APWH unit 3 test review

APWH Unit 3 Test Review
Prepare for your AP World History exam with our comprehensive quiz focused on Unit 3. This quiz covers major themes, events, and concepts from the period, including economic exchanges, demographic changes, and cultural interactions.
- 55 multiple-choice questions
- Diverse topics reflecting key historical events
- Instant feedback on answers


Based on the description of the discovery of silver in Zacatecas in the second paragraph, which of the following conclusions about Mota y Escobar is best supported?
“Migration of man and his maladies is the chief cause of epidemics. And when migration takes place, those creatures who have been in isolation longest suffer most, for their genetic material has been least tempered by the variety of world diseases. Among the major subdivisions of the species Homo Sapiens, the American Indian probably had the dangerous privilege of the longest isolation from the rest of mankind.”
Alfred Crosby, world historian, 1967
Which of the following best describes Alfred Crosby’s argument in the passage above?
Historians consider the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries to be a time of great change in cultivation methods and in the physical landscape of Latin America.
Which of the following pairings was most responsible for these changes?
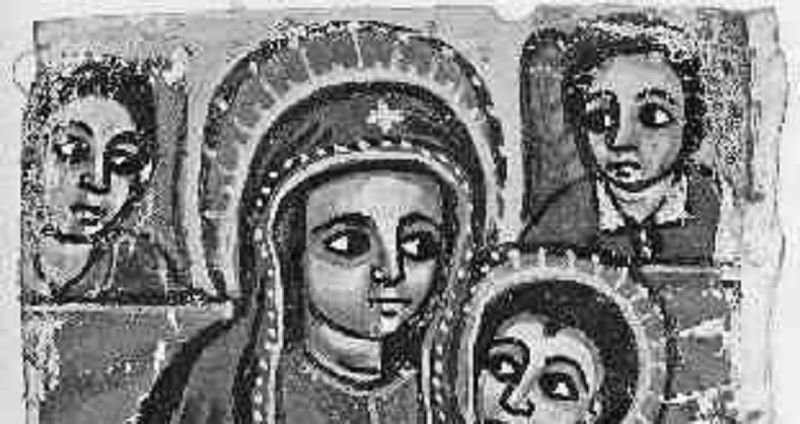





“During the reign of the Hebrew king Solomon, son of David, the Ethiopian Queen of Sheba, learning of his reputation for wisdom, came from Ethiopia to see and to hear him. Solomon, who had seven hundred queens as wives, received the Queen of Sheba into their number even though she was black. And when she later bore him a son in Ethiopia, she named him after his grandfather, David. This prince, wishing to receive the blessing of his father, came to Jerusalem when he was 22 years old. Solomon not only recognized him as his son, but had him anointed in the Temple, with all proper royal ceremony, as king of Ethiopia. This is the origin of the emperors of Ethiopia, one thousand years before the incarnation of the Son of God. Thus, when the Son of God became man and took the blood of the descendants of David, he had already given that same blood to the blacks of Ethiopia.”
Sermon delivered by Antonio Vieira, Portuguese Jesuit priest, to plantation workers in Bahia, Brazil, 1633
The sermon delivered by Vieira is best seen as evidence for which of the following?
“Wila Uma, the Inca general, addressed the Spanish [conquistadors] with the following words: ‘What are you doing to our ruler?* This is how you repay his good will? Did he not command all of his people to give you tribute? Did he not give you a house filled with gold and silver? Did he not give you his servants to serve you? What more can he give you now that you have imprisoned him? All the people of this land are so distressed by your actions, because they have lost all they possess, and their distress leaves them no choice but to hang themselves or risk everything by rebelling. Thus, I believe it would be best for you to release him from this prison to lessen the grief of these people.’ . . .
