ANZAN EEG Course Self-Assessment Programme: Part B


Welcome to the ANZAN EEG Course Self-Assessment Programme: Part B. This is for those who have already done Part A of the quiz. It is an educational tool to help you assess your progress in EEG and replicates components of the ANZAN-ASEPA Part 1 and Part 2 EEG Exams. Paediatric and adult examples are included as some knowledge of EEG throughout the age range is expected.
To zoom in on any slides, either use the trackpad, or click the 'View' and then 'Zoom' buttons at the top of the browser.


Welcome to the ANZAN EEG Course Self-Assessment Programme: Part B. This is for those who have already done Part A of the quiz. It is an educational tool to help you assess your progress in EEG and replicates components of the ANZAN-ASEPA Part 1 and Part 2 EEG Exams. Paediatric and adult examples are included as some knowledge of EEG throughout the age range is expected.
To zoom in on any slides, either use the trackpad, or click the 'View' and then 'Zoom' buttons at the top of the browser.
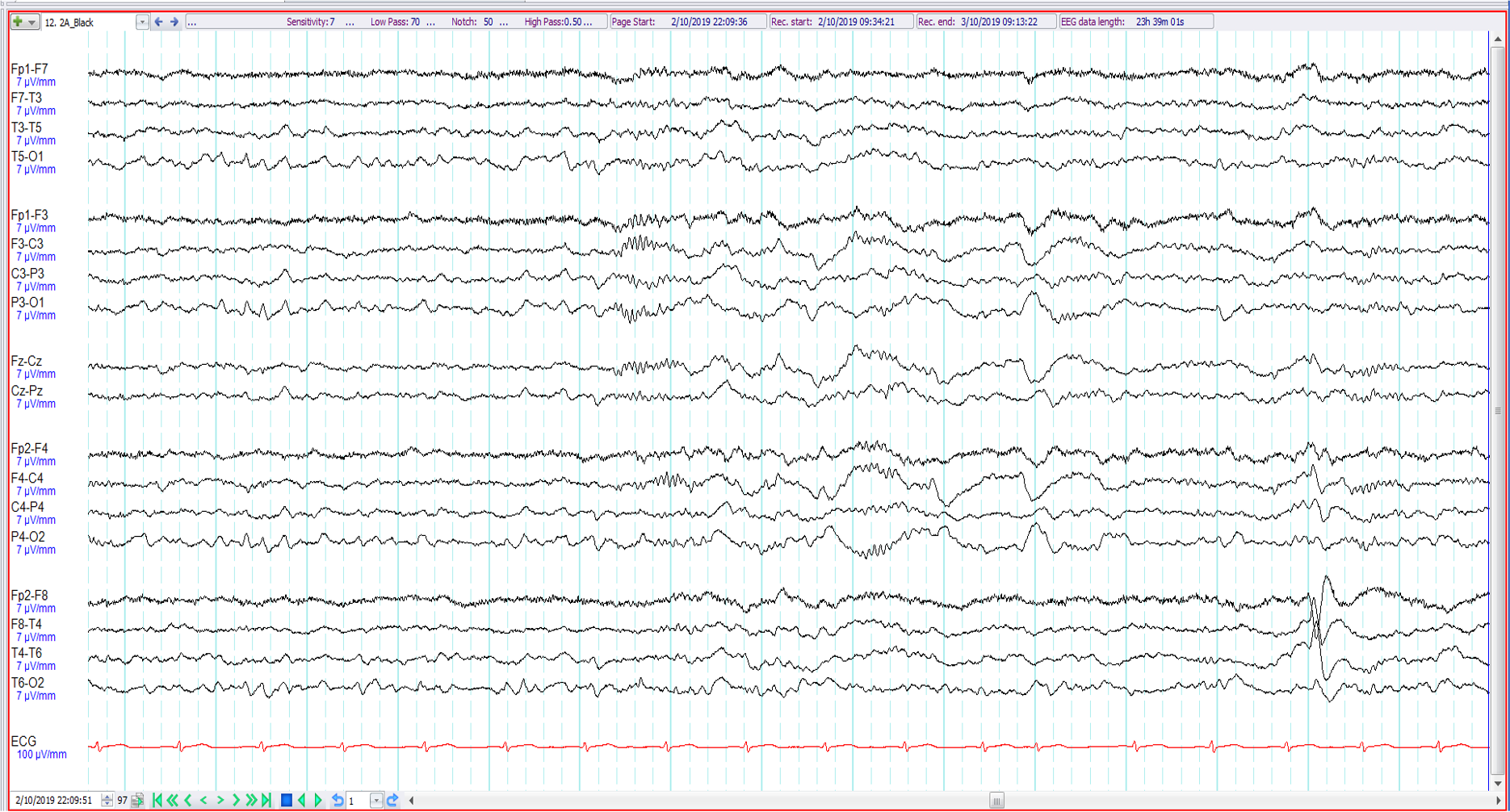
1. 67-year old with episodes of nocturnal confusion ?seizures. The following are all evident except:
Sleep spindles
Vertex waves
Positive occipital sharp transients of sleep
Wicket waves
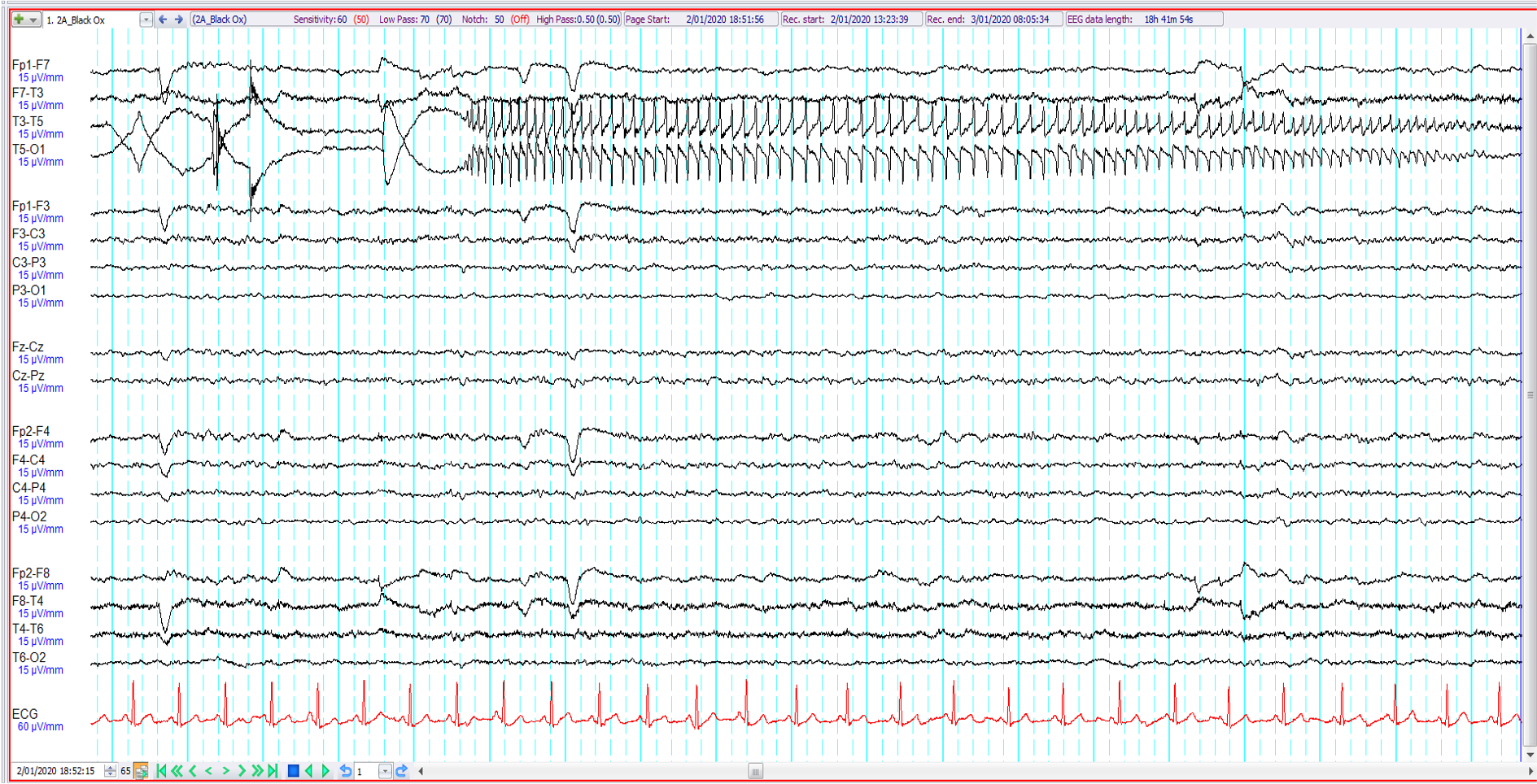
