DES 2016. Final (Part 21)
221) A 65-year-old white female comes to the ER because of persistent vomiting and epigastric pain. She has been suffering from left knee osteoarthritis for the past 6 years, and has been taking ibuprofen for the past year. She also has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease but is well controlled on her current medications. She quit smoking a few years ago. Her laboratory results are given below: ABG: pH 7.55, PCO2 46 mm Hg. Chemistry panel: Serum sodium 132 mEq/L, Serum potassium 3.0 mEq/L, Chloride 88 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 38 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl. Which of the following would describe her primary acid-base status?
Normal profile
Metabolic acidosis
. Metabolic alkalosis
. Respiratory acidosis
Respiratory alkalosis
222) A 36-year-old male is brought to the emergency department due to confusion, nausea and decreased arousal. He is unable to answer questions and no other history is available. His temperature is 36.7ׄ°C (98.2°F), respirations are 22/min and pulse is 86/min. His ABG and serum electrolyte levels are shown below: pH 7.21, PaO2 96 mmHg, PaCO2 28 mmHg, Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Serum potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Chloride 90 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 12 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 30 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.2 mg/dl. What is the most likely primary acid-base disorder in this patient?
. Non-anion gap metabolic acidosis
Anion gap metabolic acidosis
. Metabolic alkalosis
. Respiratory alkalosis
. Respiratory acidosis
223) A 56-year-old male comes to the emergency room because of a 2-day history of fever, chills, shortness of breath and productive cough. He also threw up once in the emergency room. He has been smoking for several years and occasionally drinks alcohol. On admission, his BP was 90/60, but with one liter of normal saline it improved to 120/80 mm Hg. His temperature is 38.8°C (102°F). His arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is as follows: Blood pH 7.53, PaO2 70 mmHg, PaCO2 30 mmHg, HCO3- 22 mEq/L. Which of the following best describes his primary acid-base status?
. Respiratory acidosis
Respiratory alkalosis
. Metabolic acidosis
. Metabolic alkalosis
. Normal acid base status
224) A 67-year-old male is brought to the ER because of increasing abdominal pain and nausea for the past few hours. He has multiple medical problems including type-2 diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, peripheral vascular disease, ischemic cardiomyopathy and atrial fibrillation. He has not been on anticoagulation because of recurrent bleeding peptic ulcer disease. He has had a cholecystectomy. He takes multiple medications at prescribed doses and lives at home with his family. He quit smoking 10 years ago and does not use alcohol or drugs. His temperature is 37.8°C (100.0°F), blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination shows an elderly male in acute distress. Lungs have few crackles at the bases. Heart rate is irregular. Bowel sounds are decreased and diffuse tenderness is present. There is no peripheral edema. Initial laboratory studies show the following: Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Chloride 103 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 14 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 20 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Blood glucose 198 mg/dl, Amylase 255 U/L. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Diabetic ketoacidosis
. Bowel ischemia
. Acute pancreatitis
. Acute appendicitis
. Peptic ulcer perforation
225) A 56-year-old male with a history of type-2 diabetes presents for a routine office visit. His blood work from two months ago showed hyperkalemia, and at that time his physician discontinued lisinopril. His repeat blood work done today is shown below: Chemistry panel: Serum sodium 136 mEq/L, Serum potassium 5.6 mEq/L, Chloride 110 mEq/L,Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 26 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.9 mg/dl. He currently takes glipizide, furosemide, nifedipine and aspirin. His blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg. Examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his low bicarbonate and elevated potassium?
. Chronic renal failure
. Renal tubular acidosis
. Furosemide
. Glipizide
. Nifedipine
226) A 33-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room because of altered mental status. En route to the ER, she suffers a generalized tonic clonic seizure, and once at the hospital she is confused and no further history can be obtained. You know only that she has a history of schizophrenia. On physical examination, her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows normal pupils. Her chest is clear to auscultation and her heart sounds are normal. Her abdomen is soft and nontender. Extremities have no edema. Laboratory studies show: Serum sodium 118 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dL, Serum calcium 8.4 mg/dL, Serum glucose 98 mg/dL, Urine osmolality 100 mosm/kg, Urine specific gravity 1.002. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Primary polydipsia
. Drug-induced ADH resistance
. Increased ADH production
. Drug-induced water retention
. Deficient ADH secretion
227) A 56-year-old male comes to the emergency room because of increasing shortness of breath for the last 3 days. He had a cold recently, and since then his symptoms have been worse. He has a mild productive cough but denies fever or chills. He has a several year history of smoking and has been diagnosed with emphysema. He also has a history of diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and hypothyroidism. He takes glipizide, metformin, lisinopril, furosemide, aspirin, atorvastatin and levothyroxine. Physical examination shows trace bilateral lower extremity edema and a diffuse decrease in breath sounds along with wheezing. Heart sounds are distant. His arterial blood gas shows the following: Blood pH 7.23, PaO2 88mm Hg, PaCO2 40 mm Hg, HCO3- 16mEq/L. Which of the following best describes the acid-base status of this patient?
Metabolic acidosis
Respiratory acidosis
. Mixed metabolic and respiratory acidosis
. Mixed metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis
. Normal acid-base balance
228) A 45-year-old male is brought to the emergency department in a stuporous state. He appears agitated and disoriented. His temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), respirations are 22/min, pulse is 90/min and blood pressure is 110/70 mm of Hg. His lab findings are as follows: Blood pH 7.21, PaO2 100 mmHg, PaCO2 30 mmHg, HCO3- 13 mEq/L, Serum osmolarity 350 mOsm/L, Blood glucose 90 mg/dl, Na+ 141 mEq/L, K+ 4.6 mEq/L, Cl- 100 mEq/L, BUN 28mg/dl, Creatinine 2.5 mg/dl. His urine shows the presence of rectangular, envelope-shaped crystals. His creatinine three months ago was 1.2 mg/dl. What is the most likely cause of this lab abnormality in this patient?
. Aspirin ingestion
. Ethylene glycol poisoning
. Methyl alcohol poisoning
. Uremic acidosis
. Lactic acidosis
229) A 21-year-old female comes to the office for the evaluation of fatigue and weakness. She first noticed these symptoms nine months ago. She says, "I can't exercise a lot anymore because I get fatigued very easily, but after resting for a while, I feel better, and my fatigue disappears." She then describes a recent episode of weakness while swimming in a pool, where she experienced double vision (especially when she did not look straight ahead), difficulty raising her eyelids, and swallowing problems. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
. Myasthenia gravis
. Brain tumor
Multiple sclerosis
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
230) A 27-year-old woman presents to the ER with severe vomiting and abdominal pain that started several hours ago. She describes her emesis as "yellowish." She has a history of alcohol and cocaine use. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 98/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 140/86 mmHg. Physical examination reveals dryness of the oral mucosa. Her abdomen is soft, non-distended, and without hepatosplenomegaly. Mild epigastric tenderness is present on deep palpation. Bowel sounds are increased. No rebound or rigidity is noted. She is treated with intravenous normal saline and metoclopramide. Several hours later she complains of neck pain and her neck muscles are noted to be stiff and tender. Which of the following best explains this patient's current complaints?
. Meningeal irritation
. Fat necrosis
Medication side effect
. Eosinophilic myositis
. Nerve root compression
231) A 55-year-old Caucasian male comes to the office because of numerous falls for the past few weeks. Yesterday, he felt so dizzy that he fell on the ground and hurt his knees. He has also noticed dry mouth, dry skin, and erectile dysfunction over this period. His past medical history is significant for the recent onset of resting tremors. He was diagnosed with diabetes six months ago, which is controlled with diet. His blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg supine, and 90/60 mmHg standing. Physical examination reveals rigidity and bradykinesia. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
. Idiopathic orthostatic hypotension
. Horner's syndrome
. Familial dysautonomia (Riley-Day syndrome)
. Diabetic neuropathy
. Shy-Dragger syndrome
232) A 65-year-old, obese, white female comes to the office for the evaluation of her progressively worsening memory. She considers herself "very independent," and lives alone; however, the development of her new symptoms is causing her some distress, as she often forgets to pay her bills. A detailed review of systems reveals no other symptoms, except for mild urinary incontinence. She has hypertension controlled with a beta-blocker and type 2 diabetes mellitus controlled with diet. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her blood pressure is 130/90 mmHg, pulse is 72/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 14/min. Lungs are clear to auscultation and percussion. A grade 2/6, systolic ejection murmur is heard. Abdominal examination shows no tenderness or masses. Neurological examination shows broad-based, shuffling gait and a right-sided carotid bruit. Complete blood count and serum chemistry panel are within normal limits MRI shows enlarged ventricles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Parkinsonism
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
. Multi-infarct dementia
. Pick's disease
. Alzheimer's disease
233) A 12-year-old boy is brought to the clinic for a routine health maintenance exam. He has no complaints, but mentions some spots on his back, which he noticed during his physical education class. He does not know how long they have been there. He denies any allergies. He remembers having a few seizures some years ago, which have not recurred since. He does not take any medication. The physical examination reveals several white spots and nodules measuring 2x3 cm on his back. There are freckles on his face and axilla. Closer examination reveals some nodules on his iris. What is the concerning complication that this boy is prone to?
