Dx med p3 * Q1 to 50 n Q 100 to 150 fb
1) A 63-year-old white female presents with a thyroid nodule. She denies any weight loss, change in appetite, diarrhea, heat or cold intolerance, menstrual irregularities, hoarseness and dyspnea. Her past medical history is unremarkable. There is no family history of thyroid cancer. She does not take any medications. Physical examination shows a 4-5 cm, fixed, hard, and non-tender thyroid nodule. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. Her serum TSH level is normal. Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the thyroid shows malignant cells. Which of the following is the most likely expected pathology on FNA?
. Lymphoma of the thyroid
. Papillary carcinoma of the thyroid
. Follicular carcinoma of the thyroid
. Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid
. Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid
.2) A 36-year-old female presents with headaches and visual problems. She also complains of palpitations, heat intolerance and weight loss. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She is currently on no medications. Her blood pressure is 130/60 mmHg, heart rate is 100/min and regular, and weight is 152 lb (weight one year ago was 170 lb). Physical examination reveals a symmetrically enlarged thyroid gland without any tenderness. Auscultation of the chest reveals tachycardia. She has bitemporal hemianopsia on confrontation. The rest of the physical examination is unremarkable. Her lab investigations show: Serum T3 222 ng/mL, Serum T4 13.9 mcg/dL, Serum TSH 7.9 IU/mL, Alpha subunit level elevated. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. TSH-secreting pituitary adenoma
. Generalized resistance to thyroid hormone
. Primary hypothyroidism
. Graves' disease
. Toxic multinodular goiter
.3) A 35-year-old male presents with complaints of weakness and fatigue of one year's duration. He is anorexic and has lost interest in all his activities. He also complains of cold intolerance and constipation. His blood pressure is 98/72 mmHg, temperature is 37.1°C (99°F), respirations are 14/min, and pulse is 50/min. His skin is dry and rough, nails are brittle, and hair is thin. There is no hyperpigmentation of the skin. Delayed deep tendon reflexes are noted on neurological examination. Lab studies show: Hemoglobin 10.2 g/dL, WBC count 5,000/micro-L, Neutrophils 45%, Monocytes 5%, Eosinophils 10%, Basophils 1%, Lymphocytes 40%, Serum sodium 135 mEq/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq/L. Which of the following is most consistent with this patient's findings?
. Autoimmune destruction of adrenal glands
. Adrenal tuberculosis
. Adrenal CMV infection
. Adrenoleukodystrophy
. Pituitary tumor
.4) A 60-year-old male is admitted to the hospital because of right lower lobe pneumonia. His medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, severe degenerative disease of the spine, and longstanding lower back pain. He is a chronic smoker with a 40-pack year smoking history. During his hospitalization, the laboratory report shows decreased serum calcium levels and increased phosphate levels. Further evaluation reveals increased serum intact parathyroid hormone levels. Which of the following medical conditions is most likely responsible for this patient's abnormal lab findings?
. Lung cancer
. Primary hyperparathyroidism
. Renal failure
. Thyroidectomy
. Plasma cells in marrow
.5) A 43-year-old female presents to the physician's office with muscle cramps, polydipsia and polyuria. She has no other medical problems, and does not take any medications. She does not use tobacco, alcohol or drugs. Her father died from alcoholic liver disease at age 50. Her pulse is 75/min, respirations are 13/min, blood pressure is 160/100 mmHg, and temperature is 37°C (98.6°F). Laboratory studies show: Blood glucose 115 mg/dL, Serum sodium 142 mEq/L, Serum potassium 2.7 mEq/L. Plasma renin activity is low. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Atherosclerosis of renal artery
. Fibromuscular dysplasia
. Adrenal adenoma
. Congestive heart failure
. Cirrhosis of liver
.6) A 30-year-old Hispanic male presents to the office with complaints of palpitations, tremor, nervousness and headache. His past history is insignificant. His mother has type 2 diabetes, which is well-controlled with medications. His temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse is 100/min, blood pressure is 150/80 mmHg, and respirations are 16/min. He appears anxious, sweaty and shaky. His neurological examination is non-focal, and examination of other systems is unremarkable. His fingerstick blood glucose level is 38 mg/dL. Intravenous administration of a bolus of 50% dextrose leads to the improvement of his symptoms. He is then subjected to supervise prolonged fasting. After an overnight fast, laboratory studies reveal: Blood glucose 40 mg/dl, Serum insulin 15 microU/L (normal value is < 6 microU/L with hypoglycemia), Serum pro-insulin 9 microU/L (normal value is < 20% of total immunoreactive insulin), C-peptide level 0.8 nmol/L (normal value is less than 0.2 nmol/L), Sulfonylurea Negative, IGF-II Negative. Based on the above information, what is the most likely cause of this patient's hypoglycemia?
. Beta cell tumor
. Non-beta cell tumor
. Sulfonylurea agents
. Exogenous insulin
. Glucagonoma
.7) A 35-year-old male presents to the family physician for bilateral gynecomastia. He observed a progressive increase in his breast size starting 6 months ago. He is sexually active and denies any drug use. Physical examination reveals bilateral gynecomastia and tenderness. The genito-urinary examination shows a 1 cm nodule in the right testis. Otherwise, the examination is within normal limits. The laboratory report shows: LH 3 U/L, FSH 2 U/L, testosterone 270 ng/dL (Normal 3-10 ng/dL), estradiol 115 pg/mL (Normal 20-60 pg/mL), beta HCG undetectable, AFP undetectable. Which is the most likely diagnosis?
. Leydig cell tumor
. Choriocarcinoma
. Teratoma
. Seminoma
. Endodermal sinus tumor
.8) A 39-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a "pins and needles" sensation around her mouth for the last 2-3 weeks. She gets similar sensations in her feet sometimes, along with muscle cramps, especially at the end of the day. She has no similar episodes in the past and has always been healthy. She works as a waitress and has "clean habits." Her family history is not significant. She is currently not taking any medications, and is allergic to penicillin. Her vital signs are normal. Examination is unremarkable. The patient's labs reveal: CBC: Hb 12.4 g/dl, WBC 6,000/cmm. Serum: Serum Na 140 mEq/L, Serum K 4.0 mEq/L, Chloride 100 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24 mEq/L, BUN 10 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Glucose 100 mg/dl, Calcium 6.5 mg/dl, Phosphorus, inorganic 5.8 mg/dl. Protein: Total 7.0 g/dl, Albumin 3.8 g/dl, Globulins 3.0 g/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
. Osteoporosis
. Osteomalacia
. Familial hypocalciuria
. Primary hyperparathyroidism
. Primary hypoparathyroidism
.9 A 56-year-old male presents in the emergency department with severe nausea, vomiting, polyuria polydipsia, and constipation. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. His home medications include metformin, atenolol, and hydrochlorothiazide. He has a 26-pack-year history of smoking. He drinks alcohol occasionally. He denies the use of recreational drugs. His father also has diabetes mellitus type 2. His blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg, pulse is 102/min, temperature is 36.7°C (98°F) and respirations are 16/min. His mucus membranes are dry. His lung examination reveals decreased breath sounds over the right base. The rest of the physical examination is unremarkable. The patient is subsequently admitted. Laboratory studies (obtained in the emergency department) are as follows: Serum calcium 14.8 mg/dl, Albumin 4.0 g/dl, PTH 9 pg/ml (normal 10-60 pg/ml), Serum creatinine 1.9 mg/dl, BUN 54 mg/dl, Blood glucose 180 mg/dl, 25-hydroxyvitamin D 30 ng/ml (normal 20 to 60 ng/ml), 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 30 pg/ml (normal 15 to 65 pg/ml). What is the most likely cause of this patient's hypercalcemia?
. Hypercalcemia of malignancy
. Primary hyperparathyroidism
. Hydrochlorothiazide-induced
. Dehydration
. Sarcoidosis
.10) A 63-year-old otherwise healthy male presents with a thyroid nodule. He denies any symptoms of anxiety, heat or cold intolerance, and recent changes in appetite or weight. He has hypertension, which is being treated with a beta-blocker. He does not have any other medical problems. He denies any family history of thyroid disease. His pulse is 79/min and blood pressure is 130/76 mmHg. Neck examination shows a hard, fixed, non-tender, 4 cm thyroid nodule in the right thyroid lobe. His serum TSH level is normal. Fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) shows follicular cells. Follicular carcinoma is suspected. Which of the following is necessary to make a diagnosis of follicular thyroid cancer?
. Lymph node involvement
. Invasion of the tumor capsule and blood vessels
. Secretion of calcitonin
. Presence of Hurthle cells on biopsy
. Presence of psammoma bodies
.11) A 38-year-old Caucasian female presents to the office complaining of lethargy, weight gain and fatigue. She denies headaches, pruritus or urine discoloration. She just gave birth 2 months ago via vaginal delivery; her baby is in good health and receives formula nutrition. Her delivery was complicated by vaginal bleeding that required blood transfusion, and postpartum endometritis that rapidly responded to antibiotics. She has not had any menstrual periods following delivery. Physical examination shows sparse pubic hair, dry skin and delayed tendon reflexes. Urinalysis shows no glucose or ketones. Which of the following is most likely to be responsible for this patient's condition?
. Infiltrative disorder
. Autoimmune tissue destruction
. Ischemic necrosis
. Drug effect
. Neoplasia
.12) A 56-year-old woman presents to the clinic with a 7-month history of headache and visual disturbance. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She is currently not taking any medications. She admits to smoking a pack of cigarettes daily for the last 15-years, and does not drink. On visual field examination, there is a small field defect noted in both eyes. MRI scan shows a pituitary tumor. Which of the following is the most common type of pituitary tumor?
