1) A 74-year-old man presents to your office for a routine. He has no present complaint. His medical history is significant for right knee osteoarthritis. He takes naproxen occasionally, to relieve knee pain. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His BP is 165/75 mmHg and PR is 70/min. The physical examination showed a mild systolic ejection type murmur at the base of the heat to the right. An E-KG revealed left ventricular hypertrophy and secondary ST segment and T wave change. Moderate left ventricular hypertrophy, without any flow abnormalities, was demonstrated on echocardiography. The ejection fraction was 60%. What is the most probable cause of hypertension in this patient?
Rigidity of the arterial wall
Elevated plasma renin activity
Aortic insufficiency
Increased cardiac output
Increased intravascular volume
2) A 47-year-old woman loses consciousness for 2 minutes while shopping in a supermarket. In the emergency room, she recounts feeling nausea and warmth spreading over her body immediately before passing out. She has never had a similar episode before. She has not seen a doctor for several years and does not take any medications, nor does she use tobacco, alcohol or drug. Her family history is unremarkable. Which of the following most likely caused this episode?
Cardiac arrythmia
. Seizure
Neurocardiogenic syncope
Orthostatic hypotension
Heat valve disease
3) A 25-year-old woman experiences sudden-onset palpitations and generalized weakness. During this episode, her blood pressure is 100/60 mmHg and her heat rate is 160/min and regular. She has no significant past medical history and does not take any medications. She reports having a few similar episodes in the past which she has self-treated by immersing her face in cold water. Generally, she says, cold water immersion relieves her symptoms within several minutes. This cold water therapy works by affecting which of the following?
Vascular tone
Sinoatrial node automatism
Atrioventricular node conductivity
. Purkinje fiber conduction
. Ventricular myocardium contractility
4) A 67-year-old man is evaluated for hypertension. He complains of occasional morning headaches. His past medical history is also significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease, and a stroke with residual left-sided weakness. He underwent coronary artery bypass surgery seven years ago and carotid endarterectomy five years ago. His current medication list includes lisinopril hydrochlorothiazide, amlodipine, metoprolol, aspirin, metformin and glyburide. His blood pressure is 190/120 mmHg on the right arm and 170/110 mmHg on the left arm. His heat rate is 65/min Physical examination reveals a periumbilical systolic-diastolic bruit. The latter finding is best explained by which of the following?
. Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Aortic dissection
Aortic coarctation
. Renal artery stenosis
Aorto-enteric fistula
5) A 67-year-old male is brought to the emergency department after a syncopal episode. He lost consciousness while shopping in the mall. He denies any nausea, diaphoresis, chest pain, or shortness of breath. He has had two episodes of lightheadedness over the last month but has not seen a doctor. His past medical history is significant for long-standing hypertension, which is being treated with enalapril. His blood pressure is 135/90 mmHg while supine, and 130/85 mmHg while standing. His heat rate is 64/min. ECG shows a sinus rhythm with high voltage, prolonged PR interval, prolonged QRS interval, normal QT interval and occasional premature ventricular contractions (PVC). Echocardiography reveals left ventricular hypertrophy and an ejection fraction (EF) of 55%. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's syncope?
Bradyarrhythmia
Decreased myocardial contractility
Torsades de pointes
Ventricular premature beats
Autonomic dysfunction
6) A 47-year-old male presents to your office with a two-month history of lethargy and decreased libido. His medical records reveal that he has been treated for joint pain and swelling over the last six months and was diagnosed with diabetes mellitus one year ago. Physical examination reveals hepatomegaly and testicular atrophy. Which of the following cardiac abnormalities is most likely to also be present in this patient?
Endocardial fibroelastosis
Cardiac conduction block
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Atrial septal defect
Aortic stenosis
7) A 50-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of lower extremity edema that stated several weeks ago, and slowly progressed thereafter. Her past medical history is significant for hypertension, treated with metoprolol for 2 years. Amlodipine was added recently because of inadequate control of BP with metoprolol alone. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. She has no known drug allergies. Her blood pressure is 130/80mmHg and her heart rate is 64/min. The physical examination reveals bilateral symmetric 3+ pitting edema of both lower extremities, without any skin changes or varicosities. Her neck vein pulsation is normal. Other physical findings are within normal limits. Her laboratory studies reveal the following: Serum albumin 4.5 g/dL, Total serum bilirubin 0.8 mg/dL, Serum sodium 140 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dL. Urinalysis is within normal limite. What is the most likely cause of the edema in this patient?
Venous insufficiency
Side effect of her medications
Renal disease
Liver disease
Heart failure
8) A 63-year-old man presents to the ER with substernal chest pain and diaphoresis. The pain stated one hour ago and did not remit with antacids. He has a past medical history of asthma for which he uses inhaled fluticasone and peptic ulcer disease for which he takes omeprazole. His family history is significant for prostate cancer in his father and breast cancer in his mother. Physical examination reveals a blood pressure of 160/100 mmHg and a heat rate of 90/min. A bruit is heard over the right carotid artery and a mild systolic murmur is present at the cardiac apex. Sublingual nitroglycerin and aspirin are administered in the. Within minutes, the patient reports decreased pain. Which of the following most likely accounts for this improvement in his symptoms?
Increased left ventricular compliance
Increased systemic afterload
Increased cardiac preload
. Decreased left ventricular contractility
. Decreased left ventricular volume
9) A 38-year-old female comes to your office complaining of occasional palpitations. She describes feeling a fast and irregular heartbeat. Over the past two months, she has had three such episodes, each lasting about two hours. She denies any associated chest pain, shortness of breath cough or ankle swelling. She drinks alcohol on social occasions and does not smoke cigarettes. She has no other medical problems and is not taking any medications. On physical examination, her temperature is 37.1°C (98.9°F), pulse is 80/min, blood pressure is 130/70mmHg, and respirations are 14/min. On auscultation of her heat the apical impulse is displaced and there is an S3. You also hear a pansystolic murmur, which is loudest at the apex and radiates to the axilla. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Mitral valve prolapse
Myocardial ischemia
Rheumatic heat disease
Mitral annular calcification
Infective endocarditis
10) A 42-year-old woman is evaluated for depression, mood swings and poor. She also complains of mild headaches and muscle weakness. She has had two ER visits for kidney stones over the past year. She denies any illicit drug use. Her blood pressure is 160/105 mmHg and her heat rate is 85/min. Her laboratory findings are shown below: Sodium 140mEq/L, Potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Chloride 101 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, BUN 13 mEq/L, Creatinine 0.9 mEq/L, Glucose 98 mEq/L, Calcium 11.7 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's hypertension?
Renal parenchymal disease
Renal vascular stenosis
Aortic dissection
Hypothyroidism
Parathyroid gland disease
11) A 14-year-old African American male is referred to your office after his older brother experienced sudden cardiac arrest during hiking trip. He has no current complaints. He denies any illicit drug use. His blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg and his heat rate is 75/min. Neck is supple, no jugular venous distention is appreciated. Carotid pulse seems to have dual upstroke. Lungs are clear. There is strong apical impulse and a systolic ejection type murmur along the left sternal border. Which of the following is most likely to increase the murmur intensity in this patient?
Squatting
Valsalva maneuver
Sustained handgrip
Recumbency
Leg raising
12) A 60-year-old male is brought to ER by his son because he had an episode of syncope. He was watching TV in an arm-chair when suddenly lost his consciousness without any warning sign. He had several clonic jerks while unconscious. He never had such an episode before. His past medical history is significant for acute myocardial infarction six months ago and well-controlled hypertension. His current medications include captopril metoprolol hydrochlorothiazide, clopidogrel and aspirin. His blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg and heat rate is 80/min with frequent ectopic beat. Physical examination revealed mild holosystolic apical murmur radiating to the axilla. Which of the following is the most probable pathophysiologic mechanism for his syncopal episode?