. Hemoptysis
. Pancreatitis
. Tumors
. GI bleed
. Early dementia
234) A 25-year-old woman comes to the office and complains of intermittent dizziness and an unsteady gait for the last few days. Her symptoms worsen with exercise. Her past medical history is significant for tingling and numbness of her right foot that lasted 3-4 days (1 year ago), and visual loss in her right eye which spontaneously resolved (3 years ago). She is currently nursing her 2-month-old baby. Her obstetrical history was uncomplicated. Her neurological examination shows right hyperactive deep tendon reflexes. On attempted left gaze, her left eye abducts and exhibits horizontal jerk nystagmus, but her right eye remains stationary. When she attempts to look to the right, her right eye abducts and exhibits horizontal jerk nystagmus, but her left eye remains stationary. The patient is able to converge both eyes together, without any associated nystagmus. The facial muscles show no signs of weakness. Where is the most likely site of this patient's lesion?
. Optic nerve
. Optic tract
. Optic chiasma
. Optic radiations
. Medial longitudinal fasciculus
235) A 60-year-old male complains of recent onset gait imbalance and visual illusion of to-and-fro environmental motion. The symptoms are constant. He has no associated nausea or vomiting. His past medical history includes diabetes, hypertension, and chronic renal failure, and recent enterococcal endocarditis for which he is taking ampicillin and gentamicin. On physical examination, his temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Neurologic examination shows 5/5 power and 2+ reflexes in all four extremities. Cranial nerve examination is normal. There is no nystagmus. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current condition?
. Drug toxicity
. Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
. Hypoglycemia
. Meniere's disease
. Cerebellar infarction
236) A 63-year-old accountant is brought to the emergency department after suddenly collapsing at his desk at work. He is unconscious upon arrival but regains consciousness within several minutes. His medical history is significant for stable angina, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. He has had no surgeries. His medications include atenolol, simvastatin, aspirin, and a multivitamin. Physical examination is remarkable for paralysis of the upper and lower extremities on the right side. Vibration and position sense are absent on the right side. When the flat of the right foot is stroked with a pen, the right great toe is up going and the other toes fan out. The patient's tongue deviates to the left upon protrusion. Given these findings, a lesion in which region of the brain is most likely?
. Lateral pons
. Medial pons
. Lateral medulla
. Medial medulla
. Central midbrain
237) A 60-year-old white male is brought to the physician's office for the evaluation of worsening confusion and memory loss for the past three weeks. His other complaints are muscle twitching and gait problems. He denies any fever, headache or urinary problems. He does not drink nor smoke. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.1°C (98.7°F). He displays poor grooming and is disoriented. The pertinent physical findings are nystagmus and positive extensor plantar response bilaterally. The laboratory studies are as follows: Hematocrit 40%, WBC 6,000/microl, Platelets 160,000/microl. A non-contrast head CT scan is normal. The EEG shows periodic sharp waves. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
. Pseudodementia
. Alzheimer disease
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
. Multi-infarct dementia
238) A 70-year-old retired engineer is brought to the office by his son for a routine check-up. He believes that his son is too greedy and wants all his property. He is accusing his son of "kicking him out of the house to get all of his property." He has been getting more forgetful over the past few years. His younger sibling has the same problem. He has no significant past medical history, except a history of smoking for 6 years when he was young. His blood pressure is 138/78 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, respirations are 14/min and temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). He cannot remember current events, such as the name of the current American president; however, he can still remember past political history. He is unable to concentrate, but is oriented to time, place and person. The neurological examination is nonfocal. CT scan reveals mild generalized atrophy. His HIV and RPR tests are negative. The serum electrolytes and thyroid function tests are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
. Lewy body dementia
. Alzheimer's dementia
. Multi Infarct dementia
. Neurosyphilis
. Pick's disease
239) A 54-year-old man comes to your office complaining of recurrent headaches. While observing his gait as part of your neurologic examination, you notice that he very prominently flexes his right hip and knee and his right foot slaps to the floor with each step. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this gait abnormality?
Corticospinal tract lesion
. Basal ganglia lesion
. Cerebellar dysfunction
. L5 radiculopathy
. Tarsal tunnel syndrome
240) A 33-year-old female presents to the office for the evaluation of a one-week history of lightning-like pain on the left side of her face. The pain is very sharp and feels like a burn. An episode lasts for 10 seconds, occurs 10-20 times a day, and keeps her from sleeping, eating, or working. She denies any history of trauma; medication use or recent surgery Vital signs are within normal limits. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Maxillary sinusitis
. Carotidynia
Trigeminal neuralgia
. Herpes zoster
. Burning mouth syndrome
241) A 72-year-old woman complains of difficulty "finding the right word" when she is speaking. Her daughter notes that she also frequently complains that her neighbor is stealing her newspapers when this is not the case in actuality. Recently, the patient has been having difficulty balancing her check book as well. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg and her heart rate is 90/min. The exam is otherwise unremarkable. Over the course of the next three years, the patient develops a severe memory deficit, and suffers from poor sleep, slowness of movement, shuffling gait and urinary incontinence. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Alzheimer's dementia
. Dementia with Lewy bodies
. Multi-infarct dementia
. Vitamin B12 deficiency
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
242) A 32-year-old man presents to your office with blurred vision in his right eye. He denies any pain, ocular discharge, or gritting sensation. Physical examination findings include anisocoria, right-sided ciliary injection, mild ptosis, and impaired right eye adduction. Fluorescein examination reveals a large geographic corneal staining defect. Dysfunction of which of the following nerves is most likely responsible for this patient's impaired corneal sensation?
. Optic
. Oculomotor
. Facial
. Trigeminal
. Vagal
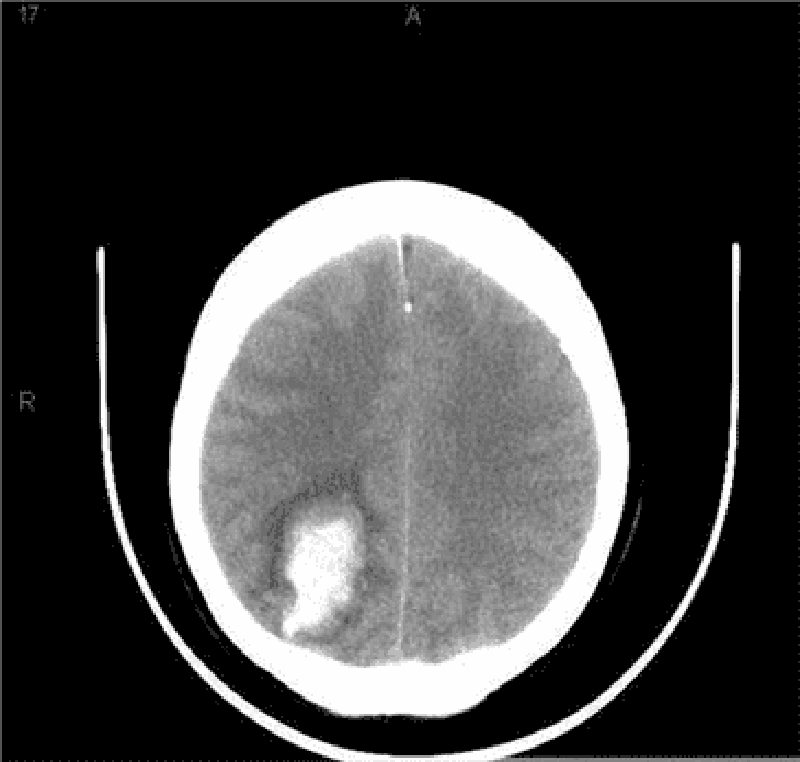
243) An 86-year -old known hypertensive woman is brought to the emergency department due to weakness of her left side, confusion, drowsiness and slurred speech for the last 2 hours. Her past medical history is significant for an inferior wall myocardial infarction 12 years ago, chronic atrial fibrillation, and severe backache secondary to osteoarthritis. She is currently on aspirin, warfarin, losartan, indomethacin, atenolol, and simvastatin. She doesn't go to anticoagulation clinic regularly. Her blood pressure is 180/110 mm Hg, temperature is 38°C (100°F), respirations are 16/min, and pulse is 70/min, irregularly irregular. The pertinent physical findings are: carotid bruit on both sides, 2/5-muscle strength in the left arm and leg, and slurred speech. Her deep tendon reflexes are exaggerated on the left side, and the Babinski sign is positive. EKG reveals atrial fibrillation. Her CT scan (performed in the ED) is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Cerebral haemorrhage
Cerebellar hemorrhage
. Cerebral infarction
. Lacunar infarction
. Subarachnoid haemorrhage
1) A 40-year-old man is brought to the emergency room because of altered mental status and gait instability. He has had two falls in the last two days. He drinks one pint of vodka daily and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. His temperature is 35.0°C (95.0°F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 14/min. He is disoriented, but not in acute distress. You note prominent horizontal nystagmus and conjugate gaze palsy in both eyes and absent ankle reflexes in both legs. His chest is clear to auscultation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
. Viral encephalitis
. Thiamine deficiency
. Hypothyroidism
. Cerebellar infarction
Opioid intoxication
2) A 16-year-old boy is recommended for admission to the neurology department for rapidly deteriorating clinical symptoms. He is a college student, living in a dormitory. During past week, he was sick. He did not recover fully and during last 3 days, his condition deteriorated. He started to have high fever, terrible headaches. His roommate said he talked about "some foolish happenings" during his high fever, and did not remember what he said later. This morning, he vomited repeatedly and his condition deteriorated rapidly. You examined him and found: febrile man in acute distress with cyanotic pallor, petechiae on his trunk and legs, purpura on his back bilaterally, with cold extremities. He is still alert, but has clammy skin, rapid pulse and labored respiration. His meningeal signs are positive. You diagnose this patient with meningococcal meningitis with systemic progression and you fear that he can develop the Waterhouse-Friderichsen syndrome. What characterizes this syndrome?
