Chir Diagnosis P1 Q 51 to 100
51) A 16-year-old boy is persuaded by his older brother to accompany him and his friends on a beer-drinking binge. This is the first such experience for the boy, and it leads to the development of severe colicky left flank pain. When rescued by his parents, he is diaphoretic and doubled up in pain. He relates that he began to urinate frequently and profusely after the third or fourth beer and that the pain seized him shortly thereafter. He is tender to fist percussion over the left costovertebral angle but is afebrile. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Bladder calculi
Low implantation of one ureter
Ureteral stone
Ureteropelvic junction obstruction
Vesicoureteral reflux
52) A 53-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife because of headache and visual changes. Approximately 3 hours ago, he had the acute onset of an extremely severe posterior headache that was non-radiating but was associated with nausea and vomiting. This headache subsided, but over the past hour he has developed mild neck stiffness and pain on flexion of his neck. The patient is not cooperative, so no additional history is known; however, his wife states that he was feeling well until recently and has no allergies. The patient appears moderately uncomfortable and is complaining of the worst headache he has ever experienced. Which of the following is the most likely cause for his symptoms?
Arteriovenous malformation
Cerebellar bleed
Putamenal bleed
Ruptured berry aneurysm
Thalamic bleed
53) A 72-year-old man has a 4-cm hard mass in the left supraclavicular area. The mass is movable and nontender and has been present and steadily growing for the past 3 months. On direct questioning the only additional findings include a 20-pound weight loss and a vague feeling of epigastric discomfort over the past 2 months. Physical examination shows evidence of the weight loss but no other significant findings in the abdominal examination. The supraclavicular mass are obvious, but no other masses can be felt anywhere else in the neck, axillas, or groins. There is occult blood in the stool, and his hemoglobin is 10.5 g/dL. Which of the following would a biopsy of the supraclavicular mass most likely reveal?
Chronic inflammation
Lymphoma
Metastatic gastric cancer
Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
Metastatic thyroid cancer
54)A 6-year-old boy has insidious development of limping with decreased motion in one hip. He complains occasionally of knee pain on that side. He walks into the office with an antalgic gait. Examination of the knee is normal, but passive motion of the hip is guarded. The child is afebrile, and the parents indicate that his gait and level of activity were completely normal all his life until this recent problem. He has not had a recent febrile illness. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Avascular necrosis of the capital femoral epiphysis
Developmental dysplasia of the hip
Hematogenous osteomyelitis of the femoral head
Septic hip
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis
55)A patient involved in a car accident sustains burst fractures of several thoracic vertebral bodies. Atthe time of admission, he has no neurologic function at all below the level of the injury and he has flaccid sphincters. After a few days, there is partial recovery of function; the remaining deficits are loss of motor function and loss of pain and temperature sensation on both sides distal to the injury, with preservation of vibratory and positional senses. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Anterior cord syndrome
Central cord syndrome
Complete cord transection
Cord hemisection
Spinal shock
56)A 51-year-old man is undergoing abdominal surgery and becomes hypotensive while under generalanesthesia. The patient had been doing well during most of the procedure but now has a blood pressure of 80/40 mm Hg. His past medical history is significant for coronary artery disease and diabetes mellitus. A pulmonary artery catheter placed prior to the procedure gives the following data: Central venous pressure 10 mmHg, Pulmonary artery pressure 60/30 mmHg, Pulmonary capillary occlusion 24 mm Hgpressure Cardiac output 2.3 L/min. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
Acute mitral regurgitation
Acute right heart failure
Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction
Sepsis syndrome
Acute left heart failure
57)A 62-year-old man complains of perineal discomfort and reports that there are streaks of fecalsoiling in his underwear. Four months ago, he had a perirectal abscess drained surgically. Physical examination shows a perineal opening in the skin lateral to the anus, and a cord-like tract can be palpated going from the opening toward the inside of the anal canal. Brownish purulent discharge can be expressed from the tract. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Anal fissure
