Oral Path Midterm Review (Mrs. B's Kahoot!)

Oral Pathology Midterm Review
Prepare for your Oral Pathology midterm with this comprehensive quiz created by Mrs. B! Dive into 45 questions covering various oral conditions, immune responses, and much more.
Test your knowledge and reinforce your learning! Key topics include:
- Diagnosis of oral lesions
- Immune responses
- Oral diseases and treatments
Which condition is NOT diagnosed through clinical appearance?
Compound odontoma
Black hairy tongue
Fordyce granules
Mandibular tori
Which condition is diagnosed through clinical appearance?
Traumatic bone cyst
Periapical cemento-osseous dysplasia
Unerupted mesiodens
Fordyce granules
Retrocuspid papillae are located on the
Palate
Floor of the mouth
Gingival margin of the lingual aspect of mandibular cuspids
Canine eminence
A lesion with a stemlike base is described as
Lobulated
Pedunculated
Macular
Sessile
Which papillae are elongated in the condition black hairy tongue?
Fungiform
Filiform
Foliate
Circumvallate
When formation of exudate is excessive, a drainage tract may develop through the injured tissue. This channel is termed:
Emigration
Erythema
Leukocytosis
A fistula
Neutrophils constitute what percentage of the entire white blood cell population?
90%
65%
20%
5%
Excessive scarring in skin is termed
Healing by tertiary intention
A hematoma
Healing by primary intention
A keloid
Aspirin burn on the oral mucosa
Requires a biopsy for diagnosis
Is painless
Caused by placing aspirin on the tooth with pain, causing necrotic tissue
Caused by ingestion of too many aspirin tablets
In the acute inflammation process, second type of white blood cells to emigrate from the blood vessel into the injured tissue is
Lymphocyte
Plasma cell
Neutrophil
Macrophage
The breakdown of cellular adhesion between epithelial cells is termed
Anaphylaxis
Nikolsky sign
Acantholysis
Cell-mediated immunity
In which type of immune response do B-lymphocytes and antibodies play the predominant role?
Passive immunity
Humoral immunity
Immune complex
Cell-mediated immunity
Which is an example of type 1 hypersensitivity?
Serum sickness
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Asthma
Immune complexes between microorganisms and blood
A prodomal period begins
The day the ulcers erupt
1 to 2 days before the onset of ulcers
1 week before the onset of ulcers
7 to 10 days before ulcers erupt
Wickham striae is a term used to describe the oral mucosa lesions of
Erythema multiforme
Lichen planus
Frictional keratosis
Linea alba
Sjogren syndrome is a(n)
Type of langerhans cell disease
Form of apthous ulcers
Allergic reaction
Autoimmune disease that affects the salivary and lacrimal glands
Treatment for Pemphigus Vulgaris includes
Antiviral drugs
Antibiotics
Antihistamines
High doses of systemic corticosteroids
The diagnosis of Behcet syndrome requires which considerations?
A history of pemphigus vulgaris
A biopsy
The presence of all three manifestations
Two of the three principal manifestations
This explosively onset condition features target, iris, or bullseye lesions.
SLE
Contact dermatitis
Erythema Multiforme
Lichen Planus
The diagnosis of type of apthous ulcers is made on the basis of their clinical appearance, location, and a _____________.
Laboratory test
Radiographic examination
Therapeutic result
Patient history
Which of these conditions are related to heart valve damage?
Geographic tongue
Scarlet fever
Strawberry tongue
Rheumatic fever
Which condition is associated with scarlet fever?
Strawberry tongue
Scrofula
Median rhomboid glossitis
Black hairy tongue
The most common site(s) for oral lesions in tuberculosis is(are) the
Uvula & fauces
Floor of the mouth & mucobuccal folds
Gingiva
Tongue & palate
Which statement is NOT true about syphilis?
The antibody titer increases if treatment has been successful
The VDRL & FTA-ABS tests are commonly used to confirm the diagnosis
It is generally treated with penicillin
Dark-field examination may be used to diagnosed syphilitic lesions on skin
Which condition does NOT contribute to the overgrowth of Candida Albicans?
