Placement Test - IGCSE BIOLOGY V01
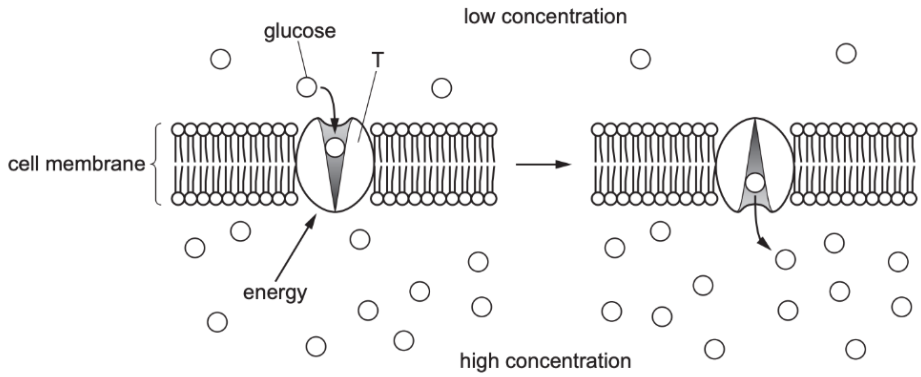
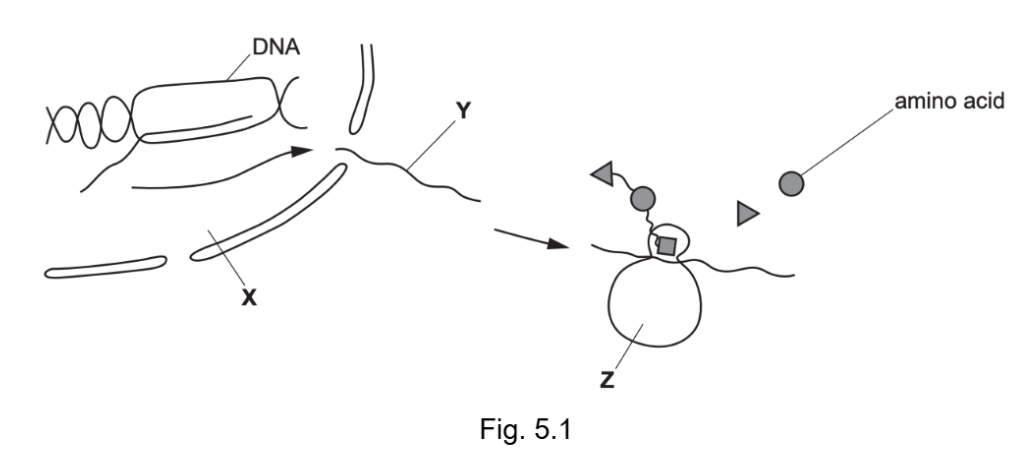
Which statement describes molecule T?
3) During inspiration, the processes listed take place.
P volume of the thorax increases
Q air rushes into the lungs
R pressure in the thorax decreases
S external intercostal muscles contract
T diaphragm moves down, ribs move upwards and outwards
What is the correct sequence for these processes?