. Anorectal carcinoma
. Fistula-in-ano
. Pilonidal cyst
. Thrombosed hemorrhoids
58)A 50-year-old woman with a history of essential hypertension presents to the emergencydepartment with sudden onset of a severe headache, nausea and vomiting, and photophobia. On examination, her BP is 160/100 mmHg. She is mildly confused and has nuchal rigidity, without focal neurologic signs. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. meningitis
. Ruptured cerebral aneurysm
. Hemorrhagic stroke
. Ischemic cerebrovascular accident
. Transient ischemic attack
59)A 72-year-old man of Norwegian ancestry has a contracted hand that can no longer be extended andplaced flat on a table. The problem developed gradually, over many years. He complains of no pain or neurologic abnormalities and, to the extent that the deformity allows, can move his fingers at will. Physical examination demonstrates the deformity described and in addition shows the presence of palpable fascial nodules. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Carpal tunnel syndrome
. De Quervain tenosynovitis
. Dupuytren contracture
. Palmar tenosynovitis
. Rheumatoid arthritis
60)A previously healthy 28-year-old woman develops significant postpartum hemorrhage, with a rapiddrop in hematocrit to 18%. Despite aggressive IV fluid resuscitation, the patient has a persistent tachycardia, labile systolic blood pressure, and poor urine output. Ongoing resuscitation includes emergency transfusion with 2 units of O-negative packed red blood cells. During transfusion of the second unit, the patient develops chills, fever, vomiting, and hypertension. These symptoms are most likely the result of which of the following?
. A febrile nonhemolytic transfusion reaction
. An anaphylactic transfusion reaction
. ABO incompatibility with acute hemolytic transfusion reaction
. Delayed hemolytic transfusion reaction
. Acute bacterial infection transmitted in the blood product
61)A 45-year-old woman underwent elective surgery for an inguinal hernia. In the postoperativerecovery room, she developed nausea, vomiting, and acute abdominal pain. She has a history of systemic lupus erythematosus, pernicious anemia, type 1 diabetes, chronic low back pain, and uterine fibroids. Her preoperative medications include monthly vitamin B-12 injections, insulin, prednisone, hydroxychloroquine, and acetaminophen. Her blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg and heart rate is 110/min. Initial laboratory studies show blood glucose of 50 mg/dl. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her condition?
. Postoperative bleeding
. Diabetic ketoacidosis
. Intra-abdominal abscess
. Intestinal obstruction
. Adrenal insufficiency
62)A 45-year-old woman, who wears high-heeled, pointed shoes, complains of pain in the forefoot afterprolonged standing or walking. Occasionally, she also experiences numbness, a burning sensation, and tingling in the area. Physical examination shows no obvious deformities and a very tender spot in the third interspace, between the third and fourth toes. There is no redness, limitation of motion, or signs of inflammation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Gout
. Hallux rigidus
. Metatarsophalangeal articulation pain
. Morton's neuroma
. Plantar fasciitis
63)A 45-year-old man presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of a skin lesion on his abdomen.He states that the lesion has been present for 1 year, but has recently enlarged over the last 2 months. The mass is nontender, and he is otherwise asymptomatic. Past history is unremarkable. Examination reveals a 3-cm, pigmented, irregular skin lesion located in the left lower quadrant of the abdomen, as shown in Figure 6-12. Heart, lung, and abdominal examination are normal. There are no palpable cervical, axillary, or inguinal lymph nodes. Chest x-ray and liver function tests are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
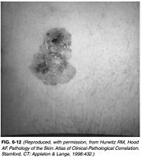
USMLE Surgery 1010 qcm

. Squamous cell carcinoma
. Basal cell carcinoma
. Merkel cell carcinoma
. melanoma
. keratoacanthoma
64)A 58-year-old man presents with pain in the left leg after walking more than one block that isrelieved with rest. On physical examination, distal pulses are not palpable in the left foot and there is dry gangrene on the tip of his left fifth toe. An ankle-brachial index on the same side is 0.5. Which of the patient’s symptoms or signs of arterial insufficiency qualifies him for reconstructive arterial surgery of the left lower extremity?