Acute adrenal insufficiency
Obstructive hydrocephalus
Endocarditis and myocarditis
. Otitis media and sinusitis
. Brain abscess
3) A 67-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office three weeks after having an ischemic stroke. She complains of transient pain in the right upper and lower limbs that can be induced even by light touch. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension and diabetes mellitus, type 2. Her current medications include enalapril, amlodipine, aspirin, and glyburide. She has right hemianesthesia due to the stroke and mild athetosis of the right hand. The strength is preserved in all four extremities. Hypersensitivity to all kinds of stimuli that induce severe pain reaction is present over the right extremities. Which of the following is the most probable location of the stroke experienced by this patient three weeks ago?
Internal capsule
. Thalamus
. Mid-brain
. Medulla
Left post-central cortex
4) A 43-year-old man presents to your office complaining of periodic involuntary head turning and head fixation to the right side. Physical examination reveals a hypertrophied right sternocleidomastoid muscle. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Parkinson's disease
. Essential tremor
. Chorea
. Akathisia
. Dystonia
5) A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of right arm weakness. He says that he first noticed the weakness two hours ago when he was unable to grip a pen. He is now unable to shake hands and walks with a mild limp. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and mild headaches over the past several days. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 180/100 mmHg, heart rate is 80/min and regular. There is mild asymmetry of the lower face, decreased muscle strength in the right arm, and an extensor plantar reflex on the right side. Sensory examination is normal. Blood glucose level is 210mg/dL. ECG shows sinus rhythm with occasional ventricular premature beats. His urine is negative for ketones and protein. Non-contrast CT scan of the head does not reveal any abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Migraine-associated vascular spasm
. Carotid artery thrombosis
. Small vessel hyalinosis
. Brain tumor
. Cardiac embolism
6) A 30-year-old, HIV-positive male, presents with left-sided paralysis of recent onset. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/80, and respirations are 16/min. The neurological examination reveals loss of recent memory, expressive aphasia, hyperreflexia, hypertonia, and up going plantars on the left side. His current medications include zidovudine, didanosine, indinavir and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. His CD4 count is 70/dl and viral load is 90,000 copies/ml by PCR. The serology is positive for Toxoplasma. CT scan shows multiple, hypodense, non-enhancing lesions with no mass effect in the cerebral white matter. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Cerebral toxoplasmosis
. Primary CNS lymphoma
. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
. AIDS dementia complex
. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
7) A 64-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office because he has had two falls within the last month. He states that he loses his balance when he tries to turn or stop suddenly while walking. Recently, he says, it has been taking him quite a while to get himself out of bed. He also complains of hand tremors that started last year in his left hand, but that now have been affecting both hands. Which of the following is the best tool to confirm his diagnosis?
Physical examination
. Lumbar puncture
. CT scan of the head
. Electroencephalography
. Nerve conduction studies
8) A 60-year-old male presents to the office and complains of muscle weakness in his extremities. Other accompanying symptoms include progressive difficulty in performing weight-carrying tasks, and a 7 kg (15 lb) weight loss during the last three months. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes daily, and consumes alcohol occasionally. His muscle strength is 3/5 in the proximal muscle groups symmetrically. His reflexes are normal. No sensory abnormality is present. Chest x-ray reveals a right lower lobe ill-defined mass. Which of the following is the most likely localization of the pathologic process in this patient?
. Peripheral nerves
. Presynaptic membrane
. Postsynaptic membrane
. Muscle membrane
. Spinal cord
9) A 47-year-old obese female comes to the office for the evaluation of recent episodes of mood instability. Her mood varies between sad and irritable. She denies any other symptoms, except for some mild forgetfulness. She tearfully shares that she is convinced that she is going to die, as her father also developed similar symptoms around the same age and died subsequently. On physical examination, writhing movements of the extremities are prominent. This patient's clinical presentation is most consistent with:
. Alzheimer's disease
. Pseudodementia
. Huntington's disease
. Hypothyroidism
. Pick's disease
10) A 70-year-old Caucasian male is brought to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of right-sided weakness and urinary incontinence about ten hours ago. His past medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes for the last 20 years and hypertension for the last 28 years. On examination, there is 3/5 power in the right upper extremity and 1/5 power in the right lower extremity. Babinski's sign is positive on the right side. The sensations are decreased on the right side of the body, more so in the right lower limb than the right upper limb. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lacunar stroke
. Anterior cerebral artery stroke
. Right middle cerebral artery stroke
. Left middle cerebral artery stroke
. Posterior cerebral artery stroke
11) A 32-year-old woman describes five episodes of intractable vomiting over the last year. The episodes last several hours and are associated with a sensation that the room is spinning or tilting. At these times, it is difficult for her to walk because she loses her balance. She cannot relate the timing of the episodes to any particular inciting event. Physical examination reveals stability in the Romberg position and during tandem walk. Proprioception is intact. Dysfunction of which of the following structures best explains this patient's symptoms?
. Posterior columns of the spinal cord
. Vagal nerve
. Optic tract
. Inner ear
. Cerebellum
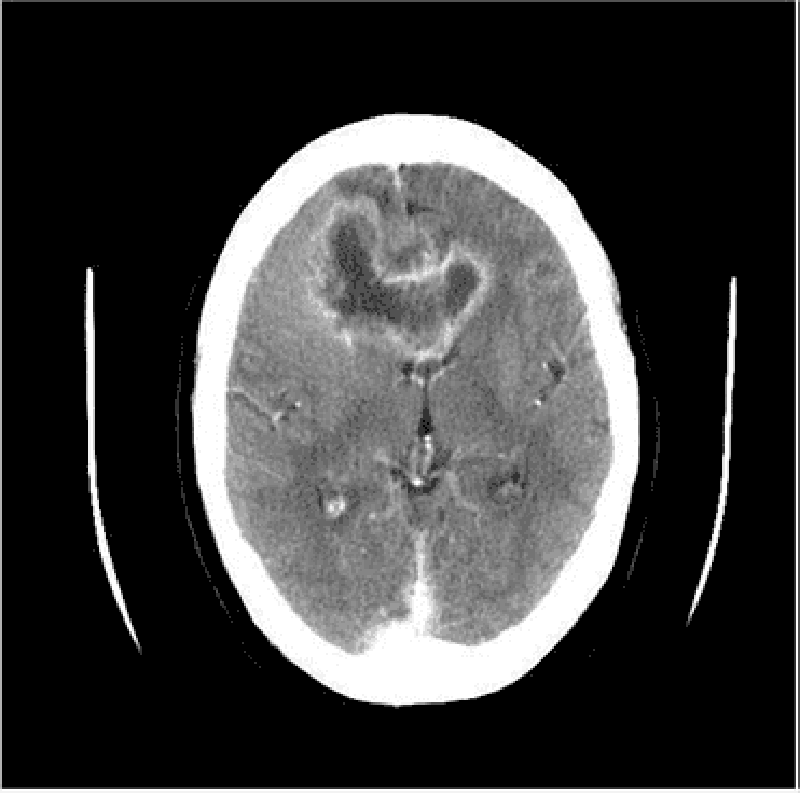
12) A 45-year-old white male presents with a 4-month history of headaches. The headache is generalized, dull, constant, and worsened by bending, coughing and sneezing. It is unresponsive to simple analgesics, and associated with nausea and vomiting. His wife says he has been acting strangely for the last few months, and she has noted a personality change. The neurological examination is non-focal. Fundoscopy reveals papilledema. His CT scan is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Brain abscess
. Metastatic brain tumor
. Glioblastoma multiforme
. Low-grade astrocytoma
Cerebral infarction
13) A 35-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department at 2 am because of severe pain 'behind the left eye' which woke him up in the middle of the night. The pain is intense and has a stabbing quality. He took ibuprofen at home but didn't get any relief. He denies fever, chills, decreased or blurred vision, cough, nausea or vomiting. He has no other medical problems. He drinks 3-4 bottles of beer daily. He has no known drug allergies. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 88/min and respirations are 14/min. The examination is unremarkable, except for left-sided ptosis and miosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Migraine headache without aura
. Migraine headache with aura
. Sinus headache
. Cluster headache
. Brain tumor
14) A 63-year-old Asian-American woman presents to the ER with a severe right-sided headache that started one hour ago. The pain is located "all around my eye." She has vomited once since the pain began. She also says that bright light aggravates the pain and she complains of seeing "halos" around light. She has never had a headache like this before. Her only medication is trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, which she has been taking for the last two days for a urinary tract infection. Her mother has a history of migraine headaches. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. On exam, she is afebrile with a pulse of 90/min. Physical exam reveals a non-reactive, dilated right pupil and erythematous right eye. There is lacrimation present. The remainder of examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies reveal an ESR of 40 mm/hr. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Meningitis
. Subarachnoid bleeding
. Angle closure glaucoma
. Cluster headache
. Migraine without aura
15) A previously healthy 8-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because he has multiple staring episodes. During these episodes, he is unresponsive to verbal or tactile stimuli, and produces lip-smacking movements. Each episode lasts for a few minutes, after which he remains confused for some time. He has no family history of any seizure disorder. His neurological examination is unremarkable. EEG performed before and after hyperventilation is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Complex partial seizure
. Typical absence seizure
. Atypical absence seizure
. Juvenile myoclonic epilepsy
. Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
16) A 1-year-old female infant is brought to the clinic by his 30-year-old mother due to feeding problems since birth. She still cannot walk nor speak. She began to sit when she was 8 months old. Her weight is in the 15th percentile, height is in the 20th percentile, and head circumference is in the 100th percentile for her age. She has multiple freckles in her armpit and groin area. She has cafe-au-lait spots on her skin, and the diameter of at least 20 of these spots is greater than 1 5mm. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Neurofibromatosis type 2
. Down syndrome
. Fetal alcoholic syndrome
. Normal development
Neurofibromatosis type 1
17) A 33-year-old Caucasian female comes to the office and complains of occasional diplopia and ptosis. These symptoms become especially prominent when she looks above her head for some time. She also complains of fatigue in her hands and leg muscles after exercising, such as swimming. Her muscle strength and double vision returns to normal after resting for some time. On examination, lid lag is observed after she is asked to look above her head for some time. No pupillary involvement is seen. The rest of the examination is normal. What is the level of the lesion in the disease that is being described?
