Placement test AS Level Chemistry V01
C4H10(g) + 6.5O2(g) → 4CO2(g) + 5H2O(l)
|
Isotope |
Abundance (%) |
|
28Si |
91.07 |
|
29Si |
4.62 |
|
30Si |
3.00 |
|
31Si |
1.31 |
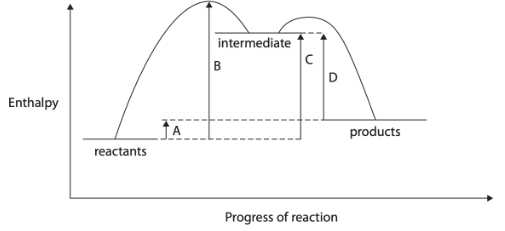
CH3COOH(aq) + NH3(aq) → CH3COONH4(aq)
So other techniques must be used. One technique is thermometric titration.
Procedure
Step 1 The temperature of 30.0 cm3 of dilute ethanoic acid in a polystyrene cup is recorded.
Step 2 Ammonia solution of concentration 1.30 mol dm-3 is added to the acid in the polystyrene cup in separate 5.00 cm3 portions. After each addition the mixture is stirred and the temperature measured.
A student carried out the experiment and plotted the graph and the initial and final temperature is 20.9 and 27.6 oC, respectively. Which of the following is the enthalpy change of neutralisation for this reaction, in kJ mol-1. [Assume that the density of all solutions is 1.00 g cm-3 and that the specific heat capacity of all solutions is 4.18 J g-1 °C-1]