Angioedema
Cancer chemotherapy
Dentures
Antibiotic therapy
The varicella-zoster virus causes a highly contagious disease in children termed
Measles
Mumps
Chickenpox
Shingles
Herpangina is caused by which virus
Coxsackievirus
Varicella-zoster virus
Epstein-Barr virus
Herpes simplex virus
In HIV infection, which test identifies the viral titer rather than circulating antibody?
PCR
Western blot
ELISA
VDRL
In herpes labialis, the amount of virus present is highest in the _______ stage.
Healing
Vesicle
Prodromal
Crusted
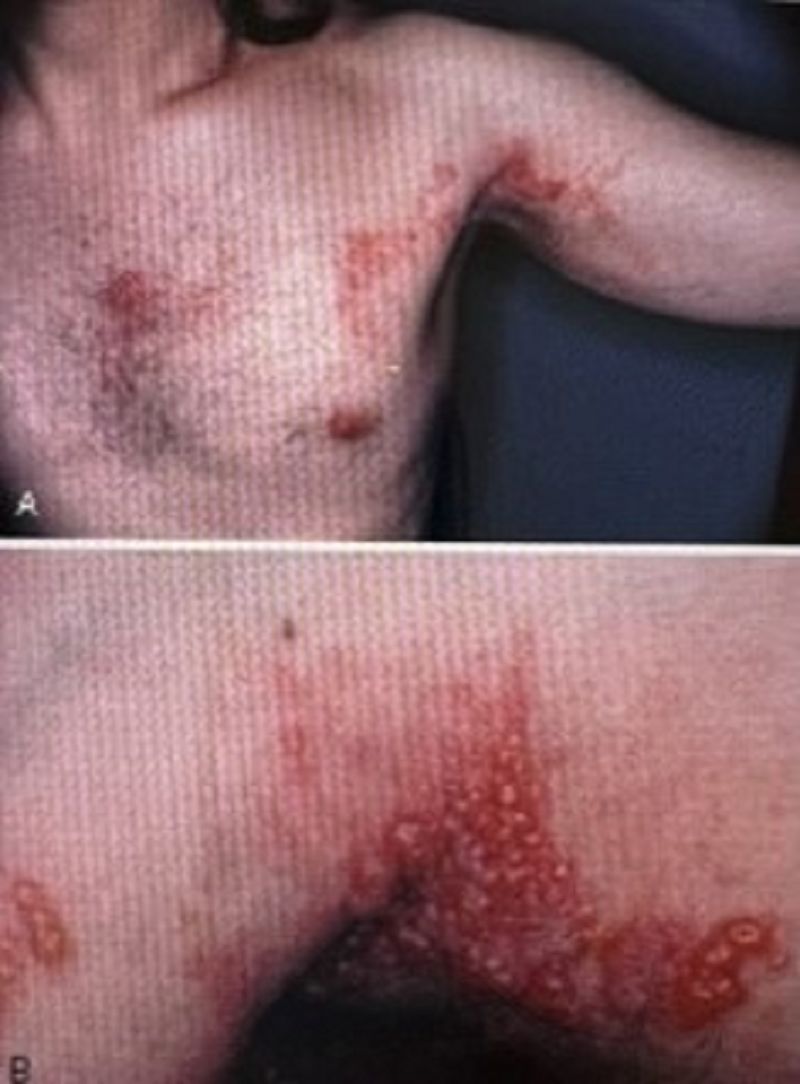
The unilateral eruption of vesicles along the distribution of a sensory nerve seen in this adult patient is a feature of
Herpes zoster or shingles
Varicella-zoster or chickenpox
Minor apthous ulcers
Recurrent intraoral herpes simplex
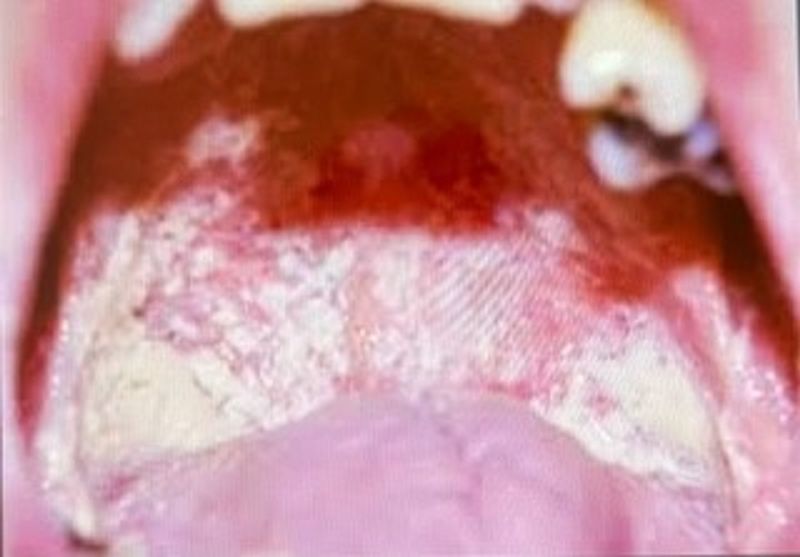
The lesions seen in this illustration most commonly appear in patients with HIV. What is the clinical diagnosis?