*Manco Inca, a previous Inca ruler and father of Titu Cusi, whom the Spanish had imprisoned after conquering the Inca capital of Cuzco in 1533
Titu Cusi, ruler of a regional Inca state established after the Spanish had conquered the Inca Empire,letter to the Spanish king detailing the abuses of the Spanish during the conquest, 1570
The sentiments expressed in the passage most directly indicate
“Wila Uma, the Inca general, addressed the Spanish [conquistadors] with the following words: ‘What are you doing to our ruler?* This is how you repay his good will? Did he not command all of his people to give you tribute? Did he not give you a house filled with gold and silver? Did he not give you his servants to serve you? What more can he give you now that you have imprisoned him? All the people of this land are so distressed by your actions, because they have lost all they possess, and their distress leaves them no choice but to hang themselves or risk everything by rebelling. Thus, I believe it would be best for you to release him from this prison to lessen the grief of these people.’ . . .
*Manco Inca, a previous Inca ruler and father of Titu Cusi, whom the Spanish had imprisoned after conquering the Inca capital of Cuzco in 1533
Titu Cusi, ruler of a regional Inca state established after the Spanish had conquered the Inca Empire,letter to the Spanish king detailing the abuses of the Spanish during the conquest, 1570
Which of the following is the most likely purpose of Titu Cusi’s letter?
[Testimony by the creole (European-ancestry) members of a lay religious brotherhood in the town of San Juan Peribán.]
“Cristobál Bernal was elected chair of our brotherhood by a margin of only two votes. Most votes in Bernal’s favor came from mulatto and mestizo brothers. However, we, the creole brothers, elected Don Carvajal, a resident of the town and owner of the hacienda and sugar mill there. We urge you to command that only creoles should vote for the positions of chair and deputy chairs and that neither mulattoes nor mestizos can serve in those positions, and that a new election must be held for these positions.”
[Response by the mulatto and mestizo brothers]
“Since the brotherhood was founded, it has had the ancient custom of voting for and electing mulattoes and mestizos as deputies. And mestizos and mulattoes make up most of the membership and help the brotherhood grow. And mestizo and mulatto brothers had donated land, which earns 25 pesos rent per year for the brotherhood. And mulatto and mestizo brothers also collect alms for the brotherhood. If this brotherhood were actually two—one for creoles only and the other for mulattoes and mestizos—then the petitioners might have a case. But there is only one brotherhood in which creoles, mestizos, and mulattoes are mixed and, being members of it, they must enjoy the rights and advantages of the said brotherhood. Without question these rights should include voting and electing their own chair and deputies.”
[Judge’s decision]
“The election is declared valid, and Bernal is confirmed as chair.”
The dispute described in the court case is most directly an effect of which of the following processes in colonial American societies?
“When we were in Canton, a port in southern China, we came across a woman who cried out in Portuguese ‘Our Father, who art in Heaven, hallowed be thy name.’ And because she could speak no more of our language, she very earnestly asked us in Chinese to tell her whether we were Christians. We replied that we were, and for proof we repeated all the rest of the Lord’s Prayer which she had left unsaid. Being assured that we were Christians, she pulled us aside, and weeping said to us, ‘Come along, Christians from the other end of the world, with your true sister in the faith of Jesus Christ.’
Furthermore, she told us that she was named Inez de Leyria, and her father was a great ambassador from Portugal to the Emperor of China. The ambassador married her mother, a Chinese woman, and made her a Christian. Along with her, many were converted to the faith of Christ.
During the five days we remained in her house, we made them a little book in Chinese, containing many good prayers.”
Account of Fernão Mendes Pinto, Portuguese explorer and merchant, circa
The activities of Inez de Leyria’s father as described in the passage best support which of the following conclusions about the period 1450–1750 C.E.?
“When we were in Canton, a port in southern China, we came across a woman who cried out in Portuguese ‘Our Father, who art in Heaven, hallowed be thy name.’ And because she could speak no more of our language, she very earnestly asked us in Chinese to tell her whether we were Christians. We replied that we were, and for proof we repeated all the rest of the Lord’s Prayer which she had left unsaid. Being assured that we were Christians, she pulled us aside, and weeping said to us, ‘Come along, Christians from the other end of the world, with your true sister in the faith of Jesus Christ.’
Furthermore, she told us that she was named Inez de Leyria, and her father was a great ambassador from Portugal to the Emperor of China. The ambassador married her mother, a Chinese woman, and made her a Christian. Along with her, many were converted to the faith of Christ.