|
renal artery |
renal vein |
glomerulus |
nephron |
ureter |
|
|
A |
yes |
no |
yes |
yes |
yes |
|
B |
yes |
yes |
no |
no |
no |
|
C |
yes |
yes |
yes |
yes |
no |
|
D |
no |
yes |
no |
no |
yes |
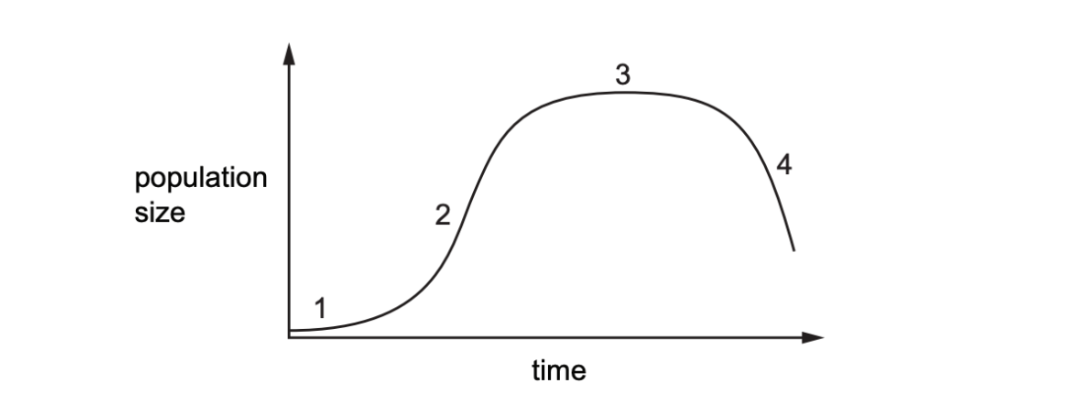
Which row shows when the reproduction rate was greater than the death rate for the numbered phases on the graph?
| reproduction rate greater than death rate | ||||
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
|
A |
/ |
/ |
/ |
x |
|
B |
/ |
/ |
x |
x |
|
C |
/ |
x |
x |
x |
|
D |
x |
/ |
/ |
/ |
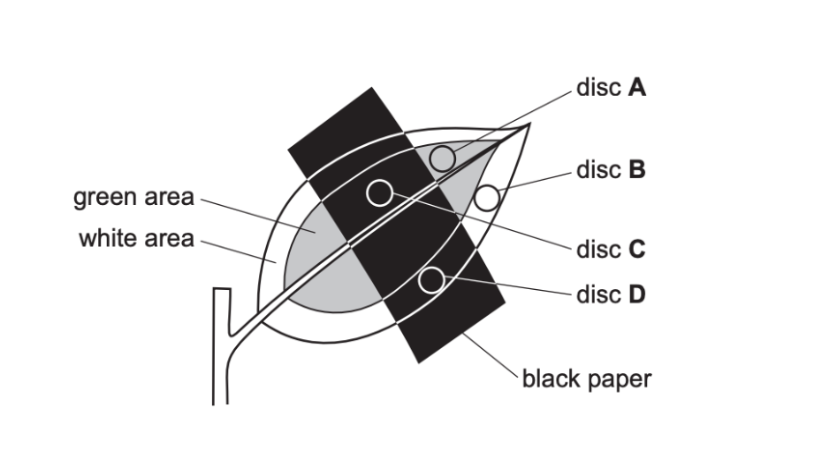
6) The diagram shows a leaf on a plant used in a photosynthesis experiment. At the start of the experiment, there is no starch in the leaf.
A piece of black paper is attached to the upper surface of the leaf. The plant is placed in bright light for 12 hours. Four discs are then cut from the leaf in the positions shown on the diagram. The discs are tested for starch.
Which disc contains starch?
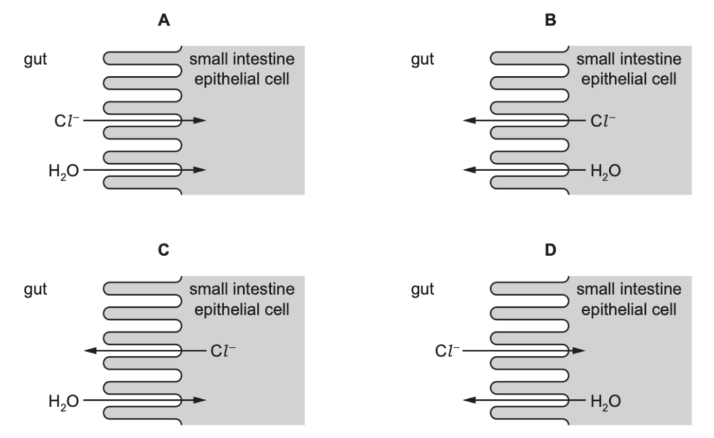
Which diagram shows the correct movement of chloride ions (Cl-) and water (H2O)?