Vasovagal reaction
Arrhythmia
Autonomic dysfunction
Seizure
Postural hypotension
13) A 54 year-old male comes to the physician because of abdominal distention. He thinks his big belly is making it hard for him to breathe. He received radiation therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma several years ago and was told that he is cured. He drinks alcohol on a regular basis. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 20/min. Examination shows a jugular venous pressure 7 cm above the sternal angle. Dullness to percussion and decreased breath sounds are noted in the right lung base. The abdomen is quite distended with an obvious fluid wave. Mild hepatomegaly is present. Extremities have 2+ lower extremity edema. Initial laboratory studies are shown below: Serum creatinine 08 mg/dL, Alburnin 4.0 mg/dL, Total bihrubin 1.0 mg/dl, Prothrombin time 11 sec. Urinalysis is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
Thoracic duct obstruction
Inelastic pericardium
Portal vein compression
Urinary protein loss
Portal vein thrombosis
14) A 32-year-old woman presents with progressively worsening dyspnea on exertion one month after returning from a vacation in Texas. She says that her symptoms have progressed to the point that she now wakes during the night with a choking sensation that improves only with sitting up. Recently her shortness of breath has required her to significantly limit her physical activity. She denies having associated chest pain, skin rash or joint pain. She has no significant past medical history. Family history is significant for thyroid cancer in her aunt and lung cancer in her father, a heavy smoker. On physical examination, her temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), pulse is 96/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, and respirations are 14/min. Bilateral pitting ankle edema is present. Her liver is enlarged 2 cm below the right costal marginal. Lung auscultation reveals decreased breath sounds at the bilateral bases. Cardiac exam reveals the presence of a third heat sound. Chest x ray shows an enlarged cardiac silhouette and small bilateral pleural effusion. EKG is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Atherosclerosis
Viral infection
Lyme disease
Coccidioidomycosis
Autoimmune disease
15) An 88-year-old female nursing home resident is brought to the hospital with a one-week history of moaning, decreased oral intake and decreased ambulation. Physical examination reveals a very thin female who is moaning and appears to be in pain. She opens her eyes spontaneously but does not respond to questions. Her blood pressure is 75/43 mmHg, pulse is 105/min, temperature is 35.5°C (96°F), and respirations are 22/min. Oxygen saturation (pulse oximetry) is 97% on room air. Her skin and oral mucosa are dry and her neck veins are flat. There is no lymphadenopathy. On chest auscultation, there are crackles in the right upper lung lobe. Abdomen is soft and non-distended. There is 2+ pitting presacral and lower extremity edema, and a deep pressure ulcer in the sacral area. Laboratory analysis reveals the following: Sodium 155mEq/L, Potassium 5.3 mEq/L, Glucose 88mg/dL, Bicarbonate 14mEq/L, BUN 151mg/dL, Creatinine 3.1mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her lower extremity edema?
Increased plasma hydrostatic pressure
Decreased plasma oncotic pressure
Renal water and sodium retention
Increased interstitial oncotic pressure
Decreased lymphatic drainage
16) A 64-year-old man complains of palpitations and progressive shortness of breath over the past several hours. He says that he also develops a choking sensation every time he tries to lie down. His medical history is significant for hypertension for the past 20 years and medication non-compliance. He also has a 35-year smoking history. He reports that his father died of a heart attack at age 70 and his mother suffered from asthma. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 170/100 mmHg and his heat rate is 130/min and irregularly irregular. Lung exam reveals bibasilar crackles. There is 2+ pitting edema of the lower extremities. Bedside echocardiography shows a left ventricular ejection fraction of 55%. Which of the following is most likely responsible for his symptoms?
Increased lung compliance
Small airway bronchoconstriction
High-output heat failure
Diastolic dysfunction
Cardiogenic shock
17) A 55-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office with muscle pain of recent onset. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and an acute myocardial infarction experienced 2 months ago. His current medications include metoprolol captopril, aspirin and simvastatin. His blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg and heat rate is 60/min. Liver function tests are slightly abnormal. Serum creatine kinase level is elevated. You suspect a drug-induced reaction. Which of the following is the most possible mechanism of drug-induced reaction in this patient?
Immune-mediated reaction
Cell surface receptor blockage
Synthetic reaction inhibition
Damage of membrane-bound lipids
Extracellular enzyme blockage
18) A 70-year-old man is brought to the Emergency Room because he lost his consciousness while working in the garden. He says that he had several episodes of near-syncope on exertion recently. His past medical history is insignificant. He is not taking any medications. His blood pressure is 110/85 mmHg and heat rate is 80/min. Point of maximal impulse is increased in intensity. Cardiac auscultation reveals ejection type systolic murmur at the base of the heat with radiation to the carotid arteries. ECG demonstrates left ventricular hypertrophy, and secondary ST segment and T wave change. What is the most probable cause of this patient's condition?
Rheumatic endocarditis
Bacterial endocarditis
Hypertension
Congenital anomaly
Age-related sclerocalcific changes
19) A 32-year-old male complains of progressive weakness and exertional dyspnea. His past medical history is significant for a knife injury to the right thigh two months ago. He has been arrested several times for robbery. He consumes alcohol regularly, and smokes crack occasionally. His younger brother died of cystic fibrosis. His blood pressure is 160/60 mmHg, and heart rate is 100/min. His extremities are warm and flushed. Carotid upstroke is brisk. The point of maximal impulse is displaced to the left, and a soft, holosystolic murmur is heard over the cardiac apex. The murmur does not change with the Valsalva maneuver. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Decreased cardiac output
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Increased cardiac preload
Papillary muscle dysfunction
Pulmonary hypertension
20) A 22-year-old college student went to the health clinic complaining of a fever over the last 5 days, fatigue, myalgias, and a bout of vomiting and diarrhea. The clinic doctor diagnosed him with acute gastroenteritis and told him to drink more fluids. Three days later, the student presents to the ED complaining of substernal chest pain that is constant. He also feels short of breath. His temperature is 100.9°F, HR is 119 beats per minute, BP is 120/75 mmHg, and RR is 18 breaths per minute. An ECG is performed revealing sinus tachycardia. A chest radiograph is unremarkable. Laboratory tests are normal except for slightly elevated WBCs. Which of the following is the most common cause of this patient’s diagnosis?
Streptococcus viridans
Influenza A
Coxsackie B virus
Atherosclerotic disease
Cocaine abuse
21) A 60-year-old man is brought to the ER by his wife because he lost consciousness in the bathroom at night. He says that he woke up, went to the bathroom to urinate, and fainted there. He rapidly recovered his consciousness without any indication of disorientation. He has never had such an episode before. He admits' problems with urination,' including difficulty with initiating urination and frequent awakening to void at night. He does not take any medication. His past medical history is insignificant. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes per day and does not consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg while supine, and 132/80 mmHg while standing. His heart rate is 70/min. His physical examination is within normal limits. The ECG is normal. What is the most probable cause of the syncopal episode in this patient?
Arrhythmia
Postural hypotension
. Situational syncope
Seizure
Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
22) A 73-year-old man presents to the ED after a syncopal episode. He had been resting in bed for approximately one week after injuring his right knee. This morning, his knee felt better and he attempted to get up from bed. However, upon attempting to stand, he sustained a brief loss of consciousness. He had no symptoms or medical history prior to the knee injury. Medications include acetaminophen and ibuprofen for knee pain. On exam, his pulse is 73/min, respirations are 14/min, and blood pressure is 136/83 mmHg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's syncope?
Cardiac arrhythmia
Valvular obstruction
Orthostatic hypotension
Vagal nerve hyperactivity
Hyperventilation
23) A 46-year-old woman is hospitalized for agitation, restlessness and poor sleep. She has been complaining of headaches recently and has gained 14 pounds over the past three months. She denies any illicit drug use. Her blood pressure is 160/110 mmHg and her heart rate is 90/min. Her laboratory findings are shown below: Sodium 142 mEq/L, Potassium 3.2 mEq/L, Chloride 98 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 26 mEq/L, BUN 12 mg/dl, Creatinine 0.9 mg/dl, Glucose 205 mg/dl, Calcium 94 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's hypertension?
Renal parenchymal disease
Hypothyroidism
Adrenal medullary disease .
Parathyroid gland disease
Adrenal cortical disease
24) A 53-year-old man presents to the emergency room with squeezing chest pain that started two hours ago. He also complains of shortness of breath that is worse when lying down. He has never had pain like this before. He has no significant past medical history and he takes no medications. A routine health maintenance visit two weeks ago was normal. On physical examination in the ER, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 100/min. Chest auscultation reveals a grade II/VI blowing systolic murmur at the cardiac apex and bibasilar crackles in the lungs. ECG shows ST segment elevations in leads I, aVL, and v1-v3. Which of the following is most likely increased in this patient?
Left atrial pressure
Right ventricular preload
Left atrial size
Left atrial pressure . Left atrial size . Left ventricular compliance . Left ventricular ejection fraction
Left ventricular compliance
25) A 35-year-old woman who has recently emigrated from Asia presents to the emergency room with acute onset of dyspnea. She denies any cough, chest pain, or fever. She has a history of rheumatic heart disease as a teen. On examination, she has an irregular pulse of 97/min, blood pressure of 125/75 mmHg and temperature of 37.2°C (98.9°F). The first heart sound is loud and a mid-diastolic rumble is heard at the apex. Crackles are present in both lung fields. ECG shows an irregularly, irregular heart rhythm and the absence of 'P' waves. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's abnormal heart rhythm?
Left atrial dilatation
Right atrial dilatation
Left ventricular dilatation
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Pulmonary hypertension
26) An 82-year-old male presents for evaluation of chronic back pain. On physical examination, he is found to have a blood pressure of 160/85 mmHg while supine and 135/70 mmHg while standing. He is otherwise healthy; his only medicine is occasional ibuprofen for back pain. Which of the following age- related changes best explains the observed finding?
Increased left ventricular wall stiffness
Decreased left ventricular contractility
Decreased baroreceptor responsiveness .
