BIOL 230 Exam 2 Part 3

BIOL 230 Exam 2 Quiz
Take your understanding of microbiology to the next level with our comprehensive BIOL 230 Exam 2 Quiz! This quiz covers essential topics such as pathogenicity, virulence factors, and mechanisms of bacterial infection.
- 50 multiple choice and checkbox questions
- Test your knowledge on topics including exotoxins and quorum sensing
- Perfect for students preparing for exams in microbiology
Does a plasmid need to incorporate itself to a genome in order to function properly?
Yes
No
___________________________ is DNA is transferred from one cell to another through direct cell contact (via a sex pilus).
Transformation
Conjugation
Transduction
____________________ is when DNA is transferred from a donor cell to a recipient cell through a bacteriophage. A bacteriophage (phage) is a virus that infects bacteria.
Transformation
Transduction
Conjugation
How do pathogens gain access to the human body?
Mucous membranes
Skin
Parenteral route
Pores
Sudoriferous glands
Sebaceous glands
Parenteral route
Most pathogens have ____________molecules on their surface. Each pathogen’s unique _________ is able to bind to a specific __________molecule found somewhere in the host.
Antigen (2x)
Adhesin (2x)
Receptors
Protein markers
Why do you think pathogens are unable to cause disease if they enter at a different site?
Different Adhesin
Lack of Adhesin
Lack of Receptors
Specific Receptors
Capsules contribute to virulence because the prevent __________________ and help adhere to epithelial surfaces.
Exocytosis
Phagocytosis
Endocytosis
The mycolic acid in the cell wall of acid-fast bacteria contributes to their virulence by:
Resisting digestion by phagocytic immune cells
Digesting blood clots
Breaking down hyaluronic acid
Resisting the effects of most antimicrobial drugs
Coagulase
Digests blood clots
Breaks down hyaluronic acid
Breaks down collagen
Coagulates host fibrinogen
Hyaluronidase
Breaks down collagen
Coagulates host fibrinogen
Digests blood clots
Breaks down hyaluronic acid
Collagenase
Breaks down collagen
Digests blood clots
Breaks down hyaluronic acid
Coagulates host fibrinogen
How would a pathogen know when its population is large enough to safely make its presence known?
Cytokine Release
Machrophages
B cells
Quorum sensing
In Quorum sensing bacteria send out chemicals called ____________________________that other bacteria in the population recognize and respond to.
Autoinducers
Isoinducets
Mediators
Allografts
Microbes may compete with their host for available nutrients, thus starving the host cells. Some bacteria produce ____________ which bind to Iron.
Spermatophore
Siderophores
Semaphore
What are examples of direct damage bacterial pathogens cause to a host?
Using the host’s nutrients
Causing direct cell damage in the immediate vicinity
Producing toxins
Inducing hypersensitivity reactions
Causing inflammatory responses
Inactivated toxin used in a vaccine (The tetanus and diphtheria components of the DTaP, Tdap, DT, and Td vaccines).
Antitoxin
Toxoid
Toxemia
Toxin
. What are the 3 types of exotoxins
A-B toxins
Membrane-disrupting toxins
Protein binding toxins
Superantigens
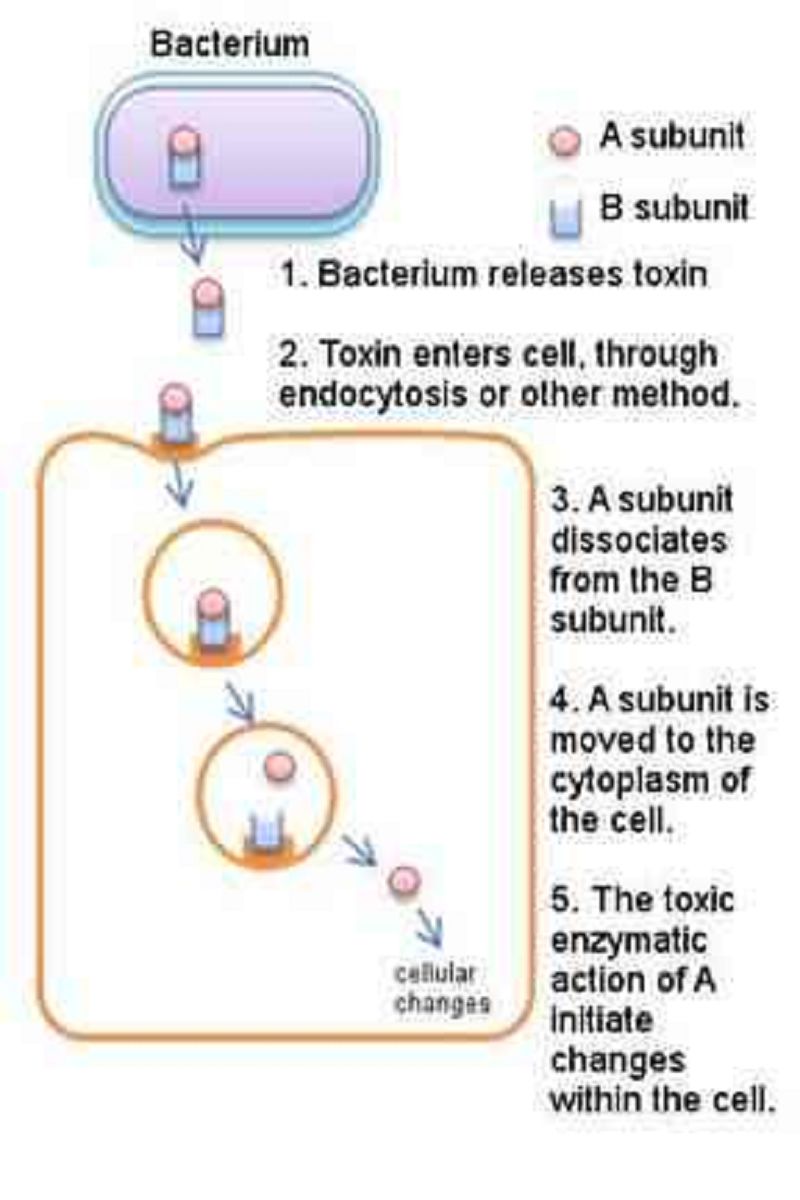
Action of an A-B Toxin. A inhibits protein synthesis.