. Ankle-brachial index less than 0.7
. Rest pain
. Claudication
. Absent palpable pulses
. Toe gangrene
65)An 84-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of 1 hour of severe back pain. He also had syncope that lasted <1 minute. Before arriving at the hospital, he had an episode of gross hematuria, which he has never had before. He also complains of some shortness of breath. He denies chest pain, cough, nausea, vomiting, headache, and neck pain. His blood pressure is 72/55 mm Hg and pulse is 112/min and regular. His pulse oximetry shows 92% on room air. His ECG shows sinus tachycardia with prominent horizontal ST segment depression in the anterior chest leads. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture
. Acute mesenteric ischemia
. Acute myocardial infarction
. Massive pulmonary embolism
. Nephrolithiasis with renal colic
66) A 54-year-old man comes to the physician because of edema of his right ankle. He reports heaviness and cramping in the same leg that is worse after a long day at work. The swelling is usually reduced significantly when he wakes up in the morning and worsens progressively throughout the day. He denies any other symptoms. He has no significant medical problems except hypertension, for which he takes atenolol. His temperature is 36.7° C (98° F), blood pressure is 120/76 mm Hg, pulse is 80/min and respirations are 16/min. JVP is normaL Lungs are clear to auscultation. There are no murmurs. There is no hepatosplenomegaly. Examination shows edema of the right ankle. Doppler examination of the leg shows no evidence of thrombosis. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his edema?
. Lymphatic obstruction
. Impaired cardiac contraction
. Reduced diastolic filling of the heart
. Increased urinary loss of protein
. Venous valve incompetence
67) A 68-year-old man presents to the physician’s office complaining of progressive dysphagia over the last 3 months associated with mild chest discomfort. He reports a 15-lb weight loss, a 30 pack-year smoking history, and occasional alcohol intake. The physical examination, including vital signs, is unremarkable. A chest x-ray was normal, and a barium esophagogram shows an irregular filling defect in the distal third of the esophagus with distortion and narrowing of the lumen. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Esophagitis with stricture
. Esophageal carcinoma
. Lung carcinoma with invasion into the esophagus
. lymphoma
. achalasia
68) A 29-year-old man presents with a 2-day history of severe left-sided scrotal pain and swelling. He is sexually active and has had "many" sexual partners. His temperature is 38.2 C (100.8 F), blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg, and pulse is 80/min. Examination shows unilateral intrascrotal tenderness and swelling. Testicular support makes the pain less intense. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Epididymitis
. Prostatitis
. Testicular torsion
. Urethritis
. Varicocele
69) A 65-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for her yearly physical examination. She has no complaints except for a recent 10-lb weight loss. Past history is pertinent for a 40 pack-year smoking history, hypertension, asthma, and hypothyroidism. Examination reveals a thin woman with normal vital signs and unremarkable heart and abdominal examinations. Lung examination reveals mild wheezing and a few bibasilar rales. A chest x-ray is obtained and is shown in Figure 6-13. A chest x-ray obtained 3 years ago was normal. Yearly laboratory tests including a CBC, electrolytes, and lipid panels are normal. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
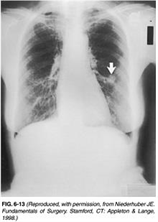
USMLE Surgery

. Small cell lung cancer
. tuberculosis
. Nonsmall cell lung cancer
. hamartoma
. abscess
70) A 24-year-old man comes to the physician because of 1 week of abdominal pain. It is localized in the right lower quadrant and somewhat exacerbated by motion. Over the past 2 days, it has radiated to the back. He initially had two episodes of vomiting but now just has decreased appetite. He had one episode of diarrhea 1 day ago. He denies urinary frequency. His other medical problems include mild intermittent asthma and gastroesophageal reflux disease. He traveled to Mexico for 5 days 1 month ago and did not have any gastrointestinal symptoms during his stay there. His mother was diagnosed with colon cancer at the age of 49 years. His temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F), blood pressure is 122/77 mm Hg, and pulse is 109/min and regular. Physical examination reveals prominent tenderness in the right lower quadrant, without rebound. Flexion of the right hip against resistance elicits significant abdominal pain. Laboratory results show:WBC count 16,000/mmHemoglobin 14.2 g/dlPlatelet count 620,000/mmPotassium 4.5 mEq/LCreatinine 1.0 mg/dlWhich of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Appendiceal perforation
