Radiology Review

Radiology Review Quiz
Test your knowledge and understanding of radiology concepts with our comprehensive quiz designed specifically for dental professionals. This engaging quiz covers a range of topics, including dental imaging techniques, interpretation of radiographs, and best practices in radiography.
Key Features:
- 30 Multiple Choice Questions
- Examines crucial radiology topics
- Ideal for dental students and practicing professionals
Identify the major technique error on your patient’s bitewing.
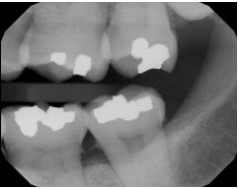
Receptor too far mesial
Occlusal plane not centered
Cone-cut
Horizontal angulation
Through the use of dental images, the dental radiographer can detect ________ that cannot be detected clinically.
1. diseases
2. lesions
3. Conditions of teeth and bones
2. lesions
3. Conditions of teeth and bones
3 only
1, 2, 3
2, 3
1, 2
An oral examination limits the practitioner to knowledge of what is seen clinically. Dental images allow the practitioner to see many conditions that are not apparent clinically.
Both statements are true.
The first statement is false; the second statement is true.
The first statement is true; the second statement is false.
Both statements are false
To avoid overlapped contacts on a periapical image,
Make certain that no more than 1/8 inch of the receptor edge extends beyond the incisal-occlusal surfaces of the teeth.
Increase vertical angulation.
Decrease vertical angulation.
Direct the x-ray beam through the interproximal regions.
When the kilovoltage is increased
Electrons move from the cathode to the anode with more speed.
Photons move from the anode to the cathode with more speed.
Electrons move from the anode to the cathode with more speed.
Photons move from the cathode to the anode with more speed.
(1) A primary advantage to digital imaging is the superior grayscale resolution that results. (1) Digital imaging uses up to 32 shades of gray.
The first statement is false; the second statement is true.
Both statements are false.
Both statements are true.
The first statement is true; the second statement is false.
A cone-cut occurs when
The receptor is underexposed
The PID was not properly aligned with the periapical receptor holder.
The exposure button was not depressed for a sufficient amount of time.
The receptor is overexposed.
A sensor with a fiber optic cable linked to the computer is placed into the mouth of the patient and exposed to x-radiation. This is an example of
Phosphor imaging.
Indirect digital imaging.
Direct digital imaging.
Use of the CCD camera.
The CMS is defined as a series of intraoral dental images that shows
All the dentulous tooth-bearing areas of the upper and lower jaws that can be verified clinically.
All the edentulous tooth-bearing areas of the upper and lower jaws.
All the dentulous tooth-bearing areas of the upper and lower jaws.
All the dentulous or edentulous tooth-bearing areas of the upper and lower jaws.
Your patient has asked why you prefer digital imaging to film. Which of the following reasons would you tell her?
The images appear in color instead of black and white.
The initial setup costs were lower than it cost to set up film.
The sensors can be autoclaved and reused.
The image appears almost instantaneously for both of us to view.
The purpose of the anode is to
Filter out nonpenetrating, longer-wavelength x-rays.
Convert electrons into x-ray photons.
Produce electrons when heated.
Absorb heat created by the production of x-rays.
How many exposures of the posterior teeth will you need to take when using the paralleling technique?
Seven
Six
Eight
Four
Your patient has a palatal torus, where should you place the receptor?
You cannot take a periapical, the patient will require a panoramic receptor.
Place the receptor on the far side of the torus.
Place the receptor in front of the torus next to the teeth you are exposing
Place the receptor on the torus.
Another term for infection control is __________, which means the absence of pathogens, or disease-causing microorganisms.
Asepsis
Antiinfective
Antiseptic
Antibiotic
Which of the following receptor holders include aiming rings that aid in the alignment of the position-indicating device (PID) with the receptor?
Snap-a-ray receptor holder
Hemostat with bite-block
Rinn XCP instruments
Stabe bite-block
According to the text, anterior periapicals are always positioned with the long portion of the receptor in a ____________ direction, and posterior periapicals the receptor is always positioned with the long portion of the receptor in a ______________ direction.
