Form 4 Geography Paper 01

Geography Quiz: Understanding Plate Tectonics and Earthquakes
Test your knowledge on plate tectonics, earthquakes, and volcanic activities through this comprehensive quiz designed for Form 4 geography students. Dive into various concepts related to Earth's dynamics and see how well you can identify important geological features!
Key Features:
- 50 multiple choice questions
- Focus on plate tectonics, earthquakes, and volcanism
- Score as you answer and learn more about our planet!
The crustal movement of plates on the earth's surface in relation to each other is termed?
Convergence
Divergence
Transform
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics have resulted in the formation of all of the following except?
Island arcs
Ocean trenches
Coral islands
Mid-oceanic ridges
Which of the following is associated with plate subduction at plate boundaries?
Convergence pf plates
Divergence of plates
Conservative plates
Sea floor spreading
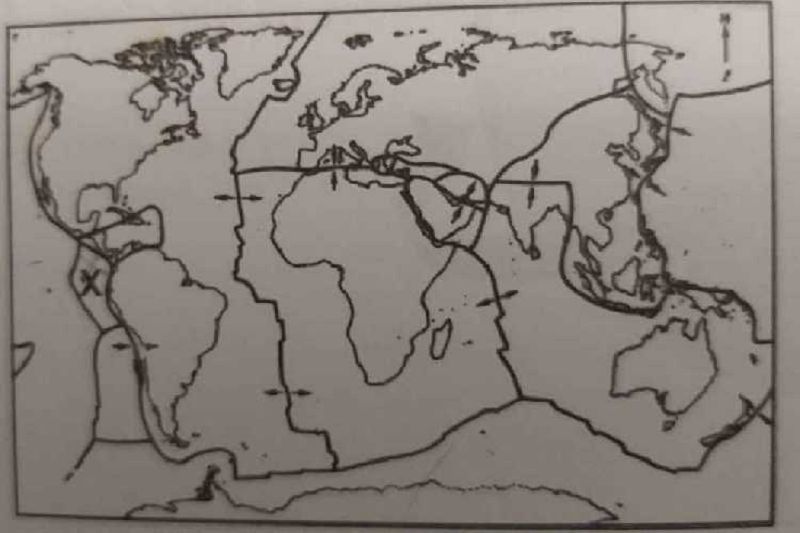
The lines drawn on the world map represent?
Earthquake zones
Hurricane belts
Plate boundaries
Mid-oceanic ridges
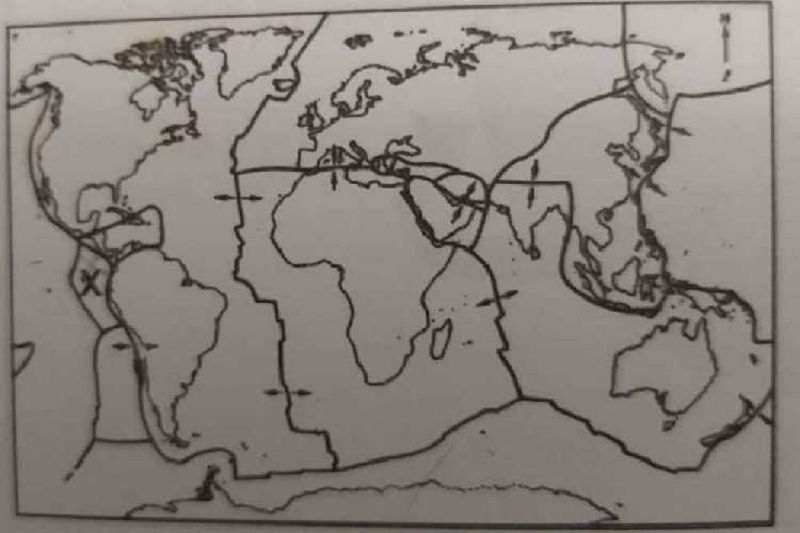
The plate at X is known as?
North America Plate
Pacific Plate
Cocos Plate
Caribbean plate
Sea floor spreading is associated with?