. Colonic malignancy
. Complicated pyelonephritis
. Inflammatory bowel disease
. Parasitic colitis
71) A 35-year-old woman is involved in a motor vehicle crash, sustaining a severe pelvic fracture, with disruption of the pelvic ring. In the trauma resuscitation room, she is confused and tachypneic, with a blood pressure of 90 mmHg systolic and a heart rate of 130/min. Laboratory investigations include serum electrolyte analysis, revealing a sodium of 139, a chloride of 103, and a bicarbonate of 14 meq/L. This patient demonstrates which of the following?
. Nonanion gap metabolic acidosis
. Anion gap metabolic acidosis
. Metabolic alkalosis
. Respiratory acidosis
. Normal serum electrolytes
72) A 1-day-old infant with Down syndrome, feeding intolerance, bilious vomiting, and a double bubble on plain radiographs (Figure 6-18). Which one is the most likely diagnostic?
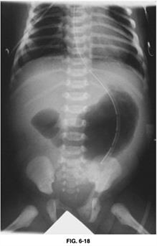
USMLE

. Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
. Annular pancreas
. Duodenal atresia
. Midgut volvulus
. intussusception
73) A 43-year-old man develops excruciating abdominal pain at 8:23 PM (he looked at his watch when the pain "hit him"). When seen in the emergency department about 30 minutes later, he has a rigid abdomen, lies motionless on the examination table, has no bowel sounds, and is obviously in great pain, which he describes as constant and encompassing the entire abdomen. There is very severe pain when deep palpation of the abdomen is attempted in any of the four quadrants. However, the examining hand cannot make much of an indentation because of the impressive muscle guarding. When the attempt is aborted, he manifests severe rebound tenderness. X-ray films show free air under both diaphragms. Which of the following does this man most likely have?
. Acute abdomen, the nature of which cannot yet be defined
. Acute inflammatory process affecting an intra-abdominal viscera
. Acute obstruction of an intra-abdominal viscera
. Ischemic process affecting intra-abdominal organs
. Perforation of the gastrointestinal tract
74) A 56-year-old woman presents for evaluation of a murmur suggestive of mitral stenosis and is noted on echocardiography to have a lesion attached to the fossa ovalis of the left atrial septum. The mass is causing obstruction of the mitral valve. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Endocarditis
. Lymphoma
. Cardiac sarcoma
. Cardiac myxoma
. Metastatic cancer to the heart
75) A 54-year-old man presents to the emergency department on transfer from another hospital at the request of the family. He was admitted to the outside hospital 2 weeks ago with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. He was treated with antibiotics, NG tube decompression, and TPN without significant improvement. He developed jaundice 2 days ago. His past history is pertinent for a 40 pack-year smoking history, chronic alcohol abuse, and diabetes. Examination reveals a mildly jaundiced patient with vital signs of temperature 100°F, pulse rate 95/min, and BP 110/60 mmHg. Cardiac examination is unremarkable, lung examination reveals decreased breath sounds at the bases bilaterally, and abdominal examination reveals fullness in the epigastrium with tenderness and voluntary guarding. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. hepatitis A
. hemolysis
. pancreatitis
. Liver metastases
. cirrhosis
76) A 65-year-old male cigarette smoker reports onset of claudication of his right lower extremity approximately 3 weeks previously. He can walk 3 blocks before the onset of claudication. Physical examination reveals palpable pulses in the entire left lower extremity, but no pulses are palpable below the right groin level. Non-invasive flow studies are obtained and are pictured here. What is the level of the occlusive process in this patient?