. Thyrotroph adenoma
. Gonadotroph adenoma
. Corticotroph adenoma
. Lactotroph adenoma
. Somatotroph adenoma
.13) A 65-year-old Hispanic male comes to the office for a routine medical check-up. He has a history of diabetes for the past twenty years, and hypertension for the past ten years. His daily medications include insulin and ramipril. He was diagnosed with nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy at his last ophthalmologic visit. Reports from his previous laboratory studies show microalbuminuria. A detailed neurological examination is performed to check for any neuropathy. Which of the following is the most common type of neuropathy found in diabetics?
. Proximal motor neuropathy
. Autonomic neuropathy
. Mononeuropathy multiplex
. Symmetrical distal polyneuropathy
. Mononeuropathy
.14) A 65-year-old man presents with a 1-day history of hematuria and sharp flank pain (rated 10 of 10) radiating toward the groin on the right side. Past medical history is significant for three prior episodes of nephrolithiasis over the past 5 years, all of which presented with a similar clinical picture. He is not taking any medication. There is no family history of renal calculi, renal disease, or endocrine disorders. His temperature is 36.9°C (98.5°F), heart rate is 125/min, and blood pressure is 132/86 mmHg. He is in obvious distress and cannot sit still on the bed. Physical examination is significant for a soft, nontender abdomen and extreme costovertebral angle tenderness on the right. Laboratory values show: Na+: 142 mEq/L, K+: 4.8 mEq/L , Cl−: 104 mEq/L, HCO −: 24 mEq/L , Ca2+: 11.0 mg/dL , PO4: 1.4 mg/dL , Mg2+: 2.0 mg/dL , Blood urea nitrogen: 12 mg/dL, Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL, Glucose: 118 mg/dL, Intact parathyroid hormone: 300 pg/mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Malignancy
Milk-alkali syndrome
Primary hyperparathyroidism
Sarcoidosis
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
.15) A 90-year-old male complains of hip and back pain. He has also developed headaches, hearing loss, and tinnitus. On physical examination the skull appears enlarged, with prominent superficial veins. There is marked kyphosis, and the bones of the leg appear deformed. Serum alkaline phosphatase is elevated. Calcium and phosphorus levels are normal. Skull x-ray shows sharply demarcated lucencies in the frontal, parietal, and occipital bones. X-rays of the hip show thickening of the pelvic brim. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Multiple myeloma
. Paget disease
. Vitamin D intoxication
. Metastatic bone disease
. Osteitis fibrosa cystica
.16) A 35-year-old white male presents with fatigue, decreased appetite, weight gain, constipation and cold intolerance. He cannot recall any stressful event. He does not take any medications. He is a non-smoker and non-alcoholic. His pulse is 47/min and blood pressure is 145/91 mmHg. Physical examination reveals cool, pale skin, coarse hair, and brittle nails. There is delayed relaxation of deep tendon reflexes. The thyroid gland is normal on palpation. Laboratory studies reveal increased serum free T3 and T4 levels, and normal serum TSH level. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Primary hypothyroidism
. Secondary hypothyroidism
. Subclinical hypothyroidism
. Generalized resistance to thyroid hormones
. Graves' disease
.17) A 65-year-old diabetic male with acute myocardial infarction complicated by cardiogenic shock is admitted in the coronary care unit. His hospital course was complicated by acute renal failure and lower GI bleeding from anticoagulation therapy. His thyroid hormone studies are abnormal. He does not have any previous history of thyroid disease. Physical examination of the thyroid gland is normal. Labs show: Triiodothyronine (T3), serum 1.4 nmol/L (normal 1.8-29 nmol/L), Thyroxine (T 4), serum 6.0 micro-g/dL (normal 5-12 micro-g/dL), Thyroid-stimulating hormone, serum 2.0 micro-U/mL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Sick euthyroid syndrome
. Primary overt hypothyroidism
. Subclinical hypothyroidism
. Central hypothyroidism
. Reidels thyroiditis
.18) A 45-year-old male presents to your office because his "hands are getting thick and swollen." He is also having difficulty with wearing shoes because his feet have become large. His blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg. On examination, he has enlarged, swollen hands and feet. He has coarse facial features, with prominent frontal bones and jaws. While you are discussing the most likely diagnosis, he appears worried and asks about the complications and risk of death associated with his condition. What is the most common cause of death in patients with this condition?
. Congestive cardiac failure
. Hypertensive nephropathy
. Stroke
. Brain tumor
. Adrenal failure
.19) A 17-year-old girl presents to the clinic because she has not yet menstruated and does not have significant breast development. Family history is significant only for some cousins who are color blind. The patient denies ethanol, tobacco, and illicit drug use and sexual activity. Physical examination reveals a normal-appearing girl in no acute distress with minimal breast development and a lack of pubic hair. She is 168 cm (5'6") tall and weighs 61.2 kg (135 lb). Cardiac examination reveals no murmurs, rubs, or gallops, with point of maximal impulse at the left mid-clavicular line between the third and fourth intercostal space. Gynecologic examination reveals a vagina without rugae and a cervix that is easily visualized. There is no discharge. A urine test is negative for β-human chorionic gonadotropin. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
Gonadal dysgenesis
Kallmann’s syndrome
Kartagener’s syndrome
Pregnancy
.20) A 26-year-old man presents with increased thirst, urinary frequency, and nocturia over the past several months. Physical examination is unremarkable. Twenty-four-hour urine osmolarity is < 300 mOsm/L. A fluid deprivation test does not result in an increased urine osmolarity. Administration of 0.03 μg/kg of desmopressin results in a urine osmolarity of 450 mOsm/L after 2 hours. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Central diabetes insipidus
Diabetes mellitus
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
Psychogenic polydipsia
Syndrome of inappropriate secretion of ADH
.21) A 48-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician because of 2 weeks of neck pain. The pain is constant and sharp (rated at 10 of 10) and is felt in the anterior portion of her neck. She also notes several weeks of loose stools and fatigue. Past medical history is significant for a viral upper respiratory infection about 1 month ago. She has a temperature of 37.9°C (100.2°F), heart rate of 96/min, and blood pressure of 136/82 mmHg. On neck examination there is diffuse enlargement of the thyroid and it is exquisitely tender to even mild palpation. Laboratory tests show a total tri-iodothyronine level of 280 ng/dL, total thyroxine of 25 μg/dL, and thyroid-stimulating hormone of 2 μU/mL (normal: 0.4–4 μU/L).Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute infectious thyroiditis
Drug-induced thyroiditis
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
Riedel’s thyroiditis
Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis
.22) A 74-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department by her daughter. The daughter states that her mother lives alone and has no significant medical problems. She says that she last saw her mother a month prior, before she left on an extended business trip. When she returned, she found her mother appeared restless and very nervous. She also appeared to have lost a noticeable amount of weight. The patient told her daughter that she had been having increased frequency of bowel movements, and felt like her heart was beating fast and funny, and that she felt like she might be coming down with a cold. Initial evaluation in the emergency department reveals sinus tachycardia and a painful, enlarged thyroid. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of her symptoms?
Autoimmune thyroiditis
Graves’ disease
Medication-induced hyperthyroidism
Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis
Toxic multinodular goiter
.23) A 32-year-old woman undergoes a cesarean section because of failure of labor to progress, and delivers a healthy baby boy. The procedure is complicated by significant intraoperative blood loss and hypotension, but the patient is successfully resuscitated. Postoperatively she experiences dull, aching, non-localized abdominal pain and nausea, but denies headache, visual changes, or abnormal edema. On postoperative day three she is passing flatus and remains afebrile, but becomes hypotensive to 90–100 mm Hg systolic and 40–50 mm Hg diastolic. She has not begun lactating despite her attempts to breast-feed her infant. Laboratory values indicate that she is hyponatremic and mildly hyperkalemic. Urinalysis and liver enzymes are normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her symptoms?
Appendicitis
HELLP syndrome
Postoperative infection
Sheehan’s syndrome
Toxic shock syndrome
.24) A 24-year-old white male presents with a persistent headache for the past few months. The headache has been gradually worsening and not responding to over-the-counter medicines. He reports trouble with his peripheral vision which he noticed while driving. He takes no medications. He denies illicit drug use but has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day since the age of 18. Past history is significant for an episode of kidney stones last year. He tells you no treatment was needed as he passed the stones, and he was told to increase his fluid intake. Family history is positive for diabetes in his mother and a brother (age 20) who has had kidney stones from too much calcium and a “low sugar problem.” His father died of some type of tumor at age 40. Physical examination reveals a deficit in temporal fields of vision and a few subcutaneous lipomas. Laboratory results are as follows: Calcium: 11.8 mg/dL (normal 8.5-10.5), Cr: 1.1 mg/dL, Bun: 17 mg/dL, Glucose: 70 mg/dL, Prolactin: 220 μg/L (normal 0-20), Intact parathormone: 90 pg/mL (normal 8-51). You suspect a pituitary tumor and order an MRI which reveals a 0.7 cm pituitary mass. Based on this patient’s presentation, which of the following is the most probable diagnosis?
. Tension headache
. Multiple endocrine neoplasia Type 1 (MEN 1)
. Primary hyperparathyroidism
. Multiple endocrine neoplasia Type 2A (MEN 2A)
. Prolactinoma
.25) A 26-year-old man with a history of kidney stones presents with 1 week of severe burning epigastric pain. He also notes several days of diarrhea and nausea but denies emesis or fever. His family history is remarkable for a paternal uncle with pancreatic cancer. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), heart rate is 88/min, respiratory rate is 16/min, and blood pressure is 125/85 mm Hg. Abdominal examination is significant for tenderness in the mid-epigastrium. Upper endoscopy reveals a 1-cm ulceration in the first part of the duodenum. This is the third episode of confirmed peptic ulcers in this patient. Laboratory studies show: Na+: 140 mEq/L, K+: 4.9 mEq/L , Cl−: 105 mEq/L, HCO −: 25 mEq/L, Ca2+: 12.0 mg/dL, PO4: 1.4 mg/dL, Mg2+: 2.0 mg/dL, Blood urea nitrogen: 10 mg/dL Creatinine: 1.0 mg/dL , Glucose: 87 mg/dL. Which of the following is most likely to be found in this patient?
