Pp2
1. The distance measured along the full length of a beam.
Clear span
Effective span
Effective span
Span
2. Classification of a load in simple beam that theoretically produces a positive moment
Axial Load
Uniformly distributed load
Point load
For a system to be in equilibrium, the sum of the external forces acting on the system must be
Equal to unity
Zero
Maximum
Infinite
The analysis of the stress, strain and deflection characteristics of structural behavior is referred to.
Stress analysis
plastic analysis
structural analysis
seismic analysis
A graphic representation of the variation in magnitude of the bending moment.
Concentrated load
Moment diagram
Shear diagram
Graphical method
The force measured from a loading at a distance from the axis of rotation
moment
External force
internal force
Moment arm
A distance between the inner faces of the support of a beam.
effective span
Span
Neutral axis
Clear span
The shear diagram of a uniformly varying load.
Curved line
Linearly increasing
Straight line
Parabolic
Branch of engineering mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of loads.
Statics
Loads
Mechanics
Analysis
. Type of load representing the weight of a prismatic beam.
Uniformly varying load
Function of X variation
Uniformly distributed load
combined load
A force acting perpendicular to the surface of an object which tend the material to slip past the adjacent part.
Shear stress
Strain
Bearing stress
Axial stress
A push or pull that tends to move a body to the direction of its action.
Internal Load
Force
Internal force
The center to center distance between the supports of a beam.
Neutral axis
Clear span
Effective span
Span
An imaginary line passing through the centroid of the cross section of a beam, along which no bending stresses occur.
Clear span
Effective span
Span
Neutral axis
A property of a body that defines its resistance to a change in angular velocity about an axis of rotation.
Brace System
Moment of inertia
None of the above
Moment of couple
The rotational force measured at a given axis at a given point on a beam.
Moment arm
internal force
Moment
External force
Formula of Moment?
Moment of Inertia
Functional meaning of Moment of Inertia
Force x Distance
Mathematical meaning of Moment of Inertia
A design analysis as a basis where the total lateral forces are distributed to the various vertical elements of the lateral force resisting system.
Horizontal torsional moments
Shear and moment diagram
Stability against overturning
Distribution of Horizontal Shear
Formula in locating the centroid of a rectangular load.
L/4
L/5
L/2
L/3
The shear diagram of a uniformly distributed load in a cantilever beam.
Diagonal line
Parabolic
Curved line
Horizontal line
Type of load that is increasing or decreasing linearly throughout the length of the beam.
Uniformly varying load
Combination load
concentrated load
A structural system that support their loads in compression.
Cables
Frames
Trusses
Arches
A vertical structural element that carries an axial force in compression.
Frame
Column
Beam
Brace
1 GPa is equal to?
1,000,000 N/ mm2
1,000,000,000 N/ mm2
1,000 N/ mm
1 N/ mm2
Comprises in five or more members in triangular units constructed with straight members whose ends are connected at joints, external forces and reactions to those forces are considered to act only at the nodes and result in forces in the members are either in tension or compression.
Load analysis
Stress, strain analysis
Truss system
Truss system
What is the weight of 1 cu. m. Of steel?
2,400 Kg
1,000 Kg
5,500 Kg
7,850 Kg
Classification of a load which is permanently attached to a structure
Permanent load
Axial load
Movable Load
Dead Load
Structural system composed of triangulated steel members that allows span on a wide area.
Horizontal frame
Surface structures
Plane Grid
Space Truss Frame
The sum total of all the external forces measured from the supports of a beam.
Resultant
reaction
Moment
Moment of inertia
These are lateral loads except one
Seismic load
Wind load
Liquefaction
Movable load
Type of beam connection free from horizontal stress.
Fixed end connection
loose connection
Pin connection
roller connection
Type of beam simply supported on both ends.
Continuous beam
Semi- continuous beam
Simple beam
Cantilever
At any cut in a beam, there are 3 possible internal reactions required for equilibrium, except one.
