DES C_Diagnosis (7) Prepared : CHILLY
A 4-year-old child presents with an enlarged submandibular node that is 4 cm in diameter, nontender, and not fluctuant. The node has been enlarged for about 4 weeks, and there is no history of fever or contact with any person who was ill. A CBC is normal, and a Mantoux test with 5 tuberculin units of PPD shows 6 mm of induration. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cat-scratch fever
Tuberculous lymphadenitis
Acute pyogenic lymphadenitis
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Atypical mycobacteria lymphadenitis
A 4-year-old child was brought in for evaluation of sleep problems. He cried and screamed within an hour of falling asleep. He seemed disoriented and confused; he did not seem aware of his parents’ presence. They were unable to arouse him to comfort him. This resolved spontaneously, and he had no recollection of the event the next morning. You informed the parents that he was most likely experiencing which of the following?
Nightmares
Night terrors
Somnambulism
Somniloquy
Narcolepsy
A 4-year-old girl is brought to the office by her parents due to a red rash and blisters. Yesterday, she had a fever and was irritable. Today, she developed the rash with blisters. Her pulse is 90/min, blood pressure is 90/60 mmHg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 39°C (102°F). On examination, there are superficial flaccid bullae and an erythematous rash diffusely distributed over her body. Nikolsky's sign is positive. Her face is edematous, and there is crusting around the mouth area. Her skin is warm and tender with exfoliation. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Scarlet fever
Erysipelas
Lmpetigo
A 4-year-old girl is brought to the office due to easy bruising and a rash for the past 3 days. She had an upper respiratory infection approximately two weeks ago. She has never had palpable bruises, hemarthroses, or deep muscle bleeding in the past. She has 2 older brothers, neither of which has had bleeding symptoms before. Her family history is negative for any bleeding disorders. Her vital signs are normal. Physical examination reveals a diffuse petechial rash on her neck, trunk, extremities and groin. There is no hepatosplenomegaly. Nonpalpable ecchymoses of varying ages are present on the shins and arms. The laboratory findings are as follows: Hemoglobin 12 .8 g/dl, Hematocrit 38.5%, WBC 6,000/mm3, Platelets 5,000/mm3, PT 12.0 sec, PTT 30 sec. Peripheral smear shows normal morphology of the red and white blood cell lines. The platelets are reduced in number, and majority of them are increased in size. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
Hemolytic uremic syndrome
Hemophilia
Von Willebrand's disease
A 4-year-old girl is brought to the office due to seizures that occurred 2 hours ago. This is her first episode. Her parents are also concerned because she is not able to carry on activities that children of her age are expected to do. On examination, there is a red flat lesion covering the left eye area and adjacent facial skin, which does not blanch on pressure, and which the parents say has been present since birth. Other pertinent findings are hemianopia, hemiparesis, and hemisensory disturbances. An x-ray of the skull shows tramline intra-cranial calcifications. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Sturge-Weber syndrome
Tuberous sclerosis
Capillary hemangioma
Epilepsy
Neurofibromatosis
A 4-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother who is concerned because her child has a vaginal discharge. Starting 2 days ago, the child began scratching her vulva and complaining of burning with urination. The child is otherwise healthy and has never had a similar problem. Examination reveals normal structural anatomy for a 4-year-old girl. There is no evidence of atrophy. There is an inflammatory erythema on the medial aspects of the labia majora and excoriations. There is a mucous discharge with a few flecks of blood intermixed. Which of the following is the most likely cause of a vaginal discharge in this patient?
Pelvic inflammatory disease
Sexual abuse
Lichen sclerosis
Vaginal foreign body
Sarcoma botyroides (embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma)
A 4-year-old girl is brought to your office by her mother for recent onset of fever and rash. For the past 4 days, she has had headaches, fever, and sore throat. She was apparently normal 4 days ago, and upon presentation of the symptoms, her mother thought that she was having a simple viral fever which would go away with time; however, she then developed a pale pink maculo-papular rash, first on the face and neck, and then it rapidly spread onto the trunk and limbs. On examination, the child is afebrile and doesn't appear ill, but there are few palpable suboccipital and posterior auricular lymph nodes. What is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
Group A beta- hemolytic streptococci
Measles virus
Rubella virus
Varicella virus
Human parvovirus
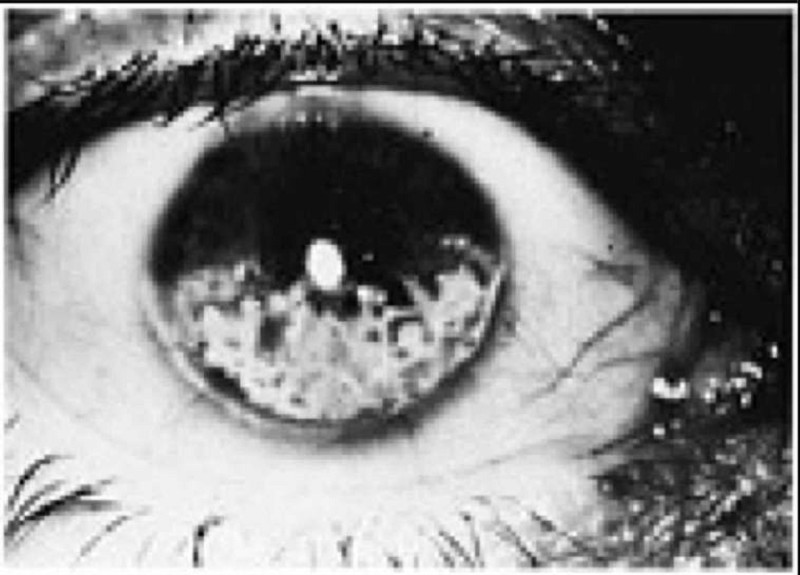
A 4-year-old girl is noticed by her grandmother to have a limp and a some-what swollen left knee. The parents report that the patient occasionally com- plains of pain in that knee. An ophthalmologic examination reveals findings as depicted in the photograph. Which of the following conditions is most likely to be associated with these findings?
Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease
Osgood-Schlatter disease
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
Henoch-Schönlein purpura
A 4-year-old immigrant boy is brought by his mother to a Medical Camp for the Uninsured for the evaluation of his inflamed right eye. He has had a nasal discharge for the past 10 days. His brother has similar symptoms. His vital signs are stable. There are follicles and inflammatory changes in the conjunctiva of his right eye. The cornea shows neovascularization. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Herpes simplex keratitis
Orbital cellulitis
Trachoma
Gonococcal conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis
A 4-year-old previously healthy but unimmunized boy presents with sudden onset of high fever, inspiratory stridor, and refusal to drink. Of the following causes of inspiratory stridor, which best fits this clinical scenario?
Epiglottitis
Vascular ring
Croup
Foreign body aspiration
Laryngeal tumor
A 4-year-old previously healthy girl presents to the emergency department with a 24-hour history of rectal bleeding and dizziness. She has no other gastrointestinal symptoms. On examination, she appears pale. Her heart rate is 140 beats/min, and she has a 20 mmHg postural drop in systolic blood pressure. The child’s abdomen is nondistended and nontender, and fresh blood and clots are in the rectal vault on rectal examination. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A bleeding Meckel’s diverticulum
Juvenile rectal polyp
Hemorrhoids
An anal fissure
Intussusception
A 4-year-old, apparently healthy child is examined by a pediatrician. The pediatrician hears a loud systolic ejection murmur with a prominent systolic ejection click. He also hears a soft, early diastolic murmur. Both murmurs are heard best at the upper right sternal border. ECG shows left ventricular hypertrophy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Aortic valve stenosis
Transposition of great arteries
Atrial septal defect
Ventricular septal defect
Tetralogy of Fallot
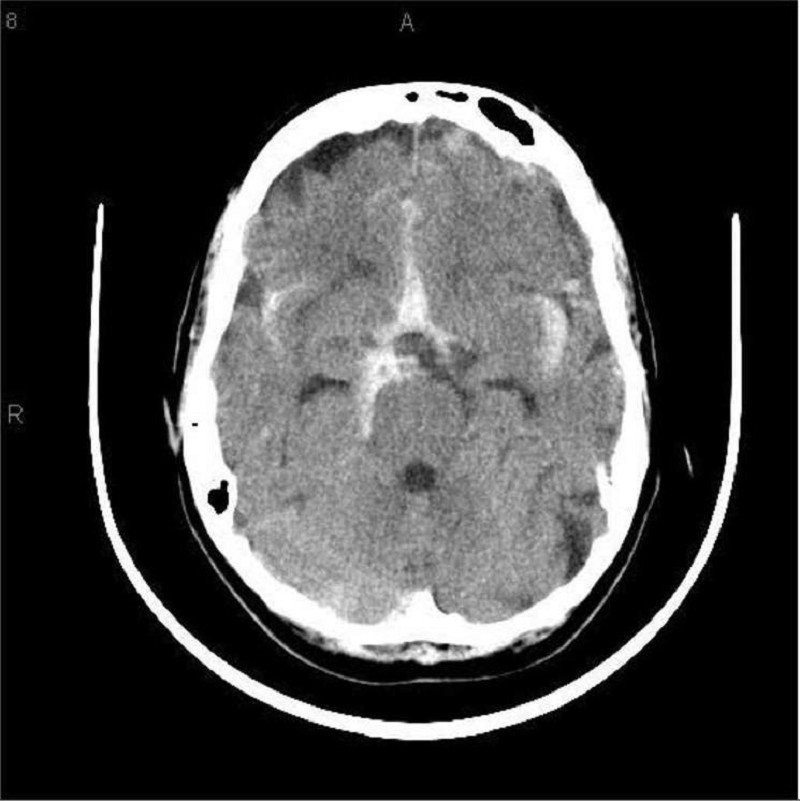
A 40-year-old Caucasian male comes to the emergency department because he is having "the worst headache" of his life. The headache is of sudden onset, and associated with nausea and vomiting. He denies any fever and trauma to head. He is not taking any medications. He has a history of migraine headaches. The neurological examination is non-focal. CT scan of the head without contrast is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's headache?
Hypertension
Extension of primary intracerebral hemorrhage
Amyloid angiopathy
Rupture of saccular aneurysm
Rupture of AV malformation
A 40-year-old Caucasian man comes to the emergency department because of fever, dry cough, and shortness of breath. Symptoms started 24 hours ago. He denies hemoptysis. He was recently discharged from the hospital after a second cycle of chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His temperature is 38.9°C (102.0°F), blood pressure is 120/70 mmHg, pulse is 112/min and respirations are 28/min. The patient's pulse oximetry showed 86% at room air. Examination shows diffuse crackles all over the lung fields. His chest x-ray shows diffuse interstitial infiltrates. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
Coccidioidomycosis
Histoplasmosis
Pneumocystis jiroveci
Tuberculosis
HIV infection
A 40-year-old female is brought to the emergency department following a motor vehicle accident in which she was the front seat passenger. She reports hitting her head against the windshield and hurting her right leg. She appears completely alert and oriented. Glasgow Coma Scale =15/15. Her pupils are equal and reactive to light. There is a bruise over the right forehead, but no tenderness is present on palpation of the cranial bones. Examination of the right leg reveals a hematoma over the thigh. Knee extension on the right is markedly reduced when compared to the left. Sensory examination reveals decreased sensory perception to both sharp and dull stimuli over the medial side of the right lower thigh and leg. All other dermatomes are intact. What nerve injury is most likely present in this patient?
