PREFI MCQ 2
What is the normalization constant in the wavefunction of particle in a ring,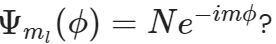
2π
√2/L
1/√2π
1/2π
√2π
The solution wavefunction for quantum particle on a ring is
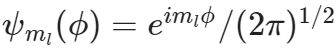 What does the symbol ml stand for?
What does the symbol ml stand for?can take on the value of 0
dependent on the other quantum number l
can be positive or negative integers
a quantum number
The other choices are ALL correct.
Which of the following is NOT a possible energy level of a quantum particle on a ring?
ℏ2/2I
-ħ
0
-2ℏ2/I
2ℏ2/I
Which of the following are possible z-component of angular momentum values of a quantum particle rotating in a ring?
ℏ2/2I
The other answers are ALL correct.
2ℏ2/I
0
-ℏ2/2I
The radial solution to hydrogenic atoms is expressed as
N^n,lp^i
None of the other choices are correct
N^n,l
N
Which quantum number refers to the angular momentum resulting from the movement of electrons around the nucleus?
N
L
Ms
S
ml
Which of the following sets of quantum numbers is not allowed?
The other choices are all correct
n=3, l=0, ml=0, ms=+½
n=3, l=1, ml=-1, ms=+½
n=2, l=2, ml=-1, ms=+½
n=2, l=1, ml=0, ms=+½
The following statements are true for the Schrodinger equation for hydrogen atom except?
The radial wavefunctions, R, though the operation R2 estimates the probability of the locating of the election from the nucleus.
The Schrodinger equation of this system is different from the treatment of the quantum 3D rotational systems in the the radius of the hydrogen atom can vary whereas in the 3D rotational system, the radius is held to be constant.
The most probably distance turns out to be the Bohr radius.
The rydberg contant may be estimated from the energy calculations in the Schrodinger equation.
What is NOT true about the radial solution to the Shrodinger equation of the hydrogenic atoms?
The allowed energy levels is dependent on the variable n and not l.
Far from the nucleus, all radial wavefunctons approach zero exponentially.
Close to the nucleus, the radial wavefunction is proportional to rn, where n is the principal quantum number.
The other statements are all correct.
What is not true about the reduced mass, u, of the system?
The reduced mass is the average mass of the two masses it is reducing
All the other statements are correct
The reduced mass estimates as if the two masses are just one
u = m1m2/m1+m2, where m1 and m2 are the two masses
For the hydrogen atom, which of the following orbitals has the lowest energy?
The other choices have all the same energy
4p
4s
4d
4f
In a hydrogen atom, the reduced mass between the proton (with mass msubN) and the electron (with mass msube), is:
Roughly equal to mN
Roughly equal to me
Roughly equal to the average of mN and me
None of the other choices is correct
Which quantum number refers to the quantum number that is inherent on the property of the electron, that is, resulting from the electron’s existence? Msubl
S
L
N
Msubs
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding Rydberg’s constant?
Quantum mechanical calculation results showed that the constant may be derived from fundamental principles.
The Rydberg constant applies only to the smallest atoms with n=1, so for Hydrogen and Helium.
The other choices are all correct.
The constant was initially determine by Rydberg experimentally.
What is the magnitude of the z-component of angular momentum of an electron with n = 3, and l = 2 and ml = 1?
3h/2pi
3h
2h
h
2h/2pi
h/2pi
None of the other choices
Which of the following is Not a correct consequence of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle?
A harmonic oscillator possess a zero-point energy.
The momentum of an electron cannot be measured exactly.
The shorter the lifetime of an excited state of an atom, the less accurately can its energy be measured.
An electron in an atom cannot be described a well-defined orbit.
Measurement of one variable in an atomic system can affect subsequent measurements of other variables.
Which quantum number does not naturally arise from the schrodinger equation?
Msubl
N
L
S
Msubs
What is the expression for the potential energy between the electron and the proton of a hydrogen atom?
V(r) = −Ze2/4πξ0r, where r is the distance from the nucleus and ξ0 is vacuum permittivity
V(r)=+Ze2/4πξ0r, where r is the distance from the nucleus and ξ0 is vacuum permittivity
None of the other choices
V(r)=+e2/4πξ0r, where r is the distance from the nucleus and ξ0 is vacuum permittivity
V(r)=−e2/4πξ0r, where r is the distance from the nucleus and ξ0 is vacuum permittivity
- The Bohr theory for the hydrogenlike atoms consists (in part), of which of the following postulates(s):
1- The electron moves around the nucleus of charge +Ze in an elliptical orbit.
2- The orbit has constant energy.
3- Transitions between orbits generate spectral lines.