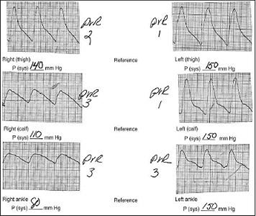
USMLE

. Right anterior tibial artery
. Right superficial femoral artery
. Right profunda femoris artery
. Right external iliac artery
. Right internal iliac artery
77) A 5-week-old infant presents with a 1-week history of progressive nonbilious emesis, associated with a 24-hour history of decreased urine output. The infant continues to be active and eager to feed. On examination, the infant has a sunken fontanelle and decreased skin turgor. The abdomen is scaphoid, and with a test feed, there is a visible peristaltic wave in the epigastrium. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Viral gastroenteritis
. Gastroesophageal reflux
. Urinary tract sepsis
. Pyloric stenosis
. Milk protein allergy
78) A 5-week-old infant presents with a 1-week history of progressive nonbilious emesis, associated with a 24-hour history of decreased urine output. The infant continues to be active and eager to feed. On examination, the infant has a sunken fontanels and decreased skin turgor. The abdomen is scaphoid, and with a test feed, there is a visible peristaltic wave in the epigastrium. The diagnosis is best confirmed by which of the following?
. Abdominal ultrasound
. Careful clinical examination with palpation of an epigastric mass
. UGI contrast study
. Surgical exploration
. endoscopy
79) An 80-year-old man is found to have an asymptomatic pulsatile abdominal mass. An arteriogram is obtained (shown below). Which of the following is the most frequent and lethal complication of this condition?
USMLE

. Rupture
. Acute thromboembolism
. Dissection
. High-output congestive heart failure
. Myocardial infarction
80) An older, overweight man complains of disabling, sharp heel pain every time his foot strikes the ground. The pain is worse in the mornings, preventing him from putting any weight on the heel. X-ray films show a bony spur matching the location of his pain, and physical examination shows exquisite tenderness to direct palpation right over that heel spur. Furthermore, when the ankle is dorsiflexed, the entire inner border of the fascia is tender to palpation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Epiphysitis of the calcaneus
. Fracture of the posterolateral talar tubercle
. Plantar fasciitis
. Posterior Achilles tendon bursitis
. Posterior tibial nerve neuralgia
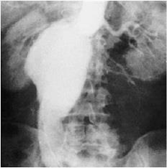
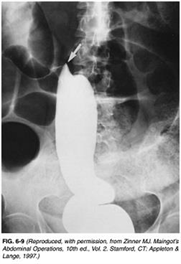
81) A 65-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office with a 6-month history of epigastric discomfort, poor appetite, and 10-lb weight loss. Past history is pertinent for hypertension, diabetes, a 30 pack-year smoking history, and occasional alcohol intake. Examination is unremarkable except for mild epigastric tenderness to deep palpation. An abdominal ultrasound reveals cholelithiasis, and one view of a UGI x-ray series is shown in Figure 6-8. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
USMLE Surgery

. Cholecystoenteric fistula
. Duodenal ulcer
. Gastric ulcer
. Gastric diverticulum
. Duodenal diverticulum
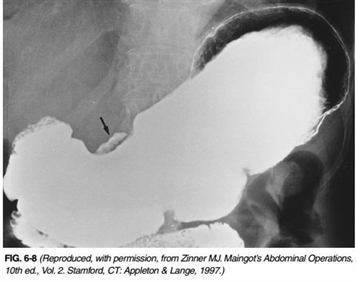
82) A 75-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from a nursing home for abdominal pain, distention, and obstipation over the last 2 days. Past history is pertinent for stroke, diabetes, atrial fibrillation, and chronic constipation. Examination reveals a temperature of 98.6°F, pulse rate 90/min and irregularly irregular, and BP 160/90 mmHg. Heart examination reveals irregularly irregular rhythm with no murmurs; lung examination reveals few bibasilar rales; and abdominal examination reveals a distended, tympanic abdomen with mild tenderness and no rebound tenderness. Plain abdominal x-rays reveal dilated loops of bowel, and a barium enema is obtained and shown in Figure 6-9. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
USMLE

. Ischemic colitis with stricture
. Diverticulitis with obstruction
. Cecal volvulus
. Sigmoid volvulus
. Colon cancer with obstruction
83) A 63-year-old man is seen because of facial swelling and cyanosis, especially when he bends over. There are large, dilated subcutaneous veins on his upper chest. His jugular veins are prominent even while he is upright. Which of the following conditions is the most likely cause of these findings?
