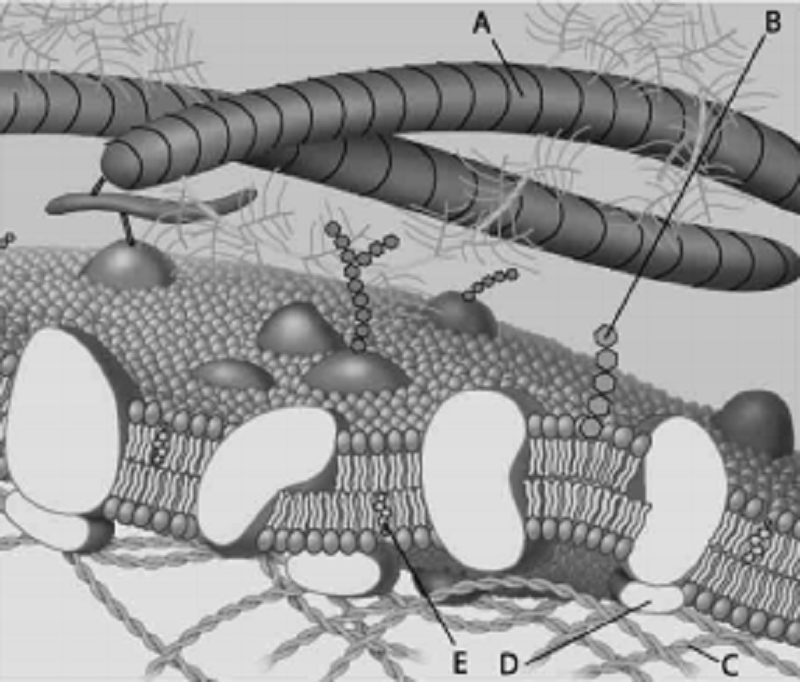
Cell Membrane Quiz
{"name":"Cell Membrane Quiz", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of cell membranes with our engaging quiz! Explore essential concepts about the structure, function, and properties of cell membranes through a series of thought-provoking questions.Key Features:Multiple choice formatCovers various aspects of cell membranesFun and educational","img":"https:/images/course1.png"}
More Quizzes
Macromolecule Mastery Quiz
1477
302 Outcome 3, practice questions on cells.
22110
What would you do in these situations?
7444
Are You an Oprah Or a Gayle?(Carrotberg, not Winfrey or King)
5218
You Supply Air to the Trailer Tanks By: CDL Air Brakes
201020648
Java Developer Test - Free Skills Assessment
201017624
Am I Over Him - Free with Instant Results
201016625
Muscle Tissue: Summation in Muscle Contraction
201023190
Color Theory - Free Design Knowledge Challenge
201017556
Bluey Trivia - Free for Fans Online
201018044
Do People Like Me - Free Likability Self‑Assessment
201016625
Socialist History & Values - Test Your Knowledge
201019952