Zones of Divergence
Zones of Convergence
Neutral or Conservative margins
Subduction zones
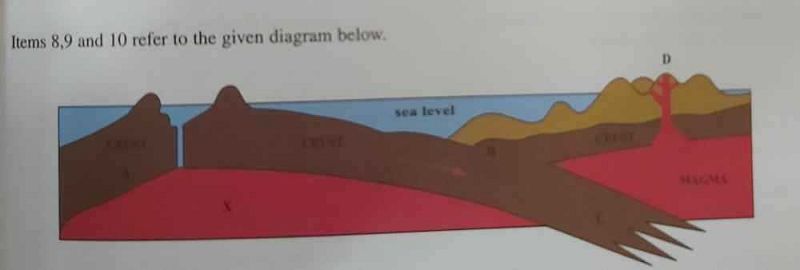
Which of the following areas are undergoing subduction?
A
B
C
D
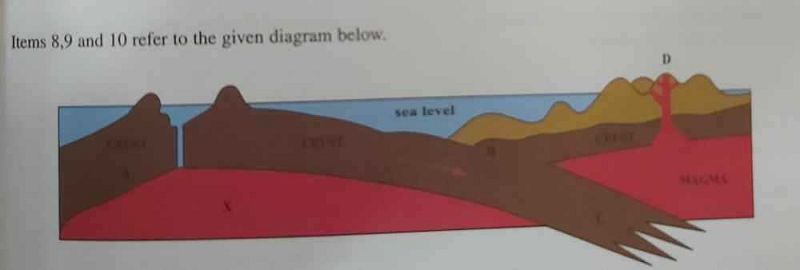
The feature produced at D is an
Fold mountain
Volcano
Fault
Crater lake
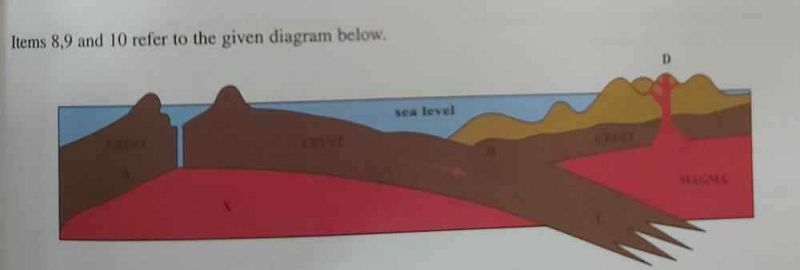
The rock at X is most likely
Marble
Limestone
Basalt
Clay
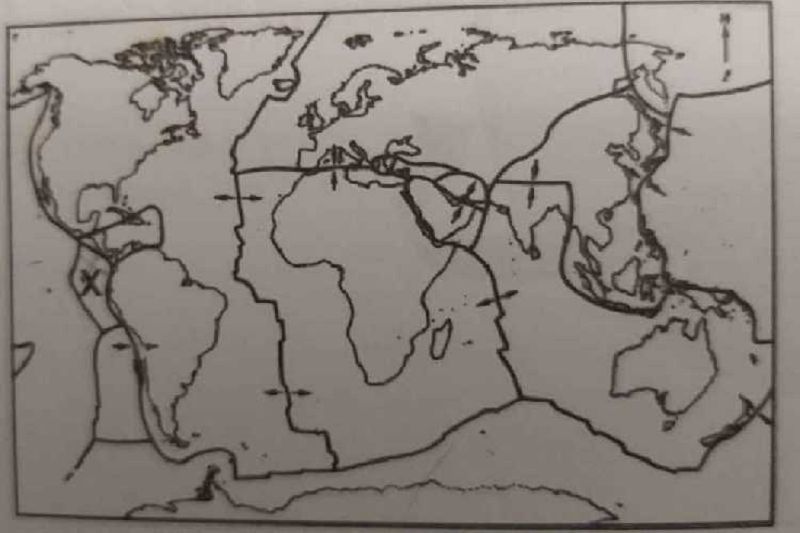
Along which of the following areas in the map does sea floor spreading occur?
Cocos plate
Caribbean plate
Mid- Atlantic ridge
Nazca Plate
Which of the following may result in earthquake occurrences? (i) Collision of two moving plates (ii) Oceanic rocks are pushed towards the continental crust (iii) Slippage along strained faults (iv) One plate passes another.
(i), (iii)
(ii), (iii)
(ii), (iii), (iv)
(i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
Earthquake intensity is measured by?
The Richter scale
Barometer
Seismographs
Geologists
The point on the earth's surface directly above the focus of an earthquake is termed the?