2. 14-year old with intellectual impairment ?seizures. The EEG shows the following:
Left rhythmic temporal theta of drowsiness (RTTD)
Sweat artefact
Electrode artefact
Left temporal electrographic seizure discharge
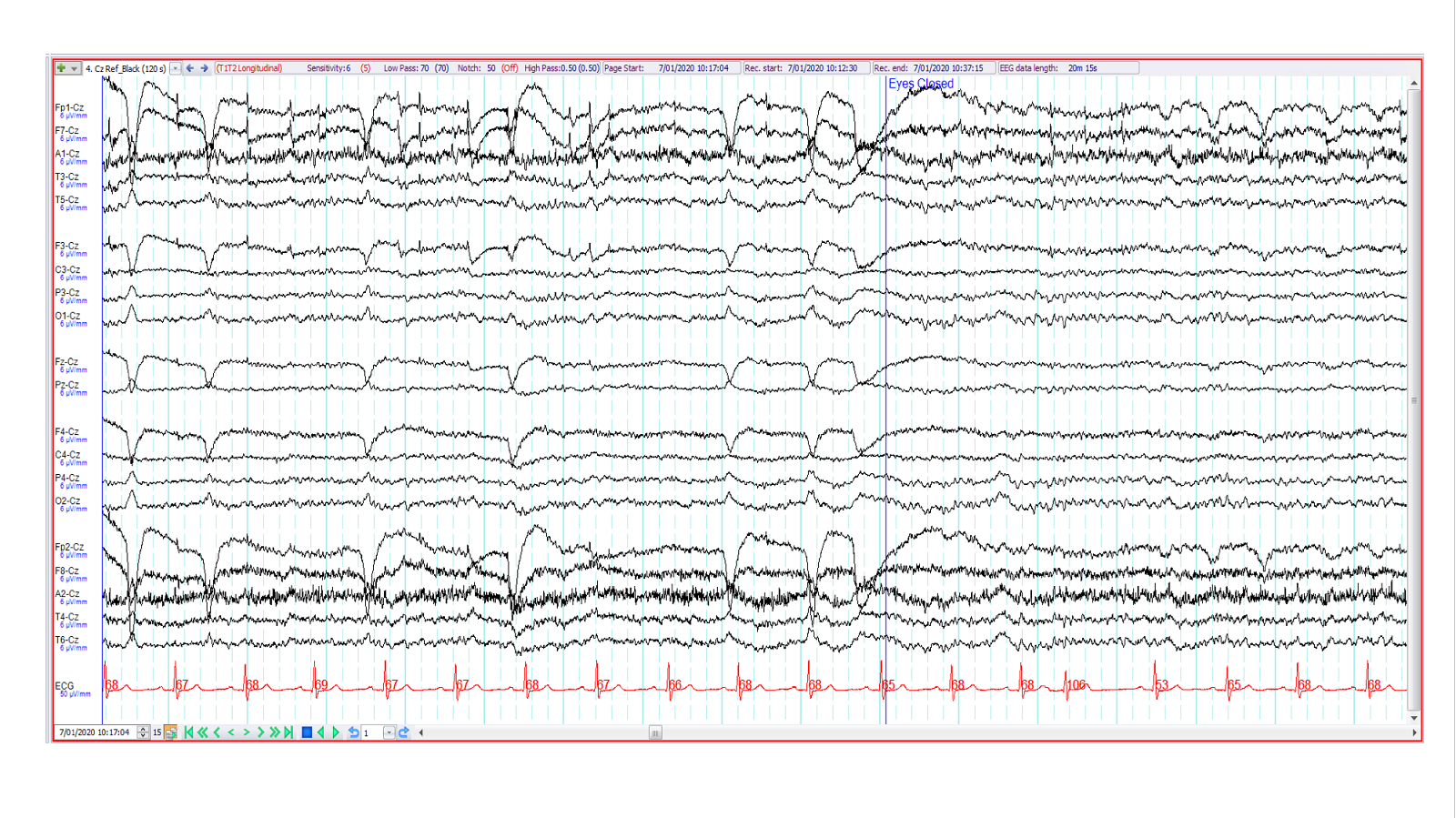
3. 22-year old with recent onset psychosis ?organic cause. The EEG (Cz referential montage) shows:
Left frontotemporal epileptiform discharges
Left temporal wicket waves
Lateral rectus spikes
Benign sporadic sleep spikes
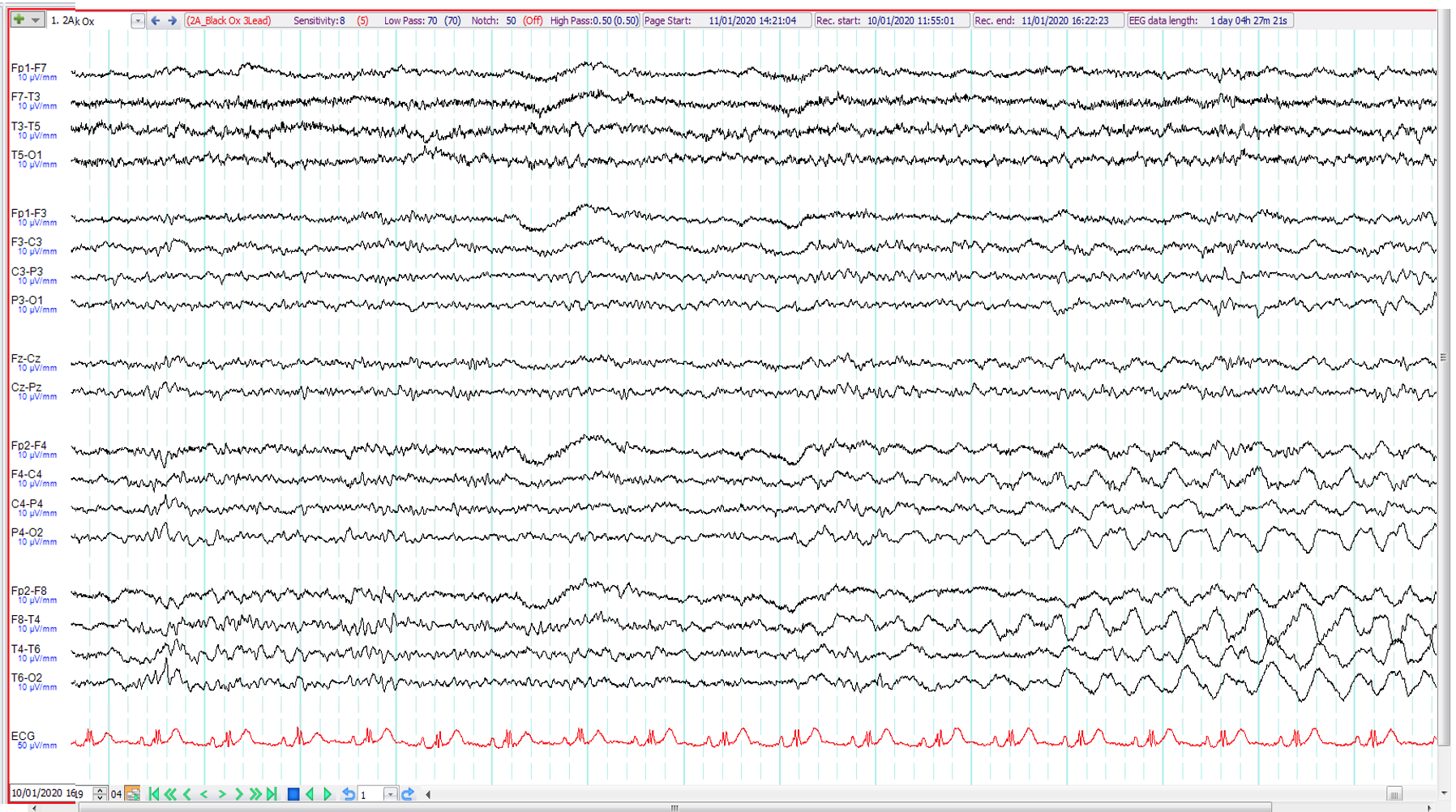
4. 19-year old. Unwitnessed motor vehicle accident ?seizure-related The EEG shows:
Right temporal intermittent rhythmic delta activity (TIRDA)
Scratching artefact
Focal seizure of right hemispheric origin
Subclinical rhythmic electrographic discharge of adults (SREDA)
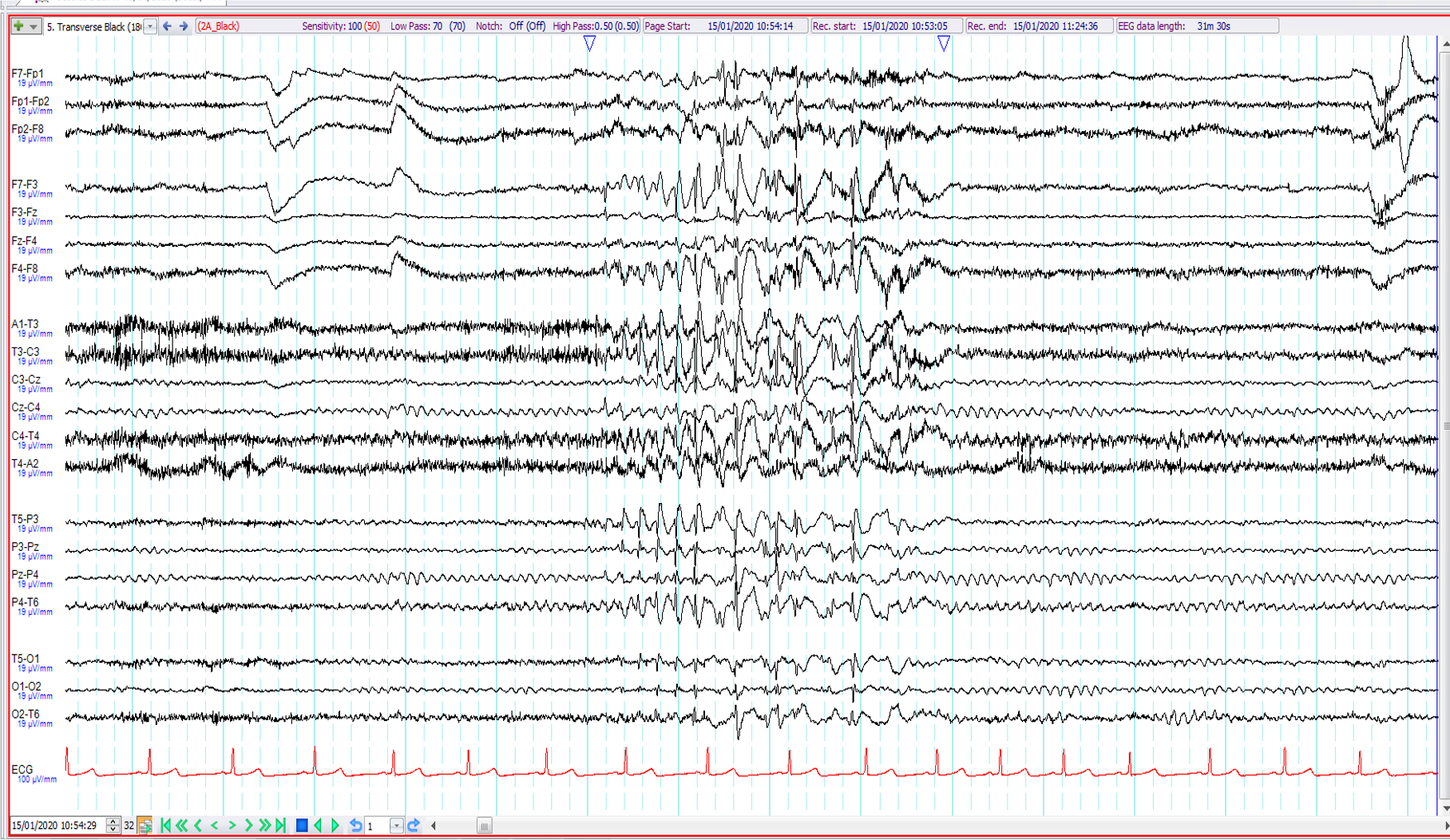
5. 12-year old. Recent onset of episodes of a flush-like sensation with behavioural arrest and loss of awareness lasting 3-5 seconds. The EEG (transverse montage) shows:
6Hz (phantom) spike and wave
Generalised irregular 5-6 Hz spike and wave activity
Generalised slow spike and wave activity
Secondary bilateral synchrony
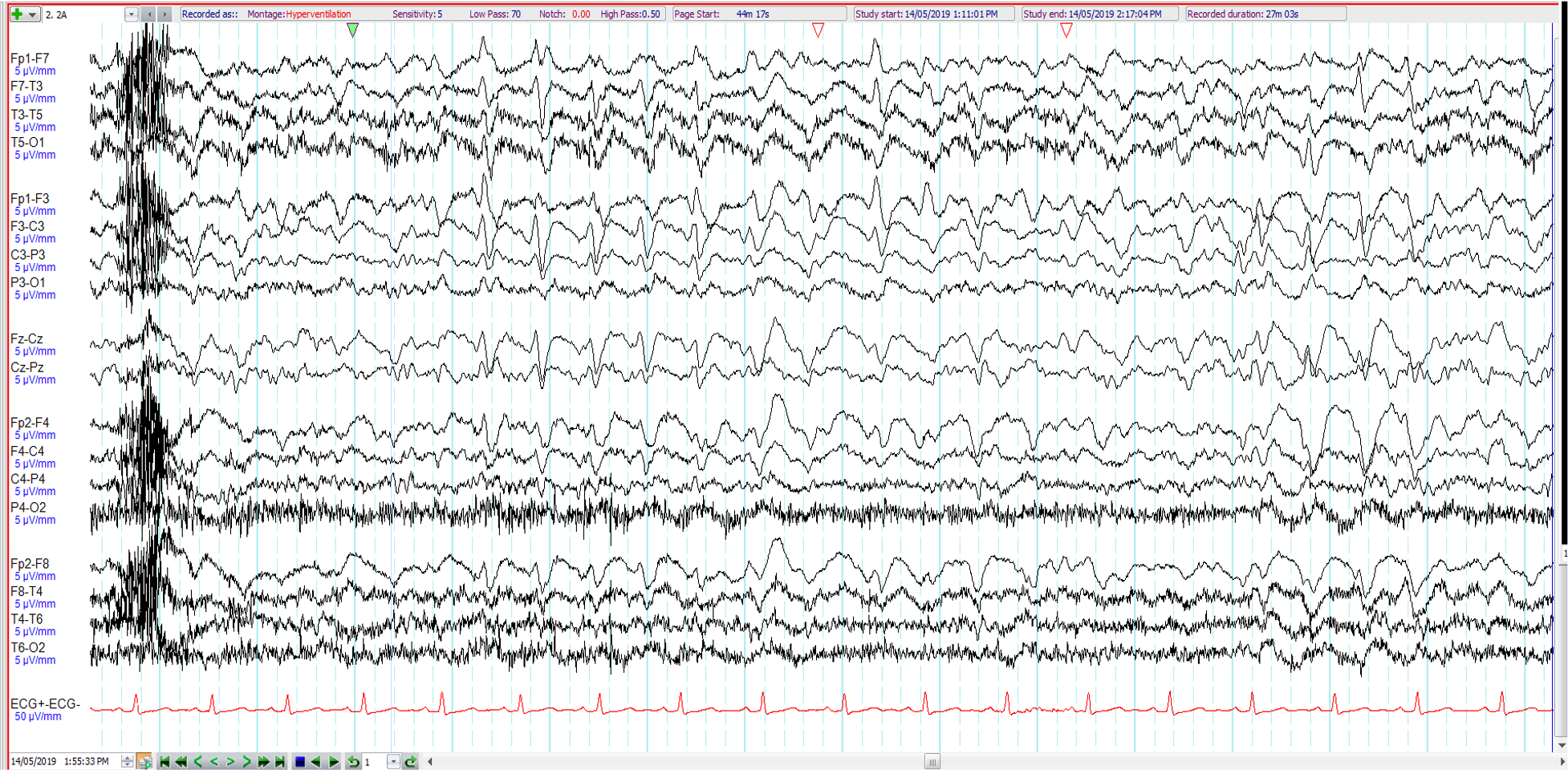
6. 58 year old, right-handed, previously well. 2 week history cognitive difficulties and dysphasia. Patient awake and oriented during EEG. The EEG shows:
Focal non-convulsive status epilepticus