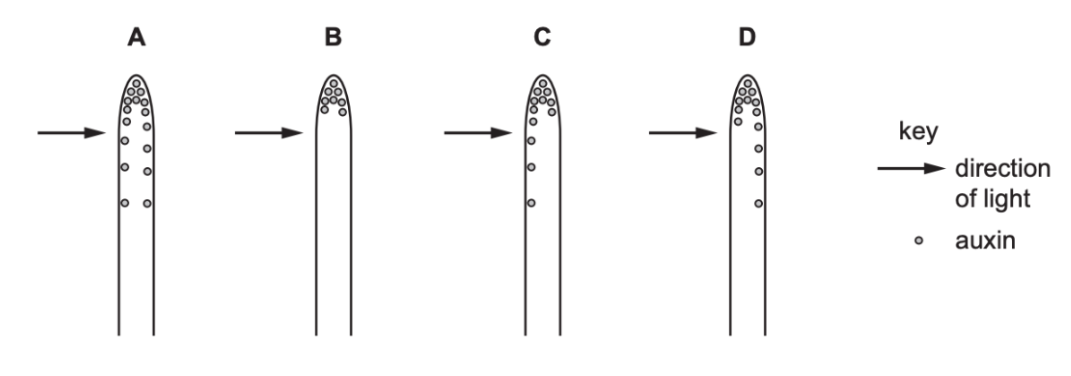

Which statement explains why the rate increases?
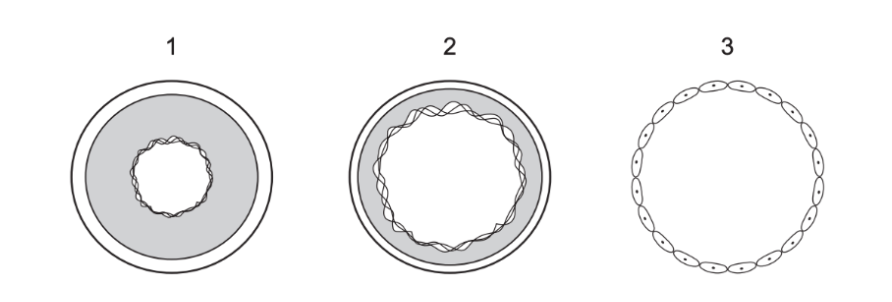
14) Where are the hormones oestrogen and progesterone produced during pregnancy?
The changes in pH are caused by the production of lactic acid.
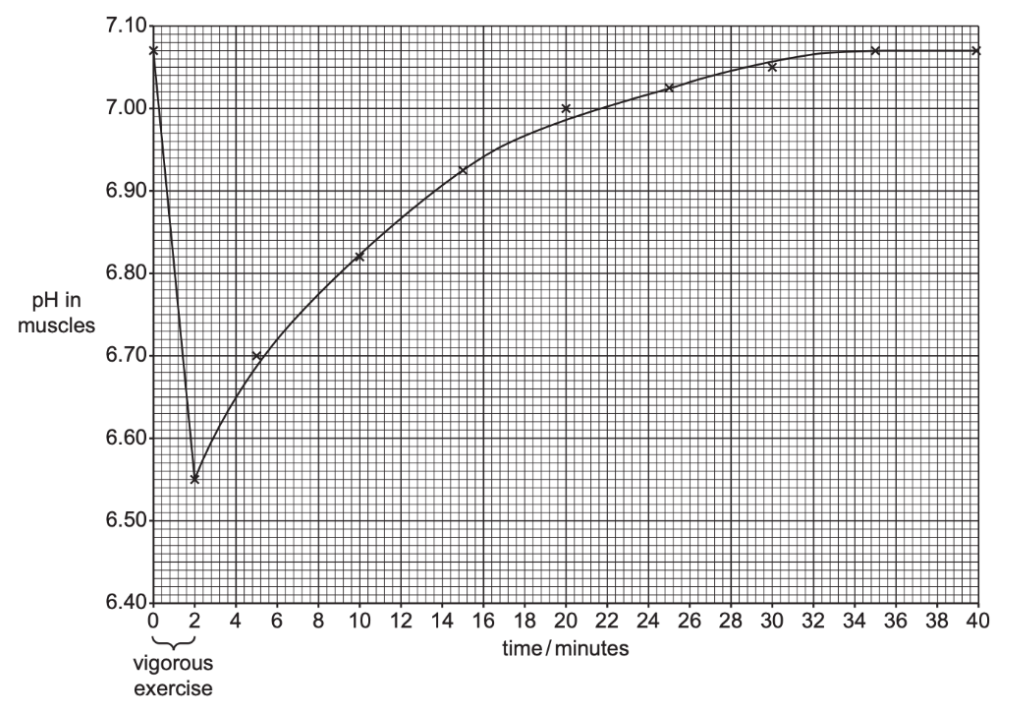
Fig. 6.1
Complete the sentences to describe and explain the results in Fig. 6.1.
The pH decreases ……(A)…… during vigorous exercise.
The body respires aerobically. The ……(B)…… produced builds up in the muscles causing an oxygen debt.