Medullary thyroid carcinoma
Papillary thyroid carcinoma
Pheochromocytoma
Prolactinoma
Squamous cell lung cancer
.26) A 52-year-old man presents to the primary care clinic for the first time. He states that he has been in good health throughout his life and takes no medications. He was once athletic but has noted a dramatic decrease in his muscle strength and exercise tolerance over the past year. On examination the patient is moderately hypertensive, with a tanned, round, plethoric face; large supraclavicular fat pads; and significant truncal obesity. He has no focal cardiovascular, pulmonary, or neurologic findings. His fasting blood sugar is 200 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most common etiology of this condition?
ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma
Adrenal tumor
Ectopic ACTH-secreting tumor
Primary adrenal hyperplasia
Small cell lung cancer
.27) A 3-year-old girl is brought to the pediatrician’s office because of an abdominal mass. Physical examination reveals short stature, coarse facial features, a protruding tongue, and an easily reducible umbilical hernia. The girl has difficulty walking and knows six words, although she is unable to form a sentence. Her mother reports no health problems and an uncomplicated pregnancy. What is the most likely cause of the patient’s condition?
Congenital hypothyroidism
Cushing’s syndrome
Neuroblastoma
Phenylketonuria
Turner’s syndrome
.28) A moderately overweight 34-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with excessive sweating, flushing, tachycardia, and nervousness. Presuming that she might be suffering from thyrotoxicosis, the physician checks her blood levels of thyroid hormones, and finds that her free thyroxine and triiodothyronine levels are elevated, while her thyroid-stimulating hormone is decreased. Her radioactive iodine uptake test shows a complete absence of iodine uptake. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Factitious thyrotoxicosis
Graves’ disease
Thyroid-stimulating hormone-secreting pi- tuitary tumor
Toxic adenoma
Toxic multinodular goiter
.29) A 28-year-old Caucasian male presents to the emergency department complaining of neck pain for the past two days. He states that a chicken bone scratched the back of his throat a week ago. Two weeks ago, he was in Arizona visiting his friends. He is otherwise healthy and has never been hospitalized. His temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), blood pressure is 125/85 mmHg, and heart rate is 120/min. On examination, he refuses to fully open his mouth. Neck movements, especially neck extension, are restricted secondary to pain. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Meningitis
. Herpangina
. Epiglottitis
. Diphtheria
. Retropharyngeal abscess
.30) A 7-year-old boy with a 6-day history of nasal discharge presents with a swollen and painful left eye. His blood pressure is 100/70 mmHg, pulse is 92/min, respirations are 18/min, and temperature is 39.4°C (103°F). Examination of the left eye reveals swollen and erythematous eyelids, mild protrusion of the eyeball, and pain with eye movements. The affected eye is tender and his visual acuity is decreased. Funduscopic examination is normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anterior uveitis
. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
. Conjunctivitis
. Optic neuritis
. Orbital cellulitis
.31) A 32-year-old male complains of difficulty hearing in his left ear for the past month. He denies any headaches, fever, chills, weight loss, or ear discharge. He is HIV positive, and is currently being treated with highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). He also takes trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole daily. His most recent CD4 count was 425/mm3. Examination of the affected ear shows a dull, hypomobile tympanic membrane. What is the most likely cause of hearing loss in this patient?
. Neoplasia
. Non-infectious effusion
. Otosclerosis
. Opportunistic infection
. Demyelinization
.32) A 36-year-old woman presents to your office with complaints of worsening throat pain for the past six days. She also has pain in her ears and neck as well as difficulty swallowing. On examination, she has excessive salivation and difficulty opening her mouth. Her temperature is 39°C (102.2°F), blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, pulse is 100/min, and respiratory rate is 18/min. Which of the following neck space infections carries the highest risk of mediastinal involvement?
. Submandibular space
. Sublingual space
. Parapharyngeal space
. Retropharyngeal space
. Retro-obital
.33) A 23-year-old male comes to your office with a 10-day history of severe headaches. He states that they are sharp in character and are mostly right-sided involving the frontal area. The headaches interfere with his sleep, and he also complains of double vision, nausea, and malaise. His blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg, pulse is 103/min, respirations are 14/min, and temperature is 38.0°C (100.5°F). Examination reveals bilateral periorbital edema. There is subtle right-sided lateral gaze palsy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Orbital cellulitis
. Acute angle-closure glaucoma
. Common migraine
. Cavernous sinus thrombosis
. Cluster headaches
.34) A 24-year-old Caucasian female complains of recurrent painful ulcers in her mouth and occasional abdominal pain. She has also unintentionally lost 5 pounds over the last six months. She is not sexually active, and denies use of tobacco, alcohol, or drugs. Past medical history is noncontributory and she takes no regular medications. Her mother suffers from asthma and her father has prostate cancer. She is afebrile with a blood pressure of 118/69 mmHg and pulse of 71/min. Physical examination reveals mild abdominal tenderness primarily in the lower abdomen without guarding or rebound. Several shallow ulcers are seen on the buccal mucosa. A biopsy of one of the ulcers demonstrates granulomatous inflammation. Her hematocrit is 42%. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
. Celiac disease
. Folic acid deficiency
. Crohn's disease
. Oral candidiasis
. Squamous cell carcinoma
.35) A 70-year-old man comes to your office with complaints of difficulty hearing. His wife says that he has been raising the television volume much louder recently. The patient claims that he can hear well when he talks to his family members at home, but he has significant difficulty hearing in restaurants or during other family gatherings, which is why he prefers to stay at home most of the time. He worked in a shipbuilding yard for 30 years, and retired five years ago. He has no history of significant noise exposure. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Otosclerosis
. Presbycusis
. Middle ear effusion
. Meniere's disease
. Acoustic neuroma
.36) A 12-year-old girl comes to the office complaining of a small amount of left-sided ear discharge that has persisted for the last three weeks. She has completed two courses of antibiotics that were prescribed during her previous visits. She also complains of hearing loss on the left side. On examination, she is afebrile. Otoscopy reveals an intact left tympanic membrane with peripheral granulation and some skin debris. The patient should be evaluated for which of the following?
. Meniere's disease
. Craniopharyngioma
. Otosclerosis
. Cholesteatoma
. Middle ear osteoma
.37) A 33-year-old Caucasian female has suffered from recurrent episodes of dizziness over the last six months. She describes the episodes as a sensation of severe spinning that last one to two hours and are accompanied by intense nausea. She also feels unsteady during the episode, and has to lie down with her eyes closed for relief. There is no particular factor that precipitates the episodes. She denies any headaches, but complains of fullness in her right ear. She has no ear pain or ear discharge. She has used some over-the-counter ear drops with minimal relief of the fullness sensation. She prefers holding her cell phone on the left side. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
. Middle ear disease
. Inner ear disease
. Cranial nerve VIII lesion
. Cerebellar disease
. Lesion in the medulla
.38) A 6-year-old boy is brought to the office by his mother due to a decreased appetite and irritability for the past three days. He also had an episode of diarrhea yesterday. Lately, he has been sitting close to the television with the volume turned up very loudly. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.5°F), blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg, and heart rate is 110/min. On examination, there is left-sided yellowish ear discharge. His nasal mucosa appears boggy and postnasal drip is present. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bullous myringitis
. Acute otitis media
. Otitis extern a
. Cholesteatoma
. Sinusitis
.39) A 28-year-old African American female complains of recurrent nasal discharge and increasing nasal congestion. She has a constant sensation of dripping in the back of her throat, and states that food has tasted bland to her recently. She is known to have sickle cell trait. She came to the emergency department for severe wheezing after taking naproxen for menstrual cramping one year ago. She has no history of head trauma. She does not smoke cigarettes, but she admits to smoking marijuana occasionally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Angiofibroma
. Inverted papilloma
. Nasal polyp
. Perforated nasal septum
. Pyogenic granuloma
.40) A 26-year-old man comes to your office with a one-week history of right-sided ear pain. The pain often wakes him up at night, and increases in severity when he chews food. He cannot recall any recent episodes of pharyngitis. He denies having any ear discharge, sinus tenderness, or skin rash. He exercises by swimming frequently at a local club. He is sexually active and uses condoms "quite regularly." He lives with his brother, who often comments on his habit of grinding his teeth at night. On examination, his ears are normal with a mild amount of wax. Pain is not elicited by pulling on the pinna. There are no hearing deficits appreciated. Mobility of the tympanic membrane is normal, and the Weber and Rinne test results are within normal limits. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ramsay Hunt syndrome
. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
. Otitis media
. Temporomandibular joint dysfunction
. Otitis externa
.41) A 43-year-old male (Patient A) is being evaluated for an esophageal disorder. Esophageal manometry tracings after a single swallow of 5 ml of water are shown on the slide below. (UE: upper esophagus, ME: middle esophagus, LES: lower esophageal sphincter). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
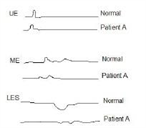
Share

. Cricopharyngeal dysfunction
. Diffuse esophageal spasm
. Achalasia
. Gastroesophageal reflux
. Mallory-Weiss syndrome
.42) A 45-year-old nurse practitioner presents to the emergency department due to painful abdominal cramps and watery diarrhea. She has about 10 to 20 bowel movements a day. She also has nocturnal bowel movements. She has had multiple hospitalizations in the past for similar problems without a definite diagnosis. A lower GI endoscopy during a previous hospitalization showed dark brown discoloration of the colon with lymph follicles shining through as pale patches. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Factitious diarrhea
. Irritable bowel syndrome
. Celiac disease
. Infectious diarrhea
. Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