. Neuromuscular junction
. Nerve conduction
. Muscle contraction
. Corticospinal tract
. Autonomic nervous system
18) A 25-year-old, HIV-positive male presents to the office with an altered mental status. He is disoriented, lethargic, and has loss of recent memory. These symptoms have been present for the last month. His current medications include zidovudine, didanosine, indinavir, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and azithromycin. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/80mm Hg, and respirations are 16/min. The neurological examination is non-focal. His CD4 count is 40/microl and viral load is 25,000 copies/ml by PCR. MRI scan reveals a solitary, irregular, weakly ring-enhancing mass in the periventricular area. The serology for Toxoplasma is positive. PCR of CSF shows EBV DNA. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Cerebral toxoplasmosis
. Primary CNS lymphoma
. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
. AIDS dementia complex
. Bacterial abscess
19) A 33-year-old Canadian female presents to the office with severe, bilateral, lightning-like pain on her face. The pain is burning and sharp in nature, occurs 20-30 times a day, and each episode lasts a few seconds. She is completely incapacitated by this pain. Prior to this event, she had weakness in her left arm, which gradually improved. She denies any history of trauma or drug use. She has no other medical problems. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 72/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 14/min. Complete neurologic examination shows no focal deficits. This type of disorder is most commonly seen in which of the following?
. Parkinson disease
. Huntington chorea
. Multiple sclerosis
. Aseptic meningitis
. Transient ischemic attack
20) A 33-year-old white man with a 9-year-history of progressive-relapsing multiple sclerosis is brought to the emergency department (ED) due to a severe flare-up. He has had several attacks before, and has recovered every time with some residual damage. The last physical examination in his medical records revealed cerebellar symptomatology, a visual defect, and central hemiparesis on the right side. MRI showed multiple, bright, signal abnormalities in the white matter supratentorially on the left side, in the cerebellum, and the left optic nerve. CSF examination revealed an increased synthesis of oligoclonal bands. In the ED, the physical examination reveals paraplegia, bladder and fecal incontinency, and absent sensation from the nipples down. What is the most likely location of this patient's new plaque?
. Cerebellum
. Posterior columns
. Upper thoracic spinal cord
. Lower thoracic spinal cord
. Supratentorially
21) A 37-year-old homeless man complains of weakness in his right arm. He says that he was smoking a cigarette when the weakness developed, causing the cigarette to fall from his hand. He also reports having mild headaches, fatigue, and chills over the last week. He admits to regular intravenous heroin use and binge drinking. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg and his heart rate is 80/min. There is asymmetry of the lower face, decreased muscle strength in the right arm, and an extensor plantar reflex on the right side. He has multiple needle tracks on his arms. ECG shows sinus rhythm with occasional ventricular premature beats. Urinalysis shows 2+ proteins. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
. Migraine-associated vascular spasm
. Carotid artery thrombosis
. Small vessel hyalinosis
. Brain tumor
. Cerebral emboli
22) A 45-year-old man comes to the office for the evaluation of excessive wasting of his extremity muscles, which is more apparent on the extensor side. The weakness began distally and asymmetrically. He recently started to have difficulties with swallowing, chewing, and speaking. He feels some movements in his face and tongue. He also has muscle stiffness. His bowel, bladder, cognitive, and sensory functions are intact. The physical examination reveals excessive wasting of his muscles, which is more prominent in the lower extremities. Fasciculation and hyperreflexia of all extremities are noted. His bulbar reflexes are decreased. What neural pathway is most likely damaged?
. Pyramidal tract
. Lower motor neuron
. Upper motor neuron
. Lower and upper motor neuron
. Cerebral cortex
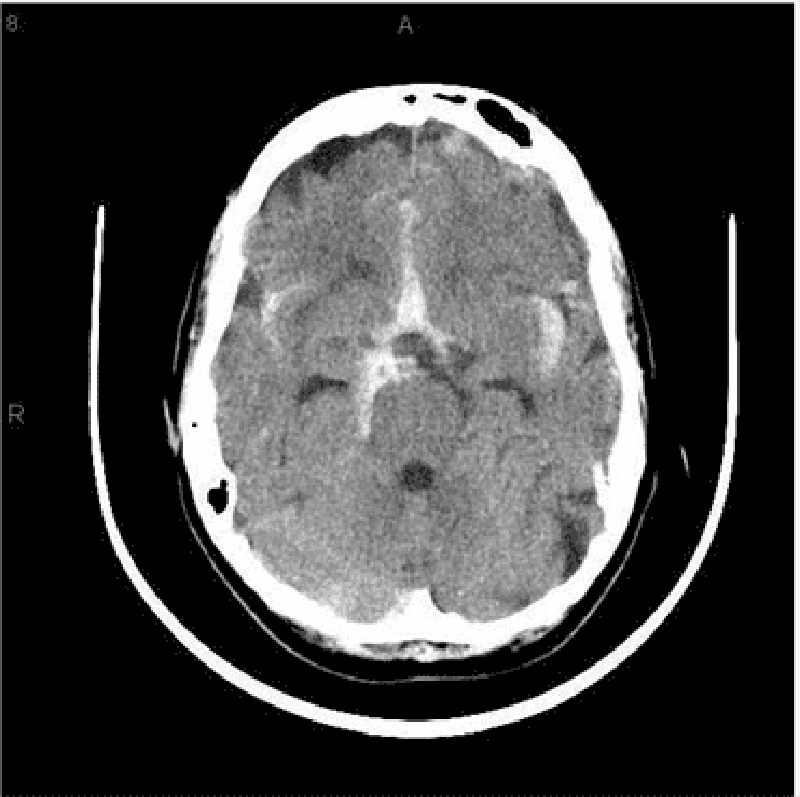
23) A 40-year-old Caucasian male comes to the emergency department because he is having "the worst headache" of his life. The headache is of sudden onset, and associated with nausea and vomiting. He denies any fever and trauma to head. He is not taking any medications. He has a history of migraine headaches. The neurological examination is non-focal. CT scan of the head without contrast is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's headache?
. Hypertension
. Rupture of saccular aneurysm
. Rupture of AV malformation
. Extension of primary intracerebral hemorrhage
. Amyloid angiopathy
24) A 67-year-old Asian male comes to the clinic for the first time. He walks very slowly as he enters the room. His chief complaint is "extreme forgetfulness" for the past 6 months. He tearfully shares that he has been "losing sleep." He used to be a very "bright and sharp" person, but is now unable to focus on his daily activities and feels "really extremely low and useless." His past medical history is significant for hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and TIA. His family history is insignificant, except for Alzheimer's dementia in his father. He does not smoke, and drinks wine only occasionally. He has been living alone for the last 6 months, after his son moved out. His physical exam is normal, except for markedly slow movements. A CT scan of the head is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Parkinson's disease
. Vascular dementia
. Alzheimer's dementia
. Pseudodementia
. Normal aging
25) A 54-year-old construction worker presents to your office complaining of a "funny sensation" in his right arm. He has no significant past medical history. His diet consists of mainly fast food and he drinks one to two litters of soda per day. He does not exercise regularly. He smokes 1½ pack of cigarettes per day. His BMI is 28.5 kg/m2. You ask the patient to stretch out his arms with the palms facing up and close his eyes. Five seconds later you observe the right palm turning inward and downward. Which of the following best explains the observed findings in this patient?
. Impaired proprioception
. Tactile sensation loss
. Cerebellar dysfunction
. Parietal lobe lesion
. Upper motor neuron lesion
26) A 53-year-old man complains of "shaking" of his right hand. He first noticed this shaking while resting in an armchair and watching TV. He reports that the shaking stopped when he reached for the remote to change the channel. On physical examination, his vital signs are within normal limits and all other organ systems appear normal. Which of the following is most likely responsible?