Decreased glomerular filtration rate
. Decreased stress-mediated catecholamine release
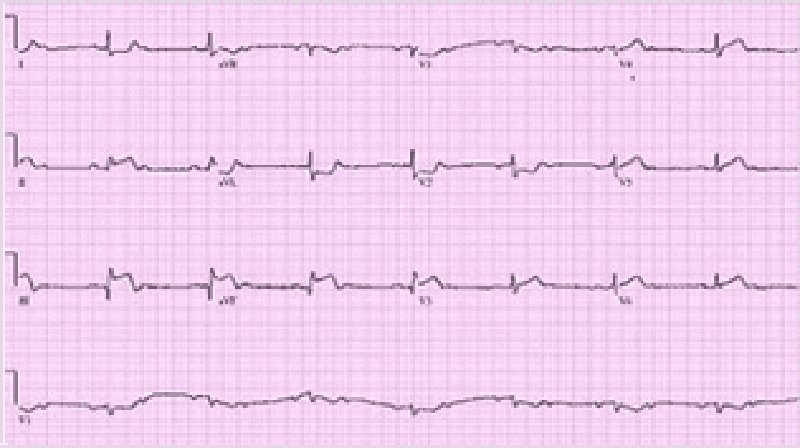
27) A 70-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department because of the sudden onset of nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and chest pain. His other medical problems include hypertension, diabetes mellitus-type 2, and aortic stenosis. He has smoked one-and-a-half packs of cigarettes daily for 30 years and drinks 4 ounces of alcohol daily. His temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), blood pressure is 100/60 mmHg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 18/min. The patient's pulse oximetry showed 98% at room air. Examination shows normal first and second he sounds. Lungs are clear to auscultation. His EKG is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism of this patient's condition?
Occlusion of the right coronary artery
Occlusion of the left circumflex artery
Inflammation of the pericardium
Vasospasm of the left circumflex artery
Occlusion of the left anterior descending artery
28) A 24-year-old male experiences syncope while shovelling snow. He regained consciousness within one minute. He has been having some shortness of breath and chest pains recently, mostly related to exercise. He denies any illicit drug use. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), and blood pressure is 126/76 mmHg, pulse is 76/min and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows a well-built male in no apparent distress. Lungs are clear. A crescendo-decrescendo systolic murmur is heard along the left sternal border without carotid radiation. Chest X-ray is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his syncopal episode?
Atrioventricular conduction delay
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Coronary atherosclerosis
Aortic dissection
Mitral valve degeneration
29) A 33-year-old woman is undergoing an elective, open cholecystectomy after 2 episodes of acute calculous cholecystitis. She suddenly becomes hypotensive, and a generalized rash is noted. Her past medical history is significant for a hypotensive episode 8 weeks ago while having protected sex with her new partner. Which of the following is the most probable cause of this patient's condition?
Acute blood loss
Septic shock
Coagulation abnormality
Pulmonary embolism
Allergic reaction
30) A 72-year-old male comes to the office with intermittent symptoms of dyspnea on exertion, palpitations, and cough occasionally productive of blood. On cardiac auscultation, a low-pitched diastolic rumbling murmur is faintly heard at the apex. What is the most likely cause of the murmur?
Rheumatic fever as a youth
Long-standing hypertension
A silent MI within the past yea
A congenital anomaly
Anemia from chronic blood loss
31) A 53-year-old male presents to your office with a two-day history of right calf pain and swelling. He describes the pain as constant and states that it is exacerbated by knee flexion. He has a history of past IV drug abuse, endocarditis, and stroke. He is currently wheelchair-bound secondary to stroke-related left-sided hemiparesis. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 100/min. There is no jugular venous distention or hepato-jugular reflux. His chest is clear to auscultation but his abdomen is enlarged with shifting dullness and a fluid wave, suggestive of ascites. His liver is palpable 3 cm below the right costal margin. His spleen is also palpable. On examination of his lower extremities, you note right-sided calf swelling and tenderness. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's ascites?
Right-sided heart failure
Pulmonary embolism
Protein C deficiency
Chronic liver disease
Paradoxical embolism
32) A 60-year-old white man comes into the Emergency Room with intensive retrosternal pain that began ten minutes ago. He has never had such pain before. His past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus, type 2, controlled with diet. His blood pressure is 150/95 mmHg and HR is 80/min. You give him one chewable tablet of aspirin and two sublingual tablets of nitroglycerin with a 5-minute interval. After the second tablet of nitroglycerin, the pain is greatly relieved. What is the most important mechanism responsible for pain relief in this patient?
Increase in coronary blood flow
Increased cardiac contractility
Dilation of resistance vessels
Dilation of capacitance vessels
Change in the activity of baroreceptors
33) A 34-year-old male who recently immigrated from Brazil presents with a 5-month history of exertional dyspnea without associated chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, or syncope. His past medical history is significant for an episode of megacolon, which was treated 2 years ago. On physical examination, there is 1+ pedal edema and mild jugular venous distention. Cardiac exam is significant for the presence of an S3, but no murmurs are heard. Chest x-ray reveals prominent cardiomegaly. Based on these findings, which of the following is most likely causing his symptoms?
Diphtheric myocarditis
Coronary artery disease
Protozoal disease
Giant cell myocarditis
Rickettsial myocarditis
34) A 12-year-old African American male is found to have a murmur during a routine sports physical. He has a family history of sudden death at a young age. It is a harsh crescendo-decrescendo murmur that begins after S1 and is best heard at the left lower sternal border. Valsalva maneuver intensifies the murmur. Which of the following is the most likely mitral valve abnormality in this patient?
Abnormal mitral leaflet motion
Dilated mitral valve annulus
Prolapse of the mitral valve
Mitral annulus calcifications
Rupture of chordae tendinae
35) A 63-year-old woman with a long history of hypertension faints after experiencing the sudden onset of severe chest pain that radiates to her back. She is rushed to the emergency room. Upon arrival she is agitated and demands quick pain relief. Her heart rate is 110/min and blood pressure is 90/50 mmHg. Jugular veins are distended. An intra-arterial catheter shows significant variation of systolic blood pressure related to the respiratory cycle. Chest x-ray reveals widening of the mediastinum. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's syncope?
Papillary muscle dysfunction
Pericardial fluid accumulation
Vagal hyperactivity
Cardiac tachyarrhythmia
Intravascular volume loss
36) A 47-year-old male was brought to the emergency room with chest pain of acute onset. The pain was associated with nausea, vomiting, and diaphoresis. He has a history of diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia. ECG reveals ST segment elevation in the anterolateral leads and ventricular premature beats (VPBs). The patient dies within the first hour after the arrival to emergency room. What is the most likely pathophysiologic mechanism responsible for this patient's death?
Asystole
Increased automaticity
Full conduction block
Electro-mechanic dissociation
Reentry
37) A 57-year-old male presents to your office with a two week history of fever, chills, and generalized weakness. His medical history is significant for a hospitalization for pyelonephritis requiring IV antibiotics six months ago. He also recently underwent cystoscopy for evaluation of persistent dysuria. His past medical history is also significant for an episode of rheumatic fever as a child and Hodgkin's lymphoma treated with chemotherapy 10 years ago. On examination, his temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), blood pressure is 150/86 mmHg, pulse is 98/min and regular, and respirations are 16/min. The patient appears slightly diaphoretic. You note a new II/VI systolic murmur and tender erythematous lesions affecting several fingertips. The remainder of the physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following bacteria is most likely responsible for his present illness?
Coxiella burnetii
Viridans streptococci
Enterococci
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus pyogenes
38) A 65-year-old man complains of lower leg swelling, fatigue and poor appetite. His past medical history is significant for recurrent chest infections, wheezing, cough, recent pyelonephritis, and arterial hypertension. He smokes 1 pack of cigarettes a day but denies alcohol or intravenous drug use. His physical examination reveals a barrel-shaped chest with bilateral scattered wheezes. His abdomen is distended and his liver edge is palpated 4 cm below the right costal margin. You note pitting edema and dilated, tortuous, superficial veins over the bilateral lower extremities. Manual pressure on the abdomen causes persistent distention of the jugular veins. The patient's serum sodium level is 135 mEq/L and his creatinine concentration is 1.2 mg/dl. An abnormality of which of the following is most likely to explain his edema?
Urinary protein excretion
Portal venous resistance
Serum albumin level
. Pulmonary artery systolic pressure
Pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
39) A 60-year-old male presents to the emergency room with the chief complaint of progressive exertional dyspnea and fatigue. He denies any chest pain, syncope, cough, or edema. He suffered an acute anterior wall myocardial infarction one month ago. Chest auscultation reveals bilateral crackles in his lower chest. Cardiac auscultation reveals a pansystolic murmur at the apex with radiation to the axilla. ECG shows previously present unchanged Q waves and a persistent ST segment elevation in the anterior leads. Based on these findings, what is the most likely underlying cause of his symptoms?
Interventricular wall rupture
Ventricular free wall rupture
Ventricular aneurysm
Right ventricular infarction
Recurrent ischemia
40) A 68-year-old white female presents to the ER complaining of sudden onset chest pain associated with two episodes of vomiting. She has hypertension for which she takes atenolol and hydrochlorothiazide. Her pulse is 60/min, blood pressure is 80/50 mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Examination shows elevated jugular venous pressure and a positive Kussmaul's sign. Her lungs are clear to auscultation. Her EKG shows 2 mm ST segment elevation in leads II, III and aVF and 1 mm ST segment depression in leads I and aVL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's hypotension?