Inner core
Continental crust
Epi- centre
Mantle
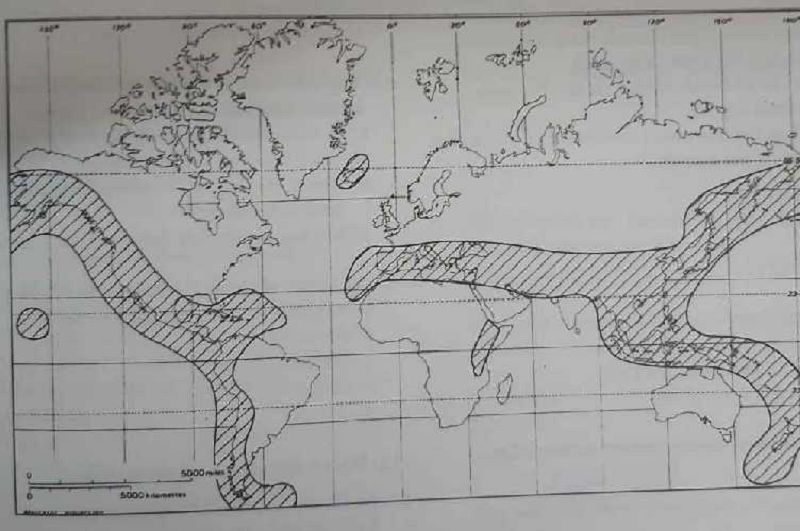
The shaded area on the map represents zones of
Hurricane activity
Conservative plate movements
Earthquakes and active volcanoes
Low population densities
Large waves resulting from movements along the sea floor are termed?
Destructive waves
Tsunamis
Submarine waves
Sea floor spreading
Predictions of earthquakes are based on? (i) Changes in water level (ii)Bulges in the earth's crust (iii) Shortened survey lines (iv) Changes in land elevation
(i), (iii), (iv)
(ii), (iii)
(i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(ii), (iv)
The following are precautionary measures against earthquake disasters, except
Stronger buildings in earthquake prone areas
Avoid building in critical areas
Timely evacuation of people from hazardous areas or buildings
Storage of adequate food and water supplies
In which of these Caribbean territories earthquakes are most likely to occur?
Barbados
Martinique
Belize
Guyana
Which feature is not related to earthquake occurances?
Plates snapping
A sudden release of energy
Solution of rocks
Buckling of the earth's surface
Which are effects of earthquake? (i) Destruction to life and property (ii) Landslide occurrences (iii) Formation of gigantic waves or tsunamis (iv) Submergence of land masses.
(i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(i), (ii), (iii)
(ii), (iii), (iv)
(i), (iii), (iv)
Most volcanic cone formations are associated with
Intrusive activities
Subduction zones
Conservative plate boundaries
Divergent plate boundaries
Which is an incorrect statement about volcanoes?
They cluster along narrow, mountainous belts
They are formed by magma which is forced through a vent or fault in the earth's crust
They are the result of tectonic activity or plate movements
They are found mostly where two plates slide past each other
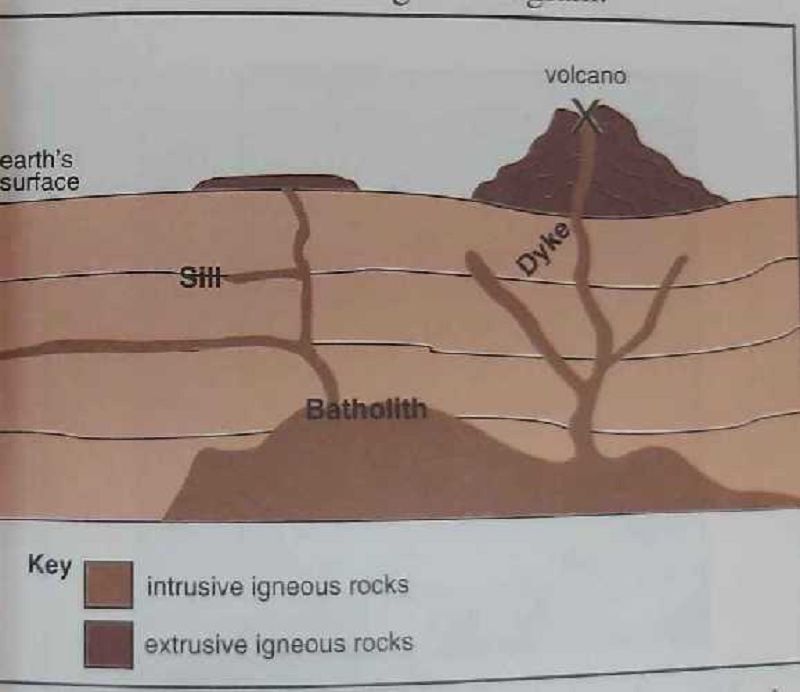
Which of the features shown in the diagram is formed by the intrusion of magma along bedding planes of rocks?