During the five days we remained in her house, we made them a little book in Chinese, containing many good prayers.”
Account of Fernão Mendes Pinto, Portuguese explorer and merchant, circa
The ability of Portuguese merchants and explorers to communicate with the local population of Canton was most likely an effect of which of the following?
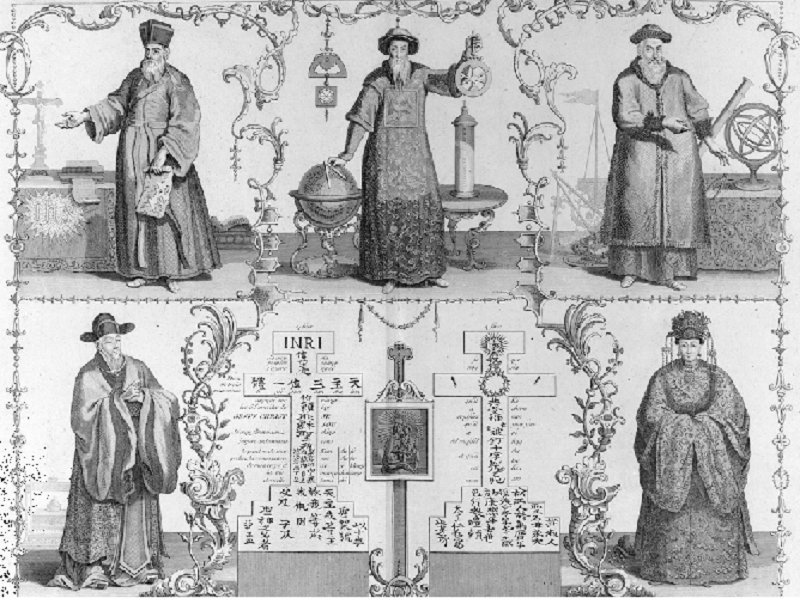
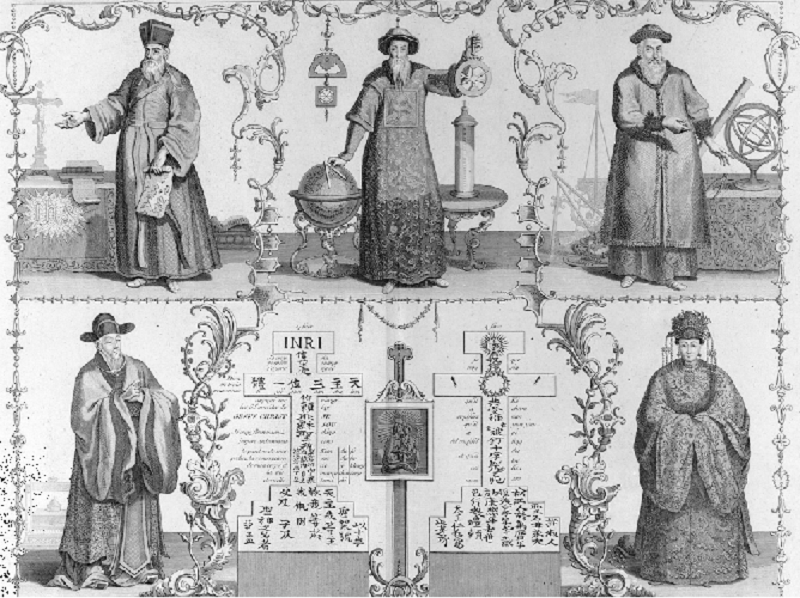
In the top panel, the engraving shows three Jesuit missionaries and scholars who served at the courts of Chinese emperors of the Ming and Qing dynasty in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. In the bottom panel, the engraving shows two Chinese Christian converts: Xu Guangxi (left) and his granddaughter, Candida Xu (right).
In the context of the period 1450–1750, which of the following most likely explains why the Qing government employed the scholars shown in the image?