. Histoplasmosis (sclerosing mediastinitis)
. Substernal thyroid
. Thoracic aortic aneurysm
. Constrictive pericarditis
. Bronchogenic carcinoma
84) A 55-year-old woman presents with a 6-month history of weight loss, abdominal cramps, and intermittent nonbloody diarrhea. On examination, her abdomen is mildly distended and there is a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant. Stool cultures yield normal fecal flora. CT scan with oral contrast demonstrates an inflammatory mass in the right lower quadrant, with thickening of the terminal ileum and ileocecal valve. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Ulcerative colitis
. appendicitis
. Crohn’s disease
. Irritable bowel syndrome
. Lactose intolerance
85) A 65-year-old woman has had pain in her right shoulder and has been treated with analgesics without relief. The CXR reveals a mass in the apex of the right chest. A transthoracic needle biopsy documents carcinoma. Superior pulmonary sulcus carcinomas (Pancoast tumors) are bronchogenic carcinomas that typically produce which of the following clinical features?
. Atelectasis of the involved apical segment
. Horner syndrome
. Pain in the T4 and T5 dermatomes
. Nonproductive cough
. Hemoptysis
86) A 45-year-old woman presents with hypertension, development of facial hair, and a 7-cm suprarenal mass. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
USMLE

. Myelolipoma
. Cushing disease
. Adrenocortical carcinoma
. Pheochromocytoma
. Carcinoid
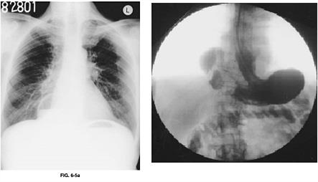
87) An 85-year-old man presents to the emergency room with an acute onset of midepigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, and hiccups starting 2 days ago. He is unable to keep any food down. Past history is pertinent for a long-standing hiatal hernia, hypertension, and diet-controlled diabetes. Examination reveals vital signs of pulse rate 82/min, BP 100/52 mmHg, respiratory rate 16/min, and temperature 97.2°F. The patient is in no acute distress, but has epigastric tenderness without guarding. Laboratory analysis revealed a hematocrit of 46 and a normal white blood cell (WBC) count. A chest x-ray is shown in Figure 6-5a. A fluoroscopically guided NG tube was placed using contrast, and his stomach was decompressed. After adequate fluid and electrolyte resuscitation, an upper gastrointestinal (UGI) contrast study was obtained and is shown in 6-5b. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Sliding hiatal hernia
. Hernia of Bochdalek (posterorlateral congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
. Hernia of Morgagni (parasternal congenital diaphragmatic hernia)
. Paraesophageal hernia
. Eventration of the diaphragm (central diaphragm)
88) An 83-year-old woman presents to a mammographic facility for a screening mammogram. The technician notices a mass in the lateral right breast. The patient denies any breast pain, nipple discharge, skin changes, or breast trauma. A right breast CC view is shown in Figure 6-7. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
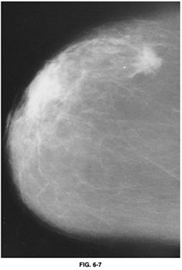
USMLE

Papilloma
Invasive carcinoma
Cystosarcoma phyllodes
DCIS
Fat necrosis
89) A 56-year-old man develops slow, progressive paralysis of the facial nerve on one side. It took several weeks for the full-blown paralysis to become obvious, and it has been present now for 3 months. It affects both the forehead and the lower face. He has no pain anywhere, and no palpable masses by physical examination. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Bell's palsy
. Facial nerve tumor
. Hemorrhagic stroke
. Parotid gland cancer
. Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland
90) A 28-year-old man with a past history of bilateral orchiopexy for cryptorchidism presents with a painless, unilateral right scrotal enlargement. On examination, there is a palpable right testicular mass and enlarged inguinal nodes. Scrotal ultrasonography demonstrates heterogeneity of the testis, with an associated hydrocele. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrated right-sided retroperitoneal adenopathy. CT scan of the chest is normal. Which of the following would help confirm the diagnosis?