Dyke
Sill
Batholith
Volcanic neck

The feature marked X is termed a?
Vent
Crater
Fissure
Fault
The following are features emitted from an erupting volcano, except?
Ash and dust
Bombs
Carbon dioxide, monoxide, water vapour
Screes
(i) Dykes, (ii) Sills, (iii) Batholiths, (iv) Hot springs. The above features have been formed as a result of
Weathering
Running water
Wave action
Vulcanicity
Lahars are
Volcanic gases
Mudflows of volcanic ash
Angular solid fragments
Extended lava flows
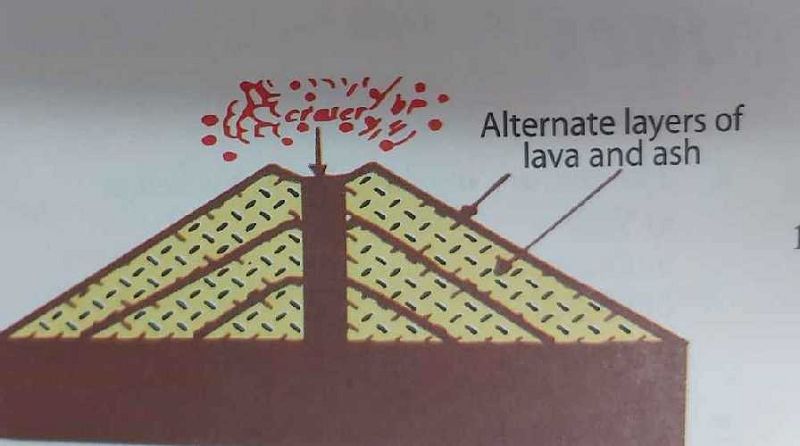
The type of volcano shown in the diagram is termed?
Ash and cinder cone
Shield
Caldera
Composite
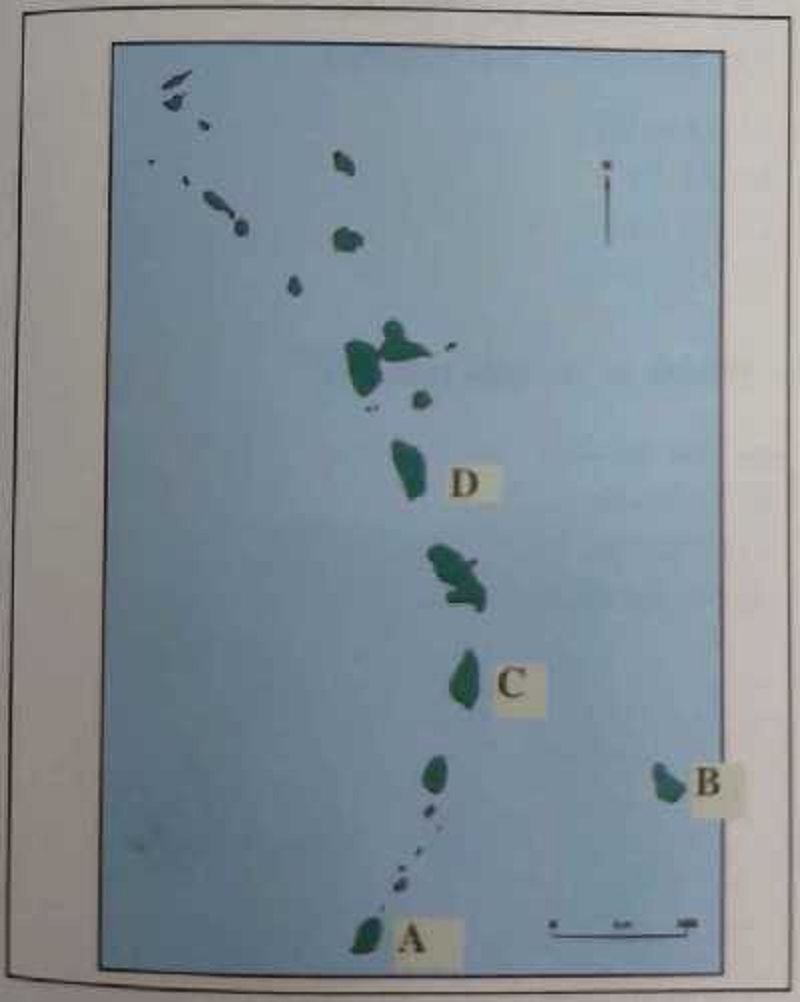
Which of the islands marked A, B, C, D is not a volcanic island?