“The Muslims are not the greatest traders in Asia, though they are dispersed in almost every part of it. In Ottoman Turkey, the Christians and Jews carry on the main foreign trade, and in Persia the Armenian Christians and Indians. As to the Persians, they trade with their own countrymen, one province with another, and most of them trade with the Indians. The Armenian Christians manage alone the whole European trade [with Persia].
The abundance of the Persian silk that is exported is very well known. The Dutch import it into Europe via the Indian Ocean to the value of near six hundred thousand livres* yearly. All the Europeans who trade in Ottoman Turkey import nothing more valuable than the Persian silks, which they buy from the Armenians. The Russians import it as well.
Persia exports to the Indies [an] abundance of tobacco, all sorts of fruit, marmalade, wines, horses, ceramics, feathers, and Turkish leather of all colors, of which a great amount is exported to Russia and other European countries. The exportation of steel and iron is forbidden in the kingdom, but it is exported notwithstanding.
There are some Persian traders who have deputies in all parts of the world, as far as Sweden on the one side and China on the other side.”
*French currency unit
Jean Chardin, French jeweler and merchant, on his travels to Safavid Persia, 1686
Based on the passage, in which of the following ways were Safavid Persian trading practices similar to those of other land-based Islamic empires during the seventeenth century?



“In the context of the Ottoman Empire, toleration [ensured] that, as a rule, non-Muslims would not be persecuted. No doubt, as dhimmis,* according to Islam, they were second-class citizens . . . Who endured a healthy dose of daily prejudice. [Nevertheless, the Ottomans tolerated religious and ethnic difference] because it had something to contribute. That is, difference added to the empire; it did not detract from it and, therefore, it was commended. Toleration had a [beneficial] quality; maintaining peace and order was good for imperial life, diversity contributed to imperial welfare. . . .
The Ottoman Empire fared better than did its predecessors or contemporaries [in tolerating religious and ethnic difference] until the beginning of the eighteenth century, largely as a result of its understanding of difference and its resourcefulness in [administrative organization]. It maintained relative peace with its various communities and also ensured that interethnic strife would not occur.”
*Islamic law defines dhimmis as non-Muslim communities living under Muslim political rule
Karen Barkey, Turkish-American historian and sociologist, Empire of Difference: The Ottomans in Comparative Perspective, published in 2008
All of the following statements about the Ottoman Empire in the period 1450–1750 are factually accurate. Which would most strongly support Barkey’s claim regarding the Ottoman state and toleration in the passage?
“Let the blessings of Allah be upon Muhammad and his companions universally. In the year 1640 C.E. I wanted to behold the mystics of every sect, to hear the lofty expressions of monotheism, and to cast my eyes upon many books of mysticism. I, therefore, examined the Book of Moses, the Gospels, and the Psalms.
Among the Hindus, the best of their heavenly books, which contain all the secrets of pure monotheism, are called the Upanishads. Because I do not know Sanskrit, I wanted to make an exact and literal translation of the Upanishads into Persian*. For the Upanishads are a treasure of monotheism and there are few thoroughly conversant with them even among the Indians. Thereby I also wanted to make the texts accessible to Muslims.
I assembled Hindu scholars and ascetics to help with the translation. Every sublime topic that I had desired or thought and had looked for and not found, I obtained from these most ancient books, the source and the fountainhead of the ocean of religious unity, in conformity with the holy Qur’an.”
*Persian was the primary language used at the Mughal court.
Dara Shikoh, son of the Mughal ruler Shah Jahan, account of the translation of the Upanishads into Persian, 1657 C.E.
Dara Shikoh’s intellectual collaborations as described in the passage are most consistent with which of the following policies of imperial states such as the Mughal Empire in the period 1450 to 1750 C.E.?
Source 1:
“[In the sixteenth through the eighteenth centuries] Europeans derived more profit from their participation in trade within Asia than they did from their Asian imports into Europe. They were able to do so ultimately only thanks to their American silver. . . . Only their American money, and not any ‘exceptional’ European ‘qualities’ permitted the Europeans [to access Asian markets]. . . . However, even with that resource and advantage, the Europeans were no more than a minor player at the Asian, indeed world, economic table [until the nineteenth century].”
