Lecture 5 & 6- Public health
All of the following are health complications of worm infestations in a child, EXCEPT
Anemia
poor nutrient absorption
impaired cognitive development
Obesity or weight gain
T/F: worm infestations in children peak at the age of 1 to 3
True
False
T/F: It is recommended to do exclusive breast-feeding for the first 4 months , then introduce solid foods at the fifth month and continue on-demand breast feeding and contin
True
False
Complementary foods can be introduced After 6 months of exclusive breast-feeding, in combination with frequent or on-demand breast-feeding.
True
False
Breast-feeding is common in well-developed countries as urbanization has led to a positive impact on defying cultural norms
True
False
Breast milk is considered a complete food that supplies all nutrients for babies from birth until they are months old
True
False
What are the requirements for safe formula feeding?
Access to safe water & electricity
Sufficient money to buy formula and utensils needed in preparation
Providing training for the mother regarding the Preparation method, use, and handling of powdered infant formula to minimize health hazards
All of the above
More than half of deaths in children under 5 years are attributed to undernutrition
True
False
Fill in the blank: At birth, the head circumference is 35 cm and it increase by ............ Cm during the first year in the baby's life
2 cm
5 cm
12 cm
7 cm
The breast milk can cause a risk of illness due to contamination
True
False
From month (0-4), the baby gains 200g per week, then from month (4-8) he gains 500g per month, then in the last 4 months of the first year the weight gain is only 40 g per week , so it can be said that the total approximate weight gain after 4 months is 2-4 kg and when the baby completes 1 year, the average weight gain is 7 kg
True
False
In the first year of a toddler life, it is expected that the he gains 7 kg totat
True
False
As the head circumference of the baby increase, the brain size increase as well
True
False
The higher proportion of brain growth and the total development of human brain occurs POST-NATALLY
True
False
What are the consequences of undernutrition in infants and young children?
a. Improved immunity
B. Stunted growth
C. Increased risk of adult chronic disease
D. Both b and c
In which region do we find the highest number of child deaths due to undernutrition?
North America
Europe
Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia
Australia
How can the growth and development of infants and young children be assessed?
A. Through blood tests
By assessing weight and length/height
Through neurological exams
D. Both a and b
What is the average length at birth for boys? a. 45 to
A. 45 to 53 cm
B. 46 to 55 cm
53 to 60 cm
D. 40 to 48 cm
At what age does the brain reach 50% of its adult weight?
1 year
2 years
3 years
4 years
When do infants maximize energy intake and minimize energy expenditure?
A. 0-3 months
B. 3-6 months
C. 6-9 months
D. 9-12 months
At birth, the brain of the baby represents 25% of its adult weight
True
False
What are the short-term effects of early Healthy nutrition in children & infants?
Improved immunity
Growth and muscle mass
Both a and b
None of the above
What are the risks associated with low birth weight and preterm birth?
Increased perinatal mortality
Delayed psychomotor development
Pulmonary morbidity
All of the above
What is childhood stunting?
Rapid linear growth
Retardation in linear growth
Increased height-for-age ratio
None of the above
What is considered underweight in relation to weight-for-age chart in children?
Weight-for-age below -1 SD
Weight-for-age below -2 SD
C. Weight-for-age below -3 SD
Weight-for-age below -4 SD
What are the long-term benefits of breastfeeding on the infant when he grows up in adulthood
Lower blood pressure
Lower prevalence of obesity and type 2 diabetes
Higher intelligence scores
All of the above
Powdered infant formula milk is sterile and it has no risk of contamination, thus it wouldn't cause an infection to the baby
True
False
In the first week after birth, preterm infants tend to grow very fast as they adjust to extra uterine nutrition
True
False
What is childhood obesity diagnosed based on?
A. Weight-for-age
B. Height-for-age
C. Weight-for-height
D. BMI-for-age chart
What is the expected growth pattern of preterm infants during the first year in terms of the weight curve chart?
