Module 3
Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4, C = 500 + .9DI If no other components of spending depend on Y, what is the slope of the equation for total expenditure, E?
.54
.9
.4
.3
According to the basic Keynesian model, if total expenditure currently is less than the level of output, then
Producers will notice their inventories increasing, so they will reduce output.
Producers will notice their inventories increasing, so they will increase output.
Producers will notice their inventories decreasing, so they will reduce output.
Producers will notice their inventories increasing, so they will increase output.
Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4 and C = 500 + .9DI, G = 600, I = 400, and (X-M) = -200. What happens to the equilibrium level of income if savings increases by 100?
Income increases by 185.2
Income decreases by 217.4
Income decreases by 185.2
Income increases by 217.4
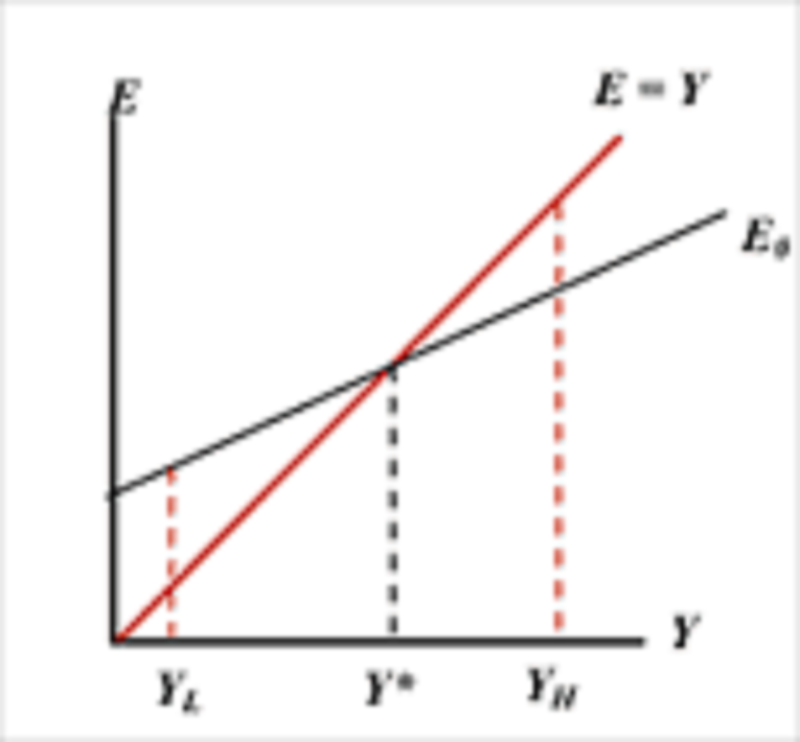
Consider the graph below: If output currently is decreasing, then
The current level of output must be equal to Y*
The current level of output must be below Y*, for example at YL
The current level of output could be value below Y*
The current level of output could be at any level above Y*
The marginal propensity to consume is
The share of any increase in income allocated to consumption expenditures.
The level of consumption spending divided by disposable income.
Smaller for high income households than it is for low income households.
The slope of the expenditure curve.
According to the basic Keynesian model, if total expenditure currently is greater than the level of output, then
Producers will notice their inventories increasing, so they will reduce output.
Producers will notice their inventories increasing, so they will increase output.
Producers will notice their inventories decreasing, so they will reduce output.
Producers will notice their inventories decreasing, so they will increase output.
Which of the following does not increase the intercept of the consumption function?
An increase in wealth
Expectations of future economic conditions become more positive
A decrease in the rate of interest
Higher expected, future government spending
According to the basic Keynesian model, if total expenditure currently is less than the level of output, then
Producers will notice their inventories increasing so they will reduce output.
Producers will notice their inventories increasing, so they will increase output.
Producers will notice their inventories decreasing, so they will reduce output.
Producers will notice their inventories decreasing, so they will increase output.
Suppose C = 50 + 0.9DI, where C is personal consumption expenditures and DI is disposable income. Suppose the tax rate is 20%. What is the expression for consumption as a function of total income, Y?
C = 50 + 0.72Y
C = 50 + 0.2Y
C = 50 + 0.18Y
C = 40 + .072Y
Suppose interest rates increase. This will
Decrease consumption and investment.
Decrease consumption but not investment.
Decrease investment but not consumption.
Increase both consumption and investment.
Which of the following is not one of the conditions necessary for an economy to be in a macroeconomic equilibrium.