Generalised slow spike and wave activity
Atypical triphasic waves
Generalised non-convulsive status epilepticus
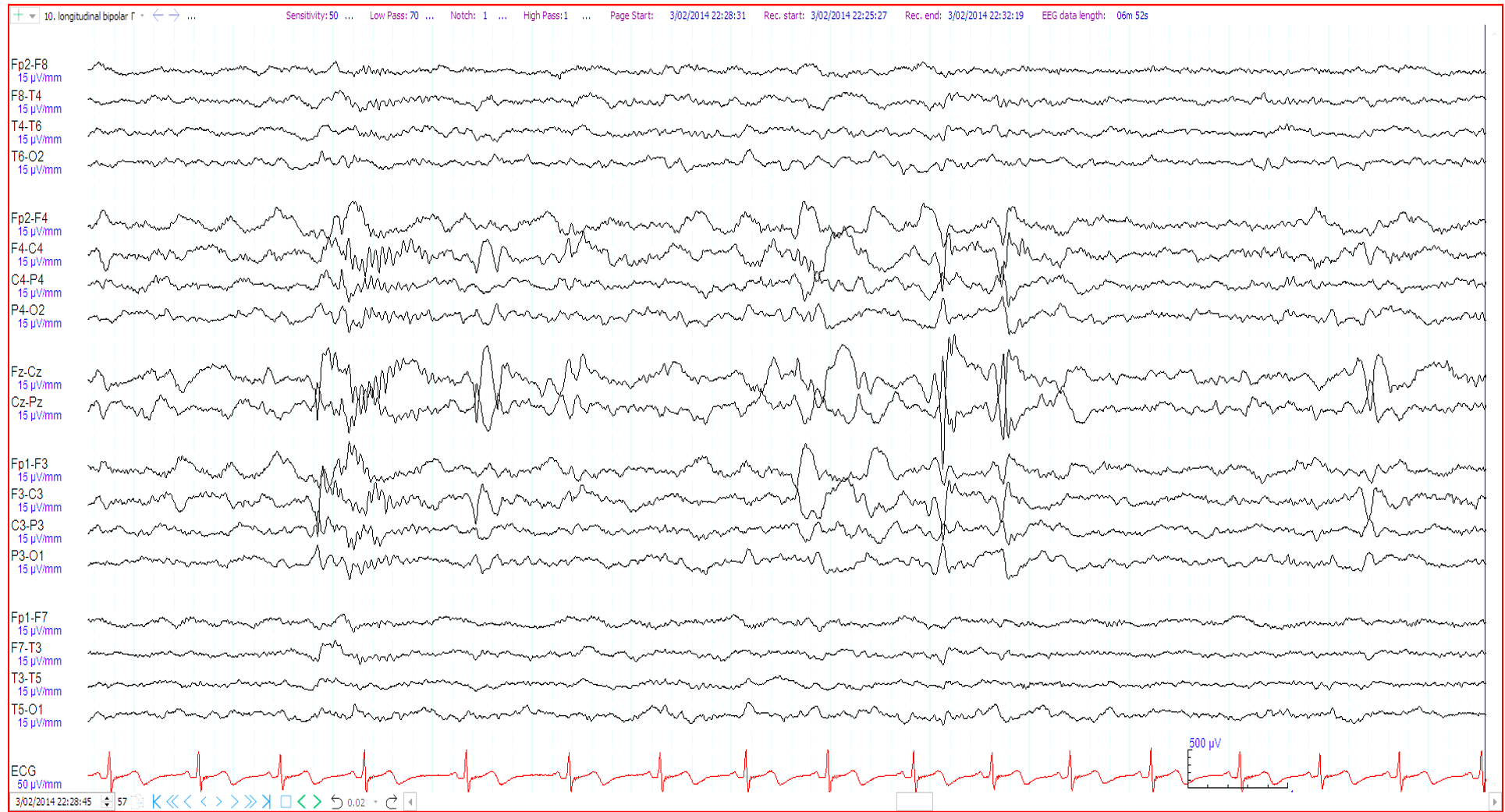
7. 8 year old. Staring episodes ?seizures. Mother has juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. The EEG shows:
Centro-temporal spikes
Generalised polyspike and wave activity
Normal stage 2 sleep
Midline spikes
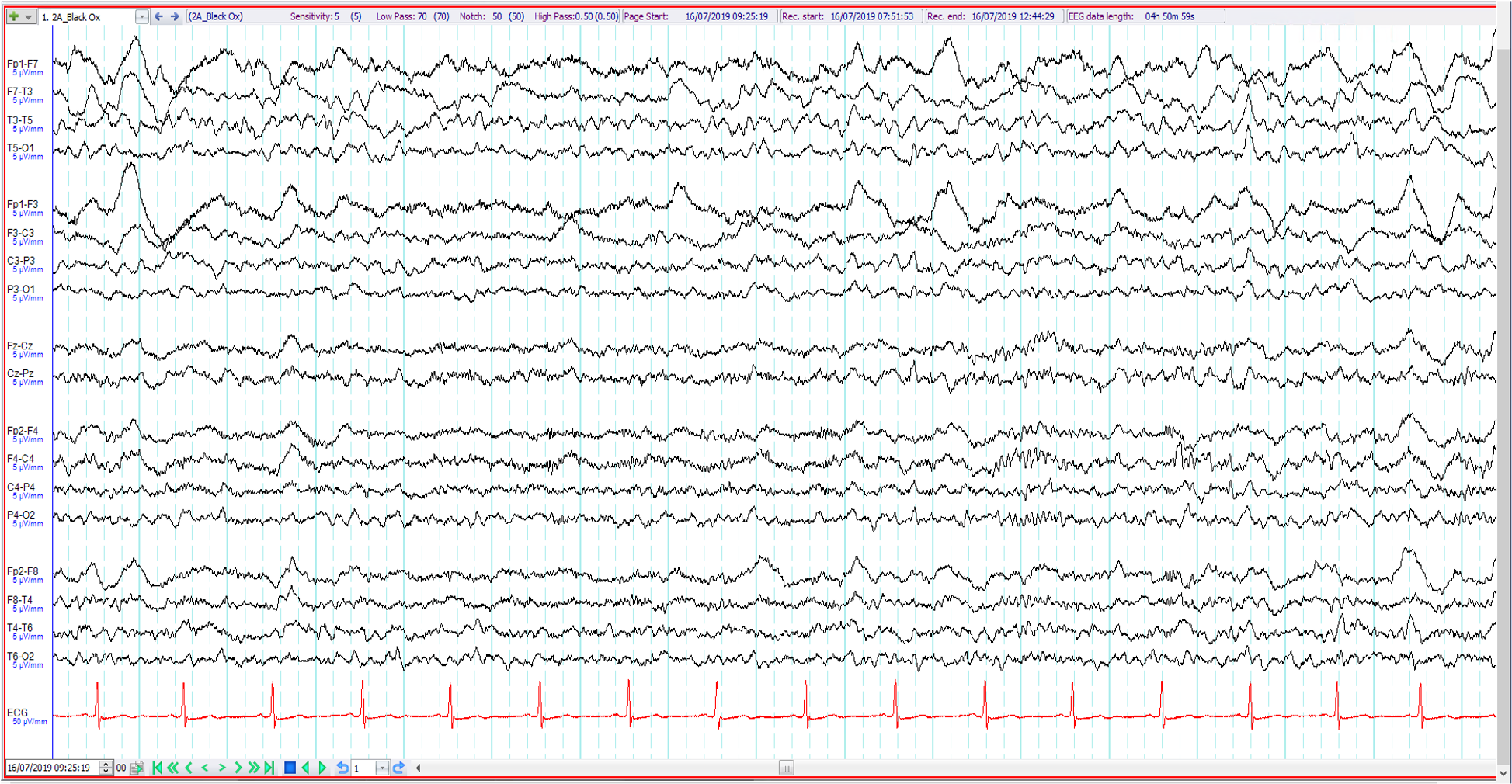
8. 79 year old. Left MCA stroke ?seizures. The EEG shows left hemispheric slowing and:
Left sided triphasic waves
Left fronto-temporal sharp waves
Left frontal zeta waves
Left temporal seizure discharge
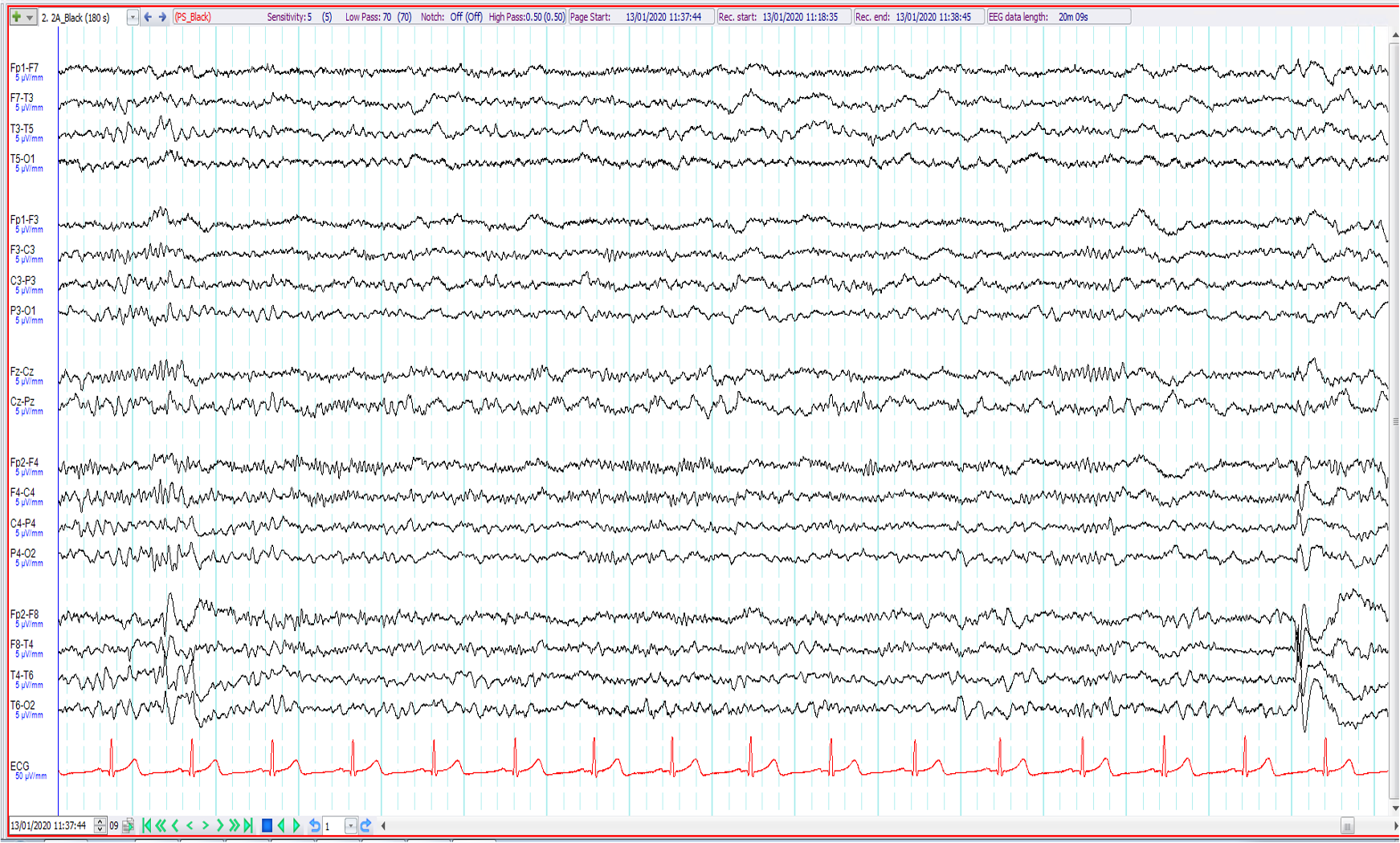
9. 52 year old alcoholic. Recent seizures followed by right hemiparesis. The EEG shows:
Right temporal epileptiform abnormalities
Right temporal wicket waves
Left temporal intermittent rhythmic delta activity (TIRDA) and right temporal epileptiform abnormalities
Right temporal epileptiform abnormalities and non-specific left hemispheric slowing
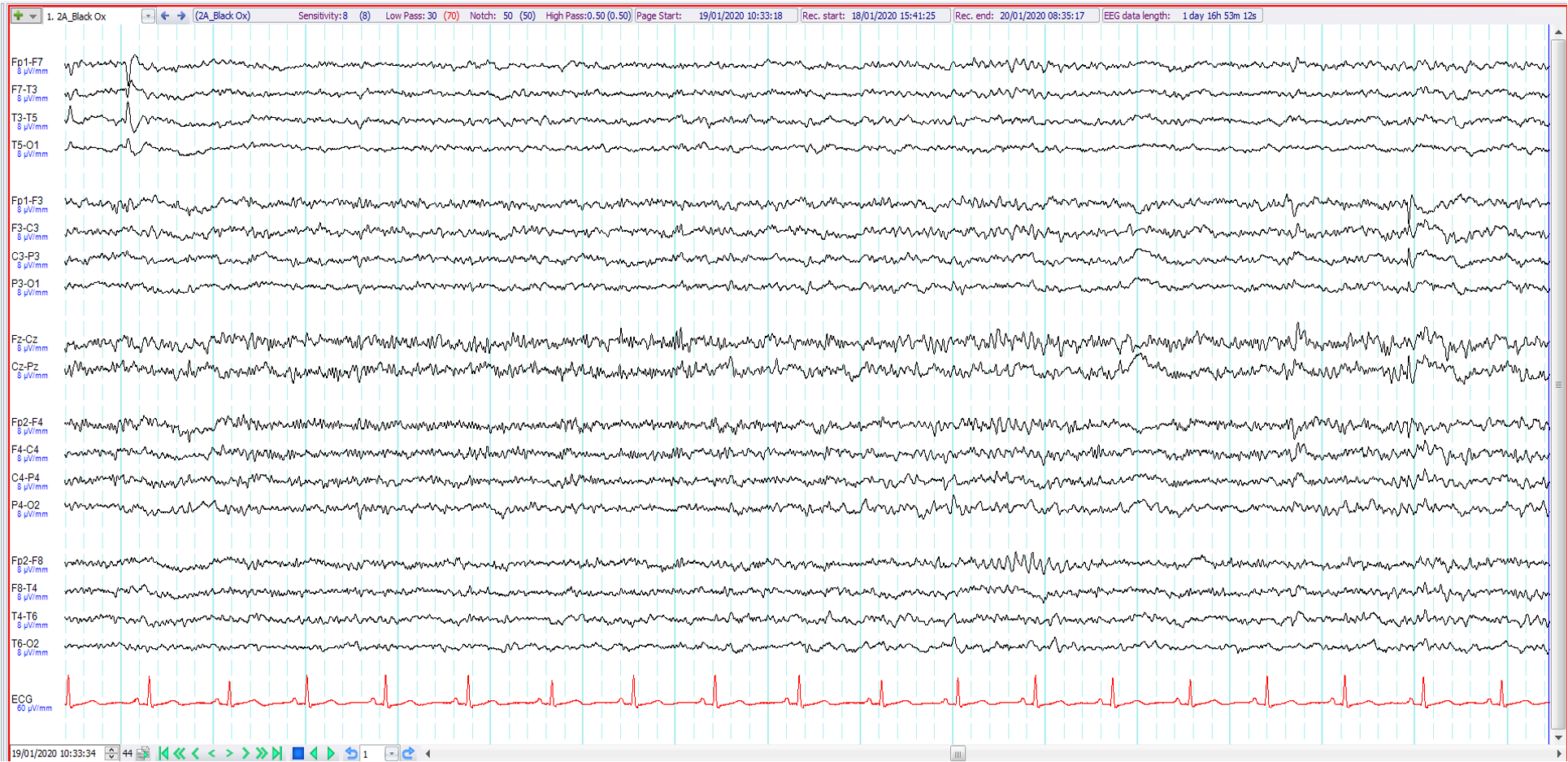
10. 22 year old. Right hemiparesis related to perinatal insult. Episodes of behavioural change ?seizures. The EEG shows:
Left centro-temporal spikes
Left temporal spikes and left frontocentral predominant benign sporadic sleep spike
Left temporal wicket waves and left frontocentral epileptiform abnormalities