Concentrated load
Bending moment
Vertical force
Shear force
Classification of a load produced by the wind.
External Load
Internal Load
Gravity Load
Lateral Load
Type of beam connection carrying the moment, horizontal, and vertical stresses.
Pin connection
loose connection
roller connection
fixed end connection
A structural element that support their loads in tension.
Cables
Trusses
Arches
Frames
What is the weight of 1 cu. m. Of concrete?
7,850 Kg
1.000 Kg
2,400 Kg
5,500 Kg
Classification of a load produced by earthquake.
Gravity Load
Seismic Load
Internal Load
External Load
Type of beam supported by a row of columns
Semi- continuous beam
Simple beam
Continuous beam
Cantilever
1 Gpa is equal to?
1 N/ mm²
1000 N/ m²
1 N/ m
1 X 1000 N/ mm²
A force that is supported by a structural element.
Reaction
Load
Shear
Moment
A rigid structural member designed to carry and transfer transverse loads across spaces to the supporting elements
Column
Foundation
Beam
Brace
Classification of a load produced by a large furniture.
Movable Load
Axial load
Permanent load
Dead Load
The amount of force required to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass one meter per second per second.
Acceleration
Newton
Velocity
Force
Classification of a load produced by a dead load.
Lateral Load
Gravity Load
Internal Load
External Load
It is a beam especially provided over an opening for a door or window to carry the wall over opening.
Lintel beam
Transom beam
Spandrel beam
Grade beam
A structural system consisting of slender elements which resist tensile or compressive axial forces
Frames
Cables
Arches
Trusses
. It is the general term applied for all forces which act upon a structure and anything else which causes stresses or deformation within a structure, or part thereof.
Loads
Reactions
Unit weights
Structure
Moving variable weights add to the dead load or an intrinsic weight of a structure.
Axial load
live load
Dead load
force polygon
. A structural system are often used in buildings and are composed of beams and columns that are either pin or fixed connected.
Frames
Cables
Arches
Trusses
A longitudinal strain developed at the mid span at the extreme top fiber of a cantilevered beam.
Moment
Compression
Tension
Shear
The deformation of a structural member as a result of loads acting on it.
Inflection
Stress
Strain
Deflection
. The formula in computing the maximum bending moment for a uniformly distributed load on simple beam.
V = WL / 2
M = WL / 8
V = WL / 2
M = WL^2 / 8
The section of a beam at which the bending moment changes from positive to negative and at this section, the magnitude of the bending moment is zero
Bending moment
Beam analysis
Inflection point
Magnitude of a force
A longitudinal strain developed at the mid span on the extreme bottom fiber of a simple beam
Shear
Moment
Tension
Compression
A longitudinal strain developed at the mid span at the extreme top fiber of a simple beam.
Shear
Compression
Tension
Moment
The distance from the support to the span of a beam where shear force is decreasing and moment is increasing.
Moment Diagram
Shear Diagram
Development length
Support analysis
A longitudinal strain that tend to elongate the object.
Moment
Shear
Compression
Tension
A longitudinal strain developed at the mid span on the extreme bottom fiber of a cantilevered beam.
Torsion
Moment
Tension
Compression
The formula in computing the maximum vertical shear for a uniformly distributed load on simple beam.