A
B
C
D
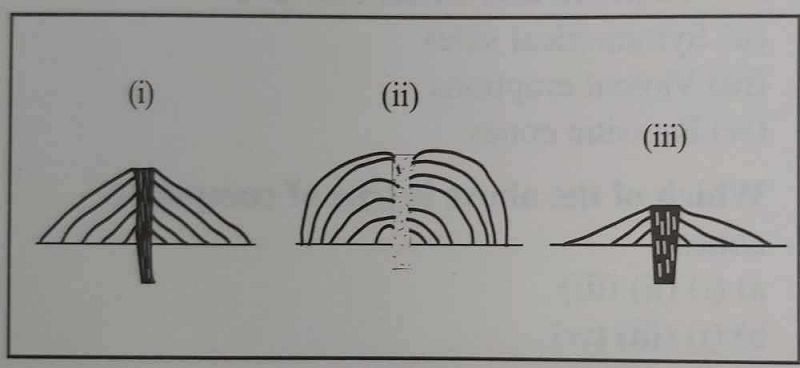
The type of volcano illustrated in each diagram is
Shield, composite, acid lava
Composite, acid lava, shield
Acid lava, composite, shield
Shield, Acid lava, Composite.
Chemical weathering is most active in climates which are
Cold
Dry and arid
Hot and wet
Hot and dry
The main processes in chemical weathering can be classified as: (i) Oxidation, (ii) Hydration and Hydrolysis (iii) Carbonation (iv) Solution
(i), (ii), (iii)
(i), (iii), (iv)
(ii), (iii), (iv)
(i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
The process by which new substances are formed when minerals in the rocks combine with water is known as?
Hydration
Oxidation
Hydrolosis
Carbonation
The level of development of Caribbean countries can be measured by using the following factors, except?
Literacy rate
Income per capital
Population density
Life expectancy
Density of a population is best described as
The total amount of people in a country
The total number of people inhabiting a specific area
The average number of persons per unit area.
The average number of people living in urban areas.
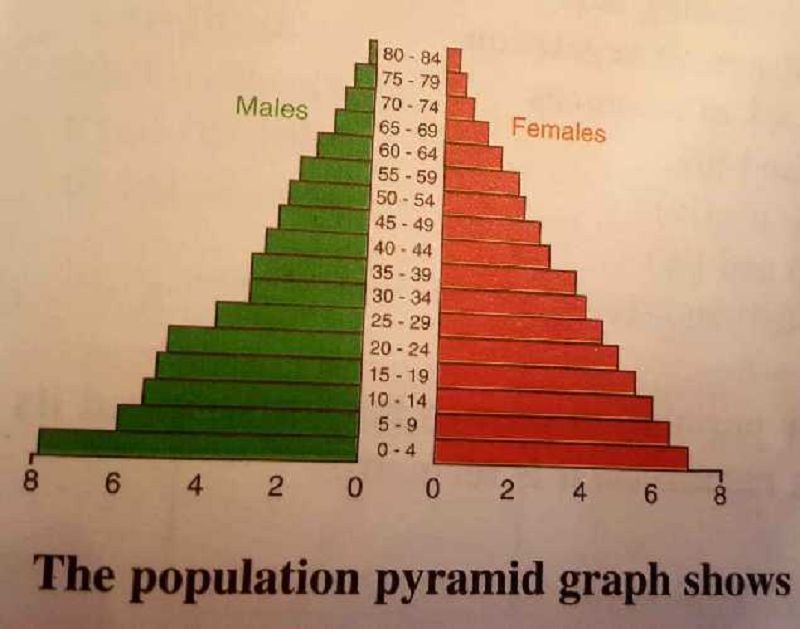
What does the population pyramid represent?
The distribution of population of a country
The amount of people in a country
The perdentage of males and females in a country
The percentage of males and females according to age structure
What factor contributes to a low infant mortality rate?