The preterm infant's weight curve is expected to cross the percentile lines during the first few months and by the end of the first year, the length of the average preterm infant is usually around the 15thpercentile
The preterm infant's weight curve is expected to cross the percentile lines during the first few months and by the end of the first year, the length of the average preterm infant is usually around the 5thpercentile
The preterm infant's weight curve is expected to cross the percentile lines during the first few months and by the end of the first year, the length of the average preterm infant is usually around the 50th percentile
The preterm infant's weight curve is expected to cross the percentile lines during the first few months and by the end of 6 months, the length of the average preterm infant is usually around the 50th percentile
Which of the following are common nutritional issues in young children < 5 years
A. Vitamin A, Vitamin D, iron, iodine, zinc deficiency
B. Undernutrition
C. Measles
D. Only a & b
E. All of the above
All of the following are the factors that affects the child survival negatively, EXCEPT
Nutrient deficiency including protein and micronutrient deficiencies
The presence of environmental hazards
Injuries
Setting personal prevention measures to control personal illness
Infants become double their birth length once they reach year one
True
False
Researches have found direct proportional relationship between breast-fed infants and their tendency to develop obesity later on in their adulthood
True
False
Breast-fed babies are less likely to develop childhood obesity later on
True
Fales
Most of growth faltering begins in utero or soon after birth
True
False
Dietary assessment analysis to check the adequacy of feeding of the infant include investigating?
The type of the feeding used (whether it is breast-feeding or formula)
The use of vitamins/minerals supplements by infants
The quantity and frequency of feeding
Solid food intake
Feeding behaviour of the baby
The cleanliness of the Feeding environment
Whether the family of the infant is avoiding certain foods/ food groups and follow alternative dietary practices
If the baby suffers from food allergies
All of the above
Which of the following is used in assessing the physiological growth in infancy
The Egyptian weight-for-age percentiles chart
The WHO weight-for-age charts using growth curves
The BMI-for age charts
The weigh-for-height percentiles chart
The body mass index-for age percentiles is used for young children aging from 2-20 years
True
False
What is ideal time to intervene with a nutritional counselling to prevent child stunting
In the preschool age from 3-5 years old
When the child is under the age of 24 months
Once the child reaches the age of 3
Non of the above
Macronutrient malnutrition such as malnutrition caused by protein-deficiency is also known as the ''silent or hidden hunger'' because it can be asymptomatic
True
False
Choose the correct statements about the recommended nutrient intake (RNIs) in infants
They can be considered an alternative to Recommended dietary allowance (RDAs_
In case the infant is > 6 months old, this value will be based on the amount of nutrient provided by the breast milk or breast milk substituents and the complementary solid food
In case the infant is <6 months old, and he is exclusively breast-fed, this value will be based on the amount of nutrient provided by the mother's milk only
This value should be regularly assessed to ensure optimal intake as a part of nutritional counselling to support the infant growth
All of the above statements are true
All of the following are considered effective and appropriate nutritional interventions for infants and young children EXCEPT
Increase the awareness of caregivers on growth monitoring children and encourage the mothers on interacting with caregivers to promote their child growth
Educating the new mothers about the principles of complementary feeding when the child is > 6 months old
Giving the lactating mothers additional food supplements in food-insecure populations such as those going through a crisis of war
Treating severely malnourished pre-schooler kids by supplementation with various micro and macro nutrients
Giving the new mothers formula milk fortified with essential micronutrients rather than breast-feeding since it has higher iron content
All of the following are appropriate feeding practices for a pre-school child EXCEPT
A) Giving him 2 child-sized servings of fruits and veggies as snacks since they're rich in iron, vit.C, vit.A
B) Force the child to eat at least 3 times per day to ensure a satisfactory nutrient intake
C) Encourage the child to eat variety of foods
D)In each meal preparation, the child should be served 3 tablespoons of food for each year of age
E) both options b & d are incorrect statements
Children of late pre school age appear to be less responsive to external cues than to their instinctive ability to self-regulate their nutrient intake
True
False
All of the following are benefits of breast-feeding for mothers EXCEPT
Decreasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels
Enhances fat loss in the early post-partum weeks
Increasing bonding with baby.
