NMDCAT Bio Quiz : Coordination and Control/Nervous & Chemical Coordination

NMDCAT Biology Quiz: Coordination and Control
Test your knowledge of the nervous system and its intricate mechanisms with our comprehensive NMDCAT Biology Quiz! This quiz consists of 58 expertly crafted multiple-choice questions covering key concepts in coordination and control, including neurological disorders, brain structures, and neurotransmitters.
Whether you're preparing for an exam or simply want to challenge yourself, this quiz is designed to help you:
- Enhance your understanding of nervous system fun
ctions - Identify key neurological conditions
- Improve your exam readiness with practical questions
1-Over-activity of sympathetic nervous system causes: A) Disturbance of vision C) Decrease in blood pressure B) Constipation D) Increase in heart rate
A
B
C
D
2-Which structures respond when they are stimulated by impulse coming through motor neuron? A) Receptors C) Effectors B) Responses D) Transducers
A
B
C
D
3-Respiratory center is located in: A) Cerebrum C) Medulla B) Cerebellum D) Hypothalamus
A
B
C
D
4-A neurological condition characterized by involuntary tremors, diminished motor activity and rigidity is called: A) Epilepsy C) Alzheimer’s disease B) Parkinson’s disease D) Cerebellar tremors
A
B
C
D
5-The part of neuron fiber which conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body is: A) Dendron C) Axon B) Dendrites D) Peripheral branch
A
B
C
D
6-The number of cranial nerves in humans is: A) 31 pairs C) 24 pairs B) 12 pairs D) 62 pairs
A
B
C
D
7-The part of brain which controls breathing, heart rate and swallowing is: A) Cerebrum C) Medulla B) Cerebellum D) Hypothalamus
A
B
C
D
8-Cause of Parkinson’s disease is death of brain cells that produce: A) Dopamine C) ADH hormone B) Acetylcholine D) Oxytocin
A
B
C
D
9-Thalamus and cerebrum are the part of: A) Spinal cord C) Hind brain B) Forebrain D) Mid brain
A
B
C
D
10-There is also evidence that high levels of ___________ may contribute to the onset of Alzheimer’s disease: A) Ca C) Mo B) Mg D) A
A
B
C
D
11-L-dopa or levodopa is used to get some relief from: A) Epilepsy C) Alzheimer’s disease B) Parkinson’s disease D) Dementia
A
B
C
D
12-The structures which respond when they are stimulated by impulse coming through motor neuron are: A) Effectors C) Responsers B) Receptors D) Transductors
A
B
C
D
13-The right and left cerebral hemispheres are connected by a thick band of nerve fibers called: A) Medulla C) Pons B) Corpus callosum D) Hippocampus
A
B
C
D
14-The part of the brain which guides smooth and accurate motions and maintains body position is called: A) Cerebrum C) Pons B) Cerebellum D) Medulla
A
B
C
D
15-Which one of the following is the effect of sympathetic nervous system? A) Constriction of bronchi C) Promotes digestion or peristalsis B) Decrease in heart rate D) Dilates the pupil
A
B
C
D
16-High levels of aluminum may contribute to the onset of which one of the following? A) Parkinson’s disease C) Alzheimer’s disease B) Epilepsy D) Gonorrhea
A
B
C
D
17-Which disease is responsible for dementia (memory loss)? A) Parkinson’s disease C) Epilepsy B) Alzheimer’s disease D) Grave’s disease
A
B
C
D
18-Neurotransmitter secreted at synapse outside the central nervous system is: A) Dopamine C) Androgen B) Polypeptide D) Acetylcholine
A
B
C
D
19-Conduction of action potentials from one node of Ranvier to another in myelinated neurons is through: A) Hyperpolarization C) Depolarization B) Resting membrane potential D) Saltatory conduction
A
B
C
D
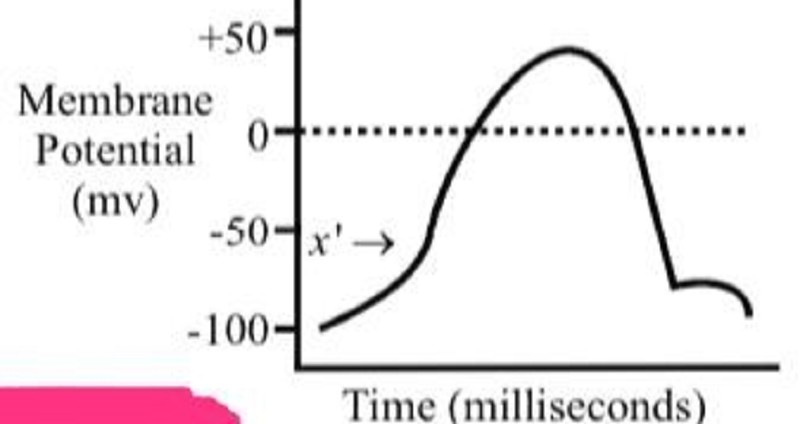