4- The frequency of the spectral lines is given by h/E
4 only
2 only
1 and 4
1,2, and 3
2 and 3
Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE about the presented solution to the hydrogenic atoms?
The solution applies to systems with only one nucleus
There was a separation into two parts: one is translation motion and the other is motion relative to the nucleus.
All the other statements are correct.
The solution applies to systems with only one proton.
The radial solution to hydrogenic atoms, is expressed as Rn,l(r)=Nn,lρlL^2l+1n−l−1(ρ)e−ρ/2. What is NOT true about the associated Laguerre polynomial in the equation?
It is expressed as the middle term L.
It is expressed as the middle term L2l+1n−l−1(ρ).
It is pre-solved by Mathematicians and solutions are just consulted from tables, just like what is done in Physical Chemistry classes.
It is the term that bridges the term that is dominant to the nucleus and the term that expresses dominance far from the nucleus.
Who said that no two electrons can have the same set of quantum numbers?
Bohr
Paul
Aufbau
Hund
What is the magnitude of the angular momentum of an electron with n= 2 and l=0?
√6h
√2h/2π
√2h
√6h/2π
0
What is the magnitude of the z-component of angular momentum of an electron with n=2 and l = 1?
√6h/2π
√2h
√2h/2π
0
√6h
Which of the following is NOT TRUE for the quantum mechanical Hydrogen atom solution?
The wavefunction solution depends on three quantum numbers.
All the statements are true, with the quantum numbers varying between two and three depending on the situation.
The wavefunction solution depends on four quantum numbers.
The wavefunction solution depends on four quantum numbers.
The wavefunction solution is separated into three separable parts: one is radial, the other two depends on angles
The solution can be easily adapted to hydrogen-like systems.
Which of these quantum numbers denote the z-component of the spin angular momentum of the electron?
S
L
N
Msubs
Msubl
What is the magnitude of the angular momentum of an electron with n=2 and l=1?
√6h/2π
√2h
√2h/2π
0
√6h
The solution the radial function for hydrogenic atoms indicate that: Note that other factors are not considered, only the radial solutions are considered.
The probability of locating the electron in the nucleus is high if l=0.
The electron can never be in the nucleus.
The probability of locating the electron in the nucleus is high if n=0.
The probability of locating the electron in the nucleus is zero.
Which of the following statements is TRUE for the energy of hydrogen atom systems?
Degeneracy is equal to n^2, if the spin quantum number is not taken into consideration.
The energy level depends on all the quantum numbers.
All the other statements are TRUE
The lowest energy level is zero.
Which of the following Schrodinger Equations have analytical solutions?
Harmonic Oscillator
3D Rotational Systems
The other choices are all correct.
3D Particle-in-a-box
2D Rotational Systems
“Now I need a drink, alcoholic of course, after the heavy sessions involving quantum mechanics.” This is a mnemonic for which famous constant:
R∞
mc2
h
π
a0
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding the Born-Oppenheimer approximation?
The nucleus is assumed to be stationary; hence, the kinetic energy of the protons is set to be zero.
The neutrons are not considered by the Born-Oppenheimer approximation.
The other statements are ALL true.
The electrostatic attraction between the protons and the electron and nucleus is approximated as zero.
The lowest orbital energy is reached when the number of electrons with the same spin is maximized. This statement describes __________.
Planck's constant
de Broglie hypothesis
Hund's Rule
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle
Pauli's Exclusion Principle
What type of particles are electrons?
bosons
cannot be determined
fermions
can be fermions and bosons
Which quantum number determines the energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom?
n and l
E
l
n
ml
In the Hamiltonian operator expression for the Helium atom, the term e2/4πϵ0r12 refers to
Electrostatic repulsion of electron 1 to electron 2
Kinetic energy of the protons
Electrostatic attraction of electron to the proton
Kinetic energy of the electron 1
Which of the following quantum numbers arose from experimentation and NOT directly from solving the Schrodinger equation?
n
ml
ms
l
All the other options were initially experimentally determined.
In the expression for the Hamiltonian of Helium atom, we have: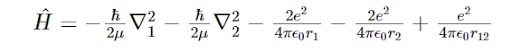 We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. What do the first and the second term signify?
We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. What do the first and the second term signify?
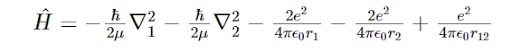 We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. What do the first and the second term signify?
We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. What do the first and the second term signify?the kinetic energy of the two electrons of the He atom.
The interactions within the Hydrogen atom that is approximated to be imbedded within the Helium atom, i.e. Helium atom is approximated to be a combination of two Hydrogen atoms.
All the other options are correct.
the interactions between one proton and one electron within the Helium atom.
the repulsion between the protons in the nucleus.
The repulsion between the electrons in the system.