. Physiological tremor
. Essential tremor
. Cerebellar dysfunction
. Basal ganglia dysfunction
. Corticospinal tract lesion
27) A 60-year-old Hispanic female is brought to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of worsening, left-sided hemiplegia, which was followed by a headache and altered mental status. She was taking her regular morning walk when she developed these symptoms. Her past medical history is remarkable for uncontrolled essential hypertension. She has been a chronic smoker for the last 30 years. The neurological examination shows flaccid paralysis on the left side, and deviation of eyes towards the right side. The CT scan is consistent with a hemorrhagic stroke. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Putamen haemorrhage
. Cerebellar hemorrhage
. Pontine hemorrhage
. Subarachnoid haemorrhage
. Ventricular haemorrhage
28) A 70-year-old Caucasian male comes to your office four weeks after experiencing an ischemic stroke. His past medical history is significant for a long history of hypertension, diabetes, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, and atrial fibrillation. You noticed that the patient has shaved only the right side of his face. When you ask him to raise his left arm, he raises his right arm. You ask him to fill in the numbers of a clock, and he puts numbers only on the right side. Which of the following areas is most likely affected by the stroke in this patient?
. Left frontal cortex
. Left temporal cortex
. Right parietal cortex
. Right occipital cortex
. Right frontal cortex
29) A 10-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother after having a seizure this morning. All he can recall before the episode is "seeing funny little lights." According to his mother, his body went stiff; he lost consciousness, and then had jerky movements of the entire body. He bit his tongue, and started to drool. The seizure lasted for about one minute. After the seizure, he appeared confused for several minutes, and passed urine. He has been complaining of a headache for the past two hours. The neurological examination is normal. What type of seizure did this patient experience?
. Childhood absence seizure
. Status epilepticus
. Simple partial seizures
. Complex partial seizures
. Tonic clonic seizure
30) A 56-year-old Hispanic male presents with right-sided arm weakness and speech difficulty. He expresses words slowly and with difficulty. His speech is agrammatic and the melody of speech is abnormal. He is able to comprehend words spoken to him. Which of the following is the most likely site of lesion in the above patient?
. Dominant parietal lobe
. Nondominant parietal lobe
Dominant frontal lobe
. Nondominant frontal lobe
. Occipital lobe
31) A 69-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a severe occipital headache, nausea and vomiting for several hours. His medical history is significant for poorly controlled essential hypertension for the last 7 years. The neurologic examination shows ataxia, right-sided facial weakness and deviation of the eyes to the left side. His CT scan is consistent with a hemorrhagic stroke. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Putamen hemorrhage
Cerebellar haemorrhage
. Pontine hemorrhage
. Subarachnoid haemorrhage
. Ventricular haemorrhage
32) A 76-year-old woman presents for a routine medical check-up. Her medical history is significant for hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypothyroidism that are controlled with oral agents. She had a stroke one year ago and has mild residual right arm weakness. Otherwise she has no physical complaints. She is widowed and lives alone. Regarding her memory, she sometimes forgets to return phone calls and take her blood pressure pills. Occasionally during conversations, she has difficulties finding the right word. She drives herself to the grocery market weekly to do her shopping, and has no difficulty managing her finances. She describes her mood as good. She visits her close friends on occasion and often has difficulty falling asleep. Her blood pressure is 135/76 mmHg and her heart rate is 65/min. Finger stick glucose and TSH levels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Alzheimer's dementia
. Depression
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
. Frontotemporal dementia
. Normal aging
33) A 59-year-old man is brought to the office by his family due to attitude problems over the last year. He has a history of memory loss and word-finding problems. He has lost interest in golf, which used to be one of his favorite sports. Recently, he has become promiscuous and has started using "dirty language," which he has never used before. He is a non-smoker. He has no significant past medical or surgical history. His uncle had similar features, for which he was admitted into a nursing home, but died soon after admission. The physical examination reveals intact visuospatial functions, intact cranial nerves, and prominent snout and grasp reflexes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lewy body dementia
. Alzheimer's disease
. Multi-infarct dementia
. Neurosyphilis
. Pick's disease
34) A 65-year-old man comes to the physician's office because of frequent falls. For the past 2 months, he has been having increasing difficulty in maintaining balance when walking or standing. He tends to lose his balance on the left side, and feels that his "left body has become weak." He also complains of occasional headaches and nausea for the past 3 months. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes mellitus-type 2 and a myocardial infarction 10 years ago. He denies the use of tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His medications include glyburide, aspirin and enalapril. His vital signs are within normal limits. When asked to get up from the chair and stand with his feet together, he tends to sway to the left, even with his eyes open. When asked to walk a few steps, he walks cautiously and lurches to the left. There is decreased resistance to passive flexion. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Major depression
. Huntington's disease
. Parkinsonism
. Cerebellar tumor
. Hemiparesis
35) A 26-year-old previously healthy white female is brought to the emergency department after having an episode of seizures one hour ago. She has a two-day history of fever and headaches, for which she has been taking acetaminophen and ibuprofen without much relief. She has no family history of seizures. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 18/min. Complete blood count and CT scan of the head are unremarkable. Her cerebral spinal fluid study shows: Opening pressure 220 mm H2O, Protein 200 mg/dl, Glucose 55 mg/dl, WBC 150/mm3, Lymphocytes 90%, Polymorphs 10%, RBC 200/cmm. What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
. Pneumococcal meningitis
. Meningococcal meningitis
. Hemophilus influenza meningitis
Herpes simplex encephalitis
. Cryptococcal meningitis
36) A 64-year-old man presents to the ER with back pain and frequent falls. He also describes difficulty initiating urination. The symptoms started one week ago and have progressed gradually. He was diagnosed with prostate cancer one year ago and treated with radiation therapy. Physical examination reveals weakness of knee and hip extension that is more pronounced on the right. Knee and ankle reflexes are absent bilaterally. Babinski sign is negative. Perianal skin is insensitive to touch but sensation in the anterolateral thigh is preserved. Which of the following is the most likely lesion location in this patient?
Peripheral nerves outside the spinal canal
. Spinal nerve roots
. Lumbar spinal cord
. Thoracic spinal cord
. Cervical spinal cord
37) A 62-year-old Caucasian woman complains of difficulty remembering important dates and appointments. She also describes poor concentration, daytime sleepiness and easy fatigability. She is concerned about her forgetfulness because her mother suffered from recurrent strokes and had severe memory loss. Her father died of chronic leukemia. Her daughter's recent job loss has caused her a lot of stress. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. Her appetite is decreased but she has gained 4 pounds over the last three months. She visited an otolaryngologist for hoarseness of recent onset. She takes over- the-counter laxatives for constipation and occasional aspirin for knee pain. She denies any other medication use. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Alzheimer's dementia
. Dementia with Lewy bodies
. Multiinfarct dementia
. Hypothyroidism
. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
38) A 46-year-old homeless man is being evaluated for frequent falls and a broad-based gait. A single tap on his patellar tendon elicits several to-and-fro leg movements. There is also nystagmus on physical examination. Which of the following additional findings would you expect most in this patient?
. Goiter
. Bradykinesia
. Intention tremor
"Clasp knife" phenomenon
. Babinski sign
39) A 66-year-old female is brought to the office by her concerned son due to increasing confusion, loss of mobility and stiff limbs. She tends to cry out for no reason. She often screams and sees, "a lion roaring in the backyard." She often sees cats in her room, even though her son does not see any. She has significant memory loss. She never had "joint problems" before. She was previously treated with haloperidol, but this only aggravated her rigidity. She is a non-smoker. She has no significant past psychiatric history. In the office, she appears alert, but disoriented and quite agitated. Her blood pressure is 136/72 mm Hg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals impaired visuospatial abilities, increased tone, normal reflexes, and coarse resting tremors in the extremities. Her CBC, electrolytes, creatinine, glucose, LFTs, TSH and B 12 levels are within normal range. The serology for syphilis is negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Lewy body dementia
. Alzheimer's disease
. Multi infarct dementia
. Neurosyphilis
. Pick's disease
40) A 59-year-old obese man comes to the office "to make sure everything is okay." Yesterday after lunch, he experienced weakness in his right upper arm and right lower extremity. He was limping, and his right hand was not strong enough to hold some heavy things. His speech was "somewhat faulty”, and he had a light diffuse headache. By dinnertime, his symptoms were resolving, and when he woke up this morning, his weakness was gone. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, for which he takes atenolol. He has been smoking 1 pack of cigarettes a day for the past 40 yrs. His blood pressure is 150/95 mm of Hg and heart rate is 78/min. The neurological examination is normal. There is a mild carotid bruit on his left side. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hemorrhagic stroke
. Completed ischemic stroke
. Transient ischemic attack
. Reversible ischemic neurologic deficit
. Cluster headache
41) A 68-year-old woman comes to the office due to the inability to move the right half of her face for the past 24 hours. Her blood pressure is 135/90 mm Hg and heart rate is 76/min. The physical examination is performed. Which of the following signs will exclude the diagnosis of central facial paresis?