Intravascular volume depletion
Pulmonary thromboembolism
Variant angina
Interventricular septum rupture
Right ventricular infarction
41) A 53-year-old man presents to your office complaining of weakness and exertional dyspnea over the last week. He denies chest pain and palpitations. He has no other past medical history. His father died of a myocardial infarction at age 55. On exam, his heart rate is 100/min and blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg. Internal jugular venous pulsation is observed 7 cm above the sternal angle. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Heart sounds are muffled. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
Decreased cardiac contractility
Left ventricular outflow obstruction
. Decreased left ventricular preload
Pulmonary hypertension
Increased right ventricular compliance
42) A 34-year-old man rushes into the ER complaining of severe substernal chest pain that began abruptly 30 minutes ago. He says that he also feels as though his heart 'is racing,' but denies any shortness of breath, cough or fever. He has never experienced pain like this before. His past medical history is significant for an appendectomy one year ago. The patient reports that his father died at age 64 due to "some heart problem" and his mother died of ovarian cancer. On physical examination, the patient is agitated and sweating profusely. His pulse is 110/min, blood pressure is160/100 mmHg, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination is normal except for dilated pupils and a small amount of blood at the external nares. EKG shows ST elevations in leads v1-v4. What is the most likely explanation for his symptoms?
Aortic dissection
Drug-induced vasospasm
Pleurodynia
Acute pericarditis
Atherosclerotic vascular disease
43) A 50-year-old white male comes into your office for a routine check-up. He has no present complaints. His past medical history is significant for hypertension controlled with a low-dose thiazide diuretic. His family history reveals non-fatal myocardial infarction in his father at the age of 47. The patient does not smoke or consume alcohol. His blood pressure is 130/75 mmHg and his heart rate is 70/min. His previous records show that his HDL level is persistently low in spite of acceptable total cholesterol and LDL levels. You prescribe niacin to raise HDL level. The patient returns in a week complaining of intensive generalized pruritis and flushing. What is the most probable cause of the patient's complaint?
Hypersensitivity reaction
Prostaglandin-related reaction
Drug interaction
Psychogenic reaction
Drug-induced vasoconstriction
44) A 63-year-old male is admitted for sudden onset severe chest pain. His ECG reveals ST elevation in leads V2-V6. He is treated with thrombolytic therapy, heparin, aspirin, metoprolol, morphine, and nitrates. A coronary angiogram performed after thrombolytic therapy reveals 50% obstruction of the left anterior descending artery. On the third day of hospitalization, the patient suddenly develops severe shortness of breath at rest and hypotension. Examination reveals a soft S1, an apical pansystolic murmur radiating to the axilla, and bibasilar crackles. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), blood pressure is 92/58 mmHg, heart rate is 102/min, and respirations are 31/min. An echocardiogram performed on the second hospital day reveals an akinetic region of the anterior wall. What is the most likely explanation for this patient's deterioration?
Pericardia! tamponade
Pulmonary embolism
Rupture of ventricular septum
Papillary muscle dysfunction
Acute aortic dissection
45) A 34-year-old female presents to your office complaining of pressure-like, substernal chest pain that has been affecting her recently when she plays active sports. Resting consistently alleviates the pain. She denies any associated nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, dyspnea, palpitations or syncope. Family history is non-contributory. On physical examination, her pulse is 79/min and blood pressure is 130/70 mmHg. Cardiac auscultation reveals a high-pitched 3/6 systolic murmur best heard at the second right intercostal space. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Chest x-ray shows a normal sized heart and clear lung fields. What is the most likely cause of this patient's chest pain?
Anomalous origin of the right coronary artery
Atherosclerotic narrowing of the coronaries
Increased myocardial oxygen demand
Increased myocardial oxygen extraction
Stretching of the papillary muscles
46) A 48-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office complaining of progressive exertional dyspnea. It has become especially bothersome over the past two months. Presently, he becomes short of breath after climbing one flight of stairs. He denies any significant problems in the past. He is not taking any medications and he denies smoking or drinking alcohol. His temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/75 mmHg and respirations are 14/min. Chest examination reveals a harsh systolic murmur that is best heard at the right second intercostal space with radiation along the carotid arteries. An S4 is heard at the apex. Based on these findings, what is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Myxomatous valve degeneration
Rheumatic heart disease
Senile calcific aortic stenosis
Bicuspid aortic valve
47) A 45-year-old man presents to the emergency department because of dyspnea, fatigue, poor appetite and weight gain over the past several weeks. He says that about four weeks ago he began to develop worsening shortness of breath with exertion and more recently has been waking at night with breathlessness. He also notes that it is sometimes difficult for him to open his eyes in the morning due to facial edema. He has no significant past medical history and he takes no medications. On physical examination, his blood pressure is 200/120 mmHg and his heart rate is 100/min. You note generalized bodily edema and distention of his jugular veins while he is sitting upright. On lung auscultation you hear bibasilar rales. Urinalysis shows trace protein, no nitrites, trace leukocyte esterase, 50+ red blood cells and occasional neutrophils. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's edema?
Renal hypoperfusion
Hypoalbuminemia
Extensive glomerular damage
Hypothyroidism
Portal hypertension
48) A 14-year-old African American male collapses and dies while playing basketball at a school tournament. He has no known past medical history. Which of the following is the most likely underlying disease in this patient?
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Coronary atherosclerosis
Ventricular septal defect
Bicuspid aorta
Aortic aneurysm rupture
49) A 46-year-old man complains of exertional dyspnea and dry cough. He also describes occasional episodes of a suffocating night-time cough that is relieved only when he stands up. His medical history is significant for a myocardial infarction six months ago. His current medications are metoprolol, aspirin and simvastatin. He does not use tobacco but drinks alcohol on social occasions. His father died of a stroke and his mother suffers from diabetes mellitus. His blood pressure is 150/100 mmHg and his heart rate is 60/min. Chest examination reveals bibasilar rales. His cardiac apex is palpated in the sixth intercostal space. The liver span is 12 cm. Bilateral pitting leg edema is also present. Which of the following most likely contributes to his edema?
High portal venous resistance
Increased renal potassium loss
Increased renal blood flow
High sodium delivery to the distal tubule
Constriction of the renal arterioles
50) A 54-year-old man with a 20-year history of chronic obstructive lung disease has a heave that is palpable at the lower left sternal border at the third, fourth, and fifth intercostal spaces. Which of the following best explains the etiology of the heave?
It is probably a displaced point of maximum impulse (PMI)
It means the patient has congestive heart failure
It means that the patient has aortic stenosis
It means the patient has right ventricular hypertrophy
It means the patient has a pericardial effusion
51) A 55-year-old man presents to the ED with chest pain and shortness of breath. His BP is 170/80 mmHg, HR is 89 beats per minute, and oxygen saturation is 90% on room air. Physical examination reveals crackles midway up both lung fields and a new holosystolic murmur that is loudest at the apex and radiates to the left axilla. ECG reveals ST elevations in the inferior leads. Chest radiograph shows pulmonary edema with a normal sized cardiac silhouette. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the cardiac murmur?
Critical aortic stenosis
Papillary muscle rupture
Pericardial effusion
CHF
Aortic dissection
52) A 66-year-old retired carpenter presents with chronic shortness of breath upon exertion. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 5 years and drinks alcohol regularly. Physical examination reveals a displaced point of maximal impulse and hepatosplenomegaly. His medications include pantoprazole for gastroesophageal reflux and sertraline for depression. Echocardiogram reveals an ejection fraction of 30% and dilated left and right ventricles. Laboratory tests show: Na+: 129 mEq/L, K+: 5.2 mEq/L, Cl−: 101 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen: 45 mg/dL, Creatinine: 1.3 mg/dL, Glucose: 134 mg/dL, Aspartate aminotransferase: 220 U/L, Alanine aminotransferase: 140 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase: 280 U/L. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his cardiac findings?
Borrelia burgdorferi
Cigarette smoking
Coxsackie B virus
Ethanol
Pantoprazole toxicity
53) A 47-year-old woman who is 2 weeks post triple bypass surgery presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of sudden onset, sharp chest pain for several hours. She is fatigued and short of breath. On physical examination she has distended neck veins that grow more distended on inspiration. Muffled heart sounds are heard. Her temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse is 133/min, blood pressure is 70/50 mmHg, respiratory rate is 30/ min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air. An echocardiogram shows a large pericardial effusion and chamber collapse; therefore, pericardiocentesis is performed. Although a large amount of blood is aspirated, the patient’s clinical picture acutely worsens. Her pain level increases substantially; pulse is 150/min, blood pressure is 60/41 mm Hg, respiratory rate is 30/ min, and oxygen saturation is 100%. Repeat echocardiography shows an even larger pericardial effusion with chamber collapse. Which complication of pericardiocentesis is most likely in this patient?
Acute left ventricular failure with pulmonary edema
Aspiration of 10 mL air into the pericardium
Laceration of a coronary vessel
Pneumothorax
Puncture of the left ventricle
54) A 29-year-old man is brought to the ED by EMS for a syncopal episode that occurred during a basketball game. A friend states that the patient just dropped to the ground shortly after scoring a basket on a fast break. On examination, you note a prominent systolic ejection murmur along the left sternal border and at the apex. An ECG reveals left ventricular hypertrophy, left atrial enlargement, and septal Q waves. You suspect the diagnosis and ask the patient to perform the Valsalva maneuver while you auscultate his heart. Which of the following is most likely to occur to the intensity of the murmur with this maneuver?