Reduces the risk of post-partum hemorrhage
Frequent breast-feeding helps to delay the return of fertility of the mother and thus helps to space children
True
False
The following are barriers to breast-feeding, EXCEPT
Insufficient information from the healthcare provider
Positive emotions about breast feeding
Workplaces are not supportive of breast feeding because the maternity leave is insufficient
Embarrassment about breast-feeding in public.
What should be done as a part of the ABCD approach for assessing nutritional status of lactating mothers?
Conducting anthropometric measurements
Checking vit.D, calcium and iron levels
Investigating if there are any signs of vitamin deficiencies, general signs of malnutrition and fluid retention
All of the above
The skinfold thickness & calf-circumferences are reliable anthropometric measurements for assessing nutritional status in pregnant women
True
False
Match each anthropometric measurement with what it would reflect in case of a pregnant women
Mid-upper-arm-circumference (MAUC)
Reflects Severe wasting
Very low pre-pregnancy BMI
Reflects higher risk of IUGR
Women with very low height (140-150cm)
Reflects past and current nutritional status
The abdomen circumference of a pregnant women acts as a proxy indicator for her skeletal pelvic structure
True
False
The hight of pregnant women can be used to predict the risk of cephalopelvic disproportion and obstructed labor
True
False
Women of short stature (height is 140-150cm) are at high risk of which complications?
Having low birth babies
Preterm delivery
Both a & b
Non of the above
The accepted range of gestational weight gain for all pregnant women is 7-10 kg
True
False
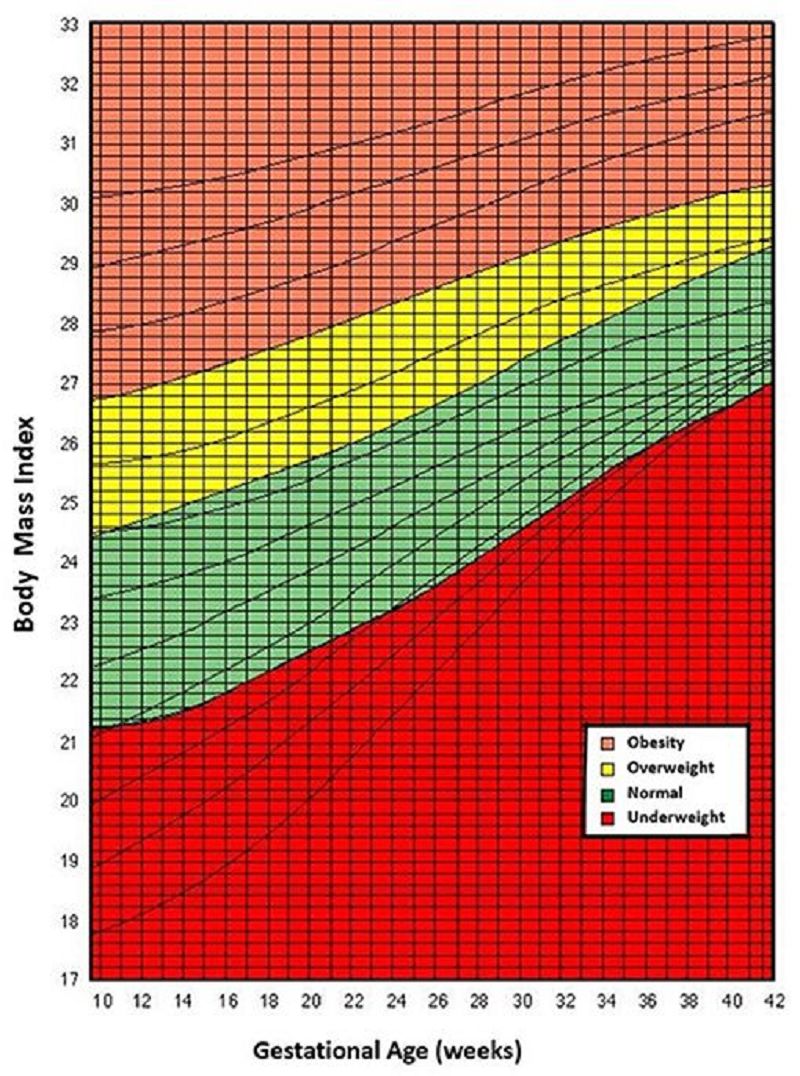
M.S. Is a pregnant women coming to your clinic to monitor her gestational weight gain, on week 25 her weight was 46, today she is at her week 38 and her weight was 50 kg, height is: 160 cm, Based on the following chart, is M.S gestational weight gain considered normal?