V = WL^2 / 8
V = WL / 8
V = WL / 2
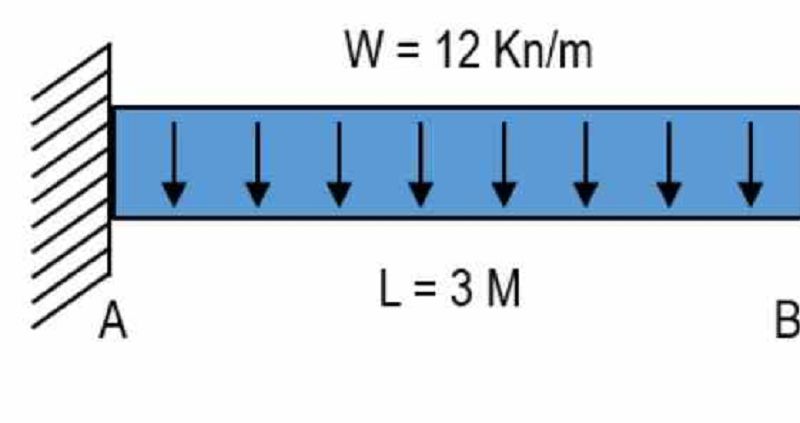
For the figure as shown, determine the vertical reaction at support A. Place your answer in Kilonewton
36
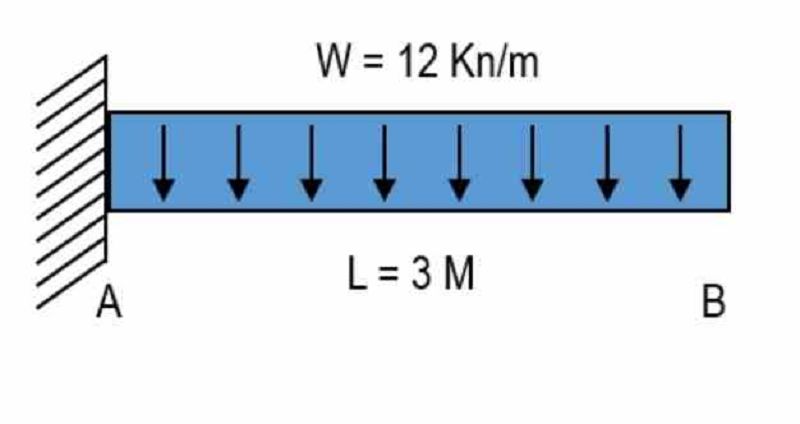
For the figure as shown, determine the moment value at support A . Place your answer in Kilonewton.meter.
-54
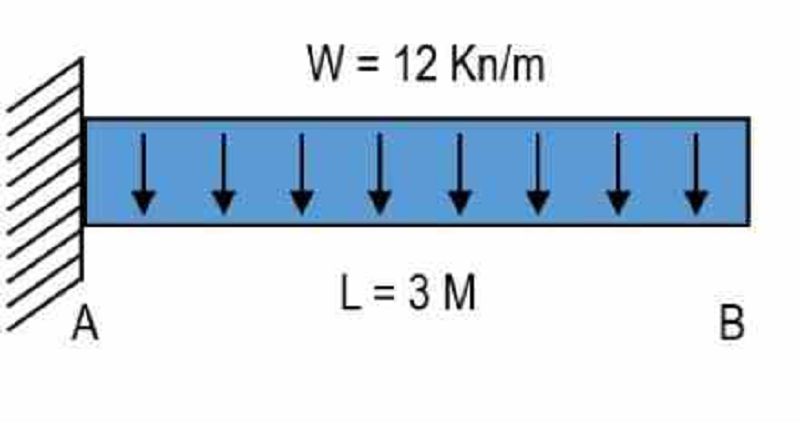
For the figure as shown, determine the vertical shear value at a distance 1.5 meters from support A . Place your answer in Kilonewton.
0
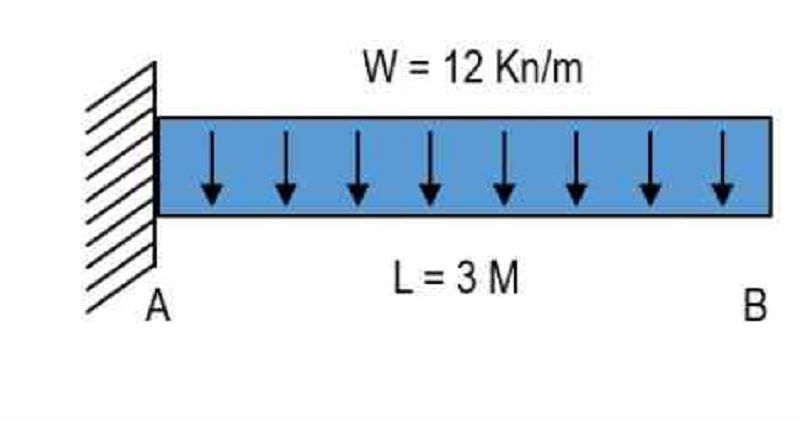
For the figure as shown, determine bending moment value at a distance 1.5 meters from support A . Place your answer in Kilonewton.meter.