Decrease
Increase
Disappear
. The intensity stays the same, but the heart skips a beat
Remain unchanged
55) A 32-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by paramedics after being found wandering downtown, apparently delirious and agitated. During transport to the hospital the patient becomes diaphoretic and tremulous and has a blood pressure to 163/100 mmHg, pulse of 102/min, and temperature of 39°C (102.2°F). On examination the patient has dilated pupils and ulcerations of his nasal septum mucosa with the residue of a white powder along the nasal alae in addition to his tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia, and agitation. Which of the following is the reason why nonselective β- blockers should be avoided in this patient?
Increased risk of late vasospasm
Risk of acutely worsening hypertension through vasoconstriction
Risk of causing acute hypotension
Risk of causing dyspnea
Risk of ventricular arrhythm
56) A 72-year-old woman had a pacemaker inserted 4 years ago for symptomatic bradycardia because of AV nodal disease. She is clinically feeling well and her ECG shows normal sinus rhythm at a rate of 68/min but no pacemaker spikes. Her pacemaker only functions when the ventricular rate falls below a pre-set interval. Which of the following best describes her pacemaker function?56) A 72-year-old woman had a pacemaker inserted 4 years ago for symptomatic bradycardia because of AV nodal disease. She is clinically feeling well and her ECG shows normal sinus rhythm at a rate of 68/min but no pacemaker spikes. Her pacemaker only functions when the ventricular rate falls below a pre-set interval. Which of the following best describes her pacemaker function?
Asynchronous
Atrial synchronous
Ventricular synchronous
Ventricular inhibited
Atrial sequential
57) A 47-year-old man is found to have edema, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. The examination of his neck veins reveals elevated venous pressure with a deep y descent. Heart size on x-ray is normal. Which of the following etiologies is not a possible explanation for this syndrome?
Rheumatism fever
TB
unknown cause
Previous acute pericarditis
Neoplastic involvement of the pericardium
58) A 62-year-old man has progressive symptoms of dyspnea, and more recently noticed difficulty lying supine. Examination shows an elevated JVP at 8 cm, with a third heart sound, pedal edema, and bibasilar crackles on auscultation. Which one of the following may be implicated in fluid retention for this condition?
Decrease renine
Increased aldosterone
Increased estrogen
Decreased vasopressin
Increased growth hormone
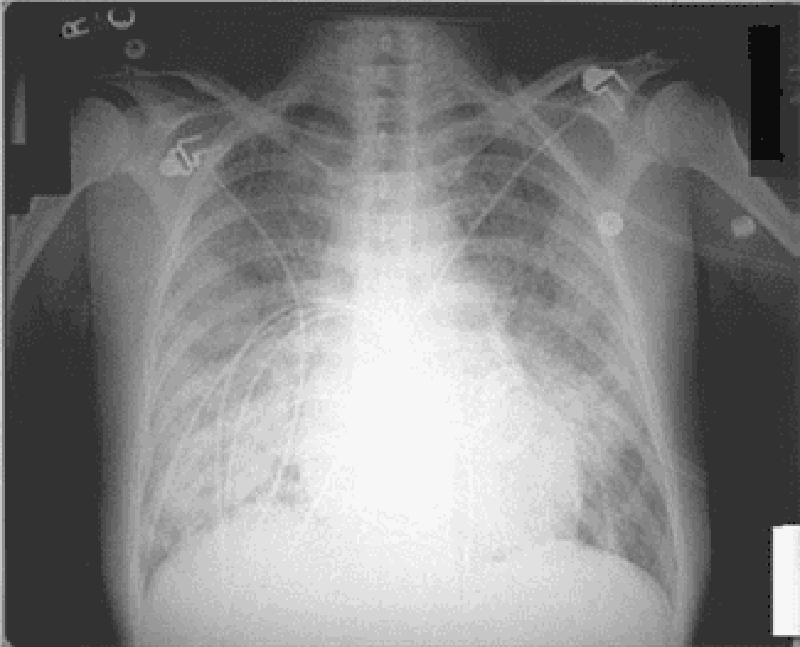
59) A 80-year-old man with Type II diabetes and hypertension presents with increasing dyspnea. He appears short of breath, blood pressure is 170/95 mmHg, pulse 100/min and regular. The JVP is at 7 cm; there is a loud second heart sound and a systolic ejection murmur at the right sternal border, which does not radiate. The lungs have bibasilar crakles up to the scapula. The CXR has bilateral infiltrates and vascular redistribution. His echocardiogram reports aortic sclerosis, concentric left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), and normal ejection fraction. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism for this condition?
Valvular heart disease
Diastolic dysfunction
Systolic dysfunction
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
Hibernating myocardium
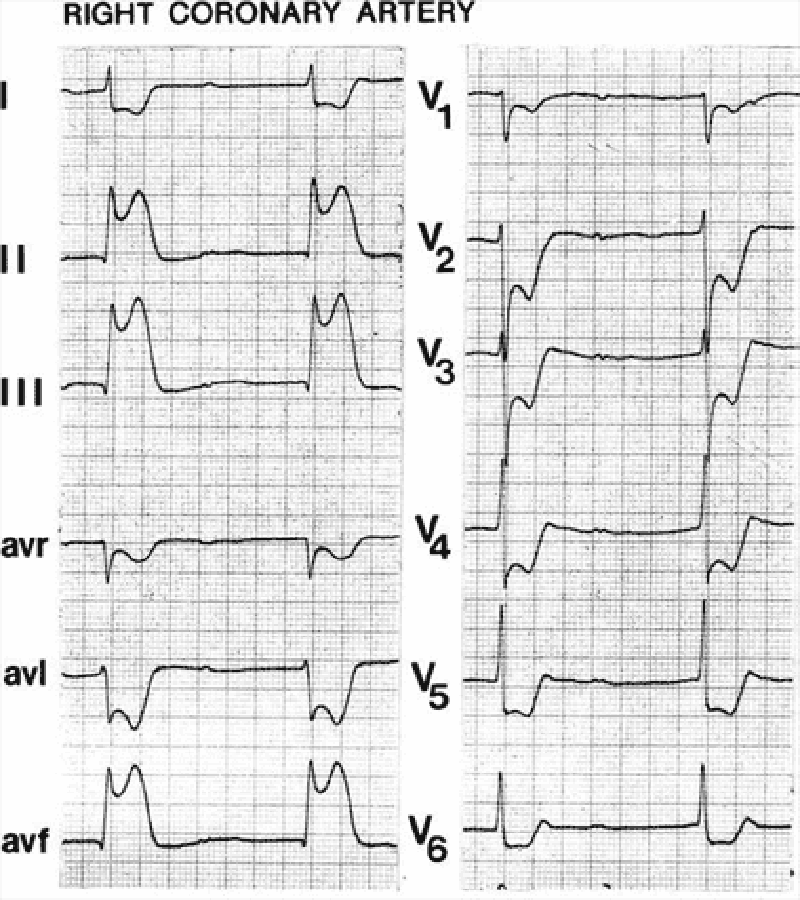
60) A 68-year-woman with hypertension and dyslipidemia presents with 30 minutes of retrosternal chest pain radiating to her neck. She is diaphoretic and in moderate distress. The ECG shows ST-segment elevation in the inferior leads. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely cause of her condition?
Aortic inflammation
Coronary plaque rupture
Pericardial inflammation
Myocarditis
Vasculitis
61) A 72-year-old man with coronary artery disease and hypertension is hospitalized after suffering a myocardial infarction 5 days ago. He suddenly complains of severe chest pain. His blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg and heart rate is 65/min. Auscultation reveals no murmurs or rubs. An ECG reveals sinus rhythm with an acute ST-segment elevation in the anteroseptal area. Urgent bedside echocardiography showed anteroseptal, lateral, and apical akinesis, mild left ventricular systolic dysfunction, and severe pericardial effusion. Within 20 minutes he is unconscious with undetectable pulses and blood pressure. What is the most likely cause of the patient’s sudden decompensation?
Free wall rupture
Left ventricular thrombus
Mitral regurgitation
Ventricular septal rupture
Pericarditis
62) While palpating the pulse of a patient, you note that the pulse wave has two peaks. You auscultate the heart and are certain that there is only one heartbeat for each two pulse waves. Which of the following best describes this finding?
Pulsus alternans
Dicrotic pulse
Pulsus parvus et tardus
Pulsus bigeminus
Pulsus bisferiens
63) A 62-year-old man with a prosthetic aortic valve develops fevers and malaise. His valve was replaced 5 years ago because of aortic stenosis from a bicuspid valve. He has a systolic ejection murmur but no other abnormalities on examination. Blood cultures are most likely to grow which of the following?