Apthous ulcer
Kaposi sarcoma
Lymphoma
Candidiasis
Which form of candidiasis is most asymptomatic?
Angular cheilitis
Chronic atrophic candidiasis
Erythematous
Pseudomembrane
An erythematous, often rhombus-shaped, flat-to-raised area on the midline of the posterior dorsal tongue describes
Hairy leukoplakia
Recurrent herpes simplex infection
Geographic tongue
Median rhomboid glossitis
Why is hairy leukoplakia a significant clinical finding in persons with HIV disease?
It may represent a malignancy of the tongue
Hairy leukoplakia may affect the function of taste buds
Its presence suggests poor oral hygiene
It is considered a predictor of the development of AIDs
Intraoral lesions of Kaposi sarcoma are often found in which two sites?
Uvula & posterior 1/3 of the tongue
Palate & gingiva
Gingiva & floor of the mouth
Labial mucosa & interdental papilla
Which epithelium-lined tract is a developmental anomaly located in the corners of the mouth?
Congenital lip pit
Fistula
Angular cheilitis
Commissural lip pit
The most common cyst observed in the oral cavity is caused by pulpal inflammation and is called a(n) ___________ cyst.
Primordial
Radicular
Eruption
Dentigerous
On x-rays, this radiolucent cyst is often heart shaped, caused by the anatomic Y shape of the area. What is it called?
Globulomaxillary
Nasolabial
Median palatine
Nasopalatine canal
What pseudocyst filled with salivary gland tissue may be an extension of the sublingual gland?
Traumatic bone cyst
Lymphoepithelial cyst
Static bone cyst
Ranula
What is the most common supernumerary tooth?
Turner tooth
Mulberry molar
Mesiodens
Distomolar
Dens in dente is often seen in conjunction with
Supernumerary roots
Tuberculated premolars
A periapical lesion
Extra cusps
Which term defines a disturbance of the maturation of the enamel matrix?
Enamel hypocalcification
Premature birth
Mulberry molar
Turner tooth
Regional odontodysplasia is also referred as
Supernumerary teeth
Taurodontism
Ghost teeth
Hypodontia
Which term describes a disorder caused by abnormalities in the genetic makeup transmitted from patient to offspring?
Developmental
Congenital
Inherited
Anomaly
Odontogenic keratocytes are a clinical component of
Gardner syndrome
Cherubism
Neurofibromatosis
Nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome
{"name":"Oral Path Midterm Review (Mrs. B's Kahoot!)", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"Prepare for your Oral Pathology midterm with this comprehensive quiz created by Mrs. B! Dive into 45 questions covering various oral conditions, immune responses, and much more.Test your knowledge and reinforce your learning! Key topics include:Diagnosis of oral lesionsImmune responsesOral diseases and treatments","img":"https:/images/course5.png"}
More Quizzes
Quiz 4 Tissues
19100
Choose the correct alternative.
3226
About your favourite brummie
1059
Vietnamese
4230
Modern Literature with Answers - Fiction Topics
15815300
Days of the Week - Free Online Practice
201017621
Polynomial Factoring - Free Algebra Practice
201021759
Which Yaelokre Character Are You? Free Online
201016918
Integumentary - Function of Ceruminous Gland Secretions
201016623
PTCB Calculations - Free Pharmacy Tech Math
201019399
What Age Should You Have Your First Kiss? Free
201017828
What Subject Should I Teach? Free - Find Your Fit
201016623