Action of an A-B Toxin. A inhibits protein synthesis.
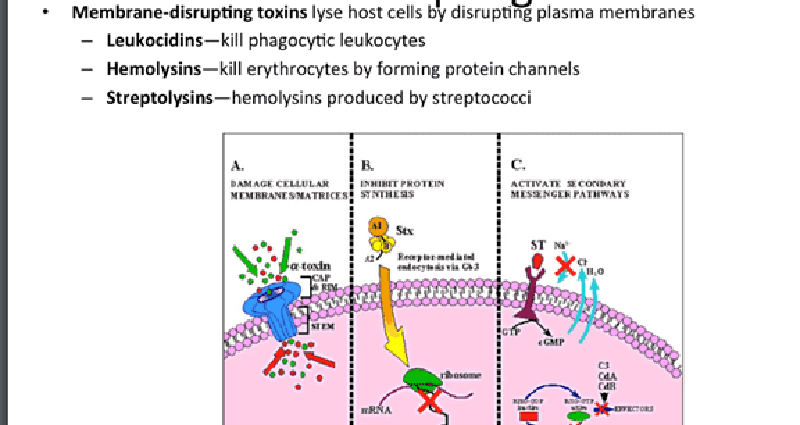
Membrane-Disrupting Toxins Cause specific host cells to lyse by disrupting their plasma membranes. There are 2 ways they disrupt plasma membranes:
Making protein channels in the plasma membrane
Disrupting the phospholipid bilayer
These toxins force host white blood cells (specifically helper T cells) to release high levels of cytokines.
A-B toxins
Superantigens
Membrane disrupting toxins
____________________________________ cause toxic shock syndrome.
Superantigens
A-B toxins
Membrane disrupting toxins
When shock is the result of endotoxin, it is called__________________________.
Toxic shock syndrome
Endotoxic shock
Systemic Anaphylaxis
In either case what causes toxic shock syndrome or endotoxic shock to develop?
The level of an immune response is harmful to the host.
The high concentration of cytokines in the body
. Why do you think knowing a pathogen’s portal of exit helps with preventing the spread of disease?
Prevention
Avoidance
Public Awareness
Each pathogen leaves the body in an attempt to infect a new host through a specific route or portal of exit.
True
False
African sleeping sickness and Chagas disease can persist in the body for extended period of time and although the immune system isn't compromised the pathogens still thrive why?
Capsules
Mycolic Acid
Antigenic Variation
Once pathogens adhere to host cells, they can cause direct damage by:
Producing waste products
Multiplying inside cells
Lysis of host cells
Toxins
Exotoxins are proteins that are secreted into the surrounding area or are released if the bacterium is killed and lysed.
True
False
___________________function by destroying specific components of the host’s cells or inhibiting precise metabolic functions.
Endotoxins
Exotoxins
Entry directly into the tissues beneath the skin or mucous membranes when these barriers are penetrated or injured.
Parenteral route
Mucous membranes
Most pathogens have a preferred portal of entry that is a prerequisite for disease. Meaning that if they gain access to the body through another portal, disease might not occur. Why?
Specific receptor
Specific environment
The presence of antigens causes the body’s Helper T cells to produce proteins called antibodies.
True
False
During an infection, the immune system responds to antibodies on the surface of invading pathogens
True
False
{"name":"BIOL 230 Exam 2 Part 3", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Take your understanding of microbiology to the next level with our comprehensive BIOL 230 Exam 2 Quiz! This quiz covers essential topics such as pathogenicity, virulence factors, and mechanisms of bacterial infection.50 multiple choice and checkbox questionsTest your knowledge on topics including exotoxins and quorum sensingPerfect for students preparing for exams in microbiology","img":"https:/images/course6.png"}
More Quizzes
Microbiology
1367
MDCAT BIOLOGY-Biodiversity (SMART INSTITUTE)
60300
Web services
1470
English final
840
Choose Your Fate - Can You Survive the Challenge?
201031768
Free Community Engagement Trivia
201030281
Should I Get a PhD - Discover Your Doctoral Style
201030637
Free General Aptitude Assessment
201029934
ERM Airway Practice Questions: Ace Your EMT Exam!
201048343
Ultimate Rock Cycle: Test Your Geology Knowledge
201023960
Free Energy Transfer 2 Quick Check
201022844
Which Reality Shifting Method Fits You Best? Take Our
201030281