Fungi
Streptococcus bovis
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Bartonella
diptheroids
64) A 28-year-old man with a history of intravenous drug abuse presents to the emergency department with a 2-day history of fever, chills, and shortness of breath. On physical examination the patient has a new heart murmur, small retinal hemorrhages, and subungual petechiae. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Group A Streptococcus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus aureus
Streptococcus viridans
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
65) A 91-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of shortness of breath over the past 2 days. She has a history of hypertension and coronary artery bypass surgery 25 years earlier. Her blood pressure is 178/92 mmHg and she has jugular venous distension, hepatomegaly, and 3+ lower extremity edema. ECG is remarkable for left ventricular hypertrophy, no ST-segment elevations or depressions, no Q waves, and no T wave abnormalities. Echocardiogram reveals an ejection fraction of 60% and left atrial dilatation. There is universal left ventricular thickening. No valvular regurgitation or stenosis was noted. Which of the following underlying conditions is the most likely cause of this patient’s symptoms?
Hypertensive heart disease
Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathyHypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy
Mitral valve prolapse
Myocarditis
Ischemic heart disease
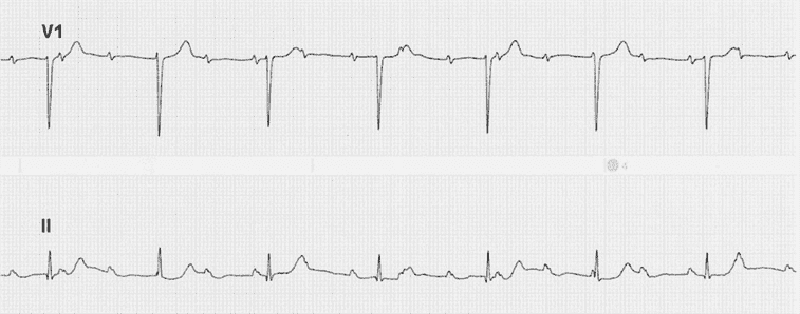
66) A 69-year-old woman complains of easy fatigue and one episode of presyncope. On examination of the jugular venous pressure (JVP), there are irregular large a waves. The ECG has fixed PP and RR intervals but varying PR intervals. Which of the following conditions is this most likely caused by?66) A 69-year-old woman complains of easy fatigue and one episode of presyncope. On examination of the jugular venous pressure (JVP), there are irregular large a waves. The ECG has fixed PP and RR intervals but varying PR intervals. Which of the following conditions is this most likely caused by?
Independent beating of atria and ventricles
Surgical removal of an atrium
A reentry phenomenon
A drug effect
A heart rate under 60 beats/min
67) A 47-year-old woman has new-onset transient right arm weakness and word finding difficulty symptoms lasting 3 hours. She is also experiencing exertional dyspnea, and had a syncopal event 1 month ago. Her echocardiogram reveals a cardiac tumor in the left atrium, it is pendunculated and attached to the endocardium. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this lesion?
Myxoma
Fibroma
rhabdomyoma
lipoma
Sarcoma
68) A 23-year-old man develops sharp left-sided chest pain, fever, and a friction rub heard at the lower left sternal border, unaffected by respiration. The pain is also aggevated by lying down and relieved by sitting up. He is otherwise well with no other symptoms and the remaining physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause for his symptoms?
Rheumatic fever
tuberculosis (TB)
Coxsackievirus
MI
Herpes simplex virus
69) A 17-year-old girl develops exertional dyspnea, but has no cough, sputum, or wheezing symptoms. On examination, she has a fixed splitting of her second heart sound and a 3/6 systolic ejection murmur heard best over the left sternal border. An echocardiogram confirms the condition. Which of the following is the best physiologic explanation for her condition?
Pulmonary blood flow is greater than systemic blood flow
Pulmonary blood flow is less than systemic blood flow
Pulmonary blood flow is equal to systemic blood flow
The left ventricle is enlarged
The systemic blood pressure is elevated
70) A 65-year-old man comes to the office and complains of pain and a rash with blisters over the left side of his chest. He has experienced pain over the area for the past 2 days. This morning, he noticed blisters while changing his shirt. He also complains of malaise and headache. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, respirations are 14/min and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F). Physical examination reveals grouped, tense vesicles arranged in a band along the left side of his chest. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of his condition?
Herpes simplex virus
Human papilloma virus
Varicella zoster virus
Poxvirus
Poison ivy
71) A 65-year-old man comes to the office with a six-month history of a non-healing ulcer on his right forearm. Physical examination demonstrates a scaling plaque with central ulceration and 1.5 cm diameter. The biopsy shows polygonal cells with atypical nuclei at all levels of the epidermis with zones of keratinization. What is the single most important risk factor for this condition?
Sunlight
Arsenic
Chronic scars
Chronic osteomyelitis
Aromatic hydrocarbons
72) A 35-year-old Caucasian male with aplastic anemia undergoes bone marrow transplantation. The donor is an HLA-matched sibling. Two weeks after the procedure, he develops a maculopapular pruritic rash that is predominantly found on his face, hands, and feet. He also complains of diarrhea. The stool is positive for occult blood. Liver function tests are abnormal. Which of the following is the most likely pathophysiologic mechanism of this patient's condition?
Activation of the donor T lymphocytes
Activation of the donor 8-lymphocytes
Activation of the host T lymphocytes
Virus-induced lymphocyte proliferation
Depression of the donor myelopoiesis
73) A 36-year-old male AIDS patient comes in due to a painful red eye. He complains of pain, discharge and redness in his left eye for the past 10 days. On physical examination, you notice redness in his left eye as well as multiple skin lesions on his face, left eyelid, inner thighs, penis and pubis. The lesions are painless, pale, shiny, dome-shaped papules with a central umbilication measuring 2-5mm in diameter. These lesions were not present on his previous visit. His CD4 count thirty days ago was 100/uL. What is the most likely etiology of this patient's skin lesions?
Human papilloma virus
Herpes simplex 1
Poxvirus
Staphylococcus
Human herpes virus 8
74) A 25-year-old woman comes to the office for the evaluation of pale patches of skin around her mouth. She noticed these lesions a few months ago, but they have become more prominent now. There is no itching, burning, or numbness over the patches. Her vital signs are stable. On examination, you notice pale white patches symmetrically distributed around her mouth. The borders of these macules are well-circumscribed and hyperpigmented. Similar lesions are also found over the areola of her breasts. She denies any history of trauma or infection. Which of the following best explains the pathology of her condition?
Post inflammatory
Destruction of melanocytes
Inherited absence of melanocytes
Infection with mycobacterium leprae
Superficial fungal infection
75) An 8-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother for a routine check-up. He has fair skin, blond hair and blue eyes. His past medical history is insignificant. His mother wants to know what the best possible photo-protection is for her son, because "his skin has always been sensitive to the sun, and he is almost unable to tan." He had two episodes of sunburn recently. Physical examination reveals several junctional nevi. Which of the following is the best response to this patient's mother?
Reassure and provide routine care
Minimize sun exposure in the middle of the day
Recommend applying sunscreens before sun exposure
Rest under trees or umbrellas during the day
Emphasize that clothing is typically useless for sun protection
76) A 30-year-old female presents with a circumferential pruritic rash over her right wrist. The rash has been present for the last two days, and she denies ever having a similar rash before. She bought a new bracelet two weeks ago, and has been wearing it on her right forearm since. Which of the following metals in jewellery is most likely to cause such symptoms?
Nickel
Gold
Silver
Platinum
Copper
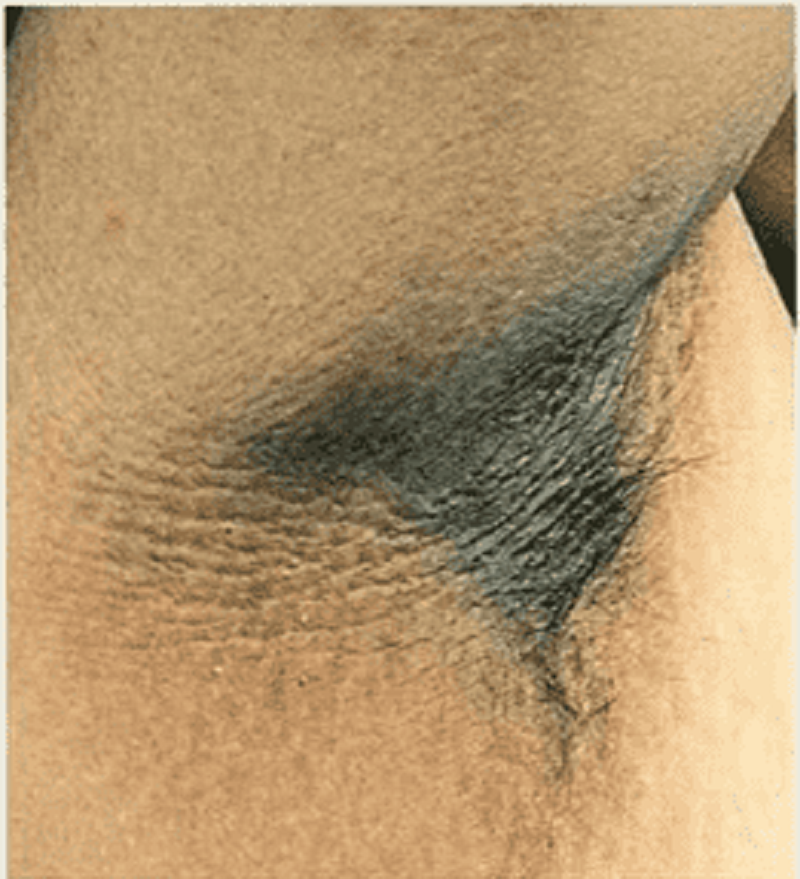
77) A 31-year-old male presents to your office with a velvety skin rash in his axilla as shown on the slide below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Vitamin D resistance
Calcitonin hypersecretion
Testosterone unresponsiveness
Insulin resistance
Serotonin hypersecretion
78) A 9-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother because of itching, burning and oozing skin lesions on both of his legs. The boy appears tanned. When asked if he had been spending time outdoors, he replies with great excitement that he just returned yesterday from a camping trip in the woods with his dad. Physical examination of both lower limbs reveals vesicles with erythema arranged in a linear fashion. Weepy and crusted lesions and edema are also present. What type of reaction is responsible for this boy's lesions?