-13.5
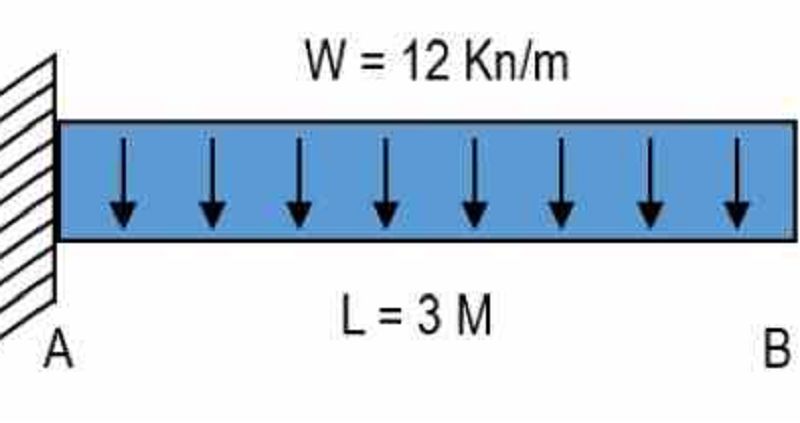
For the figure as shown, determine the moment value at support B . Place your answer in Kilonewton.meter.
0
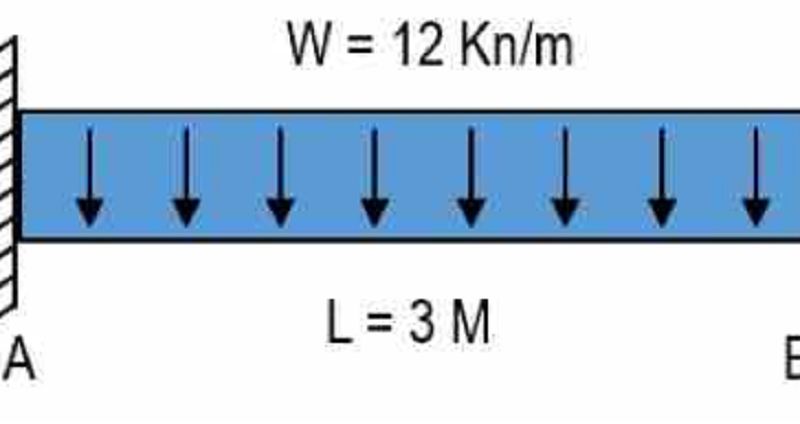
For the figure as shown, determine the distance from support A, when shear value is equal to zero. Place your answer in meter.
3
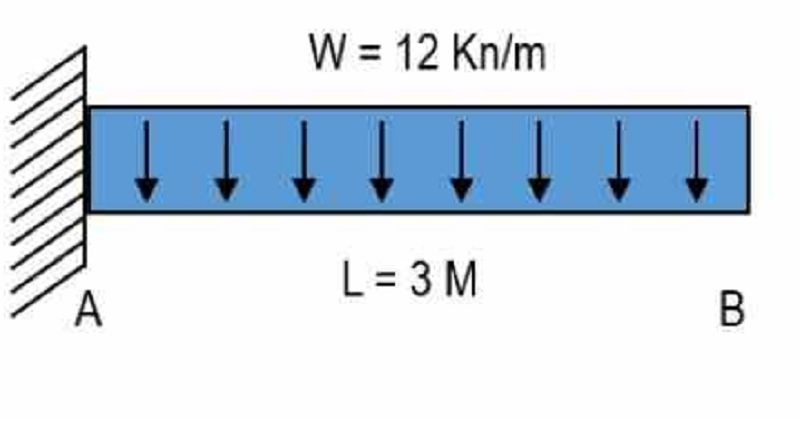
Determine the shear equation for figure.