In the expression for the Hamiltonian of Helium atom, we have: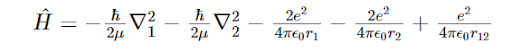 We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. What do the fifth term signify?
We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. What do the fifth term signify?
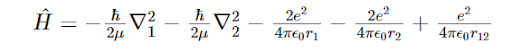 We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. What do the fifth term signify?
We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. What do the fifth term signify? the repulsion between the protons in the nucleus.
The interactions within the Hydrogen atom that is approximated to be imbedded within the Helium atom, i.e. Helium atom is approximated to be a combination of two Hydrogen atoms.
The repulsion between the electrons in the system.
the interactions between one proton and one electron within the Helium atom.
All the other options are correct.
the kinetic energy of the two electrons of the He atom.
In the expression for the Hamiltonian of Helium atom, we have: 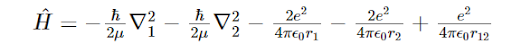 We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. The first and the third term are typically combined to express what system?
We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. The first and the third term are typically combined to express what system?
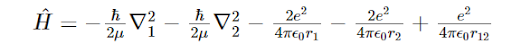 We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. The first and the third term are typically combined to express what system?
We see here the hamiltonian as the combination of five terms. The first and the third term are typically combined to express what system?All the other options are correct.
the kinetic energy of the two electrons of the He atom.
the interactions between one proton and one electron within the Helium atom.
the repulsion between the protons in the nucleus.
The repulsion between the two electrons in the system.
The interactions within the Hydrogen atom that is approximated to be imbedded within the Helium atom, i.e. Helium atom is approximated to be a combination of two Hydrogen atoms.
Why many-electron atoms are not covered in hydrogenic systems? What most important consideration needed to be factored in in the calculations?
The electron to electron repulsions need to be factored in in the calculations.
The proton to electron interactions need to be factored in in the calculations.
ALL the interactions must be considered.
The proton-to-proton interactions in the nucleus need to be factored in the calculations.
Orbital approximation is typically used as a starting point in the many-electron systems calculations. Which of the following statements is NOT true about orbital approximation?
I. The many electron-atom is considered to be a composite of H atoms.
II.The electron-electron repulsion is disregarded or ignored.
III. The total energy is the sum of the energies from the H calculation.
IV.The electron-to-electron repulsion would eventually contribute to a decrease in energy of the system.
II only
III only
All the statements are correct.
I only
IV only
Which one of the following is an incorrect orbital notation?
2s
3f
4dxy
2py
4s
Which term refers to class of particles that have full integer spins?
Quarks
Fermions
Bosons
Electrons
Which of the following statements is NOT true for perturbation theory?
This method is typically applied to systems that have analytic solutions.
The process assumes an ideal case where the system can be initially solved analytically.
This method assumes that the problem cannot be solved exactly, and that the problem can simply be approximated.
The lowest energy system after the corrections or perturbations will be adopted as the most probable solution.
The perturbations are corrections that may be added to the previously solved analytical systems.
In calculating for the property of the wavefunctions, if 1 and 2 are two states, what can be concluded if the system is antisymmetric?
𝚿(1,2) = -𝚿(2,1)
𝚿(1,2) = 𝚿(2,1)
𝚿(1,2) = -𝚿(-2,-1)
𝚿(1,2) = 𝚿(-2,-1)
Which one of the following is not a valid value for the magnetic quantum number of an electron in a 5d subshell?
0
2
1
-1
3
Which of the subshells below do not exist due to the constraints upon the angular momentum quantum number?
2d
2s
2p
All of the other choices
Which one of the following is an incorrect subshell notation?
2p
4f
3d
3s
2d
Which of the following statements can be correct for an electron that has the quantum numbers n=4 and ml=−2?
the electron is in the second principal shell
the electron must have a spin quantum number ms=1/2
the electron is in a d orbital
the electron is in a p orbital
At maximum, an f-subshell can hold ______ electrons, a d-subshell can hold ____ electrons, and a p-subshell can hold _____ electrons.
14, 10, 6
2, 8, 18
2, 6, 10
2, 12, 21
14, 8, 2
How true is the statement, "Two electrons form a triplet state"?
Always TRUE.
Cannot be determined.
Never True,
Sometimes TRUE.
The terms arising from a given configuration differ in energy. Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding their relative energies?
For a given multiplicity, the term with the highest value of L lies lowest in energy.
The level with the lowest value of J lies lowest in energy.
The other choices are ALL correct.
For a given configuration, the term of greatest multiplicity lies lowest in energy.
Which of the following electron transitions in an atom is NOT allowed?
3p→4s
1s→3s
The other choices are ALL allowed transitions.