.43) A 44-year-old white female presents with a 2-month history of low-grade fever, abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. Over the past two days, her symptoms have increased. She does not use medications and she has no allergies. She has had a 10 lb (4.5 kg) weight loss over the past four weeks. Her temperature is 38.9°C (102°F), blood pressure is 102/70 mmHg, pulse is 118/min, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows pale and dry mucus membranes. Abdominal examination shows diffuse tenderness and distention. Laboratory studies show: Hb 9.5 g/dl, WBC 16,000/cmm, Serum Na 145 mEq/L, Serum K 3.0 mEq/L. An x-ray film of the abdomen is shown below. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
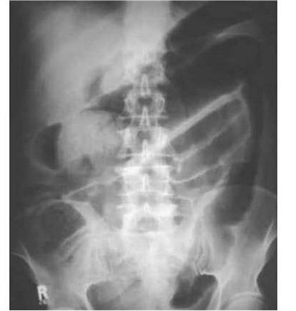
Share

. Crohn's disease
. Pseudomembranous colitis
. Toxic megacolon from ulcerative colitis
. S. Aureus gastroenteritis
. Obstructed colon cancer
.44) A 65-year-old man comes to the physician's office with a 2-month history of dysphagia. He initially had difficulty swallowing solids, but now this includes liquids. He has occasional heartburn, which usually responds well to antacids. He has lost 20 lbs of weight in the past 2 months. He has a 40 pack- year history of smoking. He has been a chronic alcoholic for 20 years. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), blood pressure is 110/80 mmHg, pulse is 66/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Barium studies show a minimally dilated esophagus with beak-shaped narrowing. Manometry shows increased lower esophageal sphincter tone. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Achalasia
. Esophageal cancer
. Scleroderma
. Peptic stricture
. Diffuse esophageal spasm
.45) Ms. Lee, a 62-year-old Chinese woman, comes with yellowness in her eyes for the past 6 weeks. She is generally feeling tired, has lost some weight, and occasionally had some nausea. She denies any altered bowel habits. She is a non-smoker but drinks 2-3 beers each night. Her dad is suffering from high cholesterol and also has had stroke. She had a dilatation and curettage for an abnormal pap smear 15 years ago. Her vitals are stable and she is afebrile. She has marked scleral icterus. An abdominal examination reveals normal bowel sounds and no organomegaly. Her stools were occult blood negative. Her liver function tests and enzymes were ordered and the results are: Total protein 6.1 g/dl, Albumin 39 g/dl, AST 67U/L, ALT 52U/L, Alkaline phosphatase 290 U/L, Total bilirubin 96 mg/dl, Direct bilirubin 89 mg/dl, Serum lipase is 46 U/L, Anti-mitochondrial antibodies negative. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
. Primary biliary cirrhosis
. Chronic pancreatitis
. Viral hepatitis
. Pancreatic carcinoma
. Hepatocellular carcinoma
.46) A 64-year-old white male with a history of severe stable angina and peripheral vascular disease undergoes coronary artery bypass surgery. His post-operative course is complicated by hypotension, which is treated successfully; however, a few hours later, he experiences abdominal pain followed by bloody diarrhea. His temperature is 37.8°C (100°F), blood pressure is 110/60 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 20/min. Abdominal examination is benign. Laboratory studies show a WBC count of 15,000/cmm with 7% bands. The lactic acid level is elevated. A CT scan is ordered. Which of the following areas of the colon will most likely show abnormal findings?
. Sigmoid colon
. Splenic flexure
. Ascending colon
. Mid transverse colon
. Hepatic flexure
.47) A 52-year-old man presents to your office after passing a black stool. He also describes occasional abdominal discomfort and nausea but denies hematemesis. He says that food seems to help his abdominal pain, so he eats frequently during the day and keeps some snacks on his night stand. As a consequence, he has gained 5 pounds over the last year. He admits that his diet is lacking in vegetables and fruit. He drinks one to two cans of beer nightly, but does not smoke or use illicit drugs. He says that his father died of colon cancer and his mother died from a stroke. Physical examination reveals a right-sided carotid bruit. The fecal occult blood test is positive. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
. Mesenteric ischemia
. Mallory-Weiss tear
. Inflammatory bowel disease
. Erosive gastritis
. Peptic ulcer disease
.48) A 35-year-old Caucasian female presents to your office with several months history of heartburn. She also describes a periodic 'sticking sensation' in her throat during the meal. Her past medical history is significant for asthma that is controlled with inhaled steroids, and acoustic neuroma that was removed 2 years ago. She does not smoke or consume alcohol. She denies any recreational drug use. She is not allergic to any medications. She works as a secretary at a private firm, and considers her work moderately stressful. Her family history is significant for breast cancer in her mother and prostate cancer in her father. Endoscopic evaluation shows mild hyperemia in the distal esophagus. Esophageal manometry reveals absent peristaltic waves in the lower two-thirds of the esophagus and a significant decrease in lower esophageal sphincter tone. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaints?
. Achalasia
. GERD with or without hiatal hernia
. Scleroderma
. Non-ulcer dyspepsia
. Diffuse esophageal spasm
.49) A 42-year-old male comes to the physician's office for evaluation of skin rash and hair loss. He has a long history of Crohn's disease and has had extensive small bowel resection resulting in short bowel syndrome. He is currently receiving total parenteral nutrition. When he does try to eat, he complains that the food does not taste good. His vital signs are stable. Examination shows alopecia and bullous, pustular lesions around the perioral and periorbital areas. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his current symptoms?
. Celiac disease
. Zinc deficiency
. Vitamin A deficiency
. Vitamin B 12 deficiency
. Systemic lupus erythematosus
.50) A 45-year-old Hispanic male comes to the emergency department because of a two-day history of intermittent abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. He has had four similar episodes in the past year. He is subsequently admitted to the floor. Radiographic and endoscopic evaluations show extensive disease from the terminal ileum to the rectum with multiple ulcerations and pseudopolyps. Biopsy of the lesion shows noncaseating granulomas and crypt abscess. Which of the following is the most characteristic feature which favors the diagnosis of Crohn's disease against that of ulcerative colitis?
. Crypt abscess
. Abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea
. Non-caseating granulomas
. Disease from terminal ileum to rectum
. Pseudopolyps
150) A 34-year-old woman comes to the office for her annual examination. She has been your patient for the last 4 years. She eats a lot of meat, but does not like fruits and vegetables. Her menstrual period began at age 12. She has two children, who are ages 13 and 11. She is in a monogamous relationship with her husband, and uses oral contraceptive pills. She smokes 1/2 pack of cigarettes daily, and drinks alcohol socially. Her mother had breast disease and had an operation, but died 1 month after the surgery due to a heart attack. She has read in "US Health News" that breast cancer is the leading culprit for cancer death among non-smoking women. She now asks you, "What is the most important risk factor for breast cancer?" What is the correct response to this patient's question?
. Parity of the woman
. Age of menarche
. Age of woman
. Use of oral contraceptive pills
. Family history of breast cancer
.101) A 66-year-old woman presents to her physician because of recurrent painless bleeding on defecation over the past month. She has regular, soft bowel movements and no history of constipation or diarrhea. A recent diagnosis of aortic stenosis was an incidental finding on echocardiogram. She takes calcium and vitamin D supplements daily. Her last colonoscopy (at age 60) was normal. Heart rate is 82/min, blood pressure is 133/72 mm Hg, respiratory rate is 12/min, and temperature is 36.6°C (97.8°F). Physical examination reveals her conjunctivae are pink and mucosa is moist. She has no abdominal tenderness or palpable masses and no hemorrhoids or fissures. Stool is hemoccult positive. Colonoscopy shows a spider-like lesion in the ascending colon. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Angiodysplasia
Crohn’s disease
Diverticulosis
Ischemic colitis
Peptic ulcer disease
.102) A 61-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department drowsy and disoriented, able only to follow simple commands. On examination her abdomen is distended and nontender, her skin has a yellow hue, and there are multiple spider nevi on her chest. In her purse, the physician finds prescriptions for peginterferon and ribavirin. When asked to raise her hands, the physician notices a coarse tremor. Laboratory tests show: Blood urea nitrogen: 17 mg/dL Creatinine kinase: 1.1 mg/dL Aspartate aminotransferase: 89 U/L Alanine aminotransferase: 93 U/L Total bilirubin: 3.1 mg/dL Ammonia: 124 μg/dL Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bleeding esophageal varices
Hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatorenal syndrome
Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis
.103) A 74-year-old man presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain. The pain is deep and aching and is localized to the left lower quadrant. The man reports multiple episodes of diarrhea over the preceding week. He also reports having multiple similar episodes of abdominal pain in the past. On physical examination he is febrile and has tenderness to palpation of the left lower quadrant. His WBC count is 23,000/mm³. Results of CT are shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
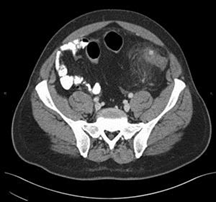
Share

Angiodysplasia
Carcinoid syndrome
Carcinoma of the colon
Diverticulitis
Infectious colitis
.104) A 51-year-old man describes 1 week of gradually worsening scrotal pain and dysuria. He is sexually active with his wife. His temperature is 100.1°F, HR 81 beats per minute, BP 140/75 mm Hg, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. On physical examination, his scrotal skin is warm and erythematous. A cremasteric reflex is present. The posterior left testicle is swollen and tender to touch. Color Doppler ultrasonography demonstrates increased testicular blood flow. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Epididymitis
. Testicular torsion
. UTI
. Testicular tumor
. Varicocele
.105) A 40-year-old woman presents to the ED complaining of fever and 1 day of increasingly severe pain in her RUQ. She denies nausea or vomiting and has no history of fatty food intolerance. The patient returned from a trip to Mexico 6 months ago. About 2 weeks ago she experienced intermittent diarrhea with blood-streaked mucus. Her BP is 130/80 mm Hg, HR is 107 beats per minute, temperature is 102°F, and RR is 17 breaths per minute. Physical examination reveals decreased breath sounds over the right lung base. Abdominal examination shows tenderness to percussion over the RUQ and normal active bowel sounds. There is no Murphy sign. Her WBC is 20,500/μL. Chest radiograph reveals a small right-pleural effusion. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Amebic abscess
. Cholecystitis
. Cryptosporidium
. Enterobiasis
. Pyogenic abscess
.106) A 20-year-old man presents with several weeks of painful rectal bleeding. He denies fever, nausea, or vomiting. He is sexually active with women only and usually uses condoms. He denies any history of CD, UC, or malignancy. He states that the pain is most severe during and immediately after defecating. Bleeding is bright red and only enough to stain the toilet paper. Which of the following is the most common etiology of painful rectal bleeding?