Diseases
Health care
Malnutrition
Low income
Which factors tend to influence the growth of population in the Caribbean? (i) Natural Increase, (ii)Immigration, (iii) High unemployment, (iv) High living standard.
(i), (ii), (iii)
(i), (iii), (iv)
(ii), (iii),(iv)
(i), (ii)
Which factors may contribute to a low population density in the Caribbean? (i) Steep gradient, (ii) Undulating land, (iii)Mangrove vegetation (iv) Lack of resources.
(i), (ii)
(ii), (iii), (iv)
(iii), (iv)
(i), (ii),(iv)
Which of the following methods Caribbean countries with relatively dense population may use to control and serve their populations? (i) Create more industrial activities (ii) Adopt population controls and educational awareness (iii) Develop various agricultural programmes (iv) Encourage young rural people to seek a better living in the city.
(i), (ii), (iii)
(ii), (iii), (iv)
(ii), (iii), (iv)
(i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
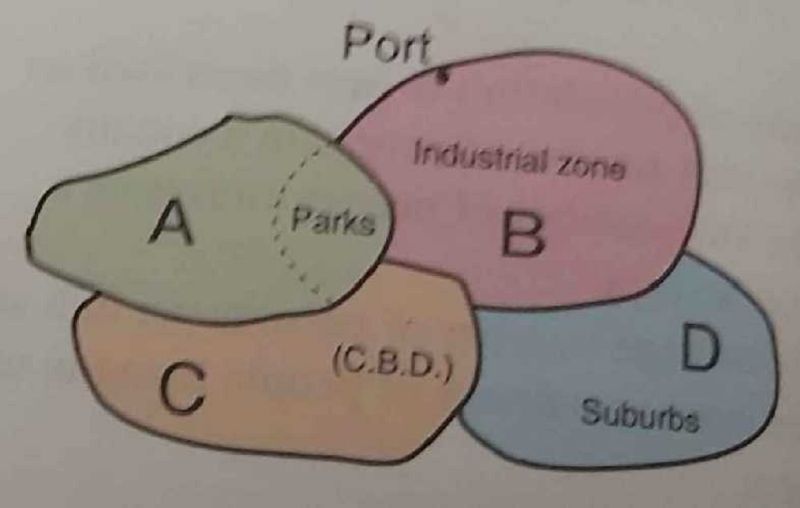
Which of the Areas A, B, C, D will the density of housing be the lowest?
A
B
C
D
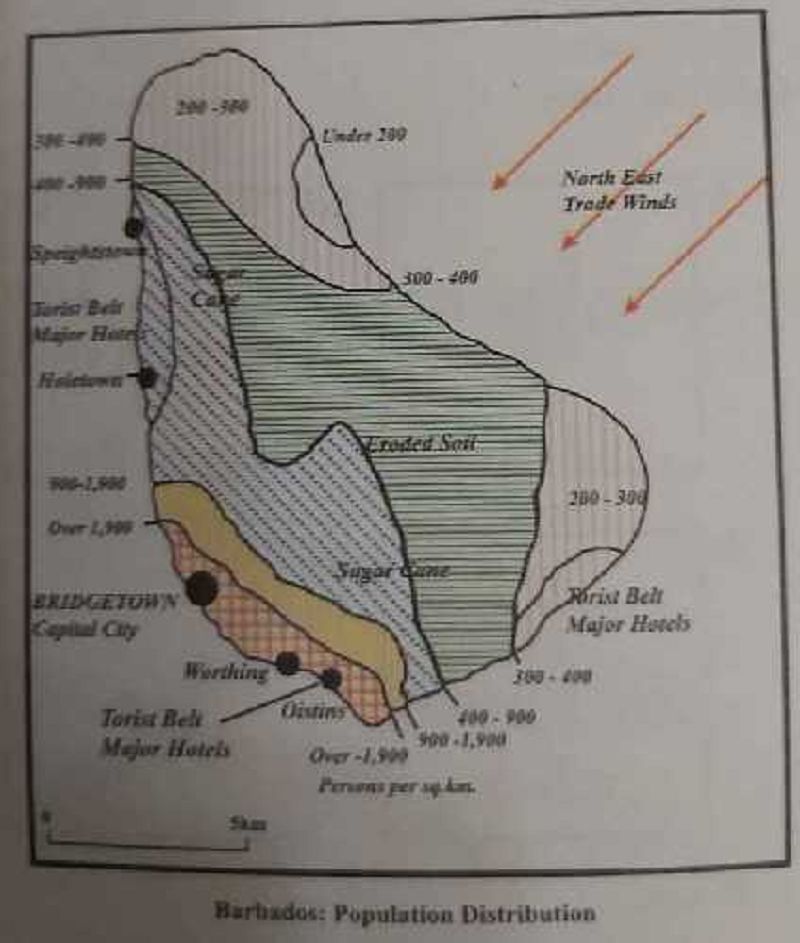
The map shows that
Most people settle on the coast
The density decreases from the south west to the north east
In each shaded area there are equal amounts of people for every sq. km
The north eastern areas have a poor transport system
The area of Tobago is 301 sq. Km and has a population of 50,282 persons. Calculate the population density( persons per sq. km) in Tobago?