Femoral nerve
Tibial nerve
Obturator nerve
Common peroneal nerve
Fibular nerve
A 40-year-old female presents with a 12-month history of episodes of chest pain and dysphagia. The episodes last from a few seconds to a few minutes. She has not had weight loss, fevers or chills. Chest-x ray, ECG and barium swallow show no abnormalities. Manometric studies show simultaneous high amplitude contractions with normal relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Zenker's diverticulum
Diffuse esophageal spasm
Achalasia
Scleroderma
Infectious esophagitis
A 40-year-old G3P2 obese patient at 37 weeks presents for her routine OB visit. She has gestational diabetes that is controlled with diet. She reports that her fasting and postprandial sugars have all been within the normal range. Her fetus has an estimated fetal weight of 6.5 lb by Leopold maneuvers. Which of the following is the best next step in her management?
Induction of labor at 38 weeks
Kick counts and routine return OB visit in 1 week
Cesarean delivery at 39 weeks to prevent shoulder dystocia
Weekly biophysical profile
Administration of insulin to prevent macrosomia
A 40-year-old G3P3 comes to your office for a routine annual GYN examination. She tells you that she gets up several times during the night to void. On further questioning, she admits to you that during the day she sometimes gets the urge to void, but sometimes cannot quite make it to the bathroom. She attributes this to getting older and is not extremely concerned, although she often wears a pad when she goes out in case she loses some urine. This patient is very healthy otherwise and does not take any medication on a regular basis. She still has regular, monthly menstrual periods. She has had three normal spontaneous vaginal deliveries of infants weighing between 7 and 8 lb. An office dipstick of her urine does not indicate any blood, bacteria, WBCs, or protein. Her urine culture is negative. Based on her office presentation and history, which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Urinary stress incontinence
Overflow incontinence
Urinary tract infection
Bladder dyssynergia
Vesicovaginal fistula
A 40-year-old male presents to the Emergency Room with a two-month history of occasional severe headache and blurring of vision. His past medical history is significant for hypertension controlled with hydrochlorothiazide for two years. His family history is significant for hypertension and diabetes. He smokes two packs a day and occasionally consumes alcohol. His blood pressure is 200/140 mmHg and heart rate is 75/min. Which of the following is most consistent with a diagnosis of malignant hypertension in this patient?
Left ventricular hypertrophy on ECG
Papilledema
Elevated serum creatinine level
Oliguria
Blood pressure ≥ 200/ 140 mmHg
A 40-year-old man develops erythema nodosum, conjunctivitis, and a pleural effusion. Over several weeks, pulmonary lesions lead to cavitation and a large, thin-walled cavity. He was traveling in Arizona before becoming ill. Sputum samples reveal mature spherules. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Streptococcus
Pneumocystis carinii
Coccidioidomycosis
Candidiasis
Staphylococcus
A 40-year-old man is brought to the emergency room because of altered mental status and gait instability. He has had two falls in the last two days. He drinks one pint of vodka daily and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. His temperature is 35.0°C (95.0°F), blood pressure is 100/70 mm Hg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 14/min. He is disoriented, but not in acute distress. You note prominent horizontal nystagmus and conjugate gaze palsy in both eyes and absent ankle reflexes in both legs. His chest is clear to auscultation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
Viral encephalitis
Thiamine deficiency
Hypothyroidism
Cerebellar infarction
Opioid intoxication
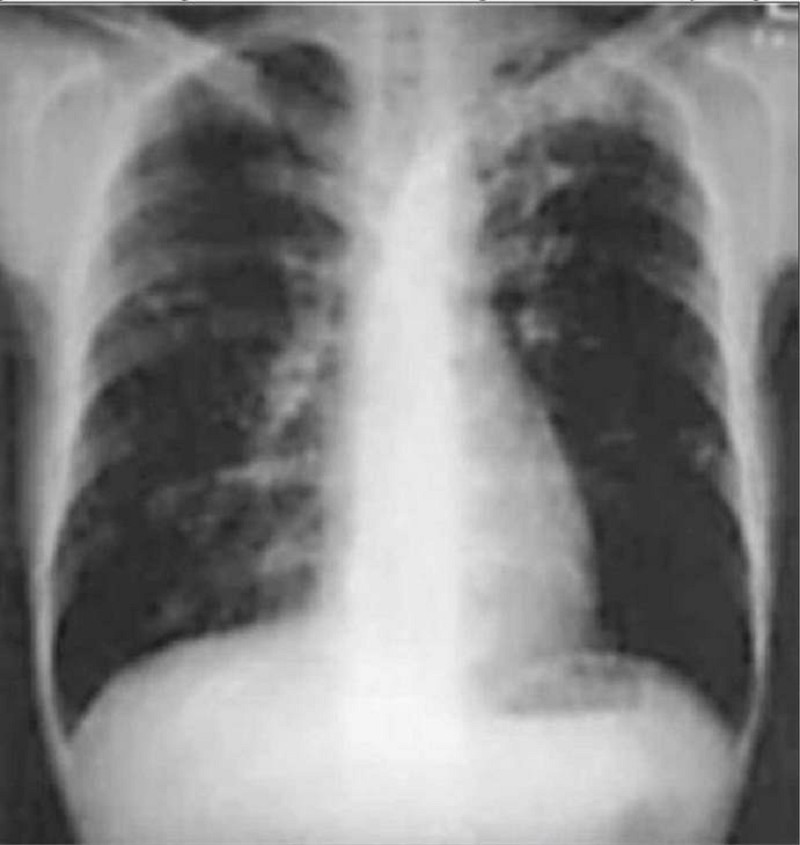
A 40-year-old man is seen for an insurance assessment. He has no past medical history and feels well. His compete physical examination is normal. His biochemistry, complete blood count (CBC), ECG, and urinalysis are also normal. His CXR is abnormal and presented in Fig. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Hamartoma of the lung
Bronchogenic carcinoma
Tuberculous granuloma of the left apex
Osteochondroma of the left 4th rib
Pulmonary metastases
A 40-year-old man presents to the emergency room with shortness of breath, cough and hemoptysis for the past two days. He says he has never had symptoms like these before. His medical history is significant for a non-healing leg ulcer and chronic purulent nasal discharge. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for the past 20 years. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.6°C (99.7°F), blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg, pulse is 94/min and respiratory rate is 18/min. Lung auscultation reveals patchy rales bilaterally. Heart sounds are regular. A 2x3cm ulcer with rolled, undermined borders is noted on the right lower leg. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for his hemoptysis?
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Wegener's granulomatosis
Bronchogenic carcinoma
Mitral stenosis
Pulmonary embolism
A 40-year-old previously healthy man presents with sudden onset of severe abdominal pain that radiates from the right loin (flank) to groin. This pain is associated with nausea, sweating, and urinary urgency. He is distressed and restless, but an abdominal examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Torsion of the right testicle
Pyelonephritis
Appendicitis
Right ureteral calculus
Acute urinary retention
A 40-year-old white male complains of weakness, weight loss, and abdominal pain. On examination, the patient has diffuse hyperpigmentation and a palpable liver edge. Polyarthritis of the wrists and hips is also noted. Fasting blood sugar is 185 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
Pancreatic carcinoma
Metabolic syndrome
Addison disease
Hemochromatosis
A 40-year-old woman is arrested by the police after she is found crawling through the window of a movie star’s home. She states that the movie star invited her into his home because the two are secretly married and “it just wouldn’t be good for his career if everyone knew.” The movie star denies the two have ever met, but notes that the woman has sent him hundreds of letters over the past 2 years. The woman has never been in trouble before and lives an otherwise isolated and unremarkable life. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Delusional disorder
Schizoaffective disorder
Bipolar I disorder
Cyclothymia
Schizophreniform disorder
A 40-year-old woman presents to the ED complaining of fever and 1 day of increasingly severe pain in her RUQ. She denies nausea or vomiting and has no history of fatty food intolerance. The patient returned from a trip to Mexico 6 months ago. About 2 weeks ago she experienced intermittent diarrhea with blood-streaked mucus. Her BP is 130/80 mm Hg, HR is 107 beats per minute, temperature is 102°F, and RR is 17 breaths per minute. Physical examination reveals decreased breath sounds over the right lung base. Abdominal examination shows tenderness to percussion over the RUQ and normal active bowel sounds. There is no Murphy sign. Her WBC is 20,500/μL. Chest radiograph reveals a small right-pleural effusion. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Amebic abscess
Cholecystitis
Cryptosporidium
Enterobiasis
Pyogenic abscess
A 40-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with a 3-day history of worsening abdominal pain, with nausea and vomiting. Examination reveals a low-grade fever and abdominal tenderness in the right upper quadrant with guarding, especially during inspiration. Laboratory findings include a mild leukocytosis and a slightly elevated bilirubin. Select the most likely diagnosis?
Gastroenteritis
Regional enteritis
Acute appendicitis
Perforated peptic ulcer
Acute cholecystitis
A 41-year-old fire-fighter comes to your office and requests for prostate cancer screening. He is concerned because his elder brother was recently diagnosed with prostate cancer, and he read in the paper that "cancers run in families." He requests to be screened urgently, as he "cannot even think of life with such a deadly disease." He has no medical complaints. He has been your patient for the past 6 years, and has no other medical history. He is on a very balanced diet, and adds that he eats a lot of garlic "so that cholesterol remains in check." He takes a low-dose aspirin daily. He does not smoke, and is only a social drinker. He admits using marijuana "once in a while” What is the best next step to address this patient's concerns?
Transurethral ultrasonogram
T ransrectal ultrasonogram
Bone scan
Perform digital rectal examination
Needle biopsy
A 41-year-old intravenous drug abuser presents with shortness of breath and pleuritic chest pain. He is febrile with a temperature of 103.5°F. He has no skin lesions and funduscopic exam is negative. He has jugular venous distension that increases with compression of the liver. The liver is pulsatile. The jugular venous pulse shows a prominent v wave. The patient has splenomegaly. Heart auscultation reveals a holosystolic murmur heard best at the left lower sternal border. The murmur increases with inspiration (Müller maneuver). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bacterial endocarditis
Pericarditis
Rheumatic fever
Mitral valve prolapse
Pericardial effusion
A 41-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 3, comes to the physician because of a 2-year history of dysmenorrhea and menorrhagia that has been increasing in intensity. She has no dyspareunia or any other symptoms. She has a history of chronic hypertension. She had a cesarean section in her 3rd pregnancy followed by surgical sterilization. Vital signs are normal. Bimanual examination shows a symmetrically enlarged and tender uterus with soft consistency and free adnexae. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Adenomyosis
Endometriosis
Leiomyomata
Endometrial carcinoma
Endometritis
A 42-year-old female with acute pericarditis develops jugular venous distention and hypotension. The ECG shows electrical alternans. Which of the following is the most likely additional physical finding?
Basilar rales halfway up both posterior lung fields
Pulsus paradoxus
Strong apical beat
Epigastric tenderness
S3 gallop
A 42-year-old male comes to the physician's office for evaluation of skin rash and hair loss. He has a long history of Crohn's disease and has had extensive small bowel resection resulting in short bowel syndrome. He is currently receiving total parenteral nutrition. When he does try to eat, he complains that the food does not taste good. His vital signs are stable. Examination shows alopecia and bullous, pustular lesions around the perioral and periorbital areas. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current symptoms?
Celiac disease
Vitamin A deficiency
Zinc deficiency
Vitamin B 12 deficiency
Systemic lupus erythematosus
A 42-year-old male presents to your office complaining of back pain that started two days ago after carrying heavy packages. He denies any weakness or sensory changes in his legs. His past medical history is insignificant. He is not taking any medications and denies drug abuse. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Physical examination reveals paravertebral tenderness. Lower extremity power is 5/5 and the deep tendon reflexes are 2+. Babinski's sign is negative. Straight-leg raising test is negative at 90 degrees. What is the most probable diagnosis in this patient?