. External hemorrhoid
. Anal fissure
. Anorectal tumor
. Internal hemorrhoid
. Venereal proctitis
.107) A premature newborn is being treated in the neonatal intensive care unit. On the sixth day of life he is noted to be lethargic and in mild respiratory distress. His heart rate is 162/min, blood pressure is 55/38 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 56/min. In addition to a distended abdomen, he has guaiac-positive stools. X-ray of the abdomen shows gas bubbles within the bowel wall. From what potentially life-threatening condition is this patient most likely suffering?
Bowel obstruction
Intussusception
Meconium ileus
Meningitis
Necrotizing enterocolitis
.108) A 65-year-old man comes to the emergency department complaining of left lower abdominal pain that began the prior morning. He became concerned when he developed bloody diarrhea overnight. He has experienced similar pain, although to a lesser degree, over the past 2 months, especially after eating. The pain usually resolved within 1–2 hours, and he never had bloody diarrhea. His past medical history is significant for coronary artery disease and hypertension. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes per day for the past 30 years. On physical examination he is afebrile, heart rate is 90/min, and blood pressure is 135/85 mm Hg. He is visibly uncomfortable but in no apparent distress. His abdominal examination is significant for left lower quadrant tenderness but no guarding or rebound. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute mesenteric ischemia
Colon cancer
Diverticulitis
Infectious colitis
Inflammatory bowel disease
.109) A 25-year-old previously healthy man experiences fatigue and malaise. One week ago he had a “viral” type illness consisting of a sore throat, fever, and myalgias. He now appears jaundiced, but the rest of the physical examination is normal. His investigations reveal a total bilirubin of 4 mg/dL (0.1–1.0 mg/dL) and a direct bilirubin of 0.3 mg/dL (0.0–0.3 mg/dL). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. hemolysis
. gallstones
. Alcoholic liver disease
. Pancreatic carcinoma
. Dubin-Johnson syndrome
.110) A 49-year-old man is brought to the ED by EMS stating that he vomited approximately three cups of blood over the last 2 hours. He also complains of epigastric pain. While examining the patient, he has another episode of hematemesis. You decide to place an NG tube. You insert the tube, confirm its placement, and attach it to suction. You retrieve 200 mL of coffee-ground blood. What is the most common etiology of an upper GI bleed?
. Varices
. Peptic ulcer
. Gastric erosions
. Mallory-Weiss tear
. Esophagitis
.111) A 63-year-old woman with cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis C is hospitalized because of confusion. She has guaiac-positive stools and a low-grade fever. She has received lorazepam for sleep disturbance. On physical examination, the patient is confused. She has no meningeal signs and no focal neurologic findings. There is hyperreflexia and a nonrhythmic flapping tremor of the wrists. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for this patient’s mental status change?
. Tuberculous meningi
. Subdural hematoma
. Alcohol withdrawal seizure
. Hepatic encephalopathy
. Central nervous system vasculitis from cryoglobulinemiatis
.112) A 40-year-old white male complains of weakness, weight loss, and abdominal pain. On examination, the patient has diffuse hyperpigmentation and a palpable liver edge. Polyarthritis of the wrists and hips is also noted. Fasting blood sugar is 185 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus
. Pancreatic carcinoma
. Addison disease
. Hemochromatosis
. Metabolic syndrome
.113) A 55-year-old white woman has had recurrent episodes of alcoholinduced pancreatitis. Despite abstinence, the patient develops postprandial abdominal pain, bloating, weight loss despite good appetite, and bulky, foul-smelling stools. KUB shows pancreatic calcifications. In this patient, you should expect to find which of the following?
Share

. Diabetes mellitus
. Malabsorption of fat-soluble vitamins D and K
. Guaiac-positive stool
. Courvoisier sign
. Markedly elevated amylase
.114) A male infant is delivered at 37 weeks’ gestation via cesarean section for breech presentation. The pregnancy was complicated by polyhydramnios. The 34-year-old mother is rubella immune and has blood type B. She is negative for Rh antibody, Group B streptococci, rapid plasma reagin, hepatitis B surface antigen, gonorrhea, and Chlamydia. At delivery there is no meconium. He has a birth weight of 2.7 kg (6 lb). The baby has a weak cry and is pale and frothing at the nose and mouth. He has nasal flaring and retractions, with a respiratory rate of 56/min. Heart rate is 140/min and he has a regular rhythm and a harsh 2/6 holosystolic murmur that is best heard at the left sternal border. On auscultation he has fine diffuse crackles in his lungs bilaterally. The infant is missing both thumbs and has fusion of the remaining digits of his upper extremities bilaterally. The pediatric resident is able to suction secretions from the patient’s nasopharynx and oropharynx; however, she is unable to pass a nasogastric or orogastric tube more than 10 cm down. X-ray of the chest is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
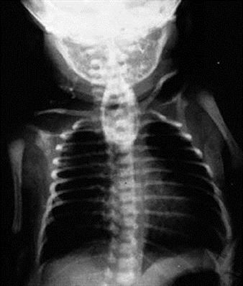
Image

Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
Pyloric stenosis
Respiratory distress syndrome
Tracheoesophageal fistula
Transient tachypnea of the new-born
.115) A 55-year-old male comes to you with complaint of fatigue for the past month. He also complains of occasional heartburn. His past medical history is significant for hepatomegaly, secondary to fatty liver. He has been drinking 3-4 shots of alcohol per day for the past 30 years. He denies smoking. His physical examination reveals pallor of skin and mucous membranes, and mild hepatomegaly. His laboratory report shows: Hb 8.5 g/dl, WBC 8,000/cmm, MCV 110 fl, Platelets 150,000/cmm, Blood glucose 118 mg/dl, BUN 16 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 1.0 mg/dl. What is the most likely cause of anemia in this patient?
. Vitamin B- 12 deficiency
. Folate deficiency
. Chronic blood loss from peptic ulcer
. Anemia of chronic disease
. Thiamine deficiency
.116) A 62-year-old Caucasian man presents to your office with occasional ear pain and a lump in his neck. His past medical history is significant for hypertension treated with hydrochlorothiazide and diabetes mellitus treated with metformin. He smokes two packs of cigarettes per day and consumes alcohol occasionally. He is not sexually active. Physical examination reveals a hard, non-tender submandibular mass that is 3 cm in diameter. Chest examination is unremarkable. Abdomen is soft and non-tender. The liver span is 8 cm and the spleen is not palpable. His extremities have no cyanosis, clubbing, or edema. Complete blood count is within normal limits. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's complaint?
. Bacterial infection
. Squamous cell carcinoma
. Herpes simplex infection
. Connective tissue disease
. Hodgkin's lymphoma
.117) A 67-year-old woman comes to her physician because she is feeling tired, all the time. She thinks that it is due to multiple surgeries she had over the past several years. She had two caesarian sections at the age of 22 and 26. She also had a thyroid surgery for Graves’s disease, 30 years ago. 12 years ago she was diagnosed with colon cancer and had undergone left hemicolectomy. She denies smoking or alcohol use. Her vitals are Temperature 36.7°C (98.2°F); BP 138/86 mm Hg; PR 77/min; RR 12/min. She looks markedly pale and has weakness in all four extremities. There is some sensory loss in lower limbs. The test for occult blood was negative. Labs came back as: Sodium 144 mEq/L, Potassium 4.2 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 24mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen 18mg/dl, Creatinine 1.0 mg/dl, Glucose 82 mg/dl, WBC 8,600/cmm, Hemoglobin 7.9, Hematocrit 25%, Platelets 176,000/cmm. The physician decides to further investigate anemia and order RBC indices and peripheral blood smear. The results are: MCV 120 fl, MCH 36 pg, MCHC 28%, Reticulocyte count 04%. Peripheral smear showed anisocytosis, poikilocytosis, 4+ macrocytes, polychromatophilia and basophilic stippling. A whole new bunch of tests are ordered and the following report is seen on the computer. Vitamin B12 106 pg/ml (N=210-911 pg/ml), Serum Folate 16.4 ng/ml (N=2.8-17.8 ng/ml), Serum Bilirubin 1.8 mg/dl, Serum LDH 2500 U/L. Gastric analysis demonstrated an absence of hydrochloric acid. What is the most probable cause of her anemia?
