of the diode. The diode act like an open switch, and its depletion region is widened. What type of diode is described? Picture also tells you the answer
Reverse biased diode
Forward biased diode
Ionized diode
Doped diode
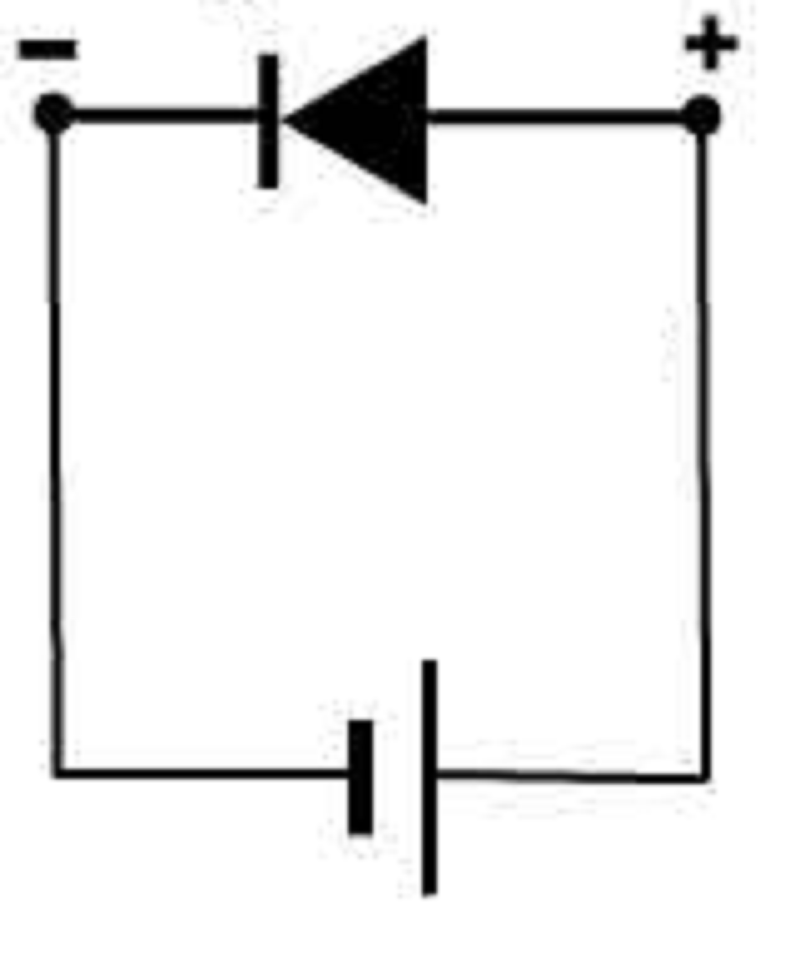
The P-type pin is connected with the anode of a voltage source and the N-type of the diode is connected with the cathode of the source. The diode act like a closed switch, and its depletion region width is reduced. What type of diode is described? Picture also tells you the answer
Reverse biased diode
Forward biased diode
Ionized diode
Doped diode
The number of electrons in the outermost shell of an atom determines its
Valence
Conduction
First band
Second band
What type of material doesn’t have a gap?
Conductor
Insulator
Silicon
Germanium
Diffusion of free electrons across the junction of an unbiased diode produces
Forward bias
Reverse bias
Breakdown
The depletion layer
Which of the following is true in case of an unbiased p-n junction diode?
Diffusion does not take place
Diffusion of electrons & holes goes on infinitely
There is zero electrical potential across the junctions
Charges establish an electric field across the junctions
When a physical contact between a p-region & n-region is established which of the following is most likely to take place?