131
139
167
184
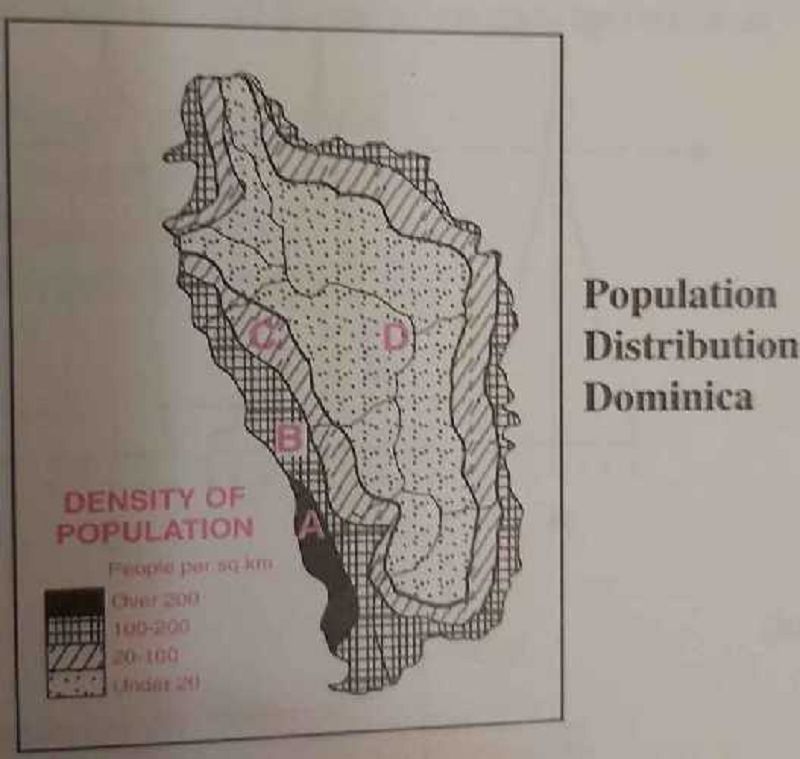
In which region would density of population be the highest?
A
B
C
D
Which of the following may explain why a region in the Caribbean may have low population density? (i) High mountainous relief (ii) Thin, infertile soil (iii) Inadequate water supplies (iv) Lack of roads
(i), (ii), (iii)
(i), (iii), (iv)
(i), (ii), (iii), (iv)
(i), (iii), (iv)

The graphs show differernt stages of a country's population development. Which graph shows the smallest of persons under 15 years?