Vertical; horizontal
Horizontal; vertical
Horizontal; horizontal
Vertical; vertical
The lead apron
Is used to protect the thyroid gland.
Is an option; use is not mandated by any state or federal law.
Is recommended for intraoral exposures.
Is not recommended for extraoral exposures.
Identify this image; it is mounted using the labial view.
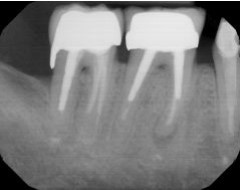
Maxillary left molars
Mandibular right molars
Maxillary left premolars
Mandibular left molars
If the milliamperage is increased, the receptor density ________, and the image appears _________.
Increases; lighter
Decreases; darker
Decreases; lighter
Increases; darker
Parallel is defined as
Cutting across or through.
Moving or lying in the same plane, always separated by the same distance and not intersecting
Intersecting at or forming a right angle
An angle of 90 degrees formed by two lines perpendicular to each other.
Your patient has a shallow palate; you should modify your technique when there is a lack of parallelism ________________.
Less than 5 degrees
Greater than 40 degrees
Less than 20 degrees
Greater than 30 degrees
When are bite-wings and periapical images prescribed?
As needed, based on the patient’s individual needs
According to a set schedule
Every year
Every other year
Sensors that cannot be sterilized
Are placed in an immersion disinfectant for an appropriate amount of time between each patient.
Should be disposed of between patients
Only need to be wiped off with a surface disinfectant between patients.
Require complete coverage with disposable plastic sleeves for each patient.
Digital imaging uses _________________ to produce an image
Processing chemistry
Radiographic film
An x-ray processor
An electronic sensor and computerized imaging system
Within the x-ray tube, electrons are generated by the
Tungsten filament in the cathode.
Tungsten filament in the anode.
Copper stem.
Molybdenum cup.
(1) You can use dental images to help educate your patient on his dental caries and periodontal disease. (2) You can also use dental images to help your patient see a picture of common conditions that cannot be seen clinically. These include cysts, extra teeth, and retained roots.
Both statements are false.
The first statement is true, and the second statement is false
The first statement is false, and the second statement is true.
Both statements are true.
According to the basic rules of paralleling, the central ray should be directed ______________ to the receptor and the long axis of the tooth.
Adjacent
Horizontal
Parallel
Perpendicular
When the distal surfaces of the canines are not visible on a premolar bite-wing image, the solution is to
Decrease the vertical angulation of the tubehead.
Change the horizontal angulation of the tubehead.
Position the anterior edge of the receptor at the midline of the mandibular canine
Increase the vertical angulation of the tubehead.
The appearance of a patient’s finger on the image is called a
Hemangioma
Phalangioma
Pericytoma
Myxoma
Vertical bite-wings are often used for patients with
Bone loss.
Mixed dentition
Sealants.
Extensive decay.
The binding energy or binding force of an electron is
Determined by the atomic number
Weaker for electrons located in inner shells than in outer shells.
Determined by the distance between the neutrons and protons within the nucleus.
Determined by the distance between the orbiting electrons and the nucleus.
Which of the following statements is true of wavelength in reference to radiation?
X-rays with shorter wavelength have less penetrating power.
X-rays with longer wavelength have less penetrating power.
Milliamperage controls the wavelength and energy of the x-ray beam.
X-rays with longer wavelength are less likely to be absorbed by matter.
A radiograph is defined as
A beam of energy that has the power to penetrate substances and record image shadows on a receptor.
A form of energy carried by waves or a stream of particles.
The art and science of making radiographs by the exposure of an image receptor to x-rays.
A picture on film produced by the passage of x-rays through an object or body.
Infection control is critical in your dental operatory because pathogens can be transmitted easily through which of the following
1. Your patient to you.
2. You to your patient.
3. From one patient to another patient.
1, 2, 3
2, 3
1, 3
1, 2
The collimator ____________
Is a solid piece of aluminum.