Electrons from N-region diffuse to P-region
Holes from P-region diffuse to N-region
Both of the above-mentioned statements are true
Nothing will happen
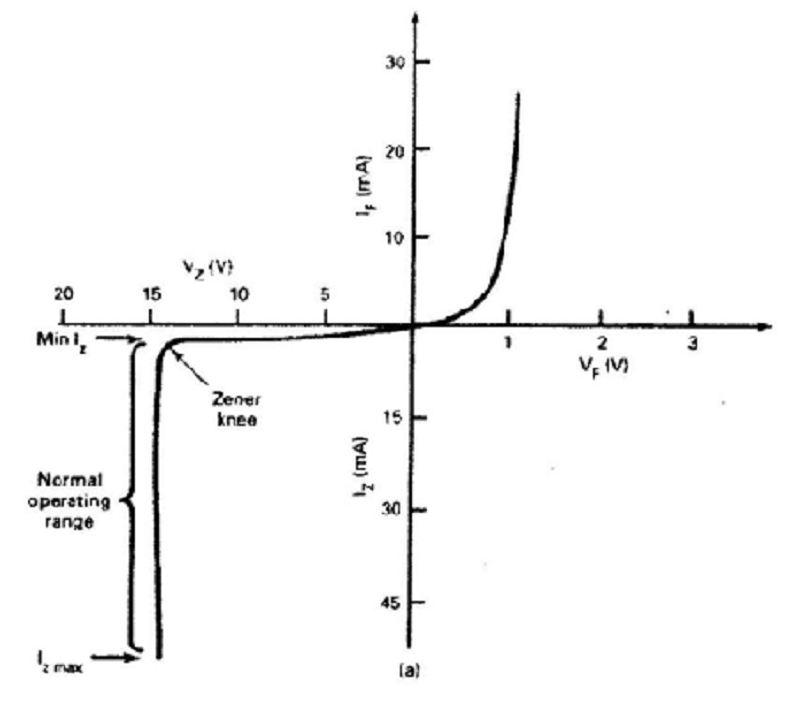
In a reverse-biased pn junction, the sudden large increase in current that occurs when a particular value of reversed voltage is reached, and which is due to ionization by the high intensity electric field in the depletion region
Zener knee effect
Hall effect
Breakdown voltage
Ionization
Define atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
The number of electrons in the nucleus of an atom
The number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
The number of protons outside of the nucleus
Which of the following is true in regards to electron shells and orbits and their energy levels?
The farther the valence shell is from the nucleus, the less attraction the nucleus has on each valence electron
The force of attraction between the positive charged nucleus and the negatively charged electron decreases with increasing distance.
Contains orbiting electrons at a certain energy level. Each shell of an atom is at a different energy level
All of the other answers
How is the maximum number of electrons a shell can hold determined?
2n^2 where n is the shell number
1n^2 where n is the shell number
3n^5 where n is the shell number
4n^2 where n is the shell number
_________ is a substance that contains atoms with several bands of electrons but with only one valence electron
Insulator
Conductor
Semiconductor
Resistor
Valence electrons are
In the closet orbit to the nucleus
In various orbits around the nucleus
In the most distant orbit from the nucleus and can form chemical bonds
Not associated with a particular atom
What do you call the potential required to remove a valence electron?
Valence potential
Threshold potential
Critical potential
Ionization potential
The valence electron of a conductor is also called a
Bound electron
Free electron
Nucleus
Proton
Which one of the following best describes free electron?
Electrons within a conducting substance
Escaped valence electron
Valence electron that has broken free of its parent atom
All of the other answers
Each valence electron in an intrinsic semiconductor establishes a
Covalent bond
Free electron
Hole
Recombination
The valence electron of a copper atom experiences what kind of attraction toward the nucleus?
None
Weak
Strong
Impossible to say
Elements that has four valence electrons are classified as
Conductor
Insulator
Semiconductor
Semi-insulator
Materials that might have eight valence electrons?
Conductor
Insulator
Semiconductor
Semi-insulator
Assume the valence electron is removed from a copper atom. The net charge of the atom becomes
0
+1
-1
+4
The sharing of valence electrons with neighboring atoms to produce a chemically stable atom in a molecule
Bound electrons
Crystal
Covalent bond
Recombination
A good conductor has how many valence electrons?