No, she is severely underweight
Yes, her BMI is normal
No, she is moderately overweight
Can not decide due to lack of information
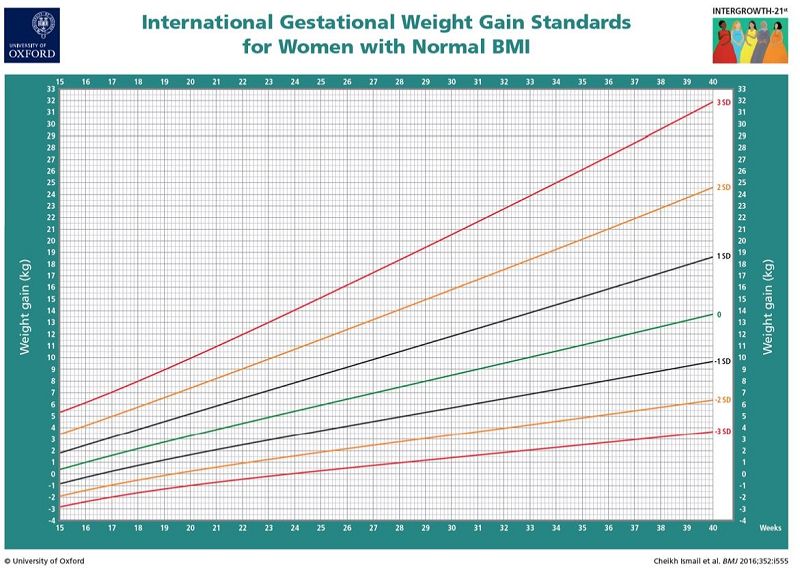
M.K is a pregnant women coming to your clinic to monitor her gestational weight gain, she had a normal BMI pre-pregnancy, and she gained a total of 6 kg in the period from week 25 gestation to week 39 gestation, based on these values and according to the given figure
Her Weight-for-gestational age is at -2 SD indicated suboptimal weight gain
She has a normal healthy weight gain
Her weight for gestational age is at +1SD indicating that she gained more weight than she should
Can not decide due to lack of information
All of the following are biochemical methods used in the assessment of nutritional status of a pregnant women EXCEPT
CBC and hemoglobin
Fasting blood glucose
Urine analysis including looking for signs of glucosuria or proteinurea
Collecting medical history and investigating clinical symptoms
Dietary intake assessment to reflect a pregnant women nutritional status includes
Food frequency questionnaire
24- dietary recall method
Writing a food diary for 24 hours
Conducting medical history collection to identify nutrition-related problems or risks
All of the above
Low pre-pregnancy weight is a predictor of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
True
False
Maternal health (the mother's health) in periods of inadequate nutritional intake is more compromised than fetal growth
True
False
The baby is considered low birth weight when his weight at birth is
Less than 3.5 kg
Less than 2.5 kg
Less than 3 kg
Between 2.7-3 kg
The following are all complications of Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR) EXCEPT
Sudden infant death syndrome
High risk of pre-natal death
Neurological issues
Normal psychomotor development
Decreased cognitive abilities
Which of the following is considered a risk factor that can lead to Intrauterine Growth Restriction (IUGR)
Cigar smoking
Low height 140-150 cm
Pre-eclampsia that is not treated
Low nutrient intake that leads to low and suboptimal gestational weight gain
Low BMI prior conception
All of the above
Which of the following can lead to the delivery of premature baby?