Multiple myeloma
Compression fracture of the vertebrae
Ankylosing spondylitis
Lumbosacral strain
Herniated disk
A 42-year-old man comes to the emergency room with the chief complaint that “the men are following me.” He also complains of hearing a voice telling him to hurt others. He tells the examiner that the news anchorman gives him special messages about the state of the world every night through the TV. Which of the following psychiatric findings best describes this last belief of the patient?
Grandiose delusion
Clouding of consciousness
Illusion
Loose association
Idea of reference
A 42-year-old man describes intermittent episodes of severe, crushing chest pain that extends to the back and the jaw and last anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. Many times the pain is accompanied by dysphagia and triggered by the ingestion of very cold or very hot liquids. However, sometimes the pain occurs for no apparent reason. There is no history of regurgitation, and, although the problem has been present for many years, there has been no progression of the symptoms. Repeated ECGs and cardiac enzymes have always been negative. Barium swallow shows an area of "corkscrew" appearance. Manometry shows that about one half of wet swallows produce repetitive simultaneous esophageal contractions of the esophageal body, and that the lower esophageal sphincter has normal pressures and exhibits normal relaxation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Achalasia of the esophagus
Diffuse esophageal spasm
Cancer of the lower esophagus
Nutcracker esophagus
Zenker's diverticulum
A 42-year-old man found vomiting in the street is brought to the ED by emergency medical services (EMS). He has a known history of alcohol abuse with multiple presentations for intoxication. Today, the patient complains of acute onset, persistent chest pain associated with dysphagia, and pain upon flexing his neck. His BP is 115/70 mmHg, HR is 101 beats per minute, RR is 18 breaths per minute, and oxygen saturation is 97% on room air. As you listen to his heart, you hear a crunching sound. His abdomen is soft with mild epigastric tenderness. The ECG is sinus tachycardia without ST-T–wave abnormalities. On chest radiograph, you note lateral displacement of the left mediastinal pleura. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Aspiration pneumonia
Acute pancreatitis
Pericarditis
Esophageal perforation
Aortic dissection
A 42-year-old man has bouts of intermittent crampy abdominal pain and rectal bleeding. Colonoscopy is performed and demonstrates multiple hamartomatous polyps. The patient is successfully treated by removing as many polyps as possible with the aid of intraoperative endoscopy and polypectomy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Ulcerative colitis
Villous adenomas
Familial polyposis
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
Crohn colitis
A 42-year-old man has had a rocky course for the 3 days following a bowel resection for intestinal perforation due to inflammatory bowel disease. His CVP had been 12 to 14 but is now 6, in the face of diminished blood pressure and oliguria. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of his hypotension?
Pulmonary embolism
Positive-pressure ventilation
Hypervolemia
Pneumothorax
Gram-negative sepsis
A 42-year-old man is undergoing chemotherapy after resection of a cecal adenocarcinoma with positive lymph nodes. You are asked to see him regarding a potential surgical complication. Which of the following potentially operable complications is a common occurrence among patients receiving systemic chemotherapy?
Acute cholecystitis
Perirectal abscess
Appendicitis
Incarcerated femoral hernia
Diverticulitis
A 42-year-old man presents to his primary care physician complaining of daytime sleepiness. He says that he often falls asleep during meetings, watching TV, and even while driving his car. He does not feel refreshed after his daytime naps, and has not experienced vivid hallucinations when falling asleep or upon awakening. He has occasional morning headaches and his wife complains that he sometimes keeps her up at night. Physical exam reveals a body mass index (BMI) of 31.3 kg/m2. An arterial blood gas is normal. What is this patient's most likely diagnosis?
Narcolepsy
Obstructive sleep apnea
Obesity hypoventilation syndrome
Central sleep apnea
Primary insomnia
A 42-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of two weeks of weakness, low-grade fevers, and exertional shortness of breath. He also notes fingertip pain and urine that has been dark and cloudy recently. On physical examination, several of his proximal inter phalangeal joints are swollen. Which of the following diagnoses is most consistent with his presentation?
Rheumatoid arthritis
Adult Still's disease
Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis
Infective endocarditis
Adrenal insufficiency
A 42-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a complaint of increasing shortness of breath when walking to get his newspaper, difficulty breathing while lying flat, and a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight gain over the past month. He is afebrile, his pulse is 75/min, and his blood pressure is 98/50 mmHg. On examination he smells of alcohol and has 2+ pitting edema in the lower extremities and a third heart sound. X-ray of the chest reveals cardiomegaly. What additional findings must be present to confirm this man’s underlying diagnosis?
Myocardial thickening and diastolic dysfunction
Pulmonary congestion and diastolic dysfunction
Left ventricular dilation and systolic dysfunction
Left ventricular dilation and aortic insufficiency
Hepato-jugular reflux and pulmonary congestion
A 42-year-old man presents with a solitary lung lesion. At the time of operation on this patient, a firm, rubbery lesion in the periphery of the lung is discovered. It is sectioned in the operating room to reveal tissue that looks like cartilage and smooth muscle. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Fibroma
Chondroma
Osteochondroma
Hamartoma
Aspergilloma
A 42-year-old man with known valvular heart disease develops a fever for 1 week. He appears unwell; findings include a pansystolic murmur at the apex that radiates to the axilla and a soft S1 sound. He has petechiae on his conjunctival sac, linear hemorrhages under a few fingernails, and painful, tender, and erythematous nodules on some of the distal fingertips. Which of the following is the most responsible mechanism for these physical findings?
Direct bacterial invasion
Vascular phenomena
Valvular damage
Preexisting cardiac dysfunction
Immune response
A 42-year-old white male presents to your office complaining of periodic breathing difficulty and wheezing. He visited an otolaryngologist for persistent nasal blockage recently. His past medical history is significant for unstable angina experienced five months ago. His current treatment includes aspirin, diltiazem, and pravastatin. He does not use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. His vital signs are within limits. What is the most probable cause of this patient's respiratory complaints?
IgE-mediated reaction
Cytotoxic antibodies
Immune complex disease
Cell-mediated hypersensitivity
Pseudo-allergic reaction
A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician because of vaginal itch and discharge, dysuria, and dyspareunia. These symptoms have been steadily worsening over the past 3 days. Pelvic examination reveals an erythematous vagina and a thin, green, frothy vaginal discharge with a pH of 6. Microscopic examination of the discharge demonstrates the presence of a pear-shaped, motile organism. Which of the following is the most likely pathogen?
Candida albicans
Herpes simplex virus
Gardnerella vaginalis
Treponema pallidum
Trichomonas vaginalis
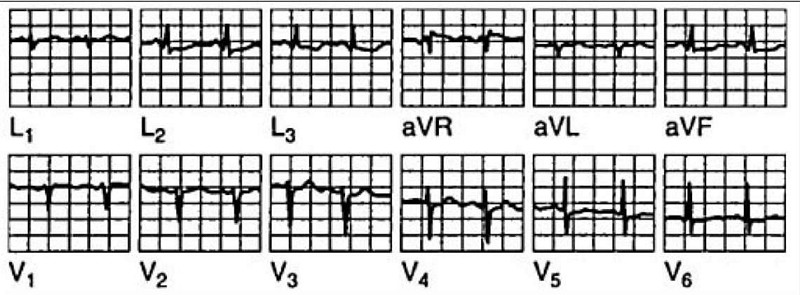
A 42-year-old woman has anterior chest pain of a somewhat atypical nature for many years. The patient’s pain has been present and relatively stable for a number of years, and the ECG shown in Fig. Is a stable one. What is the diagnosis?
Nonspecific changes
Inferior wall infarction
Anterior wall infarction
Ventricular aneurysm
Pericarditis
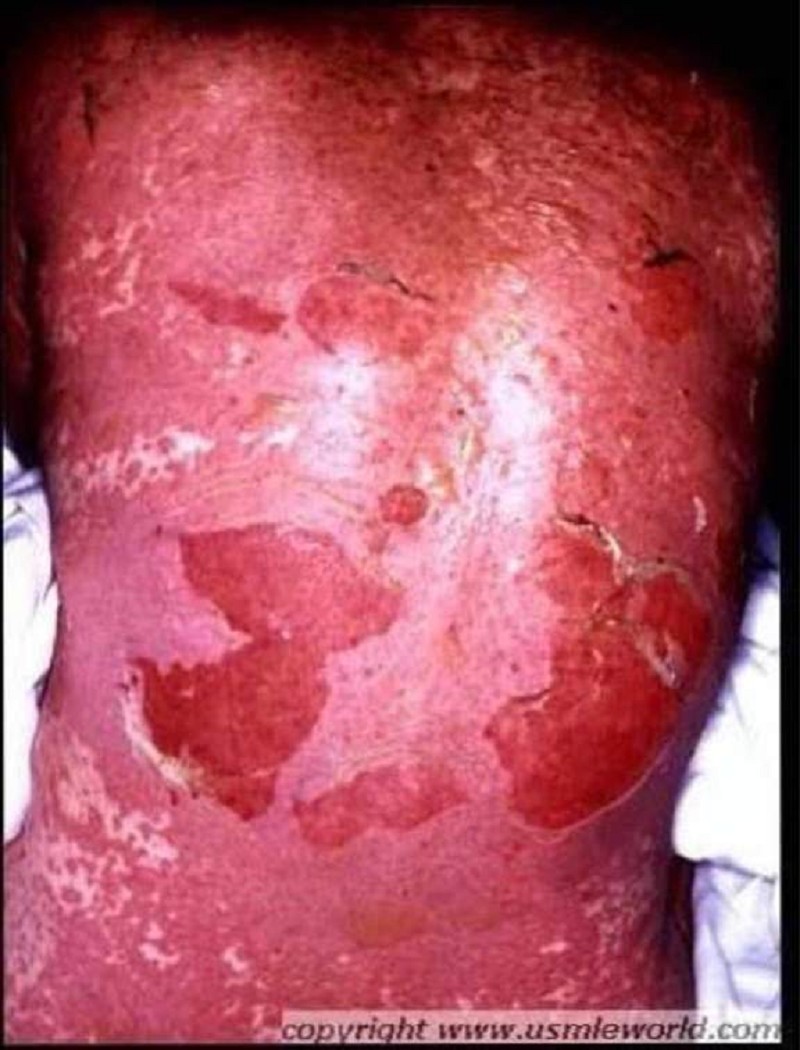
A 42-year-old woman presents with painful skin lesions. She is unable to eat or drink because the lesions have involved her mouth and throat. Her other complaints include malaise, headache, sore throat, cough, nausea and vomiting prior to the onset of the skin lesions. She was in perfect health in the past, other than an episode of urinary tract infection 3 days ago. She was prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combination for this infection. Her pulse is 92/min, respirations are 14/min, blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg, and temperature is 38.3°C (101°F). On examination, the skin is hot and tender with erythematous macules. The oral mucosa shows blistering and erosions. A picture of her back is shown below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Exfoliative dermatitis
Erythema multiforme minor
Stevens Johnson's syndrome
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
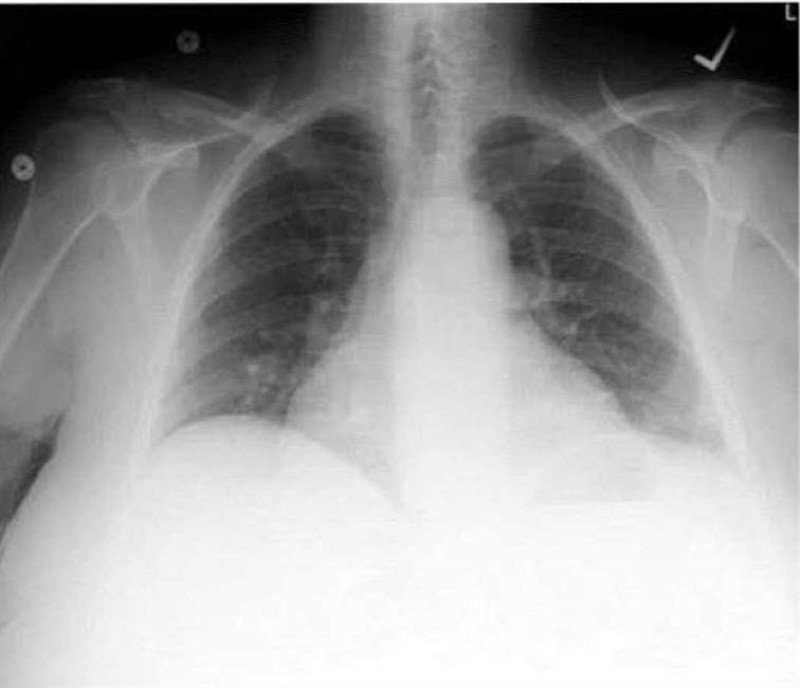
A 43-year -old man complains of progressive weakness and shortness of breath over the last two weeks. He denies any chest or muscle pain, nausea, vomiting or weight loss. He had a recent upper respiratory tract infection. His heart rate is 90/min and blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg. Jugular venous pressure is normal. Lungs are clear to auscultation. His chest x-ray is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely additional finding in this patient?