Independent left temporal and frontocentral epileptiform abnormalities
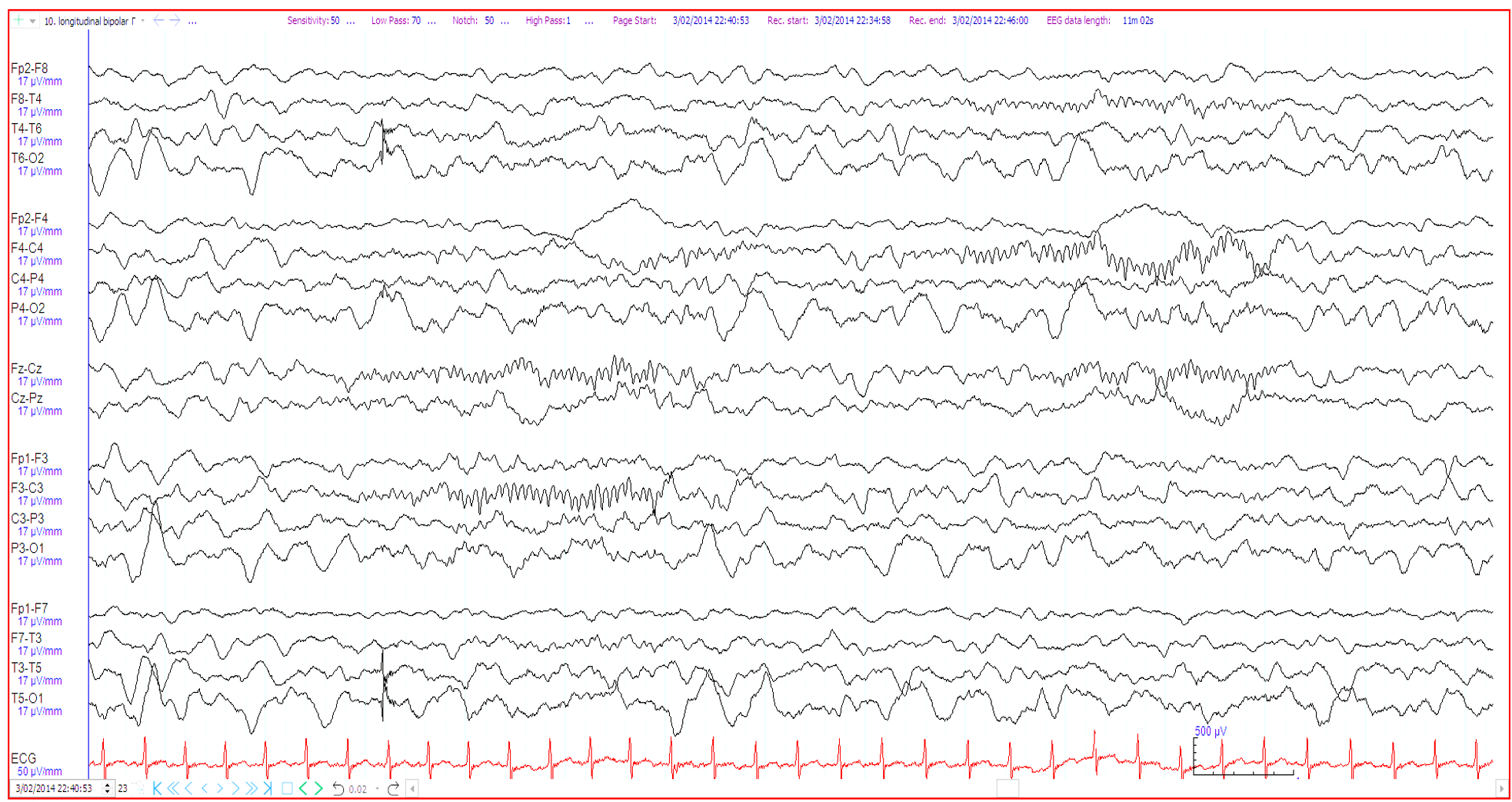
11. 6 month old. Twitching during sleep ?seizures. The EEG shows:
Bicentral brief potentially ictal rhythmic discharges (bicentral BIRDs)
Sleep spindles
Mu rhythm
Generalised paroxysmal fast activity (GPFA)
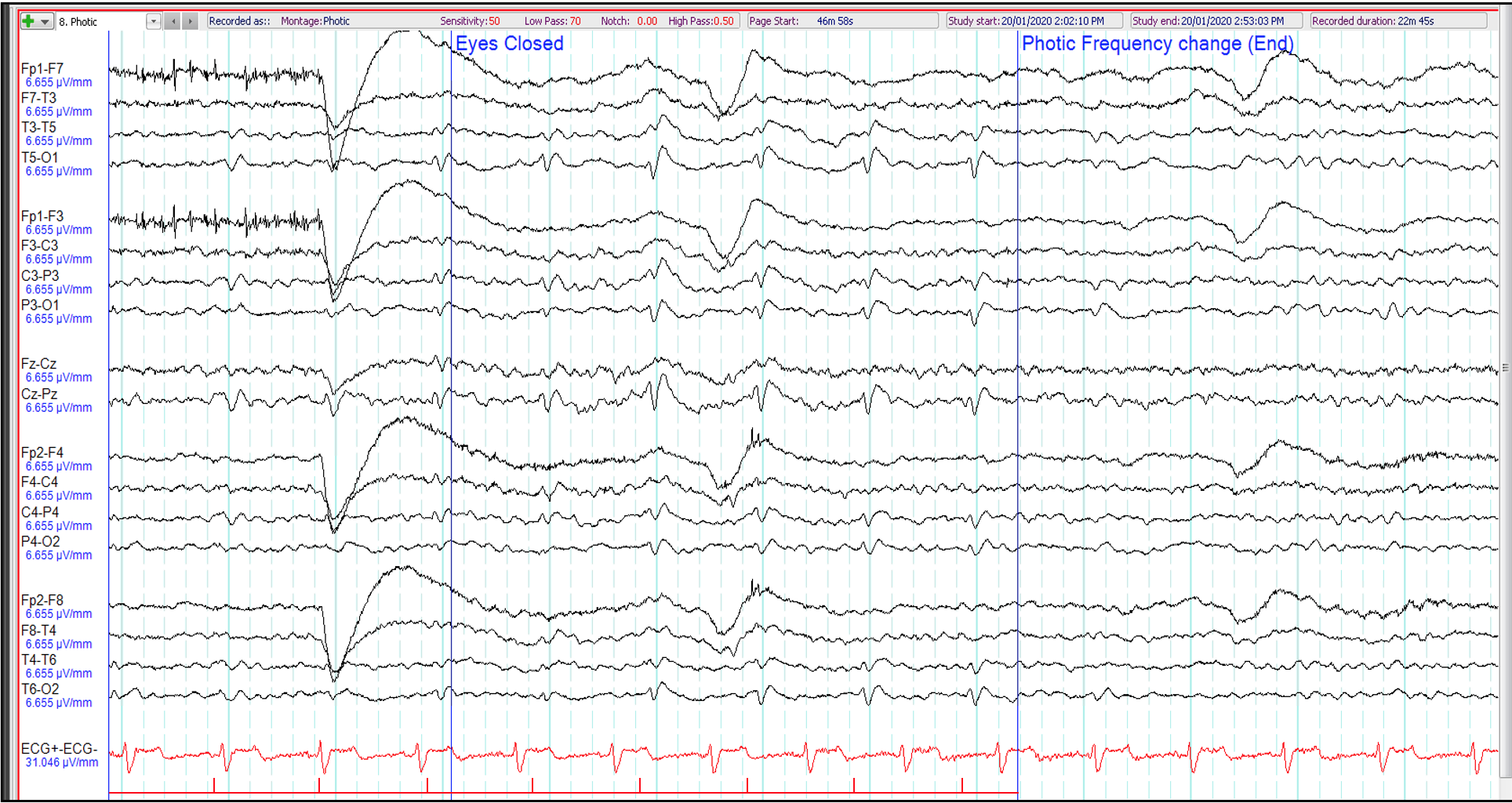
12. 84 year old. Episodic confusion. The EEG shows (during photic stimulation at 1 Hz):
Photoparoxysmal response
Photomyogenic response
Normal photic driving at low flash frequencies
Photic induced biposterior epileptiform discharges
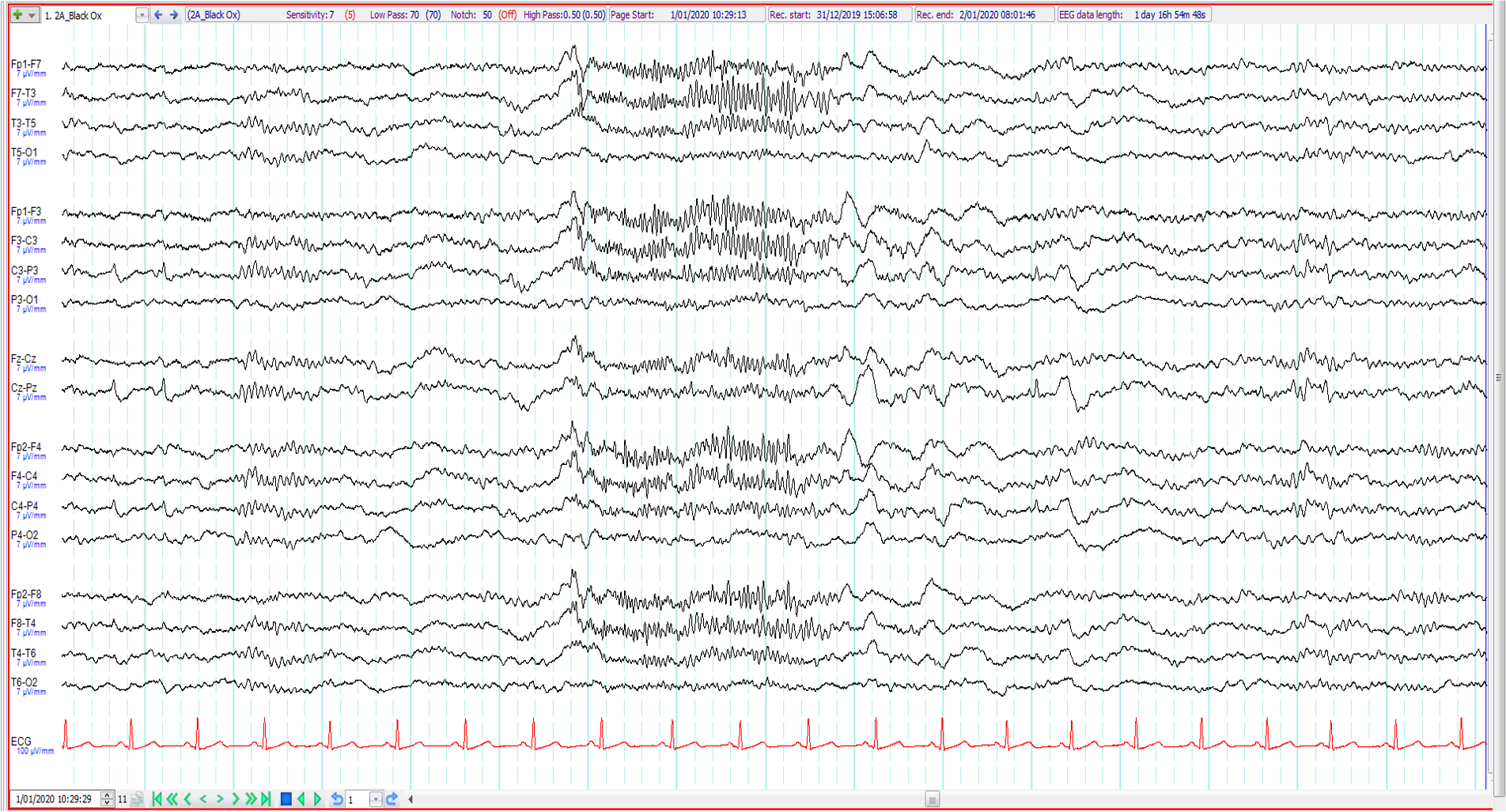
13. 15 year old. Intellectual impairment. Episodes since aged 9 involving staring with head retropulsion and eyelid flickering ?seizures. The EEG shows:
Generalised paroxysmal fast activity
Normal stage 2 sleep
Prominent myogenic artefact
Normal arousal
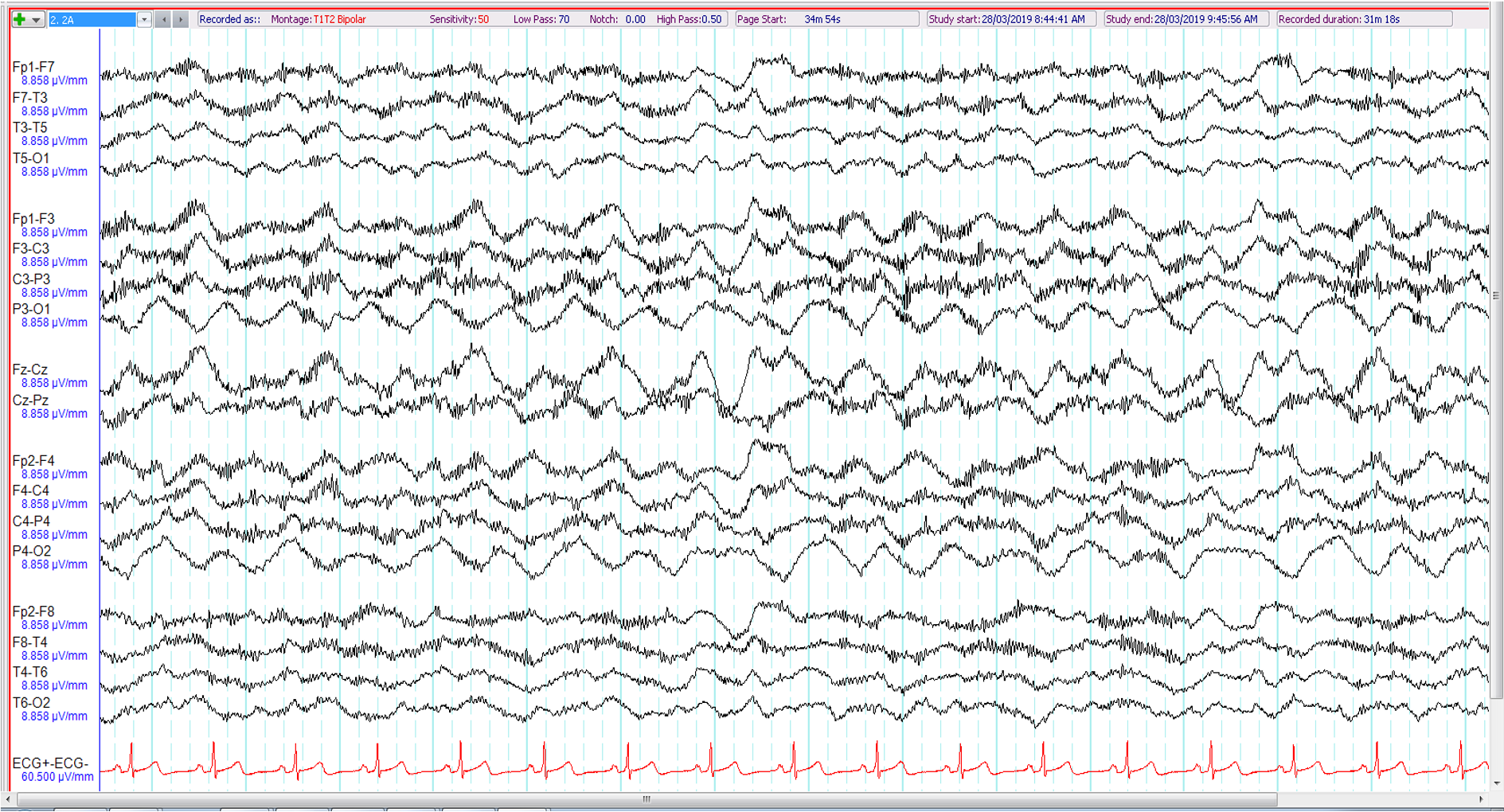
14. 30 year old with tonic clonic seizure preceded by behavioural change with psychotic features for 1 week. Patient intubated in ICU, on propofol. The EEG shows:
Normal anaesthetic effect
Non-convulsive status epilepticus
Extreme delta brush
Artefact
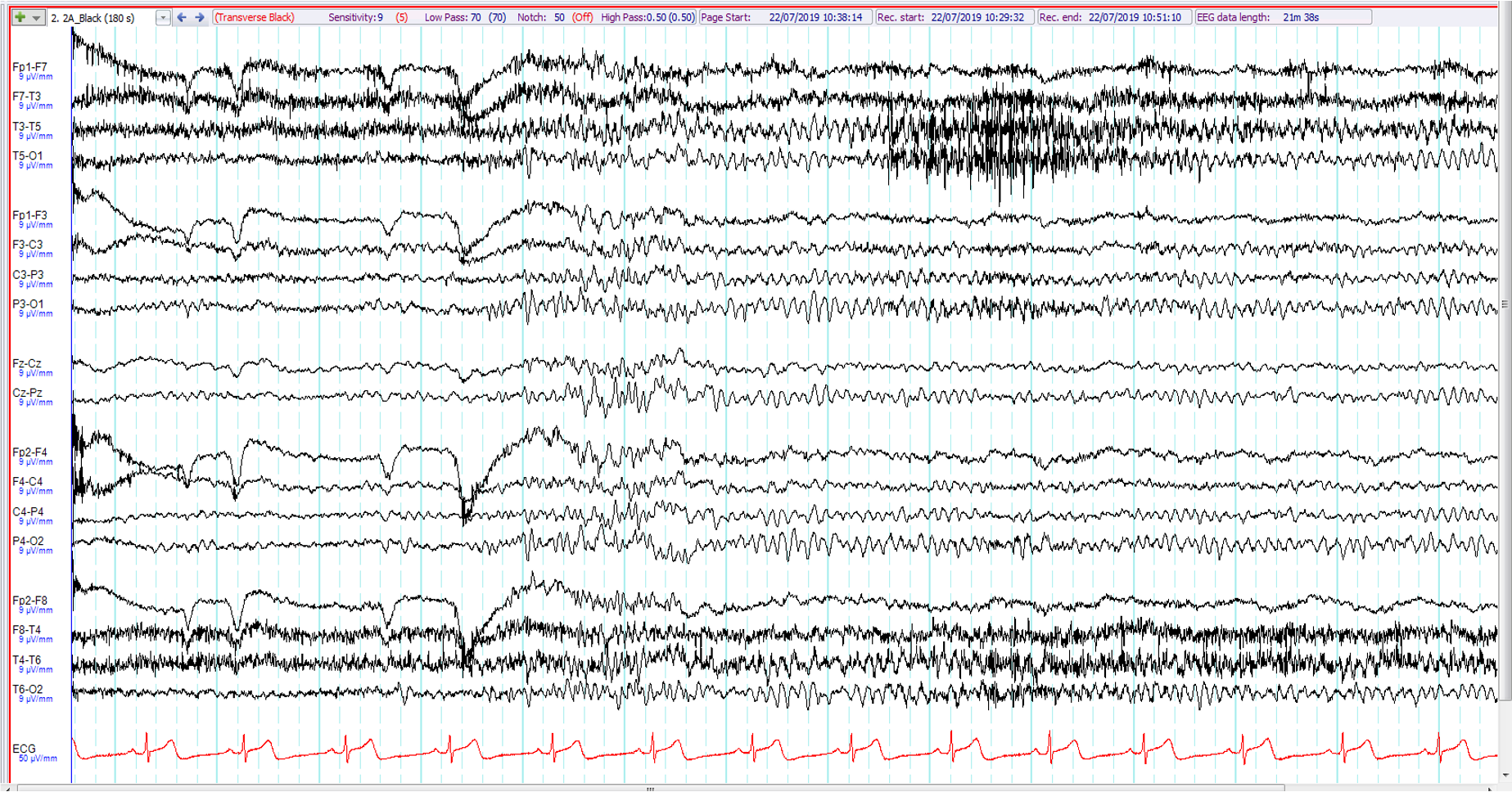
15. 14 year old with episodes of eyelid flickering with retained awareness and responsiveness ? seizures ?behavioural. The EEG shows:
Fast alpha variant
6 Hz (phantom) spike and wave
Posterior slowing of youth
Eye closure-related polyspikes
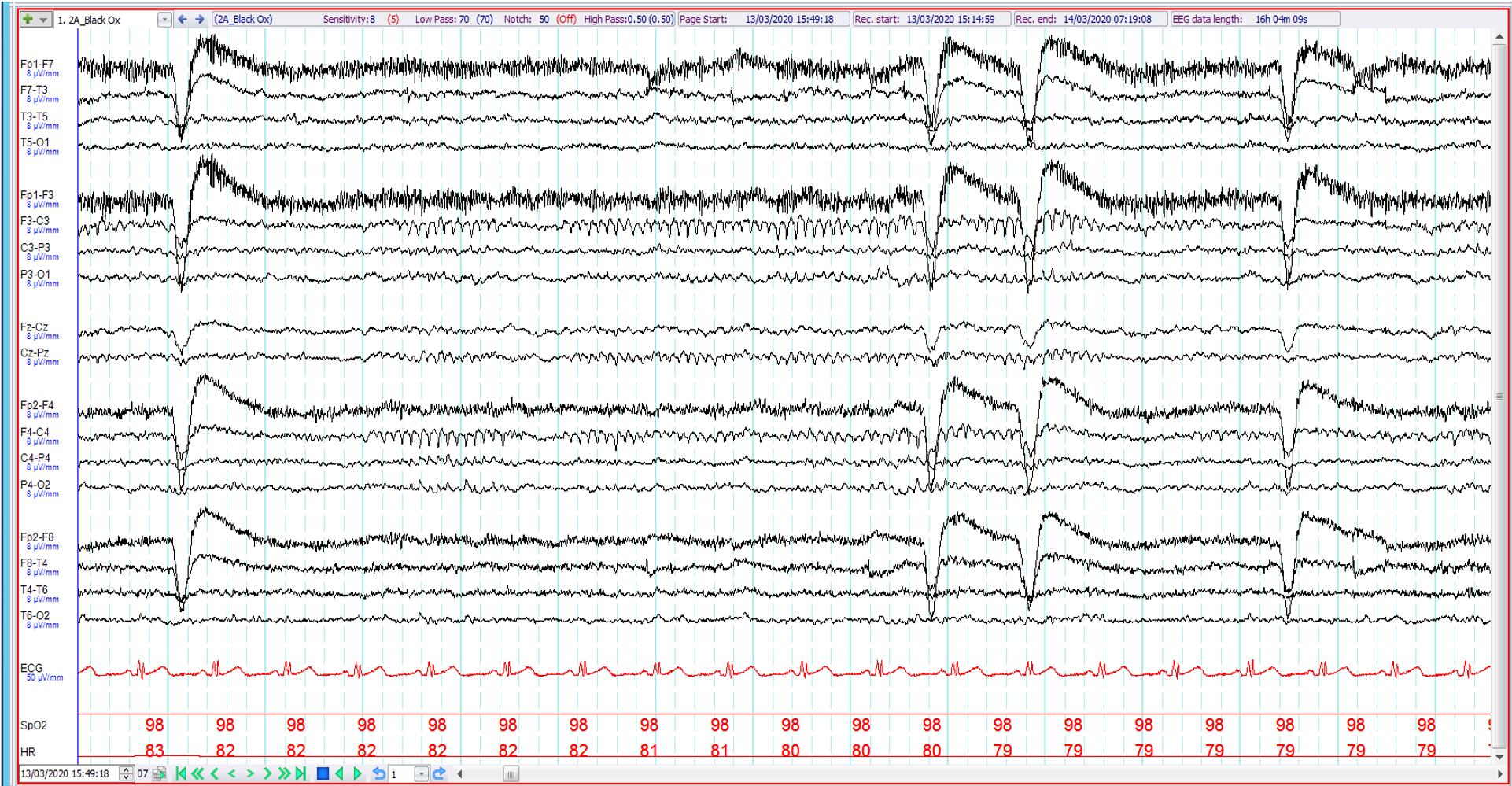
16. 22 year old. Seizures. The EEG shows:
Bicentral mu
Bicentral artefact
Sleep spindles
Bicentral electrographic seizure discharge
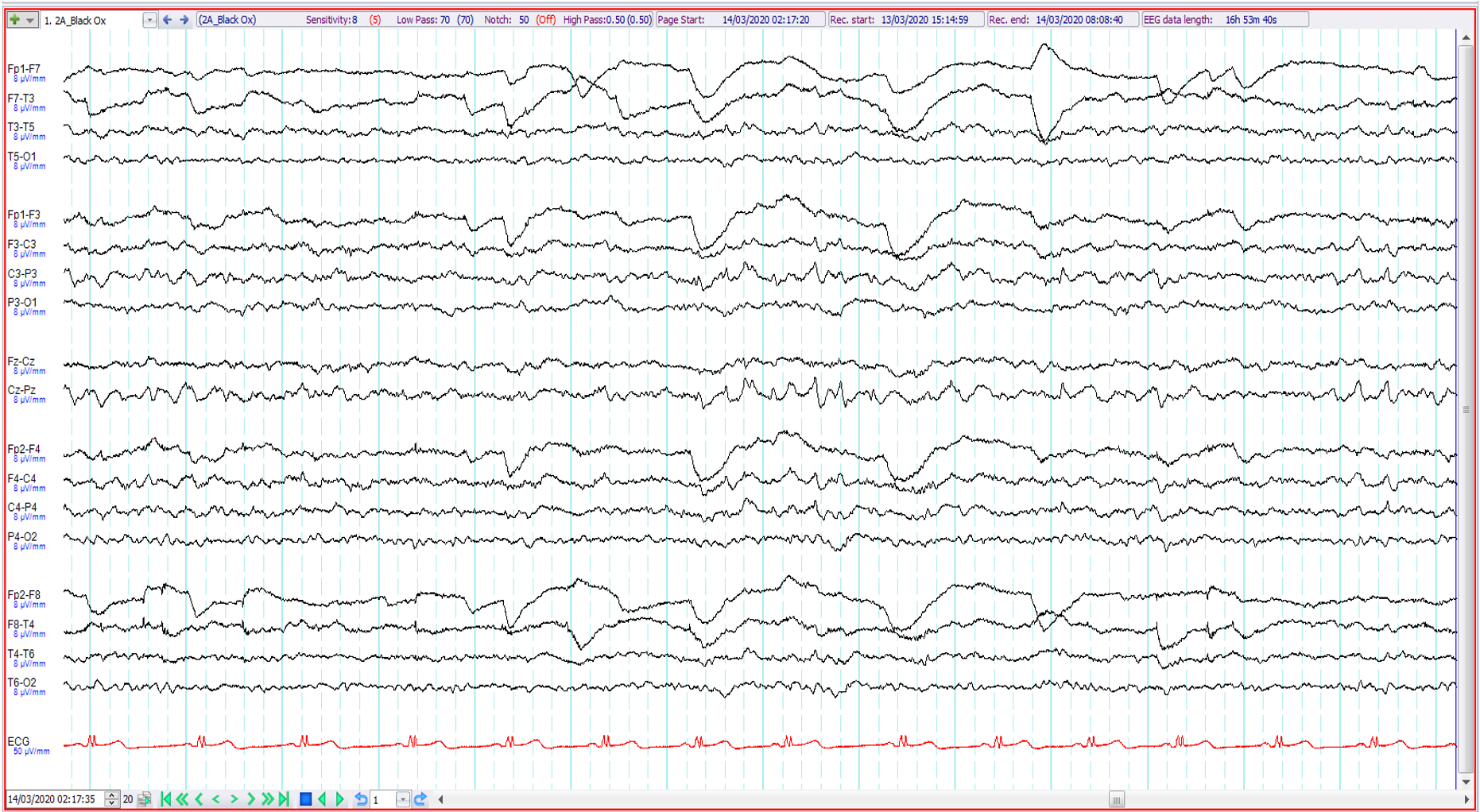
17. 22 year old. Episodes of confusion on waking ?seizures. The EEG shows:
Midline epileptiform discharges
Non-REM sleep
REM sleep
Normal wakefulness
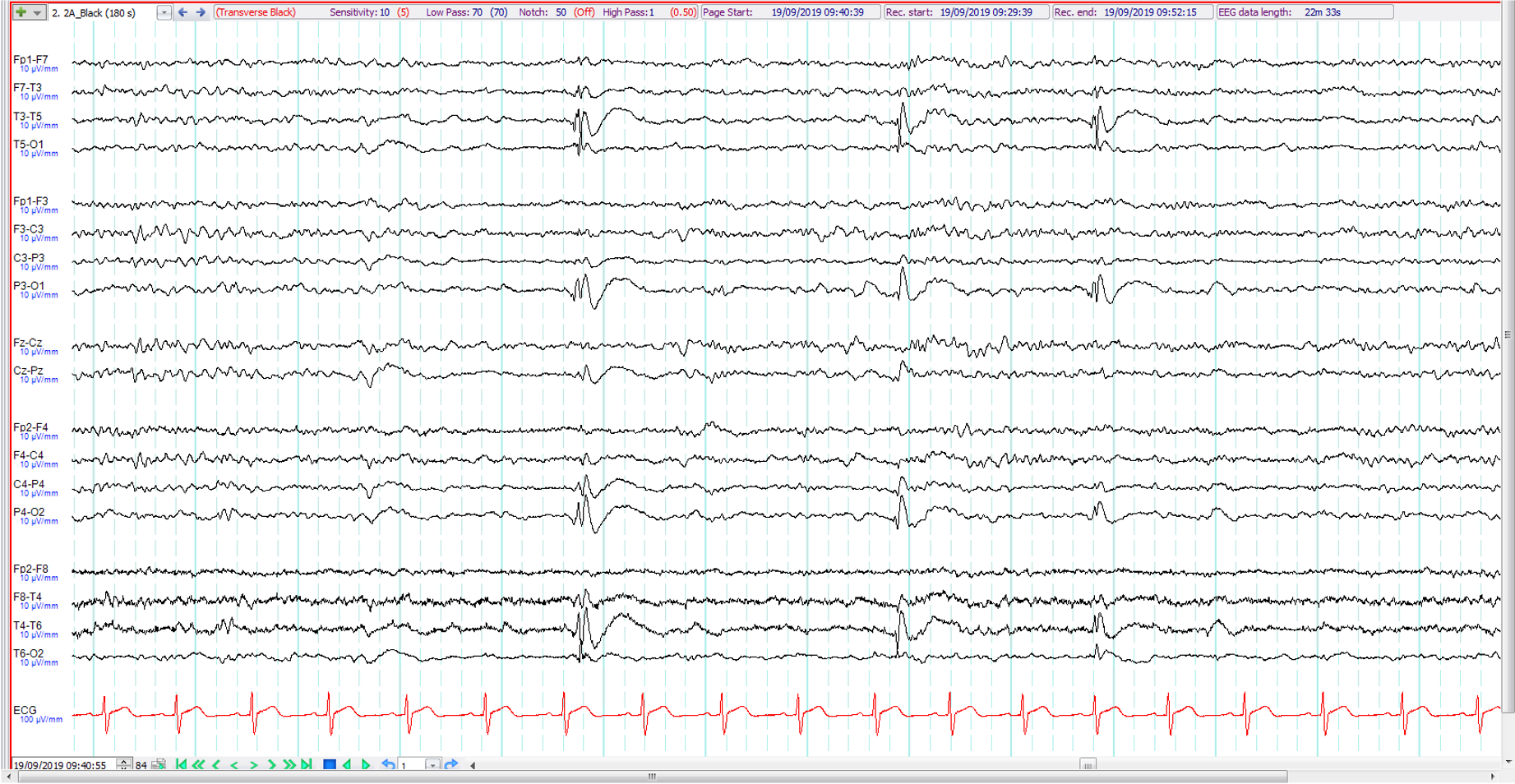
18. 12 year old. Recent onset of episodes of flashing lights followed by headaches ?migraine. The EEG shows:
Generalised epileptiform discharges
Biposterior spikes
Positive occipital sharp transients of sleep (POSTS)
6 Hz (phantom) spike and wave
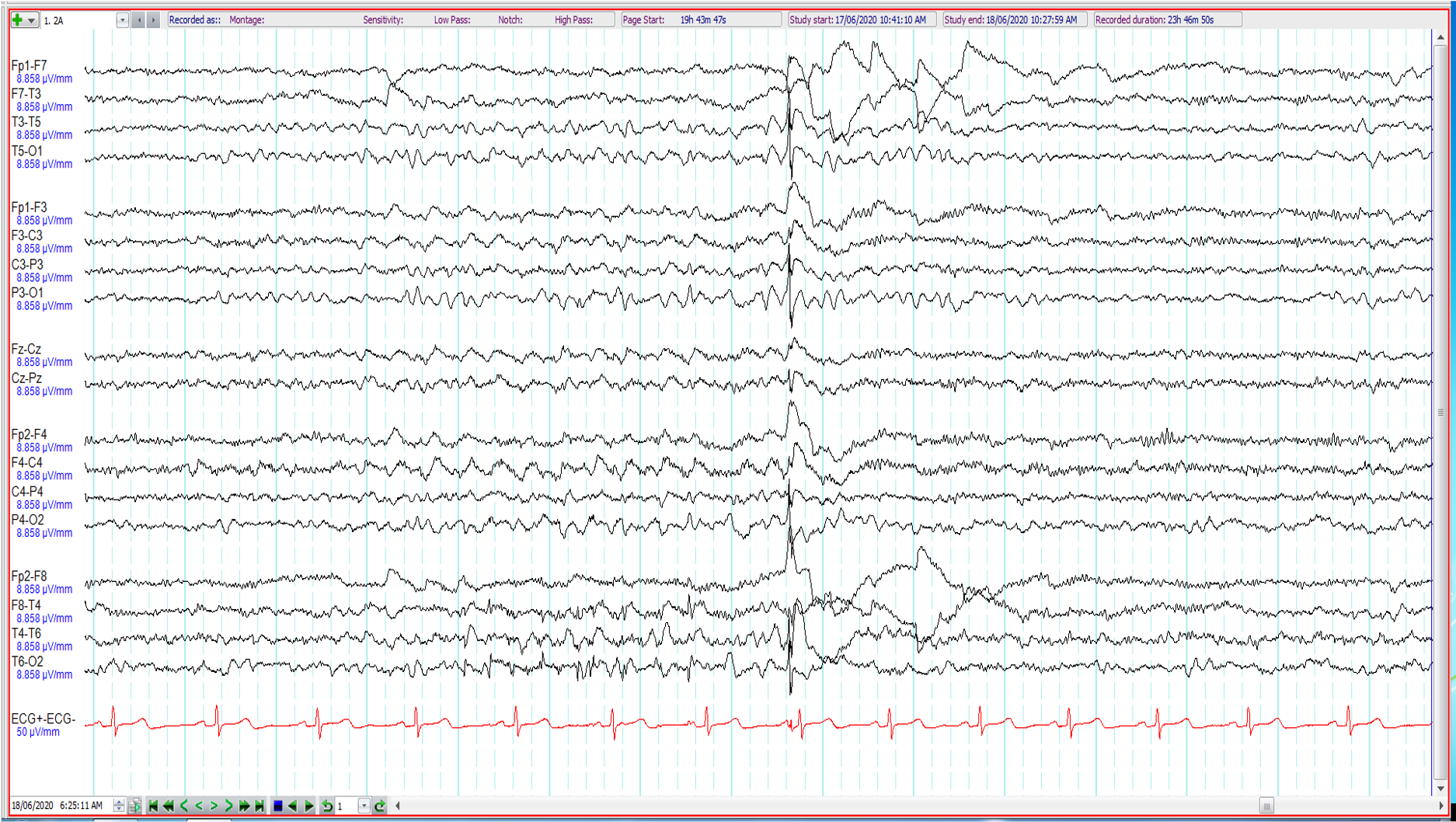
19. 37 year old. Recent onset blank spells. Previous right temporal lobectomy for mesial temporal sclerosis. The EEG shows
Generalised spike and wave discharge
Artefact
Benign sporadic sleep spike
Wicket wave
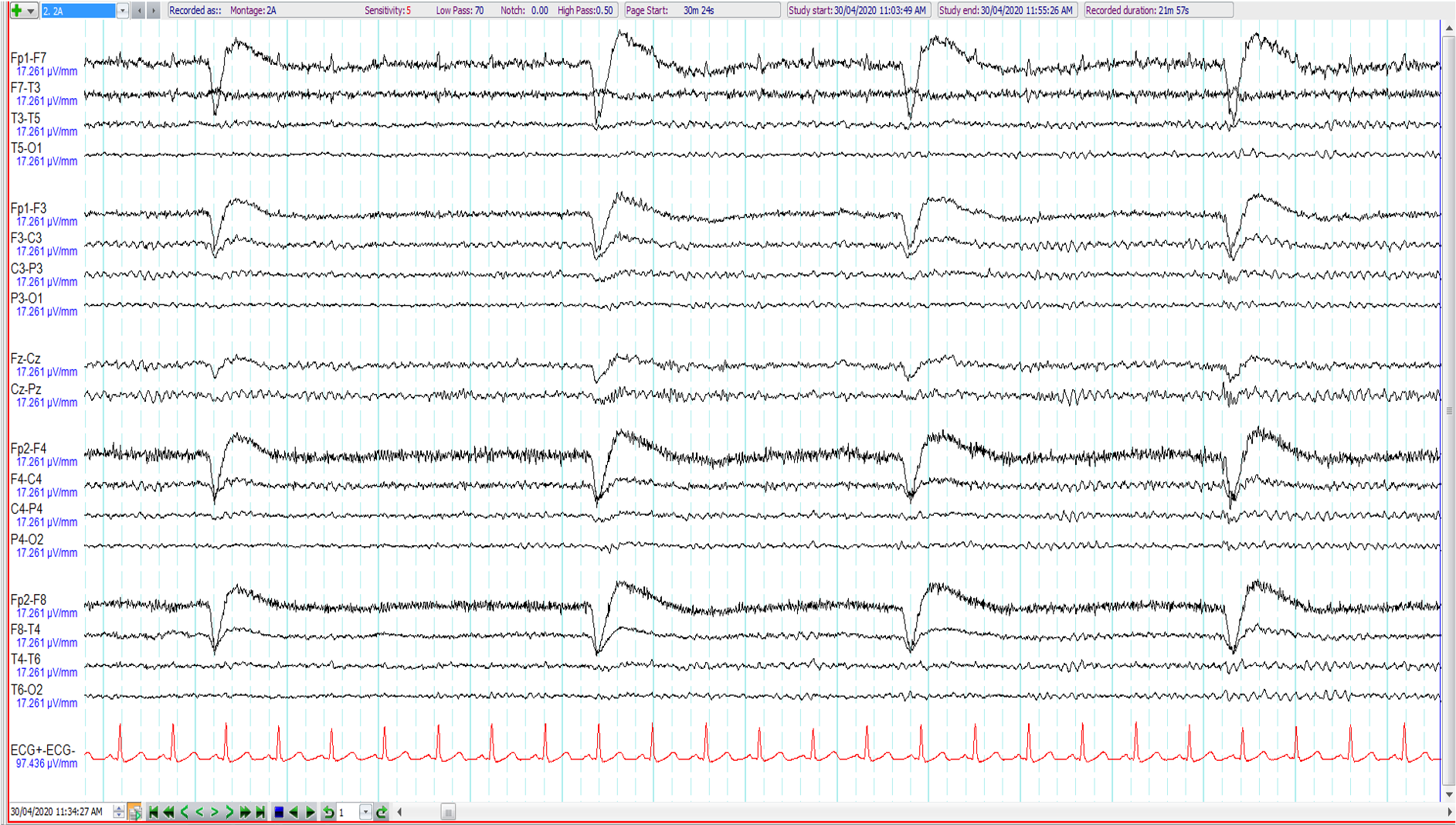
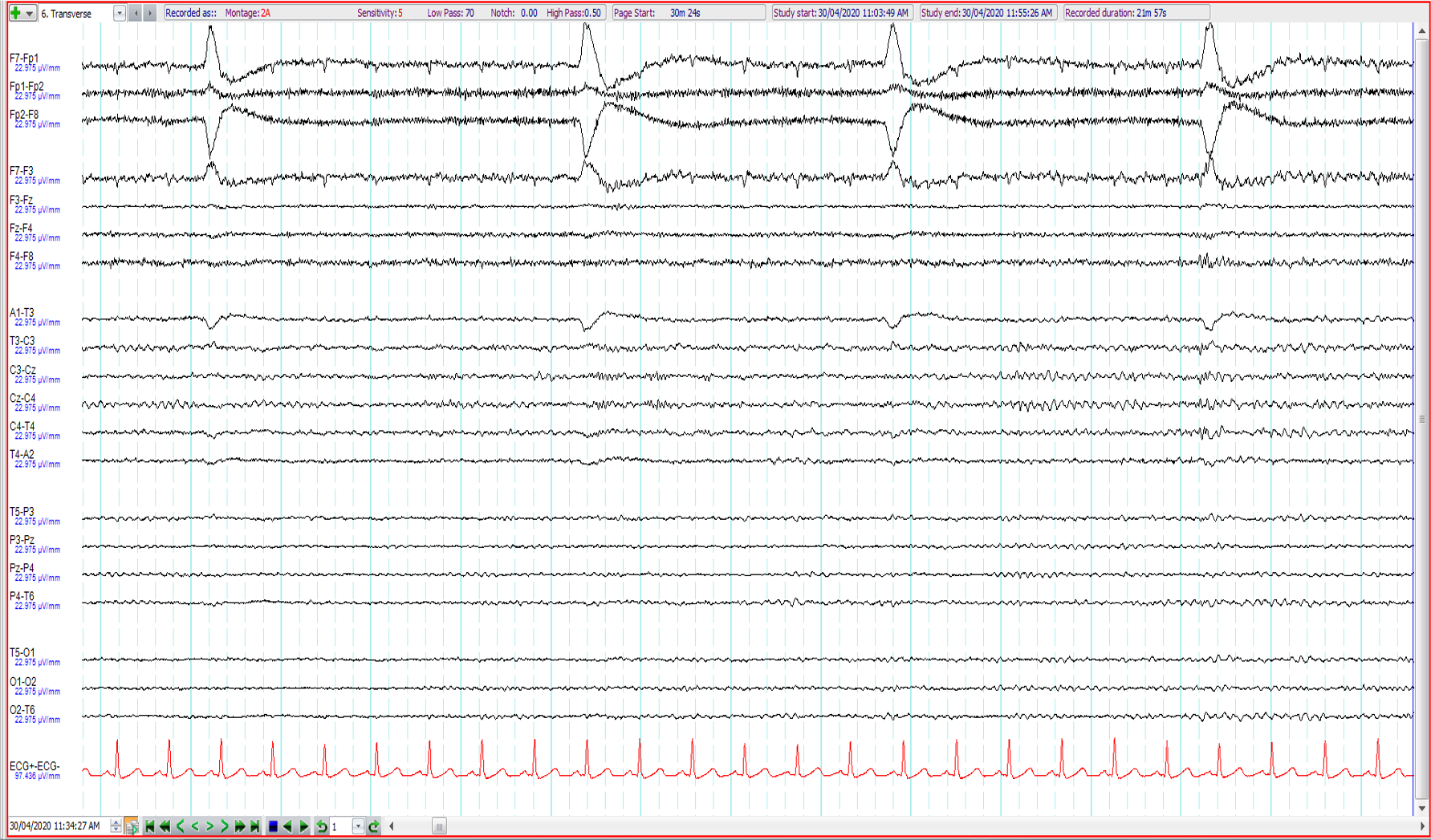
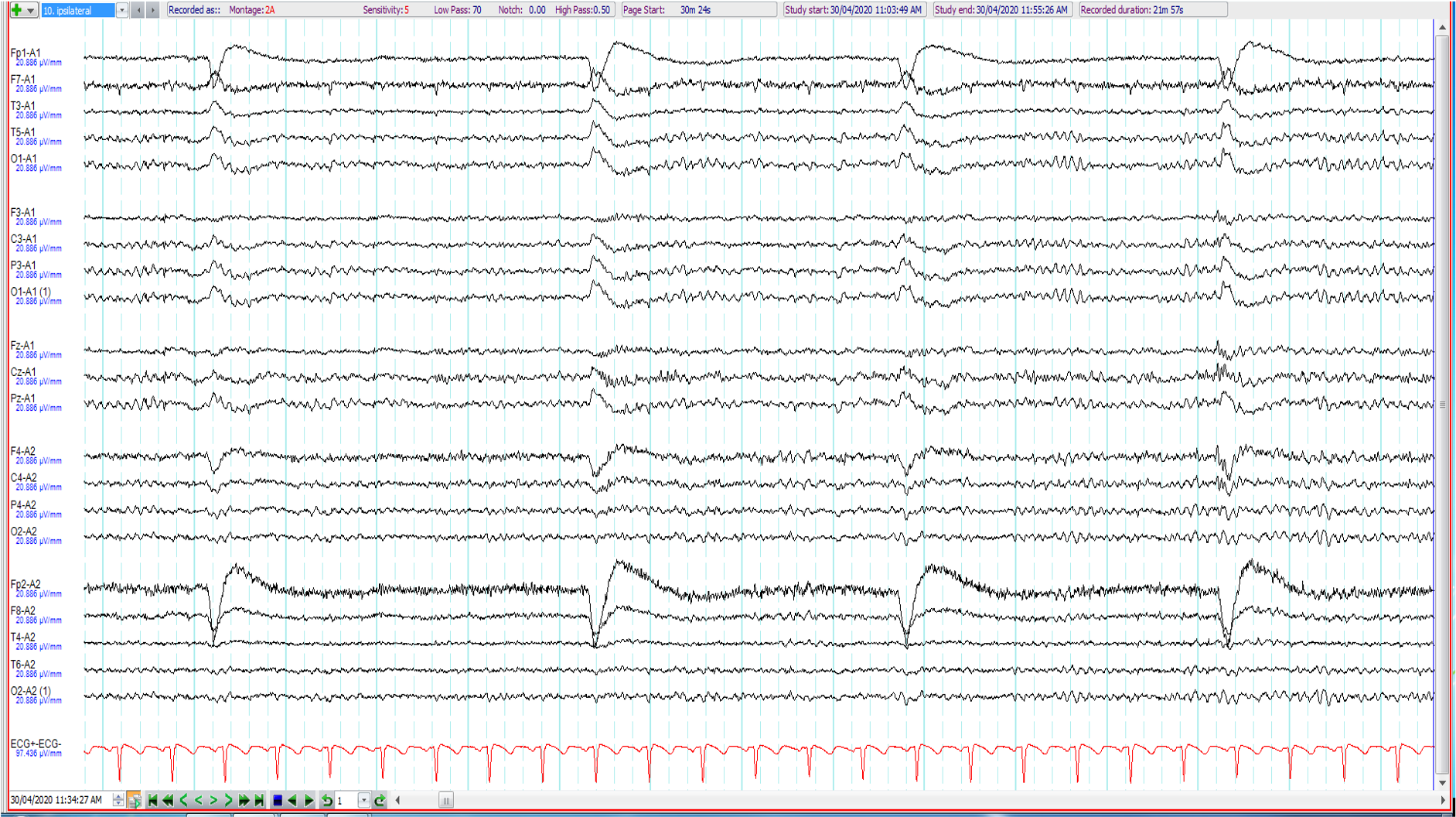
20. 33 year old. Seizures ?alcohol related. What is wrong with the EEG (longitudinal and transverse bipolar and ipsilateral ear referential montages shown)?