It takes ……(C)…… minutes for the muscle pH to return to its initial level after exercise.
During this time the ……(D)…… rate remain high.
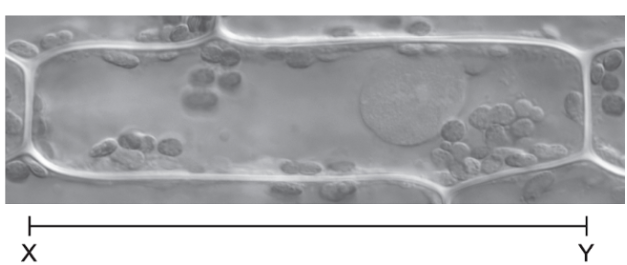
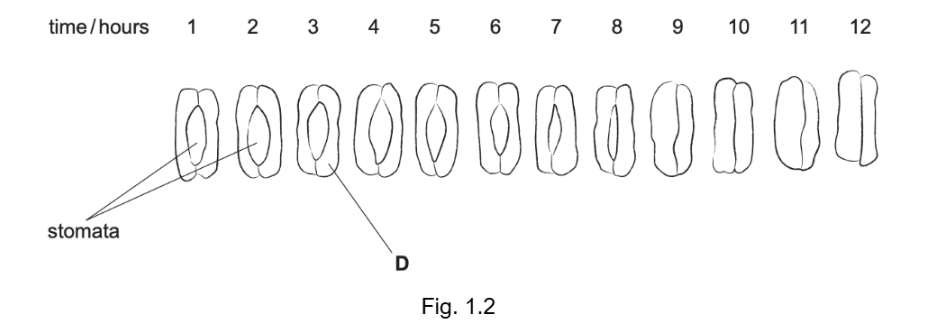
Fig. 1.2 shows a series of sketches that the student made of the stomata during the investigation.

(a) Complete Table 4.1 using the information in Fig. 4.1 by matching the names of the trophic level and one organism at each different trophic level to complete the longest food chain.
Predict the impact on the feeding relationships shown in Fig. 4.1 of overharvesting of salmon.