. Folate deficiency
. Dietary B12 deficiency
. Pernicious anemia
. Hemicolectomy
. Malabsorption syndrome
.118) A 34-year-old Caucasian man presents to your office with easy fatigability, difficulty concentrating, insomnia, and occasional muscle pain. He also complains of right hand clumsiness and some memory loss. He does not smoke and drinks one to two cans of beer on the weekends. Physical examination reveals extensor weakness of the right hand. Ankle reflexes are symmetric and there is no Babinski reflex. Laboratory studies show: Hemoglobin 8.5 g/dl, MCV 81 fl, AST 18 U/L, ALT 16 U/L, Bilirubin 0.8 mg/dl, Creatinine 2.1 mg/dl. Which of the following is most important in revealing the cause of this patient's condition?
. Vaccination history
. Family history
. Occupational history
. Nutrition
. Childhood infections
.119) A 26-year-old woman presents to your office complaining of fatigue. Her past medical history is insignificant. She was adopted in Greece and came to the United States when she was three years old. Her menstrual periods are regular and bleeding lasts three days. She does not use tobacco, alcohol, or illicit drugs. She takes no medication. Laboratory studies show: Complete blood count: Hemoglobin 10.1 g/L, MCHC 28%, MCV 70 fL, Platelets 200,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 7,500/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 33%, Monocytes 10%. Fecal occult blood test is negative. Iron therapy is initiated. When the patient returns four weeks later, her lab findings are essentially the same. This patient most likely suffers from
. Iron deficiency
. Folic acid deficiency
. Cobalamin deficiency
. Erythropoietin deficiency
. Hemoglobinopathy
.120) An 8-month-old pale child is referred by a nurse practitioner due to "pale mucous membranes, irritability, and listlessness." The stool examination is negative for occult blood, ova and parasites. Laboratory studies reveal: Hemoglobin 6.0 g/L, MCHC 25%, MCH 16.5 pg, MCV 68 fl, Reticulocytes 0.6%, Platelets 230,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 5,500/mm3, Neutrophils 56%, Eosinophils 1%, Lymphocytes 33%, Monocytes 10%, Serum Iron 40 mg/dL, TIBC 460 mg/dL (normal 300-350 mg/dL), Percent saturation of transferrin 8.7%, Total serum bilirubin 0.9 mg/dL. The peripheral blood smear shows marked anisocytosis, microcytosis, hypochromia, and poikilocytosis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Iron deficiency anemia
. Sideroblastic anemia
. Dimorphic anemia
. Megaloblastic anemia
. Anemia of chronic disease
.121) A 54-year-old Caucasian man presents to his family physician's office complaining of several months of increased fatigability. He eats meat occasionally and drinks two to three cans of beer on weekends. Physical examination reveals pale conjunctivae and hyperdynamic carotid pulses. His blood hemoglobin level is 7.7 mg/dl, WBC count is 4,500/mm3, and platelet count is 170,000/mm3 Folic acid therapy is initiated. Four weeks later the patient's hemoglobin level is 9.1 mg/dl, but he complains of new tingling in his toes. Which of the following is a likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
. Drug toxicity
. Iron deficiency
. Vitamin deficiency
. Glucose intolerance
. Extramedullary hematopoiesis
.122) A 46-year-old bank executive is referred to the clinic by her dentist. For the past 6 weeks, she has had swollen, bleeding gums. She appears pale and feels weak. She smokes half a pack of cigarettes daily and drinks alcohol socially. Her family history is not significant. Her vital signs are stable. She is afebrile. WBC 44,100 mm3, Hemoglobin 9.0 g/dL, Hematocrit 27%, Platelets 16,000/mm3. Leukocyte distribution: Blast forms 79%, Promonocytes 12%, Monocytes 8%, Lymphocytes 1%. Cytochemical analysis:Sudan black: slightly positive, Alpha-naphthyl esterase: positive, PAS reaction: negative. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. AML with maturation
. Acute promyelocytic leukemia
. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
. Acute erythroleukemia
. Acute monocytic leukemia
.123) A 65-year-old woman is being evaluated for "generalized depression." She has felt weak and fatigued ever since her husband died 4 months ago. She does not have any suicidal thoughts, but is losing interest in her daily activities. She quit smoking 24 years ago, and drinks 1-2 beers weekly. Physical examination reveals pallor and cervical lymphadenopathy. Blood work reveals: Hemoglobin 12.0 g/L, MCV 85 fl, Platelets 224,000/mm3, Leukocyte count 54,500/mm3, Neutrophils 16%, Lymphocytes 75%, Monocytes 9%. Some variants of lymphocytes and smudge cells are present. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Lymphoblastic leukemia
. Hodgkin's disease
. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
. Chronic myeloid leukemia
. Hairy cell leukemia
.124) A 54-year-old male is brought to the emergency department because of severe abdominal pain and diarrhea for the past 24 hours. He is confused and crying out in pain. His temperature is 38.6°C (101.6°F), blood pressure is 82/58 mm Hg, pulse is 118/min, and respirations are 24/min. Physical examination reveals extensive abdominal distention. There is fresh blood in his stools. Intravenous administration of normal saline is started after drawing blood for the necessary laboratory tests. The results of these tests are: Sodium 136 mEq/L, Potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen 32 mg/dL, Creatinine 1.3 mg/dL, Glucose 86 mg/dL, WBC 35,000/mm3, Hemoglobin 13.0 g/dL, Hematocrit 36%, Platelets 460,000/mm3. Leukocyte distribution:Promyelocyte 2%, Myelocytes 7%, Metamyelocytes 18%, Bands 32%, Segmented neutrophils 24%, Lymphocytes 15%. The patient's temperature continues to remain elevated during the night of admission. A broad-spectrum antibiotic is added to the IV infusion. Repeat CBC on the following morning shows a WBC count of 118,000/mm3 with essentially the same differential distribution of leukocytes. His leukocyte alkaline phosphatase score is elevated. What is the most probable diagnosis of this patient?
. CML with blast crisis
. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
. Leukemoid reaction
. Secondary polycythemia
. Myelodysplastic syndrome
.125) A 25-year-old African American man presents to your office complaining of nocturia over the past several months. He reports having to wake to urinate 2 to 3 times per night despite restricting his fluid intake. He denies any back pain, fever, dysuria, or urinary urgency. His past medical history is significant for recurrent otitis media in childhood and hepatitis A infection two years ago. He is sexually active with one partner and does not use condoms. His brother died of a "blood disease" at age 10. The man's hematocrit is 49%. Urinalysis reveals no proteinuria or sediment abnormalities. His nocturia is most likely related to:
Childhood infections
. Nephrolithiasis
. Sexual history
. Family history
. Glomerular pathology
.126) A 25-year-old African American male comes to the office with sudden-onset back pain, dark urine and an one day history of fatigue. Two days ago, he was started on trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for his sinusitis. Otherwise, his past medical history is unremarkable. Physical examination reveals significant pallor. His laboratory report shows: Hb 7.5 g/dl, Total bilirubin 3.5 mg/dl, Direct bilirubin 0.8 mg/dl, Haptoglobin decreased, LDH increased. The peripheral smear shows bite cells. His G6PD level is normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his hemolysis?
. G6PD deficiency
. Pyruvate kinase deficiency
. Galactokinase deficiency
. Sickle cell disease
. Mechanic trauma
.127) A 75-year-old Caucasian male comes to the office for his routine medical check-up. He complains of fatigue for the past month. His previous medical history is significant for calcified aortic valves and hypertension. His vital signs are stable; except for a blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg. Physical examination reveals pallor and a 4+ ejection systolic murmur in the aortic area. Lab reports show: Hb 9 g/dl, MCV 75 fl, Reticulocyte count increased, Serum LDH increased, Haptoglobin decreased, Peripheral smear fragmented RBC. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's anemia?
. Bleeding peptic ulcer
. Diverticulosis
. Macrovascular traumatic hemolysis
. Warm antibody hemolysis
. G6PD deficiency anemia
.128) A 68-year-old unconscious man is brought to the emergency department by a hospice nurse. He had seizures 2 hours ago, after which he lost consciousness. The hospice staff responded by securing his airway and giving him 2L of oxygen. He is in hospice for terminal care for stage IV esophageal carcinoma. He also had a part of his finger removed 1.5 years ago due to a skin cancer. His pulse oximetry reading is 91%. His temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), respirations are 23/min, pulse is 96/min, and blood pressure is 140/85 mmHg. He does not respond to painful stimuli. Rectal examination reveals a hard, irregular surface of an enlarged prostate. His recent prostate specific antigen level is 40. MRI shows an intracranial lesion with bleeding inside, and these findings are consistent with metastasis. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Metastatic prostatic carcinoma
. Glioblastoma multiforme
. Metastatic melanoma
. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the skin
. Metastatic esophageal carcinoma
.129) A 44-year-old woman comes to the office with complaints of weight loss and blood in her stools for the last year. Her mother is on chemotherapy for colon carcinoma. Her maternal uncle also had colon cancer, as did her first cousin who died of colon cancer at the age of 46. She is very worried that she might have the same cancer. Based on her history, she falls within the criteria for Lynch syndrome (also known as HNPCC/ Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer). Apart from the complete work-up for colon cancer, this patient should be evaluated for which of the following condition?