Audible fourth heart sound
Pulsus bisferiens
Opening snap
Fixed splitting of the second heart sound
Non-palpable point of maximal impulse
A 43-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office complaining of joint pain and swelling in her hand. On history, she endorses easy fatigability and loss of energy that has been worsening insidiously. It is especially difficult for her to do daily activities in the morning due to prolonged stiffness. She also describes frequent knee pain accompanied by a low-grade fever. She takes ibuprofen and naproxen to relieve her symptoms. Her hematocrit is 33%. The patient is at the greatest risk of which of the following?
Osteitis fibrosis cystica
Osteitis deformans
Avascular bone necrosis
Osteomalacia
Osteoporosis
A 43-year-old female presents to the physician's office with muscle cramps, polydipsia and polyuria. She has no other medical problems, and does not take any medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her father died from alcoholic liver disease at age 50. Her pulse is 75/min, respirations are 13/min, blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg, and temperature is 37°C (98.6°F). Laboratory studies show: Blood glucose 115 mg/dL, Serum sodium 142 mEq/L, Serum potassium 2.7 mEq/L. Plasma renin activity is low. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Atherosclerosis of renal artery
Adrenal adenoma
Fibromuscular dysplasia
Congestive heart failure
Cirrhosis of liver
A 43-year-old G2P2 comes to your office complaining of an intermittent right nipple discharge that is bloody. She reports that the discharge is spontaneous and not associated with any nipple pruritus, burning, or discomfort. On physical examination, you do not detect any dominant breast masses or adenopathy. There are no skin changes noted. Which of the following conditions is the most likely cause of this patient’s problem?
Breast cancer
Duct ectasia
Intraductal papilloma
Fibrocystic breast disease
Pituitary adenoma
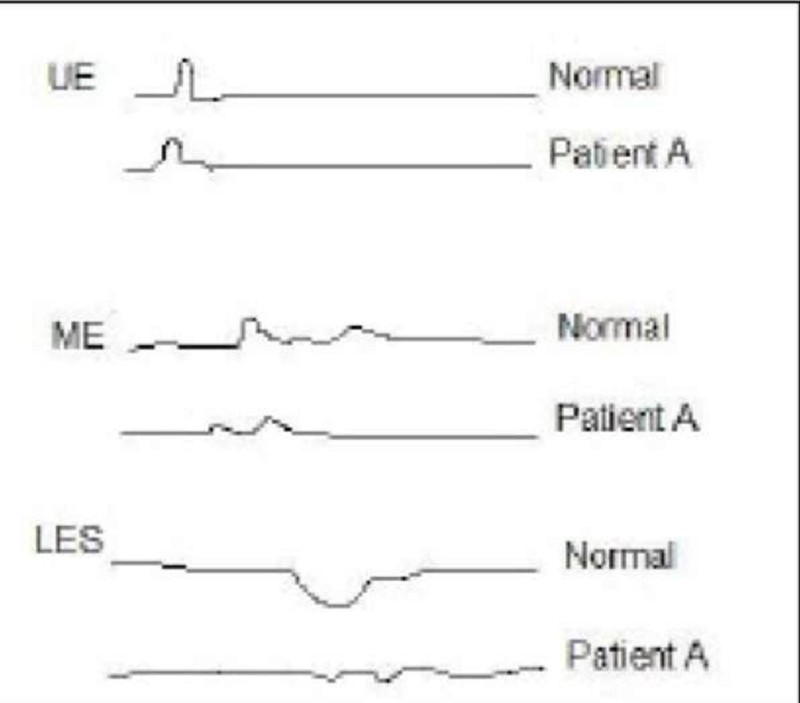
A 43-year-old male (Patient A) is being evaluated for an esophageal disorder. Esophageal manometry tracings after a single swallow of 5 ml of water are shown on the slide below. (UE: upper esophagus, ME: middle esophagus, LES: lower esophageal sphincter). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Cricopharyngeal dysfunction
Achalasia
Mallory-Weiss syndrome
Gastroesophageal reflux
Diffuse esophageal spasm
A 43-year-old male complains of right shoulder pain and weakness after falling on his outstretched hands two days ago. He denies any swelling or shoulder deformity. You passively abduct both his arms above his head and then ask him to bring his arms down slowly in an adducting motion. The right arm drops rapidly at the midpoint of its descent. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Biceps tendon tear
Lower brachial trunk injury
Long thoracic nerve injury
Rotator cuff tear
Humoral neck fracture
A 43-year-old male complains of right shoulder pain and weakness after falling on his outstretched hands two days ago. He denies shoulder deformity. The physician passively abducts both his arms above his head and then asks him to bring his arms down slowly in an adducting motion. The right arm drops rapidly at the midpoint of its descent. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Biceps tendon tear
Lower brachial trunk injury
Long thoracic nerve injury
Rotator cuff tear
Humeral neck fracture
A 43-year-old man complains of occasional red urine. He denies fever, edema, flank pain or weight loss. Specifically, he says that each urine stream starts out transparent, but turns red by the end of the stream. At times he has noticed small clots in his urine. Physical examination is within normal limits. What is the most likely cause of his complaints?
Glomerular disease
Nephrolithiasis
Urinary tract infection
Urethral injury
Bladder disease
A 43-year-old man developed a cough shortly after returning from a 1-month hiking trip in California. While there, he was hiking in the central California valleys. During his trip, he had developed a flu-like illness consisting of fever, cough, and muscle pains, which resolved spontaneously. A CXR shows a thin-walled cavity in the right upper lobe, and the sputum reveals fungal elements. Which of the following is the most likely causative organism?
Ringworm
Cryptococcus neoformans
Mycobacteria
Coccidioidomycosis
Candida albicans
A 43-year-old man develops excruciating abdominal pain at 8:23 PM (he looked at his watch when the pain "hit him"). When seen in the emergency department about 30 minutes later, he has a rigid abdomen, lies motionless on the examination table, has no bowel sounds, and is obviously in great pain, which he describes as constant and encompassing the entire abdomen. There is very severe pain when deep palpation of the abdomen is attempted in any of the four quadrants. However, the examining hand cannot make much of an indentation because of the impressive muscle guarding. When the attempt is aborted, he manifests severe rebound tenderness. X-ray films show free air under both diaphragms. Which of the following does this man most likely have?
Ischemic process affecting intra-abdominal organs
Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract
Acute obstruction of an intra-abdominal viscera
Acute inflammatory process affecting an intra-abdominal viscera
Acute abdomen, the nature of which cannot yet be defined
A 43-year-old man is evaluated for a one-year history of chronic abdominal pain. He describes episodes of epigastric and left upper quadrant pain that last for hours and are not relieved by antacids. Certain foods can precipitate the pain. He also complains of occasional diarrhea. The patient has lost 10 pounds over the last 6 months. Four years ago he was hospitalized for three days with acute abdominal pain. He smokes one pack of cigarettes a day and consumes alcohol regularly. His family history is significant for diabetes mellitus in his mother and prostate cancer in his father. Which of the following is most likely to diagnose this patient's condition?
D -xylose absorption test
Radioisotope (HIDA) scans
Serum amylase and lipase
CA 19-9 and CEA levels
Stool elastase
A 43-year-old man is hospitalized with chest pain, lightheadedness and nausea. He describes the pain as dull and non-radiating. He has never had chest pain before, but does report occasional episodes of dyspnea and coughing. His medical history is significant for eczema. He is not presently taking any medications. His family history is significant for prostate cancer in his father and rheumatoid arthritis in his mother. He does not smoke or consume alcohol. The patient is admitted to the hospital and is given aspirin, low-molecular weight heparin, metoprolol and captopril. On day 2 of his hospitalization he complains of shortness of breath. Physical examination reveals prolonged expirations and bilateral wheezes. There are no crackles. You estimate the jugular venous pressure to be 7 cm with the patient's head elevated at 45 degrees. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's current respiratory symptoms?
Pericarditis
Recurrent myocardial ischemia
Bronchial infection
Right ventricular infarction
Drug side effect
A 43-year-old man presents to your office complaining of periodic involuntary head turning and head fixation to the right side. Physical examination reveals a hypertrophied right sternocleidomastoid muscle. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Parkinson's disease
Essential tremor
Chorea
Akathisia
Dystonia
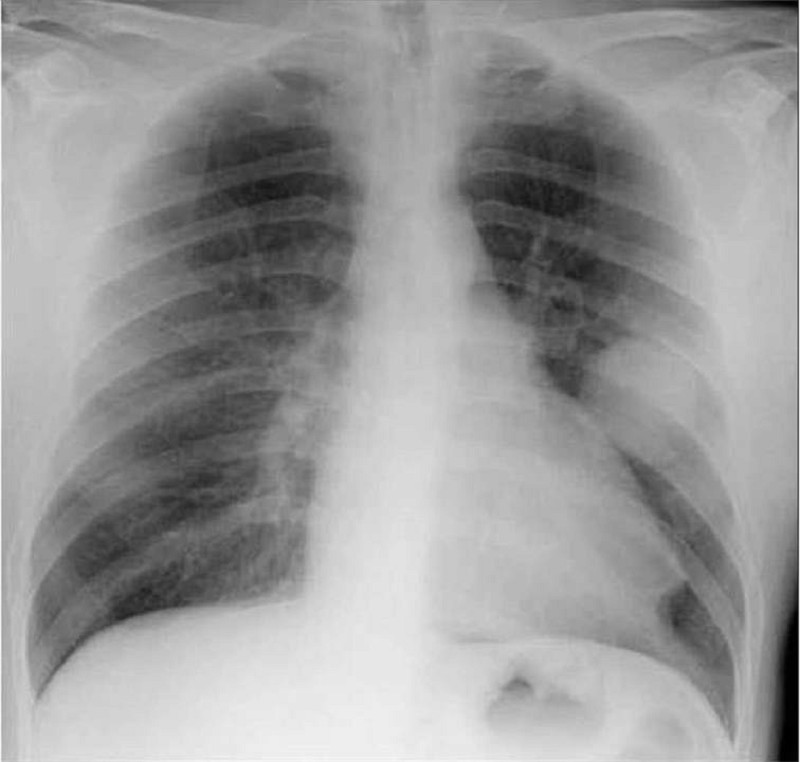
A 43-year-old man presents to your office complaint of nagging left-side chest pain that increases on deep inspiration, plus two weeks of non-productive cough. He denies chills, fever or weight loss. His medical history is significant for Hodgkin's disease treated 20 years ago with chemotherapy and radiation therapy. On physical examination today, his blood pressure is 140/90 mmHg and his heart rate is 90/min. His chest x-ray is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his chest pain?