1
2
4
8
A donor atom has how many valence electrons?
1
3
4
5
An acceptor atom contains how many valence electrons?
1
2
3
4
When a neutral atom gains 1 or more electron it is
Positive ion
Negative ion
Neutral ion
Semiconductor ion
When a neutral atom lose 1 or more electron
Positive ion
Negative ion
Neutral ion
Semiconductor ion
How many electrons can be held in the ‘L’ shell of an atom?
1
2
8
18
The amount of energy required to remove an electron from an atom
Ionization energy
Diode energy
Doping energy
Covalent energy
Which one of the following is true in regards to conductors?
It has a overlap gap
It does not conduct electricity easily
It doesn't have free electrons
It has a large band gap
It lies in between insulator and conductor, where it needs external energy (e.g. heat) to conduct electricity. It’s neither a good conductor nor a good insulator. It contains a medium band gap and it does not conduct current as well as conductors do
Semiconductor
Insulator
Diode
Rectifier
Why does a semiconductor have fewer free electrons than a conductor?
The electrons in semiconductors need to overcome the energy gap barrier to go to the conduction band
The electrons in conductors don't need to overcome the energy gap barrier to go to the conduction band.
The valence electrons of semiconductors are more tightly bound to the atoms than those of conductors
All of the other answers
A solid material in which the atoms are arranged in a symmetrical pattern
Crystal
Semiconductor
Atom
Insulator
Its disadvantage is that even though it has 4 valence electrons, its energy level is far higher and faster than silicon because it is farther away from the nucleus, making it more unstable
Gallium
Indium
Boron
Arsenic
The energy gap between the valence and conduction bands
Band gap
Covalent bond
Hole
Bound electrons
When a silicon diode is closed, a DMM will generally indicate what?
Very low
0.3 Ω
0.7 Ω
0 Ω
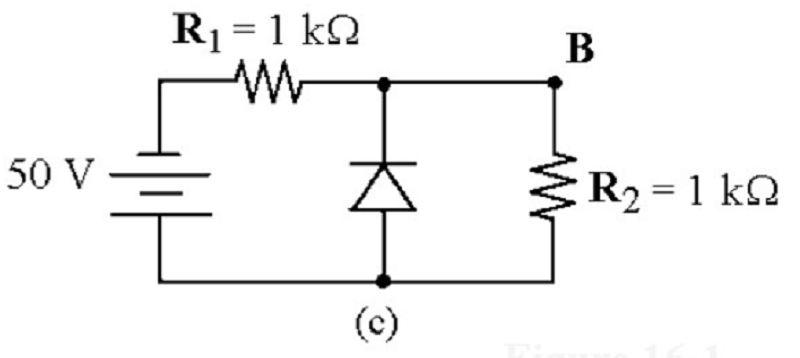
Refer to the attached image. If the diode was reverse biased, what is the voltage drop across R2?
0V
25V
50V
25.7V
{"name":"ATAC201 - midterm prep pt.1", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Prepare yourself for the ATAC201 midterm exam with our comprehensive quiz designed to test your knowledge of semiconductors and atomic structure. With 98 carefully crafted questions, you'll reinforce your understanding of key concepts and principles in the field.Key features of the quiz:Multiple choice questions covering essential topicsScore tracking to help you monitor your progressEngaging questions that challenge your comprehension","img":"https:/images/course7.png"}
More Quizzes
INORG MCQ 5
10514
UNIT-1 QUIZ-1
6330
Direct Line - Heart Breakfast Promotion
10550
Independent Writing Task 40
420
Free Basic Networking & Cybersecurity
201024449
Nursing Practice IV: Physiologic & Psychosocial Client Care
201048263
Free IT Security & Administration
201025536
Free Mean Mode Median & Range Answer Key
201023288
Discover Your God Tier Class: Free Homestuck
201033064
Can You Ace Ruth Chapter 4? with Questions & Answers
201051552
Free ELA Worksheet
201022931
Dream Pet Analysis: Find Your Perfect Furry Friend
201026249