Low pre-conceptional BMI
Suboptimal conceptional weight gain in pregnancy
Multiple subsequent pregnancies with little spacing time between births
Comorbidities during pregnancy like anaemia, placental insufficiency, hypertention
All of the above
Deficiency in which vitamins can lead to micro nutrient malnutrition in maternity and negatively influence the fatal growth
Vitamin A, C, D
Iron and zinc
Folic acid
All of the above
Which vitamin is recommended as soon as the women gets pregnant because inadequate availability of it in 21-37 conception days could lead to neural tube defects
Folic acid
Iron
Vit. B12
Vitamin A
What is the recommended daily amount of elemental iron in pregnancy to avoid nutritional deficiency?
60 mg
120 mg
325 mg
30mg
What is the recommended daily amount of calcium for a pregnant women to reduce the risk of hypertension and pre-eclampsia (hypertension in pregnancy)
1000-2000 mg
400-600 mg
3 grams
Non of the above
When is the period of time that is considered the most critical window for applying nutritional interventions in pregnant ladies
In the second trimester of pregnancy
From the beginning of pregnancy and up to the age of 2 years
During first trimester only
In the first 3 months post-partum
The BMI cut-off point of 18.5 can be used as a valid assessment tool for maternal body weight in pregnant women
True
False
The BMI cut-off point of 18.5 can be used as a valid assessment tool for maternal body weight in lactating women
True
False
Skinfold thickness and maternal calf circumferences are valid anthropometric measurements in the nutritional assessment of lactating mothers?
True
False
Fill in the blank: According to RDA for energy during lactation, a lactating mother needs additional................. Kcal in the first 6 months after giving a birth, and extra .................. Kcal for the second 6 months
230 kcal, 300 kcal
330 kcal , 400 kcal
260 kcal , 500 kcal
She doesn't need extra energy
Overweight women need to add additional 350 kcal to her total energy need if they are performing exclusive breast feeding
True
False
Extensive insufficient protein/nutrient intake for long periods in lactating women can lead to failure of breast feeding due to decreased the volume of milk production
True
False
Prolonged exclusive breast-feeding feeding beyond 6 months can cause maternal folate deficiency which leads to megaloblastic anemia
True
False
All of the following are baby-friendly practices , EXCEPT
A) Showering the baby within 1 hour of birth
B) Giving the baby a pacifier to promote latching
C) help the mother to breast fed within 1 hour of birth
D) promote skin-to-skin contact as soon as the delivery occurs
E) options a & b
E) allow the mother and her baby to stay in the same room
{"name":"Lecture 5 & 6- Public health", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"All of the following are health complications of worm infestations in a child, EXCEPT, T\/F: worm infestations in children peak at the age of 1 to 3, T\/F: It is recommended to do exclusive breast-feeding for the first 4 months , then introduce solid foods at the fifth month and continue on-demand breast feeding and contin","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/97-4762174/pregnant-bmi.jpg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Quiz on articles: made by vteachulearn.com
1580
Body parts
9416
Kenal Mengenal.
20100
HOBBIES
1059
Ultimate Ballet Terminology: Test Your Ballet Terms
201041390
Ultimate Beer Test: Master Brewing Basics
201023790
Free Stress Management Knowledge
201022197
The Great Gatsby: Ace Chapters 7-9 Trivia
201041390
Free Periodic Table: Elements & Symbols
201022527
Which Ghosts Character Are You? Find Your Spectral Type
201024809
Which NBA Star Matches You? Favorite NBA Players
201023790
ATI Maternal Newborn Final - Practice & Ace Your Exam
201029288