Salt bridge between F4 and F8
Electrodes F7 and F3 mixed up
Electrodes F7 and A1 mixed up
No issue
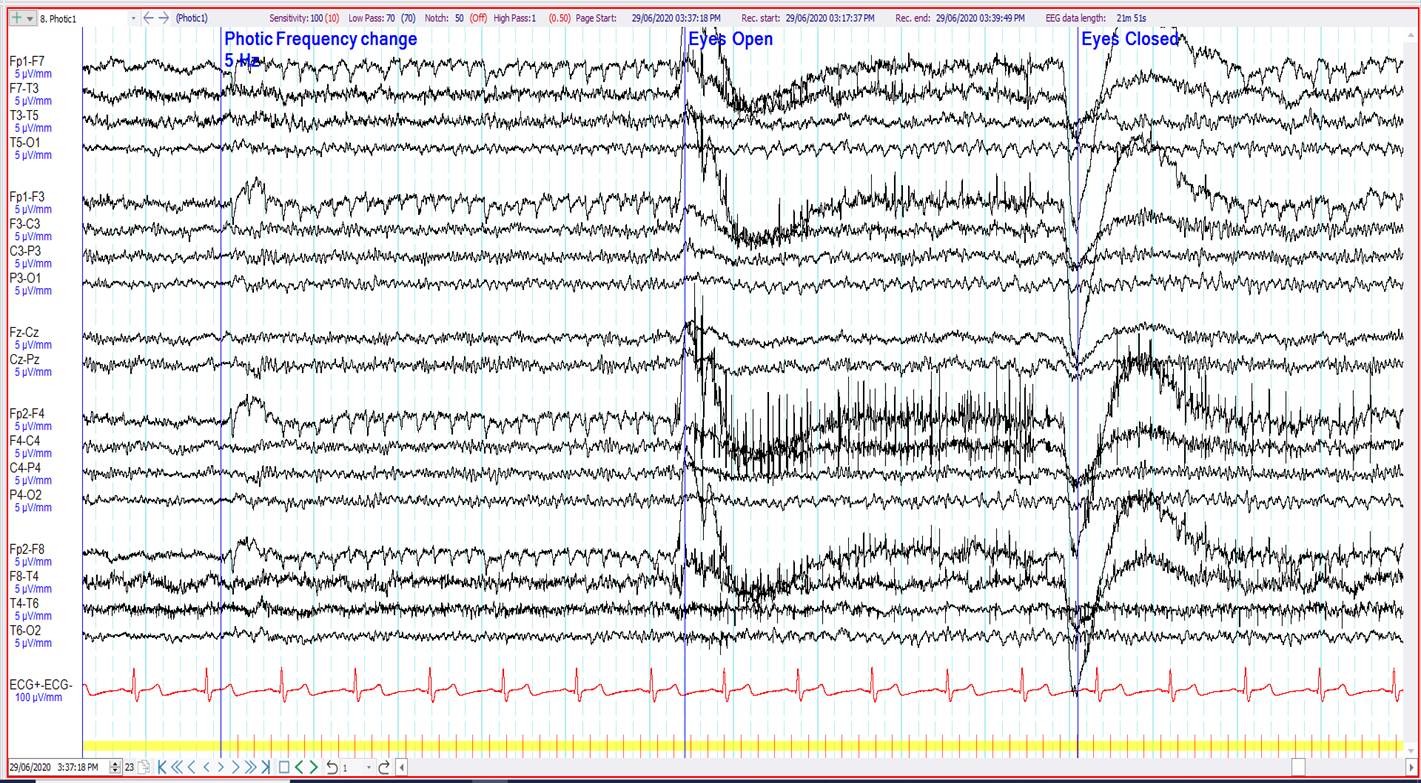
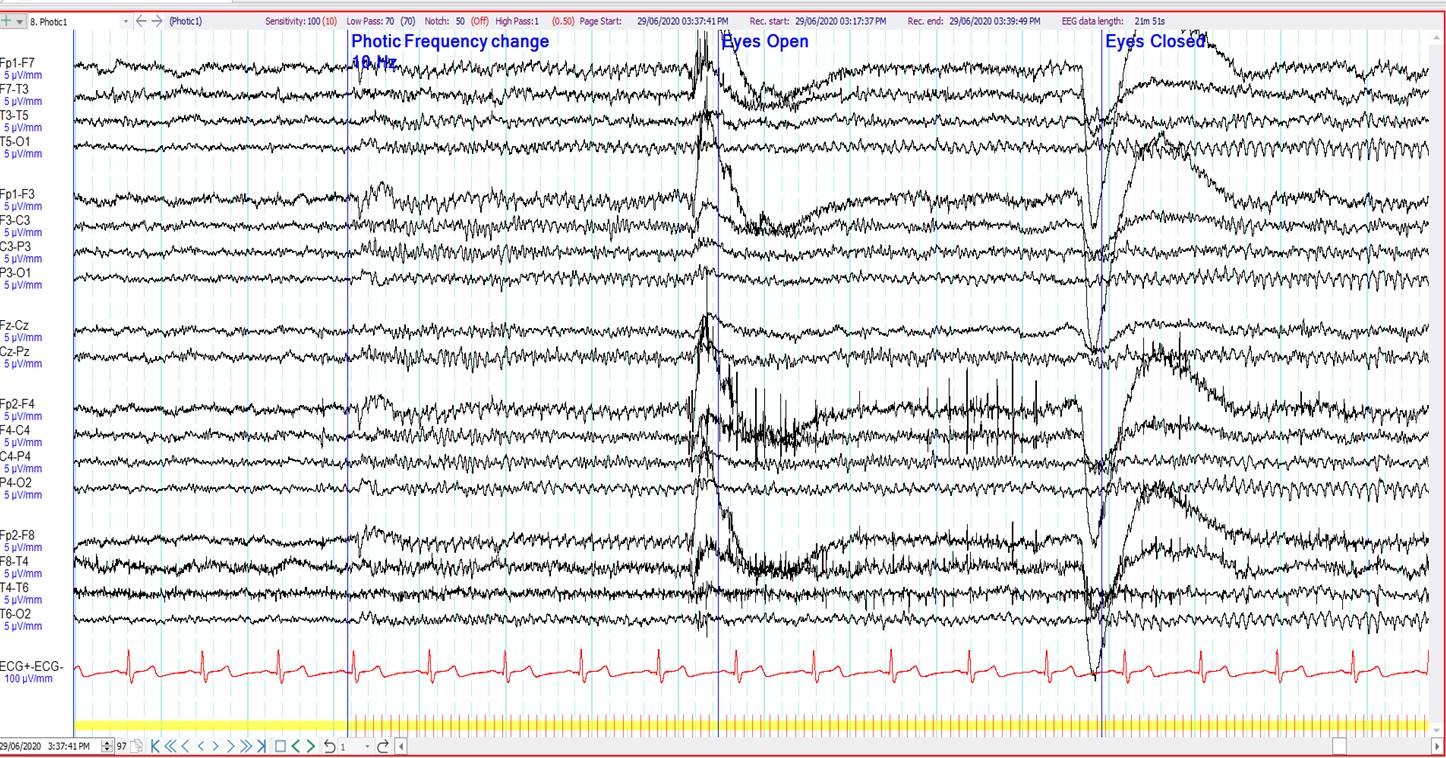
21. 72 year old. Episodic visual symptoms. What is seen anteriorly during photic stimulation at 5 and 10 Hz?
Photic driving
Photomyogenic artefact
Electroretinographic (ERG) artefact
Photoelectric artefact
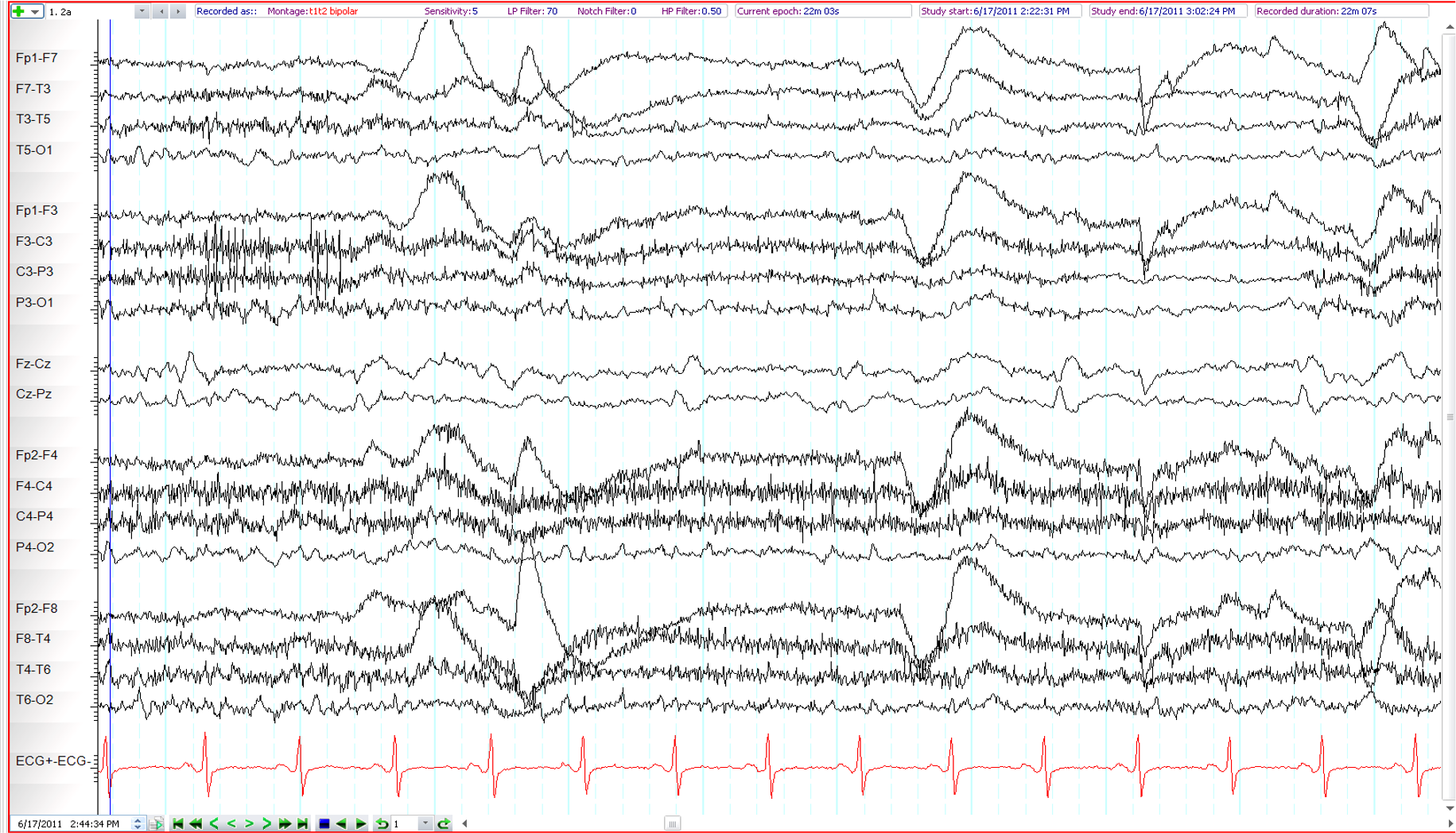
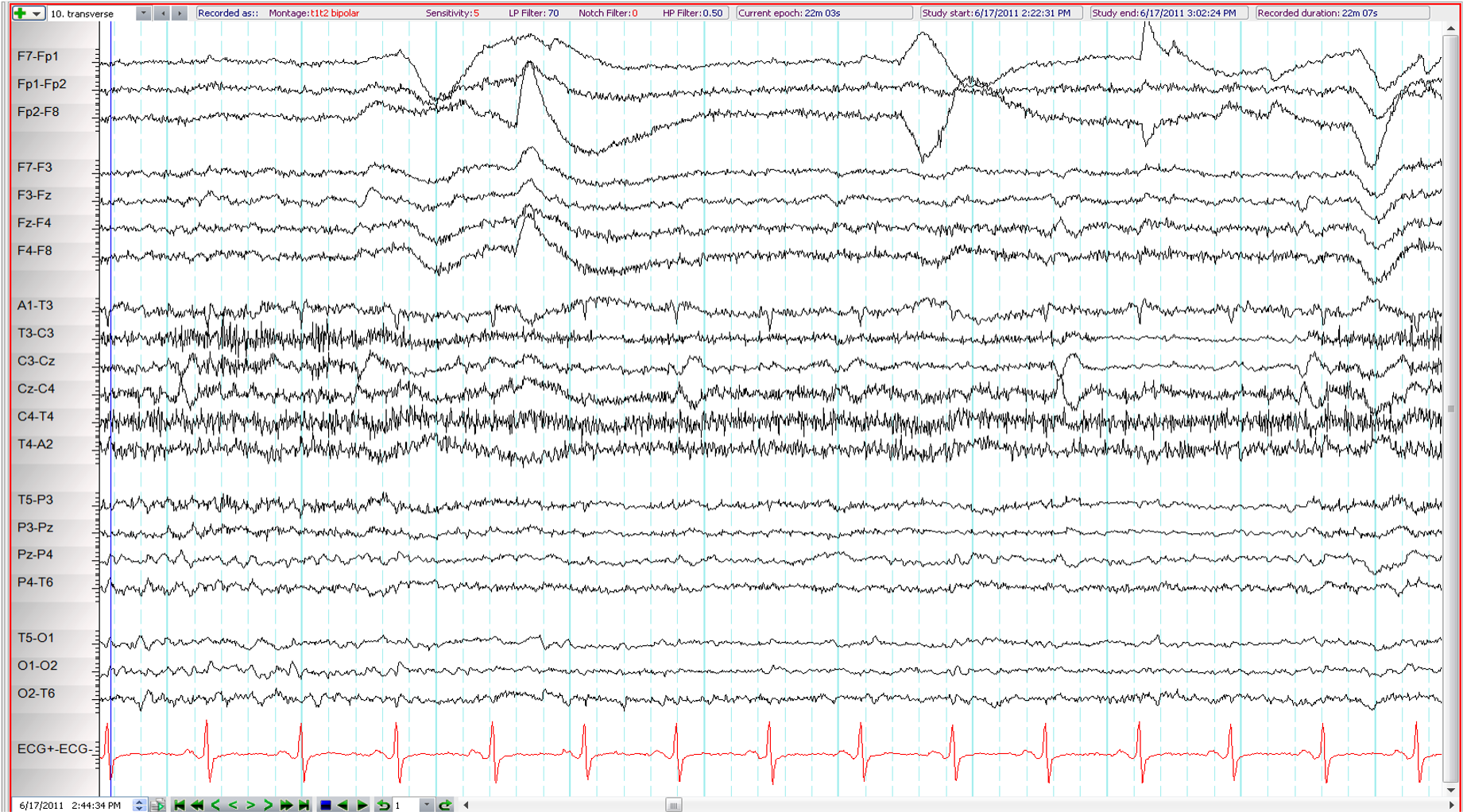
22. 67 year old. Fluctuant left hemiparesis ?seizures. What is the most important finding (longitudinal and transverse bipolar montages shown)?
Artefact over Cz
V waves
“Sawtooth” waves of REM sleep
Periodic sharp waves
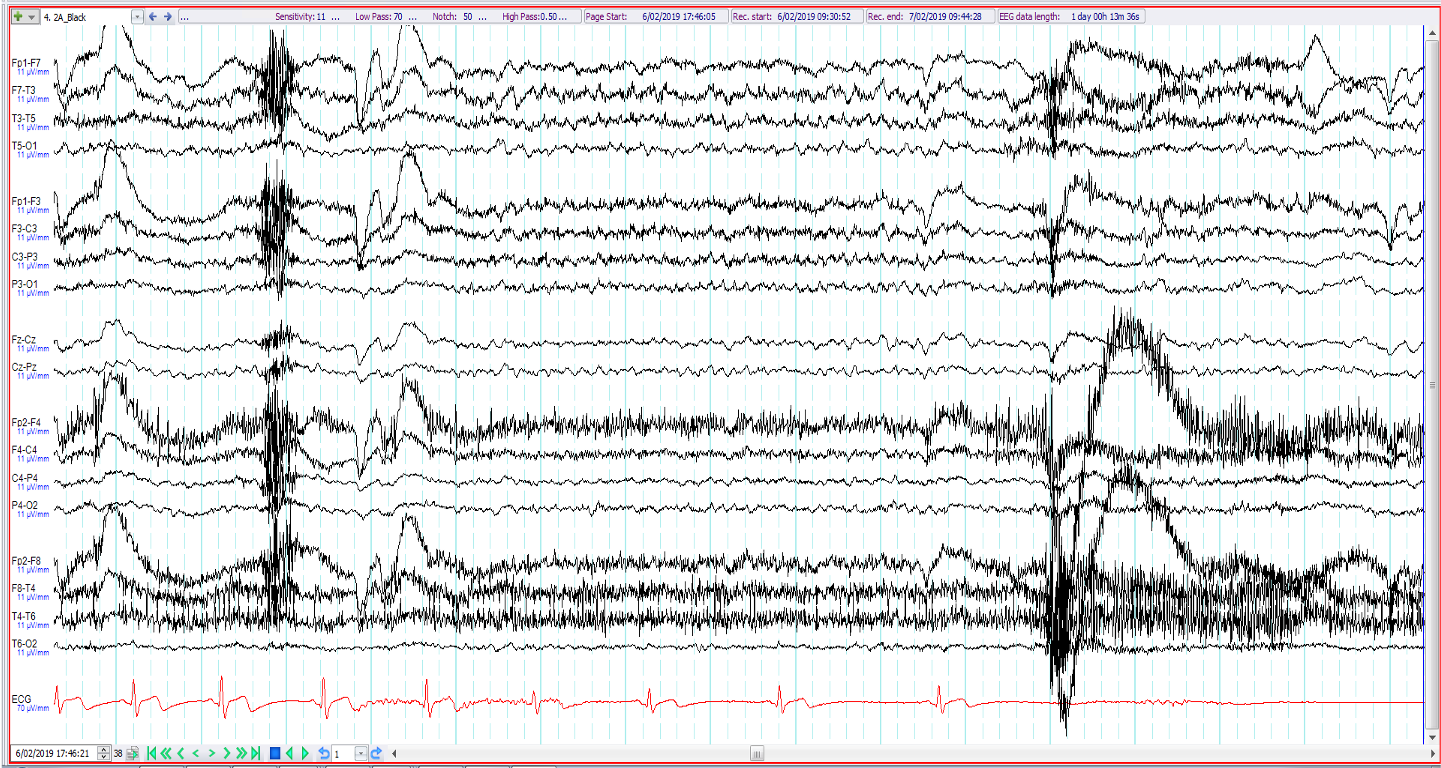
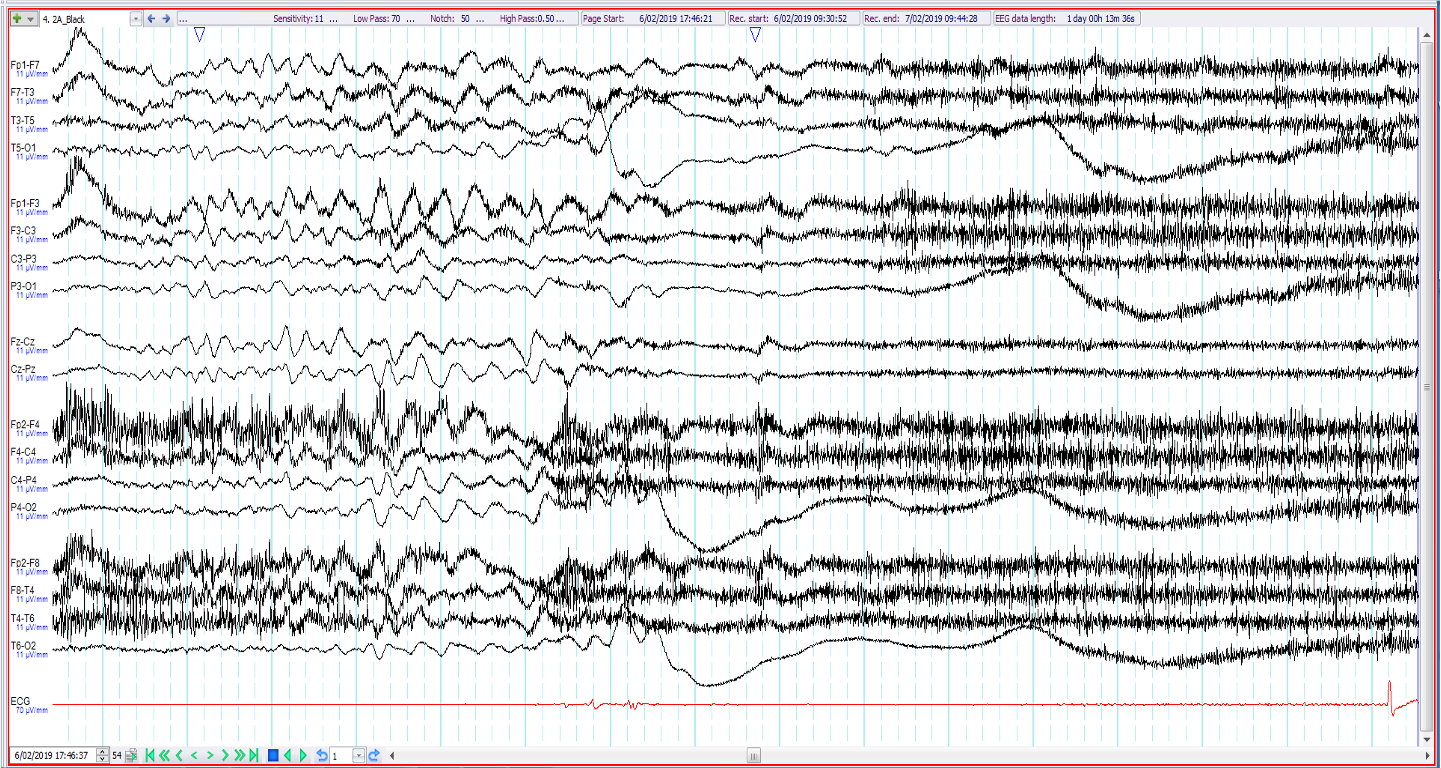
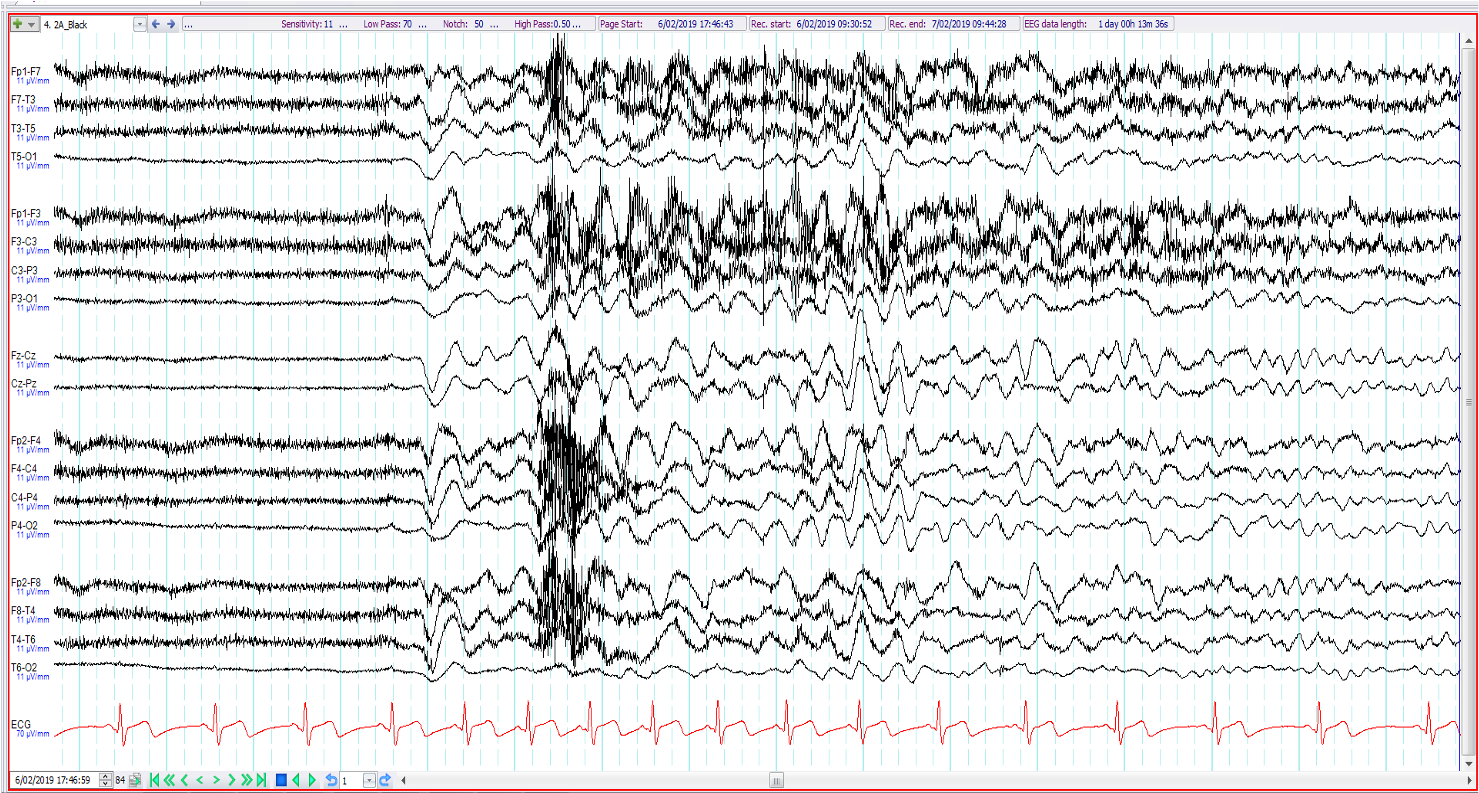
23. 39 year old. Recent onset of episodes of loss of consciousness preceded by a rising hot and uncomfortable feeling. The EEG shows (3 consecutive epochs shown):