1s→3p
4s→4p
In an atomic spectrum, which of the following electronic transitions is NOT possible?
The transition from one singlet state to another singlet state.
The transition from one triplet state to another triplet state.
The transition from a triplet state to a singlet state.
The transitions described in the other choices are ALL allowed transitions.
Which term CANNOT arise when considering a p2 configuration in atomic spectra?
F
The other choices are ALL possible.
D
S
P
The energy of the spin-orbit coupling in an atomic spectrum is described as: El,s,j=12hcA~[j(j+1)−l(l+1)−s(s+1)]. Which of the following statements regarding this equation is NOT TRUE.
l is the orbital angular momentum
A~ is the spin-orbit coupling constant, expressed as a wavenumber
j is the total angular momentum
The equation will provide information on the degeneracy of the levels.
s is the spin quantum number.
Which of the following terms may arise from the two-electron d2 configuration in atomic spectra?
The other choices are ALL possible.
S
G
F
P
Which of the following best expresses the basis of the selection rules in the transitions of electrons in different orbitals and energy levels of an atom?
A photon has an intrinsic spin angular momentum.
The angular momenta of electrons and photons interact, and in the interaction, the total angular momenta must be conserved.
the photon involved in transitions carries an intrinsic angular momentum that interacts with the electrons
the transitions involve conservation of angular momentum
Which of the following transiitons is NOT allowed in hydrogenic atoms?
Δl=0
Δml=±1
The other choices are ALL allowed.
Δl=±1
Δml=0
Δn=+2
Which electron state in an atomic spectrum is most stable, given that this state arose from the same configuration?
singlet state
triplet state
antiparallel state
The other choices have the same energy.
Consider the term symbol 3D3/2 in atomic spectra. The total angular momentum of the system is
2
3/2
Cannot be determined, more details are required.
3
Molecules are known to absorb radiation in which region of the electromagnetic spectrum:
The other choices are ALL correct.
Microwave
Visible
Infrared
Ultraviolet
Parallel electron spins result to ________ state.
triplet
singlet
doublet
the other choices are ALL possible
Which of the following statements is NOT TRUE with regards to spin-orbit coupling within an atom?
For a d electron, l=2, there are two resulting levels of total angular momentum, j=+5/2 and j=3/2.
The interaction of the spin magnetic moment with the magnetic field arising from the orbital angular momentum is called spin−orbit coupling.
The other statements are ALL correct.
For a p electron, l=1, there are two resulting levels of total angular momentum, j=+3/2 and j=1/2
For an s electron, l=0, there are two resulting levels of total angular momentum, j=+1/2 and j=−1/2.
A photon has a spin angular momentum corresponding to ___________. s=0.
s=0
s=1
The other choices are all incorrect.
s=1/2
s=3/2
Consider the term symbol 3D3/2 in atomic spectra. The total orbital angular momentum of the system is
Cannot be determined, more details are required.
2
3
3/2
An electron has an intrinsic angular momentum corresponding to __________.
The other choices are ALL incorrect.
s=3/2
s=0
s=1
s=1/2
This refers to an illustration that summarizes the energies of the states and the transitions among the atomic electronic energy levels.
Clebsch–Gordan
Transition
Term states
Grotrian
Russel-Saunders
Which of the following is NOT an energy arising from spin-orbit coupling from a d1 configuration in an atomic spectra?
−hcA~
hcA~
The other choices are ALL possible.
−32hcA~
Which of the following term transitions is forbidden in atomic spectra?
a. ΔL=0
b. ΔS=0
c. J=0 to J=0
d. ΔL=±1
e. The other choices are ALL correct.
f. ΔJ=±1
Which of the following is NOT true regarding rotational spectroscopy:
Only molecules with permanent dipole moment will exhibit changes in rotational energy as result of its interaction with light.
For molecules with odd number of electrons, ΔJ=0 is allowed.
The change in total angular momentum J, ΔJ=±1 that are generally allowed.
The other choices are ALL true.
Consider the three-electron system d3 in atomic spectra. How many D terms will arise from the configuration?
4
1
2
5
3
The total spin angular momenta of antiparallel electrons in an atom is ________.
0
-1
+1
+/- 1
The other choices are all possible.
The total spin angular momenta of parallel electrons in an atom is ________.
0
2
The other choices are all possible.
1
Consider the term symbol 3D3/2 in atomic spectra. The multiplicity of the system is _____________
3/2
3
Cannot be determined, more details are required.
2
{"name":"PREFI MCQ 2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QG2ZFFANL","txt":"What is the normalization constant in the wavefunction of particle in a ring,, The solution wavefunction for quantum particle on a ring is What does the symbol ml stand for?, Which of the following is NOT a possible energy level of a quantum particle on a ring?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}