. Pancreatic carcinoma
. Hepatic carcinoma
. Pseudomembranous colitis
. Diverticulitis
. Endometrial carcinoma
.130) A 72-year-old Hispanic man comes to the clinic with complaints of mild headache and lethargy for the past several days. He complains of cough for the past 12 years but, has been bothering him more lately. The cough is mucoid in nature. He has noticed blood in it once in a while. He has been smoking 1 pack/day for 29 years. His Temperature 37C (98.6F); BP 120/84 mmHg; PR 78/min; RR 24/min. On examination of the lungs, adventitious sounds are heard in all the lobes and scant basilar crackles. Laboratory studies show: WBC 7,600/mm3, Hemoglobin 13.6, Hematocrit 40%, Platelets 214,000/mm3, Sodium 131 mEq/L, Potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 18 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen 16 mg/dL, Creatinine 0.6 mg/dL, Glucose 95 mg/dL, Serum osmolality 260 mOsm/kg (275-295 mosm/kg H2O), Urine osmolality 310 mOsm/kg (38-1400 mosm/kg H2O). A chest x-ray shows a 2-centimeter left upper lobe nodule and mediastinal adenopathy your diagnosis is?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
. Squamous cell carcinoma
. Large cell carcinoma
. Small cell carcinoma
. Adenocarcinoma
.131) A 63-year-old Caucasian man reports occasional palpitations when exercising. He denies chest pain. Past medical history includes coronary artery disease status post coronary artery stenting, mitral valve replacement with mechanical valve, and diabetes mellitus. He consumes a well-balanced diet and takes one multivitamin tablet daily. His medications include warfarin, simvastatin, metoprolol, lisinopril, and metformin. Physical examination reveals conjunctival pallor and heart sounds consistent with the presence of a mechanical mitral valve. His hematocrit is 30%. The peripheral blood smear shows occasional schistocytes and his serum LDH level is elevated. His stool is negative for occult blood. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's anemia?
. Iron deficiency
. Folate deficiency
. Traumatic hemolysis
. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
. Autoimmune hemolysis
.132) An 80-year-old female is brought to your office, by her son, because of severe fatigue. She lives alone and is suffering from severe degenerative joint disease, which puts her in a house arrest-type state. Her son usually helps with getting grocery. Her only other medical problem is hypertension. She takes hydrochlorothiazide and acetaminophen. Her vitals are stable. On examination, she has pallor, and evidence of severe degenerative joint disease. Which of the following is the most likely cause of pallor in this patient?
. Vitamin D deficiency
. Vitamin C deficiency
. Iron deficiency
. Folate deficiency
. Chronic hemolysis
.133) A 56-year-old white male comes to the office for a health maintenance visit. He feels healthy, and is "enjoying life as much as possible in a stressed environment." He smokes 2-3 packs of cigarettes daily and drinks socially. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 160/94 mm Hg, pulse is 78/min, and respirations are 14/min. Physical examination reveals plethora of the face and moderate splenomegaly. Blood tests show the following: WBC 15,600/mm3, Hemoglobin 17 gm/dl, Hematocrit 52%, Platelets 550,000mm3, RBC count 7.5 million, Sodium 141 mEq/L, Potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Bicarbonate 22 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen 16 mg/dl, Creatinine 0.6 mg/dl, Glucose 95 mg/dl. The erythrocyte indices are all within normal range. What is the most probable diagnosis?
. Idiopathic hypertension
. Cushing syndrome
. Polycythemia vera
. Congestive heart failure
. Primary hyperaldosteronism
.134) A 49-year-old woman comes to the office and complains of a "strange, itchy rash" on her left areola which has been present for the last month. She tried applying various lotions and creams, but the lesion did not resolve. She denies having other skin conditions, except for a poison ivy rash 2 months ago. She does not take any medications and feels "goofy" when she takes penicillin. Physical examination reveals an eczemoid lesion on the left nipple. No abnormality is visible on the mammogram. Biopsy demonstrates large cells surrounded by halo-like areas which invade the epidermis. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Adenoma of nipple
. Paget's disease
. Scirrhous carcinoma
. Phyllodes tumor
. Lymphocytic carcinoma of breast
.135) A 41-year-old fire-fighter comes to your office and requests for prostate cancer screening. He is concerned because his elder brother was recently diagnosed with prostate cancer, and he read in the paper that "cancers run in families." He requests to be screened urgently, as he "cannot even think of life with such a deadly disease." He has no medical complaints. He has been your patient for the past 6 years, and has no other medical history. He is on a very balanced diet, and adds that he eats a lot of garlic "so that cholesterol remains in check." He takes a low-dose aspirin daily. He does not smoke, and is only a social drinker. He admits using marijuana "once in a while” What is the best next step to address this patient's concerns?
. Transurethral ultrasonogram
. Bone scan
. T ransrectal ultrasonogram
. Perform digital rectal examination
. Needle biopsy
.136) A 27-year-old male presents with dyspnea and fatigue. He has no family history of asthma, heart disease or any blood disorder. His vital signs are stable, and he is afebrile. The only significant findings on examination are pallor and splenomegaly. Lab studies show: Hematocrit 20%, WBC count 4,000/micro-L, Platelet count 85,000/miro-L, Bilirubin 7 mg/dl, Direct bilirubin 1.2 mg/dl, Serum LDH 500 U/L (normal value is 80-280 U/L), Serum haptoglobin 20mg/dl (normal value is 30-220 mg/dl). Peripheral blood smear shows microcytic hypochromic cells. Serum ferritin is low while total iron binding capacity (TIBC) is elevated. Reticulocyte count is 5 %. Urine dipstick testing is positive for hematuria and microscopy of urine shows 1 RBC/HPF. Repeated G6PD assays are normal. Coomb's and micro-Coomb's tests are negative. Bone marrow examination shows hypocellular marrow. Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?
. Aplastic anemia
. G6PD deficiency
. Hereditary spherocytosis
. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
.137) A 44-year-old man who comes to the office because he has had several episodes of hemoptysis for the past two months. He admits to smoking 2-3 packs of cigarettes daily for the last 24 years. Physical examination and chest x-ray are very suggestive of a lung malignancy. Chest CT and bronchoscopy with biopsy are done, and the patient goes on vacation in Aruba. The patient returns to the office after one week, and you are now holding the biopsy result in your hands. It reads, "The tumor has spread to the hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes with bony extension." Which of the following is the most appropriate opening statement?
. "How much would you like to know about your condition?"
. "I am sorry to tell you that you have lung cancer and it is fairly advanced."
. "What do you think of your symptoms?"
. "Unfortunately, the situation is more serious than what I earlier thought."
. "Would you like to have someone else with you as I don't have good news for you?"
.138) A 25-year-old male presents to his physician with dyspnea and fatigue for the last few weeks. He is a non-smoker. He denies any family history of asthma or blood disorders. He does not take any medications. Examination shows pallor, scleral icterus and splenomegaly. Lab tests show the following: Hematocrit 20%, WBC count 10,000/micro-L, Platelet count 180,000/miro-L, Total Bilirubin 7 mg/dl, Direct bilirubin 1 A mg/dl, BUN 10 mg/dl, Serum creatinine 0.7 mg/dl, Serum LDH 400 U/L (normal value is 80-280 U/L), Serum haptoglobin 160mg/dl (normal value is 30-220 mg/dl ), Reticulocyte count 8 %. Peripheral blood smear shows spherocytes with central pallor. Osmotic fragility and direct Coombs' tests are positive Based on these findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?
. Hereditary spherocytosis
. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
. Sickle cell anemia
. G6PD deficiency
.139) A 10-year-old white boy is brought to the office by his foster parents for the evaluation of severe pain in his left knee for the last few days. His left knee has been hurting so bad that he is now unable to play with his peers. The pain is continuous and non-radiating. His knee appears swollen, but he denies any history of trauma. His family history is unknown. His vital signs are stable. Physical examination reveals a pale young boy. The left knee is tender, erythematous and swollen. Blood tests reveal: WBC 12,600/mm3, Hemoglobin 9.3 g/dl, Hematocrit 29%, Platelets 201,000/mm3, ESR 40. X-ray of the knee reveals that the lower end of the femur has a central lytic lesion, onion skinning and a moth-eaten appearance with some extension into the soft tissue. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Osteomylitis
. Ewings sarcoma
. Chondrosarcoma
. Glomus tumor
. Fibrosarcoma
.140) A 56-year-old woman is complaining of cough for the past 4 months. The cough was dry initially, but only yesterday she was scared-to-death to see phlegm with blood. She is not feeling well and thinks that she has lost "a lot of weight" recently, despite no apparent change in her diet. She swears that she has never smoked a cigarette in her life. There is no history of night sweats nor contact with any person with similar complaints. She is a housewife who rarely drinks, and can't think of using recreational drugs. She is completely faithful to her husband. Her husband is also a "religious non-smoker". Her vitals are stable and lung examination reveals no significant findings. Her chest x-ray shows 1.5cm lesion in the right peripheral lung field and no evidence of any hilar or mediastinal lymph node enlargement. What is the most probable diagnosis?