20-9 In the following diagram of action potential in a neuron, “x” depicts A) Depolarization C) Repolarization B) Polarization D) Hyperpolarization
A
B
C
D
21-Random, uncontrolled activity of some cells in the brain leading to chaotic activity in both sensory and motor nerves causes patients of to see and hear different strange things. A) Epilepsy C) Alzheimer’s disease B) Parkinson’s disease D) Huntington’s disease
A
B
C
D
22-Part of hind brain responsible for the balance and equilibrium of body is called: A) Medulla C) Pons B) Cerebellum D) Thalamus
A
B
C
D
23-Brain is protected and enclosed in: A) Lumbar vertebrae C) Vertebral column B) Coccyx D) Cranium
A
B
C
D
24-Humans have homeostatic thermostat present in a specified portion of the brain that is: A) Lateral ventricle C) Spinal cord B) Thalamus D) Hypothalamus
A
B
C
D
25-The disease in which death of small number of cells in the basal ganglia leads to inability to select and initiate patterns of movement is known as: A) Fever C) Epilepsy B) Alzheimer’s disease D) Parkinson’s disease
A
B
C
D
26-A neurological disorder characterized by the decline in brain function is _________. Its symptoms are similar to those diseases that cause dementia: A) Parkinson’s disease C) Alzheimer’s disease. B) Epilepsy D) Diabetes
A
B
C
D
27-The nerve impulse which jumps from node to node in myelinated neurons is: A) Resting membrane potential C) Threshold stimulus B) Saltatory nerve impulse D) Initial nerve impulse
A
B
C
D
28-The CNS is protected by: A) Three layers of meninges C) Four layers of meninges B) One layer of meninx D) Two layers of meninges
A
B
C
D
29-White matter of spinal cord is made up of: A) Sensory nerve fibres C) Motor nerve fibres B) Myelinated nerve fibres D) Mixed nerve fibres
A
B
C
D
30-There is evidence that high levels of aluminum may contribute to the onset of: A) Parkinson’s disease C) Lesch-Nyhan syndrome B) Alzheimer’s disease D) Fragile X-syndrome
A
B
C
D
31- Pick out the pressure receptors: A) Chemoreceptors C) Photoreceptors B) Mechanoreceptors D) Thermoreceptors
A
B
C
D
32-Which of the following produce response: A) Effectors C) Nerve B) Stimulators D) Brain
A
B
C
D
33-Band of axons between two hemispheres is called: A) Corpus callosum C) Synapsis B) Corpus luteum D) Sunapse
A
B
C
D
34-Reflexes of eyes is detected by which part of brain: A) Mid brain C) Hind Brain B) Fore brain D) Cerebral hemisphere
A
B
C
D
35-Spinal cord is protected by how many layers of menninges: A) 1 C) 3 B) 2 D) 4
A
B
C
D
36-Neurosecretory cells are present in which part of brain? A) Hypothalamus C) Pons B) Hindbrain D) Cerebellum
A
B
C
D
37-Which of the following is the function of glucagon hormone? A) Glycogen → Glucose C) Glucose → Lipid B) Glucose → Glycogen D) Glucose → Protein
A
B
C
D
38-Addison’s disease is caused due to destruction of: A) Adrenal cortex C) Adrenal medulla B) Pituitary adrenal axis D) Hypothalamus
A
B
C
D
39-Which group of hormones is made up of amino acids and their derivatives? A) Vasopressin and antidiuretic hormone C) Oestrogen and testosterone B) Epinephrine and nor-epinephrine D) Insulin and glucagon
A
B
C
C
40-Ductless glands are known as: A) Endocrine glands C) Salivary glands B) Exocrine glands D) Bile glands
A
B
C
D
41-Gastrin is the hormone which is produced by the: A) Liver C) Pyloric region of stomach B) Adrenal gland D) Mucosal lining of intestine
A
B
C
D
42-Beta-cells of liver secrete a hormone that is called: A) Insulin C) Antidiuretic hormone B) Glucagon D) Gastrin
A
B
C
D
43-Vasopressin and Oxytocin are released from the: A) Placenta C) Anterior pituitary B) Ovary D) Posterior pituitary
A
B
C
D