Restricts the size and shape of the x-ray beam
Is always round.
Is fitted within the copper stem beneath the molybdenum cup.
(1) Digital sensors can be disinfected, sterilized, placed in cold sterilization, or be placed in barriers. (2) When using barriers, disinfect the sensor, cover both the sensor and the wire connection with a plastic barrier, and then cover with a finger cot to provide added protection.
Both statements are true.
The first statement is true; the second statement is false.
Both statements are false.
The first statement is false; the second statement is true.
To achieve parallelism between the receptor and the tooth, the ____________ distance must be increased to keep the receptor parallel with the long axis of the tooth.
Operator-patient
Object-receptor
Target-object
Target-receptor
Radiolucent refers to that portion of a dental image that is
Contains the tooth.
Within the plastic base.
Black.
White
You are showing your patient a bite-wing image. Your patient points to a portion of the tooth that is the most radiopaque and wants to know what it is. What portion of the tooth is your patient pointing to?
The enamel
The denton
The pulp
The periodontal ligament space
Which of the following images is used to evaluate the crown, roots, and supporting bone of a tooth?
Interproximal
Panoramic
Periapical
Occlusal
Which of the following statements is true of the receptor holder?
It requires the patient to stabilize the receptor with their hand.
It is used to align an extraoral dental x-ray receptor.
It is required when using the intraoral bisecting technique.
It is required when using the intraoral paralleling technique.
Under which of the following conditions must you wear your mask and safety glasses?
Whenever spatter and aerosolized sprays of blood and saliva are likely
If desired
Whenever the high-speed handpiece is used
Only during surgical procedures
Milliamperage regulates the _________ of electrons produced at the cathode filament.
Quantity
Speed
Quality
Power
When determining vertical angulation, if the position-indicating device (PID) is positioned above the occlusal plane and the central ray is directed _______, the vertical angulation is termed _________.
Downward; negative
Upward; positive
Downward; positive
Upward; negative
Blurred images appear on the dental image when
There is patient movement.
The film is creased.
There is a double exposure
The film is reversed.
Short teeth with blunted roots appear on the image when
The horizontal angulation is incorrect.
The vertical angulation is insufficient
The vertical angulation is excessive.
There is a cone-cut.
You have noticed that your mandibular incisors are foreshortened; how would you correct this problem?
Place receptor parallel to the long axis of the teeth.
Decrease vertical angulation.
Adjust horizontal angulation.
Adjust horizontal angulation.
An underexposed receptor results from
Excessive kilovoltage.
Inadequate tissue density.
Excessive milliamperage
Insufficient exposure time.
The bite-wing image is used in the
Periapical bisecting technique.
Occlusal technique.
Periapical paralleling technique.
Interproximal examination.
When overlapped contacts appear on a dental image, the cause is
A dropped receptor corner
An underexposed film.
Incorrect horizontal angulation.
Incorrect vertical angulation.
(1) Radiation is the emission and propagation of energy through space or a substance in the form of waves or particles. (2) Radioactivity can be defined as the process by which certain unstable atoms or elements undergo spontaneous disintegration, or decay, in an effort to attain a more balanced nuclear state.
The first statement is false; the second statement is true
The first statement is true; the second statement is false.
Both statements are true.
Both statements are false.
The teeth on your patient’s images appear very radiopaque and the periodontium and tissue appear very radiolucent. Your patient’s dental image has
High density.
Low density.
High contrast.
Low contrast.
Which of the following would be a reason to switch from film to direct digital imaging?
Digital images can be printed when needed.
The digital image cannot be incorporated into the electronic record.
The digital network makes it more difficult to store images.
Digital images cannot be electronically transmitted to other dental professionals.
Your patient is concerned about the amount of x-ray exposure she has had because she had x-rays taken quite often at her previous dental office. You explain to her that the images are necessary and you will be taking digital images which require _________ exposure than the films she previously had taken. Exposure times are ________ than that required for conventional radiography.
10% to 20% less
20% to 50% less
70% to 100% less
50% to 90% less
Identify the major placement error in this molar radiograph.