The balance of trade must be zero, or exports = imports
All output produced must be willingly purchased.
All money and other financial assets must be willingly held.
All output must be willingly produced.
Suppose that during the fourth quarter of 2011 the slope of the expenditure curve was 0.25, while the intercept was 10071 billion in 2005 dollars. The level of real GDP during the fourth quarter of 2011 was
13,428 billion in 2005 dollars.
13,331 billion in 2005 dollars.
13,491 billion in 2005 dollars.
13,271 billion in 2005 dollars.
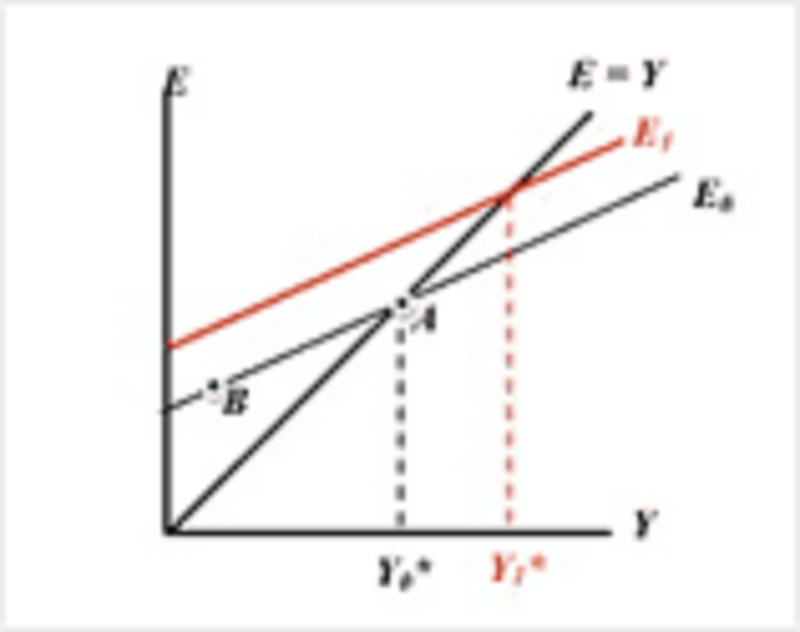
Consider the graph below.
A shift of the expenditure curve from E0 to E1 represents increased spending.
A movement along E0 from point B to point A represents increased spending.
A shift of the expenditure curve from E0 to E1 represents a decrease in net exports.
A movement along E0 from point A to point B representing increased spending.
Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4 and C = 500 + .9DI, G = 600, I = 400, and (X-M) = -200. What is the equilibrium level of output?
2826
1900
2037
1100
Suppose that during the fourth quarter of 2008 real GDP was 12,884 billion in 2005 dollars, while during the first quarter of 2009 it was only 12,663 billion, or real GDP decreased by 221 billion in 2005 dollars. If this change in real GDP was caused by a downward shift in the expenditure curve, by how much did spending decrease if the slope of the expenditure curve is 0.548?
It decreased by about 100 billion
It decreased by about 221 billion
It decreased by about 50 billion
It decreased by about 121 billion
The two properties of the consumption function assumed by the Keynesian model are
Consumption increases with disposable income and the share of disposable income consumed decreases as income increases.
Consumption increases with disposable income and the share of disposable income consumed increases as income increases.
Consumption increases with disposable income and the share of disposable income consumed does not change as income increases.
Consumption increases as saving decreases and the share of income saved decreases as wealth increases.
The assumptions of a fixed prices level and the existence of unemployed supplies of all factors of production is necessary to take care of the requirement that in order for the economy to be in equilibrium then,
All output must be willing produced.
All output produced must be willingly purchased.
All money and other financial assets must be willingly held.
The balance of trade must be zero, or exports = imports.