IgE mediated hypersensitivity
Antibody mediated hypersensitivity
. Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity
Cell mediated hypersensitivity
. Woods biopsy
79) A 15-year-old male is brought to the emergency department due to sudden-onset difficulty breathing for the past 45 minutes. He also complains of nausea, colicky abdominal pain and a swollen face. He has been suffering from bronchitis for the past 4 days, and his condition had been improving. His mother says that he had a similar episode when he had a tooth extraction 2 year ago. On examination, there is an edematous swelling of his face including the lips, hands, arms, legs, and genitals. His pulse is 82/min, blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, respirations are 18/min and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F). Which of the following best explains the pathological process of his condition?
Depressed C1q
Antibody mediated hypersensitivity
Immune complex mediated hypersensitivity
Cell mediated hypersensitivity
C 1 inhibitor deficiency
80) A 32-year-old Asian female presents to the office with a mole on her foot that recently became darker. She has always had skin that is very sensitive to sunlight. She is unable to tan, and has had several sunburns when she did not use sunscreens. Her past medical history is insignificant. Her mother had 'a kind of skin cancer.' Physical examination reveals a dark mole with irregular borders on the left foot. Which of the following is the strongest risk factor for malignancy in this patient?
Asian race
.Previous sunburns
Sun sensitivity
Recently changed mole
Age
81) A 25-year-old complains of fever and myalgias for 5 days and now has developed a macular rash over his palms and soles with some petechial lesions. The patient recently returned from a summer camping trip in Tennessee. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the rash?
Contact dermatitis Contaminated water .
Undercooked pork
Sexual exposure
Tick exposure
Contaminated water
82) A 53-year-old female presents to the clinic with an erythematous lesion on the dorsum of her right hand. The lesion has been present for the past 7 months and has not responded to corticosteroid treatment. She is concerned because the lesion occasionally bleeds and has grown in size during the past few months. On physical examination you notice an 11-mm erythematous plaque with a small central ulceration. The skin is also indurated with mild crusting on the surface. Which of the following is true about this process?
It is a malignant neoplasm of the keratinocytes with the potential to metastasize
It is an allergic reaction resulting from elevation of serum IgE
It is the most common skin cancer
It is a malignant neoplasm of the melanocytes with the potential to metastasize
. It is a chronic inflammatory condition, which can be complicated by arthritis of small and medium- sized joints
83) A 46-year-old construction worker is brought to the clinic by his wife because she has noticed an unusual growth on his left ear for the past 8 months (see photo below). The patient explains that, except for occasional itching, the lesion does not bother him. On physical examination, you notice an 8-mm pearly papule with central ulceration and a few small dilated blood vessels on the border. What is the natural course of this lesion if left untreated?
Regression over time
Local invasion of surrounding tissue and metastasis via lymphatic spread
Local invasion of surrounding tissue
Disseminated infection resulting in septicemia
This is a benign lesion and will not change
84) A 34-year-old homosexual male with a history of HIV presents to the clinic complaining of a wheezing and multiple violaceous plaques and nodules on his trunk and extremities. Physical examination of the oral mucosa reveals similar findings on his palate, gingiva, and tongue. Chest x-ray is also significant for pulmonary infiltrates. What is the most likely pathogenesis of this process?
Proliferation of neoplastic T cells
Angioproliferative disease caused by infection with human herpesvirus 8
Infection with Mycobacterium avium due to decreasing CD4 count
Disseminated HSV infection
Infection with human herpesvirus 6
85) A 40-year-old female presents with altered mental status and confusion. Last year, she was diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis, for which she is currently using indomethacin and methotrexate. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 75/min, blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, and respirations are 15/min. She is disoriented and irritable. Mucus membranes are moist. There is no jugular venous distention. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Abdomen is soft, nontender and not distended. There is no peripheral edema. Serum chemistry reveals: Sodium 122 mEq/L, Potassium 3.7 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 22 mEq/L, Blood glucose 90 mg/dL, BUN 9.0 mg/dL, Uric acid 3.0 mg/dL. Serum osmolality is 265mOsm/kg, while urine osmolality is 500 mOsm/kg. What is the most likely cause of this patient's hyponatremia?
Mineralocorticoid deficiency
Nephrotic syndrome
Syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion
Advanced renal failure
Diabetes insipidus
86) A 25-year-old woman comes into the office with a three-month history of weight loss, irritability, insomnia, and palpitations. Her past medical history is insignificant. She is not taking any current medications and denies drug abuse. Her blood pressure is 155/70 mmHg and heart rate is 110/min. Physical examination reveals lid retraction, fine tremor of the hands, and increased neck circumference. The most probable cause of hypertension in this patient is?
Hyperdynamic circulation
Increased intravascular volume
Decreased vascular compliance
. Increased peripheral vascular resistance
Sodium retention
87) A 55-year-old Caucasian male presents to the office for a routine check-up. He has no present complaints. His past medical history is significant for a long history of hypertension. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His current medications are enalapril and hydrochlorothiazide. His blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and heart rate is 80/min. Physical examination reveals a moderately overweight man (BMI = 27 kg/m2) with a waist circumference of 41 inches. The laboratory studies show: Fasting blood glucose 112 mg/dl, Total cholesterol 220 mg/dl, LDL cholesterol 140 mg/dl, Triglycerides 240 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most important pathogenic factor for this patient's condition?
Sympathetic hyperactivity
Insulin-mediated vasodilatation
Low absolute values of insulin
Impaired secretion of insulin
Insulin resistance
88) A 38-year-old Mexican male presents to the emergency department with a history of weight loss, fever, cough with sputum, nausea, abdominal pain, and postural dizziness for the last three months. Adrenal insufficiency is suspected, and cosyntropin (synthetic ACTH) stimulation test is performed. The rise of serum cortisol following an injection of cosyntropin is grossly subnormal. CT scan of the abdomen shows calcification of both adrenal glands. What is the most likely cause of this patient's adrenocortical insufficiency?
. Human immunodeficiency virus infection . . .
Adrenal haemorrhage
Tuberculosis
Autoimmune adrenalitis
Adrenal tumor .
89) A 60-year-old Caucasian male is brought to the emergency department by his daughter due to a 2- day history of confusion and lethargy. According to his daughter, he had been complaining of fatigue, anorexia, polyuria and constipation for the last several weeks. He smokes two packs of cigarettes daily, and consumes alcohol occasionally. His blood pressure is 130/90 mmHg and heart rate is 90/min. Physical examination reveals a somnolent patient who is not oriented in time. His lab values are: Serum Na 140 mEq/L, Serum K 4.0 mEq/L, Serum chloride 100 mEq/L, Serum bicarbonate 22 mEq/L, Serum creatinine 1.6 mg/dl, Serum calcium 13.4 mg/dL, Serum phosphorus 2.2 mg/dL, Blood glucose 100 mg/dL, Alkaline phosphatase 80 U/L. Chest x-ray demonstrates a right middle lobe mass and perihilar adenopathy. What is the most probable cause of this patient's symptoms?
Elevated PTH
Local cytokine production
. Metastatic osteolysis
. Parathyroid hormone-like peptide
Increased vitamin D production
90) A 51-year-old female comes to the office for a routine visit. She is apparently healthy and does not have any complaints. Physical examination reveals a thyroid nodule. She is surprised to hear about the nodule and asks, "How often does this happen? What could have caused this?" Which of the following is the most common cause of thyroid nodules?
Follicular adenoma
. Anaplastic carcinoma
Papillary carcinoma
Colloid nodule
Follicular carcinoma
91) A 46-year-old male presents with swelling of his face that is especially prominent in the periorbital area. He also complains of bilateral ankle swelling. He denies shortness of breath, fever and discoloration of urine. He is a non-smoker and non-alcoholic. His past medical history is not significant. He is currently not taking any medication. His pulse is 78/min, blood pressure is 130/70mmHg, respirations are 14/min and temperature is 37.1°C (99.0°F). Examination shows bilateral pitting ankle edema. Auscultation reveals clear lungs, normal heart sounds, and no murmurs. Dipstick urinalysis is positive for protein. 24-hour urine collection shows proteinuria of 4.6 g/day. Lab studies show: Total serum calcium 7.5 mg/dL, Albumin 2.2 g/dL, Phosphorus 3.5 mg/dL, Magnesium 2.2 mg/dL, Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his low serum calcium level?
Decreased serum albumin .
. Decreased 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D
Increase 25-hydroxylation of vitamin D
. Decreased levels of parathyroid hormone .