Radiation-induced fibrosis
Fungal pneumonia
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Secondary malignancy
Recurrence of Hodgkin's disease
A 43-year-old mildly overweight female complains of periodic right knee swelling and pain with physical activity for the past three months. She says that this problem started while on a hiking trip three months ago, at which point she experienced a 'popping' sensation in her right knee. She recalls that her knee was swollen the next day, and responded to over-the-counter pain killers. Recently, she has been having to limit her physical activities due to knee pain. On physical examination, there is tenderness of the anterior and medial right knee joint. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anterior cruciate ligament tear
Meniscal tear
Osteoarthritis
Patellar tendonitis
Anserine bursitis
A 43-year-old moderately overweight woman presents to the emergency department complaining of two days of shortness of breath. Today, while climbing stairs, she had an episode of severe lightheadedness and near syncope. Her medical history is significant for a right calf deep venous thrombosis one year ago. She takes no medications currently. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 90/50 mmHg and her heart rate is 120/min and regular Imaging studies are most likely to reveal which of the following?
Mitral stenosis
Bilateral pulmonary nodules
Pericardial effusion
Right ventricular dilation
Asymmetric hypertrophy of the intraventricular septum
A 43-year-old woman comes to the office because she has "finally decided to see a doctor." For the past four months, she has suffered from itching all over her body. She is tired of using over-the-counter products with no relief. Over the past two months, she has had loose stools, which "take forever to flush." Physical examination reveals jaundice, hepatomegaly and splenomegaly. The results of her blood work are as follows: Alkaline phosphatase 200 u/dL, Bilirubin 3.3 mg/dL, Anti-mitochondrial antibodies positive. Which of the following benign lesions of the eye is frequently associated with this patient's condition?
Chalazion
Hordeolum
Molluscum contagiosum
Xanthelasma
Stye
A 44 year old woman delivers a 3120 g (6 lb 14 oz) newborn male. Her pregnancy was normal except that she noted decreased fetal movement compared to her previous pregnancies. She declined an amniocentesis offered by her obstetrician. Physical examination of the newborn reveals an infant with facial features suggestive of Down syndrome. The infant then has bilious vomiting. An x-ray film showing the kidneys, ureters, and bladder (KUB) is performed, which shows a "double bubble" sign. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the abdominal signs and symptoms?
Duodenal atresia
Hirschsprung Disease
Malrotation
Meconium ileus
Pyloric stenosis
A 44-year-old female complains of generalized weakness, low-grade fever and joint pain. Her daily activities are limited due to joint stiffness, especially in the morning. Her hand joints are swollen symmetrically. The inferior pole of the spleen is palpable on physical examination. Her hematocrit is 34%. Liver and renal function tests are normal. Two months after the initial visit, the patient develops painful oral ulcers. Her laboratory values are: Hematocrit 33%, AST 120 U/L, ALT 90 U/L, Alkaline phosphatase 90 U/L, Bilirubin 1.1 mg/dl, Creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, BUN 16 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's current complaints?
Viral hepatitis
Lymphoid cell proliferation
Felty syndrome
Antimetabolite agent
Corticosteroid treatment
A 44-year-old male is found unresponsive and hypotensive at the scene of a high-speed motor vehicle accident. He is intubated and immediately rushed to the emergency department. The passenger in his car is pronounced dead at the scene. Physical examination in the ED shows large bruises over the entire chest wall and collapsed neck veins bilaterally. Lung exam reveals decreased breath sounds on the left side. Chest x-ray shows a large left hemothorax and a widened, rightward deviating mediastinum. The most likely diagnosis is?
Esophageal rupture
Aortic injury
Myocardial rupture
Myocardial contusion
Diaphragm rupture
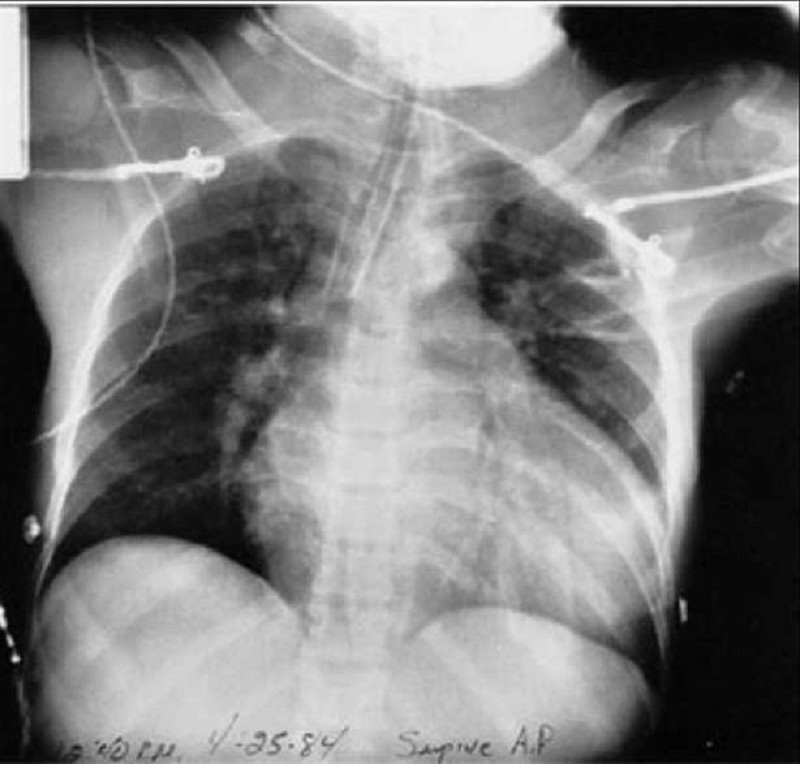
A 43-year-old woman presents to the emergency department because of chest pain, shortness of breath, and worsening fatigue for the past day. The chest pain initially worsened with lying down and improved with leaning forward, but now it seems equal in intensity over all positions. On physical examination she has labored, fast breathing and appears to be in pain. She has jugular venous distention. She is tachycardic, has a regular rhythm, and has distant heart sounds with a friction rub. Her lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally, her abdominal examination is benign, and she has no peripheral edema. Her temperature is 39.0°C (102.2°F), pulse is 126/min, blood pressure is 89/66 mmHg, respiratory rate is 32/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. X-ray of the chest is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Cardiac tamponade
Panic attack
Pericarditis
Tension pneumothorax
Decompensated congestive heart failure
A 44-year-old man complains of vague right upper abdominal discomfort that he has had for about 1 month. He describes no other symptoms, and, except for enucleation of one eye at age 21 "for a tumor," he has been in excellent health all his life. He exercises regularly and neither smoke nor drinks. The only findings on physical examination include the artificial eye and a tender, enlarged, and nodular liver. CT scan of the upper abdomen demonstrates multiple masses within the liver. Which of the following will most likely be found on biopsy of these masses?
Metastatic malignant melanoma
Metastatic retinoblastoma
Metastatic prostatic cancer
Metastatic sarcoma
Primary hepatocellular carcinoma
A 44-year-old man who comes to the office because he has had several episodes of hemoptysis for the past two months. He admits to smoking 2-3 packs of cigarettes daily for the last 24 years. Physical examination and chest x-ray are very suggestive of a lung malignancy. Chest CT and bronchoscopy with biopsy are done, and the patient goes on vacation in Aruba. The patient returns to the office after one week, and you are now holding the biopsy result in your hands. It reads, "The tumor has spread to the hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes with bony extension." Which of the following is the most appropriate opening statement?
"Unfortunately, the situation is more serious than what I earlier thought."
"Would you like to have someone else with you as I don't have good news for you?"
"What do you think of your symptoms?"
"I am sorry to tell you that you have lung cancer and it is fairly advanced."
"How much would you like to know about your condition?"
A 44-year-old obese Asian immigrant presents to the ER complaining of a persistent cough for about 3 months. He denies any fever, chills, runny nose or sputum production. He does complain of dyspnea on exertion, which also has been of a short duration. He says that over the last year, he has become progressively short of breath and is unable to sleep lying down. He denies any chest pain or diaphoresis, but has had palpitations in the past. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. On examination, he is alert and in mild distress. He has a BP of 110/70 mmHg, pulse 100/min and is afebrile. Auscultation is difficult. The chest-x ray reveals an enlarged cardiac silhouette. It appears that the left main stem bronchus is elevated. There is no other lung pathology visible. The ECG shows irregularly irregular rhythm. The pathophysiology of this condition is related to which of the following?
Acute pericarditis
Rheumatic fever
Interstitial lung disease
Malignancy
Sarcoidosis
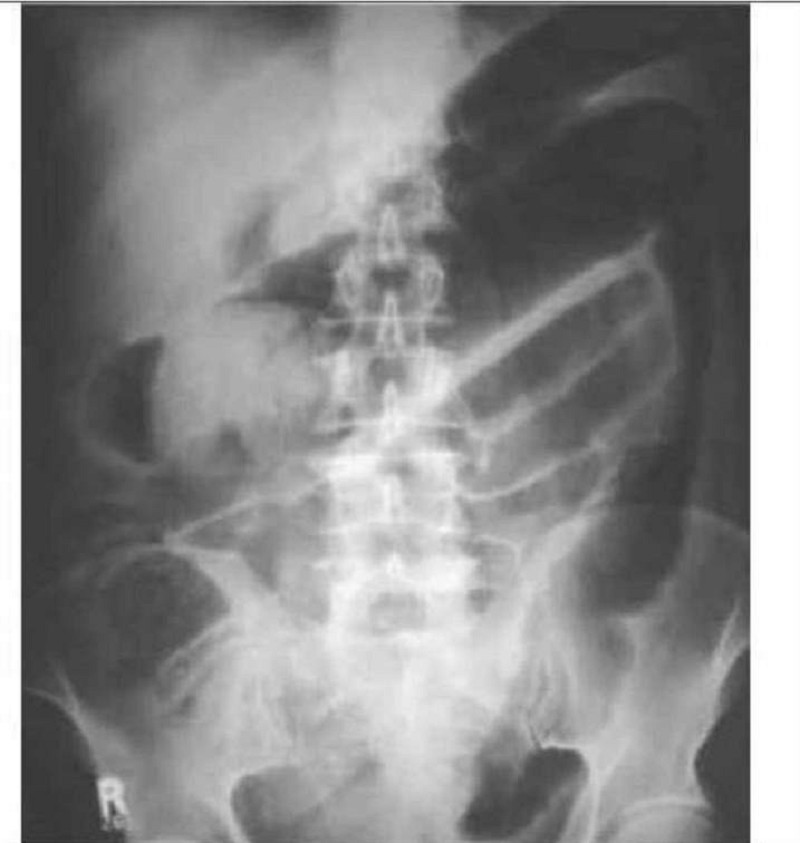
A 44-year-old white female presents with a 2-month history of low-grade fever, abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. Over the past two days, her symptoms have increased. She does not use medications and she has no allergies. She has had a 10 lb (4.5 kg) weight loss over the past four weeks. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 102/70 mmHg, pulse is 118/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows pale and dry mucus membranes. Abdominal examination shows diffuse tenderness and distention. Laboratory studies show: Hb 9.5 g/dl, WBC 16,000/cmm, Serum Na 145 mEq/L, Serum K 3.0 mEq/L. An x-ray film of the abdomen is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Crohn's disease
S. Aureus gastroenteritis
Obstructed colon cancer
Pseudomembranous colitis
Toxic megacolon from ulcerative colitis
A 44-year-old white male presents with a long history of joint pains in several joints. He has seen a physician before but no diagnosis was made. He has been taking ibuprofen with partial relief. He has now developed fever, diarrhea and weight loss. He denies any genitourinary or eye symptoms. He does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. He is a farmer. On examination, he has generalized lymphadenopathy and non-deforming arthritis. Small intestinal biopsy reveals periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS)-positive macrophages. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Reactive arthritis
Sarcoidosis
Inflammatory bowel disease
Whipple's disease
Celiac disease
A 44-year-old woman comes to the office with complaints of weight loss and blood in her stools for the last year. Her mother is on chemotherapy for colon carcinoma. Her maternal uncle also had colon cancer, as did her first cousin who died of colon cancer at the age of 46. She is very worried that she might have the same cancer. Based on her history, she falls within the criteria for Lynch syndrome (also known as HNPCC/ Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer). Apart from the complete work-up for colon cancer, this patient should be evaluated for which of the following condition?