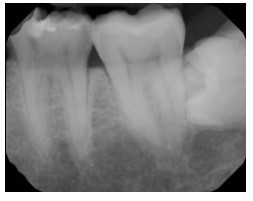
Too far mesial
Too far distal
Vertical angulation
A beam alignment device can be used to help the dental radiographer position the PID in relation to the _____________ and the receptor
Extension arm
Collimator
Control panel
Tooth
The nucleus of an atom contains
Protons.
Neutrons.
Protons and neutrons.
Electrons.
According to the basic principles of the paralleling technique, the receptor is placed in the mouth _________ to the long axis of the tooth being x-rayed, and the central ray of the x-ray beam is directed ____________ to the receptor and long axis of the tooth.
Perpendicular; perpendicular
Perpendicular; parallel
Parallel; parallel
Parallel; perpendicular
To minimize dimensional distortion, the object and receptor must be _____________ one another.
Parallel to
At a 45-degree angle to
More than the length of the PID apart from
Perpendicular to
Added filtration in the dental x-ray tubehead
Refers to the placement of tungsten discs in the path of the x-ray beam between the collimator and the tubehead seal.
Filters out shorter-wavelength x-rays from the x-ray beam.
Results in a lower-energy beam.
Results in a more penetrating useful beam.
Thermionic emission of electrons occurs at the
Copper stem.
Tungsten filament in the cathode.
Tungsten filament in the anode
Molybdenum cup.
To correct a dental image where apices do not appear,
The teeth being imaged must be firmly in contact with the bite-block.
Direct the x-ray beam through the interproximal spaces.
Increase the exposure time.
Make certain that no more than 3/4 inch of the receptor edge extends beyond the incisal-occlusal surfaces of the teeth.
You have noticed that your maxillary premolars are elongated, how would you correct this problem?
Increase vertical angulation.
Place receptor parallel to the long axis of the teeth
Decrease vertical angulation.
Adjust horizontal angulation.
Critical instruments are defined as instruments
That contact but do not penetrate bone.
That are used to penetrate soft tissue or bone.
That contact but do not penetrate soft tissue.
Or devices that do not come in contact with mucous membranes.
During an exposure
The exposure button is firmly depressed until the preset exposure time is completed.
The exposure button is briefly depressed and then released to initiate the exposure.
A beep sounds to signal initiation of the exposure.
The exposure light on the control panel is illuminated to signal the completion of the exposure.
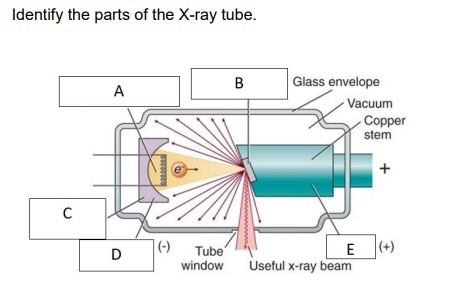
A: Filament and electron cloud, B: focal spot on tungsten target, C: electronic focusing cup, D: cathode, E: anode
{"name":"Radiology Review", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge and understanding of radiology concepts with our comprehensive quiz designed specifically for dental professionals. This engaging quiz covers a range of topics, including dental imaging techniques, interpretation of radiographs, and best practices in radiography.Key Features:30 Multiple Choice QuestionsExamines crucial radiology topicsIdeal for dental students and practicing professionals","img":"https:/images/course3.png"}
More Quizzes
Radiology Final
753838
Radiology part 2
13615
Y5/6 Climate Change Quiz
7420
Installation Art Quiz
94136
ITIL 4 - Free Knowledge Assessment Online
201015918
Subordinating Conjunctions - Free Practice
201017684
TV Trivia Questions - Free Online
201017964
ASPD Test - Free Antisocial Personality Disorder Screening
201017416
Soul Age Test - How Old Is Your Soul? Free Online
201018036
Psoriatic Arthritis - Free Symptom Checker
201017482
Portal - Test Your Aperture Science Knowledge
201020532
Which Finn Wolfhard Character Are You? Free
201018882