Andre Gunder Frank, ReOrient: Global Economy in the Asian Age, 1996
Source 2:
“The societies of Europe had been at the margins of the great trading systems, but they were at the center of the global networks of exchange created during the sixteenth century because they controlled the oceangoing fleets that knit the world into a single system. Western Europe was better placed than any other region to profit from the vast flows of goods and ideas within the emerging global system of exchange. . . . [European states] were keen to exploit the commercial opportunities created within the global economic system. They did so partly by seizing the resources of the Americas and using American commodities such as silver to buy their way into the markets of southern and eastern Asia, the largest in the world.”
David Christian, This Fleeting World: A Short History of Humanity, 2008
The two interpretations of economic history of the early modern period differ most strongly concerning
Source 1:
“[In the sixteenth through the eighteenth centuries] Europeans derived more profit from their participation in trade within Asia than they did from their Asian imports into Europe. They were able to do so ultimately only thanks to their American silver. . . . Only their American money, and not any ‘exceptional’ European ‘qualities’ permitted the Europeans [to access Asian markets]. . . . However, even with that resource and advantage, the Europeans were no more than a minor player at the Asian, indeed world, economic table [until the nineteenth century].”
Andre Gunder Frank, ReOrient: Global Economy in the Asian Age, 1996
Source 2:
“The societies of Europe had been at the margins of the great trading systems, but they were at the center of the global networks of exchange created during the sixteenth century because they controlled the oceangoing fleets that knit the world into a single system. Western Europe was better placed than any other region to profit from the vast flows of goods and ideas within the emerging global system of exchange. . . . [European states] were keen to exploit the commercial opportunities created within the global economic system. They did so partly by seizing the resources of the Americas and using American commodities such as silver to buy their way into the markets of southern and eastern Asia, the largest in the world.”
David Christian, This Fleeting World: A Short History of Humanity, 2008
The main arguments of the two sources are most similar in their emphasis on the

“Many [Ottoman] Sunni religious scholars have labeled the Sufi whirling rituals* as ‘dancing,’ and have pronounced them forbidden, branding those who approve of them as infidels. The Sufis counter that these rituals are not dancing, arguing instead that they enliven the soul through a combination of music and movement, which, they say, allows them to focus on the spiritual aspects of religion. The common people flock to the Sufis, giving them offerings and gifts. Since their whirling rituals play a big part in their popularity, they will not abandon these practices anytime soon. The Sunni scholars have written many tracts and opinions against them . . . And this tug-of-war between the two parties has brought them into a vicious circle.”
*religious observances practiced by some Sufis in the Ottoman Empire
Katip Çelebi, Ottoman official, The Balance of Truth, philosophical and scientific treatise, 1656
Which of the following conclusions regarding the Ottoman Empire is best supported by the passage?
“To the count of Katzenellenbogen, Ziegenhain, and Nidda, my gracious lord.
Pope Leo X, in the bull in which he put me under the ban, condemned my statement that ‘to fight against the Turk is the same thing as resisting God, who visits our sin upon us with this rod.’ I still confess freely that this statement is mine. The popes and bishops called for war against the Turks in the name of Christ. Yet because Christ taught that Christians shall not resist evil with violence or take revenge, it is against His name.
In how many wars against the Turks have the bishops and clergy prevented Christians from enduring heavy losses? Indeed, the king of Hungary and his bishops were beaten by the Turks at Varna* and more recently a German army would perhaps have fought with more success, if it had not contained priests. If I were an emperor, a king, or a prince in a campaign against the Turks, I would encourage my bishops and priests to stay at home and mind the duties of their office, praying, fasting, saying mass, preaching, and caring for the poor, as not only Holy Scripture, but their own canon law teaches and requires. To this I say Amen, Amen.”
*a reference to a failed Christian Crusade launched against the Ottoman Turks in 1444
Martin Luther, German theologian, sermon addressed to a German prince, 1528
A historian interpreting the views expressed in the passage would likely explain that those views were most strongly influenced by Protestant desires to