. Transscrotal needle biopsy
. Transscrotal aspiration of the hydrocele for cytology
. Radical orchiectomy through an inguinal incision
. Transscrotal exploration and orchiectomy
. Laparotomy with pelvic and retroperitoneal node dissection
91) A 45-year-old woman complains to her primary care physician of nervousness, sweating, tremulousness, and weight loss. The thyroid scan shown here exhibits a pattern that is most consistent with which of the following disorders?
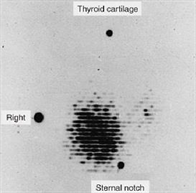
USMLE

. Hyper secreting adenoma
. Graves’ disease
. Lateral aberrant thyroid
. Papillary carcinoma of thyroid
. Medullary carcinoma of thyroid
92) The unrestrained front-seat passenger in a car that crashes sustains closed comminuted fractures of both femoral shafts. Shortly after admission, he develops a blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg, a pulse rate of 110/min, and a venous pressure of zero. He becomes pale, cold, and clammy, but the rest of his physical examination and x-ray films of the chest and pelvis are unremarkable. A sonogram of the abdomen done in the emergency department is likewise negative. Which of the following is the most likely reason for the low blood pressure?
. Blood loss at the fracture sites
. Fat embolism
. Neurogenic shock from pain
. Unrecognized intracranial bleeding
. Unrecognized pericardial tamponade
93) A 24-year-old patient with known neurofibromatosis type 2 undergoes an MRI for ringing in his ears. The MRI demonstrates lesions in bilateral auditory canals. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. Gangioneuroma
. Schwannoma
. Ependymoma
. Meningioma
. Pituitary adenoma
94) A40-year-old man with a history of alcohol abuse presents after an episode of binge drinking. He is complaining of epigastric pain, radiating to the back, associated with nausea and vomiting. On examination, he has marked tenderness in the epigastrium, with guarding, decreased bowel sounds, and moderate abdominal distention. Laboratory findings include leukocytosis and increased serum amylase and lipase. Abdominal roentgenograms demonstrate several dilated bowel loops in the upper abdomen. Select the most likely diagnosis?
. gastroenteritis
. Acute appendicitis
. Sigmoid diverticulitis
. Acute pancreatitis
. Acute cholecystitis
95) A 65-year-old man presents with a 4-day history of worsening lower abdominal pain and constipation. On examination, he is febrile (38.5°C) and has lower abdominal tenderness that is most intense in the midline and left lower quadrant associated with a palpable fullness. Laboratory findings demonstrate a moderate leukocytosis and abdominal roentgenograms show an ileus pattern. Select the most likely diagnosis?