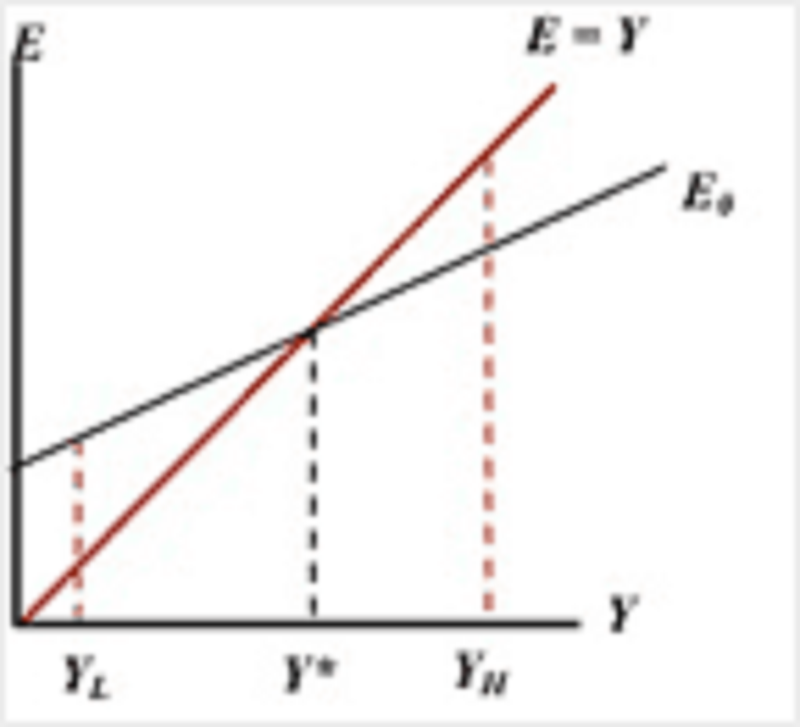
Consider the graph below. If output currently is increasing, then
The current level of output must be above Y*, for example at YH.
the current level of output must be below Y*, for example at YL
The current level of output must be equal to Y*
The current level of output could be at any level about Y*
Suppose that total income in an economy is $1,000. If the tax rate is 25% then,
Disposable income equals $750
Personal income equals $750
Consumption expenditures will equal $750
The share of income saved will be 75%
According to the income-expenditure model, changes in the observed value of real GDP are the result of
Shifts in the location of the total expenditure curve.
Changes in government spending.
Changes in next exports.
Waves of optimism and pessimism.
The assumption that the nominal rate of interest is fixed is necessary to take care of the requirement that in order for an economy to be in equilibrium then
All money and other financial assets must be willingly held.
All output produced must be willingly purchased.
All output must be willingly produced.
The balance of trade must be zero, or exports = imports.
Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4, C = 300 + .9DI, G = 600, I = 400, and (X-M) = -200. What is the equation for the total expenditure, E?
E = 1100 + 0.54Y
E = 1500 + 0.54Y
E = 800 + 0.54Y
E = 1100 + 0.9Y
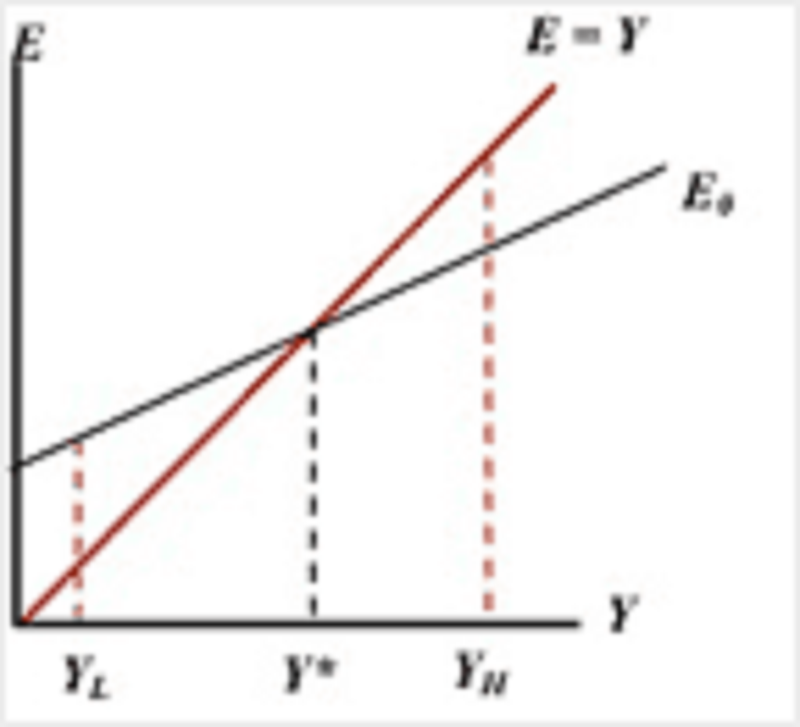
Consider the graph below. If output currently is increasing, then
The current level of output must be below Y*, for example at YL
The current level of output must be equal to Y*
The current level of output must be above Y*, for example at YL
The current level of output could be at any level above Y*
Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4 and C = 500 + .9DI, G = 600, I = 400, and (X-M) = -200. What happens to the intercept of the E curve if G is increased to 650.