A
B
C
D
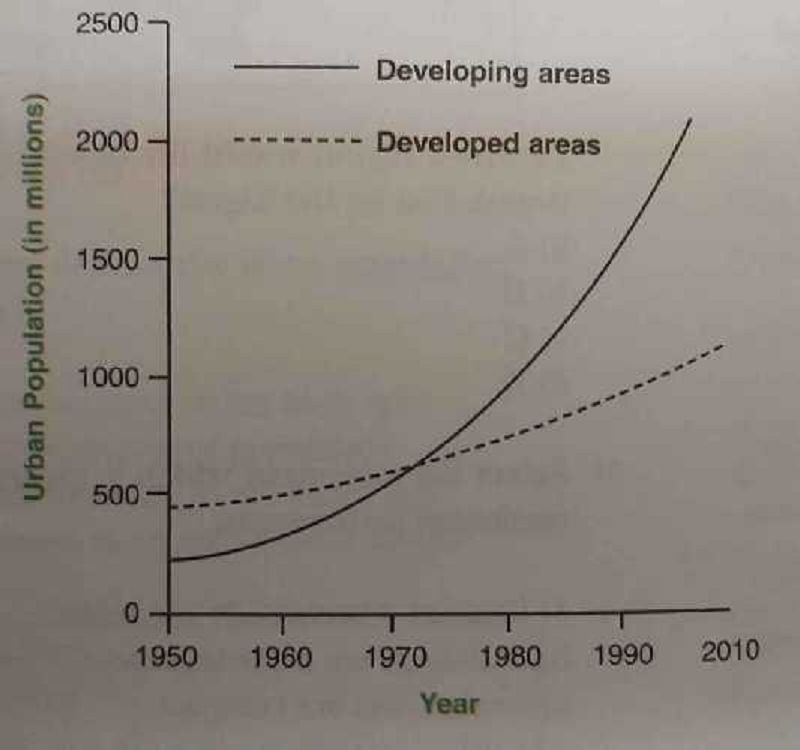
What does this diagram show?
Urban population is declining
More people will be living in urban areas by the year 2010
Developed areas will have a greater increase in urban population than developing areas by 2010
Urban areas will increase by 2010 because of people leaving rural areas.
All of the following are factors influencing a low population density in the Caribbean except?
Land with steep slopes
Forested areas
Limited employment opportunities
Lack of rainfall
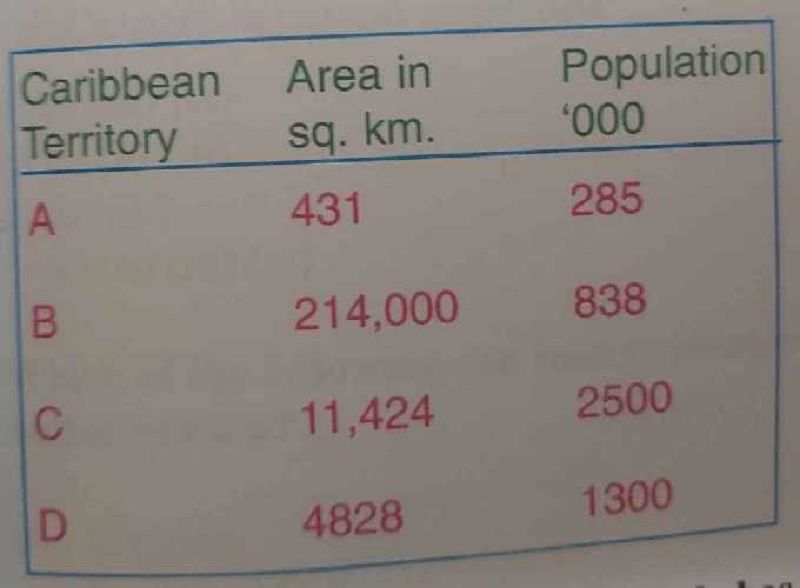
Which Caribbean country in the table has the highest population density?
A
B
C
D
The study of changes in size, distribution and character of the population is referred to as?
Population dynamics
Deomography
Natural increase
Population census
{"name":"Form 4 Geography Paper 01", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Test your knowledge on plate tectonics, earthquakes, and volcanic activities through this comprehensive quiz designed for Form 4 geography students. Dive into various concepts related to Earth's dynamics and see how well you can identify important geological features!Key Features:50 multiple choice questionsFocus on plate tectonics, earthquakes, and volcanismScore as you answer and learn more about our planet!","img":"https:/images/course8.png"}
More Quizzes
Quarter I - Module 1 Chapter Test: Study the analogy of the set of terms in each number. Click the letter of the term that will complete the analogy on the blank.
74261
1.1-1.4 geo natural disasters
13622
MCN SESSION 9-11
422123
Quiz on Science and Knowledge
105101
Ultimate Fire Safety: Test Your Knowledge Now!
201036280
Ultimate One Direction Song: Can You Guess the Lyrics?
201032923
Free Telling Time in Spanish Practice
201024125
Free LSAT: Test Your Law School Admission Skills
201041263
Test Your MLA Citation of Beowulf Skills - Free
201044402
In a Circular Flow Model Households: Test Your Econ Skills
201071906
Ace the Romeo and Juliet Final Exam: Test Your Mastery Now
201027149
Know Engineering Drawing Dimensioning Rules? Take the
201033806