. gastroenteritis
. Regional enteritis
. Acute appendicitis
. Perforated peptic ulcer
. Sigmoid diverticulitis
96) A 65-year-old man presents to the physician’s office with complaints of abdominal discomfort and jaundice for the past 3 weeks. Past history is pertinent for 30 pack-year smoking history, occasional alcohol intake, and a 5.5-mm ulcerating melanoma removed from his back 21/ 2 years ago. Examination reveals a mildly jaundiced patient with normal vital signs and a slightly distended abdomen with mild right upper quadrant tenderness and significant hepatomegaly. Which one is the most likely diagnosis?
. hepatitis A
. hemolysis
. choledocholithiasis
. Liver metastases
. cirrhosis
97) A 30-year-old man presents to the emergency department with sudden onset of severe epigastric pain and vomiting 3 hours ago. He reports a 6-month history of chronic epigastric pain occurring nearly every day and relieved by antacids. On examination, he appears sweaty and avoids movement. Vital signs reveal a temperature of 100°F, BP of 100/60 mmHg, pulse rate of 110/min, and respiratory rate of 12/min. The remainder of his examination reveals diminished bowel sounds and a markedly tender and rigid abdomen. A chest x-ray and abdominal films reveal pneumoperitoneum. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
. small-bowel obstruction
. Dead bowel
. Perforated colon carcinoma
. Perforated duodenal ulcer
. Perforated gastric ulcer
98) A 15-year-old otherwise healthy female high school student begins to notice galactorrhea. A pregnancy test is negative. Which of the following is a frequently associated physical finding?
. Gonadal atrophy
. Bitemporal hemianopsia
. Exophthalmos and lid lag
. Episodic hypertension
. Buffalo hump
99) A 65-year-old woman presents to the physician’s office for evaluation of an abnormal screening mammogram. She denies any breast masses, nipple discharge, pain, or skin changes. Past history is pertinent for hypertension. Family history is positive for postmenopausal breast cancer in a sister. She has a normal breast examination and no axillary adenopathy. The remainder of her examination is unremarkable. An MLO view of the right breast is shown in Figure 6-6a along with a magnification view of the craniocaudal (CC) film (Figure 6-6b). Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
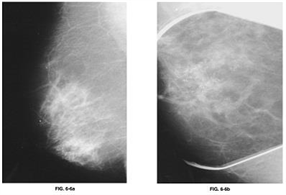
USMLE

. Milk of calcium
. LCIS with or without an invasive component
. DCIS with or without an invasive component
. Involuting fibroadenoma
. Phyllodes tumor
100) A 76-year-old man is undergoing an abdominoperineal resection for rectal cancer. During the surgery, unexpected severe bleeding is encountered, and the patient is hypotensive on and off for almost an hour. The anesthesiologist notes ST depression and T-wave flattening on the ECG monitor. Which of the following are the most likely diagnosis and the expected mortality?
. Intraoperative air embolus, 100%
. Myocardial infarction, 5% to 10%
. Myocardial infarction, 50% to 90%
. Pulmonary embolus, 5% to 10%
. Pulmonary embolus, 50% to 90%
{"name":"Chir Diagnosis P1 Q 51 to 100", "url":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/QPREVIEW","txt":"1) A 48-year-old woman develops constipation postoperatively and self-medicates with milk of magnesia. She presents to clinic, at which time her serum electrolytes are checked, and she is noted to have an elevated serum magnesium level. Which of the following represents the earliest clinical indication of hypermagnesemia?","img":"https://www.quiz-maker.com/3012/images/ogquiz.png"}
More Quizzes
How well do you know Cabrini? Answer these 20 questions and find out!
21100
Adjectives
1050
How much do you know about Dyspraxia?
520
Saving Tiger Quiz
840
The Green Room
15827175
Which Truck Make Are You? Take the Truck Personality
201027439
Which Nicki Minaj Song Are You? Free: Find Your Vibe!
201029479
Find Your Bruno Mars Song Personality - Free
201024234
Birchbark House: Chimookoman Meaning & Ojibwe Trivia
201022293
Discover Which Arthur Character You Really Are!
201028561
Free Men's Knowledge Trivia
201027986
Discover Your Marvel Character Combo - Free Personality
201026917