Pancreatic carcinoma
Pseudomembranous colitis
Hepatic carcinoma
Diverticulitis
Endometrial carcinoma
A 44-year-old woman has been complaining of a 4-year history of increasing dyspnea and fatigue. Physical examination reveals increased JVP and a reduced carotid pulse. Precordial examination reveals a left parasternal lift, loud P2, and right-sided S3 and S4. There are no audible murmurs. CXR reveals clear lung fields and an ECG shows evidence of right ventricular hypertrophy. Pulmonary function tests show a slight restrictive pattern. A diagnosis of primary pulmonary hypertension is made. Which of the following is the most likely cause of death in this condition?
Intractable left ventricular failure
Massive PE
Intractable respiratory failure
Intractable right ventricular failure or sudden death
Myocardial infarction
A 45-year-old female presents to the emergency department because of increasing somnolence and shortness of breath. Her past medical history is significant for hyperlipidemia, hypertension and type2 diabetes. She has never smoked and does not use drugs or alcohol. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 160/80 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 16/min. Her BMI is 55 kg/m2. On physical examination, she is drowsy but able to respond to commands. Jugular venous distention is difficult to visualize due to a thick neck. Lungs are clear to auscultation. Heart sounds are distant. Abdomen is obese and non-tender. Lower extremities have edema bilaterally. There are no obvious focal deficits on neurologic examination. Chest x-ray is poor in quality but no obvious abnormalities are noted. EKG shows low voltage QRS complexes but no significant ST-segment or T-wave abnormalities. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 16.0 g/L, Hematocrit 48%, Mean corpuscular volume 85 fl, Platelet count 224,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 6,600/mm3. Arterial blood gas: pH 7.30, pO2 60mmHg, pCO2 69mm Hg. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
Venous thromboembolism
Pneumocystis pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia
Pulmonary edema
Impaired chest wall compliance
A 45-year-old Haitian immigrant presents to the emergency department with a chief complaint of productive, blood-tinged cough for 2 months. He has been in the United States for 1 month. His temperature is 40.1°C (104.2°F) and heart rate is 105/min. On physical examination he appears cachectic, and pulmonary rales are heard throughout his lung fields. X-ray of the chest reveals multiple bilateral upper lobe cavitary lesions with associated intrathoracic adenopathy. Results of sputum culture are pending. Which of the following tuberculosis medications can potentially cause optic neuritis?
Ethambutol
Isoniazid
Levofloxacin
Pyrazinamide
Rifampin
A 45-year-old Hispanic male comes to the emergency department because of a two-day history of intermittent abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. He has had four similar episodes in the past year. He is subsequently admitted to the floor. Radiographic and endoscopic evaluations show extensive disease from the terminal ileum to the rectum with multiple ulcerations and pseudopolyps. Biopsy of the lesion shows noncaseating granulomas and crypt abscess. Which of the following is the most characteristic feature which favors the diagnosis of Crohn's disease against that of ulcerative colitis?
Crypt abscess
Non-caseating granulomas
Abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea
Disease from terminal ileum to rectum
Pseudopolyps
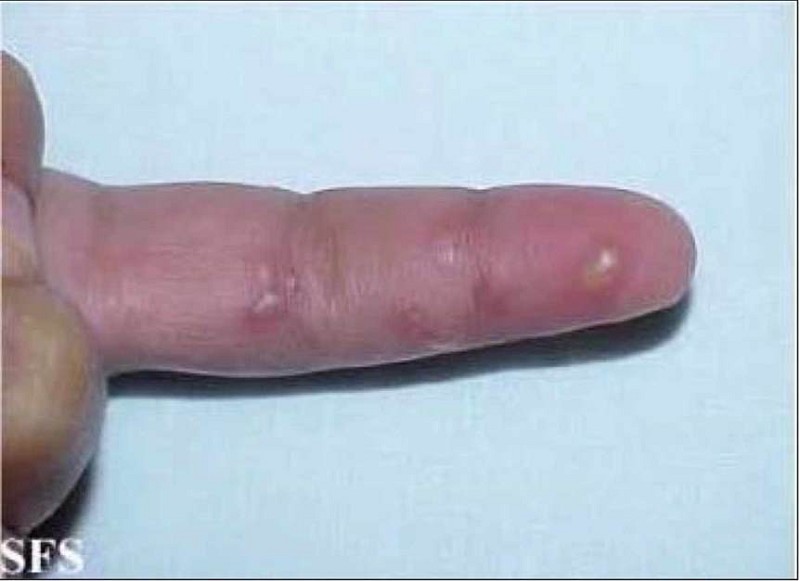
A 45-year-old male comes to you with complaints of throbbing pain over the pulp of his right index finger for the last two days. He has been feeling warm for the last three days. He denies ever having any sexually transmitted disease or cold sores in the past. On examination, he has a swollen, soft, and tender distal pulp space of the right index finger with some non-purulent vesicles. A picture of his hand is shown below. Tzanck smear of the vesicles show multinucleated giant cells. Which of the following is most likely the occupation of this patient?
A dentist
Commercial sex worker
A gardener
A tailor
A Pilot
A 45-year-old male is brought to the emergency department in a stuporous state. He appears agitated and disoriented. His temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), respirations are 22/min, pulse is 90/min and blood pressure is 110/70 mm of Hg. His lab findings are as follows: Blood pH 7.21, PaO2 100 mmHg, PaCO2 30 mmHg, HCO3- 13 mEq/L, Serum osmolarity 350 mOsm/L, Blood glucose 90 mg/dl, Na+ 141 mEq/L, K+ 4.6 mEq/L, Cl- 100 mEq/L, BUN 28mg/dl, Creatinine 2.5 mg/dl. His urine shows the presence of rectangular, envelope-shaped crystals. His creatinine three months ago was 1.2 mg/dl. What is the most likely cause of this lab abnormality in this patient?
Aspirin ingestion
Methyl alcohol poisoning
Ethylene glycol poisoning
Uremic acidosis
Lactic acidosis
A 45-year-old male presents to his physician with persistent nausea and vomiting of partially digested food for the past month. He has also lost 5 lbs of weight during this period of time. His appetite is good but he feels full after a few bites. His past medical history is significant for a one-year history of type 2 diabetes and a suicide attempt 6 months ago in which he ingested acid. He drinks alcohol and smokes one pack of cigarettes daily. His temperature is 36.80C (98.20 F), blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 16/min. Mucous membranes are dry. Examination shows succussion splash on the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Diabetic gastroparesis
Esophageal stricture
Duodenal carcinoma
Duodenal hematoma
Pyloric stricture
A 45-year-old male presents to your office because his "hands are getting thick and swollen." He is also having difficulty with wearing shoes because his feet have become large. His blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg. On examination, he has enlarged, swollen hands and feet. He has coarse facial features, with prominent frontal bones and jaws. While you are discussing the most likely diagnosis, he appears worried and asks about the complications and risk of death associated with his condition. What is the most common cause of death in patients with this condition?
Congestive cardiac failure
Hypertensive nephropathy
Stroke
Brain tumor
Adrenal failure
A 45-year-old man comes to the office for the evaluation of excessive wasting of his extremity muscles, which is more apparent on the extensor side. The weakness began distally and asymmetrically. He recently started to have difficulties with swallowing, chewing, and speaking. He feels some movements in his face and tongue. He also has muscle stiffness. His bowel, bladder, cognitive, and sensory functions are intact. The physical examination reveals excessive wasting of his muscles, which is more prominent in the lower extremities. Fasciculation and hyperreflexia of all extremities are noted. His bulbar reflexes are decreased. What neural pathway is most likely damaged?