Vasovagal syncope
Normal arousal with hypnopompic hypersynchrony
Ictal syncope
Generalised epileptiform discharge
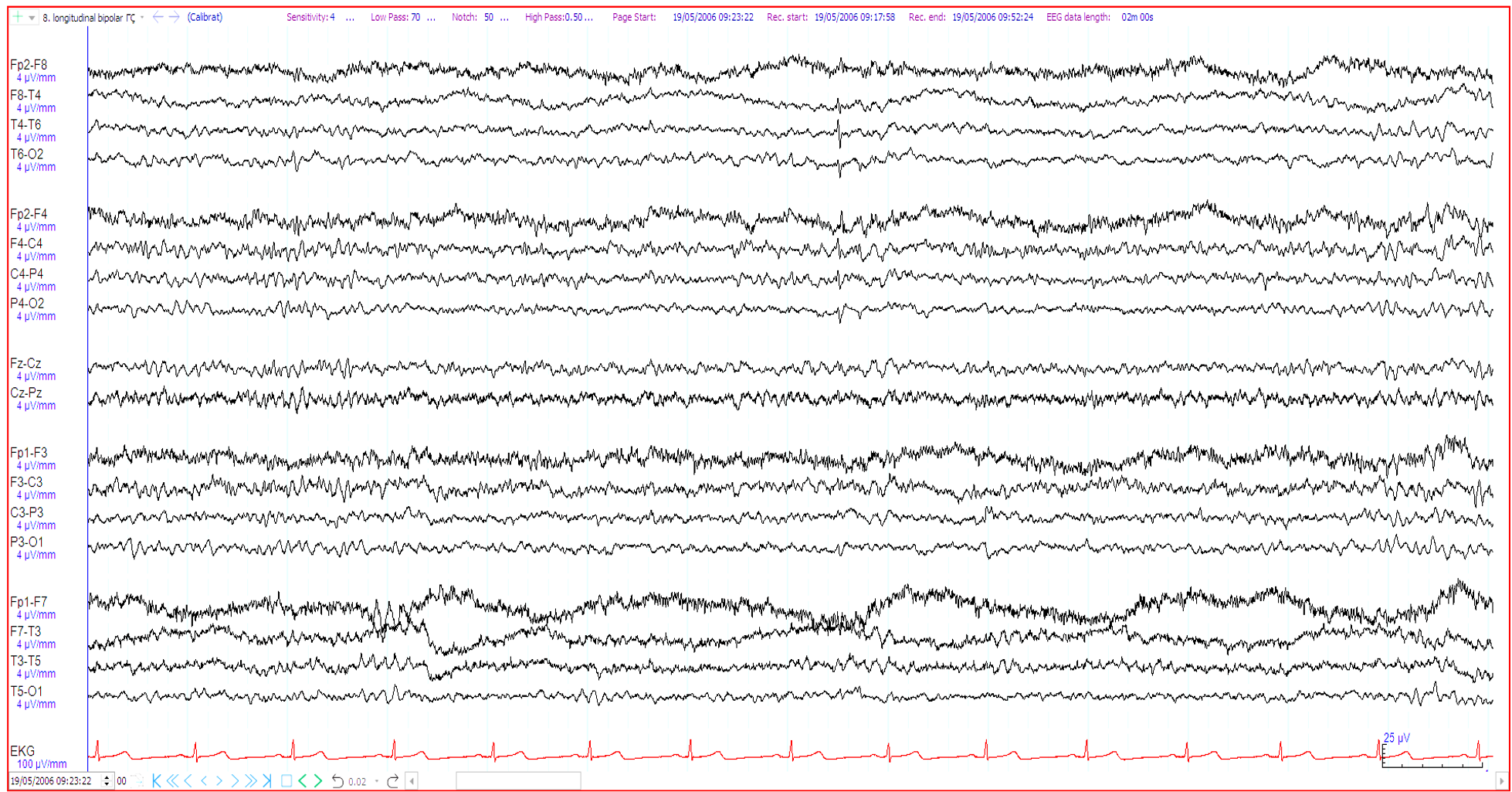
24. 59 year old. ?seizure. What does the EEG show?
Benign sporadic sleep spikes (BSSS)
Right hemispheric epileptiform discharge
Right wicket waves
14 and 6 Hz positive bursts
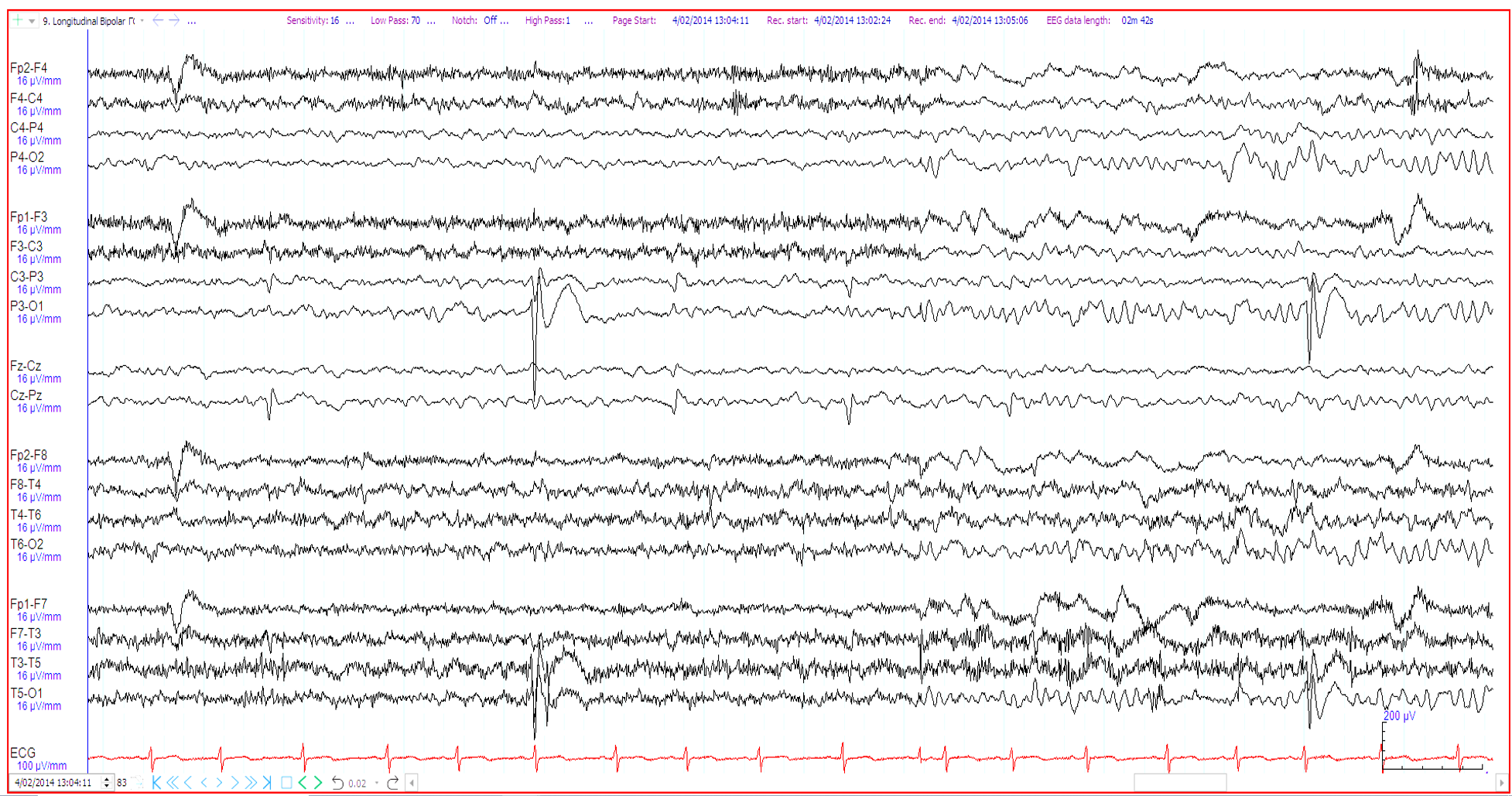
25. 6 year old, ?seizures. The EEG shows
Artefact over Pz and left occipital spikes
Artefact over O1 and parietal midline spikes
Left occipital spikes and benign sporadic sleep spikes
Left occipital spikes and independent parietal midline spikes
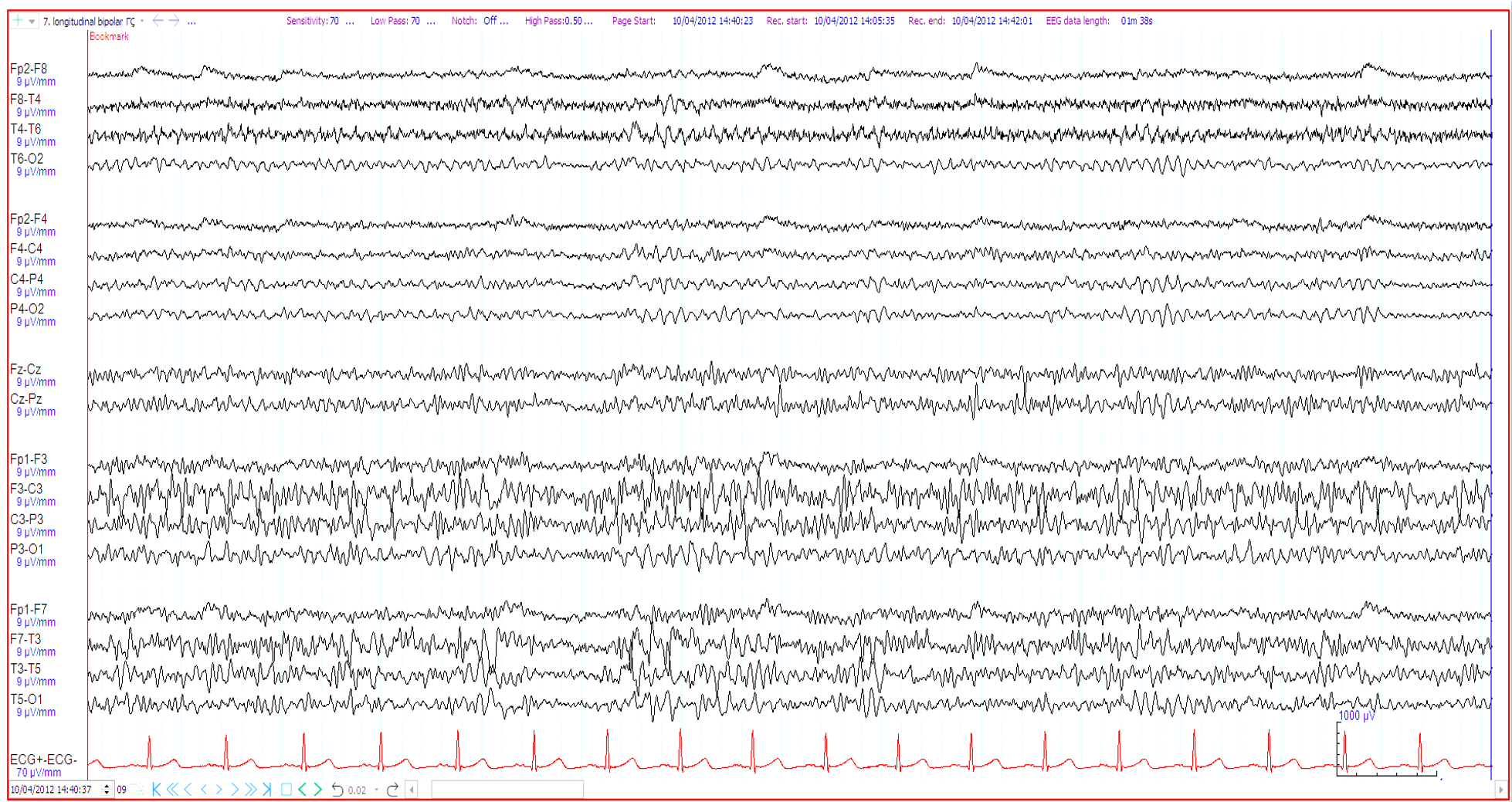
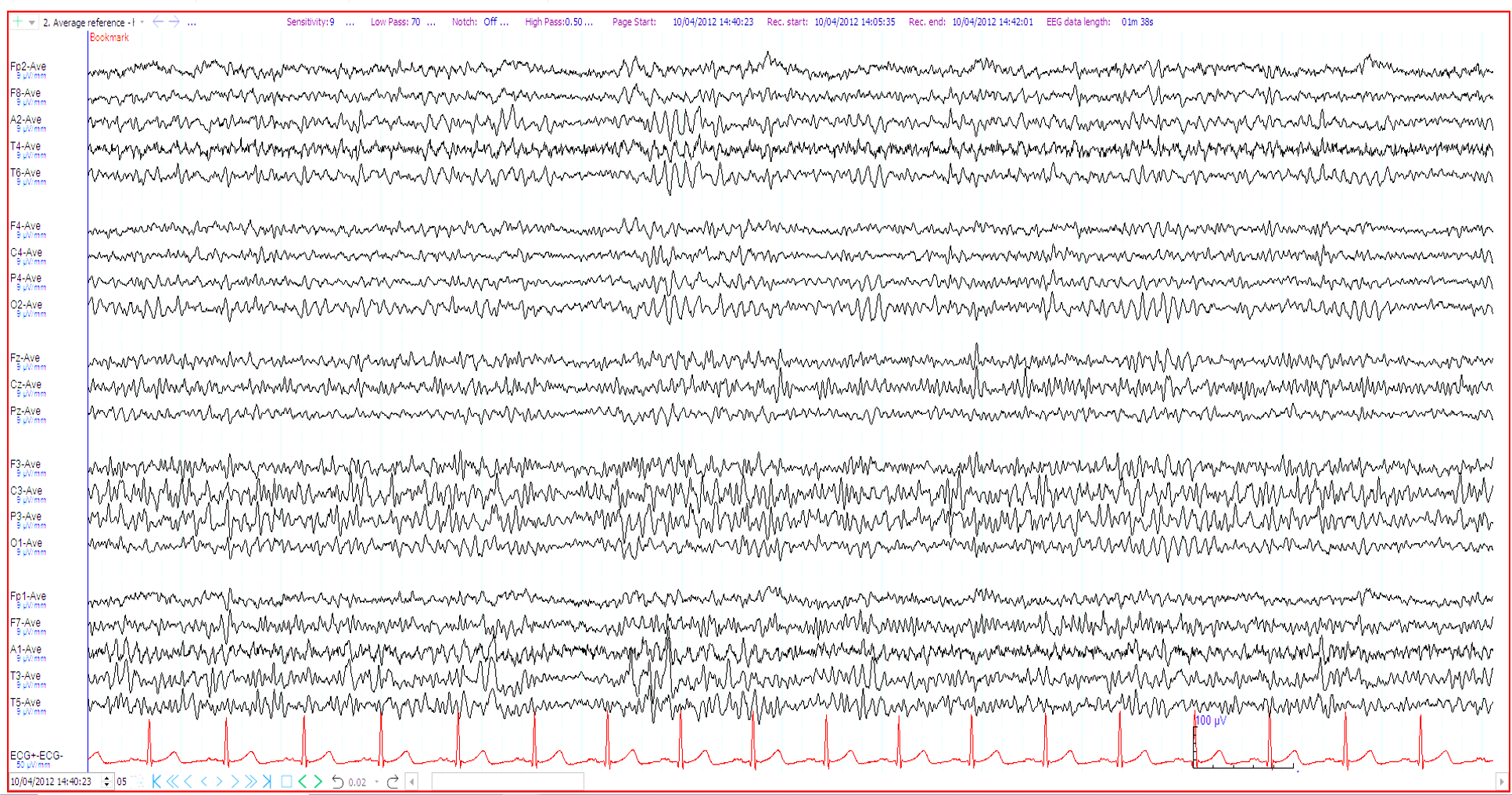
26. 25 year old ?seizures. Which additional history best matches the EEG (bipolar and referential montages shown)?