. Tuberculosis
. Sarcoidosis
. Small cell carcinoma of lung
. Squamous cell carcinoma of lung
. Adenocarcinoma of lung
.141) A 74-year-old immigrant from Colombia comes to the office and complains of having "all sorts of problems of old age." He has pain all over his body. He often has headaches and feels dizzy. He has visual problems, and finds it difficult to walk. For the last several weeks, he has been feeling weak and numb in his feet. He lives with his son, and is not happy with the way his son treats him; however, he denies receiving any form of physical abuse. His past medical history is unremarkable. His mother had "some blood disease." His vital signs are stable. Physical examination reveals multiple bruises on his body, and sensory deficits in his feet. Other significant findings include lymphadenopathy and hepatosplenomegaly. Ophthalmoscopy shows dilated, segmented, and tortuous retinal veins. Laboratory studies show: WBC 10,200 /mm3, Hemoglobin 9.6 g/dl, Hematocrit 29%, Platelets 94,000 /mm3, Sodium 141 mEq/L, Potassium 3.6 mEq/L, Blood urea nitrogen 18 mg/dl, Creatinine 0.8 mg/dl, Glucose 115 mg/dl. Serum protein electrophoresis reveals an lgM spike. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
. Multiple myeloma
. Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance
. Elderly abuse
. Heavy chain disease
.142) A 25-year-old white female presents to the clinic with persisting pain in her wrists and ankles for the last 3 months. The pain is 3/10 in intensity, and partially relieved by ibuprofen. She also has a rash on her face. She denies smoking, and drinks alcohol occasionally. Her temperature is 37.3°C (99.2°F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, pulse is 79/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical examination reveals swollen joints of the hands and ankle, as well as erythema over the bridge of the nose and the upper cheeks. There is no muscle weakness. Labs show: Hemoglobin 11.0 g/dL, Hematocrit 33%, Platelets 240,000/mm3, WBC 13,600/mm3. Leukocyte distribution:Segmented neutrophils 76%, Lymphocytes 20%, Bands 2%, Monocytes 2%. RF, ANA, and antibodies to double stranded-DNA are positive in high titers. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Scleroderma
. Systemic lupus erythematosus
. Dermatomyositis
. Polymyositis
. Mixed connective tissue disease
143) A 23-year-old man presents to the emergency room complaining of severe abdominal pain. He has also suffered from nausea and vomiting for several hours. His past medical history is insignificant, but his brother has had similar problems. He denies risky sexual behavior and intravenous drug use. On exam, his temperature is 38.8°C (101.8°F), heart rate is 102/min, and respirations are 14/min. There is tenderness in the right upper quadrant exacerbated by deep inspiration. The liver span is 7 cm. His spleen is palpated 2 cm below the left costal margin. There are no peritoneal signs. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute viral hepatitis
. Acute pancreatitis
. Gaucher's disease
. Hodgkin's lymphoma
. Hereditary spherocytosis
.144) A 60-year-old Vietnam war veteran comes for his annual examination. He does not have any complaints, other than getting tired very quickly. Physical examination reveals pallor and an enlarged spleen. CBC reveals: WBC 14,000/cmm, Hemoglobin 9.9 g/dL, Hematocrit 30%, Platelets 100,000/cmm. The lymphocytes have fine, irregular cytoplasmic projections. Cytochemical testing reveals a strong acid phosphatase reaction, which is not inhibited by tartaric acid. What is the most probable diagnosis?
. Lymphoblastic leukemia
. Hairy cell leukemia
. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
. Chronic myeloid leukemia
. Hodgkin's disease
.145) A 47-year-old woman comes to the office and complains of burning abdominal pain which has been present for the past 3 months, is grade 6/10 in severity, continuous, and relieved by taking antacids. She also complains of some constipation. Her father has a history of "ulcers in his belly." She works as a floor secretary in a surgical ward, and is not happy with her new boss. She denies any weight loss or decreased appetite. Her temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), blood pressure is 130/85 mm Hg, heart rate is 78/min, and respirations are 14/min. She is awake, alert, and oriented. The abdominal examination reveals normoactive bowel sounds and tenderness in the epigastric region, but no palpable mass. Her stools are occult blood positive. ECG reveals increased PR and shortened QT intervals. The laboratory results reveal the following: Sodium 137 mEq/dL, Potassium 4.2 mEq/dL, Chloride 101 mEq/dL, Bicarbonate 27 mEq/dL, Calcium 12.0 mg/dl, Phosphorus 2.2 mg/dl, BUN 37 mg/dl, Creatinine 1.8 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Glucagonoma
. Stress ulcer
. Parathyroid adenoma
. Vitamin-D toxicity
. Metastatic gastric carcinoma
.146) A 21-year-old Caucasian man bumped into a table in his living room two days ago and now presents to the emergency department with a swollen and tender right thigh. Pulsation is decreased over the right popliteal artery. His uncle suffered from a "blood clotting disease". This patient's history is most likely to reveal which of the following episodes in his past?
. Occasional tarry stools
. Spontaneous bruises
. Joint swelling
. Cola-colored urine
. Red papules over his trunk and lips
.147) A 7-year-old Caucasian boy is brought to your office for a routine check-up. He underwent splenectomy one year ago for persistent anemia and jaundice. He has received pneumococcal vaccination and takes penicillin prophylaxis. His uncle underwent splenectomy for "some blood disorder" in his childhood. His blood hemoglobin level is 11.5 mg/dL and MCV is 90 fl. Blood smear demonstrates occasional red blood cells with single, round, blue inclusions on Wright stain. The latter finding is most likely related to?
. Hemoglobin precipitation
. Low reticulocyte count
. Penicillin therapy
. Mechanical RBC damage
. Splenectomy
.148) A 25-year-old white female presents with a 5-day history of sore throat, extreme fatigue, and headaches. She has just returned from a spring break in Jamaica where she had "the time of her life." She smokes 2-3 cigarettes daily and occasionally drinks alcohol. Her vital signs are stable. She is afebrile. Physical examination reveals posterior cervical lymphadenopathy, mild splenomegaly, and exudative pharyngitis. Palatal petechiae are present. CBC shows: WBC 16,000/cmm with 55% lymphocytes, Hemoglobin 13 .5gm/dl, Hematocrit 4 1%, Platelets 216,000/cmm. Many variant forms of lymphocytes are seen, including cells with convoluted nuclei and highly vacuolated cytoplasm. Rapid streptococcal throat test, urinalysis, and heterophilic antibody test are all negative. What is the most likely diagnosis?
. Acute myeloid leukemia
. Chronic myeloid leukemia
. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
. Infectious mononucleosis
.149) A 2-year-old boy is brought by his mother to the emergency department because of a high-grade fever which "does not go away" with acetaminophen. For the last four days, the child has been very irritable and is crying a lot. He is also pulling his ear and not eating well. He has been generally well, other than the occasional sore throat this season. His temperature is 38.8°C (102.2°F), blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, pulse is 119/min, and respirations are 24/min. He appears well nourished, but is irritable. Physical examination reveals enlarged cervical lymph nodes and splenomegaly. The tympanic membranes are inflamed. CBC shows: WBC 81,100 /mm3, Hemoglobin 8.0 g/dL, Hematocrit 25%, Platelets 16,000 /mm3, Blast forms 80%, Prolymphocytes 10%, Lymphocytes 10%. The blast cells have condensed nuclear chromatin, small nucleoli and scant agranular cytoplasm. Subsequent histochemical staining reveals strongly positive periodic acid Schiff (PAS) reaction. No Auer rods were seen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Burkitt lymphoma
. Acute myelocytic leukemia
. Prolymphocytic leukemia
. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia
. Myelodysplastic syndrome
{"name":"Dx med p3 * Q1 to 50 n Q 100 to 150 fb", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1) A 63-year-old white female presents with a thyroid nodule. She denies any weight loss, change in appetite, diarrhea, heat or cold intolerance, menstrual irregularities, hoarseness and dyspnea. Her past medical history is unremarkable. There is no family history of thyroid cancer. She does not take any medications. Physical examination shows a 4-5 cm, fixed, hard, and non-tender thyroid nodule. There is cervical lymphadenopathy. Her serum TSH level is normal. Fine needle aspiration (FNA) of the thyroid shows malignant cells. Which of the following is the most likely expected pathology on FNA?, .2) A 36-year-old female presents with headaches and visual problems. She also complains of palpitations, heat intolerance and weight loss. Her past medical history is unremarkable. She is currently on no medications. Her blood pressure is 130\/60 mmHg, heart rate is 100\/min and regular, and weight is 152 lb (weight one year ago was 170 lb). Physical examination reveals a symmetrically enlarged thyroid gland without any tenderness. Auscultation of the chest reveals tachycardia. She has bitemporal hemianopsia on confrontation. The rest of the physical examination is unremarkable. Her lab investigations show: Serum T3 222 ng\/mL, Serum T4 13.9 mcg\/dL, Serum TSH 7.9 IU\/mL, Alpha subunit level elevated. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?, .3) A 35-year-old male presents with complaints of weakness and fatigue of one year's duration. He is anorexic and has lost interest in all his activities. He also complains of cold intolerance and constipation. His blood pressure is 98\/72 mmHg, temperature is 37.1°C (99°F), respirations are 14\/min, and pulse is 50\/min. His skin is dry and rough, nails are brittle, and hair is thin. There is no hyperpigmentation of the skin. Delayed deep tendon reflexes are noted on neurological examination. Lab studies show: Hemoglobin 10.2 g\/dL, WBC count 5,000\/micro-L, Neutrophils 45%, Monocytes 5%, Eosinophils 10%, Basophils 1%, Lymphocytes 40%, Serum sodium 135 mEq\/L, Serum potassium 4.0 mEq\/L. Which of the following is most consistent with this patient's findings?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}
More Quizzes
Can You Guess These Superheroes Without Their Uniform?
23120
HOW MUCH DO YOU KNOW ABOUT THE COUPLE ?
1267
TRANSFORMERS G1 RAAAH
19109
Word Match Challenge
420
Which Soccer Player Are You? Free Personality
201021702
ECG Test Online - Basic Interpretation (Free)
201021445
Days of the Week - Free Online Practice
201019848
Five Senses (Grade 3) - Free Science Review
201018365
Water Potential Practice Problems - Free with Answers
201019161
Sabrina Carpenter - Bestie or Rival?
201018796
Harry Potter for Kids - Which Character Are You?
201019746
Neurotransmitters Practice - Test Your Knowledge
201017434