20) Fig. 4.1 shows a drawing of a nephron in the human kidney and associated blood vessels. 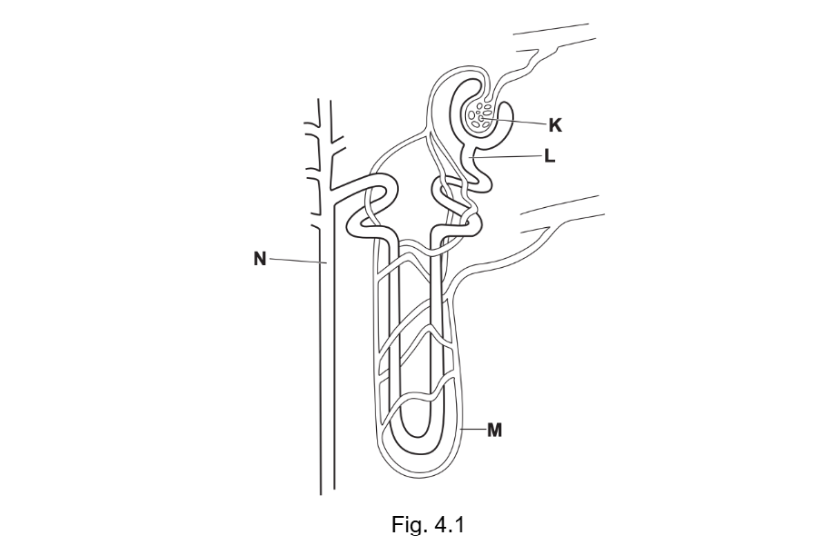
(a) Matching the structure labelled in Fig. 4.1 and its fun
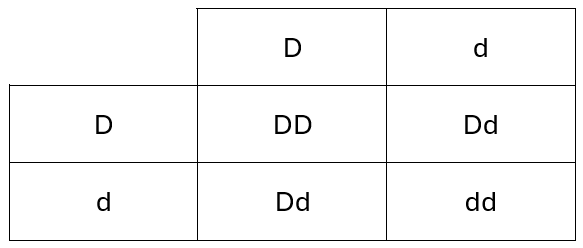
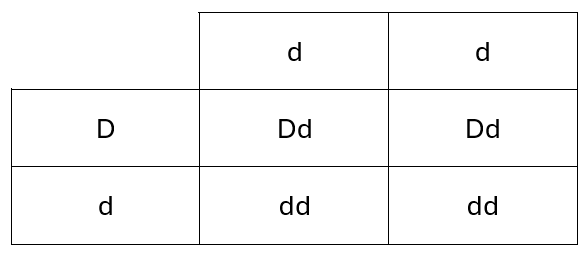
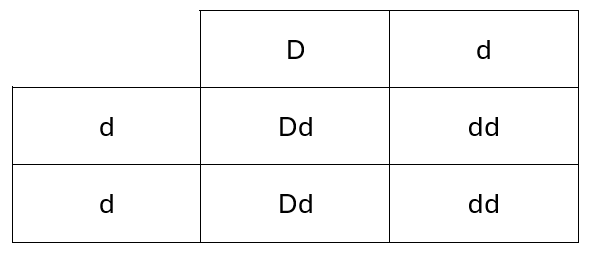
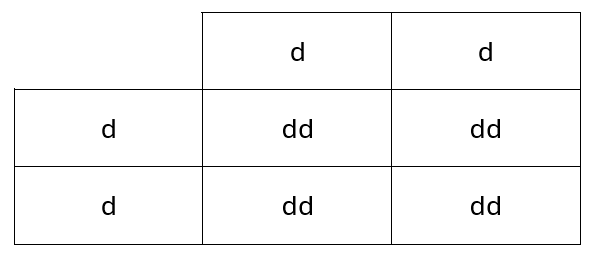
21) The Rhesus (Rh) factor is a protein that is found on the surface of red blood cells in some people. If the protein is present then the individual is Rh positive.
The allele for the presence of the Rh factor is dominant and is represented by the letter D.
The recessive allele is represented by the letter d.
If a mother is Rh negative and the fetus is Rh positive there can be problems during pregnancy.
A Rh negative mother and a heterozygous Rh positive father have a child.
Complete the Punnett square and determine the probability of the child being Rh positive.