Previous left sided craniotomy for extradural haematoma
Acute right subdural haemorrhage
On high dose benzodiazepines
Previous left sided decompressive hemi-craniectomy for ischaemic stroke
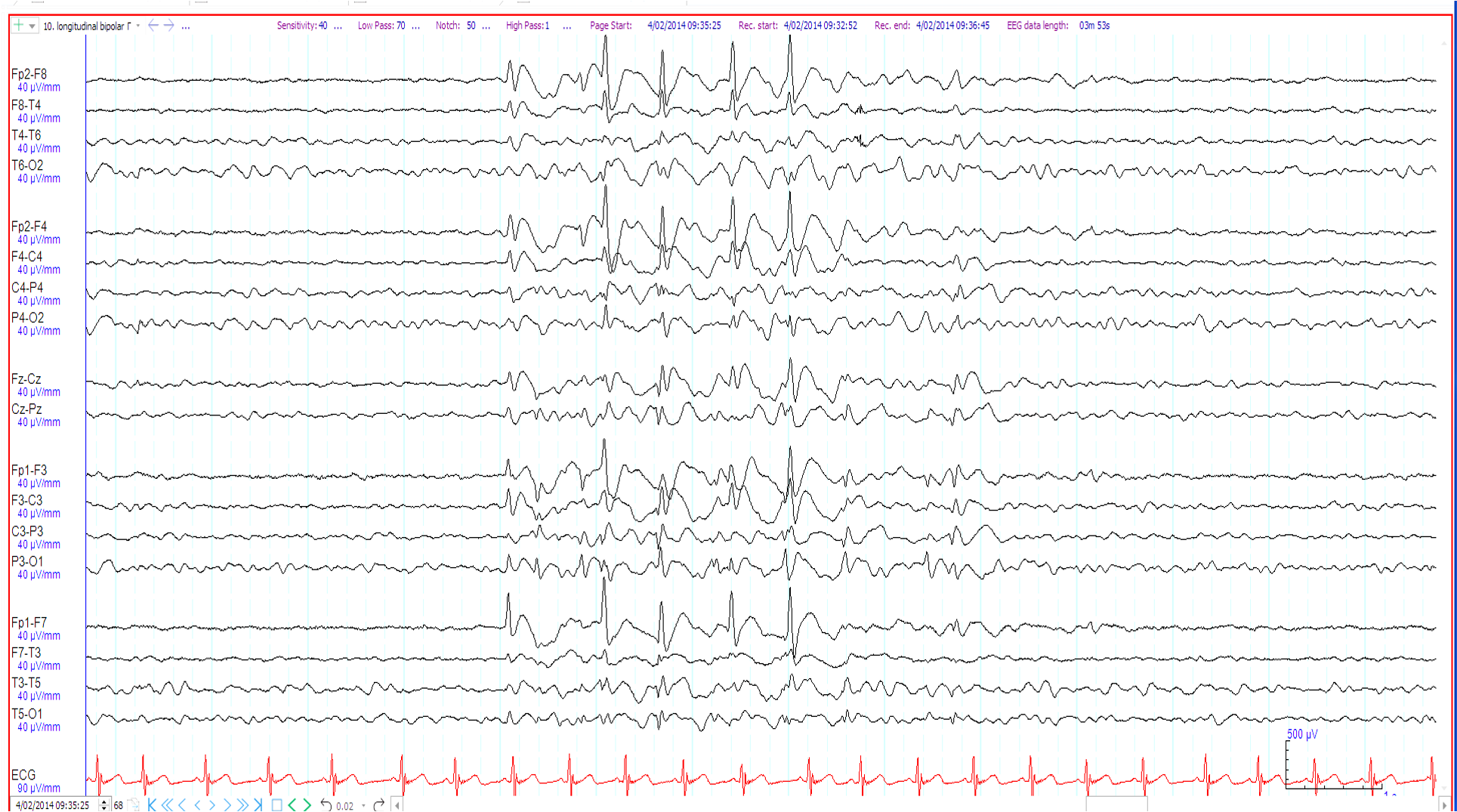
27. 6 year old with tuberous sclerosis. Recent behavioural change ?Non-convulsive status epilepticus. The EEG shows:
Generalised slow spike and wave
Triphasic waves
Normal “spikey” V waves
Non-convulsive status epilepticus
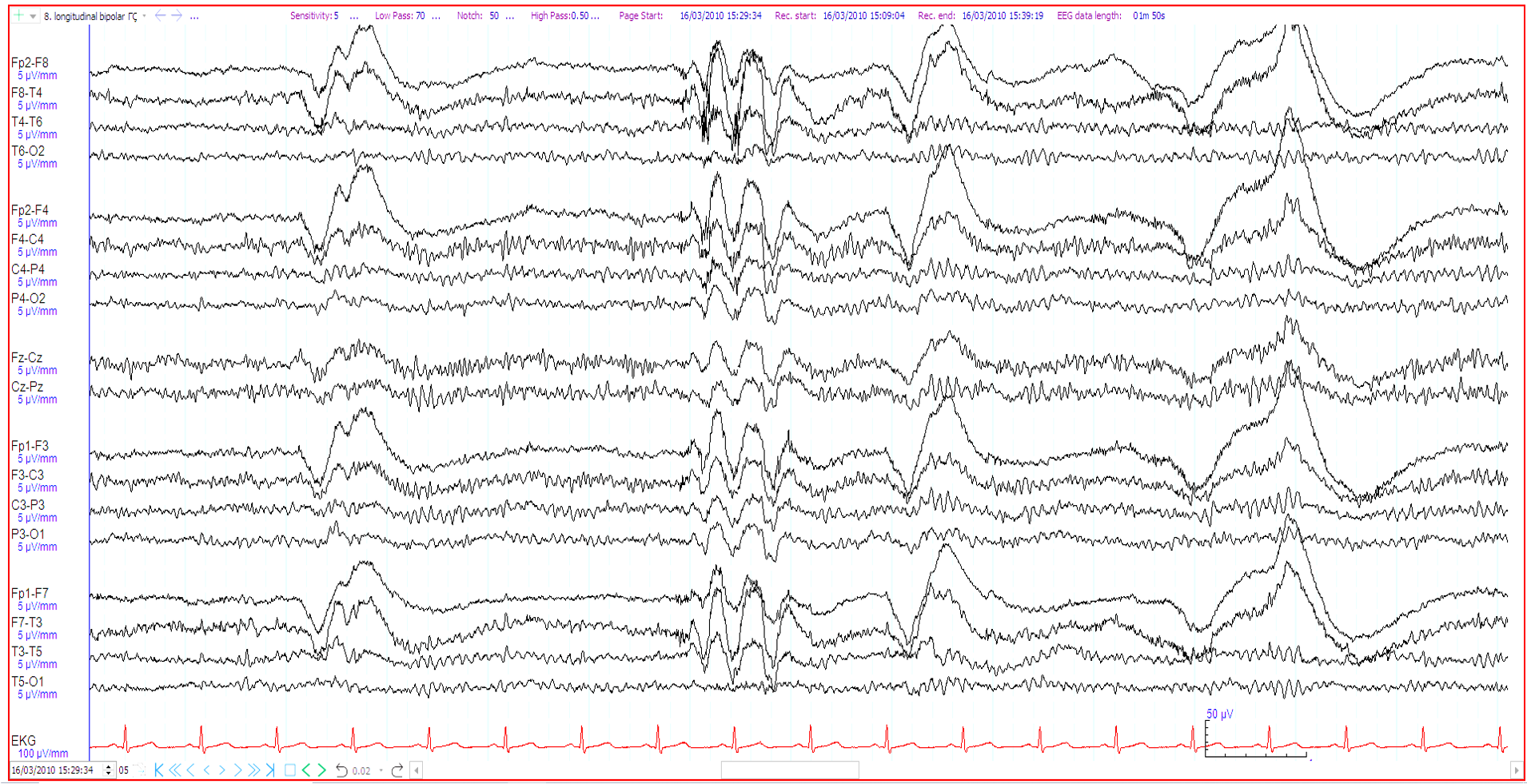
28. 55 years. Insomnia, ?nocturnal seizures. What does the EEG show?
Frontal intermittent rhythmic delta activity
Generalised spike and wave discharge
Hypnogogic hypersynchrony
Glossokinetic artefact
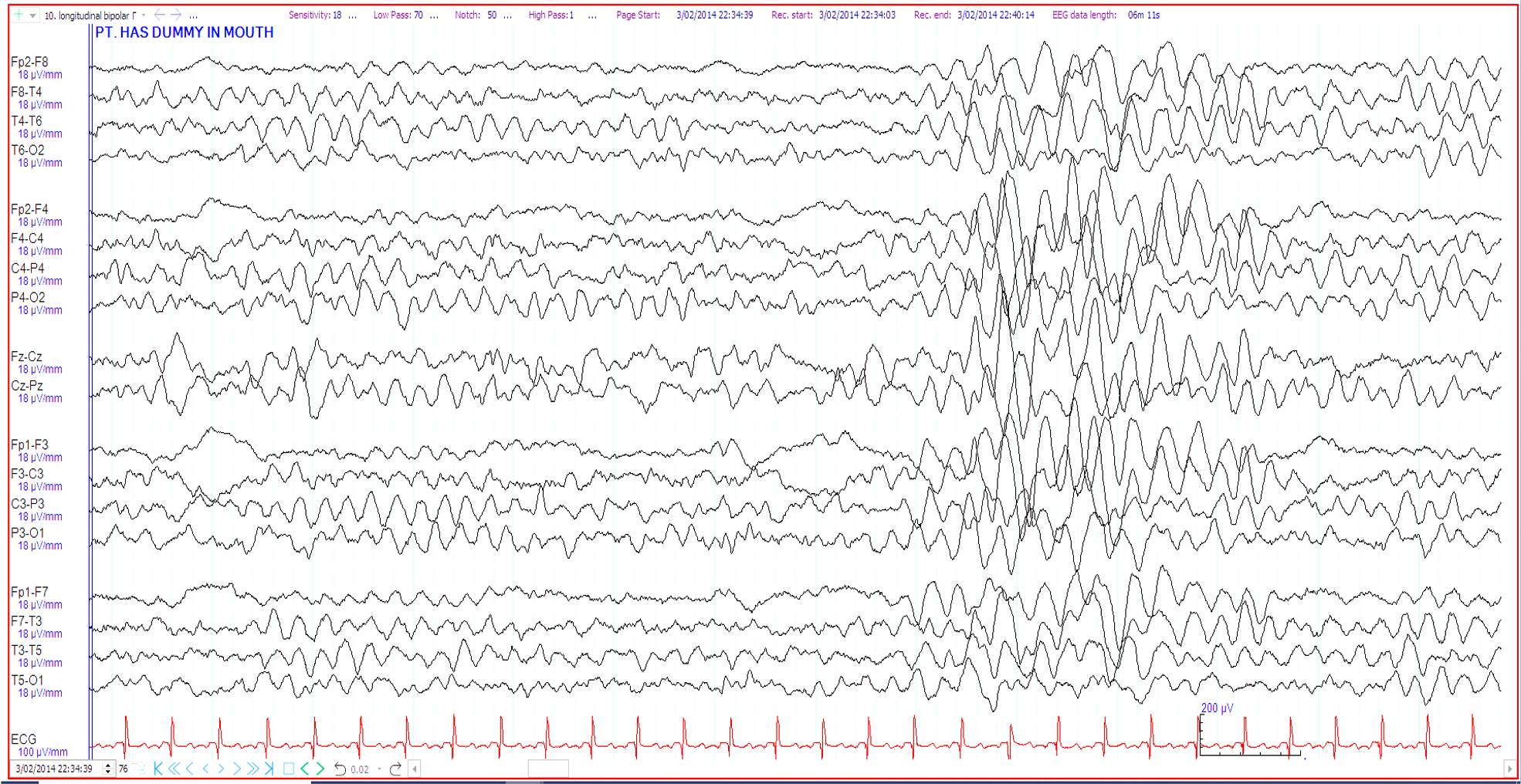
29. 18 month old. Breath holding spells. ?seizures The EEG shows:
Generalised spike and wave discharge
Frontal intermittent rhythmic delta activity (FIRDA)
Hypnopompic hypersynchrony
Hypnogogic hypersynchrony
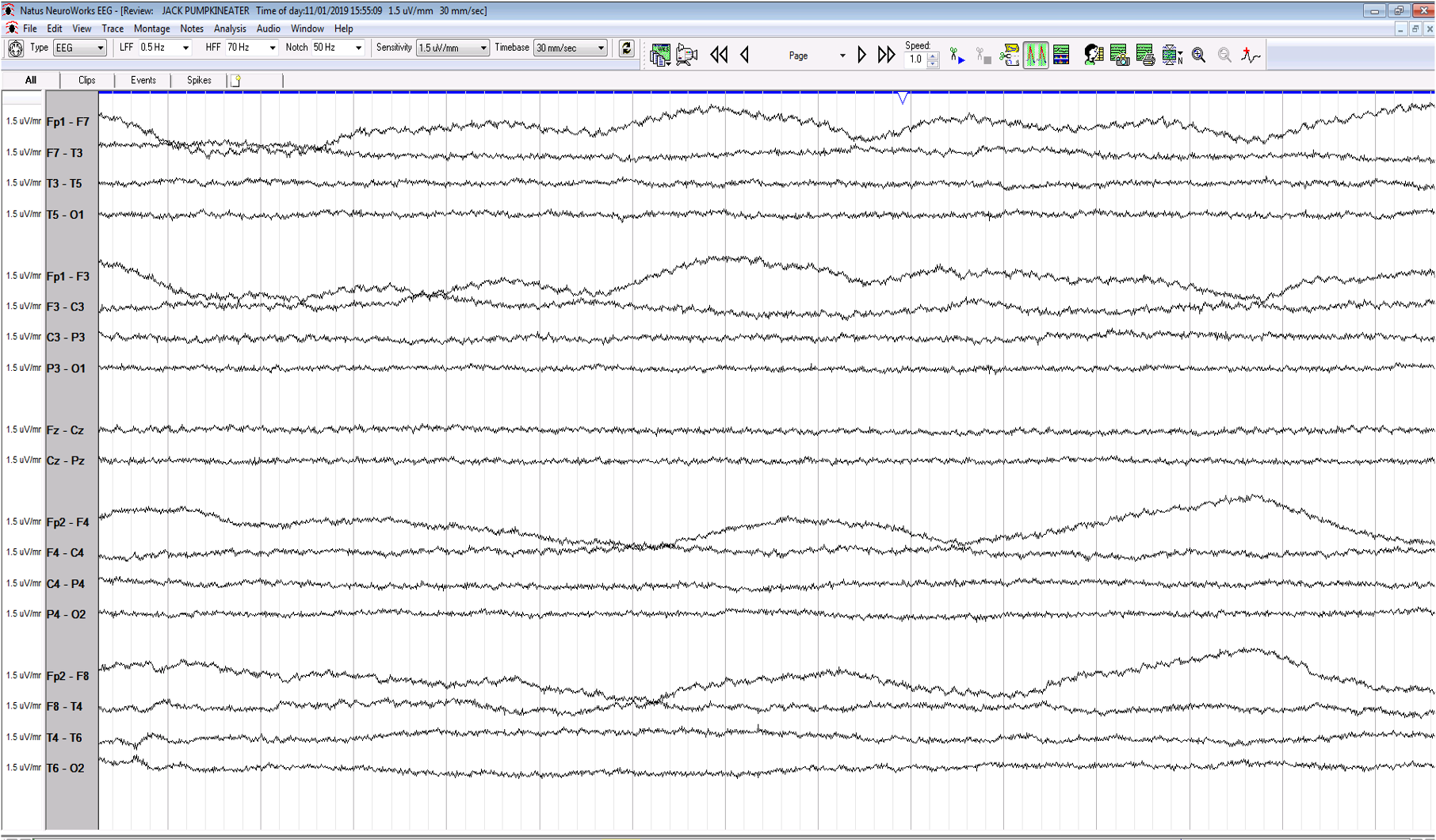
30. 27 year old, found unresponsive in a field. No other history available. On no sedative medications. What does the EEG show ? (ECG not recorded because of technical reasons)
Theta coma
Normal drowsiness with slow lateral eye movements
No EEG activity of cerebral origin, all artefact
Bilateral rhythmic temporal theta of drowsiness (RTTD)
Have you attended this course before?
Yes
No
Select your year of neurology training
One
Two
Three or more
Consultant neurologist
On a scale of 1-5 (5 being the most useful) how would you rate this Self-Assessment Programme?
How would you rate the difficulty of this Self-Assessment Programme (1 being too easy, 5 being too hard)?
{"name":"ANZAN EEG Course Self-Assessment Programme: Part B", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QUZC6AH","txt":"Welcome to the ANZAN EEG Course Self-Assessment Programme: Part B. This is for those who have already done Part A of the quiz. It is an educational tool to help you assess your progress in EEG and replicates components of the ANZAN-ASEPA Part 1 and Part 2 EEG Exams. Paediatric and adult examples are included as some knowledge of EEG throughout the age range is expected. To zoom in on any slides, either use the trackpad, or click the 'View' and then 'Zoom' buttons at the top of the browser., Have you previously attended the course?, Select year of neurology training","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}