. Dysarthria
. Absence of forehead furrows
. Normal sensations on the right side of the face
. Dropped right corner of the mouth
. Facial spasm on the right
42) A 32-year-old construction worker is brought to the emergency room after his co-workers found him confused, disoriented, and bleeding from the nose. His past medical history is unknown. According to his friends, he had been in his normal state of health this morning when he came to work. He then spent the morning moving heavy packages under direct sunlight for several hours. Presently, his blood pressure is 130/90 mmHg, heart rate is 120/min and regular, and temperature is 42°C (108°F). His skin is warm and dry and his neck is supple with no stiffness. His pupils are symmetric, mid-size and reactive to light. Deep tendon reflexes are symmetric and Babinski reflexes are downgoing bilaterally. He moves all four extremities but is unable to speak or follow simple commands. There is active bleeding from the right nostril. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Viral encephalitis
. Malignant hyperthermia
. Heat stroke
. Hypothalamic stroke
. Thyroid storm
43) A 65-year-old Caucasian male presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of weakness in his right arm and right leg. He has had episodes of transitory weakness and numbness in his right extremities over the last month, but those episodes used to resolve quickly. He denies headache, nausea, vomiting and loss of consciousness. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, type 2 and myocardial infarction experienced 2 years ago. His current medications are aspirin, metoprolol, enalapril, simvastatin, and glyburide. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 160/80 mmHg, pulse is 65/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 14/min. The physical examination reveals right-sided hemiplegia and facial paresis. His speech and praxis do not seem to be impaired. He correctly names his left and right arms. Bedside visual field testing is normal. Head CT without contrast shows no intracranial bleeding Where is the most likely location of the lesion responsible for this patient's condition?
. Middle cerebral artery occlusion
. Anterior cerebral artery occlusion
. Internal capsule involvement
. Pons lesion
. Midbrain lesion
44) A 20-year-old Caucasian male is on mechanical ventilation after sustaining a severe head trauma in a car accident. He is unresponsive to various stimuli. His blood pressure is 100/60mmHg and heart rate is 110/min. After monitoring the patient for six hours, the physician decides to do a bedside assessment of brain death. Which of the following can be observed in a patient with brain death?
. Pupillary light reaction
. Oculovestibular reaction
. Heart acceleration after atropine injection
. Spontaneous respiration at Pco2 = 60 mmHg
. Deep tendon reflexes
45) A 74-year-old woman comes to your office with her husband for a routine check-up. Her husband complains that she often forgets to take her blood pressure pills. He feels that her speech has changed because she occasionally struggles to find appropriate words. Two days ago, she drove to the nearby grocery store and did not find her way back. She has difficulty falling asleep and she always wakes up early in the morning. Her appetite is good. Which of the following is the best indicator of dementia in this patient?
. Memory impairment
. Language difficulty
. Sleep abnormalities
. Advanced age
. Impaired daily functioning
46) A 1-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his 28-year-old Caucasian mother for the evaluation of his eyes. For the past several months, he has been bumping into objects. His perinatal history is unremarkable. Physical examination of the eyes reveals a bilateral white reflex. The retina cannot be visualized properly. Fundal reflection is absent, and the pupil is white. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Congenital glaucoma
. Congenital cataract
. Retinoblastoma
. Pterygium
. glaucoma
47) A 65-year-old white man is complaining of a sudden loss of vision in his left eye which resolved after 15 minutes. "It seemed like a curtain was falling down in my eye!" said the patient. He recalls having a similar episode 3 months ago. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, for which he takes lisinopril (20mg) and hydrochlorothiazide (25mg) daily. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is normal. Fundoscopy reveals zones of whitened, edematous retina following the distribution of the retinal arterioles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Central retinal artery occlusion
. Amaurosis fugax
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Vitreous hemorrhage
. Hypertensive retinopathy
48) A 3-day-old female infant is noticed to have copious, purulent discharge from both eyes. Lid edema and chemosis are also noted. She was born by normal vaginal delivery. Her mother is a 20-year-old primigravida who had no prenatal care. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Chlamydia trachomatis
. Staphylococcus aureus conjunctivitis
. Chemical conjunctivitis
. Nasolacrimal duct obstruction
. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
49) A 22-year-old Caucasian female presents to the office with several months history of decreased visual acuity and decreased brightness sensation in the right eye. Slight exophthalmos of the right eye is present on physical examination, and ophthalmoscopy shows pallor of the right optic disk. Several cafe-au-lait spots and intensive axillary freckling are present. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's visual problems?
. Pigment retinitis
. Retinal hamartoma
. Optic glioma
. Pituitary adenoma
. Optic neuritis
50) A 65-year-old African American man comes to the emergency department due to a sudden loss of vision in his right eye. He has had diabetes, and has been treated with metformin and glyburide for the past 10 years. Visual acuity is reduced to light perception in his right eye, and normal in his left. His vital signs are normal. Ophthalmoscopy reveals loss of fundus details, floating debris and a dark red glow. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Retinal detachment
. Diabetic retinopathy
. Vitreous haemorrhage
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Age related macular degeneration
51) A 60-year-old woman complains of decreasing vision and a dull ache over her left eye for the past 12 hours. She had a successful surgical cataract extraction in her left eye five days ago. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.1°C (101.7°F). Examination of the left eye reveals a swollen eyelid, edematous conjunctiva, and exudates in the anterior chamber. Testing with Snellen's chart demonstrates decreased visual acuity in her left eye. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Conjunctivitis
. Corneal ulceration
. Uveitis
Postoperative endophthalmitis
. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
52) A 26-year-old male complains of itching and excessive watering of both eyes since this morning. He denies blurring of vision. He uses albuterol inhaler regularly for his bronchial asthma. His vital signs are normal. On examination, both eyes are noted to have conjunctival edema, hyperemia, swollen eyelids, and profuse watery discharge. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Atopic keratoconjunctivitis
. Allergic conjunctivitis
. Toxic conjunctivitis
. Blepharitis
. Dacryocystitis.
53) A 4-year-old boy is brought by his mother to a Medical Camp for the Uninsured for the evaluation of his inflamed right eye. He has had a nasal discharge for the past 10 days. His brother has similar symptoms. His vital signs are stable. There are follicles and inflammatory changes in the conjunctiva of his right eye. The cornea shows neovascularization. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Orbital cellulitis
. Trachoma
. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
. Viral conjunctivitis
54) A 60-year-old woman comes to the emergency department due to a sudden onset of severe pain in her left eye with blurred vision, nausea, and vomiting. The symptoms began a few minutes ago, while she was watching a movie in a nearby theatre. Her blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 98.4°F. Examination reveals decreased visual acuity. Her left eye appears red, with a hazy cornea, shallow anterior chamber, and dilated, fixed pupil. Her left eye is stony hard to touch. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Primary open angle glaucoma
. Conjunctivitis
. Acute angle closure glaucoma
. Anterior uveitis
. Corneal abrasion
55) A 32-year-old male construction worker presents with complaints of pain, watering, and redness in his left eye for the past 2 days. He reports having similar symptoms in the same eye a few months ago. Examination of his left eye reveals vesicles and dendritic ulcers in the cornea. His vital signs are stable. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bacterial retinitis
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
. Corneal abrasion
. Fungal keratitis
56) A 38-year-old man with AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) is complaining of diminished vision in both eyes. His CD4 count last month was 50 cells/uL. He has been on highly active antiretroviral therapy for the past several months. He is afebrile, and his vital signs are stable. Ophthalmoscopic examination reveals yellow-white patches of retinal opacification and retinal hemorrhages. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ocular toxoplasmosis
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Herpes-zoster ophthalmicus
. CMV Retinitis
. HIV retinopathy
57) A 65-year-old man presents with complaints of decreased vision in both eyes. His visual impairment has been progressively worsening over the past five months. He was diagnosed with diabetes ten years ago. His current medications are metformin and glyburide. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 98.4°F (36.88°C). Examination shows decreased visual acuity in both eyes. Ophthalmoscopy reveals microaneurysms, dot and blot hemorrhages, hard exudates, and macular edema. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Diabetic retinopathy
. Macular degeneration
Retinal detachment
. Open angle glaucoma
58) A 69-year-old white male presents to your office complaining of progressive bilateral loss of vision over the past several months. He only has problems with his central vision. His peripheral field and navigational vision are not affected. He denies smoking and alcohol intake. He does not have any history of diabetes or hypertension Two years ago, he had cataracts removed from both eyes. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Open angle glaucoma
. Macular degeneration
. Recurrent cataracts
. Central retinal artery occlusion
Retinal detachment
59) An 80-year-old white male comes to the emergency department due to a sudden loss of vision in his left eye that occurred this morning upon waking up. He has had hypertension for the past several years. Current medications include ramipril and atenolol. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 86/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F). Examination of the left eye reveals no abnormalities. Funduscopic examination shows swelling of the optic disk, retinal hemorrhages, dilated and tortuous veins, and cotton wool spots. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute angle-closure glaucoma
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Optic neuritis
. Amaurosis fugax
. Acute anterior uveitis
60) A 32-year-old woman comes to the office distraught because "the colors look washed out I" She has had this vision impairment since yesterday. She also complains of pain on eye movements. Her vital signs are stable, and she is afebrile. Examination reveals decreased visual acuity, sluggish afferent pupillary response to light, and changes in color perception. Fundoscopy reveals a swollen disc. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Orbital cellulitis
. Optic neuritis
. Acute anterior uveitis
. Open angle glaucoma
Episcleritis
61) An 85-year-old man presents with a rash over his forehead, tip of nose and left eye. He also complains of pain and decreased vision. He has had fever, malaise, and a burning sensation around his left eye for the past 5 days. His blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.1°C (101°F). Physical examination reveals a vesicular rash on the periorbital region and lid margins. The left eye is red, with chemosis of the conjunctiva. Dendriform ulcers are seen on the cornea. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Dacryocystitis
. Bacterial keratitis
. Trigeminal neuralgia
. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
62) A 75-year-old African American man comes to your office for his annual check-up. He is a known diabetic and hypertensive. His medications include lisinopril and atenolol. His vital signs are normal. Examination of his fundus reveals cupping of the optic disc. Visual field examination reveals constricted peripheral vision. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Diabetic retinopathy
. Closed angle glaucoma
. Macular degeneration
. Primary open angle glaucoma
. Cataract
63) A 65-year-old female is complaining of seeing a sudden burst of flashing lights and blurred vision in her left eye. These symptoms started this morning. She now sees small spots in her field of vision. She felt "like a curtain came down" over her eye. She had a successful cataract extraction in her left eye 4 months ago. Her vital signs are stable. Examination shows a sluggish left pupil. Ophthalmoscopy reveals retinal tears and a grayish-appearing retina. What is the most probable diagnosis?