Decreased 1-alpha-hydroxlation of 25-OH vitamin D
92) A 36-year-old white male is brought to the emergency department because of dyspnea, tachypnea, crampy pain and paresthesias in his extremities. He gives an unclear history about how he "rapidly ascended to a height of 10,000 feet” His pulse is 70/min, blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, temperature is 36.7°C (98.5°F) and respirations are 24/min. The significant physical finding on examination is carpopedal spasm. At this point, the suspected diagnosis is acute respiratory alkalosis secondary to hyperventilation. Which of the following is true regarding this patient's serum calcium level?
Fall in total plasma calcium
Fall in calcium bound to albumin
Increase in calcium bound to albumin
Fall in calcium bound to inorganic anions
Increase in calcium bound to inorganic anions
93) A 23-year-old Caucasian male with muscular weakness, vomiting and abdominal pain is brought to the emergency department. He had a minor respiratory illness 2 days ago. His past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus, type 1. He admits skipping his insulin shots yesterday and today because he had no appetite. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 27/min. His oral mucosa is dry. The laboratory values are: Serum sodium 132 mEq/L, Serum potassium 5.4 mEq/L, Serum calcium 8.9 mEq/L, Serum chloride 96 mEq/L, Serum bicarbonate 12 mEq/L, Blood glucose 470 mg/dl,BUN 19 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the increased potassium level in this patient?
Increased renal reabsorption of potassium
Decreased gastrointestinal loss
. Extracellular shift
Tissue destruction .
. Intracellular potassium excess
94) A 29-year-old white female presents to the emergency department with nausea, vomiting, severe generalized abdominal pain, and hypotension. She is subsequently admitted to the intensive care unit. Her past medical history is significant for hypothyroidism secondary to Hashimoto's thyroiditis, for which she has been taking levothyroxine. She denies smoking cigarettes, drinking alcohol, and using any intravenous drugs. Her mother also has hypothyroidism. Her blood pressure is 70/50 mmHg, heart rate is 110/min, temperature is 98.4°F (37.0°C) and respiratory rate is 24/min. Physical examination reveals dry and pigmented mucous membranes. The skin creases also show increased pigmentation. Lab studies show: Serum chemistry: Serum Na 130 mEq/L, Serum K 6.1 mEq/L, Chloride 96 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L, BUN 33 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 1.3 mg/dL, Blood glucose 56 mg/dL. CBC: Hemoglobin 10.8 g/L, Platelets 300,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 6,500/mm3, Neutrophils 70%, Eosinophils 10%, Lymphocytes 20%. The random serum cortisol level is 3.2 mcg/dL (normal=5 to 25 mcg/dL), and ACTH level is 142 pg/mL (normal= 9 to 52 pg/mL). What is the most likely involved pathophysiologic mechanism of this patient's disorder?
Autoimmune
. Infective
. Hemorrhagic
. Infiltrative
Congenital
95) A 40-year-old male patient presents with a thyroid nodule. His other complaints are episodes of palpitations, anxiety and sweating. He denies heat intolerance. His weight and appetite are normal. He has a family history of thyroid cancer. His pulse is 80/min, and blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg. Examination of the neck shows a 4-cm, hard, non-tender thyroid nodule. The urinalysis, serum sodium, serum potassium, serum calcium, serum creatinine, serum PTH, TSH, T3 and T 4 levels, and the EKG are all normal. The serum calcitonin level is elevated. The urinary levels of metanephrine and norepinephrine are increased as well. FNA biopsy of the thyroid nodule shows malignant cells. Genetic testing shows a mutation in the RETproto oncogene. Which of the following abnormalities is also present in most patients suffering from this disorder?
. Parathyroid adenoma
. Brain tumor
. Pituitary adenoma
. Pancreatic islet cell tumor
. Mucosal neuroma
96) A 45-year-old female presents complaining of constipation and abdominal pain for the past two weeks. She also complains of urinary frequency and constant thirst. Her past medical history is significant for obesity. She tells you that she has been trying very hard to lose weight, and over the past six months has even attempted various fad diets. She assures you that she supplements her intake with numerous over-the-counter vitamins and minerals. She has managed to lose 20 lbs during this time. Her medical history is also significant for atrial fibrillation for the past 4 years, for which she takes diltiazem. On physical examination, her temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 13/min. Her mucous membranes are dry, and her abdomen is soft and non- tender without rebound or rigidity. Bowel sounds are present. Urinalysis is within normal limits. Which of the following is most likely responsible for her current symptoms?
. Adrenal insufficiency
. Vitamin A overdose
. Diabetic ketoacidosis
. Vitamin D overdose
. Diltiazem
97) A 19-year-old football linebacker is admitted following a motor vehicle accident. He had an extensive cerebral bleed, which led to a deep coma. He also has fractures of the C4 vertebra, pelvis, and right femur. Following admission, he is intubated and central lines are placed. During the next few days, he develops acute renal failure due to rhabdomyolysis. While he is recovering from acute renal failure, he is found to have a serum calcium level of 12.1 mg/dL. Other investigations are: Serum albumin 3.0 g/dL, Serum creatinine 2.8 mg/dL, Serum phosphorus 3.8 mg/dL, Blood glucose 108 mg/dL, PTH 9 pg/mL, PTHrP undetectable, 1, 25-dihyroxy vitamin D 19 pg/mL (normal 20-60 kg/mL). What is the most likely cause of this patient's hypercalcemia?
. Primary hyperparathyroidism
. Malignancy
. Immobilization
. Acute renal failure
. Vitamin D intoxication
98) A 28-year-old avid mountain climber and his friend are vacationing in Andes, South America. During their mountain climbing expedition, the pair somehow manages to get lost. It has been over 16 hours since their food supply ran out. Their glycogen stores are becoming depleted, and their bodies are beginning to utilize the process of gluconeogenesis. Which of the following intermediates is alanine being converted into during this process?
. Pyruvate
. Glycerol-3-phosphate
. Citrate
. Lactate
. Transketolase
99) A 60-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office complaining of decreased hearing on the right side. He also feels that something is wrong with his head because his hat size had increased over the last two years. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and peptic ulcer disease. His current medications are hydrochlorothiazide and enalapril. He also takes ibuprofen for occasional headaches, and ranitidine for infrequent episodes of heartburn. Lab tests showed increased alkaline phosphatase levels. Which of the following is the most likely mechanism underlying this patient's condition?
. Increased osteoid deposition
. Abundant mineralization of the periosteum
Fibrous replacement of the bone
. Abnormal bone remodelling
. Bone demineralization
100) A 60-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for routine medical care. He has no complaints, takes no medications, and has a family history of DM. Examination is unremarkable. A screening laboratory test reveals a fasting blood glucose level of 152 mg/dL. One week later the test is repeated and a value of 144 mg/dL is obtained. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
Autoimmune destruction of pancreatic islet cells
Pancreatitis
Patient’s findings represent normal laboratory values
Peripheral insulin resistance
Surreptitious insulin injection
{"name":"1) A 74-year-old man presents to your office for a routine. He has no present complaint. His medical history is significant for right knee osteoarthritis. He takes naproxen occasionally, to relieve knee pain. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His BP i", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1) A 74-year-old man presents to your office for a routine. He has no present complaint. His medical history is significant for right knee osteoarthritis. He takes naproxen occasionally, to relieve knee pain. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. His BP is 165\/75 mmHg and PR is 70\/min. The physical examination showed a mild systolic ejection type murmur at the base of the heat to the right. An E-KG revealed left ventricular hypertrophy and secondary ST segment and T wave change. Moderate left ventricular hypertrophy, without any flow abnormalities, was demonstrated on echocardiography. The ejection fraction was 60%. What is the most probable cause of hypertension in this patient?, 2) A 47-year-old woman loses consciousness for 2 minutes while shopping in a supermarket. In the emergency room, she recounts feeling nausea and warmth spreading over her body immediately before passing out. She has never had a similar episode before. She has not seen a doctor for several years and does not take any medications, nor does she use tobacco, alcohol or drug. Her family history is unremarkable. Which of the following most likely caused this episode?, 3) A 25-year-old woman experiences sudden-onset palpitations and generalized weakness. During this episode, her blood pressure is 100\/60 mmHg and her heat rate is 160\/min and regular. She has no significant past medical history and does not take any medications. She reports having a few similar episodes in the past which she has self-treated by immersing her face in cold water. Generally, she says, cold water immersion relieves her symptoms within several minutes. This cold water therapy works by affecting which of the following?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/11-508429/21.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Football Committee
320
What's your Tupperware Personality?
1160
KRALJICA ELIZABETA I. IN RENESANČNO/ELIZABETINSKO GLEDALIŠČE
420
100
Free Streamer Fan Trivia - Test Your Skills
201021605
Where Is My Boyfriend Right Now? Take the Free!
201029698
Free NC Road Signs Test Review
201022909
Free Basic Accounting & Finance Knowledge Test
201023834
Hookworm Phylum: Test Your Nematode Know-How
201030037
Free: Afirmaciones que Resumen el Artículo
201023834
Ultimate Synonyms Antonyms: Test Your Vocabulary
201081440
Harry Potter Adult Compatibility: Find Your Match!
201027842