44-Chemically, insulin and glucagon are: A) Carbohydrates C) Lipids B) Proteins D) Nucleic acids
A
B
C
D
45-Hormones secreted by anterior pituitary and which control the secretions of hormones of other endocrine glands are known as: A) Release factor C) Accelerator B) Inhibitor D) Tropic or trophic hormone
A
B
C
D
46-Alpha (a) cells of islets of Langerhans secrete hormone called: A) Glucocorticoid C) Glucagon B) Insulin D) Aldosterone
A
B
C
D
47-Which of the following is a steroid hormone? A) Glucagon C) Epinephrin B) Thyroxine D) Oestrogen
A
B
C
D
48-The gonadotrophic hormones of anterior lobe of pituitary include: A) Prolactin, Thyroid stimulating hormone, Somatotrophin hormone B) Follicle stimulating hormone, Luteinizing hormone, Prolactin C) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone, Luteinizing hormone, Follicle stimulating hormone D) Lutenizing hormone, Follicle stimulating hormone, Thyroid stimulating hormone
A
B
C
D
49-Over activity of cortical hormone of adrenal gland causes: A) Addison’s disease C) Cushing’s disease B) Parkinson’s disease D) Down’s syndrome
A
B
C
D
50-How many iodine atoms are present in thyroxin? A) 3 C) 2 B) 4 D) 5
A
B
C
D
51-Thyroxin deficiency in adults results in a condition called: A) Cretinism C) Thyrotoximia B) Hypothyroidism D) myxoedema
A
B
C
D
52-@-cells of pancreas secrete a hormone known as: A) Glucagons C) Gastrin B) Insulin D) Rennin
A
B
C
D
53-Ejection of milk from mammary glands is under the control of which one of the following hormones? A) Androgen C) Progesterone B) Oxytocin D) Estrogen
A
B
C
D
54-__________hormone is antagonistic to insulin and causes increase in blood glucose level. A) Glucagon C) Calcitonin B) Nor-epinephrine D) Thyroxine
A
B
C
D
55-All the hormones released by anterior pituitary are tropic EXCEPT: A) Thyroid stimulating hormone C) Adrenocorticotrophic hormone B) Somatotrophin hormone D) Gonadotrophic hormone
A
B
C
D
56-Ovulation is suppressed by progesterone via: A) Only by inhibition of LH C) Inhibition of LH and stimulation of FSH B) Inhibition of FSH and stimulation of LH D) Inhibition of FSH and inhibition of LH
A
B
C
D
57-Which of the following hormone is antagonistic to insulin? A) Thymosin C) Gastrin B) Cortisol D) Secretin
A
B
C
D
58-Deficiency of thyroxin in children causes: A) Cretinism C) Addison’s disease B) Graves disease D) Cushing’s disease
A
B
C
D
{"name":"NMDCAT Bio Quiz : Coordination and Control\/Nervous & Chemical Coordination", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge of the nervous system and its intricate mechanisms with our comprehensive NMDCAT Biology Quiz! This quiz consists of 58 expertly crafted multiple-choice questions covering key concepts in coordination and control, including neurological disorders, brain structures, and neurotransmitters.Whether you're preparing for an exam or simply want to challenge yourself, this quiz is designed to help you:Enhance your understanding of nervous system functionsIdentify key neurological conditionsImprove your exam readiness with practical questions","img":"https:/images/course2.png"}
More Quizzes
Human Anatomy Quiz 2
402034
The Nervous System
10533
Vocabulario
35180
De strijd tegen de zee
4236
Which Miraculous Character Are You? Take the Free
201032327
Ultimate Wentworth Characters: Test Your Memory Now!
201029089
Harriet Tubman Questions: Test Your Knowledge Now!
201027325
Concepts of Machine Learning
15819881
IQ Test Quotes: Prove Your Quote Genius
201066073
Free Compliance Knowledge Assessment
201021491
Free Exam Practice to Boost Your Prep
201026794
5 Themes of Geography: Are You Up for the Challenge?
201023679