It shifts upward by 50.
It shifts upward by 0.4*50=20
It shifts upwards by 0.9*50=45
It rotates upwards.
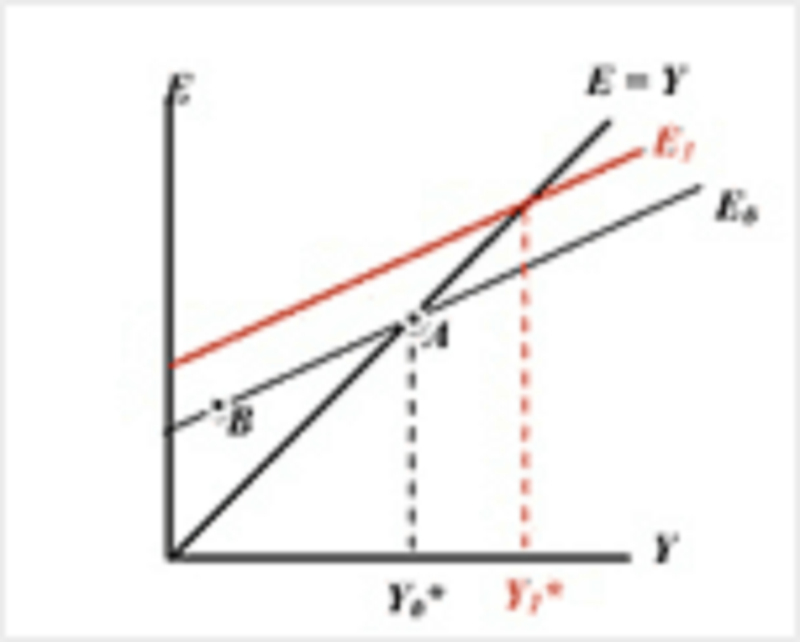
Consider the graph below. It shows that if the planned spending curve increases from E0 to E1, then
The level of output increases from Y0 to Y1 and this tells us that any data series on spending is a good candidate to be a leading economic indicator.
The level of output increases from Y0 to Y1 and this tells us that employment is a good candidate to be a leading economic indicator.
The level of output increases from Y0 to Y1 and this tells us that any data series on spending is a good candidate to be a lagging economic indicator.
The level of employment will decrease.
An increase in the income tax rate will
Shift the consumption function downwards
Cause the consumption function to rotate downwards
Shift the consumption function upwards
Cause the consupmption function to rotate upwards
The basic Keynesian model is based on
The assumptions that the price level is fixed, the nominal rate of interest is fixed and that there are unemployed supplies of all factors or production.
The assumption that the price level is fixed.
The assumptions that the price level is fixed and that there are unemployed supplies of all factors or production.
The assumption that there are unemployed supplies of all factors of production.
Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4 and C = 500 + .9DI, G = 600, I = 400, and (X-M) = -200. What happens to the total expenditure curve is the tax rate is reduced to t=0.3?
The slope increases to 0.63.
The slope decreases to 0.54.
The E curve shifts upwards.
The E curve shifts downwards.
Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4 and C = 500 + .9DI, G = 600, I = 400, and (X-M) = -200. What is the value of the multiplier?
(1/.046) = 2.17
(1/.054) = 1.85
(1/0.4) = 2.5
(1/0.1) = 10
Suppose interest rates increase. This will:
Increase consumption and investment.
Decrease consumption and investment.
{"name":"Module 3", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4, C = 500 + .9DI If no other components of spending depend on Y, what is the slope of the equation for total expenditure, E?, According to the basic Keynesian model, if total expenditure currently is less than the level of output, then, Suppose the tax rate, t = 0.4 and C = 500 + .9DI, G = 600, I = 400, and (X-M) = -200. What happens to the equilibrium level of income if savings increases by 100?","img":"https://cdn.poll-maker.com/10-460169/mod3-1.png?sz=1200"}
More Quizzes
Jak moc znáš Vojtěcha Janského
740
The Big Bang Theory
158684
The Enviroment
210
Who dat
1589
What's your Tupperware Personality?
1260
2 Lies, 1 Truth
630
How Well Do You Know The Princess Diaries?
1050
Brave New World Personality quiz
10535
How well you know Saachi??😉
320
Fictional Self quiz
1169
How well do you know Brentwood school?
11611
Melyik házhoz tartozol a Trónok Harcában?
1050