. Choroidal rupture
. Retinal detachment
. Central retinal artery occlusion
. Proliferative diabetic retinopathy
. Exudative macular degeneration
64) A 65-year-old woman presents with complaints of pain and swelling over the inner aspect of her right eye for the past two days. Examination of the eye reveals tenderness, edema, and redness over the medial canthus. Slight pressure over the area causes expression of purulent material. Visual acuity is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Episcleritis
. Dacryocystitis
. Hordeolum
. Chalazion
. Orbital cellulitis
65) A 65-year-old man complains of gradual onset blurred vision for the past two months. He also has difficulty driving at night and reading fine print. He has diabetes and hypertension. His medications include ramipril and metoprolol. His vital signs are stable. His best corrected vision is OD (right eye) 20/80, OS (left eye) 20/100, with full fields. Ophthalmoscopic examination with good pupillary dilatation reveals a loss of transparency of lens in both eyes. The red fundal reflex is normal, but retinal details are difficult to visualize. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Open angle glaucoma
. Retinal detachment
. Macular degeneration
. Cataract
. Central retinal vein occlusion
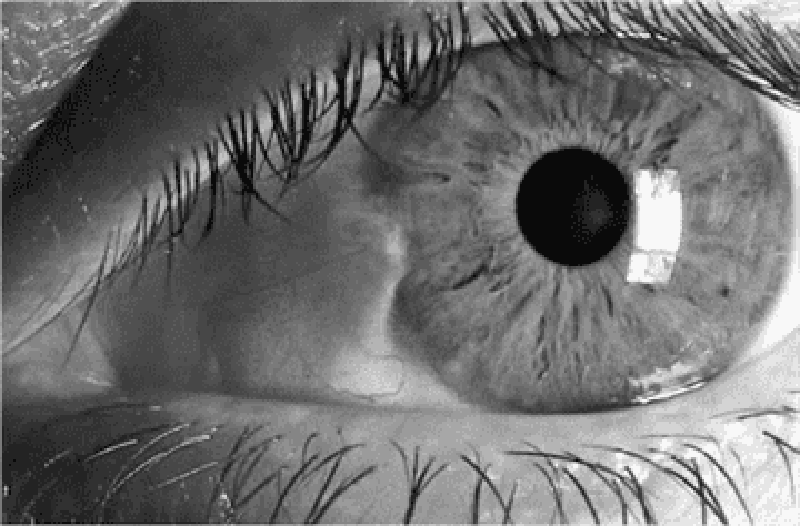
66) A 31-year-old nurse in your hospital has noticed a lesion in her left eye. She denies change in vision, pain, fevers, or discharge. A picture of her eye is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hordeolum
. Chalazion
. Dacryocystitis
. Pinguecula
. Pterygium
67) A 35-year-old woman presents with a right-sided red eye for 3 days. She denies pain and notes that she has watery discharge from the eye. She has been coughing and congested for the past 5 days. On examination, the patient has a temperature of 98.4°F, HR of 72 beats per minute, BP of 110/70 mm Hg, and RR of 14 breaths per minute. Her visual acuity is 20/20. On inspection, the conjunctiva is erythematous with minimal chemosis and clear discharge. The slit-lamp, fluorescein, and funduscopic examinations are otherwise unremarkable. The patient has a nontender, preauricular lymph node and enlarged tonsils, without exudates. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Gonococcal conjunctivitis
. Bacterial conjunctivitis
. Viral conjunctivitis
. Allergic conjunctivitis
. Pseudomonal conjunctivitis
68) The local sorority house recently installed a sun-tanning station. Two days later three sorority girls present to the ED with bilateral eye pain, tearing, and photophobia. After ophthalmic anesthesia instillation, a complete eye examination is performed. Visual acuity is normal. Extraocular eye movements are intact and pupils are equal, round, and reactive to light. IOP is normal. Slit-lamp examination is normal, but fluorescein examination under cobalt blue light illuminates small dots throughout the cornea. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ultraviolet keratitis
. Anterior uveitis
. Herpes simplex keratitis
. Allergic conjunctivitis
. Corneal ulcer
69) A 22-year-old man presents to the ED for left eye pain. He was in an altercation yesterday and was punched in the left eye. On examination, his left eye is ecchymotic and the eyelids are swollen shut. He has tenderness over the infraorbital rim but no step-offs. You use an eyelid speculum to examine his eye. His pupils are equal and reactive to light. His visual acuity is normal. On testing extraocular movements, you find he is unable to look upward with his left eye. He also complains of diplopia when looking upward. Funduscopic examination is normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Orbital blowout fracture
. Ruptured globe
. Retinal detachment
. Cranial nerve III palsy
. Traumatic retrobulbar hematoma
70) You are examining the pupils of a patient. On inspection, the pupils are 3 mm and equal bilaterally. You shine a flashlight into the right pupil and both pupils constrict to 1 mm. You then shine the flashlight into the left pupil and both pupils slightly dilate. What is this condition called?
. Anisocoria
. Argyll Robertson pupil
. Afferent pupillary defect
. Horner syndrome
. Normal pupil reaction
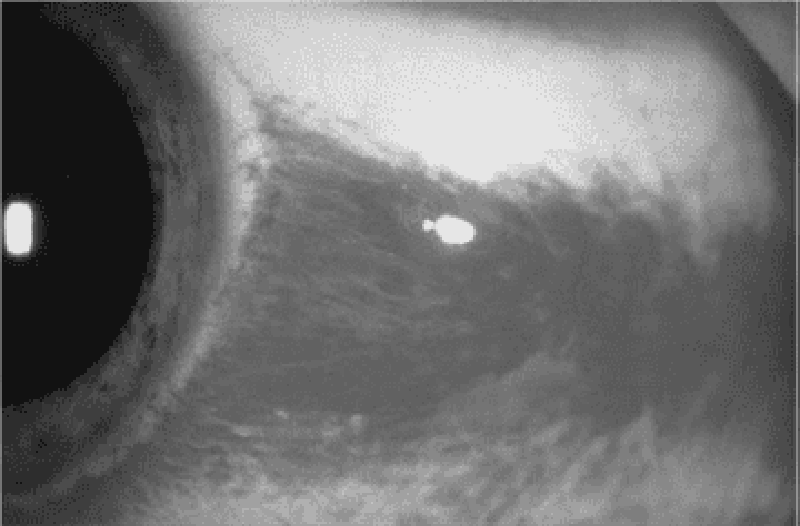
71) A 65-year-old man with a history of diabetes, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and atrial fibrillation presents with loss of vision in his left eye since he awoke 6 hours ago. The patient denies fever, eye pain, or eye discharge. On physical examination of the left eye, vision is limited to counting fingers. His pupil is 3 mm and reactive. Extraocular movements are intact. Slit-lamp examination is also normal. The dilated funduscopic examination is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Retinal detachment
. Central retinal artery occlusion
. Central retinal vein occlusion
. Vitreous hemorrhage
. Acute angle-closure glaucoma
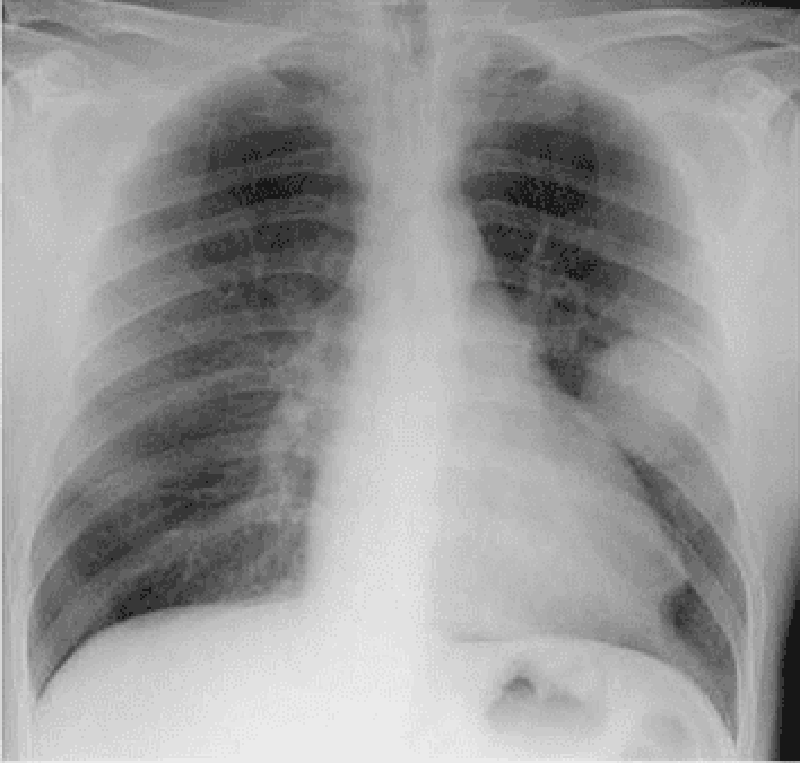
72) A 43-year-old man presents to your office complaint of nagging left-side chest pain that increases on deep inspiration, plus two weeks of non-productive cough. He denies chills, fever or weight loss. His medical history is significant for Hodgkin's disease treated 20 years ago with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. On physical examination today, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 90/min. His chest x-ray is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his chest pain?