-6X + 36
-6X + 36
-12X + 36
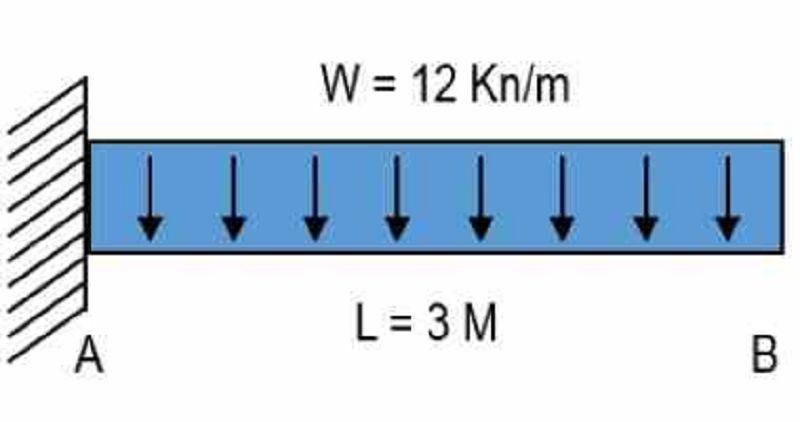
Determine the moment equation for figure
Vertical straight line
Horizontal straight line
Curved line
Diagonal straight line
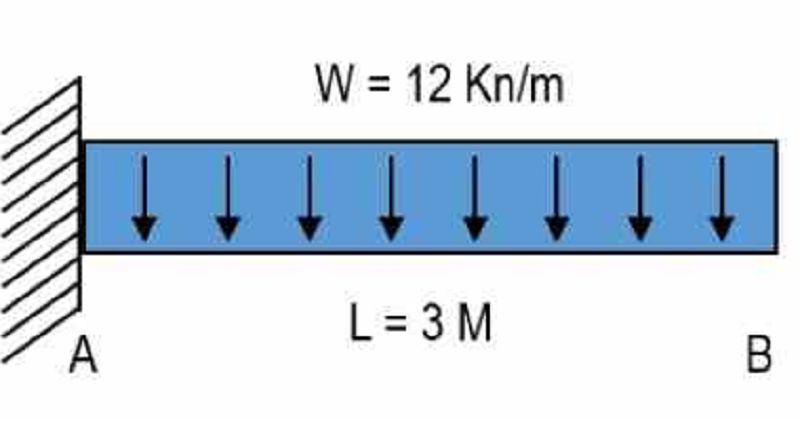
Determine the configuration of the shear line diagram for figure.
Vertical straight line
Vertical straight line
Curved line
Diagonal straight line
{"name":"Pp2", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1. The distance measured along the full length of a beam., 2. Classification of a load in simple beam that theoretically produces a positive moment, For a system to be in equilibrium, the sum of the external forces acting on the system must be","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/CDN/89-4343810/tos-e.jpg?sz=1200-00000000000842205300"}
More Quizzes
Guess the missing letters
8424
Cell Cycle
15827
MO_METROLOGIE SI OCEANOGRAFIE 1
301562
VETINGUN E VENDOS TI !
100
Which Hocus Pocus Character Are You? Free
201017927
Am I Ready to Be a Parent - Free Self-Assessment
201016592
Am I Pretty - Free Instant Beauty Score
201016592
Women's Sports Trivia - Free Online Challenge
201019982
Southeast States and Capitals - Free Online
201018070
Swine Showmanship Questions - Free Practice
201017927
Unusual Hobbies - Test Your Knowledge
201019887
MS Paint Online Test - Free Tools & Shortcuts Practice
201022290