Pyramidal tract
Upper motor neuron
Lower motor neuron
Lower and upper motor neuron
Cerebral cortex
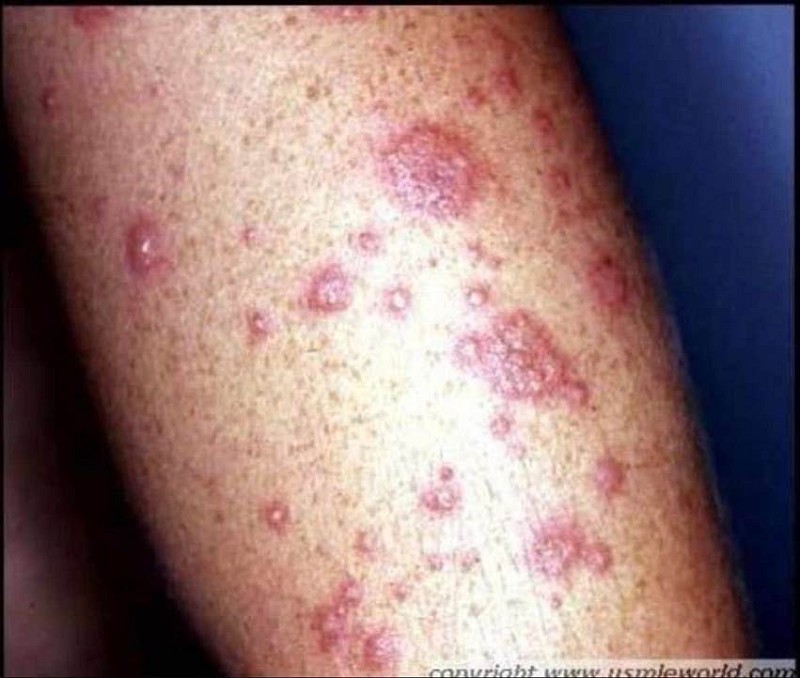
A 45-year-old man is brought to the office due a sudden onset of skin lesions and fever. He is unable to eat or drink due to the pain in his mouth and throat. His wife says that he was complaining of a headache, malaise, and joint pain prior to developing the skin lesions. Generally, he has been in good health, other than an episode of sinusitis, for which he was prescribed trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole 5 days ago. His pulse is 92/min, blood pressure is 110/80 mmHg, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.4°F). On examination, both conjunctivae are inflamed. There is erythema, blistering and ulceration over the oral mucosa. There is an erythematous rash over the trunk and cutaneous lesions over the hands, arms and feet. Some of the lesions are shown in the picture below. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Erythema multiforme minor
Toxic shock syndrome
Impetigo
A 45-year-old man presents to the physician’s office complaining of dysphagia and retrosternal pressure and pain of 2-year duration. The symptoms have worsened over the last 3 months. He has a 30 pack-year smoking history and drinks beer on weekends. Vital signs include a BP of 150/90 mmHg, pulse rate of 90/min, and respiratory rate of 12/min, with a normal temperature. Examination reveals a thin man with a normal heart, lung, and abdomen examination. An esophagogram reveals a 6-cm, smooth, concave defect in the midesophagus with sharp borders. Esophagoscopy reveals intact overlying mucosa and a mobile tumor. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Esophageal carcinoma
Benign esophageal polyp
Bronchogenic carcinoma with invasion of the esophagus
Leiomyoma
Lymphoma
A 45-year-old man presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a posterior neck mass. The mass has been present for years, but has slowly enlarged over the last 2 years. Examination reveals a subcutaneous mass that is soft, nontender, and movable. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
Thyroid carcinoma
Cystic hygroma
Acute suppurative lymphadenitis
Thyroglossal duct cyst
Lipoma
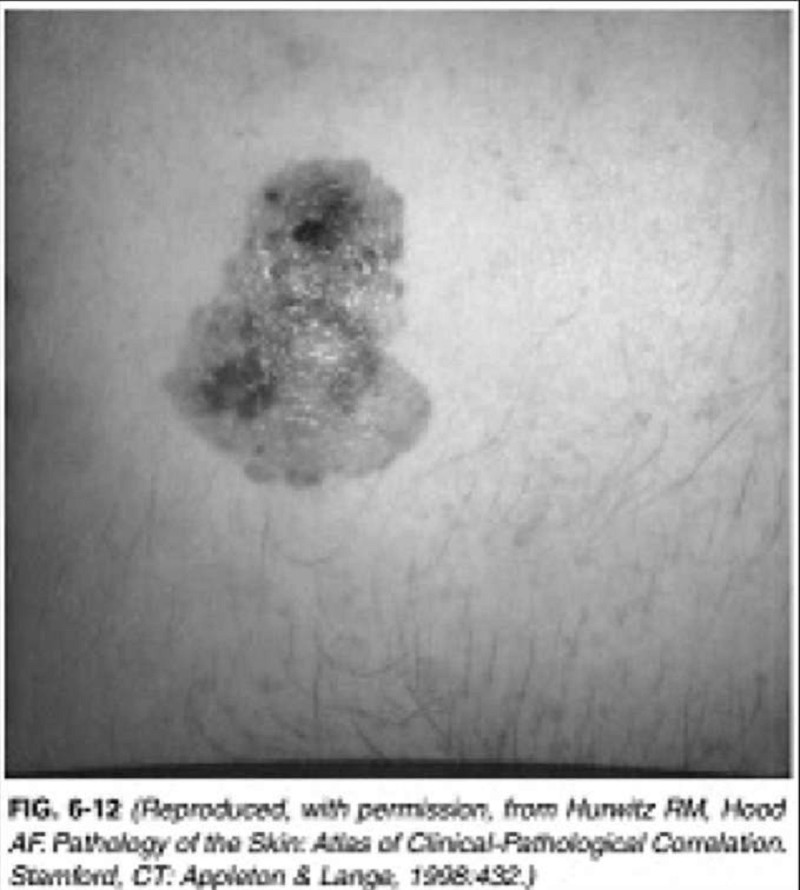
A 45-year-old man presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a skin lesion on his abdomen. He states that the lesion has been present for 1 year, but has recently enlarged over the last 2 months. The mass is nontender, and he is otherwise asymptomatic. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals a 3-cm, pigmented, irregular skin lesion located in the left lower quadrant of the abdomen, as shown in Figure 6-12. Heart, lung, and abdominal examination are normal. There are no palpable cervical, axillary, or inguinal lymph nodes. Chest x-ray and liver function tests are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Squamous cell carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma
Melanoma
Keratoacanthoma
Basal cell carcinoma
A 45-year-old man with a chronic psychotic disorder is interviewed after being admitted to a psychiatric unit. He mimics the examiner’s body posture and movements during the interview. Which of the following terms best characterizes this patient’s symptom?
Folie á deux
Dereistic thinking
Echolalia
Echopraxia
Fugue
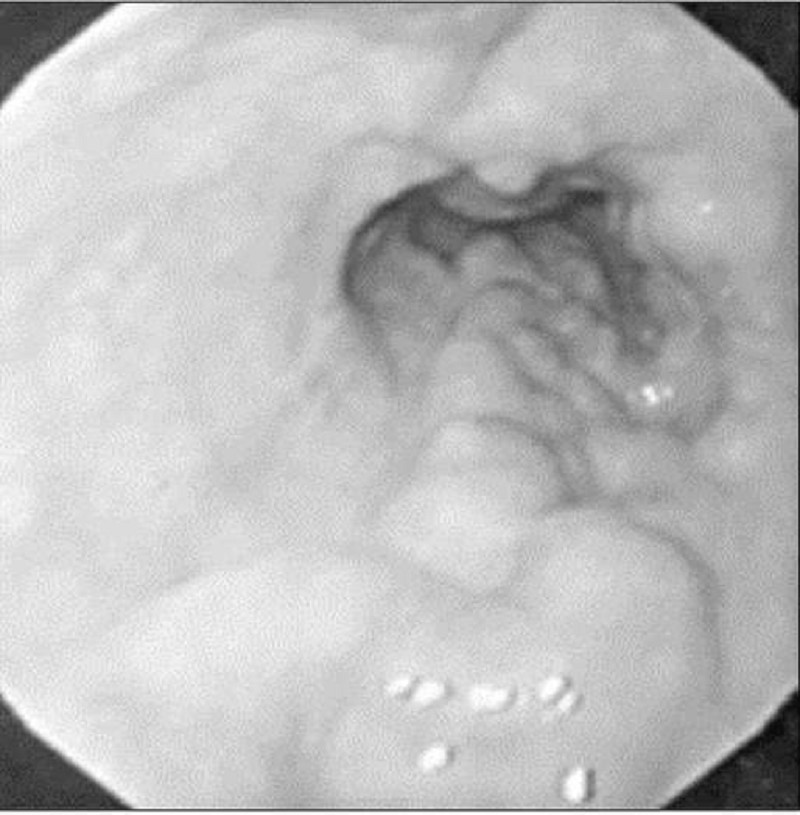
A 45-year-old man with a long history of alcohol intake comes into the emergency room with upper gastrointestinal (UGI) bleeding. Urgent endoscopy reveals the following findings. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Esophageal varices
Esophageal carcinoma
Foreign body
Tertiary waves
Barrett’s esophagus
A 45-year-old man with Parkinson disease has macular areas of erythema and scaling behind the ears and on the scalp, eyebrows, glabella, nasolabial folds, and central chest. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Tinea versicolor
Psoriasis
Seborrheic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis
Dermatophyte infection
A 45-year-old mildly overweight male recovering from an anterior wall myocardial infarction develops sudden onset of left-sided chest pain. He appears agitated and restless. Two minutes later, he is unresponsive. His pulse is not palpable and ECG monitor shows sinus tachycardia at the rate of 130/min. He presented five days earlier with substernal chest pain and diaphoresis. He has had no dyspnea, extremity swelling or palpitations since admission. His past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus type 2. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Interventricular wall rupture
Pulmonary infarction
Ventricular free wall rupture
Recurrent ischemia
Right ventricular infarction
A 45-year-old mildly overweight male recovering from an anterior wall myocardial infarction develops sudden onset of sharp pain in the left side of his chest. He presented five days earlier with substernal chest pain and diaphoresis. He has had no dyspnea, extremity swelling or palpitations since admission. His past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus type 2. He seems mildly restless, especially in the supine position. The pain improves when sitting up and leaning forward. His breathing is fast and shallow due to the pain. His lungs are clear on auscultation. His blood pressure is 120/78 mmHg and his heart rate is 60/min There is no change in blood pressure upon deep inspiration. ECG shows sinus rhythm with new diffuse ST segment elevation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Interventricular wall rupture
Pulmonary infarction
Recurrent ischemia
Ventricular free wall rupture
Acute pericarditis
A 45-year-old mildly overweight smoker presents with occasional episodes of nocturnal substernal chest pain that wakes her up from sleep. The episodes last 15-20 minutes and resolve spontaneously. She denies any illicit drug use. She leads a sedentary lifestyle but states that she can climb two flights of stairs without any discomfort. Her pulse is 78/min and regular, blood pressure is 130/70 mmHg and respirations are 13/min. Auscultation of her heart and lungs is unremarkable. Extended ambulatory ECG monitoring reveals transient ST segment elevations in leads V4-V6 during the pain attack. The pathophysiology of this patient's condition is most similar to that of which of the following?
Lacunar stroke
Abdominal aortic aneurysm
Intermittent claudication
Raynaud phenomenon
Pulmonary embolism
A 45-year-old nurse practitioner presents to the emergency department due to painful abdominal cramps and watery diarrhea. She has about 10 to 20 bowel movements a day. She also has nocturnal bowel movements. She has had multiple hospitalizations in the past for similar problems without a definite diagnosis. A lower GI endoscopy during a previous hospitalization showed dark brown discoloration of the colon with lymph follicles shining through as pale patches. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Factitious diarrhea
Celiac disease
Irritable bowel syndrome
Infectious diarrhea
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
A 45-year-old policeman presents to your office complaining of tiredness and sleepiness. He says that his job seems tiring to him recently. It is difficult for him to get up in the morning and go to work. He goes to bed early because he feels tired and sleepy. Two months ago, he was investigating a case of massive murder. He slipped on the blood on the floor, fell and hit his head. He also describes recent abdominal pain that is constant and gnawing, interfering with his sleep. His appetite is poor, and he lost 15 pounds over the last month. Physical examination is significant only for tenderness and fullness in the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Duodenal ulcer
Pancreatic cancer
Major depressive episode
Post-traumatic stress disorder
Chronic subdural hematoma
A 45-year-old recently immigrated Mexican farmer comes to your office complaining of dyspnea, fatigue and abdominal distention for the past two months. On physical exam, his temperature is 37°C (98°F), blood pressure is 126/80 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are16/min. You note pedal edema, elevated jugular venous pressure with positive Kussmaul's sign, and increased abdominal girth with free fluid. Chest auscultation reveals decreased heart sound intensity at the apex and an early heart sound following S2. The jugular venous pressure tracing shows prominent 'x’ and 'y' descents. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
Cor pulmonale
Tuberculosis
Trypanosoma cruzi infection
Psittacosis
Pneumoconiosis
A 45-year-old tennis player comes to your office with a complaint of pain over the lateral side of the right elbow. He has been a professional tennis player for 15 years but has never had this kind of pain before. Range of motion at both elbows is normal. There is point tenderness over the lateral side of the distal end of right humerus. Pain is exacerbated by extension of wrist against resistance. The rest of the physical examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Lateral epicondylitis
Posterior interosseous nerve entrapment
Radial tunnel syndrome
Rupture of long head of biceps tendon
Rotator cuff injury
A 45-year-old white male comes to your office for evaluation of diarrhea of 8-months duration. He says that he has lost almost 15 lbs during the past 8 months. He denies any blood in the stools. 24-hour stool collection reveals fecal fat of 10 gm/day. Stool microscopy reveals no pathogens and no leucocytes. D-xylose test was performed which shows that less than 2 grams of D-xylose is excreted in urine in 5 hours. D-xylose test was re-performed after 4-week treatment with antibiotics but excretion is still less than 2 grams in 5 hours. Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
Lactose intolerance
Pancreatic insufficiency
Bacterial overgrowth
Celiac disease
Terminal ileal disease
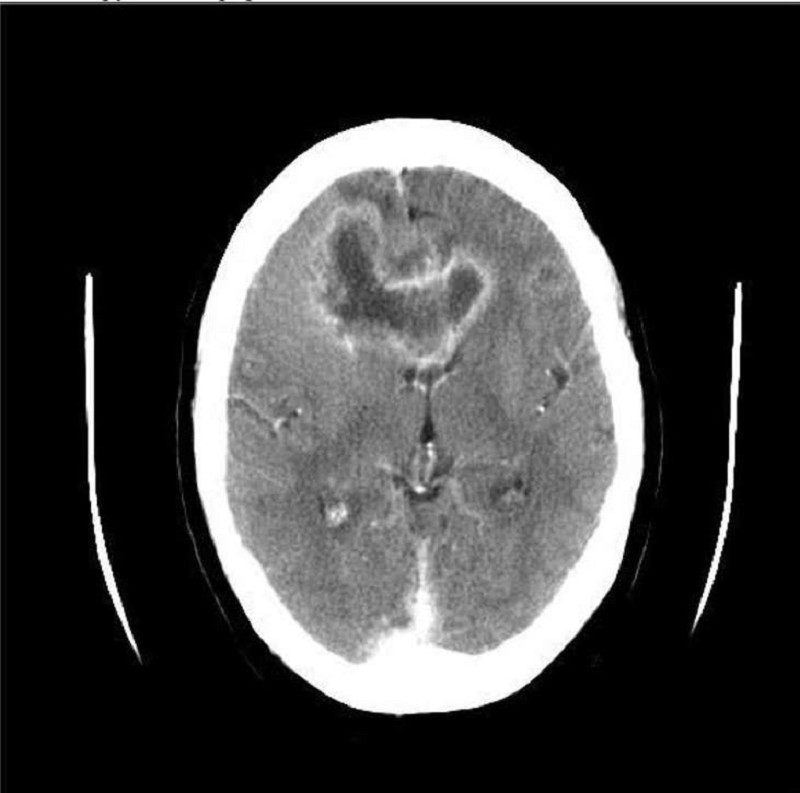
A 45-year-old white male presents with a 4-month history of headaches. The headache is generalized, dull, constant, and worsened by bending, coughing and sneezing. It is unresponsive to simple analgesics, and associated with nausea and vomiting. His wife says he has been acting strangely for the last few months, and she has noted a personality change. The neurological examination is non-focal. Fundoscopy reveals papilledema. His CT scan is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Brain abscess
Glioblastoma multiforme
Low-grade astrocytoma
Cerebral infarction
Metastatic brain tumor
A 45-year-old woman comes to her physician for help with her insomnia. She states “ever since my husband died, I just can’t sleep.” The patient states her 57-year-old husband died suddenly of a heart attack 9 weeks ago. Since that time, the patient has had a very depressed mood, had been crying, has lost interest in activities, is fatigued, and has insomnia. Which of the following symptoms, if present, should make the physician think this patient has a major depression instead of bereavement?