. Radiation-induced fibrosis
. Recurrence of Hodgkin's disease
. Fungal pneumonia
. Pulmonary tuberculosis
Secondary malignancy
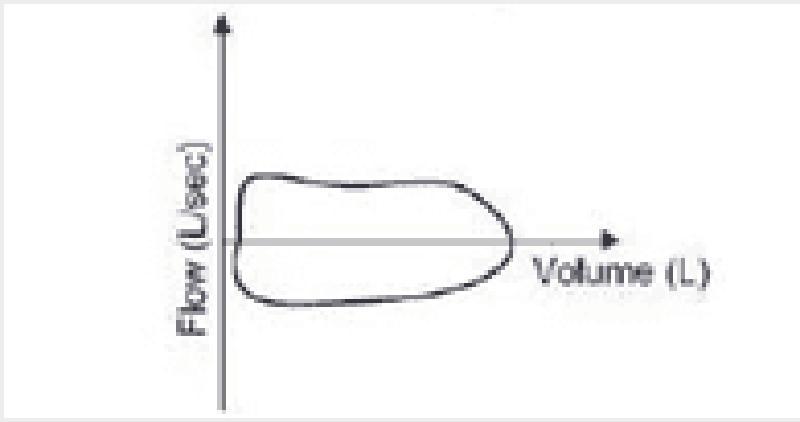
73) A 56-year-old woman is brought to the hospital from a local restaurant after suddenly becoming short of breath. Her flow-volume loop is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
. Asthma attack
. Pneumothorax
. Pulmonary edema
. Laryngeal edema
. Panic attack
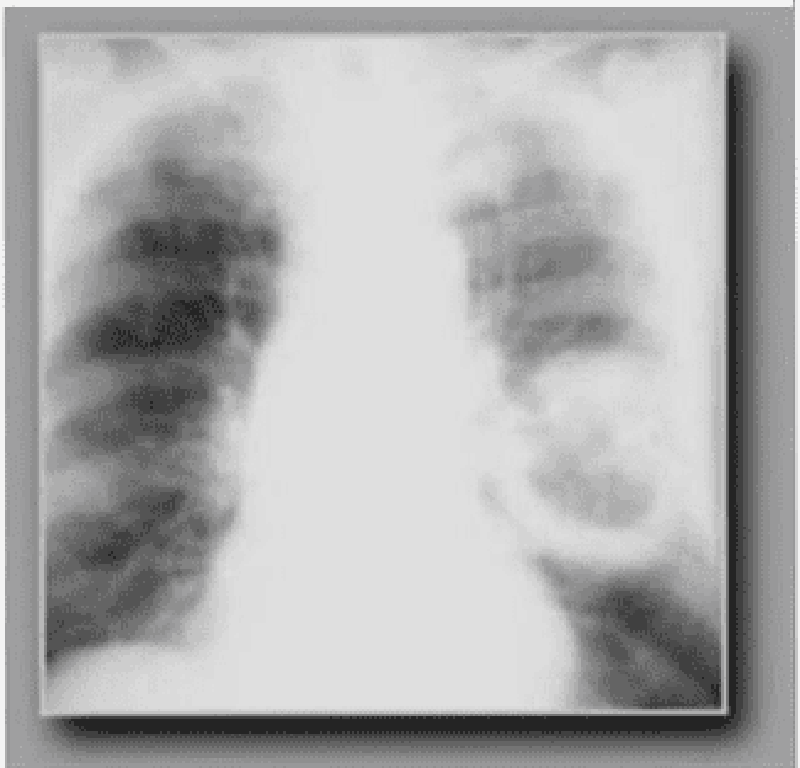
74) A 54-year-old black male from the southeast USA presents to you with complaints of generalized malaise, fever, and a cough. He claims that he has had intermittent hemoptysis for the past six months. He denies smoking and has never had tuberculosis. Examination is unremarkable and his chest x-ray is shown below. On changing position, you notice that the part of the lesion seen on x-ray also moves. The most likely diagnosis is?
. Lung abscess
. Pulmonary embolism
. Aspergilloma
. Histoplasmosis
. Bronchiectasis
75) A 66-year-old male presents to the emergency department with acute onset of severe chest pain and dyspnea. He localizes the pain to the right upper chest, and says that it is aggravated by deep breathing and coughing. On physical examination, his pulse is 116/min and regular, blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, and respirations are 22/min. His lungs are clear to auscultation. Chest x-ray is unremarkable. EKG shows sinus tachycardia. CT angiogram of the chest shows a thrombus in the right pulmonary artery. Which of the following is the most likely source of his pulmonary thrombus?
. Clot in the right heart
. Upper extremity deep vein clot
. Renal vein clot
. Calf vein clot
. Iliofemoral vein clot
76) A 35-year-old male presents to the emergency room complaining of increasing shortness of breath, fever and malaise for several days. His past medical history is significant for two years of recurrent sinusitis. He is a former smoker and has an occasional glass of wine. His temperature today is 38.4°C (101.1°F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination reveals an illappearing male in mild respiratory distress. Patchy rales are appreciated on lung auscultation. Chest x-ray reveals multiple nodular densities bilaterally. His serum creatinine is 2.7 mg/dl and urinalysis shows red blood cell casts. Which of the following would be most helpful in diagnosing his condition?
. Serum alpha fetoprotein
. CT scan of the chest
. Serum antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody
Sputum acid fast stain
. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
77) A 64-year-old male presents to the ER with a one-week history of progressive exertional dyspnea. Each of the past two nights he has awakened with a choking sensation and has had to sit up to catch his breath. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and a myocardial infarction two years ago. He takes a baby aspirin and lisinopril daily. His blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, and his heart rate is 110/min, irregularly irregular. His temperature is 98°F (36.7°C) and his respiratory rate is 24/min. His oxygen saturation is 91% on room air. There is moderate jugular venous distention. Markedly reduced breath sounds are heard over the right lung base. Which of the following most likely underlies this patient's physical findings?
. Lung tissue consolidation
. Atelectasis
. Bronchoconstriction
. Pleural effusion
. Emphysema
{"name":"DES 2016. Final (Part 21)", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"221) A 65-year-old white female comes to the ER because of persistent vomiting and epigastric pain. She has been suffering from left knee osteoarthritis for the past 6 years, and has been taking ibuprofen for the past year. She also has a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease but is well controlled on her current medications. She quit smoking a few years ago. Her laboratory results are given below: ABG: pH 7.55, PCO2 46 mm Hg. Chemistry panel: Serum sodium 132 mEq\/L, Serum potassium 3.0 mEq\/L, Chloride 88 mEq\/L, Bicarbonate 38 mEq\/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg\/dl. Which of the following would describe her primary acid-base status?, 222) A 36-year-old male is brought to the emergency department due to confusion, nausea and decreased arousal. He is unable to answer questions and no other history is available. His temperature is 36.7ׄ°C (98.2°F), respirations are 22\/min and pulse is 86\/min. His ABG and serum electrolyte levels are shown below: pH 7.21, PaO2 96 mmHg, PaCO2 28 mmHg, Serum sodium 140 mEq\/L, Serum potassium 3.6 mEq\/L, Chloride 90 mEq\/L, Bicarbonate 12 mEq\/L, Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 30 mg\/dl, Serum creatinine 1.2 mg\/dl. What is the most likely primary acid-base disorder in this patient?, 223) A 56-year-old male comes to the emergency room because of a 2-day history of fever, chills, shortness of breath and productive cough. He also threw up once in the emergency room. He has been smoking for several years and occasionally drinks alcohol. On admission, his BP was 90\/60, but with one liter of normal saline it improved to 120\/80 mm Hg. His temperature is 38.8°C (102°F). His arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis is as follows: Blood pH 7.53, PaO2 70 mmHg, PaCO2 30 mmHg, HCO3- 22 mEq\/L. Which of the following best describes his primary acid-base status?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/11-488439/hc.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Natanael cano
1580
Exception
100
Olivia Quiz
740
Pandemic quiz
100
Cups and Saucers - Free Tea Party Etiquette
201029242
TF2 - Test Your Team Fortress 2 Knowledge
201020791
Questions About Tsunamis - Test Your Knowledge
201022056
Which Assassin's Creed III Character Are You? (Free)
201021151
What's My Curse? Try the Curse Breaker
201021029
Diwali - Free Trivia on the Festival of Lights
201030705
Fred or George Weasley - Who's Your Perfect Match?
201019907
American Dream - Test Your Knowledge (Free)
201025705