The patient feels that she would be better off dead
The patient has marked functional impairment
The patient has lots of guilt about not recognizing that the chest pain her husband was having was the start of a heart attack
The patient has mild psychomotor retardation
The patient reports hearing the voice of her dead husband calling her name twice
A 45-year-old woman comes to the office for the evaluation of reddened areas over her face (flushed skin). These areas worsen every time she drinks something hot or goes out in hot, sunny weather. Her vital signs are stable. On examination, there is evident erythema over her nose, cheeks, forehead and chin with telangiectasias, pustules and papules. What is the most likely diagnosis?
Acne vulgaris
Carcinoid syndrome
Seborrheic dermatitis
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Rosacea
A 45-year-old woman comes to your office with a three-month history of fatigue, exertional dyspnea, and non-productive cough. She has also been having difficulty swallowing. Her only other medical problems are Raynaud's phenomenon, heartburn, and high blood pressure. On examination, diffuse thickening of the skin with telangiectasia is noted. Her current medications include amlodipine, enalapril, and ranitidine. What is the most probable pathologic mechanism of her pulmonary complaints?
Pulmonary fibrosis
Aspiration pneumonia
Pulmonary vascular lesions
Bronchogenic carcinoma
Restriction of chest movement
A 45-year-old woman has bilateral breast pain that is most severe premenstrually. On palpation, there is excessive nodularity, tenderness, and cystic areas that diminish in size after menses. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Fibrocystic disease
Breast cancer
Intraductal papilloma
Engorgement attributable to increased prolactin
Fibroadenomas
A 45-year-old woman has severe symptoms of epigastric and abdominal pain after eating. A trial of acid suppression therapy with proton pump inhibitors (PPI) only partially improved her symptoms. She undergoes elective outpatient upper endoscopy, which is positive for a small duodenal ulcer. Two hours later, she is short of breath and complaining of severe anterior chest pain, which is made worse with deep inspiration. On examination, she looks unwell, blood pressure is 150/90 mm Hg, pulse 110/min, and lungs are clear. Heart sounds are normal but an “extra crunching” type sound is intermittently heard. CXR demonstrates air surrounding the heart. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute pericarditis
Acute cardiac ischemia
Pneumothorax
Acute mediastinitis
Aortic dissection
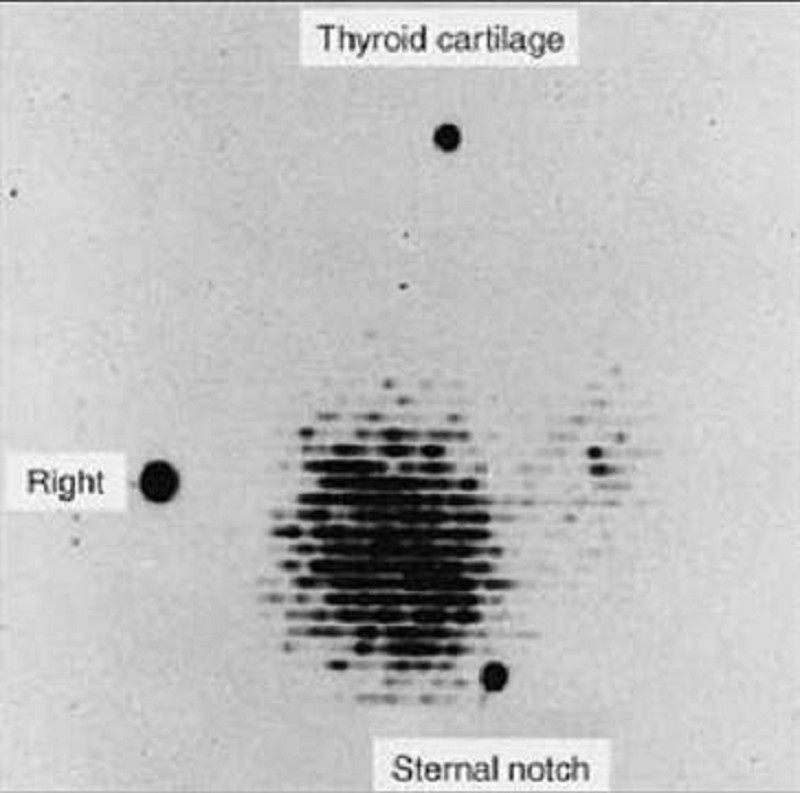
A 45-year-old woman complains to her primary care physician of nervousness, sweating, tremulousness, and weight loss. The thyroid scan shown here exhibits a pattern that is most consistent with which of the following disorders?
Hyper secreting adenoma
Graves’ disease
Medullary carcinoma of thyroid
Lateral aberrant thyroid
Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
A 45-year-old woman presents with hypertension, development of facial hair, and a 7-cm suprarenal mass. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Myelolipoma
Cushing disease
Adrenocortical carcinoma
Pheochromocytoma
Carcinoid
A 45-year-old woman underwent elective surgery for an inguinal hernia. In the postoperative recovery room, she developed nausea, vomiting, and acute abdominal pain. She has a history of systemic lupus erythematosus, pernicious anemia, type 1 diabetes, chronic low back pain, and uterine fibroids. Her preoperative medications include monthly vitamin B-12 injections, insulin, prednisone, hydroxychloroquine, and acetaminophen. Her blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg and heart rate is 110/min. Initial laboratory studies show blood glucose of 50 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
Postoperative bleeding
Intra-abdominal abscess
Diabetic ketoacidosis
Intestinal obstruction
Adrenal insufficiency
A 45-year-old woman, who wears high-heeled, pointed shoes, complains of pain in the forefoot after prolonged standing or walking. Occasionally, she also experiences numbness, a burning sensation, and tingling in the area. Physical examination shows no obvious deformities and a very tender spot in the third interspace, between the third and fourth toes. There is no redness, limitation of motion, or signs of inflammation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Gout
Metatarsophalangeal articulation pain
Morton's neuroma
Hallux rigidus
Plantar fasciitis
A 46-year-old bank executive is referred to the clinic by her dentist. For the past 6 weeks, she has had swollen, bleeding gums. She appears pale and feels weak. She smokes half a pack of cigarettes daily and drinks alcohol socially. Her family history is not significant. Her vital signs are stable. She is afebrile. WBC 44,100 mm3, Hemoglobin 9.0 g/dL, Hematocrit 27%, Platelets 16,000/mm3. Leukocyte distribution: Blast forms 79%, Promonocytes 12%, Monocytes 8%, Lymphocytes 1%. Cytochemical analysis:Sudan black: slightly positive, Alpha-naphthyl esterase: positive, PAS reaction: negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
AML with maturation
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Acute promyelocytic leukemia
Acute erythroleukemia
Acute monocytic leukemia
A 46-year-old homeless man is being evaluated for frequent falls and a broad-based gait. A single tap on his patellar tendon elicits several to-and-fro leg movements. There is also nystagmus on physical examination. Which of the following additional findings would you expect most in this patient?
Goiter
Bradykinesia
Intention tremor
"Clasp knife" phenomenon
Babinski sign
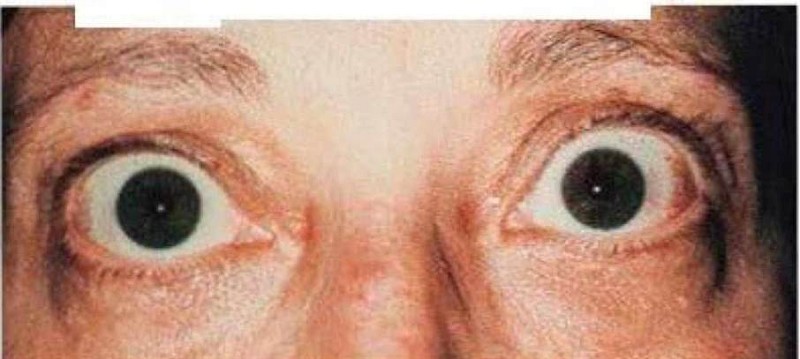
A 46-year-old female complains of a "sandy" sensation in her eyes. Review of systems is notable for a 6 pound weight loss over the last month. A picture of her eyes is shown on the slide below. Which of the following most likely underlies this finding?
High circulating thyroxine level
Increased intraocular pressure
Increased intracranial pressure
Periorbital lymphocytic infiltration
Bilateral facial nerve compression
{"name":"DES C_Diagnosis (7) Prepared : CHILLY", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"A 4-year-old child presents with an enlarged submandibular node that is 4 cm in diameter, nontender, and not fluctuant. The node has been enlarged for about 4 weeks, and there is no history of fever or contact with any person who was ill. A CBC is normal, and a Mantoux test with 5 tuberculin units of PPD shows 6 mm of induration. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/18-739256/image.jpeg?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
How well do you know your classmates?
10515
Naval Competence and Qualifications Test (NCQT)
10525
Hospitality Hut Station Test- NSO
100
The Mechanical Shop
520
Lean Practitioners Exam: Test Your Lean Operations Skills
201054597
Free PostgreSQL Knowledge Assessment
201025982
Which Chainsaw Man Character Are You? Free Personality
201028719
Animal Farm Exam: Challenge Your Novel Knowledge
201047621
Discover What Kind of Eyes You Have - Free Eye Shape Test
201029354
Free Waves Unit Test Review
201025280
ProProfs Sterile Processing: Ace CRCST Chapter 17
201055987
Ultimate Muscle Car Trivia: Test Your Knowledge
201047621